Candida Species (Volatile) Metabotyping through Advanced Comprehensive Two‐Dimensional Gas Chromatography
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Yeasts Species and Growth Conditions
2.2. Exometabolome Profiling of Candida Species Cultures
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
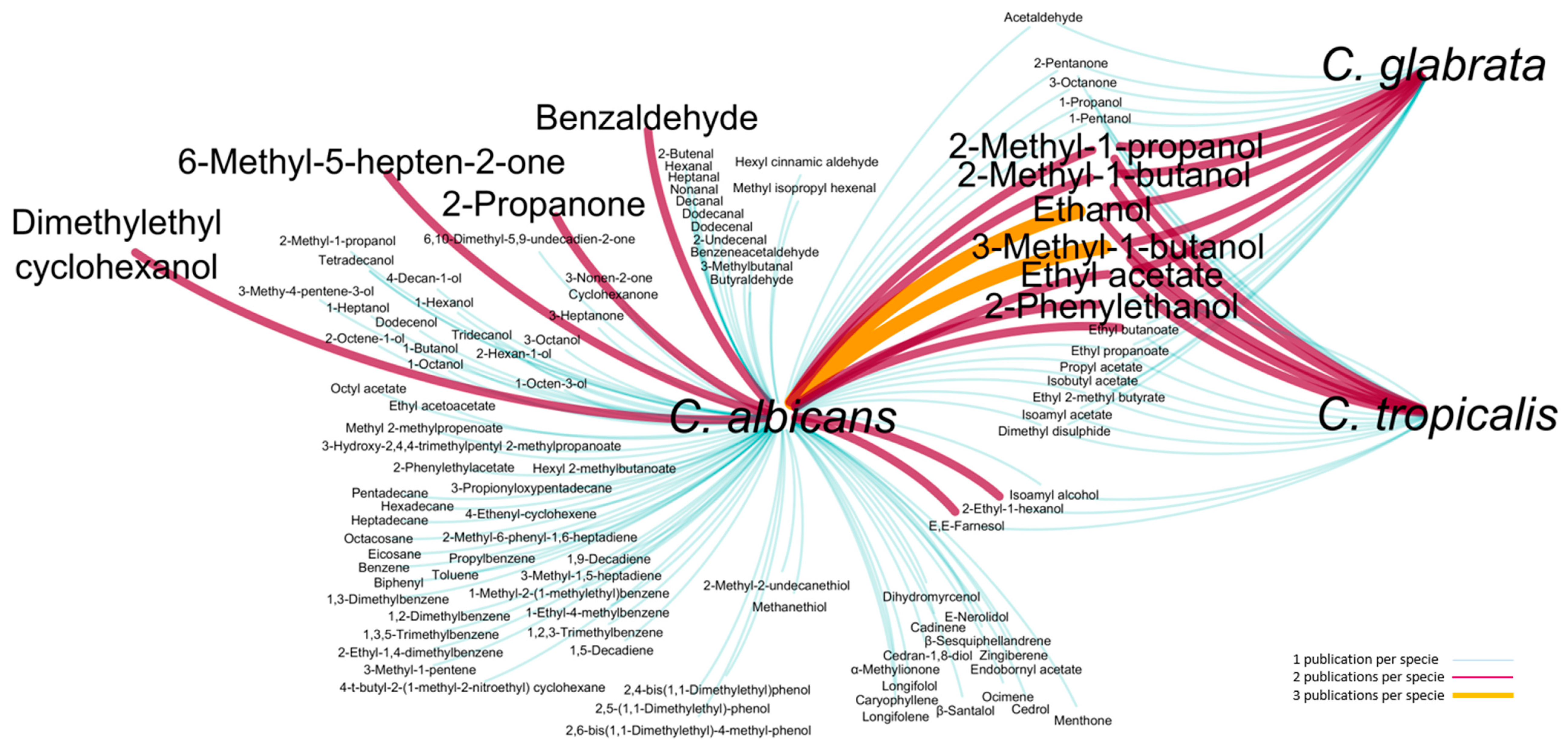
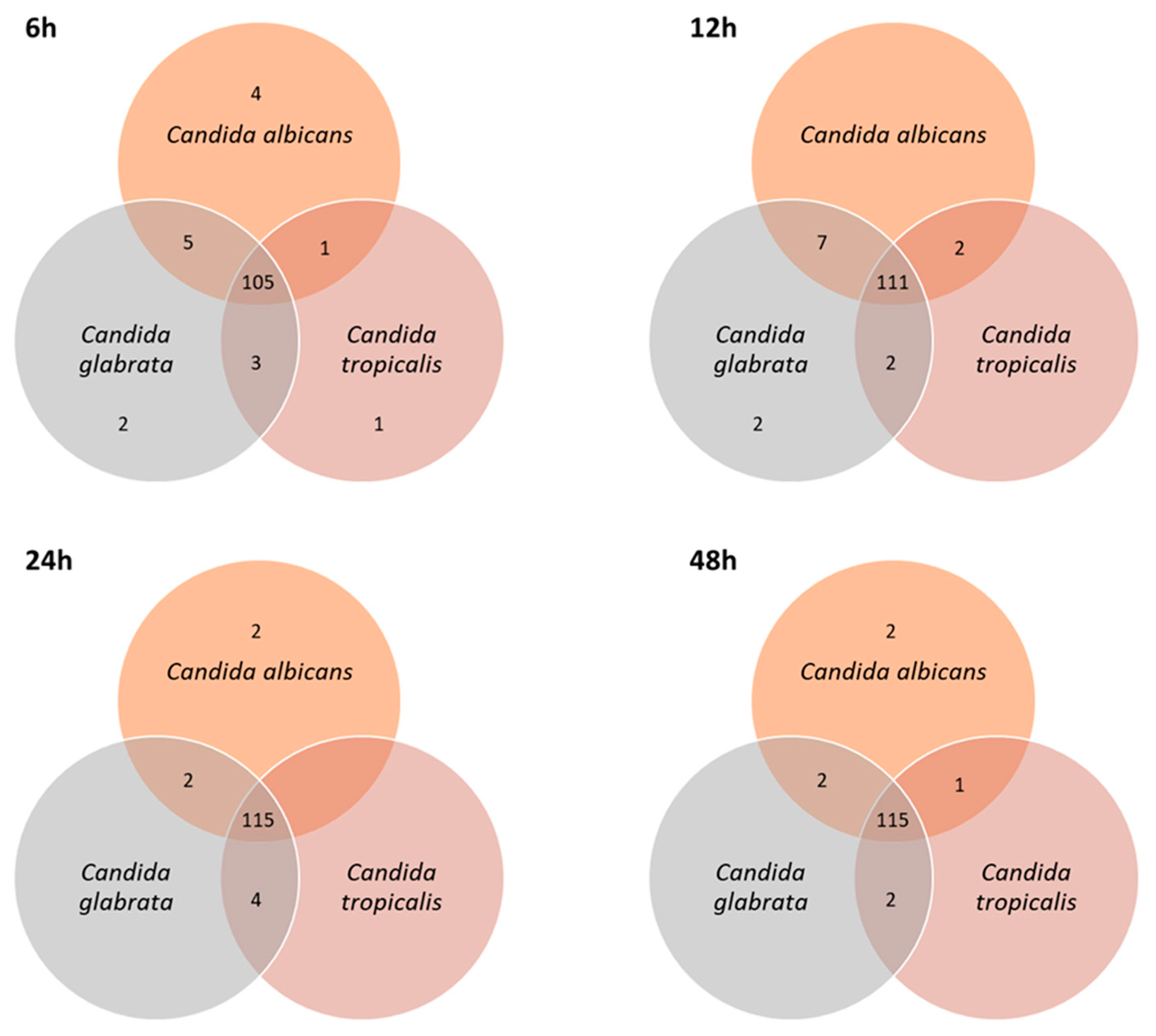
3.1. Candida spp. Exometabolome
3.2. Exploring the Potential of Exometabolome on Candida Species Distinction
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, G.D.; Denning, D.W.; Gow, N.A.R.; Levitz, S.M.; Netea, M.G.; White, T.C. Hidden killers: Human fungal infections. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pfaller, M.A.; Diekema, D.J. Epidemiology of invasive candidiasis: A persistent public health problem. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 133–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dadar, M.; Tiwari, R.; Karthik, K.; Chakraborty, S.; Shahali, Y.; Dhama, K. Candida albicans—Biology, molecular characterization, pathogenicity, and advances in diagnosis and control—An update. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 117, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderone, R.A.; Clancy, C.J. Candida and Candidiasis, 2nd ed.; Richard, A., Calderone, C.J.C., Eds.; American Society for Microbiology Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Pellon, A.; Sadeghi Nasab, S.D.; Moyes, D.L. New Insights in Candida albicans Innate Immunity at the Mucosa: Toxins, Epithelium, Metabolism, and Beyond. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, L.S.; Reyes, C.M.; Stolpman, M.; Speckman, J.; Allen, K.; Beney, J. The direct cost and incidence of systemic fungal infections. Value Health 2002, 5, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noble, S.M.; Gianetti, B.A.; Witchley, J.N. Candida albicans cell type switches and functional plasticity in the mammalian host. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 15, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Sudbery, P. Candida albicans, a major human fungal pathogen. J. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Dantas, A.; Lee, K.K.; Raziunaite, I.; Schaefer, K.; Wagener, J.; Yadav, B.; Gow, N.A. Cell biology of Candida albicans–host interactions. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2016, 34, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ting, S.Y.; Ishola, O.A.; Ahmed, M.A.; Tabana, Y.M.; Dahham, S.; Agha, M.T.; Musa, S.F.; Muhammed, R.; Than, L.T.L.; Sandai, D. Metabolic adaptation via regulated enzyme degradation in the pathogenic yeast Candida albicans. J. Mycol. Med. 2017, 27, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hube, B. Fungal adaptation to the host environment. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2009, 12, 347–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dujon, B.; Sherman, D.; Fischer, G.; Durrens, P.; Casaregola, S.; Lafontaine, I.; De Montigny, J.; Marck, C.; Neuvéglise, C.; Talla, E.; et al. Genome evolution in yeasts. Nature 2004, 430, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunke, S.; Hube, B. Two unlike cousins: Candida albicans and C. glabrata infection strategies. Cell Microbiol. 2013, 15, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lackey, E.; Vipulanandan, G.; Childers, D.S.; Kadosh, D. Comparative evolution of morphological regulatory functions in Candida species. Eukaryot. Cell 2013, 12, 1356–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sibley, C.D.; Peirano, G.; Church, D.L. Molecular methods for pathogen and microbial community detection and characterization: Current and potential application in diagnostic microbiology. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2012, 12, 505–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherkaoui, A.; Hibbs, J.; Emonet, S.; Tangomo, M.; Girard, M.; Francois, P.; Schrenzel, J. Comparison of Two Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry Methods with Conventional Phenotypic Identification for Routine Identification of Bacteria to the Species Level. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Posteraro, B.; Torelli, R.; De Carolis, E.; Posteraro, P.; Sanguinetti, M. Update on the laboratory diagnosis of invasive fungal infections. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franco-Duarte, R.; Černáková, L.; Kadam, S.; SKaushik, K.; Salehi, B.; Bevilacqua, A.; Corbo, M.R.; Antolak, H.; Dybka-Stępień, K.; Leszczewicz, M.; et al. Advances in chemical and biological methods to identify microorganisms—From past to present. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jahagirdar, V.L.; Davane, M.S.; Aradhye, S.C.; Nagoba, B.S. Candida species as potential nosocomial pathogens—A review. Electron. J. Gen. Med. 2018, 15, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, S.E.; Chen, S.C.A.; Meyer, W.; Halliday, C.L. A New Age in Molecular Diagnostics for Invasive Fungal Disease: Are We Ready? Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bean, H.D.; Dimandja, J.M.D.; Hill, J.E. Bacterial volatile discovery using solid phase microextraction and comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2012, 901, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karageorgopoulos, D.E.; Vouloumanou, E.K.; Ntziora, F.; Michalopoulos, A.; Rafailidis, P.I.; Falagas, M.E. β-D-glucan assay for the diagnosis of invasive fungal infections: A meta-analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, 750–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, C.A.; Burklund, A.; Stefanuto, P.; Schwartzman, J.D.; Hill, J.E. Comprehensive volatile metabolic fingerprinting of bacterial and fungal pathogen groups Comprehensive volatile metabolic fi ngerprinting of bacterial and fungal pathogen groups. J. Breath Res. 2018, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieniawska, E.; Sawicki, R.; Golus, J.; Georgiev, M.I. Untargetted metabolomic exploration of the mycobacterium tuberculosis stress response to cinnamon essential oil. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nazmul Huda, M.; Winnike, J.H.; Crowell, J.M.; O’Connor, A.; Bennett, B.J. Microbial modulation of host body composition and plasma metabolic profile. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hornby, J.M.; Jensen, E.C.; Lisec, A.D.; Tasto, J.J.; Jahnke, B.; Shoemaker, R.; Dussault, P.; Nickerson, K.W. Quorum Sensing in the Dimorphic Fungus Candida albicans Is Mediated by Farnesol Quorum Sensing in the Dimorphic Fungus Candida albicans Is Mediated by Farnesol. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 2982–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, C.P.; Gonçalves Silva, D.; Rudnitskaya, A.; Almeida, A.; Rocha, S.M. Shedding light on Aspergillus Niger volatile exometabolome. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cailleux a Bouchara, J.; Daniel, V. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis of volatile organic compounds produced by some micromycetes. Chromatographia 1992, 34, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotter, J.M.; Langford, V.S.; Wilson, P.F.; McEwan, M.J.; Chambers, S.T. Real-time detection of common microbial volatile organic compounds from medically important fungi by Selected Ion Flow Tube-Mass Spectrometry (SIFT-MS). J. Microbiol. Methods 2005, 63, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.; Henriques, M.; Azeredo, J.; Rocha, S.M.; Coimbra, M.A.; Oliveira, R. Morphogenesis control in Candida albicans and Candida dubliniensis through signaling molecules produced by planktonic and biofilm cells. Eukaryot. Cell 2007, 6, 2429–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hertel, M.; Hartwig, S.; Schütte, E.; Gillissen, B.; Preissner, R.; Schmidt-Westhausen, A.M.; Paris, S.; Kastner, I.; Preissner, S. Identification of signature volatiles to discriminate Candida albicans, glabrata, krusei and tropicalis using gas chromatography and mass spectrometry. Mycoses 2016, 59, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perl, T.; Jünger, M.; Vautz, W.; Nolte, J.; Kuhns, M.; Borg-von Zepelin, M.; Quintel, M. Detection of characteristic metabolites of Aspergillus fumigatus and Candida species using ion mobility spectrometry—Metabolic profiling by volatile organic compounds. Mycoses 2011, 54, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, N.; Mirzajani, F.; Rezadoost, H.; Karimi, A.; Fallah, F.; Ghassempour, A.; Aliahmadi, A. Initial study of three different pathogenic microorganisms by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. F1000Research 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.; Henriques, M.; Azeredo, J.; Rocha, S.M.; Coimbra, M.A.; Oliveira, R. Candida species extracellular alcohols: Production and effect in sessile cells. J. Basic Microbiol. 2010, 50 (Suppl. S1), 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalli, S.; Horn, O.J.; Grochowalski, A.R.; Cooper, D.G.; Nicell, J.A. Origin of 2-ethylhexanol as a VOC. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 140, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greguš, P.; Vlčková, H.; Buchta, V.; Kestřanek, J.; Křivčíková, L.; Nováková, L. Ultra high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry analysis of quorum-sensing molecules of Candida albicans. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 53, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childers, D.S.; Kadosh, D. Filament condition-specific response elements control the expression of NRG1 and UME6, key transcriptional regulators of morphology and virulence in Candida albicans. PLoS ONE 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alves, Z.; Melo, A.; Figueiredo, A.R.; Coimbra, M.A.; Gomes, A.C.; Rocha, S.M. Exploring the saccharomyces cerevisiae volatile metabolome: Indigenous versus commercial strains. PLoS ONE 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martins, C.; Brandão, T.; Almeida, A.; Rocha, S.M. Metabolomics strategy for the mapping of volatile exometabolome from Saccharomyces spp. widely used in the food industry based on comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 2228–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, S.M.; Freitas, R.; Cardoso, P.; Santos, M.; Martins, R.; Figueira, E. Exploring the potentialities of comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography coupled to time of flight mass spectrometry to distinguish bivalve species: Comparison of two clam species (Venerupis decussata and Venerupis philippinarum). J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1315, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, I.; Santos, M.; Rudnitskaya, A.; Saraiva, J.A.; Almeida, A. A comprehensive look into the volatile exometabolome of enteroxic and non-enterotoxic Staphylococcus aureus strains. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2019, 108, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, D.; Sá, C.; Cardoso, P.; Pires, A.; Rocha, S.M.; Figueira, E. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety The role of volatiles in Rhizobium tolerance to cadmium: Effects of aldehydes and alcohols on growth and biochemical endpoints. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, P.; Santos, M.; Freitas, R.; Rocha, S.M.; Figueira, E. Response of Rhizobium to Cd exposure: A volatile perspective. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 802–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, I.; Rocha, S.M.; Coimbra, M.A.; Marriott, P.J. Headspace solid-phase microextraction combined with comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography time-of-flight mass spectrometry for the determination of volatile compounds from marine salt. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 5511–5521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prebihalo, S.E.; Berrier, K.L.; Freye, C.E.; Bahaghighat, H.D.; Moore, N.R.; Pinkerton, D.K.; Synovec, R.E. Multidimensional gas chromatography: Advances in instrumentation, chemometrics, and applications. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 505–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiehn, O.; Robertson, D.; Griffin, J.; van der Werf, M.; Nikolau, B.; Morrison, N.; Sumner, L.W.; Goodacre, R.; Hardy, N.W.; Taylor, C.; et al. The metabolomics standards initiative (MSI). Metabolomics 2007, 3, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodacre, R.; Broadhurst, D.; Smilde, A.K.; Kristal, B.S.; Baker, J.D.; Beger, R.; Bessant, C.; Connor, S.; Capuani, G.; Craig, A.; et al. Proposed minimum reporting standards for data analysis in metabolomics. Metabolomics 2007, 3, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, L.W.; Amberg, A.; Barrett, D.; Beale, M.H.; Beger, R.; Daykin, C.A.; Fan, T.W.M.; Fiehn, O.; Goodacre, R.; Griffin, J.L.; et al. Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis Chemical Analysis Working Group (CAWG) Metabolomics Standards Inititative (MSI). Metabolomics 2007, 3, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salvador, Â.C.; Baptista, I.; Barros, A.S.; Gomes, N.C.; Cunha, Â.; Almeida, A.; Rocha, S.M. Can Volatile Organic Metabolites Be Used to Simultaneously Assess Microbial and Mite Contamination Level in Cereal Grains and Coffee Beans? PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Dool, H.; Kratz, P.D. A generalization of the retention index system including linear temperature programmed gas—Liquid partition chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1963, 11, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deorukhkar, S.C.; Saini, S. Laboratory approach for diagnosis of candidiasis through ages. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2014, 3, 206–218. [Google Scholar]
- Thewes, S.; Moran, G.P.; Magee, B.B.; Schaller, M.; Sullivan, D.J.; Hube, B. Phenotypic screening, transcriptional profiling, and comparative genomic analysis of an invasive and non-invasive strain of Candida albicans. BMC Microbiol. 2008, 8, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahazar, N.H.; Zakuan, Z.; Norhayati, H.; MeorHussin, A.S.; Rukayadi, Y. Optimization of culture medium for the growth of Candida sp. and Blastobotrys sp. as starter culture in fermentation of cocoa beans (Theobroma cacao) using response surface methodology (RSM). Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 20, 154–159. [Google Scholar]
- Drgona, L.; Khachatryan, A.; Stephens, J.; Charbonneau, C.; Kantecki, M.; Haider, S.; Barnes, R. Clinical and economic burden of invasive fungal diseases in Europe: Focus on pre-emptive and empirical treatment of Aspergillus and Candida species. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 33, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, L.L.; Han, T.; Wu, J.Z.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Zhang, H.; Huang, B.K.; Rahman, K.; Qin, L.P. Comparative research of chemical constituents, antifungal and antitumor properties of ether extracts of Panax ginseng and its endophytic fungus. Phytomedicine 2009, 16, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radulovic, N.; Blagojevic, P.; Palic, R. Comparative study of the leaf volatiles of Arctostaphylos uva-ursi (L.) Spreng. and Vaccinium vitis-idaea L. (Ericaceae). Molecules 2010, 15, 6168–6185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caldeira, M.; Perestrelo, R.; Barros, A.S.; Bilelo, M.J.; Morete, A.; Camara, J.S.; Rocha, S.M. Allergic asthma exhaled breath metabolome: A challenge for comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1254, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poligné, I.; Collignan, A.; Trystram, G. Characterization of traditional processing of pork meat into boucané. Meat Sci. 2001, 59, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, I.; Coimbra, M.A.; Barros, A.S.; Marriott, P.J.; Rocha, S.M. Can volatile organic compounds be markers of sea salt? Food Chem. 2015, 169, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.C.; Nunes, C.; Rocha, M.A.M.; Rodrigues, A.; Rocha, S.M.; Saraiva, J.A.; Coimbra, M.A. High pressure treatments accelerate changes in volatile composition of sulphur dioxide-free wine during bottle storage. Food Chem. 2015, 188, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ádámová, M.; Oriňák, A.; Halás, L. Retention indices as identification tool in pyrolysis-capillary gas chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1087, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali-Heravi, M.; Zekavat, B.; Sereshti, H. Characterization of essential oil components of Iranian geranium oil using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry combined with chemometric resolution techniques. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1114, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza Ramos, M.F.; Carlos Siani, A.; Romero Tappin, M.R.; Cavalcante Guimarães, A.; Lahoz da Silva Ribeiro, J.E. Essential oils from oleoresins of Protium spp. of the Amazon region. Flavour Fragr. J. 2000, 15, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petronilho, S.; Rocha, S.M.; Ramírez-Chávez, E.; Molina-Torres, J.; Rios-Chavez, P. Assessment of the terpenic profile of Callistemon citrinus (Curtis) Skeels from Mexico. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 46, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Guo, Y.; Suo, X.; Yuan, J. Comparative analysis of chemical components of essential oils from different samples of Rhododendron with the help of chemometrics method. Arch. Anim. Nutr. 2006, 60, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, H.T.; Petronilho, S.; Villaverde, J.J.; Coimbra, M.A.; Domingues, M.R.M.; Ebrahimian, Z.J.; Silvestre, A.J.; Rocha, S.M. Assessment of the sesquiterpenic profile of Ferula gummosa oleo-gum-resin (galbanum) from Iran. Contributes to its valuation as a potential source of sesquiterpenic compounds. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 44, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarević, J.; Radulović, N.; Palić, R.; Zlatković, B. Chemical analysis of volatile constituents of berula erecta (Hudson) coville subsp. erecta (Apiaceae) from Serbia. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2010, 22, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriamaharavo, N.R. Retention Data; NIST Mass Spectrometry Data Center: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bicalho, B.; Pereira, A.S.; Aquino Neto, F.R.; Pinto, A.C.; Rezende, C.M. Application of high-temperature gas chromatography-mass spectrometry to the investigation of glycosidically bound components related to cashew apple (Anacardium occidentale L. var. nanum) Volatiles. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewison, T.; Knox, C.; Neveu, V.; Djoumbou, Y.; Guo, A.C.; Lee, J.; Liu, P.; Mandal, R.; Krishnamurthy, R.; Sinelnikov, I.; et al. YMDB: The Yeast Metabolome Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sudbery, P.E. Growth of Candida albicans hyphae. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemfack, M.C.; Gohlke, B.-O.; Toguem, S.M.T.; Preissner, S.; Piechulla, B.; Preissner, R. mVOC 2.0: A database of microbial volatiles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 1261–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lemfack, M.C.; Nickel, J.; Dunkel, M.; Preissner, R.; Piechulla, B. mVOC: A database of microbial volatiles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 744–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Ibáñez, J.; Pazos, F.; Chagoyen, M. MBROLE 2.0-functional enrichment of chemical compounds. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, E.J.; Teixeira, J.A.; Brányik, T.; Vicente, A.A. Yeast: The soul of beer’s aroma—A review of flavour-active esters and higher alcohols produced by the brewing yeast. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 1937–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, D.D.; Wang, Y.; Dai, B.D.; Li, X.X.; Zhao, L.X.; Cao, Y.B.; Yan, L.; Jiang, Y.Y. ECM17-dependent methionine/cysteine biosynthesis contributes to biofilm formation in Candida albicans. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2013, 51, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, C.F.; Silva, S.; Henriques, M. Candida glabrata: A review of its features and resistance. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 33, 673–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Metabolite | ID Kegg | ID YMDB | Pathways a | MSI Level b | RICalc c | RILit d | Previously Reported for C. albicans, C. glabrata and C. tropicalis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACIDS | |||||||||
| Octanoic acid | C06423 | YMDB00676 | Fatty acid biosynthesis | 1 | 1192 | 1188 [27] | - | - | - |
| Nonanoic acid | C01601 | YMDB01761 | Biotin metabolism | 1 | 1303 | 1280 [27] | - | - | - |
| Decanoic acid | C01571 | YMDB00677 | Fatty acid biosynthesis | 2 | 1391 | 1379 [27] | - | - | - |
| ALCOHOLS | |||||||||
| Aliphatic | |||||||||
| 1-Propanol | C05979 | YMDB00441 | Glycerolipid metabolism | 1 | 580 | 580 [27] | [28] | [28] | [28] |
| 2-Methyl-1-propanol | C14710 | YMDB00573 | - | 1 | 612 | 612 [27] | [28,31] | [28,31] | [28,31] |
| 1-Butanol | C06142 | YMDB01386 | Butanoate metabolism | 1 | 659 | 644 [27] | [27] | - | - |
| 2/3-Methyl-1-butanol | - | YMDB00567 | Leucine degradation | 1 | 718/708 | 718 [27] | [27,28,30,31] | [28,31] | [28,31] |
| 1-Hexanol | - | YMDB01473 | - | 1 | 883 | 878 [27] | [27] | - | - |
| 1-Heptanol | - | YMDB01475 | - | 1 | 980 | 975 [27] | [27] | - | - |
| 1-Octen-3-ol | C14272 | YMDB01352 | - | 1 | 990 | 980 [27] | [27] | - | - |
| 2-Ethyl-1-hexanol | C02498 | YMDB01330 | - | 2 | 1029 | 1029 [27] | [27,33] | - | [35] |
| 1-Octanol | C00756 | YMDB00808 | - | 1 | 1084 | 1079 [27] | [27] | - | - |
| 1-Nonanol | C14696 | - | - | 2 | 1173 | 1173 [27] | - | - | - |
| 1-Decanol | C01633 | YMDB00826 | - | 1 | 1283 | 1278 [27] | - | - | - |
| 2-Undecanol | - | - | - | 1 | 1307 | 1301 [27] | - | - | - |
| 1-Dodecanol | C02277 | - | - | 1 | 1476 | 1476 [27] | - | - | - |
| Aromatic | |||||||||
| 2-Phenyl-2-propanol | - | - | - | 2 | 1091 | 1090 [27] | - | - | - |
| 2-Phenylethanol | C05853 | YMDB01072 | Phenylalanine metabolism | 1 | 1126 | 1120 [27] | [27,30] | [32] | [32,34] |
| ALDEHYDES | |||||||||
| Aliphatic | |||||||||
| Acetaldehyde | C00084 | YMDB00022 | Phenylalanine metabolism | 1 | 548 | 548 [27] | [29] | [28] | - |
| 2-Propenal | - | YMDB00812 | - | 2 | 582 | 563 [39] | - | - | - |
| 2-Methyl-propanal | - | - | - | 2 | 591 | 576 [39] | - | - | - |
| 3-Methylbutanal | C07329 | YMDB00499 | - | 2 | 624 | 633 [27] | - | - | - |
| 2-Butenal | - | - | - | 2 | 633 | 633 [27] | [29] | - | - |
| 2-Methyl-butanal | - | - | - | 2 | 649 | 643 [27] | - | - | - |
| 3-Methyl-2-butenal | - | - | - | 2 | 792 | 789 [39] | - | - | - |
| Hexanal | - | YMDB01759 | - | 1 | 801 | 801 [27] | [27] | - | - |
| Octanal | - | YMDB00824 | - | 1 | 1001 | 1001 [27] | - | - | - |
| Nonanal | - | - | - | 1 | 1106 | 1106 [27] | [27] | - | - |
| Decanal | C12307 | YMDB01340 | - | 1 | 1212 | 1207 [27] | [27] | - | - |
| 2-Undecenal | - | - | - | 2 | 1370 | 1364 [27] | [27] | - | - |
| Dodecanal | C02278 | - | - | 1 | 1432 | 1407 [27] | [27] | - | - |
| Aromatic | |||||||||
| Benzaldehyde | C00261 | YMDB01326 | Toluene and xylene degradation | 1 | 965 | 965 [27] | [27,33] | - | - |
| Benzeneacetaldehyde | - | YMDB00116 | Phenylalanine metabolism | 1 | 1046 | 1046 [27] | [27] | - | - |
| 2,5-Dimethylbenzaldehyde | - | - | - | 2 | 1220 | 1208 [55] | - | - | - |
| 4-(1-Methylethyl)-benzaldehyde | - | - | - | 2 | 1226 | 1243 [27] | - | - | - |
| α-Ethylidenbenzeneacetaldehyde | - | - | - | 2 | 1283 | 1280 [39] | - | - | - |
| 2,4,6-Trimethylbenzaldehyde | - | - | - | 2 | 1314 | 1323 [56] | - | - | - |
| 3,5-di-tert-Butyl-4-hydroxybenzaldehyde | - | - | - | 2 | 1777 | 1767 [39] | - | - | - |
| HYDROCARBONS | |||||||||
| Alkanes | |||||||||
| Nonane | - | - | - | 1 | 900 | 900 [27] | - | - | - |
| 1-Dodecene | - | - | - | 2 | 1195 | 1191 [57] | - | - | - |
| Heptadecane | C01816 | - | - | 1 | 1701 | 1701 [27] | [27] | - | - |
| Aromatic | |||||||||
| Toluene | C01455 | - | Toluene and xylene degradation | 1 | 753 | 759 [27] | [27] | - | - |
| Ethylbenzene | C07111 | - | Ethylbenzene degradation | 2 | 865 | 860 [27] | - | - | - |
| Styrene | C07083 | - | Styrene degradation | 2 | 889 | 895 [39] | - | - | - |
| Isopropylbenzene | C14396 | - | - | 2 | 922 | 927 [27] | - | - | - |
| Propylbenzene | - | - | - | 2 | 953 | 953 [27] | [27] | - | - |
| α-Methylstyrene | - | - | - | 2 | 980 | 985 [27] | - | - | - |
| 1,2,4,5-Tetramethylbenzene | C14534 | - | - | 2 | 1123 | 1123 [27] | - | - | - |
| 1,4-Di-tert-butylbenzene | - | - | - | 2 | 1257 | 1264 [58] | - | - | - |
| Biphenyl | C06588 | - | Biphenyl degradation | 2 | 1389 | 1383 [27] | [27] | - | - |
| 1-Butylheptylbenzene | - | - | - | 2 | 1636 | 1633 [59] | - | - | - |
| 1-Propyloctylbenzene | - | - | - | 2 | 1648 | 1645 [59] | - | - | - |
| 1-Butyloctylbenzene | - | - | - | 2 | 1738 | 1731 [59] | - | - | - |
| 1-Propylnonylbenzene | - | - | - | 2 | 1751 | 1741 [59] | - | - | - |
| 1-Ethyldecylbenzene | - | - | - | 2 | 1776 | 1764 [59] | - | - | - |
| ESTERS | |||||||||
| Aliphatic | |||||||||
| Ethyl acetate | C00849 | YMDB00569 | - | 1 | 601 | 601 [27] | [28,31] | [28,31] | [28,31] |
| Ethyl propanoate | - | YMDB01331 | - | 1 | 685 | 688 [39] | [28] | [28] | [28] |
| Isobutyl acetate | - | YMDB00572 | - | 2 | 763 | 769 [27] | [31] | [31] | [31] |
| Ethyl butanoate | - | YMDB01385 | - | 1 | 806 | 806 [27] | [28,33] | [28] | [28] |
| Butyl ethanoate | - | - | - | 2 | 818 | 818 [27] | - | - | - |
| Isoamyl ethanoate | - | YMDB00571 | - | 2 | 877 | 877 [27] | - | - | - |
| Hexyl ethanoate | - | YMDB01384 | - | 2 | 1017 | 1014 [39] | - | - | - |
| Ethyl octanoate | C12292 | YMDB01354 | - | 1 | 1195 | 1195 [27] | - | - | - |
| Ethyl nonanoate | - | YMDB01354 | - | 1 | 1301 | 1295 [27] | - | - | - |
| 3-Hydroxy-2,4,4-trimethylpentyl 2-methypropanoate | - | - | - | 2 | 1382 | 1376 [27] | - | - | - |
| Propanoic acid, 2-methyl-, 1-(1,1-dimethylethyl)- -2-methyl-1,3-propanediyl ester | - | - | - | 2 | 1601 | 1607 [60] | - | - | - |
| Lauryl acetate | - | - | - | 2 | 1613 | 1608 [38] | - | - | - |
| Isopropyl myristate | D02296 | - | - | 2 | 1830 | 1834 [60] | - | - | - |
| Aromatic | |||||||||
| Methyl benzoate | - | - | - | 2 | 1101 | 1101 [27] | - | - | - |
| 2-Benzylacrylic acid methyl ester | - | - | - | 2 | 1345 | 1339 [27] | - | - | - |
| 2-Octyl benzoate | - | - | - | 2 | 1714 | 1708 [39] | - | - | - |
| KETONES | |||||||||
| 2-Propanone | C00207 | YMDB01701 | Propanoate metabolism | 1 | 559 | 559 [27] | [27,29] | - | - |
| 2-Butanone | C02845 | - | - | 1 | 577 | 590 [27] | - | - | - |
| 2-Pentanone | C01949 | - | - | 2 | 677 | 664 [27] | [31] | [31] | [31] |
| 2,3-Pentanedione | - | YMDB01434 | - | 2 | 677 | 665 [27] | - | - | - |
| 4-Methyl-2-pentanone | - | - | - | 2 | 725 | 729 [61] | - | - | - |
| 3-Penten-2-one | - | - | - | 2 | 731 | 717 [27] | - | - | - |
| 2,3-Heptanedione | - | - | - | 2 | 836 | 836 [39] | - | - | - |
| 5-Methyl-2-hexanone | - | - | - | 2 | 860 | 860 [27] | - | - | - |
| 4-Heptanone | - | - | - | 2 | 871 | 871 [27] | - | - | - |
| 6-Methyl-2-heptanone | - | - | - | 2 | 953 | 932 [39] | - | - | - |
| 2-Nonanone | - | YMDB01383 | - | 2 | 1095 | 1095 [27] | - | - | - |
| Phenylacetone | C15512 | - | - | 2 | 1135 | 1135 [27] | - | - | - |
| 1-Phenyl-1-butanone | - | - | - | 2 | 1258 | 1254 [27] | - | - | - |
| 2-Undecanone | C01875 | YMDB01592 | - | 2 | 1301 | 1295 [27] | - | - | - |
| 2-Tridecanone | - | - | - | 2 | 1501 | 1495 [27] | - | - | - |
| TERPENIC COMPOUNDS | |||||||||
| Monoterpenic compounds | |||||||||
| α-Pinene | - | - | - | 1 | 932 | 937 [27] | - | - | - |
| Verbenene | - | - | - | 2 | 953 | 958 [27] | - | - | - |
| 3-Carene | - | - | - | 1 | 1011 | 1009 [39] | - | - | - |
| Limonene | C06078 | YMDB01727 | - | 1 | 1028 | 1028 [27] | - | - | - |
| β-Ocimene | - | - | - | 2 | 1040 | 1039 [62] | - | - | - |
| Dihydromyrcenol | - | - | - | 2 | 1073 | 1073 [27] | [27] | - | - |
| Linalool tetrahydride | - | - | - | 2 | 1101 | 1101 [27] | - | - | - |
| Linalool | - | - | - | 1 | 1101 | 1107 [27] | - | - | - |
| Fenchyl alcohol | C02344 | - | Biosynthesis of secondary metabolites | 2 | 1118 | 1123 [27] | - | - | - |
| Dihydroterpineol | - | - | - | 2 | 1145 | 1142 [63] | - | - | - |
| Pinocarvone | C09884 | - | Limonene and pinene degradation | 2 | 1168 | 1168 [27] | - | - | - |
| Borneol | C01411 | - | - | 1 | 1173 | 1174 [27] | - | - | - |
| Carvone | C11383 | YMDB01648 | Limonene and pinene degradation | 2 | 1251 | 1249 [39] | - | - | - |
| Geraniol | C01500 | YMDB01700 | Biosynthesis of secondary metabolites | 1 | 1260 | 1265 [39] | - | - | - |
| Endobornyl acetate | - | - | - | 2 | 1295 | 1289 [27] | [27] | - | - |
| β-Terpenyl acetate | - | - | - | 2 | 1357 | 1351 [27] | - | - | - |
| Sesquiterpenic compounds | |||||||||
| α-Copaene | - | - | - | 2 | 1357 | 1370 [64] | - | - | - |
| Longifolene | C09699 | - | Biosynthesis of secondary metabolites | 2 | 1418 | 1413 [27] | [33] | - | - |
| β-Farnesene | - | - | - | 1 | 1460 | 1458 [39] | - | - | - |
| Geranyl acetone | - | YMDB01701 | Propanoate metabolism | 2 | 1460 | 1458 [39] | - | - | - |
| α-Curcumene | - | - | - | 2 | 1494 | 1486 [39] | - | - | - |
| α-Farnesene isomer | - | - | - | 2 | 1501 | 1495 [65] | - | - | - |
| α-Farnesene isomer | - | - | - | 2 | 1519 | 1515 [39] | - | - | - |
| Calamenene | - | - | - | 2 | 1530 | 1530 [27] | - | - | - |
| Nerolidol | C09704 | - | Biosynthesis of secondary metabolites | 1 | 1566 | 1566 [27] | [30] | - | - |
| Caryophyllene oxide | C16908 | - | - | 2 | 1612 | 1610 [66] | - | - | - |
| 2,3-Dihydrofarnesol | - | - | - | 2 | 1695 | 1696 [67] | - | - | - |
| E,E-Farnesol | C01493 | YMDB00404 | Biosynthesis of secondary metabolites | 1 | 1731 | 1730 [39] | [26,30] | - | [34] |
| Farnesal | C03461 | - | Sesquiterpenoid biosynthesis | 2 | 1751 | 1744 [39] | - | - | - |
| NORISOPRENOID | |||||||||
| α-Methylionone | - | - | - | 2 | 1489 | 1482 [27] | [27] | - | - |
| PHENOLS | |||||||||
| 2-(1,1-Dimethylethyl)-4-methylphenol | - | - | - | 2 | 1366 | 1360 [27] | - | - | - |
| 5-Methyl-2,4-diisopropylphenol | - | - | - | 2 | 1466 | 1496 [68] | - | - | - |
| 2,4-Bis(1,1′-dimethylethyl)phenol | - | - | - | 2 | 1520 | 1514 [27] | [27] | - | - |
| Nonylphenol | C14993 | - | - | 2 | 1760 | 1720 [69] | - | - | - |
| SULPHUR COMPOUNDS | |||||||||
| Methanethiol | C00409 | YMDB00062 | Cysteine and methionine metabolism | 2 | 563 | 551 [39] | [29] | - | - |
| Dimethyl disulfide | C08371 | YMDB01438 | - | 2 | 725 | 728 [27] | [27] | [31] | [31] |
| Thiazole | - | - | - | 2 | 736 | 727 [39] | - | - | - |
| 2-Methyl-thiophene | - | - | - | 2 | 763 | 759 [27] | - | - | - |
| 3-(Methylthio)propanal | - | YMDB01466 | - | 2 | 912 | 912 [27] | - | - | - |
| Dimethyl trisulfide | C08372 | YMDB01438 | - | 2 | 969 | 969 [27] | - | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Costa, C.P.; Bezerra, A.R.; Almeida, A.; Rocha, S.M. Candida Species (Volatile) Metabotyping through Advanced Comprehensive Two‐Dimensional Gas Chromatography. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1911. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8121911
Costa CP, Bezerra AR, Almeida A, Rocha SM. Candida Species (Volatile) Metabotyping through Advanced Comprehensive Two‐Dimensional Gas Chromatography. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(12):1911. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8121911
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosta, Carina Pedrosa, Ana Rita Bezerra, Adelaide Almeida, and Sílvia M. Rocha. 2020. "Candida Species (Volatile) Metabotyping through Advanced Comprehensive Two‐Dimensional Gas Chromatography" Microorganisms 8, no. 12: 1911. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8121911
APA StyleCosta, C. P., Bezerra, A. R., Almeida, A., & Rocha, S. M. (2020). Candida Species (Volatile) Metabotyping through Advanced Comprehensive Two‐Dimensional Gas Chromatography. Microorganisms, 8(12), 1911. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8121911








