Discovery of Two Brominated Oxindole Alkaloids as Staphylococcal DNA Gyrase and Pyruvate Kinase Inhibitors via Inverse Virtual Screening
Abstract
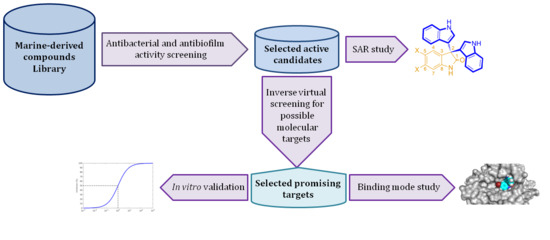
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Library Construction
2.2. Bacterial Strains
2.3. Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
2.4. Biofilm Assay
2.5. In Vitro Enzymes Assay
2.6. In Silico Inverse Screening
2.7. Docking Analysis
2.8. ADME Studies
2.9. Toxicity Profiling
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Inhibitory Activity Screening
3.2. Antibiofilm Activity
3.3. Structure–Activity Relationship (SAR) Study
3.4. Inverse Virtual Screening
3.5. In Vitro Assay
3.6. In Silico Binding Mode Study
3.7. In Silico ADME/Tox Prediction
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manunga, J.; Olak, J.; Rivera, C.; Martin, M. Prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in elective surgical patients at a public teaching hospital: An analysis of 1039 patients. Am. Surg. 2012, 78, 1096–1099. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khamash, D.F.; Voskertchian, A.; Tamma, P.D.; Akinboyo, I.C.; Carroll, K.C.; Milstone, A.M. Increasing clindamycin and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole resistance in pediatric Staphylococcus aureus infections. J. Ped. Infec. Dis. Soc. 2019, 8, 351–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miguel, C.P.V.; Mejias, A.; Leber, A.; Sanchez, P.J. A decade of antimicrobial resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: A single center experience. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mittal, V. Biofilm and antimicrobial resistance. In Biofilms in Human Diseases: Treatment and Control; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 285–298. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, T.; Lou, Q.; Wu, Y.; Hu, J.; Yu, F.; Qu, D. Impact of the Staphylococcus epidermidis LytSR two-component regulatory system on murein hydrolase activity, pyruvate utilization and global transcriptional profile. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vasu, D.; Sunitha, M.M.; Srikanth, L.; Swarupa, V.; Prasad, U.V.; Sireesha, K.; Sarma, P.V.G.K. In Staphylococcus aureus the regulation of pyruvate kinase activity by serine/threonine protein kinase favors biofilm formation. 3 Biotech 2015, 5, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomsen, I.P.; Liu, G.Y. Targeting fundamental pathways to disrupt Staphylococcus aureus survival: Clinical implications of recent discoveries. JCI Insight 2018, 3, 210–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zoraghi, R.; Worrall, L.; See, R.H.; Strangman, W.; Popplewell, W.L.; Gong, H.; Finlay, B.B. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) pyruvate kinase as a target for bis-indole alkaloids with antibacterial activities. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 44716–44725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, N.S.; Dullaghan, E.M.; Finlay, B.B.; Gong, H.; Reiner, N.E.; Selvam, J.J.P.; Zoraghi, R. Discovery and optimization of a new class of pyruvate kinase inhibitors as potential therapeutics for the treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 1708–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janupally, R.; Medepi, B.; Brindha, P.; Suryadevara, P.; Jeankumar, V.U.; Kulkarni, P.; Sriram, D. Design and Biological Evaluation of Furan/Pyrrole/Thiophene-2-carboxamide Derivatives as Efficient DNA GyraseB Inhibitors of Staphylococcus aureus. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2015, 86, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.D.; Ziora, Z.M.; Blaskovich, M.A. Quinolone antibiotics. Med. Chem. Comm. 2019, 10, 1719–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tari, L.W.; Trzoss, M.; Bensen, D.C.; Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Lam, T.; Stidham, M. Pyrrolopyrimidine inhibitors of DNA gyrase B (GyrB) and topoisomerase IV (ParE). Part I: Structure guided discovery and optimization of dual targeting agents with potent, broad-spectrum enzymatic activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 1529–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasšicč, T.; Katsamakas, S.; Hodnik, Z.; Ilasš, J.; Brvar, M.; Solmajer, T.; Montalvão, S.; Paãvi, T.; Banjanac, M.; Ergović, G.; et al. Discovery of 4, 5, 6, 7-tetrahydrobenzo [1, 2-d] thiazoles as novel DNA gyrase inhibitors targeting the ATP-binding site. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 5501–5521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Lü, X. New Strategy on Antimicrobial-resistance: Inhibitors of DNA Replication Enzymes. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 1761–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masadeh, M.M.; Alzoubi, K.H.; Ahmed, W.S.; Magaji, A.S. In Vitro Comparison of Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Activities of Selected Fluoroquinolones against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Pathogens 2019, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kobayashi, J. Search for new bioactive marine natural products and application to drug development. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 64, 1079–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El-Hawary, S.S.; Sayed, A.; Mohammed, R.; Hassan, H.; Zaki, M.; Rateb, M.; Abdelmohsen, U. Epigenetic modifiers induce bioactive phenolic metabolites in the marine-derived fungus Penicillium brevicompactum. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Hawary, S.S.; Sayed, A.M.; Mohammed, R.; Khanfar, M.; Rateb, M.E.; Mohammed, T.A.; Abdelmohsen, U.R. New Pim-1 kinase inhibitor from the co-culture of two sponge-associated actinomycetes. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 538–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Hawary, S.S.; Sayed, A.M.; Mohammed, R.; Hassan, H.M.; Rateb, M.E.; Amin, E.; Wajant, H. Bioactive Brominated Oxindole Alkaloids from the Red Sea Sponge Callyspongia siphonella. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Durcik, M.; Tammela, P.; Barančoková, M.; Tomašič, T.; Ilaš, J.; Kikelj, D.; Zidar, N. Synthesis and Evaluation of N-Phenylpyrrolamides as DNA Gyrase B Inhibitors. Chem. Med. Chem. 2018, 13, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Axerio-Cilies, P.; See, R.H.; Zoraghi, R.; Worral, L.; Lian, T.; Stoynov, N.; Swayze, R. Cheminformatics-driven discovery of selective, nanomolar inhibitors for staphylococcal pyruvate kinase. ACS Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, M.T.; Zoraghi, R.; Reiner, N.; Suzen, S.; Ohlsen, K.; Lalk, M.; Hilgeroth, A. Novel inhibitors of the methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)-pyruvate kinase. J. Enz. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 1666–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jones, S. Permeability rules for antibiotic design. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huigens, R.W.; Morrison, K.C.; Hicklin, R.W.; Flood, T.A., Jr.; Richter, M.F.; Hergenrother, P.J. A ring-distortion strategy to construct stereochemically complex and structurally diverse compounds from natural products. Nat. Chem. 2013, 5, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoenfelder, S.M.; Lange, C.; Prakash, S.A.; Marincola, G.; Lerch, M.F.; Wencker, F.D.; Ziebuhr, W. The small non-coding RNA RsaE influences extracellular matrix composition in Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm communities. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 15, e1007618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kitchen, D.B.; Decornez, H.; Furr, J.R.; Bajorath, J. Docking and scoring in virtual screening for drug discovery: Methods and applications. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 935–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlsen, K.; Lorenz, U. Novel targets for antibiotics in Staphylococcus aureus. Future Microbiol. 2007, 2, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, T.J. Antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Current status and future prospects. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 430–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronkin, S.M.; Badia, M.; Bellon, S.; Grillot, A.L.; Gross, C.H.; Grossman, T.H.; Wei, Y. Discovery of pyrazolthiazoles as novel and potent inhibitors of bacterial gyrase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 2828–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Ito, S.; Shimizu-Ibuka, A.; Sakai, H. Crystal structure of pyruvate kinase from Geobacillus stearothermophilus. J. Biochem. 2008, 144, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Molecular Target | Function | Mode of Action | Binding Energy (5-Tris) | Binding Energy (6-Tris) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FtsZ | GTPase | Cell division | −6.3 | −6.0 |
| PK | Pyruvate kinase | Glycolysis | −8.8 | −6.9 |
| SpsB | Signal Peptidase | Protein secretion | −3.9 | −5.0 |
| Isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase | Protein biosynthesis | Protein modification | −5.3 | −4.0 |
| Peptide deformylase | Protein modification | −5.8 | −4.9 | |
| Peptidyl transferase | Protein biosynthesis | Protein modification | 3.9 | 4.1 |
| rRNA methyltransferase | Protein biosynthesis | Protein modification | −4.2 | −5.5 |
| Threonyl−tRNA synthetase | Protein biosynthesis | Protein modification | −5.1 | −5.2 |
| Gyr A | DNA gyrase | DNA replication | −4.3 | −4.8 |
| Gyr B | DNA gyrase | DNA replication | −7.3 | −9.9 |
| ParE | Topoisomerase IV | DNA replication | −5.4 | −5.1 |
| Ddl | D-alanine ligase | Peptidoglycan synthesis | −4.1 | −4.8 |
| MurB | UDP-N-acetylglucosamine-enolpyruvyl reductase | Peptidoglycan synthesis | −6.1 | −5.5 |
| PBP2 | Peptidoglycan glycosyl transferase | Peptidoglycan synthesis | −3.6 | −3.8 |
| DHFR | Dihydrofolate reductase | Cellular regulation | −6.9 | −6.1 |
| YycG/YycF | Autolysis | Cellular regulation | −6.7 | −6.2 |
| FabF | B-ketoacyl-synthase I/II | Fatty acid synthesis | −3.6 | −3.5 |
| FabI | Enoly-acyl-carrier protein reductase | Fatty acid synthesis | −4.3 | −4.2 |
| LigA | DNA ligase | Stress response | −7.0 | −6.1 |
| TrxB | Thioredoxin reductase | Stress response | −5.9 | −5.0 |
| Tested Compound | IC50 (Ki) ± S.D. µM a | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| DNA Gyrase | Pyruvate Kinase | Topoisomerase IV | |
| 5-Tris | 11.4 ± 0.03 (Ki: 7.75 ± 0.05) | 6.6 ± 0.05 (Ki: 5.6 ± 0.02) | 33.17 ± 0.04 |
| 6-Tris | 2.1 ± 0.08 (Ki: 1. 5 ± 0.03) | 23.2 ± 0.06 (Ki: 21.9 ± 0.04) | 25.14 ± 0.03 |
| Novobiocin | 0.12 ± 0.01 | * | 0.22 ± 0.01 |
| Compound | Lipinski a | BBB b | GIT Absorption c | Solubility d | CYP2D6 e | Bioavailability Score f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-Tris | Yes | Yes | High | Moderate | Yes | 0.55 |
| 6-Tris | Yes | Yes | High | Moderate | Yes | 0.55 |
| Compound | 5-Tris | 6-Tris |
|---|---|---|
| Mutagenicity | Mutagen | Mutagen |
| Carcinogenicity (mouse) | Positive | Positive |
| Carcinogenicity (rat) | Negative | Negative |
| hERG inhibition (cardiotoxicity) | Ambiguous | Moderate Risk |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sayed, A.M.; Alhadrami, H.A.; El-Hawary, S.S.; Mohammed, R.; Hassan, H.M.; Rateb, M.E.; Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Bakeer, W. Discovery of Two Brominated Oxindole Alkaloids as Staphylococcal DNA Gyrase and Pyruvate Kinase Inhibitors via Inverse Virtual Screening. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8020293
Sayed AM, Alhadrami HA, El-Hawary SS, Mohammed R, Hassan HM, Rateb ME, Abdelmohsen UR, Bakeer W. Discovery of Two Brominated Oxindole Alkaloids as Staphylococcal DNA Gyrase and Pyruvate Kinase Inhibitors via Inverse Virtual Screening. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(2):293. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8020293
Chicago/Turabian StyleSayed, Ahmed M., Hani A. Alhadrami, Seham S. El-Hawary, Rabab Mohammed, Hossam M. Hassan, Mostafa E. Rateb, Usama Ramadan Abdelmohsen, and Walid Bakeer. 2020. "Discovery of Two Brominated Oxindole Alkaloids as Staphylococcal DNA Gyrase and Pyruvate Kinase Inhibitors via Inverse Virtual Screening" Microorganisms 8, no. 2: 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8020293
APA StyleSayed, A. M., Alhadrami, H. A., El-Hawary, S. S., Mohammed, R., Hassan, H. M., Rateb, M. E., Abdelmohsen, U. R., & Bakeer, W. (2020). Discovery of Two Brominated Oxindole Alkaloids as Staphylococcal DNA Gyrase and Pyruvate Kinase Inhibitors via Inverse Virtual Screening. Microorganisms, 8(2), 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8020293