Abstract
Crataegus sp. is a tree that grows in temperate zones with worldwide distribution and is commonly known in Mexico as tejocote. The use of products derived from Crataegus in traditional medicine, food, and cosmetics has increased over the last few years and the relevance of this plant has also grown. Here, we report a disease that was observed in tejocote plants that grew both in the wild and in greenhouses in Puebla (Mexico). The disease was characterized by necrotic spots on the leaf ranging from brown to reddish tones that were accompanied by structures on the back of the leaf. Furthermore, we investigated the fungal genera associated with infected leaves in wild tejocote plants, from which we recovered Alternaria sp., Aureobasidium sp., Dreschlera sp., Fusarium sp., Paecilomyces sp. and Ulocladium sp. genera. Inoculation on healthy Crataegus sp. plants with isolate UAP140 showed similar symptoms as observed in nature, while inoculation with UAP127 resulted in the development of necrotic lesions in the leaf. The identity of these isolates was further studied through the phylogenetic analysis of the ribosomal DNA internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region, where isolate UAP140 showed the highest identity with Fusarium equiseti and isolate UAP127 was similar to Alternaria arborescens. To our knowledge, this is the first report of a characteristic disease developed in Crataegus sp. plants in Mexico where the fungal community associated to the lesion was analyzed. Further studies would be necessary to determine the ecological and environmental implications of the microbiome on the appearance and development of the disease.
1. Introduction
Crataegus sp. (Rosaceae: Maloideae), commonly known as hawthorn and in Mexico as tejocote, is an important cultivar with different uses in medicine [1] and the ornamental and food industries. Hawthorns grow as large shrubs or small trees that usually have thorns and produce bright to dark green leaves with margins that range from nearly entire to serrate or deeply lobed. The bushes or trees produce dense clusters of flowers and colored berries that vary between yellow and bright red or black [2]. Crataegus is native to northern temperate zones and it has been located in North America, East Asia, Central Asia and Europe, while in Latin America, it is mainly distributed in Mexico, Guatemala, Honduras, Costa Rica, Peru and Ecuador [3].
In Mexico, Crataegus is cultivated in the states of Mexico, Puebla, Tlaxcala, Chiapas, Michoacán, Hidalgo and Morelos [4], where the economic relevance of this cultivar is highly estimated. In medicine, it has been used to treat cardiovascular diseases [5,6], given that hawthorn fruits have been shown to have a tonic effect on the heart and are often used in the treatment of weak heart conditions, especially when accompanied by high blood pressure [7]. Hawthorn preparations have been used for their sedative actions to treat the early stages of congestive heart failure and to reduce total plasma cholesterol [8]. Its activity as an astringent allows its use in heavy menstrual bleeding and in diarrhea, while other properties such as antioxidant, antispasmodic, diuretic and antihypertensive functions have also been documented [7,9,10]. Traditionally, it has been used in the Mexican food industry to produce cakes, jams and beverages [11], but also as a source of pectin and vitamin C [12].
Unfortunately, microbial agents pose serious threats to Crataegus production around the world. Some fungal diseases have been reported for hawthorn species, including the cedar-hawthorn rust generated by Gymnosporangium globosum, the cedar-quince rust produced by Gymnosporangium clavipes [13] and the leaf blight and fruit rot associated with Monilinia johnsonii. Interestingly, only one report links this agent to Crataegus plants in Mexico [13] and there are no other reports for microbial agents with pathogenic effect in this species. Despite the cultural and economic relevance of this plant in Mexico, few efforts have been devoted to the identification of microbial pathogens that affect the health and production of this cultivar. During 2010–2011, leaf spot symptoms that evolved into necrotic lesions were observed on Crataegus leaves in several fields and greenhouses in the state of Puebla (Mexico). Initial lesions appeared as small, circular, dark brown spots. Subsequently, numerous lesions gradually enlarged with a necrotic center and brown margin until they occupied larger areas of the leaf. Similar lesions have been described in some Crataegus and other rosacea [13,14]; however, unlike for those reports, no lesions on the fruits developed (unlike the disease depicted here).
The objective of this work was the identification of the fungal agents that caused the characteristic spots accompanied by the appearance of structures on the back of tejocote leaves, a disease that was observed in Crataegus plants from Puebla (Mexico) and that we describe here for the first time. Given the economic relevance of Crataegus in Mexico, the development of improved strategies to mitigate the impact of this disease would be relevant to maintain this cultivar and its health.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Leaves
Symptomatic and apparently healthy leaves were collected in the wild from the mountainous region called Tepeaca belonging to the state of Puebla, Mexico (latitude 98°07′37.62″, longitude 19°00′58.99″). Crataegus leaves were placed in sterile Petri dishes, placing each leaf in a different Petri dish, and transferred to the laboratory for further manipulation.
2.2. Fungal Isolation and Purification
Fungi were isolated from Crataegus leaves. Small sections of the diseased leaves were handled to recover the fungal population, while healthy leaves were also recovered from the same plant and processed in the same way. To identify the causative agent of the injury observed in the leaves, the structures developed on the surface of the leaf were cut and placed in potato dextrose agar (PDA) and V8 agar. To investigate if the isolates recovered from these structures were also occupying the plant as epiphytes, a wet cotton swab was used and passed over the leaf surface. The cotton was then immersed in 1 mL of sterile water, serial dilutions (10−1, 10−2 and 10−3) were prepared and 100 μL of each dilution were plated over PDA and V8 agar. Finally, to find out if the isolates were also inhabiting the plant as endophytes, fungal isolates were recovered from disinfected tissue. To accomplish this, the tissue surface was disinfected by immersion for 30 s in water, 1 min in 1% NaOCl and 3 min in 70% ethanol. After this treatment, the tissue was rinsed with sterile water, macerated, and serial dilutions (10−1, 10−2 and 10−3) were prepared. As before, 100 μL of each dilution was spread over PDA agar and V8 agar. All plates were incubated at 30 °C for 6 days. The isolates obtained were purified by re-inoculation in PDA or V8 plates.
2.3. Phenotypic Identification
General identification of the isolated fungi was performed using traditional morphological methods according to the macroscopic features (mycelium type, color and growth type) as well as the identification of the microscopic reproductive structures observed using the microculture technique [15], as depicted before [16]. The structures developed were compared to the reported references [17,18].
2.4. Inoculum Preparation
Isolates phenotypically correlated to the genera Alternaria sp. (isolates UAP035, UAP119 and UAP127), Aureobasidium sp. (isolates UAP078, UAP087 and UAP096), Drechslera sp. (UAP123), Fusarium sp. (UAP140, UAP168), Paecilomyces sp. (UAP133) and Ulocladium sp. (UAP108, UAP120) were individually grown for 4 days in yeast extract/phosphate/sucrose (YEPS) broth at 30 °C. Spore suspensions were obtained by vigorously mixing the inoculum. The thick suspension was then filtered. The concentration of the remaining suspension was counted with an hemocytometer and the suspension was diluted as necessary. Individual isolates were tested at a concentration of 8 × 106 conidia/mL, while a mixture of individual isolates at the same concentration was also tested.
2.5. Plant Infection Assay
To evaluate the potential of the isolates to produce disease in the plant, 20 leaves of 3-month-old healthy plants of Crataegus were inoculated superficially or by injection with the inoculum prepared as depicted before. To inoculate the plant on the surface of the leaf, we created a 1-cm long laceration and then deposited 50 μL of the inoculum directly on the cut. In the inoculation through injection, we injected 100 μL of the inoculum directly on the midrib of the leaf to favor its distribution through the veins. As negative controls, 20 leaves were treated as described, but sterile media was used instead of the inoculum. Trees were monitored for 35 days after infection.
2.6. Molecular Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis
DNA was extracted from pure fungal cultures using the Wizard Genomic DNA Purification Kit (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. PCR amplification was carried out using the following primers: ITS1F (5′-CTTGGTCATTTAGAGGAAGTAA-3′) [19] and LR5 (5′-TCCTGAGGGAAACTTCG-3′) [20]. These primers were purchased from IDT Technologies Inc. (USA) and have been used previously to amplify the ITS region between the 18S and 28S rRNA fungal genes. PCR amplification was performed as previously described [21] in a MultiGene II Thermal Cycler (Labnet International, Inc., Edison, NJ, USA). The PCR protocol consisted of an initial denaturation step at 95 °C for 5 min, followed by 35 cycles of 35 s denaturation at 95 °C, 35 s annealing at 55 °C, and 2 min elongation at 72 °C. The PCR amplification was terminated by incubating for 10 min at 72 °C. Successful PCR amplification was confirmed by visualizing the products (7 μL) by electrophoresis on a 1% agarose/TBE gel and subsequent staining in ethidium bromide for 10 min. Single bands corresponding to different PCR products were purified from gel using the QIAEX II Gel Extraction Kit (QIAGEN, Germantown, MD, USA). Pure DNA was sequenced in both orientations using the Sequencing Services from MACROGEN (Korea) and compared to the sequences deposited in GenBank (NCBI). Sequence comparison and phylogenetic relationships were analyzed using the CLC software (QIAGEN, Germantown, MD, USA). The closest known relative for each sequence was determined using a BLAST(NCBI) search. The evolutionary relationship was inferred according to the Maximum Likelihood Phylogeny 1.2 method using CLC Main Workbench 7.9.1. The bootstrap analysis considered a total of 100 replicates.
3. Results
3.1. Disease Symptoms
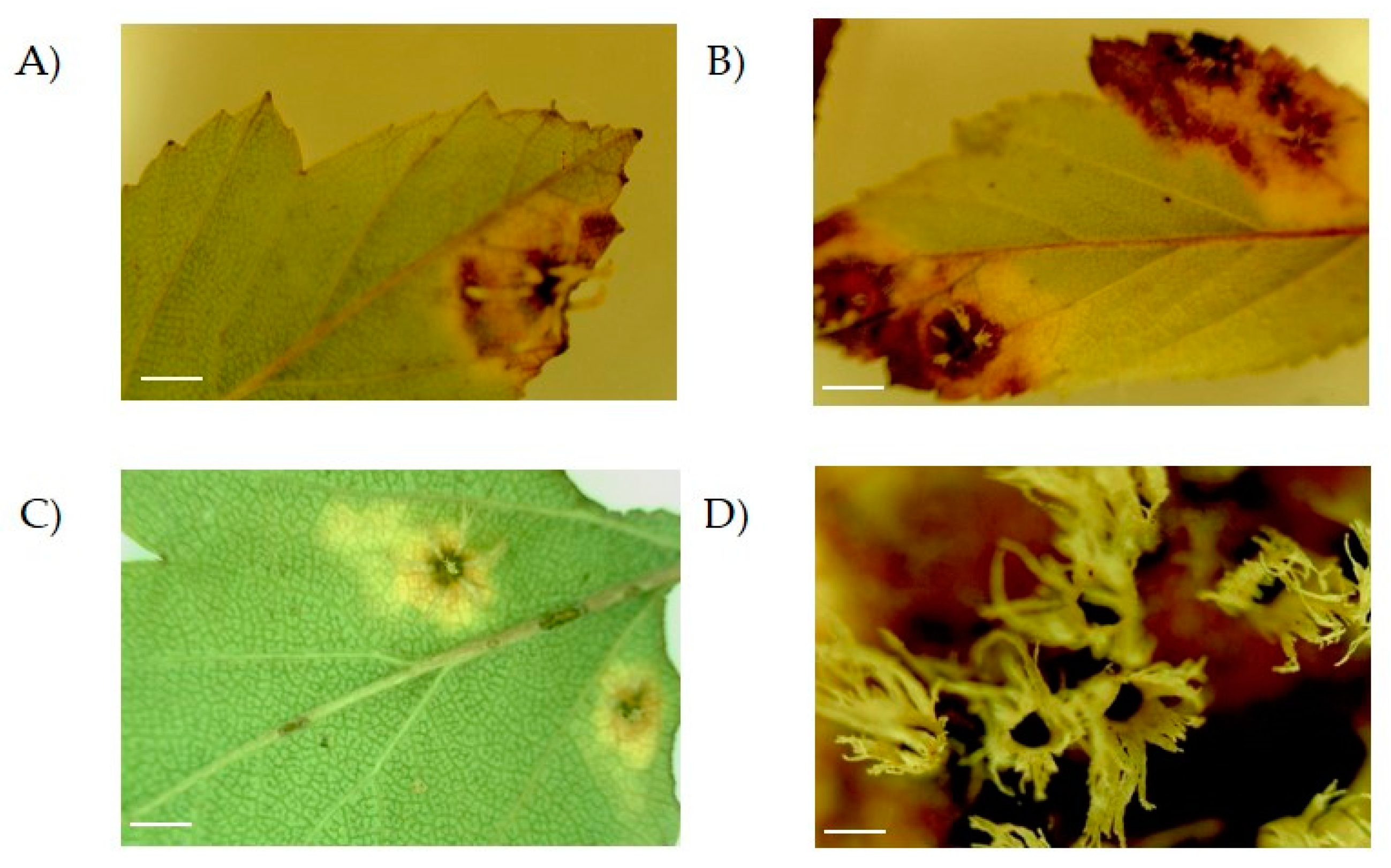
During 2010–2011, lesions were observed in leaves of Crataegus trees that were growing in the wild and in greenhouses in several locations across Puebla (Mexico). In these plants, lesions appeared as small, circular, dark brown spots (Figure 1A,C). Besides, larger lesions with a necrotic center and brown margin occupying broader areas of the leaf were observed (Figure 1B). On top of this, lesions developed white structures on the back of the leaf accompanied by an almost total necrosis (Figure 1B,D).
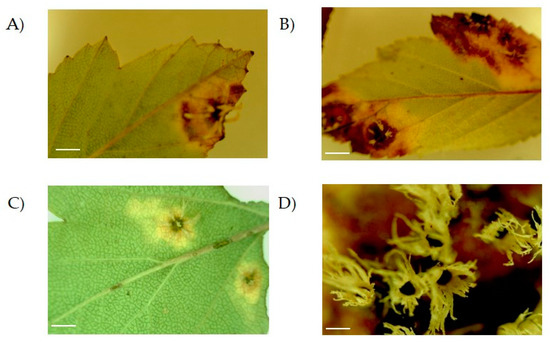
Figure 1.
Lesions observed on leaves of Crataegus sp. plants. Samples were observed using the microscope with the 10X objective. The lesion evolved as a yellow and brown spot on the surface covering different parts of the leaf (compare (A), (B) and (C); scale bar = 0.5 cm). An enlarged view of the structures can be observed in (D) with the 40X objective; scale bar = 0.5 mm.
3.2. Fungal Community Associated to the Leaf Spot in Crataegus spp Plants
To determine not only the fungal pathogen but also to assess the general fungal population of the Crataegus plants with this lesion, we intended to identify the fungal genus associated to the leaf spot. To accomplish this, fungal isolates were recovered from the structures, from the injured part of the leaf which constitutes the endophytic fungal population, and from the surface of the lesion that corresponded to the epiphytic fungal community. According to the phenotypical characteristics observed (Figure S1), 18 genera were identified inhabiting the diseased leaves of Crataegus.
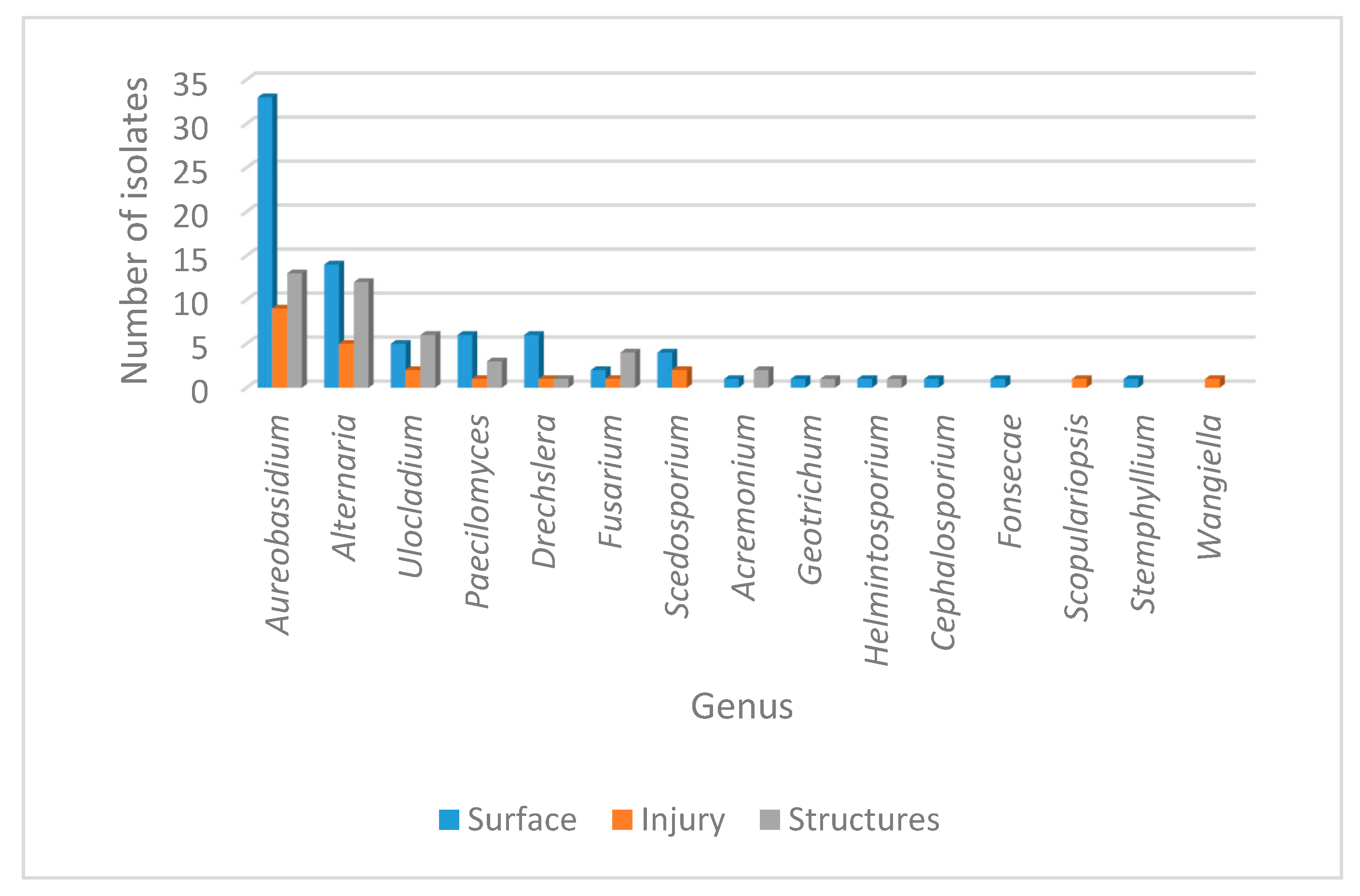
Considering the origin of the sample, fungal incidence is presented in Table 1. A variable distribution as epiphytes, endophytes or isolates from the structures for the 18 genera was observed, with a total of 149 isolates identified. As expected, the largest population corresponded to the epiphytic community with 80 isolates, followed by the structures with 44 isolates and finally the endophytic group with 25 isolates. Overall, the most prevalent genera recovered from the three types of samples were Aureobasidium sp. and Alternaria sp. However, several genera also showed a significant distribution over the three different origins, including Ulocladium sp., Paecilomyces sp., Dreschelera sp. and Fusarium sp. Interestingly, some genera were recovered exclusively from one origin; that was the case for Cephalosporium sp., Fonsecae sp., Phialophora sp. and Stemphylium sp. (recovered only as epiphytes), while Scopulariopsis sp. and Wangiella sp. were found only as endophytes. The only genus restricted to the structures was Trichosporum sp. The general distribution of the different genera phenotypically identified is presented in Figure 2.

Table 1.
Frequency of isolation for the genera identified according to their origin.
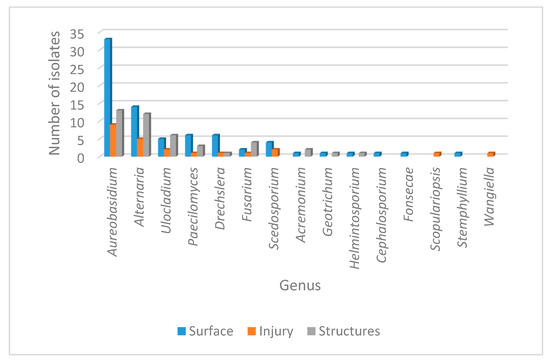
Figure 2.
Abundance of fungal genera isolated from leaf disease in Crataegus. The number of fungal isolates corresponding to the different genera identified phenotypically is shown. Isolate distribution is presented for the surface (blue), for injured tissue (orange) and for the structures (gray).
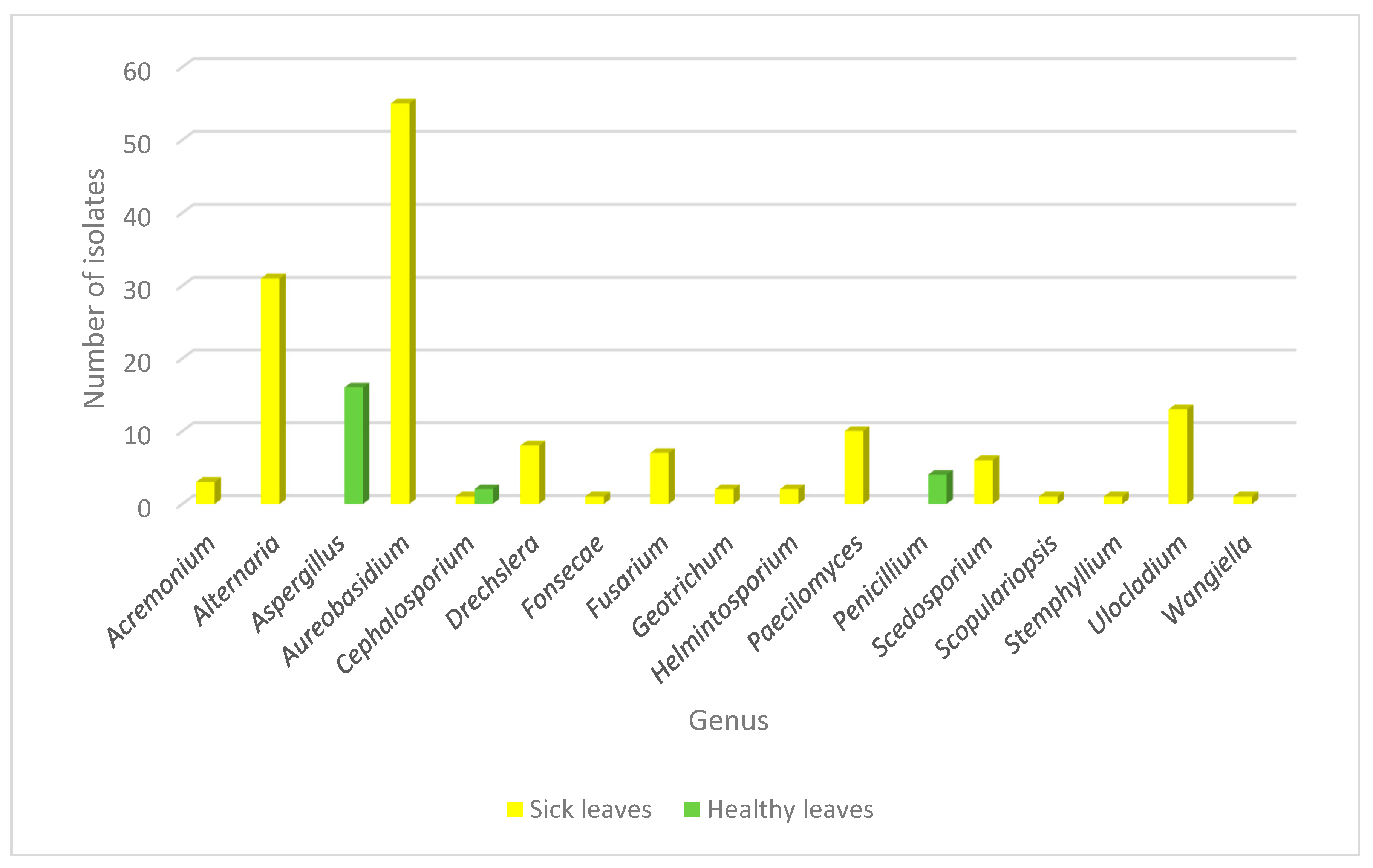
In a similar manner, fungal epiphytic and endophytic isolates were recovered from the tissue of healthy leaves from the same plant in order to analyze the fungal population inhabiting the plant from both healthy and diseased backgrounds. Using this approach, the genera recovered from healthy plants were Aspergillus sp., Cephalosporium sp. and Penicillium sp. Interestingly, Aspergillus sp. and Penicillium sp. were found only in healthy leaves and none of the genera found as endophytes or in the galls were identified in healthy tissue. Cephalosporium sp. was the only genus that was isolated from both healthy and diseased tissue, but in the last context, it appeared only once as an epiphyte (Figure 3).
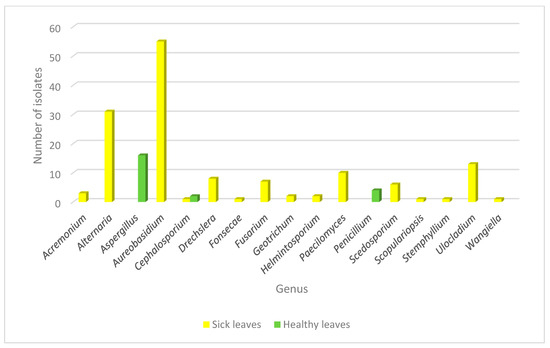
Figure 3.
Abundance of fungal genera isolated from diseased and healthy leaves in Crataegus. Fungal distribution identified in the endophytic and epiphytic population in healthy (green) and sick (yellow) leaves is shown.
Recapitulating, we recovered isolates associated to six genera that were highly prevalent in the injured leaves and that were recovered from the three different origins: as epiphytes, as endophytes and from the galls. These genera were Aureobasidium sp., Alternaria sp., Dreschelera sp., Fusarium sp., Paecilomyces sp. and Ulocladium sp.
3.3. Pathogenicity Assay
To assess the capability of the isolated fungi to produce an injury on healthy tejocote plants, some isolates that were recovered from the lesions of the tejocote leaves were inoculated individually and their effect on the leaf was evaluated. For this purpose, we inoculated the isolates indicated in Table 2 and plants were monitored for the appearance of signs of disease on the leaves.

Table 2.
Isolates evaluated in the pathogenesis assays and the genus phenotypically identified.
We tested two different forms of inoculation: by injection or on the surface after laceration (as described in Material and Methods).
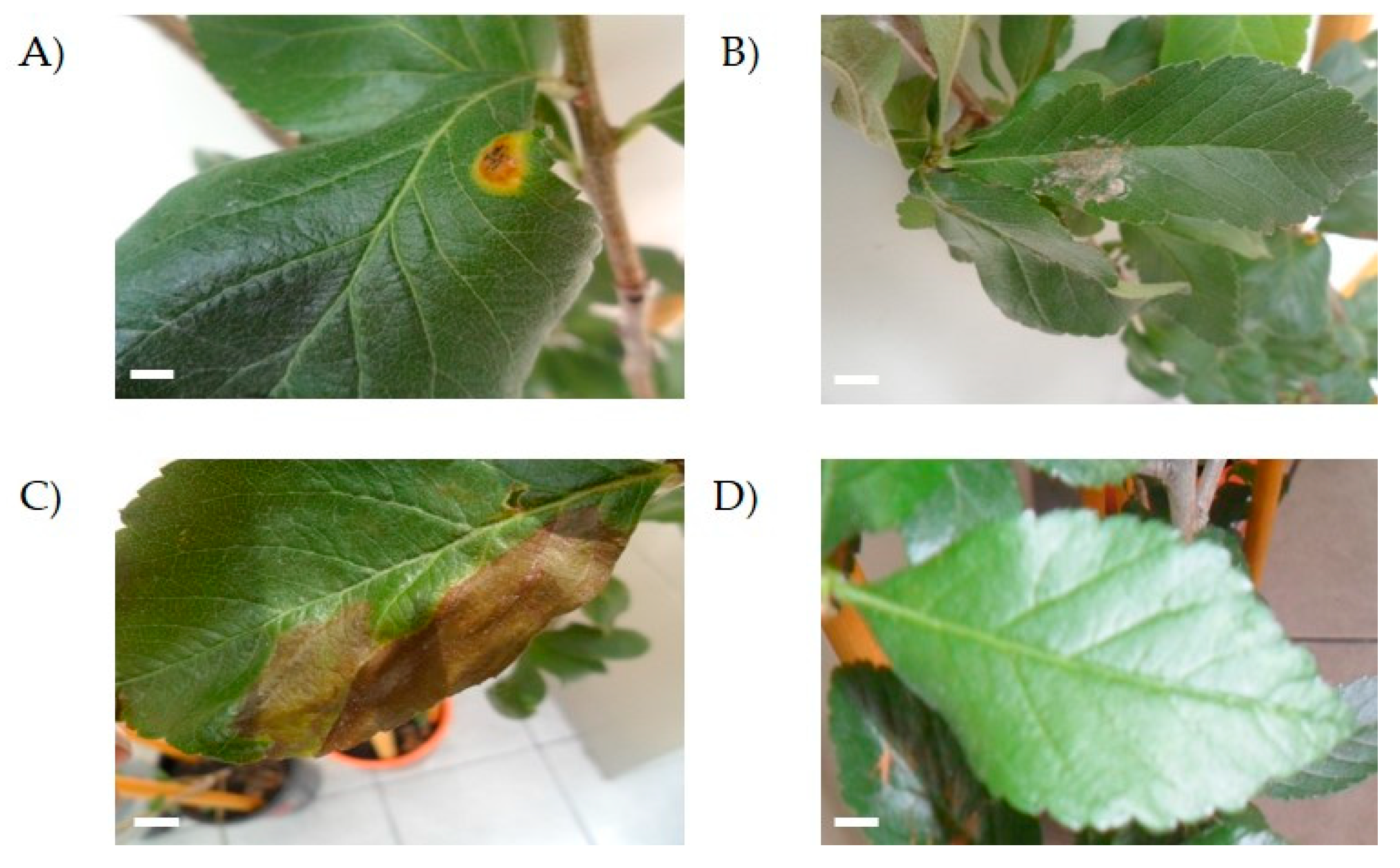
When inoculated by injection, isolates UAP140 and UAP168 showed the ability to develop a lesion in the leaves of healthy tejocote plants 10 days after the injection. Plants continued to be observed until day 35 after the injection, when the control plants remained asymptomatic (Figure 4) and none of the plants inoculated with the other isolates caused disease.
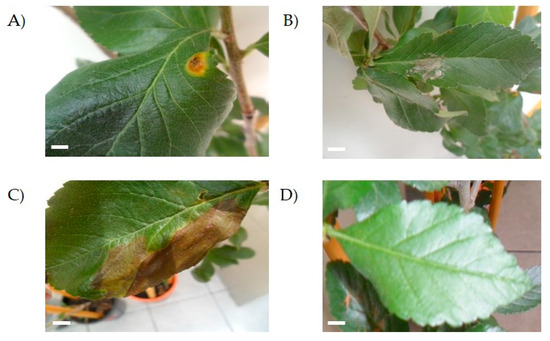
Figure 4.
Pathogenicity test in healthy Crataegus sp. trees. The image shows injuries produced by isolates UAP140 (A), UAP168 (B) and UAP127 (C) in three-month-old trees. Control trees remained uninfected 35 days after infection (D). Scale bar = 0.5 mm.
Plants inoculated with isolates UAP127, UAP140 and UAP168 developed spots on the leaf (Figure 4). However, while isolate UAP168 caused white spots on the leaf surface (Figure 4B), isolate UAP127 produced big necrotic lesions that extended on the surface of the leaf (Figure 4C). On the other hand, isolate UAP140 developed small brown spots surrounded by a yellow circle that highly resembled the features depicted for the original lesion observed in tejocote plants sampled at the beginning of this study (Figure 4A). On the other hand, leaves inoculated superficially did not develop any symptoms, even at the end of the observation period (Figure 4D).
3.4. Molecular Identification
To further characterize the isolates with a pathogenic effect in the plant, the molecular identification of the isolates UAP127 and UAP140 which produced discrete lesions on the surface of the leaves was done. To accomplish this, a pair of primers that have been designed to bind to a conserved region in the 18S and 28S genes and that allow the amplification of the ITS regions flanking the 5.8S gene were used. NCBI BLAST analysis showed that isolate UAP127 bears high similarity (99%) to the sequences of Alternaria arborescens, while isolate UAP140 was highly similar (99%) to Fusarium equiseti. The resulting sequences of the present isolates were submitted to GenBank (accession numbers MK742717 and MK680058, respectively).
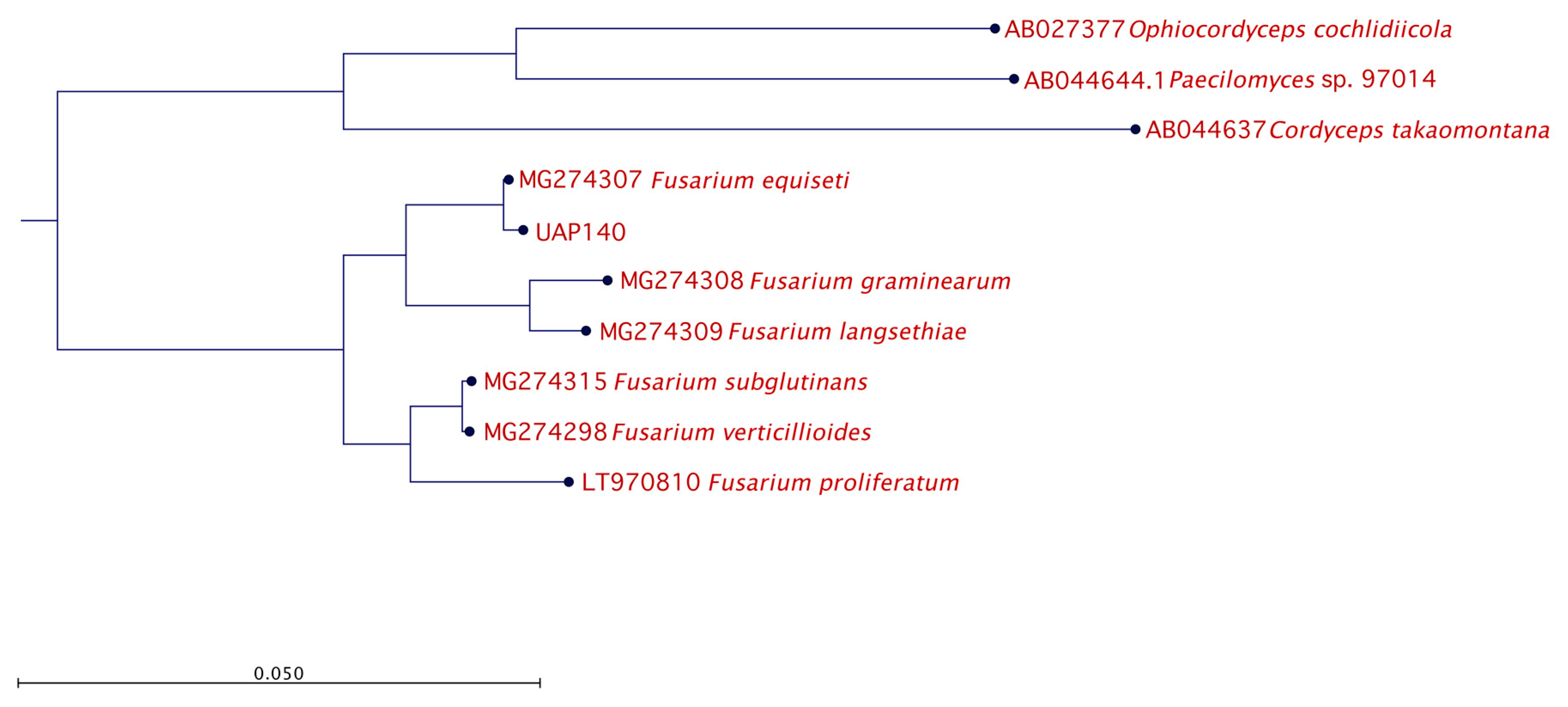
The identified genera Alternaria and Fusarium are well known due to their ability to have a pathogenic effect over a broad spectrum of plants. However, given that the lesion developed in the pathogenicity test with isolate UAP140 was very similar to the original lesion observed at the beginning of this study, we continued our phylogenetic analysis using this isolate, phenotypically identified as Fusarium sp. To this end, isolate UAP140 was compared with reference sequences of F. equiseti and other Fusarium species while using three distant ascomycetes as an outgroup and the phylogenetic tree is presented in Figure 5. With these observations, our molecular results confirmed the identity of the isolates.
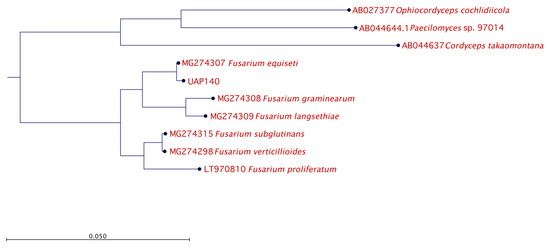
Figure 5.
Phylogenetic relationship for isolate UAP140. The tree with the highest log likelihood is shown. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths measured in the number of substitutions per site. The analysis involved six Fusarium reference nucleotide sequences with a total of 100 replicates in the bootstrap analysis, while three non-related fungal species were used as the outgroup.
4. Discussion
4.1. Pathogens for Crataegus spp.
Traditionally, insects like Rhagoletis pomonella Walsh (Diptera: Tephritidae) are the most studied pests affecting Crataegus spp. orchards in Mexico [22]. However, microbial infections are starting to emerge in plantations and the detection of pathogenic agents is relevant in order to avoid damages in production. As leaf spot disease may pose a severe threat to commercial Crataegus producers, adequate pathogen identification and disease control is required to reduce economic losses.
According to the characteristics observed in the diseased tejocote plant, it was logical to propose that fungal strains could cause the observed lesion, mainly due to the structures that developed on the back of the leaf. So far, few reports of microbial pathogens for Crataegus species are available. Reported diseases for hawthorn include fire blight caused by Erwinia amylovora, the cedar-hawthorn rust generated by Gymnosporangium globosum, the cedar-quince rust produced by Gymnosporangium clavipes and leaf blight and fruit rot caused by Monilinia johnsonii [23]. Diplocarpon mespili (asexual: Entomosporium mespili) is also a common fungal pathogen causing leaf spot in Crataegus spp. [14]. However, none of the reported diseases correlate with the symptoms that are reported here.
4.2. The Fungal Community Associated to Diseased Crataegus spp. Plants
The detection of the fungal agent in plant material can be difficult, particularly when the pathogen is present at low infection levels or when the disease is advanced, providing a context where other pathogenic or opportunistic agents could increase the damage to the plant. In this study, a total of eighteen different genera were isolated from injured tejocote plants. Although some of the genera identified have been reported as phytopathogenic, there are no reports of a fungal genus associated to the lesion that we report here for tejocote plants.
In this study, the most prevalent genera were Aureobasidium, Alternaria, Ulocladium, Paecilomyces, Drechslera and Fusarium. However, the isolates with the ability to produce a disease in healthy tejocote plants corresponded to the genera Alternaria and Fusarium.
It has been reported that Alternaria sp. causes leaf spot for different hosts and in some cases, it can cause conidia to emerge from the injury (this was observed in this study for tejocote leaves) [24]. The genus Alternaria is ubiquitous and abundant in the atmosphere, soil, seeds and agricultural facilities. It includes plant pathogenic and saprophytic species that may affect crops in the field or can cause harvest and postharvest decay of plant products. [25] Alternaria sp. have been reported as a pathogen for apple, carnation, carrots, cruciferous, cucumber, tomato [26], geranium [27] and other plants, highlighting the need for a proper detection and control system. Some species have been associated to a particular disease. For example, Alternaria iridiaustralis was reported as the causative agent of leaf spot on Iris ensata in China [28]. Several efforts have been developed to identify plant pathogens in Korea, where Alternaria tenuissima was linked to the first report of leaf spot caused on black chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa) [29] and Alternaria simsimi was associated to the first report of a pathogen causing leaf spot on sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) [30]. Another serious disease worldwide is leaf spot and blight disease of sunflower, which is caused by Alternaria helianthi (Hansford) Tubaki and Nishihara and molecular detection approaches have been developed in order to avoid economic losses [24]. In this regard, genotyping assays have been developed recently in order to identify Alternaria species causing the important and widespread citrus brown spot disease [31,32].
In this work, the isolate UAP140 that belongs to the genus Fusarium was able to produce similar lesions to those observed in diseased tejocote plants from Mexican plant orchards. Fusarium sp. has been reported as phytopathogen for beets [33], strawberry [34], corn [35] and lettuce [36], while different Fusarium species have been associated with the development of leaf spots in orchids [37], onion [38], and wild rocket [39], amongst others.
It has been reported that species of Fusarium and Alternaria could be pathogens of the same plant. For example, three fungal diseases of opium poppy in Eastern Uttar Pradesh have been reported [40], including damping of opium seedlings caused by Fusarium solavi (Mart) Sacc and leaf spot caused by Alternaria alternata (Fr) Keisler. According to the characteristics observed in the original lesion in correlation to the pathogenicity test performed in this work, it could be tempting to propose that the presence of both Fusarium and Alternaria species are necessary to produce the disease observed in tejocote leaves. These two fungal genera are widely distributed, and they could easily coexist in different environments. Interestingly, lesions similar to those reported here have been observed in other Rosaceae plants in Mexico and other locations, like Central Park in New York (personal observation; Rebeca Martínez and Nancy Martínez), suggesting that the disease is widespread in North America.
4.3. The Context of the Disease
Many of the species identified in this study have been previously reported as phytopathogens. However, none of them have been associated to the lesions reported in this work. On the other hand, some of the less frequently isolated species have usually been considered as opportunistic pathogens, like Geotrichum sp. that has only recently been associated with sour rot of loquat [41], fruit rot of strawberry [42] and sour rot of peaches in USA and Pakistan [43,44]. With the conditions tested in this study, we were not able to fully reproduce the original symptoms found in the diseased tejocote plants. For this reason, it would be tempting to propose that more than one fungal species could be responsible for the disease in the plant. Moreover, considering the abundance of fungal isolates recovered from diseased tejocote plants, we could also propose that there could be an existing condition necessary for the infection or for the appearance of the leaf spot with the structures on the back that we observed, given that (as for every organism) in plants, symptoms occur both because of the action of the pathogen and the response of the host.
Overall, this work constitutes the first report for characteristic leaf spot in Crataegus plants. We uncovered the fungal community associated to this lesion through phenotypic identification and we showed the capability of some of these isolates to have a pathogenic effect on healthy plants. Finally, we confirmed the identity of the isolates with phytopathogenic activity using a molecular approach.
To our knowledge, this study constitutes the first report aiming to identify pathogenic fungi causing leaf spot disease accompanied by leaf structures in Mexican tejocote orchards. However, further studies would be necessary in order to confirm that the isolate UAP127 that correlates with Alternaria arborescens and isolate UAP140 that proved to be similar to Fusarium equiseti are responsible for the characteristic lesion developed in Crataegus sp. and other Rosaceae.
5. Conclusions
In summary, this study provides a comprehensive view of the abundance, diversity, composition and pathogenic activity of the fungal population associated with Crataegus leaf spots, reported for the first time in this study. A combined phenotypic and molecular approach allowed the identification of 18 fungal genera associated with these diseased leaves, indicating that the general health condition of the plant is compromised due to the fungal infection. Furthermore, some isolates had the ability to develop different injuries in healthy tejocote plants. According to the phytopathogenic test, the isolate that was found to be highly similar to Fusarium equiseti was able to develop leaf spots similar to those depicted for the original lesion. The results from this work are relevant for further treatment of diseased tejocote plants, an important cultivar with different applications and great economic relevance to Mexican production.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2076-2607/8/3/459/s1.
Author Contributions
The overall approach of this study was designed by N.M.-M. and R.D.M.-C. S.S.-C. conducted the experiments. M.d.l.C.M.-S. directed fungal phenotypical identification. All authors were involved in experiment design, data analysis and manuscript preparation. All authors have read and agree to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Partial funding was received from VIEP-BUAP.
Acknowledgments
Sonia Salazar Cerezo received a fellowship for graduate studies from CONACYT.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest
References
- Chang, Q.; Zuo, Z.; Harrison, F.; Chow, M.S. Hawthorn. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2002, 2, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phipps, J.B.; O’Kennon, R.; Lance, R.W. Hawthorns and Medlars; Timber Press: Portland, OR, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Núñez-Colín, C.; Nieto-Angel, R.; Barrientos-Priego, A.F.; Sahagún-Castellanos, J.; Segura, S.; González-Andrés, F. Variability of three regional sources of germplasm of tejocote (Crataegus spp.) from central and southern Mexico. Genet. Resour. Crop. Evol. 2008, 55, 1159–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto-Angel, R.; Borys, M.W. Enfoques tecnológicos en la fruticultura. In Un tributo a Raúl Mosqueda, 1st ed.; Universidad Autónoma de Chapingo: Chapingo, México, 2008; Germoplasma y usos del tejocote en México. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, R.; Abuharfeil, N.; Shabsoug, B. The effect of Crataegus aronica aqueous extract in rabbits fed with high cholesterol diet. Eur. J. Sci. Res. 2008, 22, 352–360. [Google Scholar]
- Pittler, M.H.; Schmidt, K.; Ernst, E. Hawthorn extract for treating chronic heart failure: Meta-analysis of randomized trials. Am. J. Med. 2003, 114, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güven, K.; Yücel, E.; Çetintaş, F. Antimicrobial activities of fruits of Crataegus and Pyrus species. Pharm. Biol. 2006, 44, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahri-Sahloul, R.; Ben Fredj, R.; Boughalleb, N.; Shriaa, J.; Saguem, S.; Hilbert, J.L.; Harzallah-Skhiri, F. Phenolic composition and antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of extracts obtained from Crataegus azarolus L. var. aronia (Willd.) Batt. ovaries calli. J. Bot. 2014, 2014, 623651. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, S.K.; Jain, V.; Verma, D.; Khamesra, R. Crataegus Oxyacantha—A Cardioprotective herb. J. Herbal Med. Toxicol 2007, 1, 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- Bahri-Sahloul, R.; Ammar, S.; Fredj, R.B.; Saguem, S.; Grec, S.; Trotin, F. Polyphenol contents and antioxidant activities of extracts from flowers of two Crataegus azarolus L. varieties. Pakistan J. Biol. Sci. 2009, 12, 660–668. [Google Scholar]
- Nieto-Angel, R. Frutales Nativos. In Un recurso fitogenético de México, 1st ed.; Universidad Autónoma de Chapingo: Chapingo, México, 2007; Colección, conservación y caracterización del tejocote (Crataegus spp.); pp. 26–118. [Google Scholar]
- Nieto-Angel, R.; Borys, M.W. Relaciones fisiológicas y morfológicas de injertos de frutales sobre tejocote (Crataegus spp.) como portainjerto. Revista Chapingo Serie. Hortic. 1999, 5, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado-Rosales, D.; Nieto-López, E.H.; Téliz-Ortiz, D.; Ayala-Escobar, V.; Silva-Rojas, H.V.; Nieto-Angel, R.; Leyva-Mir, S.G.; Jimenez-Nieto, A.; Méndez-Inocencio, C. First report of Gymnosporangium clavipes Cooke Peck affecting Crataegus mexicana var. Chapeado and C. gracilior in Mexico. Res. Plant Dis. 2015, 21, 250–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, W.A.; Lyon, H.H. Diseases of Trees and Shrubs, 2nd ed.; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Prats, G. Microbiología clínica. Ed. Médica Panamericana 2006, 366. [Google Scholar]
- Salazar-Cerezo, S.; Martínez-Montiel, N.; Cruz-López, M.C.; Martínez-Contreras, R. Fungal diversity and community composition of culturable fungi in Stanhopea tigrina cast gibberellin producers. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koneman, E. Diagnóstico Microbiólogico: Texto y Atlas a color; Editorial Médica Panamericana: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2001; p. 1432. [Google Scholar]
- Arenas, R. Micología Médica Ilustrada, 3rd ed.; Mc Graw-Hill: México, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Gardes, M.; Bruns, T.D. ITS primers with enhanced specificity for Basidiomycetes application to the identification of mycorrhizae and rusts. Mol. Ecol. 1993, 2, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilgalys, R.; Hester, M. Rapid Genetic Identification and Mapping of Enzymatically Amplified Ribosomal DNA from Several Cryptococcus Species. J. Bac. 1990, 172, 4238–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munguía-Pérez, R.; Díaz-Cabrera, E.; Martínez-Montiel, N.; Muñoz-Rojas, J.; Martínez-Contreras, R. Fungal diversity in soil samples from a Mexican region with endemic dermatomycoses. Micol. Apl. Int. 2011, 23, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Rull, J.; Aluja, M.; Feder, J.; Berlocher, S. Distribution and host range of hawthorn-infesting Rhagoletis (Diptera: Tephritidae) in Mexico. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2006, 99, 662–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, H.Y.; Lee, K.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, S.K. First Report of Gymnosporangium globosum Causing American Hawthorn Rust in Korea. Plant Pathol. J. 2008, 24, 84–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udayashankar, A.C.; Chandra Nayaka, S.; Archana, B.; Anjana, G.; Niranjana, S.R.; Mortensen, S.N.; Lund, O.S.; Prakash, H.S. Specific PCR-based detection of Alternaria helianthi: The cause of blight and leaf spot in sunflower. Arch. Microbiol 2012, 194, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logrieco, A.; Bottalico, A.; Mul, G.; Moretti, A.; Perrone, G. Epidemiology of toxigenic fungi and their associated mycotoxins for some Mediterranean crops. Eur J. Plant. Pathol 2003, 109, 645–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, G.B.; Campbell, C.L.; Lucas, L.T. Introduction to Plant Diseases: Identification and Management, 2nd ed.; Van Nostrand Reinhold Company: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Daughtrey, M.L. Plagas y enfermedades de las plantas en macetas con flores; American Phytopathological Society, Ed.; Mundi-Prensa: Madrid, España, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.; Tao, Y.Q.; Fan, X.Y.; Oh, S.K.; Lu, H.X.; Denga, J.X. Identification and Characterization of Alternaria iridiaustralis Causing Leaf Spot on Iris ensata in China. Mycobiology 2018, 46, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wee, J.I.; Park, J.H.; Back, C.G.; You, Y.H.; Chang, T. First Report of Leaf Spot Caused by Alternaria tenuissima on Black Chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa) in Korea. Mycobiology 2016, 44, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.P.; Paul, N.C.; Lee, H.B.; Yu, S.H. First Record of Alternaria simsimi Causing Leaf Spot on Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) in Korea. Mycobiology 2014, 42, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garganese, F.; Schena, L.; Siciliano, I.; Prigigallo, M.I.; Spadaro, D.; De Grassi, A. Characterization of Citrus-Associated Alternaria Species in Mediterranean Areas. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garganese, F.; Ippolito, A.; di Rienzo, V.; Lotti, C.; Montemurro, C.; Sanzani, S.M. A new high-resolution melting assay for genotyping Alternaria species causing citrus brown spot. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 4578–4583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, V.; Rengifo, J.; Khan, M.; Geiser, D.M.; Mansfield, M.; Secor, G. First Report of a novel Fusarium species causing yellowing decline of sugar beet in Minnesota. Plant. Dis. 2008, 92, 1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koike, S.T.; Kirkpatrick, S.C.; Gordon, T.R. Fusarium wilt of strawberry caused by Fusarium oxysporum in California. Plant. Dis 2009, 93, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa, M.; Rodríguez, R.; Guerrero, B.; González, M.; Pons, J.; Jiménez, J.; Ramírez, J.; Andrio, E.; Mendoza, M. Caracterización de especies de Fusarium asociadas a la pudrición de raíz de maíz en Guanajuato, México. Iberoamericana de Fitopatología 2010, 28, 124–134. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, M.R.; Subbarao, K.V.; Raid, N.R.; Kurtz, E.A. Plagas y enfermedades de la lechuga; American Phytopathological Society, Ed.; Mundi-Prensa: Madrid, España, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.S.; Park, J.H.; Back, C.G.; Park, M.J. First report of Fusarium subglutinans causing leaf spot disease on Cymbidium orchids in Korea. Mycobiology 2015, 43, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkunan, V.; Ji, P. First Report of Leaf Spot on Onion Caused by Fusarium acuminatum in Georgia. Plant. Dis. 2013, 97, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garibaldi, A.; Gilardi, G.; Ortu, G.; Gullino, M.L. First Report of Leaf Spot of Wild Rocket (Diplotaxis tenuifolia) Caused by Fusarium equiseti in Italy. Plant Dis. 2015, 99, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, R.; Tripathi, R.D.; Johri, J.K.; Shukla, D.S. Some new fungal diseases of opium poppy (Papaver somniferum). J. Plant Pathol. 1987, 3, 213–217. [Google Scholar]
- Hafeez, R.; Akhtar, N.; Shoaib, A.; Bashir, U.; Haider, M.S.; Awan, Z.A. First report of Geotrichum candidum from Pakistan causing postharvest sour rot in loquat (Eriobotrya Japonica). J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2015, 25, 1737–1740. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, M.; Hamid, M.I.; Ghazanfar, M.U.; Akhtar, N.; Raza, M. First report of fruit rot of strawberry caused by Geotrichum candidum in Pakistan. Plant. Dis. 2016, 100, 1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michailides, T.J.; Morgan, D.P.; Day, K.R. First report of sour rot of California peaches and nectarines caused by yeasts. Plant Dis. 2004, 88, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.W.; Rehman, A.; Malik, A.U.; Iqbal, Z.; Amin, M.; Ali, S.; Hameed, A.; Sarfraz, S. First Report of Geotrichum candidum Causing Postharvest Sour Rot of Peach in Punjab, Pakistan. Plant Dis. 2017, 101, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).