Bacillus cytotoxicus Isolated from a Pristine Natural Geothermal Area Reveals High Keratinolytic Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples Collection
2.2. Isolation of Keratinolytic Microorganisms
2.3. Proteolytic Potential on Solid Media
2.4. Qualitative Evaluation of Feather Degradation
2.5. Identification of Feather-Degrading Isolates: DNA Extraction, 16S rRNA Gene Amplification, and Cytotoxin K-1 (CytK-1) Gene Amplification
2.6. Biochemical and Extracellular Enzymatic Characterization of Bacillus Cytotoxicus (B. cytotoxicus) Isolates
2.7. Keratinase Production and Analytical Determination of Proteolitical Activity
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Identification of the Bacterial Isolates
3.2. Characterization of the Proteolytic and Keratinolytic Capacity of the Isolates
3.3. Quantification of the Keratinolitic Activity of the Most Efficient B. citotoxicus Isolates
3.4. Biochemical and Extracellular Enzymatic Profile Characterization of the B. cytotoxicus Isolates
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Urbieta, M.S.; Donati, E.R.; Chan, K.G.; Shahar, S.; Sin, L.L.; Goh, K.M. Thermophiles in the genomic era: Biodiversity, science, and applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 633–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiacchiarini, P.; Lavalle, L.; Giaveno, A.; Donati, E. First assessment of acidophilic microorganisms from geothermal Copahue-Caviahue system. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 104, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbieta, M.S.; Toril Gonzalez, E.; Giaveno, M.A.; Aguilera Bazàn, A.; Donati, E.R. Archaeal and bacterial diversity in five different hydrothermal ponds in the Copahue region in Argentina. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 37, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbieta, M.S.; Gonzalez-Toril, E.; Aguilera Bazàn, A.; Giaveno, M.A.; Donati, E. Comparison of the microbial communities of hot springs waters and the microbial biofilms in the acidic geothermal area of Copahue (Neuquen, Argentina). Extremophiles 2015, 19, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, C.; Donati, E. Effects of different energy sources on cell adhesion and bioleaching of a chalcopyrite concentrate by extremophilic archaeon Acidianus copahuensis. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 162, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavello, I.; Urbieta, M.S.; Segretin, A.B.; Giaveno, A.; Cavalitto, S.; Donati, E.R. Assessment of Keratinase and Other Hydrolytic Enzymes in Thermophilic Bacteria Isolated from Geothermal Areas in Patagonia Argentina. Geomicrobiol. J. 2018, 35, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, M.A.; Urbieta, M.S.; Donati, E. Arsenic-tolerant microbial consortia from sediments of Copahue geothermal system with potential applications in bioremediation. J. Basic Microbiol. 2019, 59, 680–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesce, A.H. The Domuyo geothermal area, Neunquèn, Argentina. GRC Trans. 2013, 37, 309–314. [Google Scholar]
- Atalah, J.; Càceres-Moreno, P.; Espina, G.; Blamey, J.M. Thermophiles and the applications of their enzymes as new biocatalysts. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 280, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, C.T.; Pellenz, L.; Pereira, J.Q.; Brandelli, A.; Daroit, D.J. Screening of Bacteria for Protease Production and Feather Degradation. Waste Biomass Valorization 2016, 7, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daroit, D.J.; Brandelli, A. A current assessment on the production of bacterial keratinases. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2014, 34, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, A.B.; Antranikian, G. Keratin Degradation by Fervidobacterium pennavorans, a Novel Thermophilic Anaerobic Species of the Order Thermotogales. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 2875–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manczinger, L.; Rozs, M.; Vágvölgyi, C.; Kevei, F. Isolation and characterization of a new keratinolytic Bacillus licheniformis strain. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 19, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.G.; Swarnalatha, S.; Gayathri, S.; Nagesh, N.; Sekaran, G. Characterization of an alkaline active thiol forming extracellular serine keratinase by the newly isolated Bacillus pumilus. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 104, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazotto, A.M.; Coelho, R.R.R.; Cedrola, S.M.L.; De Lima, M.F. Keratinase production by three Bacillus spp. using feather meal and whole feather as substrate in a submerged fermentation. Enzym. Res. 2011, 2011, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sangali, S.; Brandelli, A. Feather keratin hydrolysis by a Vibrio sp. strain kr2. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 89, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, E.; Cannavan, F.S.; Duarte, F.R.S.; Taffarel, J.A.S.; Tsai, S.M.; Brandelli, A. Characterization of feather-degrading bacteria from Brazilian soils. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2011, 65, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Lee, C.G.; Casale, E.S.; Shih, J.C. Purification and Characterization of a Keratinase from a Feather-Degrading Bacillus licheniformis Strain. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1992, 58, 3271–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Toni, C.H.; Richter, M.F.; Chagas, J.R.; Henriques, J.A.; Termignoni, C. Purification and characterization of an alkaline serine endopeptidase from a feather-degrading Xanthomonas maltophilia strain. Can. J. Microbiol. 2002, 48, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingeberg, M.; Galunsky, B.; Sjoholm, C.; Kasche, V.; Antranikian, G. Purification and Properties of a Highly Thermostable, Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Resistant and Stereospecific Proteinase from the Extremely Thermophilic Archaeon Thermococcus stetteri. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 3098–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sako, Y.; Chavez Croocker, P.; Ishida, Y. An extremely heat-stable extracellular proteinase (aeropyrolysin) from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Aeropyrum pernix K1. FEBS Lett. 1997, 415, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nam, G.W.; Lee, D.W.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, N.J.; Kim, B.C.; Choe, E.A.; Hwang, J.K.; Suhartono, M.T.; Pyun, Y.R. Native-feather degradation by Fervidobacterium islandicum AW-1, a newly isolated keratinase-producing thermophilic anaerobe. Arch. Microbiol. 2002, 178, 538–547. [Google Scholar]
- Riessen, S.; Antranikian, G. Isolation of Thermoanaerobacter keratinophilus sp. nov.; a novel thermophilic, anaerobic bacterium with keratinolytic activity. Extremophiles 2001, 5, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kublanov, I.V.; Perevalova, A.A.; Slobodkina, G.B.; Lebedinsky, A.V.; Bidzhieva, S.K.; Kolganova, T.V.; Kaliberda, E.N.; Rumsh, L.D.; Haertle, T.; Bonch-Osmolovskaya, E.A. Biodiversity of Thermophilic Prokaryotes with Hydrolytic Activities in Hot Springs of Uzon Caldera, Kamchatka (Russia). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ionata, E.; Canganella, F.; Bianconi, G.; Benno, Y.; Sakamoto, M.; Capasso, A.; Rossi, M.; La Cara, F. A novel keratinase from Clostridium sporogenes bv. pennavorans bv. nov.; a thermotolerant organism isolated from solfataric muds. Microbiol. Res. 2008, 163, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, T.; Yamada, Y.; Mitsuya, H.; Shigeri, Y.; Yoshida, Y.; Saito, Y.; Matsui, H.; Watanabe, K. Sustainable and practical degradation of intact chicken feathers by cultivating a newly isolated thermophilic Meiothermus ruber H328. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 82, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidmar, B.; Vodovnik, M. Microbial Keratinases: Enzymes with Promising Biotechnological Applications. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 56, 312–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Rajput, R.; Sharma, R.; Gupta, N. Biotechnological applications and prospective market of microbial keratinases. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 9931–9940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas, G.R.; Bengochea, L.; Mas, L.C. Hydrothermal surface alteration in the Copahue Geothermal Field (Argentina). In Proceedings of the Twenty-First workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering, Stanford, CA, USA, 22–24 January 1996; pp. 241–246. [Google Scholar]
- Cavello, I.A.; Cavalitto, S.F.; Hours, R.A. Biodegradation of a Keratin Waste and the Concomitant Production of Detergent Stable Serine Proteases from Paecilomyces lilacinus. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 167, 945–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riffel, A.; Lucas, F.; Heeb, P.; Brandelli, A. Characterization of a new keratinolytic bacterium that completely degrades native feather keratin. Arch. Microbiol. 2003, 179, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D. Genomic DNA isolation from different biological materials. In Protocols for Nucleic Acid Analysis by Nonradioactive Probes. Methods in Molecular Biology; Hilario, E., Mackay, J., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guinebretiere, M.H.; Fagerlund, A.; Granum, P.E.; Nguyen-The, C. Rapid discrimination of cytK-1 and cytK-2 genes in Bacillus cereus strains by a novel duplex PCR system. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 259, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buzzini, P.; Martini, A. Extracellular enzymatic activity profiles in yeast and yeast-like strains isolated from tropical environments. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 93, 1020–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves-Prado, H.F.; Pavezzi, F.C.; Leite, R.S.R.; De Oliveira, V.M.; Sette, L.D.; DaSilva, R. Screening and Production Study of Microbial Xylanase Producers from Brazilian Cerrado. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 161, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guinebretiere, M.H.; Auger, S.; Galleron, N.; Contzen, M.; De Sarrau, B.; De Buyser, M.L.; Lamberet, G.; Fagerlund, A.; Granum, P.E.; Lereclus, D.; et al. Bacillus cytotoxicus sp. nov. is a novel thermotolerant species of the Bacellus cereus Group occasionally associated with food poisoning. Int. J. Syst. Evolut. Micriol. 2013, 63, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contzen, M.; Hailer, M.; Rau, J. Isolation of Bacillus cytotoxicus from various commercial potato products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 174, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.Q.; Lopes, F.C.; Petry, M.V.; Da Costa Medina, L.F.; Brandelli, A. Isolation of three novel Antarctic psychrotolerant feather-degrading bacteria and partial purification of keratinolytic enzyme from Lysobacter sp. A03. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014, 88, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Azeredo, L.A.I.; De Lima, M.B.; Coelho, R.R.R.; Freire, D.M.G. Thermophilic protease production by Streptomyces sp. 594 in submerged and solid-state fermentations using feather meal. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 100, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.M.; Richter, C.S.; MacKenzie, J.M.; Shih, J.C.H. Isolation, Identification, and Characterization of a Feather-Degrading Bacterium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 1509–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohamedin, A.H. Isolation, identification and some cultural conditionsof a protease-producing thermophilic Streptomyces straingrown on chicken feather as a substrate. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 1999, 43, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, J.M.; Yang, J.I.; Chen, W.M.; Pan, M.H.; Tsai, M.L.; Lai, Y.J.; Hwang, A.; Pan, B.S.; Lin, C.Y. Purification and characterization of a thermostable keratinase from Meiothermus sp. I40. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2012, 70, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, S.K.; Konwarh, R.; Mukherjee, A.K. Purification, characterization and biotechnological application of an alkaline β-keratinase produced by Bacillus subtilis RM-01 in solid-state fermentation using chicken-feather as substrate. Biochem. Eng. J. 2009, 45, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bihari, Z.; Vidèki, D.; Mihalik, E.; Szvetnik, A.; Szabò, Z.; Balàzs, M.; Kesseru, P.; Kiss, I. Degradation of Native Feathers by a Novel Keratinase-Producing, Thermophilic Isolate, Brevibacillus thermoruber T1E. Z. Nat. C 2010, 65, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shrinivas, D.; Naik, G.R. Characterization of alkaline thermostable keratinolytic protease from thermoalkalophilic Bacillus halodurans JB 99 exhibiting dehairing activity. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2011, 65, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qian, Y.; Cao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Chang, Z.; Huang, H. Production and Characterization of Keratinolytic Proteases by a Chicken Feather-Degrading Thermophilic Strain, Thermoactinomyces sp. YT06. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 2190–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korkmaz, H.; Hur, H.; Dincer, S. Characterization of alkaline keratinase of Bacillus licheniformis strain HK-1 from poultry waste. Ann. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 201–211. [Google Scholar]
- Ramnani, P.; Gupta, R. Keratinases vis-á-vis conventional proteases and feather degradation. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 23, 1537–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwary, E.; Gupta, R. Medium optimization for a novel 58kDa dimeric keratinase from Bacillus licheniformis ER-15: Biochemical characterization and application in feather degradation and dehairing of hides. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 6103–6110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porres, J.M.; Benito, M.J.; Lei, X.G. Functional expression of keratinase (kerA) gene from Bacillus licheniformis in Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol. Lett. 2002, 24, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeevana Lakshmi, P.; Kumari Chitturi, C.M.; Lakshmi, V.V. Efficient Degradation of Feather by Keratinase Producing Bacillus sp. Int. J. Microbiol. 2013, 2013, 608321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laba, W.; Choinska, A.; Rodziewicz, A.; Piegza, M. Keratinolytic abilities of Micrococcus luteus from poultry waste. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2015, 46, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gurav, R.G.; Jadhav, J.P. Biodegradation of keratinous waste by Chryseobacterium sp. RBT isolated from soil contaminated with poultry waste. J. Basic Microbiol. 2013, 53, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, T.; Shankar, T.; Thangapandian, V.; Ramasubramanian, V. Optimization of Cultural Condition for Keratinase Production Using Bacillus cereus TS1. Insight Microbiol. 2013, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeong, J.H.; Lee, O.M.; Jeon, Y.D.; Kim, J.D.; Lee, N.R.; Lee, C.Y.; Son, H.J. Production of keratinolytic enzyme by a newly isolated feather-degrading Stenotrophomonas maltophilia that produces plant growth-promoting activity. Process Biochem. 2010, 45, 1738–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lateef, A.; Oloke, J.K.; Gueguim Kana, E.B.; Sobowale, B.O.; Ajao, S.O.; Bello, B.Y. Keratinolytic activities of a new feather-degrading isolate of Bacillus cereus LAU 08 isolated from Nigerian soil. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2010, 64, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhfakh, N.; Ktari, N.; Haddar, A.; Mnif, I.H.; Dahmen, I.; Nasri, M. Total solubilisation of the chicken feathers by fermentation with a keratinolytic bacterium, Bacillus pumilus A1, and the production of protein hydrolysate with high antioxidative activity. Process Biochem. 2011, 46, 1731–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Jain, P.C.; Agrawal, S.C. Feather degradation by Streptomyces exfoliatus CFS 1068. Ann. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, D.K.; Das, A.; Thatoi, H.; Mondal, K.C.; Mohapatra, P.K.D. Keratinase Production and Biodegradation of Whole Chicken Feather Keratin by a Newly Isolated Bacterium under Submerged Fermentation. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 167, 1040–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouacem, K.; Bouanane-Darenfed, A.; Zara Jaouadi, N.; Joseph, M.; Hacene, H.; Ollivier, B.; Fardeau, M.L.; Bejar, S.; Jaouadi, B. Novel serine keratinase from Caldicoprobacter algeriensis exhibiting outstanding hide dehairing abilities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 86, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, T.; De Buyser, M.L.; Granum, P.E. A new cytotoxin from Bacillus cereus that may cause necrotic enteritis. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagerlund, A.; Brillard, J.; Furst, R.; Guinebretiere, M.H.; Granum, P.E. Toxin production in a rare and genetically remote cluster of strains of the Bacillus cereus group. BMC Microbiol. 2007, 7, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rau, J.; Perz, R.; Klitti, G.; Contzen, M. Cereulide forming presumptive Bacillus cereus strains from food-differentiating analyses using cultural methods, LC-MS/MS, PCR, and infrared spectroscopy in consideration of thermotolerant isolates. Berl. Munch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 2009, 122, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carlin, F.; Brillard, J.; Broussolle, V.; Clavel, T.; Duport, C.; Jobin, M.; Guinebretiere, M.H.; Auger, S.; Sorokine, A.; Nguyen-The, C. Adaptation of Bacillus cereus, an ubiquitous worldwide-distributed foodborne pathogen, to a changing environment. Food. Res. Int. 2010, 43, 1885–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinebretiere, M.H.; Thompson, F.L.; Sorokin, A.; Normand, P.; Dawyndt, P.; Ehling-Schulz, M.; Svensson, B.; Sanchis, V.; Nguyen-The, C.; Heyndrickx, M.; et al. Ecological diversification in the Bacillus cereus Group. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 851–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
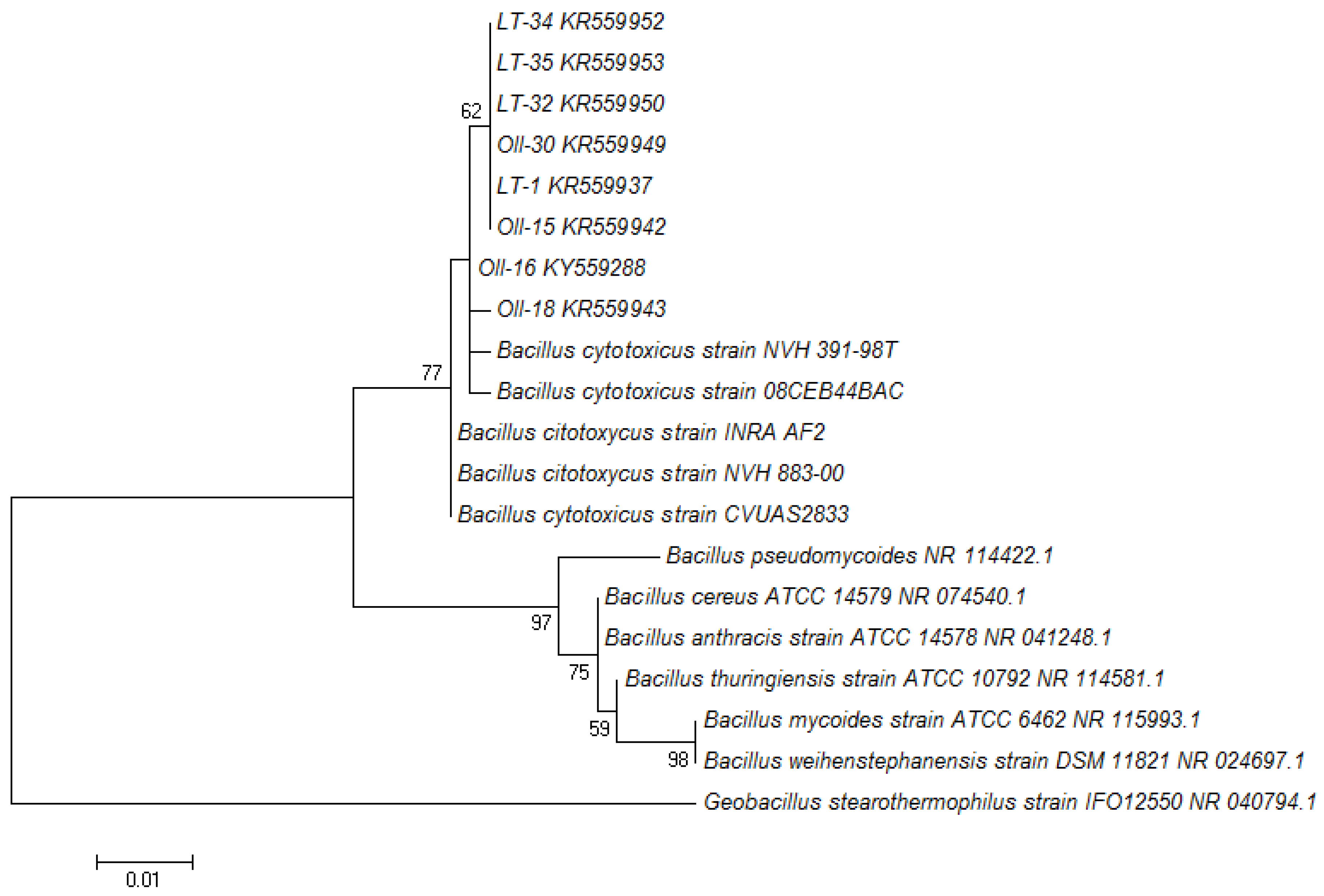
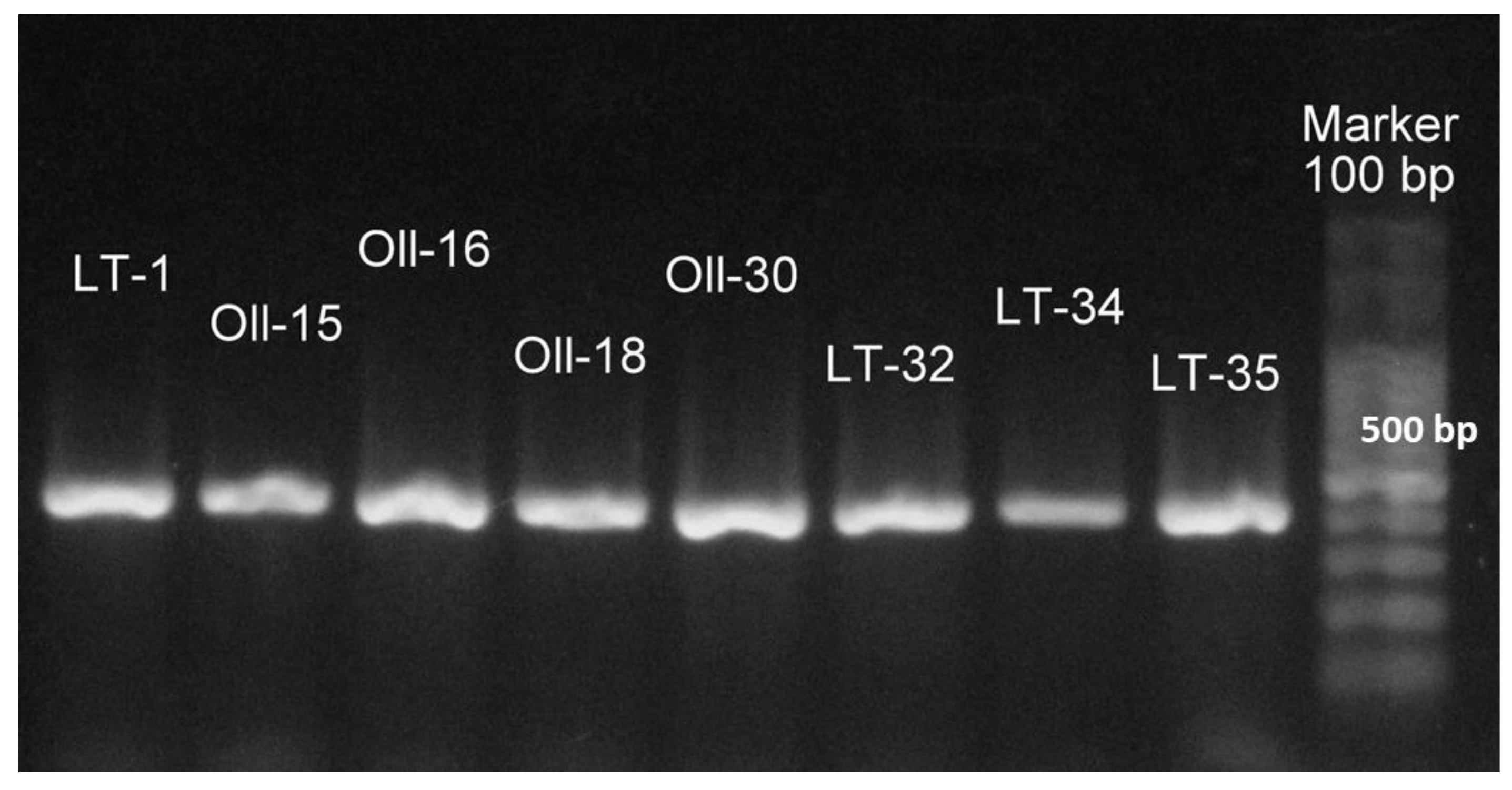
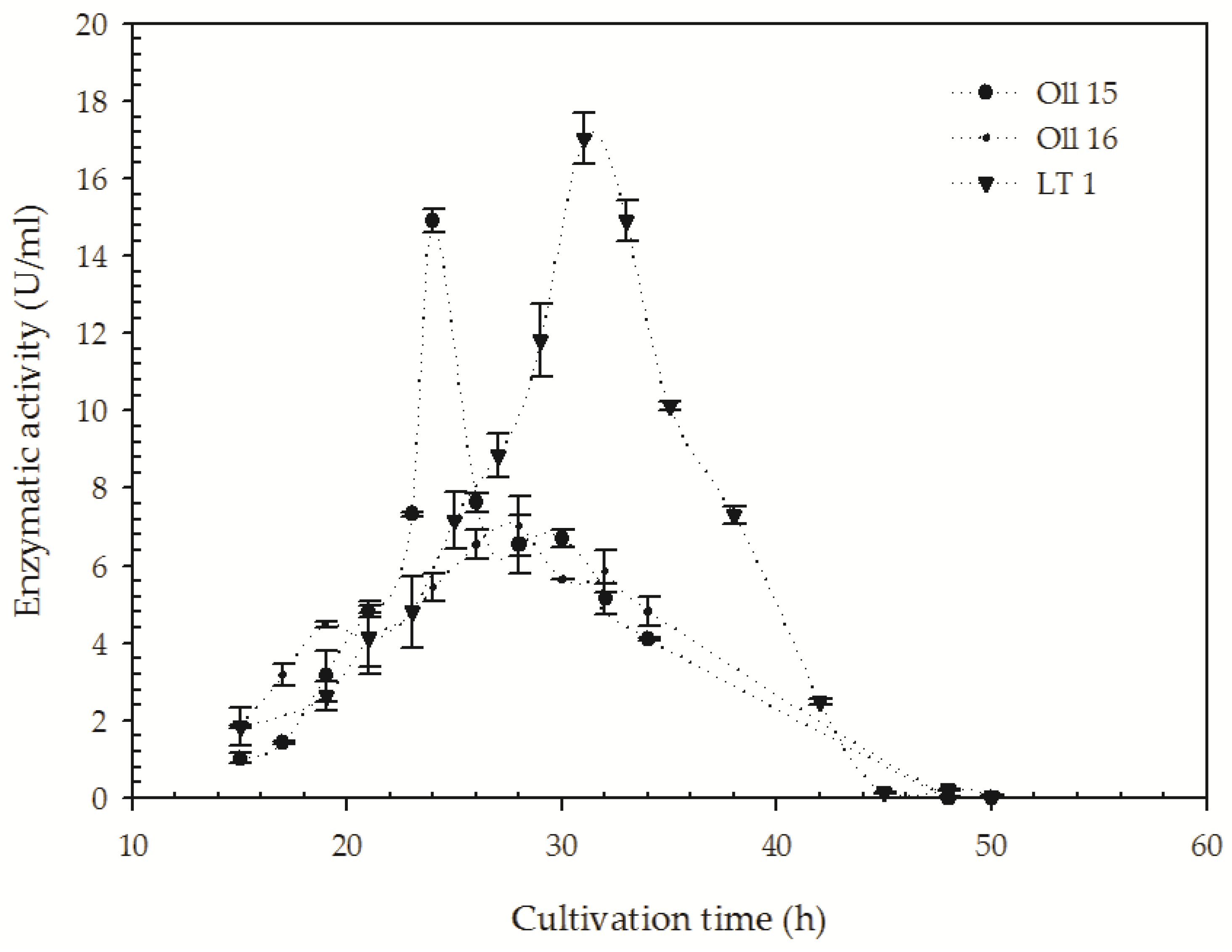
| Isolate | Colony Diameter (C; mm) | Hydrolysis Diameter (H; mm) | H/C Ratio | Taxonomic Identification | NCBI Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LT-1 | 5.09 ± 0.23 | 15.61 ± 0.26 | 3.06 | Bacillus cytotoxicus (B. cytotoxicus) | KR559937 |
| LT-2 | 4.33 ± 0.28 | - | B. licheniformis | KY859160 | |
| LT-6 | 5.32 ± 0.28 | 10.21 ± 0.12 | 1.91 | B. licheniformis | KR559939 |
| LT-7 | 4.65 ± 0.33 | 9.56 ± 0.13 | 2.05 | B. licheniformis | KR559940 |
| LT-8 | 5.45 ± 0.28 | 10.13 ± 0.15 | 1.85 | B. licheniformis | MF993534 |
| Oll-13 | 8.34 ± 0.34 | 11.22 ± 0.20 | 1.34 | B. licheniformis | KY859165 |
| Oll-15 | 5.16 ± 0.11 | 14.15 ± 0.45 | 2.74 | B. cytotoxicus | KR559942 |
| Oll-16 | 6.14 ± 0.24 | 15.43 ± 0.21 | 2.51 | B. cytotoxicus | KY559288 |
| Oll-18 | 6.22 ± 0.36 | 14.32 ± 0.23 | 2.30 | B. cytotoxicus | KR559943 |
| Oll-30 | 6.18 ± 0.31 | 14.16 ± 0.13 | 2.30 | B. cytotoxicus | KR559949 |
| LT-32 | 7.22 ± 0.21 | 15.02 ± 0.12 | 2.10 | B. cytotoxicus | KR559950 |
| LT-34 | 6.33 ± 0.25 | 15.54 ± 0.54 | 2.45 | B. cytotoxicus | KR559952 |
| LT-35 | 7.17 ± 0.18 | 15.31 ± 0.12 | 2.13 | B. cytotoxicus | KR559953 |
| B. cytotoxicus LT-1 | B. licheniformis Oll-15 | B. thermoruber T1E [45] | B. licheniformis PWD-1 [41] | S. thermonitrificans MG104 [42] | M. ruber H328 [26] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Growth substrate | 10 g·L intact chicken feathers | 10 g·L intact chicken feathers | 10 g·L intact goose feathers | 10 g·L hammer-milled feathers | 10 g·L intact chicken feathers | 30 g·L intact chicken feathers |
| Incubation temperature | 50 °C | 50 °C | 50 °C | 50 °C | 50 °C | 55 °C |
| Incubation time | 1 day | 1 day | 7 days | 7–10 days | 2–3 days | 6 days |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cavello, I.; Urbieta, M.S.; Cavalitto, S.; Donati, E. Bacillus cytotoxicus Isolated from a Pristine Natural Geothermal Area Reveals High Keratinolytic Activity. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 796. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8060796
Cavello I, Urbieta MS, Cavalitto S, Donati E. Bacillus cytotoxicus Isolated from a Pristine Natural Geothermal Area Reveals High Keratinolytic Activity. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(6):796. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8060796
Chicago/Turabian StyleCavello, Ivana, María Sofía Urbieta, Sebastián Cavalitto, and Edgardo Donati. 2020. "Bacillus cytotoxicus Isolated from a Pristine Natural Geothermal Area Reveals High Keratinolytic Activity" Microorganisms 8, no. 6: 796. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8060796







