Isolation and Characterization of a New Endophytic Actinobacterium Streptomyces californicus Strain ADR1 as a Promising Source of Anti-Bacterial, Anti-Biofilm and Antioxidant Metabolites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation of Endophytic Actinobacteria
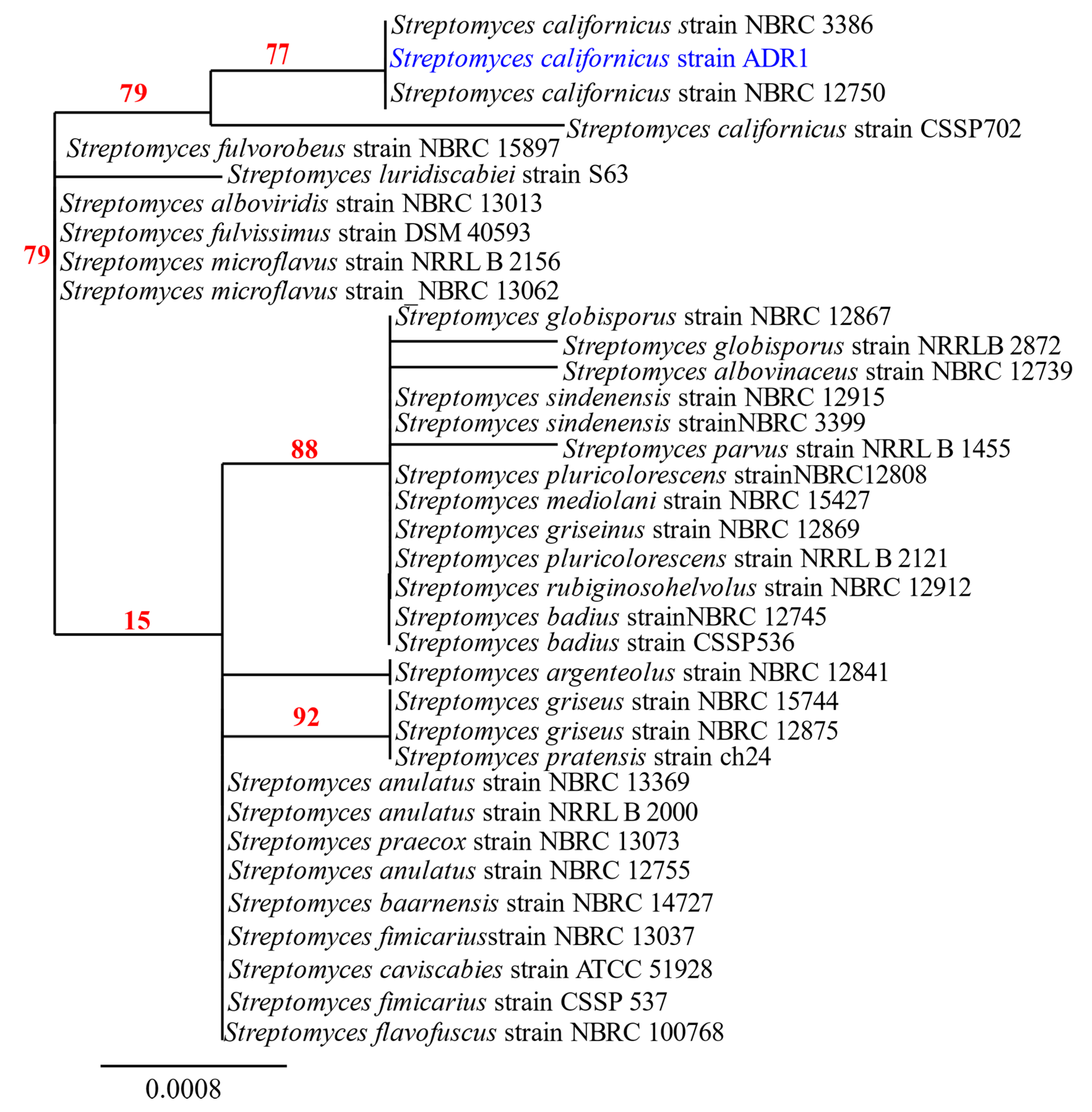
2.2. Molecular Identification and Characterization of the Isolate ADR1
2.3. Production of Secondary Metabolites
2.4. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.5. Antibiofilm Assay
2.6. Antioxidant Activity
2.7. Hemolytic Activities
2.8. Secondary Metabolite Profiling and GC-MS Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Identification and Characterization of the Isolate ADR1
3.2. Antibacterial Spectrum of ADR1 Metabolites Against Significant Gram-Positive Pathogens
3.3. Anti-Biofilm Activity of ADR1 Metabolites Against S. aureus and MRSA
3.4. Antioxidant Activity of the ADR1 Metabolites
3.5. Haemolytic Activity
3.6. Secondary Metabolite Profiling and GC-MS Analysis of Metabolite Extract
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chernov, V.M.; Chernova, O.A.; Mouzykantov, A.A.; Lopukhov, L.L.; Aminov, R.I. Omics of antimicrobials and antimicrobial resistance. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2019, 14, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prioritization of Pathogens to Guide Discovery, Research and Development of New Antibiotics for Drug-Resistant Bacterial Infections, Including Tuberculosis; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Ch’ng, J.H.; Chong, K.; Lam, L.N.; Wong, J.J.; Kline, K.A. Biofilm-associated infection by enterococci. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.D.; McFeters, G.A.; Stewart, P.S. Biofilm resistance to antimicrobial agents. Microbiol 2000, 146, 547–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowe, S.; Wagner, N.J.; Li, L.; Beam, J.E.; Wilkinson, A.D.; Radlinski, L.C.; Zhang, Q.; Miao, E.A.; Conlon, B.P. Reactive oxygen species induce antibiotic tolerance during systemic Staphylococcus aureus infection. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, A.V.; Bartosch, B.; Isaguliants, M.G. Oxidative stress in infection and consequent disease. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 3496043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohanski, M.A.; Dwyer, D.J.; Hayete, B.; Lawrence, C.A.; Collins, J.J. A common mechanism of cellular death induced by bactericidal antibiotics. Cell 2007, 130, 797–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keren, I.; Wu, Y.; Inocencio, J.; Mulcahy, L.R.; Lewis, K. Killing by bactericidal antibiotics does not depend on reactive oxygen species. Science 2013, 339, 1213–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liguori, I.; Russo, G.; Curcio, F.; Bulli, G.; Aran, L.; Della-Morte, D.; Gargiulo, G.; Testa, G.; Cacciatore, F.; Bonaduce, D.; et al. Oxidative stress, aging, and diseases. Clin. Interv. Aging 2018, 13, 757–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, R.; Antala, S.; Wang, A.; Amaral, F.E.; Rampersaud, R.; Larussa, S.J.; Planet, P.J.; Ratner, A.J. Cigarette smoke increases Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation via oxidative stress. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 3804–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, K.K.; Pichika, M.R. Artificial intelligence in drug development: Present status and future prospects. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.L.G.; Andricopulo, A.D. ADMET modeling approaches in drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patridge, E.; Gareiss, P.; Kinch, M.S.; Hoyer, D. An analysis of FDA-approved drugs: Natural products and their derivatives. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 204–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Dubey, A.K. Diversity and applications of endophytic actinobacteria of plants in special and other ecological niches. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berdy, J. Thoughts and facts about antibiotics: Where we are now and where we are heading. J. Antibiot. 2012, 65, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Dubey, A.K. Endophytic actinomycetes as emerging source for therapeutic compounds. Indo Glob. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 5, 106–116. [Google Scholar]
- Silver, L.L. Challenges of antibacterial discovery. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 24, 71–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Liu, N.; Li, X.; Ding, Y.; Shang, F.; Gao, Y.; Ruan, J.; Huang, Y. Red soils harbor diverse culturable actinomycetes that are promising sources of novel secondary metabolites. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 3086–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, D.N.; Padmavathy, S. Impact of endophytic microorganisms on plants, environment and humans. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 250693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coombs, J.T.; Franco, C.M. Isolation and identification of actinobacteria from surface-sterilized wheat roots. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 5603–5608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Nakeeb, M.A.; Lechevalier, H.A. Selective isolation of aerobic actinomycetes. Appl. Microbiol. 1963, 11, 75–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, M.; Nomura, S. Humic acid-vitamin agar. A new medium for the selective isolation of soil actinomycetes. J. Ferment. Technol. 1987, 65, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohseni, M.; Norouzi, H.; Hamedi, J.; Roohi, A. Screening of antibacterial producing actinomycetes from sediments of the Caspian Sea. Int. J. Mol. Cell. Med. 2013, 2, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Du Toit, E.A.; Rautenbach, M. A sensitive standardised micro-gel well diffusion assay for the determination of antimicrobial activity. J. Microbiol. Methods 2000, 42, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farris, M.H.; Olson, J.B. Detection of Actinobacteria cultivated from environmental samples reveals bias in universal primers. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 376–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dereeper, A.; Guignon, V.; Blanc, G.; Audic, S.; Buffet, S.; Chevenet, F.; Dufayard, J.F.; Guindon, S.; Lefort, V.; Lescot, M.; et al. Phylogeny.fr: Robust phylogenetic analysis for the non-specialist. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 1, W465–W469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dereeper, A.; Audic, S.; Claverie, J.M.; Blanc, G. BLAST-EXPLORER helps you building datasets for phylogenetic analysis. BMC Evol. Biol. 2010, 10, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guindon, S.; Gascuel, O. A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst. Biol. 2003, 52, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisimova, M.; Gascuel, O. Approximate likelihood ratio test for branchs: A fast, accurate and powerful alternative. Syst. Biol. 2006, 55, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevenet, F.; Brun, C.; Banuls, A.L.; Jacq, B.; Chisten, R. TreeDyn: Towards dynamic graphics and annotations for analyses of trees. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirling, E.B.; Gottlieb, D. Methods for characterization of Streptomyces species. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1966, 16, 313–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for Bacteria that grow aerobically, approved standard. 9th ed. CLSI document M07-A9. Clin. Lab. Stand. Inst. 2012, 32, 1–68. [Google Scholar]
- Sivaranjani, M.; Gowrishankar, S.; Kamaladevi, A.; Pandian, S.K.; Balamurugan, K.; Ravi, A.V. Morin inhibits biofilm production and reduces the virulence of Listeria monocytogenes—An in vitro and in vivo approach. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 237, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakkiyaraj, D.; Pandian, K.S.T. In vitro and in vivo antibiofilm activity of a coral associated actinomycete against drug resistant Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. Biofouling 2010, 26, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Islam, M.B.; Biswas, M.; Khurshid Alam, A.H.M. In vitro antioxidant and free radical scavenging activity of different parts of Tabebuia pallida growing in Bangladesh. BMC Res. Notes 2015, 8, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, F.M.; Biribo, S.S.N.; Selvaraj, G.; Oppedisano, F.; Warren, S.; Seduadua, A.; Mulholland, E.K.; Carapetis, J.R. As a bacterial culture medium, citrated sheep blood agar is a practical alternative to citrated human blood agar in laboratories of developing countries. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 3346–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoola, G.A.; Coker, H.A.B.; Adesegun, S.A.; Bello, A.A.A.; Obaweya, K.; Ezennia, E.C.; Atangbayila, T.O. Phytochemical screening and antioxidant activities of some selected medicinal plants used for malaria therapy in southwestern Nigeria. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2008, 7, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar]
- Subramaniam, D.; Menon, T.; Elizabeth, H.L.; Swaminathan, S. Anti-HIV-1 activity of Sargassum swartzii a marine brown alga. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, E43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Savithramma, N.; Rao, M.L.; Suhrulatha, D. Screening of medicinal plants for secondary metabolites. Middle-East J. Sci. Res. 2011, 8, 579–584. [Google Scholar]
- Suetsuna, K.; Seino, A.; Kudo, T.; Osajima, Y. Production, and biological characterization, of Dideoxygriseorhodin C by a Streptomyces sp. and its taxonomy. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1989, 53, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Panzone, G.; Trani, A.; Ferrari, P.; Gastaldo, L.; Colombo, L. Isolation and structure elucidation of 7,8-dideoxy-6-oxo-griseorhodin C produced by Actinoplanes ianthinogenes. J. Antibiot. 1997, 50, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuge, N.; Furihata, K.; Shin-Ya, K.; Hayakawa, Y.; Seto, H. Novel antibiotics pyrisulfoxin A and B produced by Streptomyces californicus. J. Antibiot. 1999, 52, 505–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, S.; Bhikshapathi, D.V.R.N.; Krishnaveni, J.; Veerabrahma, K. Isolation of borrelidin from Streptomyces californicus—An Indian soil isolate. Indian J. Biotechnol. 2008, 7, 349–355. [Google Scholar]
- Gozari, M.; Mortazavi, M.S.; Bahador, N.; Tamadoni Jahromi, S.; Rabbaniha, M. Isolation and screening of antibacterial and enzyme producing marine actinobacteria to approach probiotics against some pathogenic vibrios in shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Iran J. Fish Sci. 2016, 15, 630–644. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.; Singh, T.A.; Bharat, B.; Bhasin, S.; Modi, H.A. Approach towards different fermentative techniques for the production of bioactive actinobacterial melanin. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2018, 7, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.P.N.; Xiao, M.; Li, W.J. Fungal and bacterial pigments: Secondary metabolites with wide applications. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1113. [Google Scholar]
- Ser, H.L.; Yin, W.F.; Chan, K.G.; Khan, T.M.; Goh, B.H.; Lee, L.H. Antioxidant and cytotoxic potentials of Streptomyces gilvigriseus MUSC 26T isolated from mangrove soil in Malaysia. Prog. Microbes Mol. Biol. 2018, 1, a0000002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chaudhari, C.N.; Tandel, K.; Grover, N.; Bhatt, P.; Sahni, A.K.; Sen, S.; Prahraj, A.K. In vitro vancomycin susceptibility amongst methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Med. J. Armed Forces India 2014, 70, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Horiuchi, K.; Shiota, S.; Hatano, T.; Yoshida, T.; Kuroda, T.; Tsuchiya, T. Antimicrobial activity of oleanolic acid from Salvia officinalis and related compounds on vancomycin-resistant Enterococci (VRE). Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 1147–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maasjost, J.; Mühldorfer, K.; Cortez de Jäckel, S.; Hafez, H.M. Antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium isolated from poultry flocks in Germany. Avian Dis. 2015, 59, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gos, F.M.W.R.; Savi, D.C.; Shaaban, K.A.; Thorson, J.S.; Aluizio, R.; Possiede, Y.M.; Rohr, J.; Glienke, C. Antibacterial activity of endophytic actinomycetes isolated from the medicinal plant Vochysia divergens (Pantanal, Brazil). Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girão, M.; Ribeiro, I.; Ribeiro, T.; Azevedo, I.C.; Pereira, F.; Urbatzka, R.; Leão, P.N.; Carvalho, M.F. Actinobacteria isolated from Laminaria ochroleuca: A source of new bioactive compounds. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddharth, S.; Vittal, R.R.; Wink, J.; Steinert, M. Diversity and bioactive potential of actinobacteria from unexplored regions of Western Ghats, India. Microorganisms 2020, 7, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schillaci, D.; Petruso, S.; Raimondi, M.V.; Cusimano, M.G.; Cascioferro, S.; Scalisi, M.; La Giglia, M.A.; Vitale, M. Pyrrolomycins as potential anti-Staphylococcal biofilms agents. Biofouling 2010, 26, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tote, K.; Berghe, D.V.; Deschacht, M.; de Wit, K.; Maes, L.; Cos, P. Inhibitory efficacy of various antibiotics on matrix and viable mass of Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2009, 33, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, T.A.; Dos Santos, T.F.; de Almeida, M.E.; Junior, L.A.; Andrade, E.F.; Rezende, R.P.; Marques, L.M.; Romano, C.C. Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus biofilm by Lactobacillus isolated from fine cocoa. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brambilla, L.Z.S.; Endo, E.H.; Cortez, D.A.G.; Filhoa, B.P.D. Anti-biofilm activity against Staphylococcus aureus MRSA and MSSA of neolignans and extract of Piper regnellii. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2017, 27, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Liu, M.; Liu, Y.; Qin, L.; Jin, M.; Wang, Z. Antimicrobial Activity and mechanism of action of Dracocephalum moldavica L. extracts against clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.; Li, J.; Peng, Y.; Huang, Z.; Ren, Q.; Lu, J. The role and mechanism of thiol-dependent antioxidant system in bacterial drug susceptibility and resistance. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 27, 1940–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elswaifi, S.F.; Palmieri, J.R.; Hockey, K.S.; Rziqalinski, B.A. Antioxidant nanoparticles for control of infectious disease. Infect. Disord. Drug Targets (Former. Curr. Drug Targets-Infect. Disord.) 2009, 9, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, D. Antioxidants and cardiovascular risk factors. Diseases 2016, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passari, A.K.; Mishra, V.K.; Singh, G.; Singh, P.; Kumar, B.; Gupta, V.K.; Sarma, R.K.; Saikia, R.; Donovan, A.O.; Singh, B.P. Insights into the functionality of endophytic actinobacteria with a focus on their biosynthetic potential and secondary metabolites production. Sci. Rep. 2018, 7, 11809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimal, C.I.V.; Kumar, P.P.; Agastian, P. In vitro α-glucosidase inhibition and antioxidative potential of an endophyte species (Streptomyces sp. loyola UGC) isolated from Datura stramonium L. Curr. Microbiol. 2013, 67, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhuri, M.; Paul, A.K.; Pal, A. Isolation and assessment of metabolic potentials of bacteria endophytic to carnivorous plants Drosera Burmannii and Utricularia Spp. Biosci. Biotechnol. Res. Asia 2019, 16, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garratty, G.; Arndt, P. Drugs that have been shown to cause drug-induced immune hemolytic anemia or positive direct antiglobulin tests: Some interesting findings since 2007. Immunohematology 2014, 30, 66–79. [Google Scholar]
- Marques, M.A.; Citron, D.M.; Wang, C.C. Development of Tyrocidine A analogues with improved antibacterial activity. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 6667–6677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosges, R.; Baues, C.M.; Schroder, T.; Sahin, K. Acute bacterial otitis externa: Efficacy and safety of topical treatment with an antibiotic ear drop formulation in comparison to glycerol treatment. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2011, 27, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guleria, V.S.; Sharma, N.; Amitabh, S.; Nair, V. Ceftriaxone-induced hemolysis. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2013, 45, 530–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T.; Biswas, M.K.; Chatterjee, S.; Roy, P. In-vitro study on the hemolytic activity of different extracts of Indian medicinal plant Croton bonplandianum with phytochemical estimation: A new era in drug development. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2018, 8, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, V.; Singla, R.K.; Dubey, A.K. Inhibition of biofilm and virulence factors of Candida albicans by partially purified secondary metabolites of Streptomyces chrestomyceticus strain ADP4. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2018, 11, 925–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumbi, B.P.; Moodley, B.; Birungi, G.; Ndungu, P.G. Target, suspect and non-target screening of silylated derivatives of polar compounds based on single Ion monitoring GC-MS. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, M.Z.M.; Zayed, M.Z.; Ali, H.M.; Abd El-Kareem, M.S.M. Chemical composition, antioxidant and antibacterial activities of extracts from Schinus molle wood branch growing in Egypt. J. Wood Sci. 2016, 62, 548–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari, T.; Kafil, H.S.; Asnaashari, S.; Farajnia, S.; Delazar, A.; Baek, S.C.; Hamishehkar, H.; Kim, K.H. Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of essential oils from the aerial parts of Pinus eldarica grown in Northwestern Iran. Molecules 2019, 24, E3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Peng, C.; Zhou, Q.M.; Wan, F.; Xie, X.F.; Guo, L.; Li, X.H.; He, C.J.; Dai, O. Chemical composition and antibacterial activity of essential oils from different parts of Leonurus japonicus Houtt. Molecules 2013, 18, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.Q.; Guo, C.J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, W.M.; Wang, C.C.; Gao, J.M. Asperaculanes A and B, two sesquiterpenoids from the fungus Aspergillus aculeatus. Molecules 2014, 20, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, R.A.; El-Anssary, A.A. Plants Secondary Metabolites: The Key Drivers of the Pharmacological Actions of Medicinal Plants in Herbal Medicine; Philip, F., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; pp. 11–30. [Google Scholar]
- Karak, P. Biological activities of flavonoids: An overview. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 10, 1567–1574. [Google Scholar]
- Gbahou, F.; Davenas, E.; Morisset, S.; Arrang, J.M. Effects of betahistine at histamine H3 receptors: Mixed inverse agonism/agonism in vitro and partial inverse agonism in vivo. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 334, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, B.; Uddina, M.D.J.; Pataric, P.; Das, M.; Maitia, D.; Manna, K. Estimation of alkaloids and phenolics of five edible cucurbitaceous plants and their antibacterial activity. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 7, 223–227. [Google Scholar]






| ISP Media | Growth | Substrate Mycelium | Aerial Mycelium | Diffusible Pigments | Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ISP-1 (Tryptone-Yeast Extract Broth) | Abundant | Crimson red | White | No | Shrinked and depressed with irregular edges |
| ISP-2 (Yeast extract- Malt extract Agar) | moderate | Wine Red | Pale green | Yellow | Elevated, smooth, regular edges |
| ISP-3 (Oatmeal agar) | Abundant | Wine Red | Dusty green | Light violet | Shrinked, pits formation, regular edges |
| ISP-4 (Inorganic salt starch agar) | Moderate | Dark pink | Light pink | Light pink | Flat, wavy edges, pointed centre |
| ISP-5 (Glycerol asparagine agar base) | Abundant | Pink | Dusty green | No | Elevated, Round, smooth edges |
| ISP-6 (Peptone yeast extract iron agar) | Moderate | Rusty red | White | Light pink | Elevated at centre, Round, smooth edges |
| ISP-7 (Tyrosine agar) | Scanty | Light pink | Whitish Pink | No | Pin pointed at centre, flat, round and smooth edges |
| S. No. | Reference Strains of Gram-Positive Pathogens | Zone of Inhibition (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 | 22.5 ± 0.58 |
| 2 | S. aureus ATCC 25923 | 19 ± 0.42 |
| 3 | S. aureus ATCC 13709 | 20 ± 0.5 |
| 4 | S. epidermis ATCC 12228 | 18 ± 0.45 |
| 5 | Methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) ATCC 43300 | 21.3 ± 0.27 |
| 6 | MRSA 562 (clinical strain) | 19 ± 0.25 |
| 7 | Enterococcus faecium ATCC 49224 | 16.5 ± 0.4 |
| 8 | E. faecium AIIMS | 19.4 ± 0.47 |
| 9 | E. faecalis ATCC 29212 | 17 ± 0.52 |
| Chemical Class of Metabolites | Testes/Reagents Used | Observations | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Terpenoids | Salkowski Test | Reddish brown coloration at the interface | + |
| Phenols | Folin–Ciocalteu Test | Blue coloration was appeared | + |
| Flavonoids | Ferric chloride Test | Formation of greenish colour | + |
| NaOH, HCl | Intense yellow coloration after adding HCl | ||
| Terpenes | Salkowski Regent | Appearance of golden colour in the chloroform layer | + |
| Alkaloids | Wagner’s Test | Formation of reddish-brown precipitate | + |
| Anthocyanins | HCl, Ammonia | Appearance of pink-red, turns blue | + |
| Anthraquinones | H2SO4, Chloroform, Ammonia | Light pink coloured layer of ammonia | + |
| Glycosides | Keller–Killiani Test | A reddish-brown colour ring at the junction of the two layers | + |
| Tannins | Lead Acetate Test | No precipitation was observed | − |
| Saponins | Foam Test | No frothing was observed | − |
| Lactones | Pyridine, sodium nitroprusside, NaOH | No change in coloration was observed | − |
| Coumarins | Alcoholic NaOH | Yellow fluorescence was not appeared on the paper soaked in NaOH | − |
| Sterols | Salkowski Test | No red colour was appeared in the lower layer (two layers formed) | − |
| Lignins | Gallic acid | No appearance of Olive-green coloration | − |
| Carbohydrates | Fehling’s Test | No reddish violet ring appeared | − |
| Fatty acids | Ether | No appearance of transparence on filter paper | − |
| Proteins | Biuret Test | No violet coloration was observed | − |
| S. No. | RT (min) | Similarity Index (SI) | Reference Compounds | Chemical class | Therapeutic Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 11.945 | 88 | Methanoazulen-9-ol, decahydro-2,2,4,8-tetramethyl-stereoisomer | Sesquiterpene (alpha-Caryophyllene alcohol) | Antibacterial, antioxidant, antiinflammatory [73] |
| 2 | 13.089 | 96 | Naphtho[2,3-g]-1,6,2,5-dioxasilaborocin | Organoboranic acid | No activity reported |
| 3 | 13.231 | 85 | 2-[(trimethylsilyl)oxy]-4-methoxyacetophenone | Flavonoid | No activity reported |
| 4 | 14.519 | 90 | 5-z-methyl-2-z-hydroxycarbonyl-5-e-ethenyl-4-z-propen-2-ylcyclohexanone | Terpenoids (Asperaculane B type) | Anticonvulsant drug design pharmacophore, sodium channel blocker, GABA-transaminase inhibitors [76] |
| 5 | 15.102 | 92 | 1,2-benzenedicarboxylic acid | Diisobutyl phthalate | No activity reported |
| 6 | 16.068 | 88 | 2-pyridineethanamine, n-methyl-n-[2-(4-pyridinyl)ethyl] | Alkaloid (betahistine types) | Vasodilation and reduction of endolymphatic pressure [79] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, R.; Dubey, A.K. Isolation and Characterization of a New Endophytic Actinobacterium Streptomyces californicus Strain ADR1 as a Promising Source of Anti-Bacterial, Anti-Biofilm and Antioxidant Metabolites. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8060929
Singh R, Dubey AK. Isolation and Characterization of a New Endophytic Actinobacterium Streptomyces californicus Strain ADR1 as a Promising Source of Anti-Bacterial, Anti-Biofilm and Antioxidant Metabolites. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(6):929. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8060929
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Radha, and Ashok K. Dubey. 2020. "Isolation and Characterization of a New Endophytic Actinobacterium Streptomyces californicus Strain ADR1 as a Promising Source of Anti-Bacterial, Anti-Biofilm and Antioxidant Metabolites" Microorganisms 8, no. 6: 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8060929
APA StyleSingh, R., & Dubey, A. K. (2020). Isolation and Characterization of a New Endophytic Actinobacterium Streptomyces californicus Strain ADR1 as a Promising Source of Anti-Bacterial, Anti-Biofilm and Antioxidant Metabolites. Microorganisms, 8(6), 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8060929





