Repurposing Anti-diabetic Drugs to Cripple Quorum Sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Chemicals
2.2. Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) of Tested Drugs and Their Sub-MIC Effect on Bacterial Growth
2.3. Violacein Inhibition Assay
2.4. Biofilm Inhibition Assay
2.5. Motilities Inhibition Assay
2.6. Protease Inhibition Assay
2.7. Hemolysin Inhibition Assay
2.8. Elastase Inhibition Assay
2.9. Pyocyanin Inhibition Assay
2.10. Inhibition Assay of Oxidative Stress Resistance
2.11. Quantitative RT-PCR of QS and Virulence Genes
2.11.1. RNA Extraction
2.11.2. Real Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
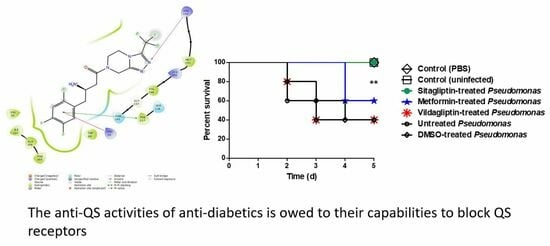
2.12. Mice Survival Assay
2.13. Molecular Modeling Study of Anti-Diabetic Drugs Binding to QS Receptors
3. Results
3.1. Determination of MIC Anti-Diabetic Drugs and Their Effect on Bacterial Growth
3.2. Inhibition Violacein Pigment Production
3.3. Inhibitory Effect of Tested Anti-Diabetic Drugs on the P. aeruginosa Virulence Factors
3.3.1. Inhibition of Biofilm Formation
3.3.2. Inhibition of P. aeruginosa Motilities
3.3.3. Inhibition of P. aeruginosa Virulence Enzymes
3.3.4. Inhibition of P. aeruginosa Pigment
3.4. Resistance to Oxidative Stress
3.5. Down Regulation of P. aeruginosa QS Genes
3.6. In Vivo Protection Activity
3.7. Docking of Anti-Diabetic Drugs to QS Receptors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Livermore, D.M.; British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy Working Party on The Urgent Need: Regenerating Antibacterial Drug Discovery and Development; Blaser, M.; Carrs, O.; Cassell, G.; Fishman, N.; Guidos, R.; Levy, S.; Powers, J.; Norrby, R.; et al. Discovery research: The scientific challenge of finding new antibiotics. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 1941–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, V.C.; Purohit, H.J. Quenching the quorum sensing system: Potential antibacterial drug targets. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 37, 121–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutherford, S.T.; Bassler, B.L. Bacterial quorum sensing: Its role in virulence and possibilities for its control. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a012427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Chen, J.; Yang, C.; Yin, Y.; Yao, K. Quorum Sensing: A Prospective Therapeutic Target for Bacterial Diseases. Biomed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 2015978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remy, B.; Mion, S.; Plener, L.; Elias, M.; Chabriere, E.; Daude, D. Interference in Bacterial Quorum Sensing: A Biopharmaceutical Perspective. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, H.A.; Hegazy, W.A.H. Repurposing anti-diabetic drug “Sitagliptin” as a novel virulence attenuating agent in Serratia marcescens. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memariani, H.; Memariani, M.; Ghasemian, A. An overview on anti-biofilm properties of quercetin against bacterial pathogens. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 35, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pushpakom, S.; Iorio, F.; Eyers, P.A.; Escott, K.J.; Hopper, S.; Wells, A.; Doig, A.; Guilliams, T.; Latimer, J.; McNamee, C.; et al. Drug repurposing: Progress, challenges and recommendations. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.A.; Jadhav, P.R.; Deshmukh, Y.A. Prescribing pattern and efficacy of anti-diabetic drugs in maintaining optimal glycemic levels in diabetic patients. J. Basic Clin. Pharm. 2014, 5, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, I.; Gregg, B. Metformin; a review of its history and future: From lilac to longevity. Pediatr. Diabetes 2017, 18, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cegelski, L.; Marshall, G.R.; Eldridge, G.R.; Hultgren, S.J. The biology and future prospects of antivirulence therapies. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasko, D.A.; Sperandio, V. Anti-virulence strategies to combat bacteria-mediated disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papaioannou, E.; Utari, P.D.; Quax, W.J. Choosing an appropriate infection model to study quorum sensing inhibition in Pseudomonas infections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 19309–19340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaynes, R.; Edwards, J.R.; National Nosocomial Infections Surveillance System. Overview of nosocomial infections caused by gram-negative bacilli. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 41, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyczak, J.B.; Cannon, C.L.; Pier, G.B. Establishment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection: Lessons from a versatile opportunist. Microbes Infect. 2000, 2, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morata, L.; Cobos-Trigueros, N.; Martinez, J.A.; Soriano, A.; Almela, M.; Marco, F.; Sterzik, H.; Nunez, R.; Hernandez, C.; Mensa, J. Influence of multidrug resistance and appropriate empirical therapy on the 30-day mortality rate of Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteremia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 4833–4837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhas, M.; Eberl, L.; Tummler, B. Quorum sensing: The power of cooperation in the world of Pseudomonas. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, T.B.; Givskov, M. Quorum-sensing inhibitors as anti-pathogenic drugs. Int. J. Med Microbiol. 2006, 296, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winzer, K.; Williams, P. Quorum sensing and the regulation of virulence gene expression in pathogenic bacteria. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2001, 291, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentzer, M.; Wu, H.; Andersen, J.B.; Riedel, K.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Bagge, N.; Kumar, N.; Schembri, M.A.; Song, Z.; Kristoffersen, P.; et al. Attenuation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence by quorum sensing inhibitors. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 3803–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.S.; Iglewski, B.H. P. aeruginosa quorum-sensing systems and virulence. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2003, 6, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, C.S.; Bolig, T.; Torabi-Parizi, P. Mechanisms and Targeted Therapies for Pseudomonas aeruginosa Lung Infection. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 197, 708–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Lv, G.; Cheng, X.; Ma, X.; Wang, W.; Gui, J.; Hu, J.; Lu, M.; Chu, G.; Chen, J.; et al. Guidelines on multidisciplinary approaches for the prevention and management of diabetic foot disease (2020 edition). Burn. Trauma 2020, 8, tkaa017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalca, Y.; Jansch, L.; Bredenbruch, F.; Geffers, R.; Buer, J.; Haussler, S. Quorum-sensing antagonistic activities of azithromycin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1: A global approach. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 1680–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choo, J.H.; Rukayadi, Y.; Hwang, J.K. Inhibition of bacterial quorum sensing by vanilla extract. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 42, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issac Abraham, S.V.; Palani, A.; Ramaswamy, B.R.; Shunmugiah, K.P.; Arumugam, V.R. Antiquorum sensing and antibiofilm potential of Capparis spinosa. Arch. Med Res. 2011, 42, 658–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, T.; Kaneda, K.; Nakagawa, Y.; Isa, K.; Hara-Hotta, H.; Yano, I. A novel extracellular cyclic lipopeptide which promotes flagellum-dependent and -independent spreading growth of Serratia marcescens. J. Bacteriol. 1992, 174, 1769–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, T.; Yin, W.F.; Chan, K.G. Inhibition of quorum sensing-controlled virulence factor production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 by Ayurveda spice clove (Syzygium aromaticum) bud extract. Sensors 2012, 12, 4016–4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmoteleb, A.; Troncoso-Rojas, R.; Gonzalez-Soto, T.; Gonzalez-Mendoza, D. Antifungical Activity of Autochthonous Bacillus subtilis Isolated from Prosopis juliflora against Phytopathogenic Fungi. Mycobiology 2017, 45, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossignol, G.; Merieau, A.; Guerillon, J.; Veron, W.; Lesouhaitier, O.; Feuilloley, M.G.; Orange, N. Involvement of a phospholipase C in the hemolytic activity of a clinical strain of Pseudomonas fluorescens. BMC Microbiol. 2008, 8, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohman, D.E.; Cryz, S.J.; Iglewski, B.H. Isolation and characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO mutant that produces altered elastase. J. Bacteriol. 1980, 142, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, T.; Manefield, M. Pyocyanin promotes extracellular DNA release in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassett, D.J.; Schweizer, H.P.; Ohman, D.E. Pseudomonas aeruginosa sodA and sodB mutants defective in manganese- and iron-cofactored superoxide dismutase activity demonstrate the importance of the iron-cofactored form in aerobic metabolism. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 6330–6337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruber, J.D.; Chen, W.; Parnham, S.; Beauchesne, K.; Moeller, P.; Flume, P.A.; Zhang, Y.M. The role of 2,4-dihydroxyquinoline (DHQ) in Pseudomonas aeruginosa pathogenicity. PeerJ 2016, 4, e1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parai, D.; Banerjee, M.; Dey, P.; Chakraborty, A.; Islam, E.; Mukherjee, S.K. Effect of reserpine on Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing mediated virulence factors and biofilm formation. Biofouling 2018, 34, 320–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Lee, S.H.; Byun, Y.; Park, H.D. 6-Gingerol reduces Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation and virulence via quorum sensing inhibition. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfaky, M.A.; El-Halawany, A.M.; Koshak, A.E.; Alshali, K.Z.; El-Araby, M.E.; Khayat, M.T.; Abdallah, H.M. Bioassay Guided Isolation and Docking Studies of a Potential β-Lactamase Inhibitor from Clutia myricoides. Molecules 2020, 25, 2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, H.W.; Talbot, G.H.; Bradley, J.S.; Edwards, J.E.; Gilbert, D.; Rice, L.B.; Scheld, M.; Spellberg, B.; Bartlett, J. Bad bugs, no drugs: No ESKAPE! An update from the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, M.; Zeighami, H.; Bikas, R.; Heidari, A.; Rafiee, F.; Haghi, F. Inhibitory activity of metal-curcumin complexes on quorum sensing related virulence factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. AMB Express 2020, 10, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Feng, W.; Lai, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Rong, L.; Sun, F.; Chen, Y. Quercetin inhibits Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation via the vfr-mediated lasIR system. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 149, 104291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiee, F.; Haghi, F.; Bikas, R.; Heidari, A.; Gholami, M.; Kozakiewicz, A.; Zeighami, H. Synthesis, characterization and assessment of anti-quorum sensing activity of copper(II)-ciprofloxacin complex against Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. AMB Express 2020, 10, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hema, M.; Vasudevan, S.; Balamurugan, P.; Adline Princy, S. Modulating the Global Response Regulator, LuxO of V. cholerae Quorum Sensing System Using a Pyrazine Dicarboxylic Acid Derivative (PDCA(py)): An Antivirulence Approach. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, O.; Pukin, A.V.; Quarles van Ufford, H.C.; Kemmink, J.; de Mol, N.J.; Pieters, R.J. Functionalization of a Rigid Divalent Ligand for LecA, a Bacterial Adhesion Lectin. ChemistryOpen 2015, 4, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senwar, K.R.; Sharma, P.; Reddy, T.S.; Jeengar, M.K.; Nayak, V.L.; Naidu, V.G.; Kamal, A.; Shankaraiah, N. Spirooxindole-derived morpholine-fused-1,2,3-triazoles: Design, synthesis, cytotoxicity and apoptosis inducing studies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 102, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, M.R.; Jakobsen, T.H.; Bang, C.G.; Cohrt, A.E.; Hansen, C.L.; Clausen, J.W.; Le Quement, S.T.; Tolker-Nielsen, T.; Givskov, M.; Nielsen, T.E. Triazole-containing N-acyl homoserine lactones targeting the quorum sensing system in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 1638–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Guo, B.; Bai, Y.; Lu, H.; Dong, Y. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Azamacrolide Comprising the Triazole Moiety as Quorum Sensing Inhibitors. Molecules 2018, 23, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottomley, M.J.; Muraglia, E.; Bazzo, R.; Carfi, A. Molecular insights into quorum sensing in the human pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa from the structure of the virulence regulator LasR bound to its autoinducer. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 13592–13600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chugani, S.; Greenberg, E.P. The influence of human respiratory epithelia on Pseudomonas aeruginosa gene expression. Microb. Pathog. 2007, 42, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lintz, M.J.; Oinuma, K.; Wysoczynski, C.L.; Greenberg, E.P.; Churchill, M.E. Crystal structure of QscR, a Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing signal receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 15763–15768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; He, J.; Rahme, L.G. Mutation analysis of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa mvfR and pqsABCDE gene promoters demonstrates complex quorum-sensing circuitry. Microbiology 2006, 152, 1679–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, S.A.; Ojo-Fakunle, V.T.; Woertman, J.; Veldhuizen, E.J. The natural antimicrobial carvacrol inhibits quorum sensing in Chromobacterium violaceum and reduces bacterial biofilm formation at sub-lethal concentrations. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavrodi, D.V.; Bonsall, R.F.; Delaney, S.M.; Soule, M.J.; Phillips, G.; Thomashow, L.S. Functional analysis of genes for biosynthesis of pyocyanin and phenazine-1-carboxamide from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 6454–6465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Contreras, R.; Nunez-Lopez, L.; Jasso-Chavez, R.; Kwan, B.W.; Belmont, J.A.; Rangel-Vega, A.; Maeda, T.; Wood, T.K. Quorum sensing enhancement of the stress response promotes resistance to quorum quenching and prevents social cheating. ISME J. 2015, 9, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eligar, V.S.; Bain, S.C. A review of sitagliptin with special emphasis on its use in moderate to severe renal impairment. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2013, 7, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, M.R.; Giglio, K.; Fay, D.; Filiatrault, M.J. Physiological and genetic characterization of calcium phosphate precipitation by Pseudomonas species. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Target Gene | Sequence (5′–3′) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| lasI | For: CTACAGCCTGCAGAACGACA | [35] |
| Rev: ATCTGGGTCTTGGCATTGAG | ||
| lasR | For: ACGCTCAAGTGGAAAATTGG | [35] |
| Rev: GTAGATGGACGGTTCCCAGA | ||
| rhlI | For: CTCTCTGAATCGCTGGAAGG | [35] |
| Rev: GACGTCCTTGAGCAGGTAGG | ||
| rhlR | For: AGGAATGACGGAGGCTTTTT | [35] |
| Rev: CCCGTAGTTCTGCATCTGGT | ||
| pqsA | For: TTCTGTTCCGCCTCGATTTC | [34] |
| Rev: AGTCGTTCAACGCCAGCAC | ||
| pqsR | For: AACCTGGAAATCGACCTGTG | [35] |
| Rev: TGAAATCGTCGAGCAGTACG | ||
| rpoD | For: GGGCGAAGAAGGAAATGGTC | [34] |
| Rev: CAGGTGGCGTAGGTGGAGAAC |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hegazy, W.A.H.; Khayat, M.T.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Nassar, M.S.; Bakhrebah, M.A.; Abdulaal, W.H.; Alhakamy, N.A.; Bendary, M.M. Repurposing Anti-diabetic Drugs to Cripple Quorum Sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091285
Hegazy WAH, Khayat MT, Ibrahim TS, Nassar MS, Bakhrebah MA, Abdulaal WH, Alhakamy NA, Bendary MM. Repurposing Anti-diabetic Drugs to Cripple Quorum Sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(9):1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091285
Chicago/Turabian StyleHegazy, Wael A. H., Maan T. Khayat, Tarek S. Ibrahim, Majed S. Nassar, Muhammed A. Bakhrebah, Wesam H. Abdulaal, Nabil A. Alhakamy, and Mahmoud M. Bendary. 2020. "Repurposing Anti-diabetic Drugs to Cripple Quorum Sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa" Microorganisms 8, no. 9: 1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091285
APA StyleHegazy, W. A. H., Khayat, M. T., Ibrahim, T. S., Nassar, M. S., Bakhrebah, M. A., Abdulaal, W. H., Alhakamy, N. A., & Bendary, M. M. (2020). Repurposing Anti-diabetic Drugs to Cripple Quorum Sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microorganisms, 8(9), 1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091285