Comparative Evaluation of Band-Based Genotyping Methods for Mycobacterium intracellulare and Its Application for Epidemiological Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Samples
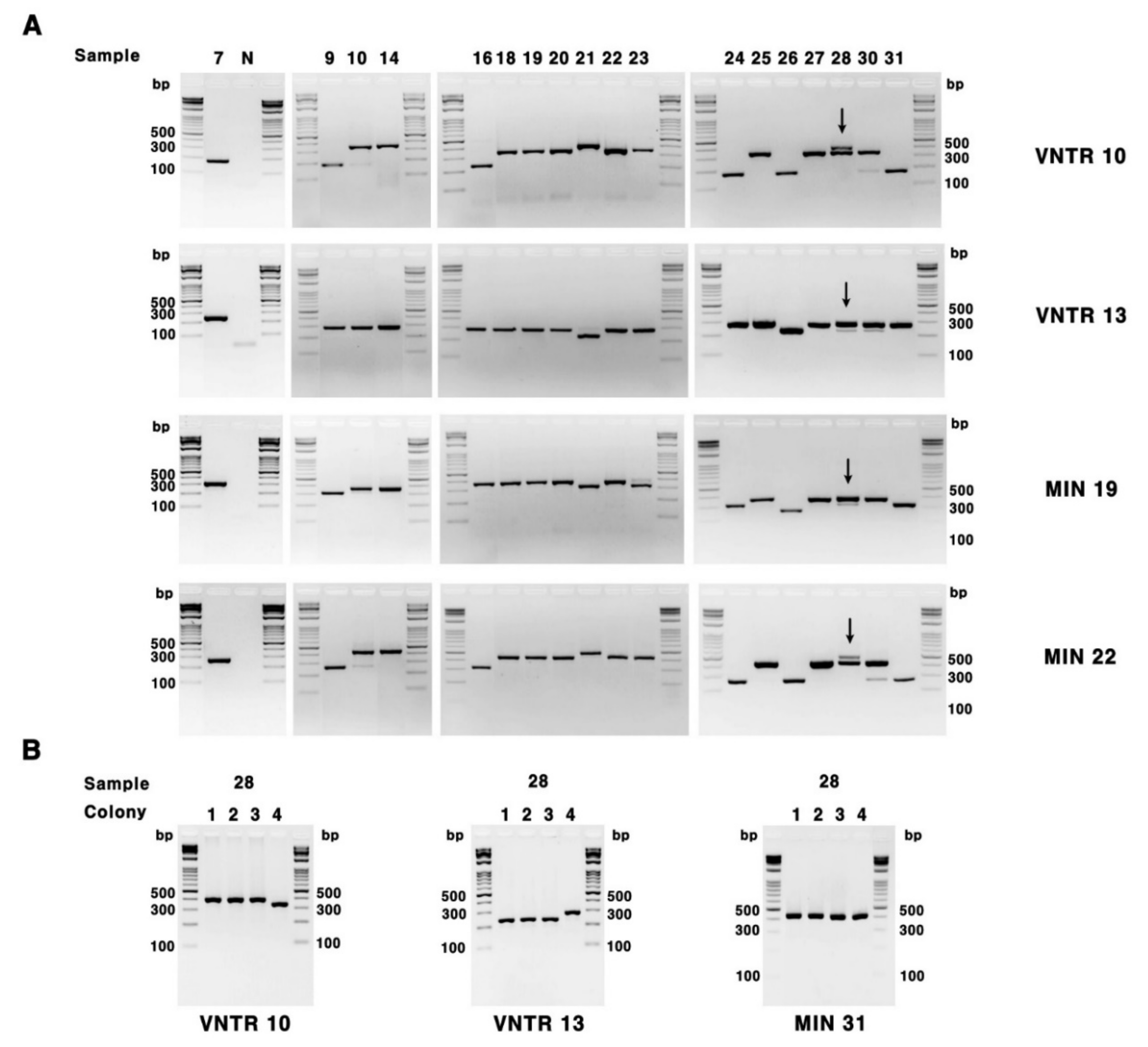
2.2. VNTR and VNTR-MIRU
2.3. Rep-PCR
2.4. PFGE
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. VNTR and VNTR-MIRU Typing
3.2. PFGE
3.3. Rep-PCR
3.4. Minimum Spanning Tree
3.5. Allelic Diversity of VNTR Loci
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kwon, Y.S.; Koh, W.J. Diagnosis and Treatment of Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Lung Disease. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2016, 31, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akram, S.M.; Attia, F.N. Mycobacterium avium intracellulare. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sakatani, M. The non-tuberculous mycobacteriosis. Kekkaku 2005, 80, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marras, T.K.; Daley, C.L. Epidemiology of human pulmonary infection with nontuberculous mycobacteria. Clin. Chest Med. 2002, 23, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.I.; Shin, S.J.; Shin, M.K. Differential Genotyping of Mycobacterium avium Complex and Its Implications in Clinical and Environmental Epidemiology. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tichenor, W.S.; Thurlow, J.; McNulty, S.; Brown-Elliott, B.A.; Wallace, R.J., Jr.; Falkinham, J.O., 3rd. Nontuberculous Mycobacteria in household plumbing as possible cause of chronic rhinosinusitis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1612–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iakhiaeva, E.; McNulty, S.; Brown Elliott, B.A.; Falkinham, J.O., 3rd; Williams, M.D.; Vasireddy, R.; Wilson, R.W.; Turenne, C.; Wallace, R.J., Jr. Mycobacterial interspersed repetitive-unit-variable-number tandem-repeat (MIRU-VNTR) genotyping of mycobacterium intracellulare for strain comparison with establishment of a PCR-based database. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arbeit, R.D.; Slutsky, A.; Barber, T.W.; Maslow, J.N.; Niemczyk, S.; Falkinham, J.O., 3rd; O’Connor, G.T.; von Reyn, C.F. Genetic diversity among strains of Mycobacterium avium causing monoclonal and polyclonal bacteremia in patients with AIDS. J. Infect. Dis. 1993, 167, 1384–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazurek, G.H.; Hartman, S.; Zhang, Y.; Brown, B.A.; Hector, J.S.; Murphy, D.; Wallace, R.J., Jr. Large DNA restriction fragment polymorphism in the Mycobacterium avium-M. intracellulare complex: A potential epidemiologic tool. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1993, 31, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tenover, F.C.; Arbeit, R.D.; Goering, R.V. How to select and interpret molecular strain typing methods for epidemiological studies of bacterial infections a review for healthcare epidemiologists. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 1997, 18, 426–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichikawa, K.; Yagi, T.; Inagaki, T.; Moriyama, M.; Nakagawa, T.; Uchiya, K.; Nikai, T.; Ogawa, K. Molecular typing of Mycobacterium intracellulare using multilocus variable-number of tandem-repeat analysis: Identification of loci and analysis of clinical isolates. Microbiology 2010, 156 Pt 2, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dauchy, F.A.; Degrange, S.; Charron, A.; Dupon, M.; Xin, Y.; Bebear, C.; Maugein, J. Variable-number tandem-repeat markers for typing Mycobacterium intracellulare strains isolated in humans. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koeuth, T.; Versalovic, J.; Lupski, J.R. Differential subsequence conservation of interspersed repetitive Streptococcus pneumoniae BOX elements in diverse bacteria. Genome Res. 1995, 5, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hulton, C.S.; Higgins, C.F.; Sharp, P.M. ERIC sequences: A novel family of repetitive elements in the genomes of Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium and other enterobacteria. Mol. Microbiol. 1991, 5, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, M.J.; Ames, G.F.; Smith, N.H.; Robinson, E.C.; Higgins, C.F. Repetitive extragenic palindromic sequences: A major component of the bacterial genome. Cell 1984, 37, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, W.J.; Moon, S.M.; Kim, S.Y.; Woo, M.A.; Kim, S.; Jhun, B.W.; Park, H.Y.; Jeon, K.; Huh, H.J.; Ki, C.S.; et al. Outcomes of Mycobacterium avium complex lung disease based on clinical phenotype. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1602503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Versalovic, J.; Koeuth, T.; Lupski, J.R. Distribution of repetitive DNA sequences in eubacteria and application to fingerprinting of bacterial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991, 19, 6823–6831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heras, J.; Dominguez, C.; Mata, E.; Pascual, V.; Lozano, C.; Torres, C.; Zarazaga, M. GelJ--a tool for analyzing DNA fingerprint gel images. BMC Bioinform. 2015, 16, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burki, D.; Bernasconi, C.; Bodmer, T.; Telenti, A. Evaluation of the relatedness of strains ofMycobacterium avium using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1995, 14, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, P.R.; Gaston, M.A. Numerical index of the discriminatory ability of typing systems: An application of Simpson’s index of diversity. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1988, 26, 2465–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selander, R.K.; Caugant, D.A.; Ochman, H.; Musser, J.M.; Gilmour, M.N.; Whittam, T.S. Methods of multilocus enzyme electrophoresis for bacterial population genetics and systematics. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1986, 51, 873–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamvar, Z.N.; Tabima, J.F.; Grunwald, N.J. Poppr: An R package for genetic analysis of populations with clonal, partially clonal, and/or sexual reproduction. PeerJ 2014, 2, e281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ichikawa, K.; van Ingen, J.; Koh, W.J.; Wagner, D.; Salfinger, M.; Inagaki, T.; Uchiya, K.I.; Nakagawa, T.; Ogawa, K.; Yamada, K.; et al. Genetic diversity of clinical Mycobacterium avium subsp. hominissuis and Mycobacterium intracellulare isolates causing pulmonary diseases recovered from different geographical regions. Infect. Genet Evol. 2015, 36, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, K.; Ito, Y.; Hirai, T.; Kubo, T.; Maekawa, K.; Togashi, K.; Ichiyama, S.; Mishima, M. Association between polyclonal and mixed mycobacterial Mycobacterium avium complex infection and environmental exposure. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2014, 11, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeon, S.; Lim, N.; Kwon, S.; Shim, T.; Park, M.; Kim, B.J.; Kim, S. Molecular Typing of Mycobacterium intracellulare Using Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis, Variable-Number Tandem-Repeat Analysis, Mycobacteria Interspersed Repetitive-Unit-Variable-Number Tandem Repeat Typing, and Multilocus Sequence Typing: Molecular Characterization and Comparison of Each Typing Methods. Osong Public Health Res. Perspect. 2014, 5, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.Y.; Lee, S.T.; Jeong, B.H.; Park, H.Y.; Jeon, K.; Kim, J.W.; Shin, S.J.; Koh, W.J. Genotyping of Mycobacterium intracellulare isolates and clinical characteristics of lung disease. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2013, 17, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, M.; Prolla, T.A.; Liskay, R.M.; Petes, T.D. Destabilization of tracts of simple repetitive DNA in yeast by mutations affecting DNA mismatch repair. Nature 1993, 365, 274–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozenberger, B.A.; Roeder, G.S. A unique pathway of double-strand break repair operates in tandemly repeated genes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1991, 11, 1222–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherrer, S.; Landolt, P.; Carroli, N.; Stephan, R. Molecular Characterization of Mycobacterium avium subsp. hominissuis of Two Groups of Lymph Nodes, Being Intradermal Tuberculin or Interferon-Gamma Test Positive and Negative, Isolated from Swiss Cattle at Slaughter. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujita, K.; Ito, Y.; Hirai, T.; Maekawa, K.; Imai, S.; Tatsumi, S.; Niimi, A.; Iinuma, Y.; Ichiyama, S.; Mishima, M. Genetic relatedness of Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex isolates from patients with pulmonary MAC disease and their residential soils. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2013, 19, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kikuchi, T.; Watanabe, A.; Gomi, K.; Sakakibara, T.; Nishimori, K.; Daito, H.; Fujimura, S.; Tazawa, R.; Inoue, A.; Ebina, M.; et al. Association between mycobacterial genotypes and disease progression in Mycobacterium avium pulmonary infection. Thorax 2009, 64, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rindi, L.; Lari, N.; Garzelli, C. Virulence of Mycobacterium avium Subsp. hominissuis Human Isolates in an in vitro Macrophage Infection Model. Int. J. Mycobacteriol. 2018, 7, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| loci Strains | VNTR | MIRU | Types 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 3 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 22 | 31 | 33 | ||
| 7 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 3 | A |
| 9 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 5 | B |
| 10 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 5 | C |
| 14 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 4 | D |
| 16 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | E |
| 18 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 4 | D |
| 19 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 4 | F |
| 20 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 4 | D |
| 21 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 3 | G |
| 22 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 3 | H |
| 23 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 4 | I |
| 24 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 3 | J |
| 25 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 4 | K |
| 26 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 3 | L |
| 27 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 4 | K |
| 28 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 3 | G |
| 29 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 3 | H |
| 30 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 4 | D |
| 31 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | M |
| Allelic Diversity (h) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| loci | France (n = 52) | USA (n = 41) | Japan (n = 74) | Japan (n = 74) | Japan, Korea, The Netherlands, USA (n = 116) | Korea (n = 70) | Korea (n = 44) | Korea (n = 101) |
| VNTR 1 | - | - | 0.46 | 0.5 | 0.44 | 0.18 | 0.09 | 0 |
| VNTR 2 | - | - | 0.58 | 0.73 | 0.58 | 0.69 | 0.5 | 0.61 |
| VNTR 3 | - | - | 0.27 | 0.57 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.17 | 0.48 |
| VNTR 4 | - | - | 0.69 | 0.72 | 0.71 | 0.5 | 0.61 | 0.61 |
| VNTR 5 | - | - | 0.4 | 0.52 | 0.44 | 0.33 | 0.36 | 0.15 |
| VNTR 6 | - | - | 0.65 | 0.57 | 0.63 | 0.21 | 0.53 | 0 |
| VNTR 7 | - | - | 0.62 | 0.58 | 0.62 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.66 |
| VNTR 8 | - | - | 0.52 | 0.6 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.51 | 0.38 |
| VNTR 9 | - | - | 0.07 | 0.54 | 0.24 | 0.42 | 0.63 | 0.6 |
| VNTR 10 | - | - | 0.56 | 0.68 | 0.57 | 0.27 | 0.46 | 0.6 |
| VNTR 11 | - | - | 0.54 | 0.59 | 0.56 | 0.64 | - | 0.54 |
| VNTR 12 | - | - | 0.3 | 0.39 | 0.31 | 0.39 | 0.44 | 0.3 |
| VNTR 13 | - | - | 0.54 | 0.44 | 0.53 | 0.55 | 0.49 | 0.54 |
| VNTR 14 | - | - | 0.21 | 0.45 | 0.25 | 0.27 | 0.13 | 0 |
| VNTR 15 | - | - | 0.55 | 0.48 | 0.54 | 0.54 | 0.51 | 0.5 |
| VNTR 16 | - | - | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 0.21 | 0 | 0 |
| MIRU 3 | 0.74 | 0.70 | - | - | - | - | - | 0.65 |
| MIN 18 | 0.72 | 0.75 | - | - | - | - | 0.46 | 0.6 |
| MIN 19 | 0.63 | 0.59 | - | - | - | - | 0.68 | 0.66 |
| MIN 20 | 0.71 | 0.69 | - | - | - | - | 0.45 | 0.69 |
| MIN 22 | 0.68 | 0.67 | - | - | - | - | 0.43 | 0.6 |
| MIN 31 | 0.59 | 0.48 | - | - | - | - | 0.33 | 0.49 |
| MIN 33 | 0.83 | 0.76 | - | - | - | - | 0.53 | 0.55 |
| references | [12] | [7] | [11] | [24] | [23] | [26] | [25] | in this study |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shin, J.-I.; Ha, J.-H.; Lee, D.-H.; Choi, J.-G.; Kim, K.-M.; Lee, S.J.; Jeong, Y.Y.; Lee, J.D.; Jung, M.; Baik, S.-C.; et al. Comparative Evaluation of Band-Based Genotyping Methods for Mycobacterium intracellulare and Its Application for Epidemiological Analysis. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091315
Shin J-I, Ha J-H, Lee D-H, Choi J-G, Kim K-M, Lee SJ, Jeong YY, Lee JD, Jung M, Baik S-C, et al. Comparative Evaluation of Band-Based Genotyping Methods for Mycobacterium intracellulare and Its Application for Epidemiological Analysis. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(9):1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091315
Chicago/Turabian StyleShin, Jeong-Ih, Jong-Hun Ha, Dong-Hae Lee, Jeong-Gyu Choi, Kyu-Min Kim, Seung Jun Lee, Yi Yeong Jeong, Jong Deog Lee, Myunghwan Jung, Seung-Chul Baik, and et al. 2020. "Comparative Evaluation of Band-Based Genotyping Methods for Mycobacterium intracellulare and Its Application for Epidemiological Analysis" Microorganisms 8, no. 9: 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091315
APA StyleShin, J.-I., Ha, J.-H., Lee, D.-H., Choi, J.-G., Kim, K.-M., Lee, S. J., Jeong, Y. Y., Lee, J. D., Jung, M., Baik, S.-C., Lee, W. K., Kang, H.-L., Shin, M.-K., & Yoo, J.-W. (2020). Comparative Evaluation of Band-Based Genotyping Methods for Mycobacterium intracellulare and Its Application for Epidemiological Analysis. Microorganisms, 8(9), 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091315





