Catabolic Reductive Dehalogenase Substrate Complex Structures Underpin Rational Repurposing of Substrate Scope
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Molecular Biology
2.2. Transformation Protocols
2.3. Heterologous Expression
2.4. Protein Purification
2.5. Cofactor Analysis
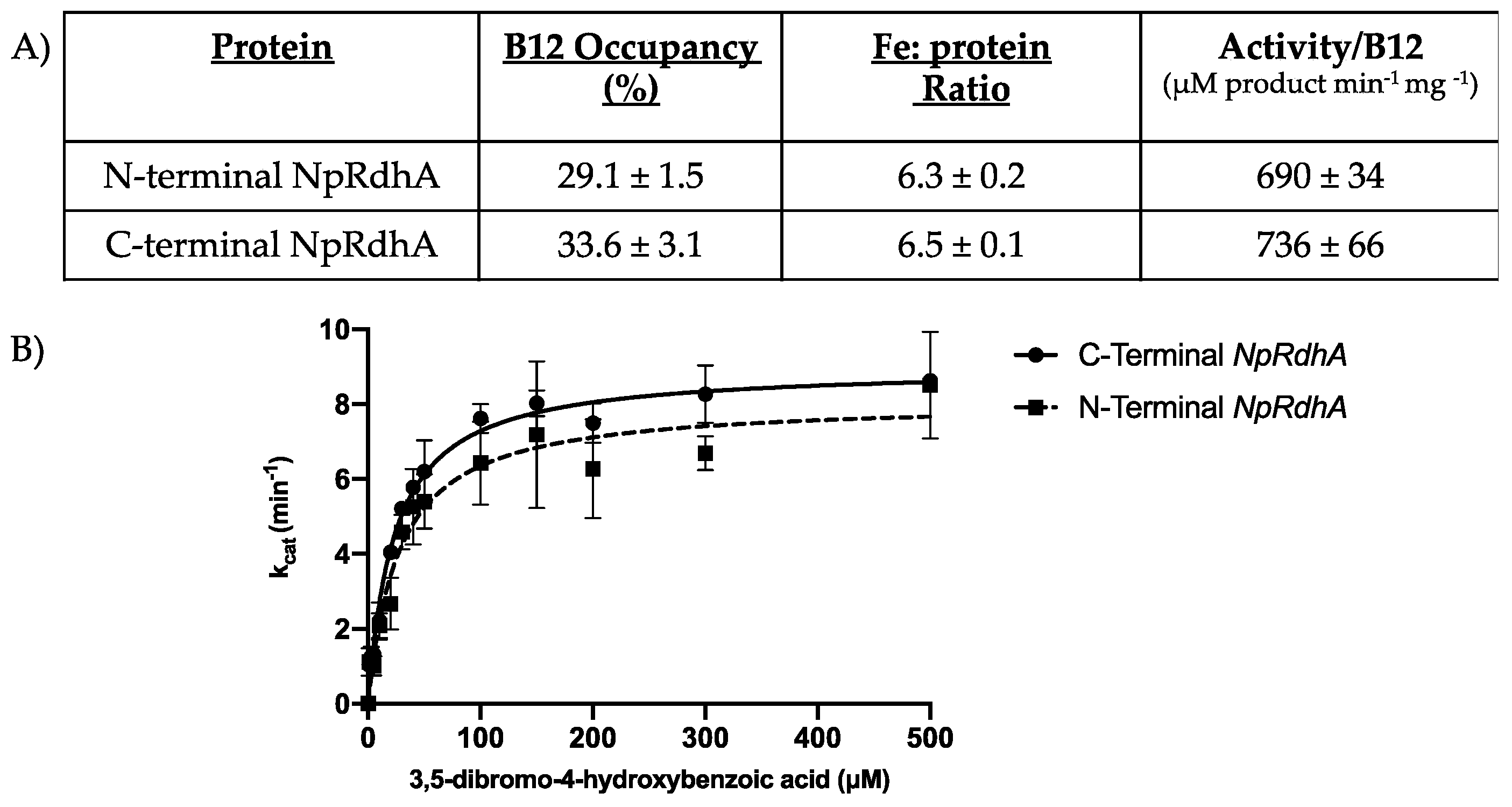
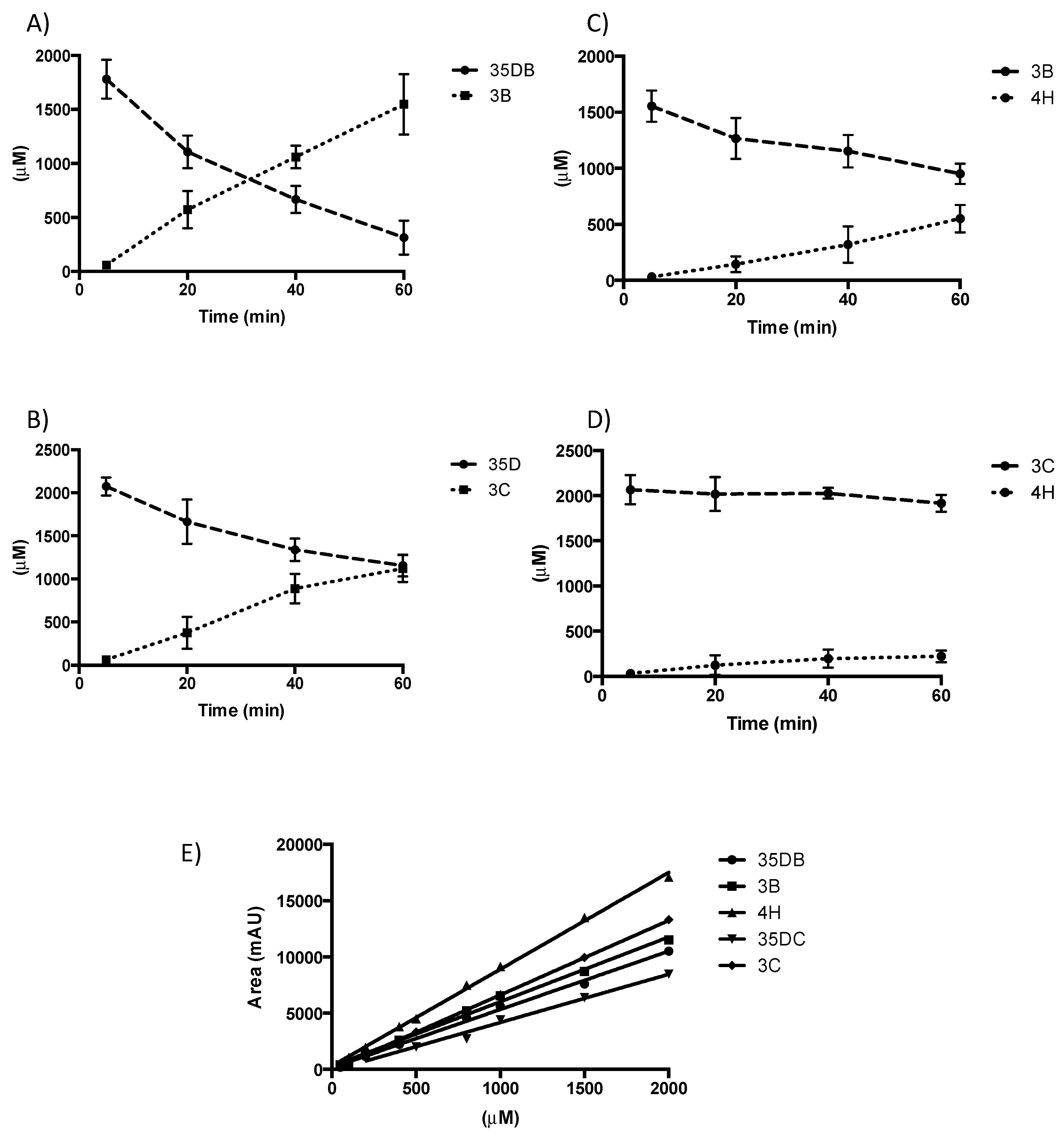
2.6. NpRdhA Activity Analysis
2.7. HPLC Analysis
2.8. Crystallogenesis
2.9. Diffraction Data Collection and Data Processing
2.10. EPR Spectroscopy
3. Results
3.1. Purification and Characterization of N-Terminally Hexa-Histidine Tagged NpRdhA
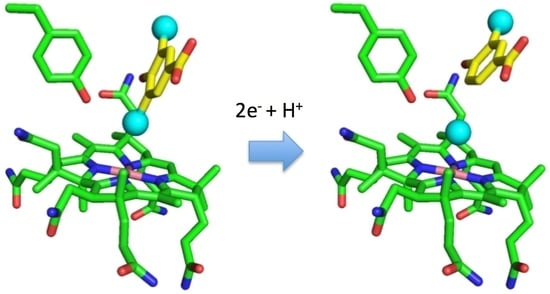
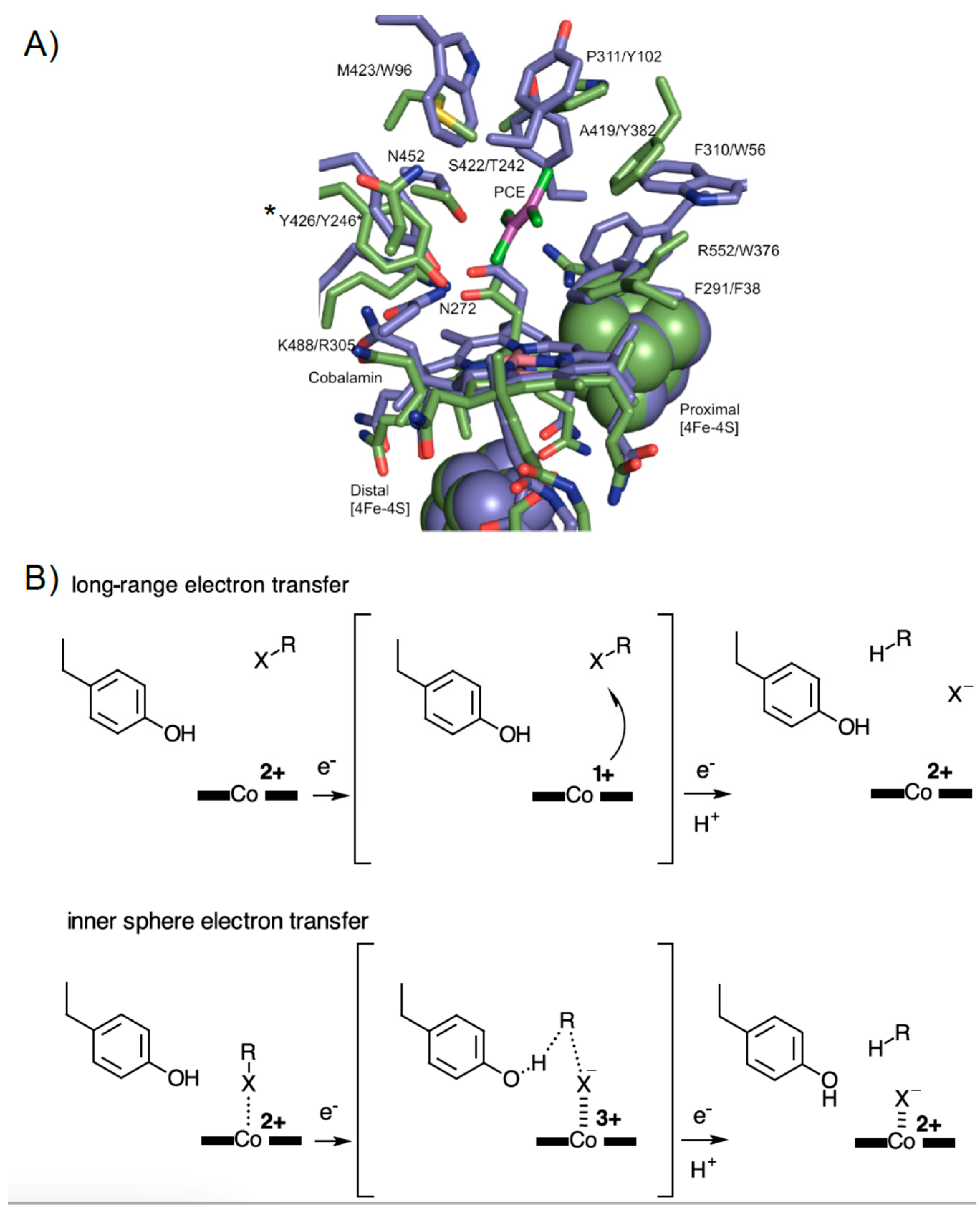
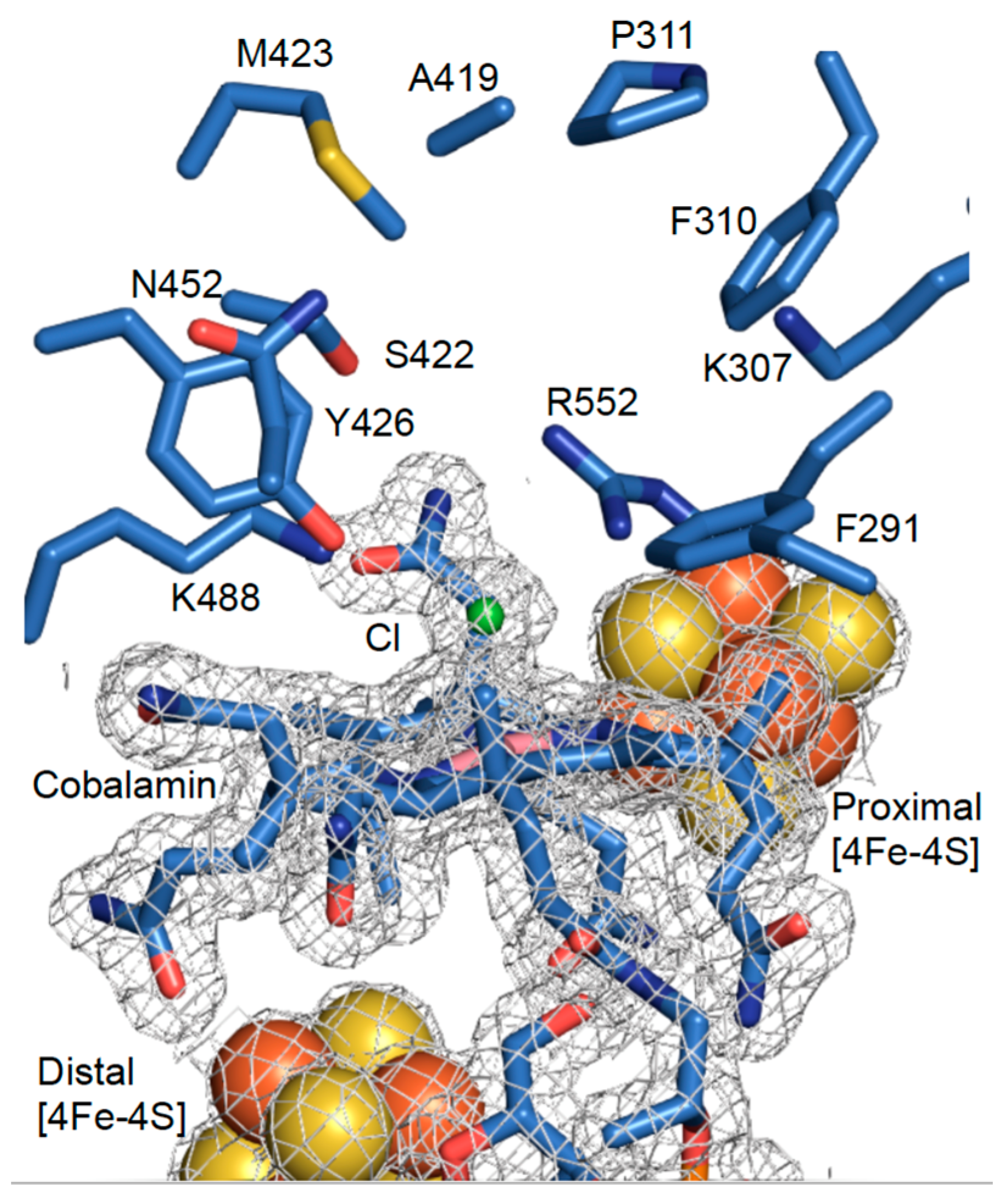
3.2. High-Resolution Crystal Structure of N-Terminally Tagged NpRdhA
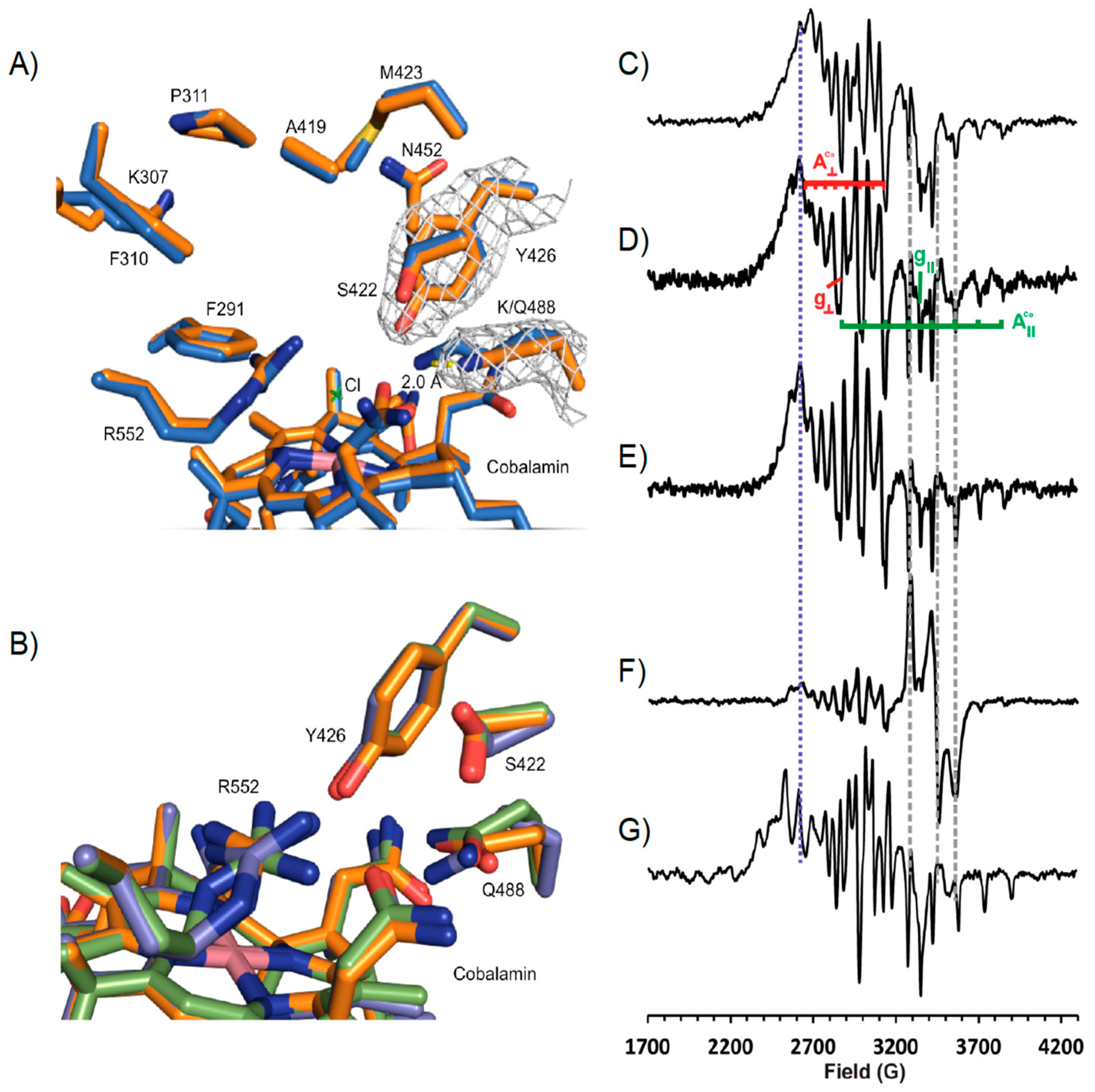
3.3. Crystal Structure of NpRdhAN Ligand Complexes
3.4. Structure of NpRdhAN K488Q Variant
3.5. Rational Mutagenesis of NpRdhA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leys, D.; Adrian, L.; Smidt, H. Organohalide Respiration: Microbes Breathing Chlorinated Molecules. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jugder, B.; Ertan, H.; Bohl, S.; Lee, M.; Marquis, C.P.; Manefield, M. Organohalide Respiring Bacteria and Reductive Dehalogenases: Key Tools in Organohalide Bioremediation. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamieson, A.J.; Malkocs, T.; Piertney, S.B.; Fujii, T.; Zhang, Z. Bioaccumulation of Persistent Organic Pollutants in the Deepest Ocean Fauna. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Löffler, F.E.; Edwards, E.A. Harnessing Microbial Activities for Environmental Cleanup. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2006, 17, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atashgahi, S.; Häggblom, M.M.; Smidt, H. Organohalide Respiration in Pristine Environments: Implications for the Natural Halogen Cycle. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 934–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zanaroli, G.; Negroni, A.; Häggblom, M.M.; Fava, F. Microbial Dehalogenation of Organohalides in Marine and Estuarine Environments. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fincker, M.; Spormann, A.M. Biochemistry of Catabolic Reductive Dehalogenation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2017, 86, 357–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hug, L.A.; Maphosa, F.; Leys, D.; Lo, F.E.; Smidt, H.; Edwards, E.A.; Adrian, L.; Löffler, F.E.; Smidt, H.; Edwards, E.A.; et al. Overview of Organohalide-Respiring Bacteria and a Proposal for a Classification System for Reductive Dehalogenases. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 20120322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Müller, J.A.; Rosner, B.M.; Von Abendroth, G.; Meshulam-Simon, G.; McCarty, P.L.; Spormann, A.M. Molecular Identification of the Catabolic Vinyl Chloride Reductase from Dehalococcoides Sp. Strain VS and Its Environmental Distribution. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 4880–4888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jugder, B.E.; Ertan, H.; Lee, M.; Manefield, M.; Marquis, C.P.; Mane, M.; Marquis, C.P. Reductive Dehalogenases Come of Age in Biological Destruction of Organohalides. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 595–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohner, S.T.; Spormann, A.M. Identification of a Reductive Tetrachloroethene Dehalogenase in Shewanella Sediminis. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 20120326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, K.; Huang, L.; Xu, C.; Liu, X.; He, J.; Zinder, S.H.; Li, S.; Jiang, J. Molecular Characterization of the Enzymes Involved in the Degradation of a Brominated Aromatic Herbicide. Mol. Microbiol. 2013, 89, 1121–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maphosa, F.; De Vos, W.M.; Smidt, H. Exploiting the Ecogenomics Toolbox for Environmental Diagnostics of Organohalide-Respiring Bacteria. Trends Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommer, M.; Kunze, C.; Fesseler, J.; Schubert, T.; Diekert, G.; Dobbek, H. Structural Basis for Organohalide Respiration. Science 2014, 346, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunze, C.; Bommer, M.; Hagen, W.R.; Uksa, M.; Dobbek, H.; Schubert, T.; Diekert, G. Cobamide-Mediated Enzymatic Reductive Dehalogenation via Long-Range Electron Transfer. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, K.A.P.; Quezada, C.P.; Fisher, K.; Dunstan, M.S.; Collins, F.A.; Sjuts, H.; Levy, C.; Hay, S.; Rigby, S.E.J.; Leys, D. Reductive Dehalogenase Structure Suggests a Mechanism for B12-Dependent Dehalogenation. Nature 2015, 517, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krasotkina, J.; Walters, T.; Maruya, K.A.; Ragsdale, S.W. Characterization of the B12- and Iron-Sulfur-Containing Reductive Dehalogenase from Desulfitobacterium Chlororespirans. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 40991–40997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmitz, R.P.H.; Wolf, J.; Habel, A.; Neumann, A.; Ploss, K.; Svatos, A.; Boland, W.; Diekert, G. Evidence for a Radical Mechanism of the Dechlorination of Chlorinated Propenes Mediated by the Tetrachloroethene Reductive Dehalogenase of Sulfurospirillum Multivorans. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 7370–7375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, T.; von Reuß, S.H.; Kunze, C.; Paetz, C.; Kruse, S.; Brand-Schön, P.; Nelly, A.M.; Nüske, J.; Diekert, G. Guided Cobamide Biosynthesis for Heterologous Production of Reductive Dehalogenases. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johannissen, L.O.; Leys, D.; Hay, S. A Common Mechanism for Coenzyme Cobalamin-Dependent Reductive Dehalogenases. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 6090–6094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liao, R.Z.; Chen, S.L.; Siegbahn, P.E.M. Which Oxidation State Initiates Dehalogenation in the B12-Dependent Enzyme NpRdhA: CoII, CoI, or Co0? ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 7350–7358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costentin, C.; Robert, M.; Savéant, J.M. Does Catalysis of Reductive Dechlorination of Tetra- and Trichloroethylenes by Vitamin B12 and Corrinoid-Based Dehalogenases Follow an Electron Transfer Mechanism? J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 12154–12155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, S.J.; Lawrence, A.D.; Biedendieck, R.; Deery, E.; Frank, S.; Howard, M.J.; Rigby, S.E.J.; Warren, M.J. Elucidation of the Anaerobic Pathway for the Corrin Component of Cobalamin (Vitamin B12). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 14906–14911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Collins, F.A.; Fisher, K.; Payne, K.A.P.; Gaytan Mondragon, S.; Rigby, S.E.J.; Leys, D. NADPH-Driven Organohalide Reduction by a Nonrespiratory Reductive Dehalogenase. Biochemistry 2018, 57, 3493–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GraphPad Prism Version 8.4.4. GraphPad Software: San Diego, CA, USA. Available online: www.graphpad.com (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Potterton, E.; Briggs, P.; Turkenburg, M.; Dodson, E. A Graphical User Interface to the CCP4 Program Suite. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2003, 59, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adams, P.D.; Afonine, P.V.; Bunkóczi, G.; Chen, V.B.; Davis, I.W.; Echols, N.; Headd, J.J.; Hung, L.W.; Kapral, G.J.; Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W.; et al. PHENIX: A Comprehensive Python-Based System for Macromolecular Structure Solution. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCoy, A.J.; Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W.; Adams, P.D.; Winn, M.D.; Storoni, L.C.; Read, R.J. Phaser Crystallographic Software. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2007, 40, 658–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emsley, P.; Cowtan, K. Coot: Model-Building Tools for Molecular Graphics. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2004, 60, 2126–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terwilliger, T.C.; Klei, H.; Adams, P.D.; Moriarty, N.W.; Cohn, J.D. Automated Ligand Fitting by Core-Fragment Fitting and Extension into Density. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2006, 62, 915–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigfridsson, K.G.V.; Chernev, P.; Leidel, N.; Popović-Bijelić, A.; Gräslund, A.; Haumann, M. Rapid X-Ray Photoreduction of Dimetal-Oxygen Cofactors in Ribonucleotide Reductase. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 9648–9661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yi, J.; Orville, A.M.; Skinner, J.M.; Skinner, M.J.; Richter-Addo, G.B. Synchrotron X-Ray-Induced Photoreduction of Ferric Myoglobin Nitrite Crystals Gives the Ferrous Derivative with Retention of the O-Bonded Nitrite Ligand. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 5969–5971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kunze, C.; Diekert, G.; Schubert, T. Subtle Changes in the Active Site Architecture Untangled Overlapping Substrate Ranges and Mechanistic Differences of Two Reductive Dehalogenases. FEBS J. 2017, 284, 3520–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Primer | Sequence |
|---|---|
| NpRdhAN-pPT7-F | GGAGGTGAAATGTACAATGGTCCAAACTAGTTTCGAACATCACCATCACCATCACTCAGCTGGTGAAAACTTATATTTCCAAGGCGCCCAGATCTCCATGCGCCTTTATTCCAATCG |
| NpRdhAN-pPT7-R | GGCCGGTACCGGATCCTTAGCCAGCGCTAGATTTAAGAC |
| NpRdhA-K488Q-F | TCCGTTTATTGGTCCTCGTTCCAAAAGTATCGTTTTTACAA |
| NpRdhA-K488Q-R | TTGTAAAAACATACTTTTGGAACGAGGACCAATAAACGGA |
| NpRdhA-A419M-F | AAGGAGCTTCAGGTGATGATTGGATTTCAATGAGTCAGTCCATGCGT |
| NpRdhA-A419M-R | ACGCATGGACTGACTCATTGAAATCCAATCAT CACCTGAAGCTCCTT |
| Structure (PDB Code) | NpRdhAN (6ZXU) | NpRdhAN:35-DB-4-OH (6ZXX) | NpRdhAN:3-B-4-OH (6ZY1) | NpRdhAN-K488Q (6ZY0) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data Collection | ||||
| Space Group | C 2 | C 2 | C 2 | C 2 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 175.11 170.96 107.87 | 180.18 170.39 107.96 | 175.87 170.10 107.65 | 176.35 169.57 107.80 |
| β (°) | 98.37 | 99.15 | 98.35 | 98.33 |
| Resolution (Å) | 121.7–1.73 (1.91–1.73) | 123.1–1.99 (2.26–1.99) | 106.51–1.99 (2.21–1.99) | 106.66–2.13 (2.44–2.13) |
| Rmeas | 0.104 (0.873) | 0.149 (0.886) | 0.181 (0.827) | 0.196 (1.238) |
| I/σI | 8.7 (1.6) | 7.3 (1.8) | 6.8 (1.7) | 8.2 (1.8) |
| Completeness (%) | 93.0 (58.0) | 94.5 (75.5) | 94.0 (78.5) | 94.5 (74.6) |
| Redundancy | 3.3 (2.3) | 3.4 (3.2) | 3.5 (3.1) | 7.0 (6.7) |
| Refinement | ||||
| No. Reflections | 201,352 (685) | 97,499 (302) | 112,203 (229) | 84,097 (316) |
| Rwork/Rfree | 0.1723/0.2026 (0.3239/0.3074) | 0.1812/0.2233 (0.3106/0.3295) | 0.1769/0.2180 (0.2354/0.2923) | 0.1841/0.2328 (0.3054/0.5585) |
| Nr Atoms Protein | 15,975 | 16,128 | 15,902 | 16,508 |
| Nr Atoms Solvent | 1703 | 696 | 968 | 305 |
| Ion/Ligand | 15 | 21 | 15 | 12 |
| Protein B-factor (Å2) | 27.1 | 31.7 | 23.7 | 36.0 |
| Solvent B-factor (Å2) | 33.3 | 32.9 | 27.8 | 34.2 |
| Rmsd Bond Length (Å) | 0.009 | 0.010 | 0.014 | 0.010 |
| Rmsd Bond Angles (°) | 1.556 | 1.507 | 1.072 | 1.541 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Halliwell, T.; Fisher, K.; Payne, K.A.P.; Rigby, S.E.J.; Leys, D. Catabolic Reductive Dehalogenase Substrate Complex Structures Underpin Rational Repurposing of Substrate Scope. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091344
Halliwell T, Fisher K, Payne KAP, Rigby SEJ, Leys D. Catabolic Reductive Dehalogenase Substrate Complex Structures Underpin Rational Repurposing of Substrate Scope. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(9):1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091344
Chicago/Turabian StyleHalliwell, Tom, Karl Fisher, Karl A. P. Payne, Stephen E. J. Rigby, and David Leys. 2020. "Catabolic Reductive Dehalogenase Substrate Complex Structures Underpin Rational Repurposing of Substrate Scope" Microorganisms 8, no. 9: 1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091344
APA StyleHalliwell, T., Fisher, K., Payne, K. A. P., Rigby, S. E. J., & Leys, D. (2020). Catabolic Reductive Dehalogenase Substrate Complex Structures Underpin Rational Repurposing of Substrate Scope. Microorganisms, 8(9), 1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091344