Alleviation Effects of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis XLTG11 on Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strain and Culture
2.2. Animals and Experimental Design
2.3. Histopathological Analysis
2.4. Colonic MPO Activity and Serum Proinflammatory Cytokines
2.5. Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.6. Gut Microbiota Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of B. lactis XLTG11 on DSS-Induced Colitis Symptoms
3.2. Effects of B. lactis XLTG11 on Colon Histopathological Analysis
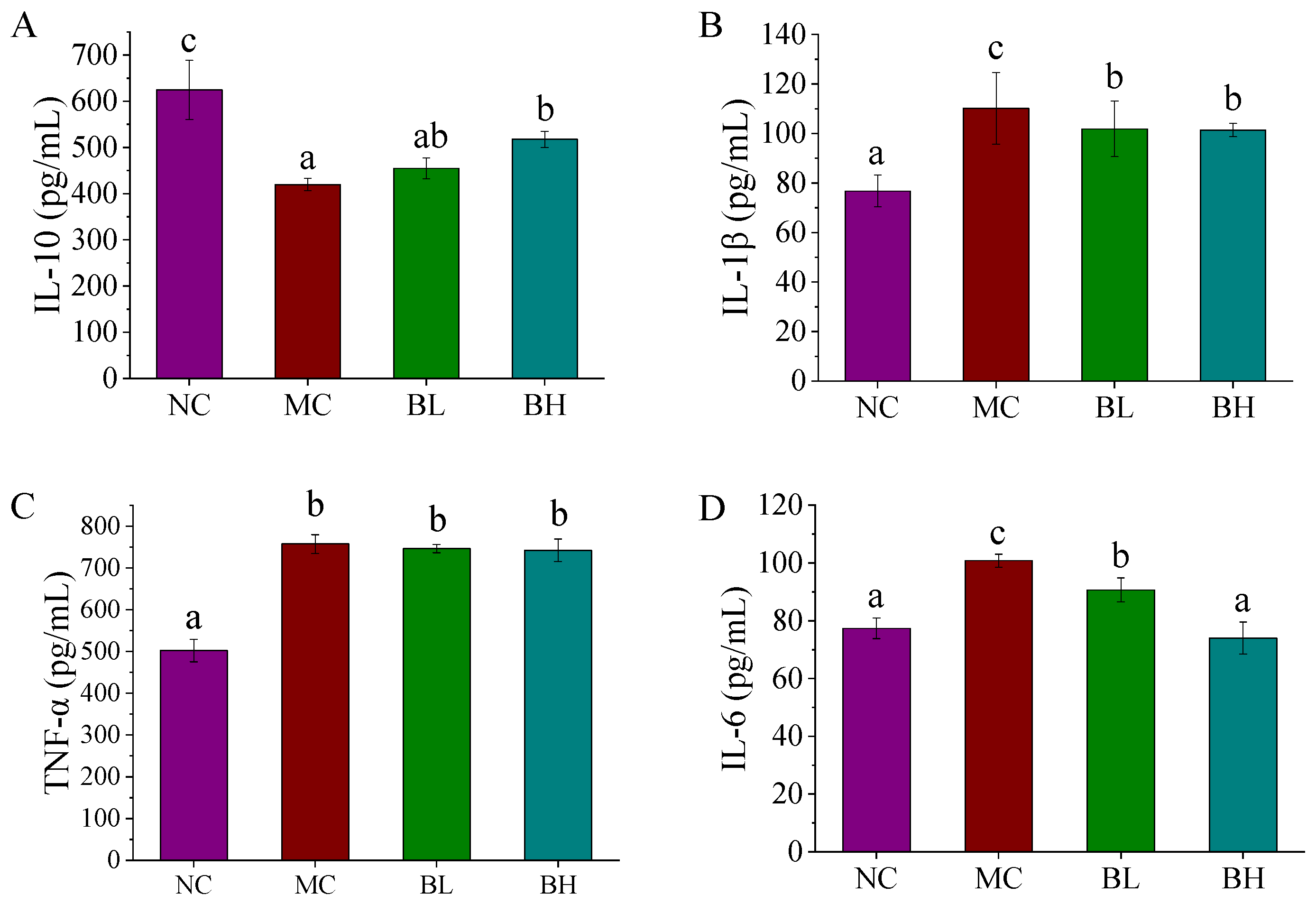
3.3. Effects of B. lactis XLTG11 on Inflammatory Cytokines
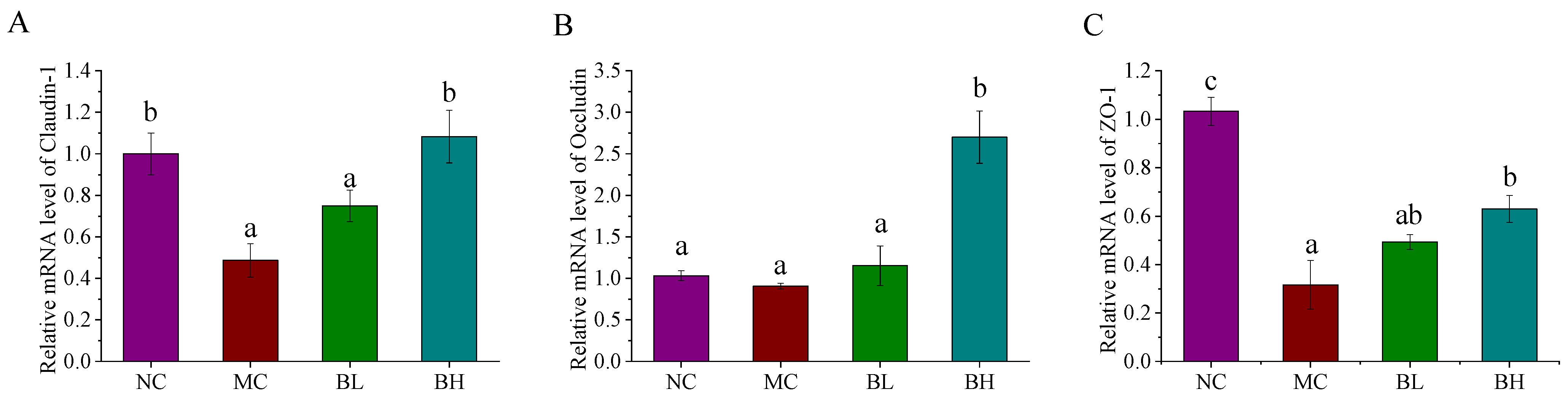
3.4. Effects of B. lactis XLTG11 on Claudin-1, Occludin, and ZO-1 mRNA Expression
3.5. Effects of B. lactis XLTG11 on the TLR4/MYD88/NF-ĸB Signaling Pathway
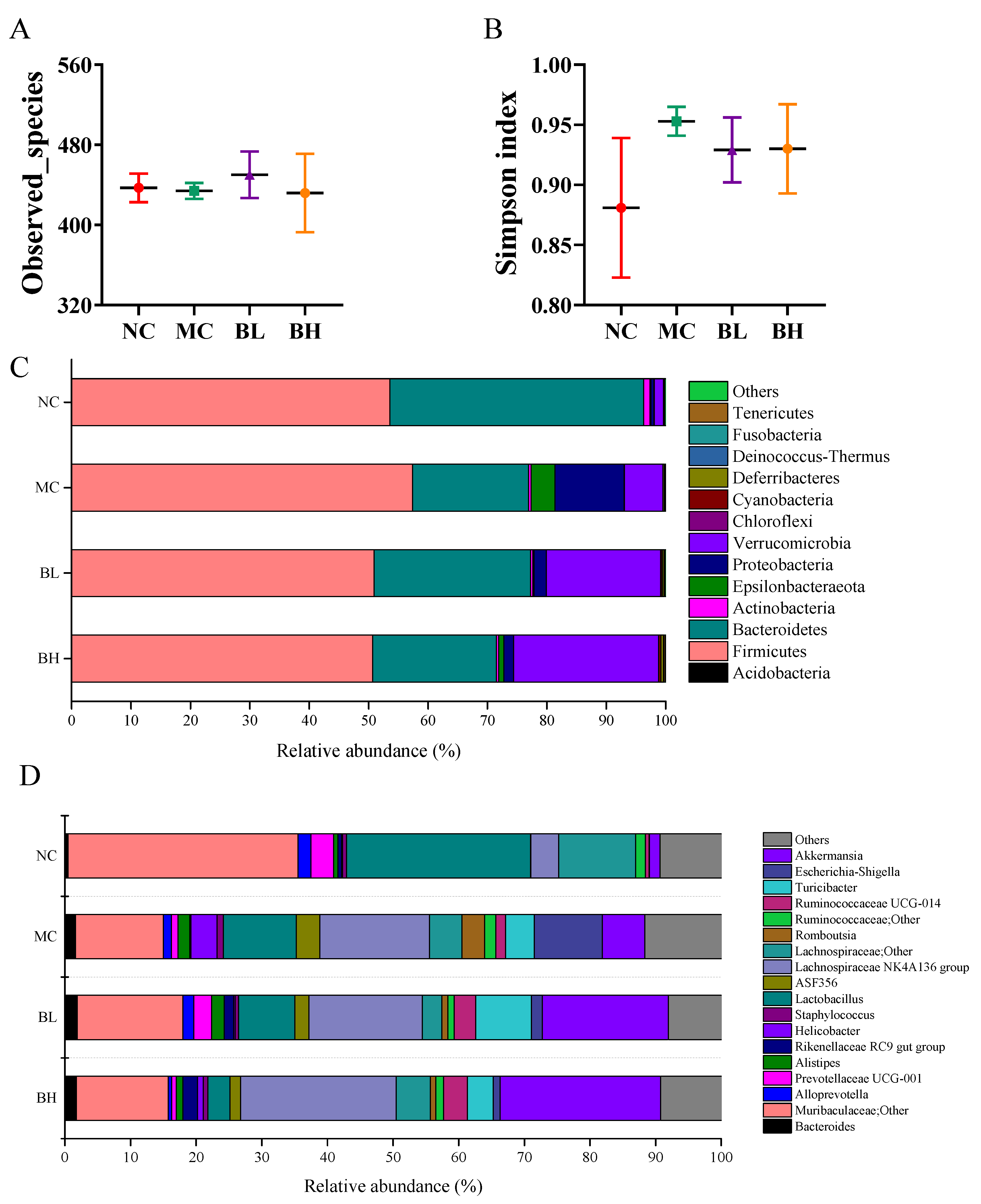
3.6. Effects of B. lactis XLTG11 on Structure and Composition of Gut Microbiota
3.7. Correlation Analysis between UC-Related Symptoms, Related Gene Expression and Dominant Gut Microbiota
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaplan, G.G.; Ng, S.C. Understanding and Preventing the Global Increase of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, Y.; Zheng, C. Effects of Alpinetin on Intestinal Barrier Function, Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Ulcerative Colitis Mice. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 355, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gophna, U.; Sommerfeld, K.; Gophna, S.; Doolittle, W.F.; Zanten, S. Differences between Tissue-Associated Intestinal Microfloras of Patients with Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 4136–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Fan, F.; Cao, Q. Modified Pulsatilla decoction attenuates oxazolone-induced colitis in mice through suppression of inflammation and epithelial barrier disruption. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 1173–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feuerstein, J.D.; Akbari, M.; Tapper, E.B.; Cheifetz, A.S. Systematic review and meta-analysis of third-line salvage therapy with infliximab or cyclosporine in severe ulcerative colitis. Ann. Gastroenterol. Q. Publ. Hell. Soc. Gastroenterol. 2016, 29, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, K.D.; Connor, S.J.; Walls, D.M.; Gollins, J.; Stewart, S.K.; Bewtra, M.; Baumblatt, G.L.; Holubar, S.D.; Greenup, A.-J.; Sechi, A.; et al. Patients with Ulcerative Colitis Are More Concerned About Complications of Their Disease than Side Effects of Medications. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2016, 22, 940–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, A.; Inoue, R.; Inatomi, O.; Bamba, S.; Naito, Y.; Andoh, A. Gut microbiota in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ng, S.C.; Bernstein, C.N.; Vatn, M.H.; Lakatos, P.L.; Loftus, E.V.; Tysk, C.; Colombel, J.F. Geographical variability and environmental risk factors in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 2013, 62, 630–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickard, J.M.; Zeng, M.Y.; Caruso, R.; Núñez, G. Gut microbiota: Role in pathogen colonization, immune responses, and inflammatory disease. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 279, 70–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonsson, A.L.; Bäckhed, F. Role of gut microbiota in atherosclerosis. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2017, 14, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Presti, A.; Zorzi, F.; Del Chierico, F.; Altomare, A.; Cocca, S.; Avola, A.; de Biasio, F.; Russo, A.; Cella, E.; Reddel, S.; et al. Fecal and Mucosal Microbiota Profiling in Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santoru, M.L.; Piras, C.; Murgia, A.; Palmas, V.; Camboni, T.; Liggi, S.; Ibba, I.; Lai, M.A.; Orrù, S.; Blois, S.; et al. Cross sectional evaluation of the gut-microbiome metabolome axis in an Italian cohort of IBD patients. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, R.; Reiff, C.; Russell, R.K.; Bisset, W.M.; Berry, S.H.; Mukhopadhya, I.; Thomson, J.M.; El-Omar, E.; MHold, G.L. Colonic mucosal bacterial diversity of de-novo extensive paediatric ulcerative colitis by next-generation sequencing. Gut. 2011, 60, A146–A147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkusa, T.; Koido, S. Intestinal microbiota and ulcerative colitis. J. Infect. Chemother. 2015, 21, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Roy, B.C.; Khan, S.A.; Septer, S.; Umar, S. Microbiome, Metabolome and Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Microorganisms 2016, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khani, S.; Hosseini, H.M.; Taheri, M.; Nourani, M.R.; Abbas, A. Probiotics as an Alternative Strategy for Prevention and Treatment of Human Diseases: A Review. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Targets 2012, 11, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, H.; Rashmi, H.M.; Batish, V.K.; Grover, S. Probiotics as potential biotherapeutics in the management of type 2 diabetes—prospects and perspectives. Diabetes 2013, 29, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claes, I.; Keersmaecker, S.; Vanderleyden, J.; Lebeer, S. Lessons from probiotic–host interaction studies in murine models of experimental colitis. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 1153–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bron, P.A.; Kleerebezem, M.; Brummer, R.J.; Cani, P.D.; Mercenier, A.; Macdonald, T.T.; Garcia-Ródenas, C.; Wells, J.M. Can probiotics modulate human disease by impacting intestinal barrier function? Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 117, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanahan, F. Probiotics in perspective. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 1808–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, R.; Zuo, F.; Ma, H.; Chen, S. Exopolysaccharide-Producing Bifidobacterium adolescentis Strains with Similar Adhesion Property Induce Differential Regulation of Inflammatory Immune Response in Treg/Th17 Axis of DSS-Colitis Mice. Nutrients 2019, 11, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Din, A.U.; Hassan, A.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Wang, G. Inhibitory effect of Bifidobacterium bifidum ATCC 29521 on colitis and its mechanism. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 79, 108353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Jin, Y.; Stanton, C.; Paul Ross, R.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Yang, B.; Chen, W. Alleviation effects of Bifidobacterium breve on DSS-induced colitis depends on intestinal tract barrier maintenance and gut microbiota modulation. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 369–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinozaki, Y.; Yokota, S.; Miwakeichi, F.; Pokorski, M.; Aoyama, R.; Fukuda, K.; Yoshida, H.; Toyama, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Okada, Y. Structural and functional identification of two distinct inspiratory neuronal populations at the level of the phrenic nucleus in the rat cervical spinal cord. Brain Struct. Funct. 2019, 224, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gad-Elkareem, M.A.M.; Abdelgadir, E.H.; Badawy, O.M.; Kadri, A. Potential antidiabetic effect of ethanolic and aqueous-ethanolic extracts of Ricinus communis leaves on streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, H.W.; Yue, Y.H.; Han, H.; Chen, X.L.; Lu, Y.G.; Zheng, J.M.; Hou, H.T.; Lang, X.M.; He, L.L.; Hu, Q.L.; et al. Effect of toll-like receptor 3 agonist poly I:C on intestinal mucosa and epithelial barrier function in mouse models of acute colitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Ke, C.; Guo, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, B. Lactobacillus plantarum L15 Alleviates Colitis by Inhibiting LPS-Mediated NF-κB Activation and Ameliorates DSS-Induced Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 575173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mago, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast Length Adjustment of Short Reads to Improve Genome Assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelin, Y.; Wegener, P.L.; Pablo, Y.; Jan, G.; Elmar, P.; Christian, Q.; Timmy, S.; Jörg, P.; Wolfgang, L.; Oliver, G.F. The SILVA and “All-species Living Tree Project (LTP)” taxonomic frameworks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 42, 643–648. [Google Scholar]
- Claudio, H.C.; Francesca, A.; Alba, R.N.; Teresa, V.; Pablo, M.C.; Abelardo, M.; Patricia, R.M.; Julio, G. Effect of a Ropy Exopolysaccharide-Producing Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis Strain Orally Administered on DSS-Induced Colitis Mice Model. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 868. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Brenner, M.; Yang, W.L.; Wang, P. Recombinant human MFG-E8 ameliorates colon damage in DSS- and TNBS-induced colitis in mice. Lab. Investig. A J. Tech. Methods Pathol. 2015, 95, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Zheng, P.; Liu, X.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, Z. Calycosin attenuates dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced experimental colitis. Iran. J. Basic Med. Ences 2017, 20, 1056–1062. [Google Scholar]
- Chassaing, B.; Aitken, J.D.; Malleshappa, M.; Vijay-Kumar, M. Dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis in mice. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2014, 104, 15.25.1–15.25.14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Chen, H.; Gao, H.; Wang, J.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P.; Chen, W. Bifidobacterium breve CCFM683 could ameliorate DSS-induced colitis in mice primarily via conjugated linoleic acid production and gut microbiota modulation. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 49, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Zhao, S.; Zhou, J.; Yan, J.; Wang, L.; Du, X.; Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Cai, W.; Wu, J. Curcumin alleviates DSS-induced colitis via inhibiting NLRP3 inflammsome activation and IL-1β production. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 104, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sadi, R.; Guo, S.; Dokladny, K.; Smith, M.A.; Ye, D.; Kaza, A.; Watterson, D.M.; Ma, T.Y. Mechanism of interleukin-1β induced-increase in mouse intestinal permeability in vivo. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2012, 32, 474–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, L.; Nalle, S.C.; Shen, L.; Turner, E.S.; Singh, G.; Breskin, L.A.; Khramtsova, E.; Khramtsova, G.; Tsai, P.; Fu, Y. TNFR2 Activates MLCK-Dependent Tight Junction Dysregulation to Cause Apoptosis-Mediated Barrier Loss and Experimental Colitis. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Sadi, R.; Ye, D.; Boivin, M.; Guo, S.; Hashimi, M.; Ereifej, L.; Ma, T.Y. Interleukin-6 Modulation of Intestinal Epithelial Tight Junction Permeability Is Mediated by JNK Pathway Activation of Claudin-2 Gene. PLoS ONE 2013, 9, e85345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, B.; Alli, R.; Vogel, P.; Geiger, T.L. IL-10 modulates DSS-induced colitis through a macrophage-ROS-NO axis. Mucosal Immunol. 2014, 7, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xie, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, W.; Xiang, H. Combination of probiotics with different functions alleviate DSS-induced colitis by regulating intestinal microbiota, IL-10, and barrier function. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, L.W.; Artis, D. Intestinal epithelial cells: Regulators of barrier function and immune homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Wang, A.; Zeng, X.; Hou, C.; Liu, H.; Qiao, S. Lactobacillus reuteri I5007 modulates tight junction protein expression in IPEC-J2 cells with LPS stimulation and in newborn piglets under normal conditions. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Su, L.; Shen, L.; Clayburgh, D.R.; Nalle, S.C.; Sullivan, E.A.; Meddings, J.B.; Abraham, C.; Turner, J.R. Targeted Epithelial Tight Junction Dysfunction Causes Immune Activation and Contributes to Development of Experimental Colitis. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Srutkova, D.; Schwarzer, M.; Hudcovic, T.; Zakostelska, Z.; Drab, V.; Spanova, A.; Rittich, B.; Kozakova, H.; Schabussova, I. Bifidobacterium longum CCM 7952 Promotes Epithelial Barrier Function and Prevents Acute DSS-Induced Colitis in Strictly Strain-Specific Manner. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Yue, W.; Luo, X. Toll-like receptor 2 monoclonal antibody or/and Toll-like receptor 4 monoclonal antibody increase counts of Lactobacilli and Bifidobacteria in dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 27, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biasi, F.; Leonarduzzi, G.; Oteiza, P.I.; Poli, G. Inflammatory bowel disease: Mechanisms, redox considerations, and therapeutic targets. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 1711–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, X.; Wei, Z.; Wang, J.; Kou, J.; Liu, W.; Fu, Y.; Yang, Z. Alpinetin attenuates inflammatory responses by suppressing TLR4 and NLRP3 signaling pathways in DSS-induced acute colitis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Yin, Q.; Zhong, Q.; Lv, F.L.; Yu, Z.; Li, J.Q.; Wang, J.Z.; Su, B.Y.; Yang, Q.W. Heme activates TLR4-mediated inflammatory injury via MyD88/TRIF signaling pathway in intracerebral hemorrhage. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aderem, A. Role of Toll-like receptors in inflammatory response in macrophages. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 29, s16–s18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Li, Y.; Shen, L.; Zhang, R.; Yang, L.; Li, M.; Li, K.; Fichna, J. The Anti-Inflammatory Effect and Intestinal Barrier Protection of HU210 Differentially Depend on TLR4 Signaling in Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Murine Colitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filali, M.; Lalonde, R.; Theriault, P.; Julien, C.; Calon, F.; Planel, E. Cognitive and non-cognitive behaviors in the triple transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease expressing mutated APP, PS1, and Mapt (3xTg-AD). Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 234, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Effect of the antioxidant Mesna (2-mercaptoethane sulfonate) on experimental colitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2003, 48, 1177–1185. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.M.; Jeong, J.J.; Kang, G.D.; Kim, K.A.; Choi, H.S.; Kim, D.H. Timosaponin AIII and its metabolite sarsasapogenin ameliorate colitis in mice by inhibiting NF-κB and MAPK activation and restoring Th17/Treg cell balance. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 25, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.L.; Tang, H.L.; Zhu, S.Y.; Peng, H.R.; Qi, Z.T.; Wang, W. RIP3 deficiency exacerbates inflammation in dextran sodium sulfate-induced ulcerative colitis mice model. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2017, 35, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, P.; Yuan, H. Therapeutic Efficacy of the Traditional Chinese Medicine Baishaoqiwu on TNBS-induced Colitis is Associated with Down-regulation of the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. In Vivo 2016, 30, 181–186. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez, B.; Delgado, S.; Blanco-Míguez, A.; Lourenço, A.; Gueimonde, M.; Margolles, A. Probiotics, gut microbiota and their influence on host health and disease. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1600240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, P.G.; Li, J.N. Advances in the understanding of the intestinal micro-environment and inflammatory bowel disease. Chin. Med. J. 2020, 133, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Liu, Y.; Song, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, F.; Luo, Y.; Qian, F.; Mu, G.; Tuo, Y. The ameliorative effect of Lactobacillus plantarum-12 on DSS-induced murine colitis. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 5205–5222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Du, P.; Xie, Q.; Wang, N.; Li, B. Protective effects of tryptophan-catabolizing Lactobacillus plantarum KLDS 1.0386 against dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis in mice. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 10736–10747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, N.R.; Whon, T.W.; Bae, J.W. Proteobacteria: Microbial signature of dysbiosis in gut microbiota. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setoyama, H.; Imaoka, A.; Ishikawa, H.; Umesaki, Y. Prevention of gut inflammation by Bifidobacterium in dextran sulfate-treated gnotobiotic mice associated with Bacteroides strains isolated from ulcerative colitis patients. Microbes Infect. 2003, 5, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Q.; Sun, W.; Shan, X.; Jiang, H.; Cai, C.; Hao, J.; Li, G.; Yu, G. Carrageenan-induced colitis is associated with decreased population of anti-inflammatory bacterium, Akkermansia muciniphila, in the gut microbiota of C57BL/6J mice. Toxicol. Lett. 2017, 279, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrien, M.; Belzer, C.; Vos, W.M.D. Akkermansia muciniphila and its role in regulating host functions. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 106, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, J.; Li, S.; Wang, Q.; Guan, X.; Qian, L.; Li, J.; Zheng, Y.; Lin, B. Pediococcus pentosaceus B49 from human colostrum ameliorates constipation in mice. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 5607–5620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.N.; Meng, X.C.; Dong, Y.F.; Zhao, X.H.; Li, J.N. Effects of probiotics and prebiotics on intestinal microbiota in mice with acute colitis based on 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Chin. Med. J. 2019, 132, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhya, I.; Hansen, R.; El-Omar, E.M.; Hold, G.L. IBD-what role do Proteobacteria play? Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, D.J.; Drasar, B.S. Dysentery in World War 1: Shigella a century on. Lancet 2014, 384, 1651–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bosshard, P.P.; Zbinden, R.; Altwegg, M. Turicibacter sanguinis gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel anaerobic, Gram-positive bacterium. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2002, 52, 1263–1266. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saulnier, D.M.; Riehle, K.; Mistretta, T.A.; Diaz, M.A.; Mandal, D.; Raza, S.; Weidler, E.M.; Qin, X.; Coarfa, C.; Milosavljevic, A.; et al. Gastrointestinal Microbiome Signatures of Pediatric Patients With Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1782–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.S.; Li, W.B.; Wang, H.Y.; Ma, Y.M.; Zhao, X.H.; Yang, H.; Qian, J.M.; Li, J.N. VSL#3 can prevent ulcerative colitis-associated carcinogenesis in mice. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 4254–4262. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yan, F.; Li, N.; Shi, J.; Li, H.; Li, B. Lactobacillus acidophilus alleviates type 2 diabetes by regulating hepatic glucose, lipid metabolism and gut microbiota in mice. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 5804–5815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, N.; Wang, S.; Xu, B.; Liu, F.; Huo, G.; Li, B. Alleviation Effects of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis XLTG11 on Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in Mice. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2093. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9102093
Wang N, Wang S, Xu B, Liu F, Huo G, Li B. Alleviation Effects of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis XLTG11 on Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in Mice. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(10):2093. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9102093
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Nana, Song Wang, Baofeng Xu, Fei Liu, Guicheng Huo, and Bailiang Li. 2021. "Alleviation Effects of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis XLTG11 on Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in Mice" Microorganisms 9, no. 10: 2093. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9102093
APA StyleWang, N., Wang, S., Xu, B., Liu, F., Huo, G., & Li, B. (2021). Alleviation Effects of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis XLTG11 on Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in Mice. Microorganisms, 9(10), 2093. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9102093






