Achromobacter spp. Surgical Site Infections: A Systematic Review of Case Reports and Case Series
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Study Selection
2.4. Data Collection Process and Items
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
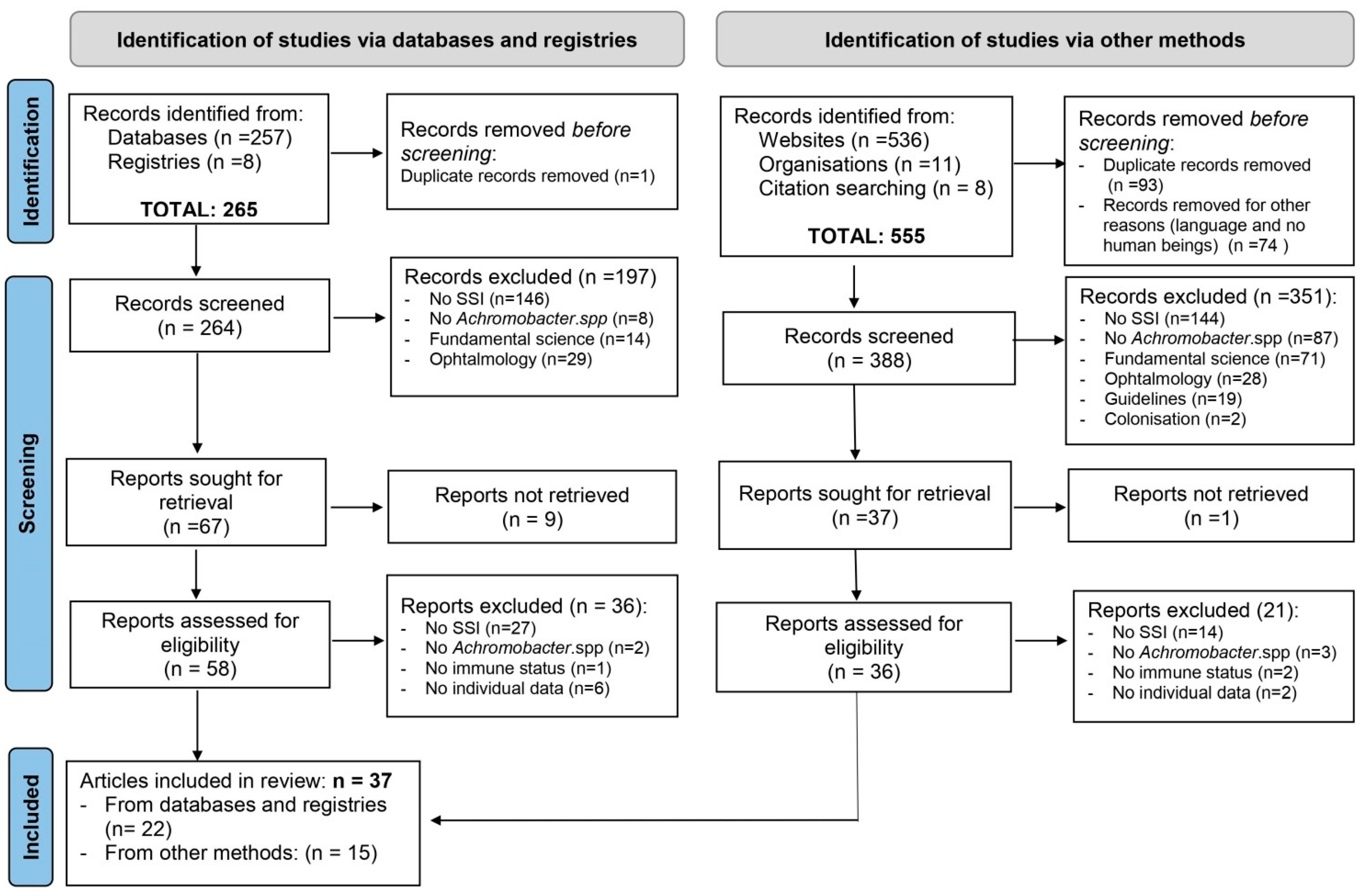
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Descriptive Analysis of Included Cases
3.3.1. Demographics
3.3.2. The Patients’ Immune Status
3.3.3. Surgical Data and Infections
3.3.4. Isolated Strains
3.3.5. Treatments and Outcomes
3.3.6. Origin of Infection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tucci, G.; Romanini, E.; Zanoli, G.; Pavan, L.; Fantoni, M.; Venditti, M. Prevention of surgical site infections in orthopaedic surgery: A synthesis of current recommendations. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 224–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santé Publique France. National Prevalence Survey of Nosocomial Infections and Anti-Infective Treatments in Healthcare Facilities. Results 2017. Available online: https://www.santepubliquefrance.fr/maladies-et-traumatismes/infections-associees-aux-soins-et-resistance-aux-antibiotiques/infections-associees-aux-soins/documents/enquetes-etudes/enquete-nationale-de-prevalence-des-infections-nosocomiales-et-des-traitements-anti-infectieux-en-etablissements-de-sante-mai-juin-2017 (accessed on 13 September 2019). (In French)
- Santé Publique France. National Prevalence Survey of Surgical Site Infections in Healthcare Facilities. Results, 2017. Available online: http://www.cpias-ile-de-france.fr/surveillance/iso/RappRAISIN2017.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2019). (In French)
- Marion-Sanchez, K.; Pailla, K.; Olive, C.; Le Coutour, X.; Derancourt, C. Achromobacter spp.. healthcare associated infections in the French West Indies: A longitudinal study from 2006 to 2016. BMC Infect Dis. 2019, 19, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barragán, E.P.; Pérez, J.S.; Corbella, L.; Orellana, M.A.; Fernández-Ruiz, M. Achromobacter xylosoxidans bacteremia: Clinical and microbiological features in a 10-year case series. Rev. Esp. Quimioter. 2018, 31, 268–273. [Google Scholar]
- Derber, C.; Elam, K.; Forbes, B.; Bearman, G. Achromobacter species endocarditis: A case report and literature review. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 22, e17–e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinod, V.; Kumar, A.; Sanjeevan, K.; Dinesh, K.; Karim, S. Perinephric abscess due to Achromobacter xylosoxidans following de-roofing of renal cyst. Surg. Infect. 2013, 14, 422–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmaja, K.; Lakshmi, V.; Rao, M.; Mishra, R.; Rosy, C.; Sritharan, V. Prosthetic valve endocarditis with aortic root abscess due to Achromobacter xylosoxidans subsp denitrificans—A rare case report. Int. J. Infect Control. 2013, 9, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Cerezo, J.; Suárez, I.; Ríos, J.J.; Pena, P.; Garcia de Miguel, M.J.; De José, M.; Monteagudo, O.; Linares, P.; Barbado-Cano, A.; Vázquez, J.J. Achromobacter xylosoxidans bacteraemia: A 10-year analysis of 54 cases. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2003, 22, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeukens, J.; Freschi, L.; Vincent, A.T.; Emond-Rheault, J.G.; Kukavica-Ibrulj, I.; Charette, S.J.; Levesque, R.C. A pan-genomic approach to understand the basis of host adaptation in Achromobacter. Genome Biol. Evol. 2017, 9, 1030–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swenson, C.E.; Sadikot, R.T. Achromobacter respiratory infections. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2015, 12, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marion-Sanchez, K.; Lion, F.; Olive, C.; Cailleaux, G.; Roques, F. Mediastinitis superinfected by Achromobacter xylosoxidans. A case report. J. Infect. Chemother. 2018, 24, 987–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, K.; Tada, S.; Matsumoto, T.; Miyase, S.; Kamio, T.; KSakurai, K.; Lida, M. A novel bacterium Achromobacter xylosoxidans as a cause of liver abscess: Three case reports. J. Hepatol. 2005, 43, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, D.; Paul, M.; Hoeprich, D. Postoperative infection of an aortic prosthesis with Achromobacter xylosoxidans. West J. Med. 1982, 136, 153–154. [Google Scholar]
- Arroyo, J.C.; Jordan, W.; Lema, M.W.; Brown, A. Diversity of plasmids in Achromobacter xylosoxidans isolates responsible for a seemingly common-source nosocomial outbreak. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1987, 25, 1952–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozer, B.; Serarslan, Y.; Duran, N.; Akdemir, G.; Onlen, Y. Postoperative meningitis due to a rare pathogen: Alcaligenes xylosoxidans. Cent. Eur. J. Med. 2009, 4, 532–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Nirkhiwale, S.; Gupta, P.; Phatak, S. Achromobacter xylosoxidans mesh related infection: A case of delayed diagnosis and management. J. Infect. 2012, 64, e1–e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hal, S.; Stark, D.; Marriott, D.; Harkness, J. Achromobacter xylosoxidans subsp. xylosoxidans prosthetic aortic valve infective endocarditis and aortic root abscesses. J. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 57, 525–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawant, A.; Srivatsa, S.; Castro, L. Alcaligenes xylosoxidans endocarditis of a prosthetic valve and pacemaker in a 62-year-old woman. Tex. Heart Inst. J. 2013, 40, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Tsay, R.; Lin, L.; Chiou, C.; Liao, J.; Chen, C.; Ch Liu, C.; Young, T. Alcaligenes xylosoxidans bacteremia: Clinical features and microbiological characteristics of isolates. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2005, 38, 194–199. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, Y.; Kim, N.H.; Shin, D.H.; Park, O.Y.; Kim, W.; Jeong, M.H.; Cho, J.G.; Park, J.C.; Kang, J.C. Pacemaker lead endocarditis caused by Achromobacter xylosoxidans. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2004, 19, 291–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, M.; Papireddy, M.; Kulkarni, S. A rare case of complicated Achromobacter xylosoxidans endocarditis and its successful management. Abstract published at Hospital Medicine 2016, March 6–9, San Diego, Calif. J. Hosp. Med. 2016, 11, Abstract 439. [Google Scholar]
- United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Healthcare Safety Network surgical site infection definition criteria. In World Health Organization, Protocol for Surgical Site Infections Surveillance with the Focus on Setting with Limited Resources; WHO Document Production Services: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ministère de la santé, de la jeunesse et des sports DGS/DHOS, CTINILS. Definitions of Healthcare Associated Infections. 2007; (in French). Available online: https://solidarites-sante.gouv.fr/IMG/pdf/rapport_vcourte.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2007).
- Santé Publique France. National Prevalence Survey of Nosocomial Infections and Anti-Infective Treatments in Healthcare Facilities. Auditor’s guide 2017. Available online: http://www.cpias.fr/ES/surveillance/2017_ENP2017_Guide_Complet_4avril2017.pdf (accessed on 4 April 2017). (In French)
- Harrop, J.S.; Styliaras, J.C.; Ooi, Y.C.; Radcliff, K.E.; Vaccaro, A.R.; Wu, C. Contributing factors to surgical site infections. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2012, 20, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferroir, J.P.; Milleron, B.; Denis, M.; Guillard, A. Un germe exceptionnellement à l’origine de méningites, l’ Achromobacter xylosoxidans. La Presse Médicale 1991, 20, 1090. [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand, M.S.; Cleveland, K.O. Successful treatment with doripenem of ventriculitis due to Achromobacter xylosoxidans. QJM 2014, 107, 923–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, B.; Snell, J.; Lapage, S. Strains of Achromobacter xylosoxidans from clinical material. J. Clin. Path. 1977, 30, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santaeufemia, S.; Amador, R.; Alonso, M.; Pinedo, B.; Mena-Bernal, H.; Talavera, G. Alcaligenes xylosoxidans Infections in Children; Five Cases in Different Sites. 2014. Available online: https://ibimapublishing.com/articles/PRIJ/2014/519461/ (accessed on 11 March 2014).
- Shigeta, S.; Yasunaga, Y.; Honzumi, K.; Okamura, H.; Kumata, R.; Endo, S. Cerebral ventriculitis associated with Achromobacter xylosoxidans. J. Clin. Path. 1978, 31, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tena, D.; Martínez, N.; Losa, C.; Solís, S. Skin and soft tissue infection caused by Achromobacter xylosoxidans: Report of 14 cases. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 46, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amato, R.; Salemi, M.; Mathews, A.; Cleri, D.; Reddy, G. Achromobacter xylosoxidans (Alcaligenes xylosoxidans subsp. xylosoxidans) meningitis associated with a gunshot wound. J. Clin. Microbial. 1988, 26, 2425–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, S.; Ou, T.; Hsieh, Y.; Lee, W.; Lin, Y.; Lee, W. Complicated intra-abdominal infection caused by extended drug–resistant Achromobacter xylosoxidans. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2009, 42, 176–180. [Google Scholar]
- Rafael, A.; Keshavamurthy, S.; Sepulveda, E.; Miranda, C.; Okamoto, T.; Pettersson, G. Intracardiac abscess with cutaneous fistula secondary to ventricular septal defect repair simulating sternal wound infection. Tex. Heart Inst. J. 2014, 41, 324–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokuyasu, H.; Fukushima, T.; Hirofumi Nakazaki, H.; Shimizu, E. Infective endocarditis caused by Achromobacter xylosoxidans: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Intern Med. 2012, 51, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Taylor, P.; Fischbein, L. Prosthetic knee infection due to Achromobacter xylosoxidans. J. Rheumatol. 1992, 19, 992–993. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Réseau de Prévention des Infections Associées aux Soins, Forum Infections Nosocomiales. Available online: https://www.preventioninfection.fr/le-forum-repias/ (accessed on 30 April 2004).
- Rotter, J.; Graffeo, C.; Perry, A.; Gilder, H.; Wilson, J.; Link, M. Polymicrobial intracerebral abscess growing Mycobacterium avium complex and Achromobacter xylosoxidans: Case report and literature review. World Neurosurg. 2020, 141, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, S.; Yeşilyurt, E.; Yılmaz, N.; Gürel, A.; Gürtan, E.; Sanal, L. Achromobacter xylosoxidans infection in urinary tract in a secondary kidney stone patient: Case Report. J. Surg. Med. 2018, 2, 406–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, N.; Koilara, N.; Kato, H.; Singh, T.; Karri, K.; Thakur, K. First documented case of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) tube-associated bacterial peritonitis due to Achromobacter species with literature review. Case Rep. Gastrointest. Med. 2020, 16, 4397930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lofgren, R.P.; Nelson, A.E.; Crossley, K.B. Prosthetic valve endocarditis due to Achromobacter xylosoxidans. Am. Heart J. 1981, 101, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi Yang, N.; George, F.; Kah Woon, L. Resolution of concomitant Achromobacter xylosoxidans burn wound infection without adjustment of antimicrobial therapy. Indian J. Plast. Surg. 2014, 47, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linde, L.M.; Heins, H.L. Bacterial endocarditis following surgery for congenital heart disease. NEJM 1960, 233, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinley, K.P.; Laundy, T.J.; Masterton, R.G. Achromobacter Group B replacement valve endocarditis. J. Infect. 1990, 20, 262–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C.; Nam, C.H.; Park, I.S.; Yoon, J.Y.; Jung, K.A.; Hwang, S.H. Achromobacter xylosoxidans infection following total knee arthroplasty. J. Korean Orthop. Assoc. 2014, 49, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Revati, S.; Renoy, H. A rare instance of recurrent Achromobacter infection in an immunocompetent individual. Int. J. Contemp. Med. Res. 2019, 6, 35–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelbaum, P.C.; Campbell, D.B. Pancreatic abscess associated with Achromobacter group Vd biovar 1. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1980, 12, 282–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirel, A.; Inan, N.; Akpinar, H.; Iris, N.E. Hospital-acquired urosespis caused by Achromobacter xylosoxidans. Mediterr. J. Infect. Microb. Antimicrob. 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köppen Climate Classification. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Köppen_climate_classification (accessed on 1 September 2004).
- Awadh, H.; Mansour, M.; Aqtash, O.; Shweihat, Y. Pneumonia due to a rare pathogen: Achromobacter xylosoxidans, subspecies denitrificans. Case Rep. Infect Dis. 2017, 3969682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spilker, T.; Vandamme, P.; Lipuma, J.J. Identification and distribution of Achromobacter species in cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2013, 12, 298–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astagneau, P. La mortalité attribuable aux infections Hospitalières. ADSP 2002, 38, 27–29. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Guo, J.; Yan, W.; Jin, Y.; Pan, F.; Fang, X.; Qin, L.; Liu, C. Hospital-acquired pneumonia due to Achromobacter xylosoxidans in the elderly: A single-center retrospective study in Beijing. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2017, 11, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marion-Sanchez, K.; Olive, C.; Platon, M.G.; Cesarine, M.; Derancourt, C.; Pailla, K. Achromobacter xylosoxidans in hospital environments: Achromobacter xylosoxidans in hospital environments: Still waters run deep! Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 114, 470–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günther, F.; Merle, U.; Frank, U.; Gaida, M.M.; Mutters, N.T. Pseudobacteremia outbreak of biofilm-forming Achromobacter xylosoxidans—environmental transmission. BMC Infect Dis. 2016, 16, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Isler, B.; Kidd, J.T.; Stewart, A.G.; Harris, P.; Paterson, D.L. Achromobacter infections and treatment options. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e01025-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Scheme 1. Surgical Procedures Including Prosthesis or Implant | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case Characteristics | Surgical Procedures | |||||||
| Case no. | Author year (ref) | Country State/city Climate * | Age (Y) | Sex | Main Disease and Associated Pathologies | Immune Status | Type of Surgery | Description |
| 1 | Derber 2011 [6] | USA Virginie Cfa | 54 | F | Tetralogy of Fallot, Blalock-Taussig shunt as a child, total repair as a teenager | Comp | Heart | Bovine pulmonary valve replacement |
| 2 | Gelfand 2014 [28] | USA Tennessee Dfa | 29 | F | Spina Bifida and placement of a ventriculo-peritoneal shunt in early childhood. | Comp | Neurological | Replacement of VP shunt |
| 3 | Gupta 2012 [17] | India Lucknow Csa | 65 | M | Small paraumbilical hernia | Comp | Digestive | Open mesh repair |
| 4 | Van Hal 2008 [18] | Australia Sydney Cfa | 37 | M | Native valve endocarditis, intravenous drug user | Comp | Heart | Aortic valve replacement |
| 5 | Olson 1981 [14] | USA California Csa | 35 | M | Dissection of the aortic root, aortic stenosis, and insufficiency | Comp | Heart | Aortic resection and Daflon tube graft insertion |
| 6 | Santaeufemia 2014 [30] | Spain Madrid Csa | 0.16 | F | Congenital hydrocephalus | Comp | Neurological | Reducer cranioplasty and VP shunt |
| 7 | Sawant 2013 [19] | USA California Csa | 62 | F | Chronic heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic kidney disease | Comp | Heart | Bioprosthetic aortic valve replacement and placement of pace-maker |
| 8 | Shigeta 1978 [31] | Japan Fukushima Cfa | 9 | F | Arachnoid cyst | Comp | Neurological | Arachnoid cyst and VP shunt |
| 9 | Shigeta 1978 [31] | Japan Fukushima Cfa | 8 | M | Thalamic tumor | Supp | Neurological | VP shunt |
| 10 | Tena 2014 [32] | Spain Guadalajara Csa | 57 | F | No underlying disease | Comp | Orthopedic | Total knee arthroplasty |
| 11 | Ahn 2004 [21] | Korea Iksan Dfa | 35 | M | Chronic heart failure | Comp | Heart | Pacemaker placement |
| 12 | Padmaja 2013 [8] | India Hyderabad Aw | 17 | M | Congenital aortic stenosis | Comp | Heart | Prosthetic aortic valve replacement |
| 13 | Rafael 2014 [35] | USA Ohio Dfa | 50 | F | Splenomegaly, pancytopenia, ventricular septal defect | Supp | Heart | Ventricular septal defect repair |
| 14 | Linde 1960 [44] | USA California Csa | 20 | M | Tetralogy of Fallot | Comp | Heart | Definitive repair using Ivalon patch |
| 15 | Tokuyasu 2012 [36] | Japan Tottori Cfa | 86 | F | Chronic heart disease | Comp | Heart | Prosthetic aortic valve replacement |
| 16 | Taylor 1991 [37] | USA Missouri Dfa | 53 | F | Rheumatoid arthritis | Supp | Orthopedic | Prosthetic knee replacement |
| 17 | Bhattarai 2016 [22] | USA Illinois Dfa | 37 | F | Chronic heart disease, intravenous drug user | Comp | Heart | Mitral valve replacement |
| 18 | Marion- Sanchez 2018 [12] | Martinique Fort-de-France AM | 81 | M | Chronic heart disease | Comp | Heart | Mitral valve remplacement |
| 19 | MarionSanchez 2019 [4] | Martinique Fort-de-France AM | 58 | M | Digestive ulcer | Comp | Thoracic | Esophageal stent placement |
| 20 | MarionSanchez 2019 [4] | Martinique Fort-de-France AM | 41 | M | Biliary stenosis | Comp | Digestive | PEG tube placement |
| 21 | Lofgren 1981 [42] | USA Minneapolis Dfa | 77 | F | Rheumatic aortic stenosis | Comp | Heart | Prosthetic aortic valve replacement |
| 22 | Tripathi 2020 [41] | USA Lexington Cfa | 65 | M | Distal common bile duct stone, chronic alcoholism, tonsillar adenocarcinoma | Supp | Digestive | PEG tube placement |
| 23 | McKinley 1989 [45] | UK Aylesbury Cfb | 28 | M | Aortic valve regurgitation | Comp | Heart | Aortic valve replacement |
| 24 | Lee 2014 [46] | Korea Seoul Dwa | 52 | M | Osteoarthritis | Comp | Orthopedic | Total knee arthroplasty |
| Subgroup 2—Surgical Procedures without Prosthesis or Implant | ||||||||
| Case Characteristics | Surgical Procedures | |||||||
| Case no. | Author Year (Ref) | Country State/City Climate * | Age (Y) | Sex | Main Disease and Associated Pathologies | Immune Status | Type of Surgery | Description |
| 25 | Ferroir 1988 [27] | France Paris Cfb | 54 | F | Pneumocephalus, Hodgkin disease | Supp | Thoracic | Lobectomy |
| 26 | Holmes 1977 [29] | UK London Cfb | 38 | F | Breast Carcinoma, steroid, and hormonal therapy, chemo and radiotherapy. | Supp | Gynecological | Mastectomy |
| 27 | Ozer 2009 [16] | Turkey Hatay Csa | 38 | M | Traffic accident, central facial paralysis | Comp | Neurological | Removal of arachnoid cyst by craniotomy |
| 28 | Santaeufemia 2014 [30] | Spain Madrid Csa | 13 | M | Trafic accident, open fracture of the proximal left tibia and fibula | Comp | Orthopedic | Osteosynthesis |
| 29 | Shigeta 1978 [31] | Japan, Fukushima Cfa | 49 | M | Meningioma | Supp | Neurological | Meningioma resection by craniotomy |
| 30 | Tena 2014 [32] | Spain Guadalajara Csa | 47 | F | Mandibular abscess | Comp | Stomatological | Submandibular abscess debridement |
| 31 | Tena 2014 [32] | Spain Guadalajara Csa | 18 | H | Pilonidal cyst | Comp | Digestive | Cyst removal |
| 32 | Tsay 2005 [20] | Taïwan Changhua Cfa | 46 | M | Empyema | Comp | Thoracic | Decortication of empyema |
| 33 | D’Amato 1988 [33] | USA New York Dfb | 14 | M | Totally transected spinal cord after gunshot to the chest | Comp | Thoracic | Ligation of bleeding vessels and repair of lung laceration |
| 34 | Asano 2005 [13] | Japan Kumamoto Cfa | 52 | F | Cholecystolithiasis | Comp | Digestive | Cholecystectomy |
| 35 | Asano 2005 [13] | Japan Kumamoto Cfa | 57 | M | Cholecystolithiasis | Comp | Digestive | Cholecystectomy |
| 36 | Asano 2005 [13] | Japan Kumamoto Cfa | 52 | M | Cholecystolithiasis | Comp | Digestive | Cholecystectomy |
| 37 | Vinod 2013 [7] | India Kerala AM | 51 | M | Simple renal cyst | Comp | Neurological | Laparoscopic deroofing of a simple renal cyst |
| 38 | Teng 2009 [34] | Taïwan Taipei Cfa | 27 | M | Cholecystolithiasis | Comp | Digestive | Cholecystectomy |
| 39 | CPIAS 2003 [38] | France Paris Cfb | 36 | M | Achilles tendon rupture | Comp | Orthopedic | Achilles tendon |
| 40 | Rotter 2020 [39] | USA Minnesota Dfb | 70 | M | Mucocele | Comp | Neurological | Resection of left frontal sinus and zygomatico-maxillary mucocele |
| 41 | Sari 2018 [40] | Turkey Yozgat Dsb | 56 | M | Kidney stone | Comp | Nephro- logical | Intrarenal surgery for kidney stone |
| 42 | MarionSanchez 2019 [4] | Martinique Fort-de-France AM | 74 | M | History of colorectal Adenocarcinoma, Peritonitis | Supp | Digestive | Exploratory laparotomy |
| 43 | MarionSanchez 2019 [4] | Martinique Fort-de-France AM | 63 | F | Chronic heart disease | Comp | Heart | Double coronary bypass |
| 44 | MarionSanchez 2019 [4] | Martinique Fort-de-France AM | 65 | F | Arteritis | Comp | Vascular | Femorofemoral bypass |
| 45 | Linde 1960 [44] | USA California Csa | 4 | M | Defect of interventricular septum | Comp | Heart | Direct closure |
| 46 | Zhi Yang 2014 [43] | Singapore Af | 46 | F | Extensive thermal burns (41.5% of the total body) | Supp | Reconstructive | Burn excision and staged, free and cadaveric skin grafting |
| 47 | Revati 2019 [47] | India Kerala AM | 40 | F | Cholelithiasis | Comp | Digestive | Cholecystectomy |
| 48 | Appelbaum 1980 [48] | USA Pennsylvania Cfa | 75 | M | Cholecystitis | Comp | Digestive | Laparotomy |
| 49 | Demirel 2015 [49] | Turkey Istanbul Csa | 59 | F | Bladder tumor | Supp | Urological | Transurethral tumorectomy |
| Subgroup 1—Surgical Procedures Including Prosthesis or Implant | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Infections Topographies | Treatments and Outcomes | |||||
| Case no. | Infection, Depth | Delay (Days) | Identified Species/Associated Bacteria | Suspected Origin of Infection | Treatments | Outcomes |
| 1 | Endocarditis, deep | 120 | Ax subsp. denitrificans/ No | Ukn | Piperacillin/Tazobactam, Imipenem/Cilastatin/ Levofloxacin | Recov |
| 2 | Ventriculitis, deep | 30 | Ax/No | Ukn | Doripenem | Recov |
| 3 | Abscess, deep | Ukn | Ax/No | Mesh | Ceftriaxone, Levofloxacin | Recov |
| 4 | Endocarditis deep | 180 | Ax/No | Duckpond water used to solubilize drugs for injection | Meropenem | Recov |
| 5 | Mediastinitis, deep | 180 | Ax/No | Ukn | Carbenicillin/ Cotrimoxazole/Rifampin, Moxalactam/Rifampin, Azlocillin/Rifampin | Death |
| 6 | Ventriculitis, deep | 20 | Ax/No | Ukn | Ceftazidime/Meropenem | Recov |
| 7 | Endocarditis, deep | 90 | Ax/No | Exposing leg ulcers to water outdoors | Piperacillin/Tazobactam, Meropenem/ Cotrimoxazole, Meropenem/Rifampin/Amikacin | Recov |
| 8 | Ventriculitis, deep | 12 | Ax/No | Aqueous Chlorhexidine solution diluted with non-sterile tap water. | Chloramphenicol | Recov |
| 9 | Ventriculitis, deep | 30 | Ax/Serratia marcescens | Aqueous Chlorhexidine solution diluted with non-sterile tap water. | Chloramphenicol | Recov |
| 10 | Wound infection, superficial | Ukn | Ax/No | Ukn | Ukn | Recov |
| 11 | Endocarditis, deep | 2920 | Ax/No | Scaling and root planning at local dental clinic | Ceftazidime/Piperacillin | Recov |
| 12 | Endocarditis, deep | 150 | Ax subsp. denitrificans/No | Ukn | Meropenem/ Levofloxacin, Meropenem/Cotrimoxazole | Recov |
| 13 | Intracardiac abscess, deep | 10,585 | Ax/No | Ukn | Piperacillin/ Tazobactam/Cotrimoxazole | Recov |
| 14 | Endocarditis, deep | 3 | Achromobacter spp./No | Contamination of extracorporal heart pump | Chloramphenicol/Sulfonamides | Death |
| 15 | Endocarditis, deep | 1825 | Ax/No | Ukn | Meropenem | Death |
| 16 | Abscess, deep | Ukn | Ax/No | Ukn | Ceftazidime, Imipenem/Cotrimoxazole | Recov |
| 17 | Endocarditis, deep | Ukn | Ax/No | Cocaïne mixed with stored tap water | Meropenem | Recov |
| 18 | Mediastinitis, deep | 20 | Ax/Staphylococcus aureus | Water leaks in the ceiling in intensive care unit | Piperacillin/Tazobactam, Meropenem/Vancomycin, Ceftazidime | Death |
| 19 | Mediastinitis, deep | 10 | Achromobacter spp./No | Ukn | Meropenem/Vancomycin | Recov |
| 20 | Abscess, deep | 90 | Achromobacter spp/No | Ukn | Tazobactam | Recov |
| 21 | Endocarditis, deep | 120 | Ax/No | Ukn | Cotrimoxazole/Moxalactam | Death |
| 22 | Peritonitis, deep | 16 | Achromobacter spp./No | Ukn | Piperacillin/Tazobactam, Meropenem/Vancomycin | Death |
| 23 | Endocarditis, deep | 135 | Achromobacter Group B/No | Ukn | Cefuroxime/Gentamycin | Recov |
| 24 | Prosthetic infection deep | 395 | Ax/No | Ukn | Cefazolin Ciprofloxacin Imipenem | Recov |
| Subgroup 2—Surgical Procedures without Prosthesis or Implant | ||||||
| Infections Topographies | Treatments and Outcomes | |||||
| Case no. | Infection, Depth | Delay (Days) | Identified Species/Associated Bacteria | Suspected Origin of Infection | Treatments | Outcomes |
| 25 | Meningitis, deep | 15 | Ax/No | Aerosol | Metronidazole/Imipenem | Recov |
| 26 | Wound infection, superficial | 270 | Ax/No | Ukn | Ukn | Ukn |
| 27 | Meningitis, deep | 3 | Ax/No | Ukn | Meropenem | Recov |
| 28 | Wound infection, superficial | 11 | Ax/No | Ukn | Imipenem, Vancomycin | Recov |
| 29 | Ventriculitis, deep | 6 | Ax/No | Aqueous Chlorhexidine solution diluted with non-sterile tap water. | Ukn | Recov |
| 30 | Cervical abscess, superficial | Ukn | Ax/Candida albicans | Ukn | Ciprofloxacin | Recov |
| 31 | Gluteal abscess, superficial | Ukn | Ax/No | Ukn | Cotrimoxazole | Recov |
| 32 | Wound infection, superficial | Ukn | Ax/No | Ukn | Cefepime | Recov |
| 33 | Meningitis, deep | 15 | Ax/No | Gunshot | Cotrimoxazole/Ceftazidime | Recov |
| 34 | Liver abscess, deep | 150 | Ax/No | Ukn | Ukn | Recov |
| 35 | Liver abscess, deep | 1140 | Ax/No | Ukn | Ukn | Death |
| 36 | Liver abscess, deep | 660 | Ax/No | Ukn | Ukn | Death |
| 37 | Perinephric abscess, deep | 730 | Ax/No | Ukn | Levofloxacin/ Cotrimoxazole, Cefoperazone/Sulbactam, Levofloxacin/Cotrimoxazole | Recov |
| 38 | Liver abscess, deep | 16 | Ax/Escherichia coli | Ukn | Cefpirome, Colistin | Recov |
| 39 | Wound infection, superficial | 75 | Ax subsp. Denitrificans Escherichia coli, Morganella morganii | Ukn | Myambutol/ Ciprofloxacin/Clarithromycin | Recov |
| 40 | Abscess, deep | 3650 | Ax/S.epidermidis, S. salivarius Mycobacterium avium | Spread via the auditory canal | Ertapenem, Cefriaxone/ Cotrimoxazole Meropenem | Recov |
| 41 | Urinary tract infection, deep | Ukn | Ax/No | Ukn | Ciprofloxacin/ Ceftriaxone/Methenamine hippurate | Recov |
| 42 | Abscess, deep | 14 | Achromobacter spp./Stenotrophomonas Maltophilia, Candida albicans | Ukn | Tazobactam/Amikacin | Death |
| 43 | Mediastinitis, deep | 9 | Achromobacter spp./E coli | Ukn | Tazobactam/Amikacin Cefotaxime/Amikacin, Cefotaxime/Fosfomycin | Recov |
| 44 | Wound infection, superficial | 53 | Achromobacter spp./No | Ukn | No antibiotic therapy | Recov |
| 45 | Endocarditis, deep | 2 | Achromobacter spp./No | Contamination of the heart-lung machine | Chloramphenicol/ Streptomycin/Sulfadiazine | Recov |
| 46 | Wound infection, superficial | 11 | Ax/Acinetobacter baumannii | Ukn | Piperacillin/Tazobactam Polymixin B | Recov |
| 47 | Abscess deep | Ukn | Achromobacter spp./No | Endogenous via biliary tract | Piperacillin/Tazobactam | Recov |
| 48 | Abscess deep | Ukn | Achromobacter Group Vd biovar 1/No | Ukn | Cefazolin Gentamycin | Death |
| 49 | Urosepsis deep | 30 | Ax/No | Ukn | Cefuroxime Meropenem Cotrimoxazole | Recov |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ronin, E.; Derancourt, C.; Cabié, A.; Marion-Sanchez, K. Achromobacter spp. Surgical Site Infections: A Systematic Review of Case Reports and Case Series. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2471. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9122471
Ronin E, Derancourt C, Cabié A, Marion-Sanchez K. Achromobacter spp. Surgical Site Infections: A Systematic Review of Case Reports and Case Series. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(12):2471. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9122471
Chicago/Turabian StyleRonin, Eve, Christian Derancourt, André Cabié, and Karine Marion-Sanchez. 2021. "Achromobacter spp. Surgical Site Infections: A Systematic Review of Case Reports and Case Series" Microorganisms 9, no. 12: 2471. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9122471
APA StyleRonin, E., Derancourt, C., Cabié, A., & Marion-Sanchez, K. (2021). Achromobacter spp. Surgical Site Infections: A Systematic Review of Case Reports and Case Series. Microorganisms, 9(12), 2471. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9122471






