Abstract
Fermentation processes have been used for centuries for food production and preservation. Besides the contribution of fermentation to food quality, recently, scientific interest in the beneficial nature of fermented foods as a reservoir of probiotic candidates is increasing. Fermented food microbes are gaining attention for their health-promoting potential and for being genetically related to human probiotic bacteria. Among them, Lactiplantibacillus (Lpb.) plantarum strains, with a long history in the food industry as starter cultures in the production of a wide variety of fermented foods, are being investigated for their beneficial properties which are similar to those of probiotic strains, and they are also applied in clinical interventions. Food-associated Lpb. plantarum showed a good adaptation and adhesion ability in the gastro-intestinal tract and the potential to affect host health through various beneficial activities, e.g., antimicrobial, antioxidative, antigenotoxic, anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory, in several in vitro and in vivo studies. This review provides an overview of fermented-associated Lpb. plantarum health benefits with evidence from clinical studies. Probiotic criteria that fermented-associated microbes need to fulfil are also reported.
1. Introduction
Traditional fermented foods are a rich reservoir of live and active microbes; indeed, they are considered the main source of lactic acid bacteria (LAB) in nature [1]. Besides their nutritional properties, fermented foods are garnering more attention for the microbes that they carry. These microbes are able to synthetize compounds during fermentation with high health-modulating potential, such as organic acids, short chain fatty acids, vitamins or peptides [2]. Beyond the ability to produce bioactive and nutritive compounds, food-associated microbes share other genetic and phenotypic traits similar to those present in probiotic strains of the same species [2]. Similar to probiotics, food-borne microorganisms can survive in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and exert beneficial effects on the host. Although no empirical studies have provided precise numbers, it is estimated that large quantities of live LAB (approximately 108–1011 CFU/d) are ingested through the consumption of fermented foods [3].
The consumption of fermented foods has been associated with numerous health benefits [2,4]. In recent years, there has been an increase in epidemiological and clinical reports that confirm their benefits, mainly associated with an improvement in health and a reduction in disease risk [5]. Recent investigations have pointed to a shaping of the gut microbiota when it is in contact with beneficial and safe microbes [3]. According to Marco and colleagues [3], the potential of food-borne microbes can be addressed in “the old friend hypothesis”, which suggests that “exposure to nonharmful or commensal microbes in foods may “engage” with the mucosal surfaces of the digestive tract, fine-tuning the immune system, bolstering gut function, and reinforcing the ability of the human symbiont to mitigate susceptibility to the development of chronic diseases”.
For decades, LAB have been extensively used in food fermentation due their nonharmful nature. Among LAB, one of the more versatile and promising species is Lactobacillus plantarum or, as it has recently been denominated, Lactiplantibacillus (Lpb.) plantarum subsp. plantarum [6]. Lpb. plantarum is a straight rod shaped (bacillus), Gram-positive, nonmotile, nonspore-forming, microaerophilic, mesophilic bacterium. Although is a catalase negative, some strains grown under special conditions possess true catalase and maganese-containing pseudocatalase activities [7]. The cell wall contains either ribitol- or glycerol- teichoic acid type, although some strains have an unusual teichoic acid. Peptidoglycan of the cell wall is of the meso-diaminopimelic acid (DAP) type. Included in the group of facultative heterofermentative bacilli, Lpb. plantarum strains possess cassettes of carbohydrate utilization genes that allow them to adapt to different ecological environments. Typically isolated from fermented foods, Lpb. plantarum strains can be encountered in a wide variety of niches, that includes the GI tract, stools, fermented foods, and plants, amongst others. For decades, Lpb. plantarum strains have been used in the food industry as starter cultures in the production of cheeses, olives and a wide variety of fermented foods and beverages, contributing to their organoleptic properties, flavor and texture [8]. One example food in which high concentrations of Lpb. plantarum can be found is table olives. Table olives are one of the oldest and most popular fermented foods, consumed all over the world and produced principally in the Mediterranean area (Italy, Spain and Greece); their main isolates, Lpb. pentosus and Lpb. plantarum, may be found in quantities of around 108 CFU/g [9,10]. However, the impact of the consumption of these food-dominant strains on the host, either when consumed directly or as a part of a fermented food, is still unclear. Moreover, it is not yet known whether food-associated strains go on to become members of the gut microbiome. Currently, Lpb. plantarum strains are also being investigated for their health-promoting properties [7].
As will be discussed throughout the literature review, Lactiplantibacillus plantarum strains isolated from foods sources have been shown to display properties similar to those of therapeutic probiotic strains.
2. Selection Criteria for Health-Promoting Bacteria
So far, according to the FAO/WHO, only microorganisms isolated from the human GI tract are recommended for use as probiotics in humans [11]. Probiotics are live microorganisms that, when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit on the host [12,13]. However, new evidence has highlighted the potential of food-associated microorganisms as probiotics [14]. For all strains, regardless of origin, the selection procedure follows the same criteria. Both food-related and commensal strains isolated from human GI tract have to be isolated, carefully characterized and demonstrated to provide a health benefit in order to be considered a probiotic. The FAO/WHO established a global standard for evaluating probiotics and health-promoting strains that can be summarized as follows [11,12]:
● Strain identification
According to the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), an unequivocal taxonomic identification at strain level has to be performed for all microorganisms intentionally used in the food chain [15].
● Safety properties
Many lactobacilli have a long history of safe human use, having been used as starter cultures in fermented foods. As a result, many lactobacilli have been classified as “Generally Recognized as Safe” by the FDA, and have received “Qualified Presumption of Safety” by the EFSA. This notwithstanding, every strain intentionally used for industrial application or as a probiotic must be evaluated for safety with robust methods before it can be considered for real-life applications [16]. In 2019, the EFSA published a public consultation which stated the requirements for whole genome sequence analyses of microorganisms intentionally used in the food chain. The document “encourages” data to be obtained from whole genome sequencing (WGS) in order to perform accurate risk assessments. Data from in silico analyses can provide information about gene encoding for antimicrobial resistance, i.e., those related with virulence, pathogenicity and/or toxigenicity should be evaluated.
● Functional strain characterization for probiotic attributes
Ability to tolerate acid/bile stress and adhesion to intestinal epithelial cells are the first properties to be evaluated. When consumed, bacteria must overcome several stresses encountered in the GI tract, including osmotic variations and low pH. Stresses to microorganisms which begin in the mouth, with the lysozyme contained in saliva, continue in the stomach, where the pH ranges between 1.5 and 3.0. Microorganisms can also be exposed to pepsin and lipase, and finally, in the upper intestine, to bile [17]. Thus, an important step toward the selection of potential probiotic candidates is to investigate strain behavior under conditions which mimic the GI tract, in particular, acid/bile tolerance.
The lumen of the GI tract is composed of commensal microbiota, a mucus layer and epithelial cells. The monolayer of epithelial cells separates the intestinal mucosal, produced by goblet cells, and the commensal microbiota, from the immune cells, forming the gut epithelial barrier [18]. This intestinal epithelial barrier acts as a defense against infections, and its alterations have been associated with a number of disease states [19]. When consumed regularly, ingested bacteria or probiotics form part of the “transient microbiome”, i.e., they are not stable colonizers, but this transient passage allows them to interact with commensal bacteria and epithelial cells, and ultimately, to provide health benefits [20].
● Clinical validation
All probiotic candidates need validation of their health benefits through double-blind and randomized clinical studies in humans or in the organism for which they are intended [13].
3. Genomic Insight into Food-Borne Lpb. plantarum Species
Advances in next generation sequencing in recent years have led to the completion and publication of a significant number of Lpb. plantarum genome sequences. To date (December 2020), 560 Lpb. plantarum genomes are publicly available from the NCBI repository, of which 135 are complete. According to the published data, the genome size of Lpb. plantarum strains ranges from 2.91 to 3.7 Mbp in length, making Lpb. plantarum one of the largest genomes within the lactobacilli group, with a GC content of approximately 44%. Moreover, the number of coding sequences (CDSs) ranges between 1964 for Lpb. plantarum WHE92 to 3526 for Lpb. plantarum SRCM101258.
The first Lpb. plantarum to be completely sequenced was the strain WCFS1, isolated from human saliva, in 2003 [21]. However, it was not until 2009 that the first strain isolated from fermented foods was sequenced, the type strain ATCC14917T. Since then, a number of new genomes of Lpb. plantarum isolated from different sources have been sequenced and are available from the NCBI database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome/genomes/1108, accessed on 9 Febraury 2021). These strains encompass a wide variety of niches including but not limited to dairy products, meat products, vegetables and traditional fermented foods (i.e., kimchi) amongst others.
In-depth analysis of the genomic sequence of WCFS1 has deepened our understanding of the species and has served as a reference for further in silico studies based on its prediction/annotation of genes as a first approach to predict phenotypes. Major advances in the identification of genes related to GI survival, interactions with other microorganisms and the host, the ability to resist oxidative stress and the environmental adaptability of strains are described for Lpb. plantarum isolated from fermented foods. In this regard, Lpb. plantarum sequences encoding genes for adhesion to intestinal cells and mucus, such as mannose-specific adhesion (msa) and collagen binding proteins (cnaB), are both involved in the bacterial colonization and competition against pathogenic bacteria [22]. Food-borne Lpb. plantarum strains encodes genes for a number of stress-related proteins. The presence of the osmoregulatory system OpuC, the chaperones groES-groEL and the hcrA-dnaK-dnaJ-GrpE operon, NADH oxidases and peroxidases or thiol and manganese transporters confer advantages upon the strains, allowing them to survive in the harsh conditions of the GI tract [23,24]. Moreover, the presence in the genome of Lpb. plantarum strains of prophages and the CRISPR-Cas system are also considered advantageous, since both are involved in the defense against bacteriophage infections. A genome sequence analysis of Lpb. plantarum prophages indicated that Sha1 and Phig1 occur most abundantly [22]. Regarding the presence of the CRISPR-Cas system, most Lpb. plantarum display the class 2 CRISPR-Cas system (type II) with four genes, i.e., cas9, cas1, cas2, and csn2 [25].
It has been proposed that Lpb. plantarum strains possess in their genome a lifestyle adaptation region or lifestyle island, i.e., a region specific to Lpb. plantarum strains, mainly consisting of sugar transport and utilization, as well as serving an extracellular function, the encoding of genes [23]. This region appears to be key to the successful environment-adaptability of Lpb. plantarum strains. The capacity of Lpb. plantarum strains to ferment a variety of sugars has received significant attention, as their efficient transport systems lead to their high adaptability and their ability to survive in different ecological niches. Comparative genomic studies of Lpb. plantarum strains isolated from different sources showed that most of the genes encoded in the “lifestyle adaptation region” were nonconserved among strains, and encoded predicted plantaricin and exopolysaccharide biosynthesis genes, prophages and mobile elements [23]. These findings support the high genome plasticity of Lpb. plantarum, which, together with efficient metabolism, make them one of the most nomadic and versatile species.
In the following subsections, we will discuss major findings in exopolysaccharides and plantaricin production discovered in food-associated Lpb. plantarum strains.
3.1. Production of Exopolysaccharides
Exopolysaccharides (EPS) are high molecular weight and biodegradable polymers formed by monosaccharide residues of sugar and sugar derivatives and produced by a wide range of bacteria [26]. EPS can be subdivided based on their structure into two groups: hetero and homopolysaccharides, i.e., comprised of a repeating oligosaccharide, or a repeating monosaccharide, respectively.
EPS producing strains are typically described as “ropy” or “nonropy”, which describes the threads drawn with a needle from the surface of the colonies or fermented liquid containing the EPS producing culture [27]. EPS produced by LAB are secreted polysaccharides which can remain attached to the cell envelope in the form of a capsular polysaccharide (CPS), or be released into the surrounding environment [28]. The production of EPS by LAB is a widespread phenomenon which has received substantial attention in recent years based on attributes such as their biodegradability, biocompatibility and nontoxicity. In bacteria, EPS also has a protective nature; it allows bacteria to adhere to and recognize other bacteria and surfaces, and offers protection from heavy metals, phage infection and biofilm formation [29].
Genomic studies on Lpb. plantarum have highlighted the diversity in the genetic characterization and organization of the EPS loci within the species. Unlike other species such as Lactobacillus (Lb.) johnsonii and Lb. helveticus, which encode a single cluster, Lpb. plantarum harbors multiple EPS associated clusters, with up to five independent loci in an individual strain [30]. One of the best characterized EPS-clusters in Lpb. plantarum is that of strain WCFS1 [24]. The genome of WCFS1 encodes four chromosomal clusters of EPS genes, two involved in capsular polysaccharide formation (cps2A-J and cps4A-J) and another two clusters predicted to lack genes encoding chain-length control functions and a priming glycosyl-transferase (cps1A-I and cps3A-J) [31]. EPS producing Lpb. plantarum strains have been isolated from different sources, and their molecular characteristics are usually strain-dependent [31,32]. The strain Lpb. plantarum LP90, isolated from wine, possess cps3 and cps4 and a strain dependent cps2, while ST-III and ZJ316 encode the clusters cps3 and cps4 [33,34], and JDM1, P8 and 16 only encode the cps4 cluster [34]. Variability amongst EPS clusters in Lpb. plantarum strains is observed within clusters cps1A-I to cps3A-J. The gene cluster cps4A-J is the most conserved amongst the species [31]. Among the essential genes found within cluster cps4A-J are tyrosine kinases, phosphotyrosine phosphatase, a priming glycosyltransferase, glycosyltransferases, a flipase and a polysaccharide polymerase [30].
It has previously been shown that, in species with multiple EPS clusters like Lpb. plantarum, each cluster has a different function and a different biological impact. The study conducted by Remus and colleagues evaluated the four CPS gene clusters encoded by Lpb. plantarum WCFS1 and their impact in host-microbe interactions [31]. While deletions in cps1A-I did not affect to the production of polysaccharides, mutations in the other three clusters were shown to considerably reduce the levels of surface polysaccharides. However, only mutations in the cps1A-I cluster affected the molar mass and the composition of the EPS. Moreover, mutations in these clusters also impact on the toll-like receptor (TLR) recognition, and thus, on the activation of the Nuclear Factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-kB). When compared with the wild-type, individual mutations in the clusters appeared to slightly modify the TLR2-signaling response, while the deletion of all clusters elicited a drastically increased NF-kB activation [31].
The production of EPS has had a significant impact on the pharmacological and food industries due its physicochemical properties. It has been shown that EPS produced by some LAB improves food texture, affecting the rheological properties, such as mouthfeel and matrix formation, along with the finished quality of fermented foods [35]. Moreover, beneficial effects such as anticarcinogenicity, antithrombotic, antioxidant and immunomodulating activities have also been attributed to EPS [36]. EPS isolated from the food-associated strains C70, Y0175 and OF101, isolated from Chinese Paocai, and a traditional fermented cereal beverage, respectively, showed antioxidant properties [37,38]. In addition, EPS isolated from camel milk, KX041 showed both immune activity and DPPH/ABTS radical scavenging activities [39]. Antitumor and antibacterial properties have been also observed from the EPS isolated from Lpb. plantarum strains MTCC9510 and 86, respectively [40,41]. For these reasons, the scale-up of EPS production has been studied, as well as their applicability in food and pharmaceutical industries [35,36].
3.2. Production of Bacteriocins
Bacteriocins are, by definition, ribosomally synthesized peptides used by bacteria as a defense mechanism against other bacteria. Most of the bacteriocins produced by LAB are small, cationic, heat-stable, amphiphilic and membrane-permeabilizing peptides [42]. Bacteriocins produced by Lpb. plantarum are known as plantaricins. In recent years, bacteriocins produced by LAB have gained interest in industry due to their potential role as biopreservatives [43]. Since they can be degraded by proteolytic enzymes, bacteriocins are presented as a natural, safe and effective strategy to combat foodborne pathogens and spoilage bacteria in comparison with current chemical preservatives or the use of antibiotics [44]. However, the use of bacteriocins has some limitations, such as the efficacy of pathogen elimination and their elevated cost.
Characterization and complete understanding of the bacteriocin loci is important, since it has been proven that variations in gene sequences, composition and organization may affect the antimicrobial activity of bacteriocins [45]. There are six main features of plantaricins producing by Lpb. plantarum strains [46]. All plantaricins are produced as precursors with a double glycine moiety by the genes plnE and plnF, and further exported by the PlnG and PlnH proteins [47]. Bacteriocins are divided into four categories, based on structure, molecular weight, heat persistence and molecular organization [48]. The majority of the plantaricins produced by Lpb. plantarum are usually included in both class I and II. Class I includes bacteriocins which are post-translationally modified, containing a lanthionine, and are commonly named lantibiotics. In this group, plantaricins C and W are found [49,50]. In general, bacteriocins belonging to class II are heat-stable, unmodified and nonlanthionine-containing. Class II is a heterogeneous group of bacteriocins subdivided into class IIa, pediocin PA-1 like bacteriocins; IIb, two-peptide bacteriocins; IIc, circular peptide bacteriocins; and IId, linear and single-peptide bacteriocins without a pediocin-domain. Plantaricins JK, EF S and NC8 belong to class IIb, while plantaricin STSH8, C19 and 423 belong to class IIa [16,51,52,53]. Production of plantaricins JK and EF is induced by plantaricin A, belonging to class IIc [54]. Finally, class III consists of large heat labile bacteriocins poorly represented in LAB. Lpb. plantarum strains, producing one or more types of plantaricins, have been isolated from different fermented foods [16] (Table 1). Generally, Lpb. plantarum species are considered a source of a variety of strong plantaricin producers.

Table 1.
Most characterized plantaricins produced by Lpb. plantarum strains isolated from various fermented foods.
4. Health Benefits of Food-Associated Lpb. plantarum Strains
In the following subsections, we will describe some of the most characterized health-beneficial activities of Lpb. plantarum strains isolated from fermented foods. In general, the mechanisms by which probiotic bacteria mediate their health benefits are: (1) modulation of commensal microbiota; (2) exclusion or inhibition of pathogens; (3) enhancement of the intestinal epithelial barrier by increasing mucin production and tight junctions formation; (4) modulation of the immune system; and (5) production of bioactive molecules. Figure 1 presents a simplified graphic of the main mechanisms of action of Lpb. plantarum strains which will be further described in this review.
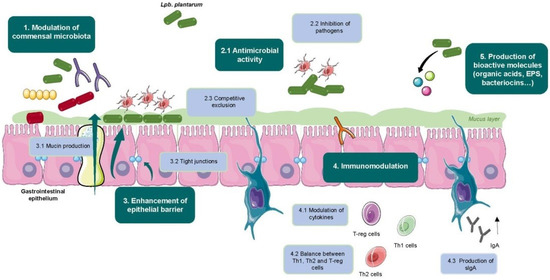
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of action of Lpb. plantarum health benefits. Graphical illustrations were created using items from Servier Medical Art by Servier, available at https://smart.servier.com/ under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License.
4.1. Antimicrobial Activity
Among the beneficial effects of Lpb. plantarum, one of the most studied and desirable among probiotic properties is their antimicrobial potential. It has been shown that Lpb. plantarum species are endowed with a wide spectrum of antibacterial activity against many food spoilage microbes (such as bacteria, yeasts and molds) and various enteropathogenic bacteria [86]. Therefore, several Lpb. plantarum strains have been considered as promising probiotic candidates to be applied in the food industry and human medicine as bio-preservatives and bio-therapeutics alternatives, respectively. Recent studies showed the ability of food-associated Lpb. plantarum strains to inhibit both Gram-positive and -negative bacteria, such as Listeria monocytogenes, Staphylococcus aureus, Enterococcus, Bacillus, Clostridium, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Helicobacter pylori, Yersinia enterocolitica, Campylobacter jejuni, Klebsiella, Salmonella, Shigella and Escherichia coli (including E. coli 0157:H7) among others (Table 1). Good antifungal activity has also been shown against various yeast and mold species, including Aspergillus, Candida spp. and Fusarium [87]. Several studies have examined the antagonist effects of Lpb. plantarum strains isolated from different fermented foods against food spoilage and/or pathogenic microorganisms [88,89,90,91]. The antimicrobial activity is mainly exerted by the production of antimicrobial compounds, such as organic acids, hydrogen peroxide, EPS and bacteriocins production; this, as well as many others beneficial properties, should be considered strain specific, and thus, need to be characterized on a strain level.
Regarding the inhibition of food spoilage and food pathogen bacteria, Lpb. plantarum species have been applied as starter cultures in the fermentation processes of many fermented foods (sauerkraut, table olives, dairy products, fermented sausages, etc.). Such fermentation process improve both food quality and safety, and prolong the shelf-life of final products by inhibiting food spoilage microbes, mainly through organic acid production and competition for nutrients [92]. As olives ferment, the lactic acid production by Lpb. plantarum lowers the pH, inhibiting the growth of spoilage microbes which are sensitive to acidic conditions, significantly improving microbiological stability and food safety [10]. Strong inhibitory activity has been reported of lactic acid at low pH against Gram-negative bacteria (i.e., Escherichia coli and Salmonella Enteritidis), spore-forming bacteria and diverse yeasts and molds [93]. The antifungal activity of Lpb. plantarum is mainly due to the production of organic acids [94], 3-hydroxylated fatty acids (i.e., 5-oxododecanoic acid, 3-hydroxy decanoic acid and 3-hydroxy-5-dodecenoic acid [95]) and cyclic dipeptides as cyclo (Gly-Leu), cyclo (Phe-Pro), cyclo(Phe-OH-Pro), cyclo (Leu-Pro) [96].
Besides the above-mentioned antimicrobial compounds, Lpb. plantarum strains are also producers of EPS and bacteriocins, leading to remarkable inhibition of the activity of pathogens [87]. Currently, bacteriocins are presented as natural, safe and effective strategies to outcompete food-borne pathogens and spoilage bacteria in comparison with current chemical preservatives or the use of antibiotics [44]. The spectrum of action of plantaricins is extremely diverse. Normally, most plantaricins are active against either Gram-positive or -negative bacteria, although there are some cases in which plantaricins are active against both (such as plantaricin ZJ5 or LP84) [16] (see Table 1). The potential of some plantaricins, such as plantaricin C11 and NA, is remarkable; these inhibit Listeria monocytogenes, an invasive foodborne pathogen [53]. Table 1 reports the most characterized plantaricins produced by Lpb. plantarum strains isolated from various fermented foods. Regarding EPS production, the bioactivity of these compounds produced by Lpb. plantarum against pathogens, such as antiadhesion and antibiofilm properties, has been described in some studies [29,36]. Pathogen persistence and biofilm production, due to the resistance of some pathogens to antibiotics, can lead to chronic infections and present serious challenges in the food industry [97]. The antimicrobial activity of Lpb. plantarum has gained interest in the food industry due to their potential role as biopreservative agents [43].
On the other hand, Lpb. plantarum have been shown to be able to inhibit a wide spectrum of host-pathogenic bacteria, including the most harmful bacteria, Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli; as such, they are considered a promising antibiotic alternative [98]. Zhang and coworkers reported significant pathogen inhibition by Lpb. plantarum ZDY 2013, a strain isolated from fermented bean. Lpb. plantarum ZDY 2013 was shown to outcompete and inhibit strains of Bacillus cereus, well-known enterotoxic and pathogen species, as well as to be effective as a pretreatment for the prevention of Helyicobacter pylori infection and related gastric mucosal inflammation [99].
Lpb. plantarum species have been also investigated for potential antimicrobial properties toward human skin pathogens, e.g., Pseudomonas aeruginosa and the methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus species, in order to potentially use some strains as bio-control agents for wound infections [100]. Probiotic lactobacilli have been widely investigated as possible therapeutic alternatives for the prevention of recurrences of vulvovaginal candidiasis, a common infection by Candida albicans among women [101]. Additionally, some studies have reported strong in vitro and in vivo antifungal activity against Candida albicans by Lpb. plantarum strains [102,103]. Interestingly, Beck and coworkers recently investigated three Lpb. plantarum strains isolated from Kimchi, a Korean traditional fermented food, for their antimicrobial activities against Candida albicans and Gardnerella vaginalis, suggesting their potential as probiotic candidates for the treatment of mucosal infections [103].
Based on all the evidence confirming the potent antimicrobial activity of Lpb. plantarum against a wide variety of food-spoilage and pathogenic microbes, as well as their well-established application as starter cultures, food-associated Lpb. plantarum strains are promising as bio-preservative agents in the food industry and/or as probiotics for alternative biotherapies in medicine.
4.2. Antigenotoxic and Antimutagenic Activity
Daily exposure to a huge variety of environmental and food-related mutagens, mainly linked to Western diets and modern lifestyle, has led to increased scientific interest in dietary interventions to modulate the risk of genotoxicity and related GI disease. In the gut, a variety of genotoxic compounds (mainly delivered by foods) can often be found. They can be broadly defined as primary food mutagens (i.e., mycotoxins, vegetable glycosides), secondary food mutagens (i.e., originating from cooking processes such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and heterocyclic amines) and endogenous compounds (i.e., nitrosamines) [104]. It has been shown in preclinical and clinical studies that they are involved in the development of different tumors, such as colorectal, prostate and breast cancers [105,106] In addition, we are constantly exposed to a wide variety of environmental and exogenous compounds, commonly used in cosmetics, food packaging and/or in thousands of everyday products, such as heavy metals, phenolic derivates (i.e., BPA), phthalates, nitrosamines, Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDEs), Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) and many others, also called endocrine disruptors (EDs). Recently, exposure to EDs has been linked to metabolic disorders, such as diabetes, obesity [107] and many other adverse outcomes, including carcinogenic effects through DNA damage in different organs (i.e., liver, pancreas and intestine) [108].
However, some microbial communities that inhabit the gut have antigenotoxic properties that can cause significant reduction in the biological activity of these chemical compounds [109]. These protective activities have also been reported for some fermented foods, such as fermented soy milk [110]. Epidemiological and clinical-experimental evidence also confirmed the intimate diet-health relationship, in which the commensal bacteria play a key role in the modulation of genotoxic and mutagenic risk at the intestinal level [111,112].
From this perspective, several studies have noted that food-associated microbes that are widely ingested may be related to reduced colon cancer incidence from environmental risk factors, such as dietary and exogenous xenobiotics [106]. Recently, Garcia-Gonzalez and coworkers extensively reviewed both in vitro and in vivo studies, providing supportive evidence that food-associated and/or probiotics LAB have the ability to play a protective role at the GI level by inhibiting the biological activity of genotoxic compounds, and thus preventing DNA damage, an early event in the carcinogenesis [108]. It has been suggested that food-associated LAB can reduce the genotoxicity of such chemical molecules by either binding or bio-converting them to unreactive compounds [113], although the exact mechanism for this is not yet fully understood. Among LAB, Lpb. plantarum strains isolated form Italian dairy products have been reported to be effective against the nitroarene, 4-nitroquinoline-1-oxide (4-NQO) and the alkylating agent, N-methyl-N’-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine (MNNG), two potent model genotoxins [104,109]. Moreover, Walia and coworkers, investigating the DNA-bioprotective activity of microbes associated with fermented foods of the North-Western Himalayas, reported a high genotoxicity inhibition against 4-NQO and furazolidone (>90%) of some Lpb. plantarum strains, statistically similar to that expressed by the well-known probiotic strain, Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus strain LGG (88.9%). Prete and coworkers, carried out a screening within Lpb. plantarum species, assessing the antigenotoxicity of 18 Lpb. plantarum strains isolated from different fermented foods (table olives, sourdough and raw-milk cheeses) against 4-NQO. Their study confirmed the considerable potential of Lpb. plantarum species to inhibit the genotoxic effect of carcinogenic compounds, albeit with evident strain-specificity [114]. The food-associated Lpb. plantarum DNA-bioprotective effect has been also established on human colon adenocarcinoma (Caco-2) cells against Aflatoxin B1, one of the most well-known mycotoxins with hepato-carcinogenic effects [115].Recently, Lpb. plantarum LUHS135 and Lacticaseibacillus paracasei LUHS244 from fermented cereals were investigated as candidates for the reduction of some mycotoxins (i.e., aflatoxin B1, ochratoxin A, HT-2 toxin, T-2 toxin [116].
Beside their bioprotective role against food-related mutagens, Lpb. plantarum strains have been also investigated for their ability to counteract environmental mutagens, showing a bio- protective effect in the case of waterborne cadmium [117] and triclosan exposure [118]. The ability of food microbes and/or probiotics to detoxify and degrade environmental chemical compounds is now emerging as a new bioremediation tool. Recent studies reported potential in vitro ability of dairy LAB to bind BPA [119] and pesticides [120]. A recent study explored the antigenotoxic activity of two Lpb. plantarum probiotic strains, IMC510 and IMC513, previously characterized for other functional activities [114,121,122] against two different EDs [108], confirming the role of Lpb. plantarum in inhibiting genotoxicity and DNA damage. Considering the increasing need for bio-protection and bio-remediation from carcinogenic and mutagenic compounds, the ability of microbes to protect from DNA-damage is emerging as an innovative functional property, representing the basis for new, bio-protective diet interventions to reduce chronic gut pathologies, that deserve to be investigated with further in vivo studies.
4.3. Bile Salt Hydrolase Activity
Bile is one of the environmental challenges that microorganisms must endure in order to survive in the gastrointestinal environment. Typically, a liter of bile is secreted by the liver into the intestinal tract every day, which represents a serious challenge for ingested strains [123]. Bile is a digestive secretion that is required for the emulsification and intestinal absorption of dietary fats, lipids and lipophilic vitamins. Bile acids (BAs), cholesterol, phospholipids and conjugated bilirubin are among the major constituents of bile. BAs are hydroxylated steroids synthesized in the liver from cholesterol, stored in the gall bladder, and released in the small intestine following food consumption. They play a major role in the emulsification and solubilization of lipids, facilitating their absorption and digestion, and in the elimination of cholesterol [123]. Bile acids are surface active, amphipathic molecules, and their ability to act as detergents also allows them to interact with bacterial membrane lipids, causing cell membrane disruption as well as triggering DNA damage, thereby conferring potent antimicrobial properties on bile [124]. Prior to secretion in bile, primary BAs are conjugated at their side chains with either taurine (tauro-conjugated) or glycine (glyco-conjugated). After being released into the duodenum, conjugated bile acids are subject to chemical modifications by the gut microbiota through bacterial bile salt hydrolase (BSH) enzymes [123]. Once they are in their deconjugated form, after removal of glycine or taurine, bile salts can be excreted with the feces due to their lower water solubility [125]. In this respect, the ability to hydrolyze bile salts, also known as BSH activity, has been included among the criteria for probiotic strain selection [126]. In terms of bacterial survival in the gut environment, it is generally considered necessary to evaluate the ability of potentially probiotic bacteria to endure bile acid-related stress [126]. The production of BSH enzymes provides bacteria with a mechanism with which to survive in the gastrointestinal tract, as conjugated bile acids are known to be toxic to bacteria, contributing to both microbial bile resistance and colonization of the GI environment. The ability to metabolize bile acids, which is a conserved microbial adaptation, is considered a common feature of gut microorganisms and is distributed across the major phyla of bacteria in the gut, as well as the gut Archaea [127]. BSH deconjugation activity has been primarily characterized among GI commensal species such as Bifidobacterium [128], Clostridium [129], Enterococcus [130], Listeria [131], Lactobacillus [132,133], including Lpb. plantarum species [134]. Lpb. plantarum WCFS1 was the first Lpb. plantarum strain in which bsh genes were described [135]. Functional analyses performed on other Lpb. plantarum strains revealed a family of four bile salt hydrolase proteins [125], among which BSH1 seems to be the main one responsible for the ability of Lpb. plantarum to metabolize BAs. Recently, Prete and colleagues reported early evidence of BSH activity in food-associated Lpb. plantarum strains, even though they were not gut-associated strains [136]. Moreover, variations in BAs deconjugation were found among the strains, which confirmed the strain-dependent nature of this property, that cannot be generalized within a species or a genus, as previously reported by several investigators [123].
Currently, microbial bile tolerance is increasingly gaining attention due to its potential impact on physiological processes; thus, BSH activity could be a desirable feature in strain selection. In this respect, microbial BSH activity was recently identified as a form of gut microbial activity that mediates a microbe-host dialogue that functionally regulates host lipid metabolism and plays a crucial role in cholesterol metabolism. Bile acids act as biological signaling molecules, whose interactions with some host receptors such as the nuclear bile acid receptor (also known as farnesoid X receptor, FXR) or the bile acid-activated membrane G protein-coupled receptors, TGR5 (aka Gpbar-1, G-protein-coupled bile acid receptor) appear to play a role in stimulating energy metabolism, protecting liver and intestine from inflammation and steatosis, and improving insulin sensitivity, as well as playing a significant role in weight loss [137,138]. In particular, FXR is involved in regulating BA synthesis and enterohepatic circulation in the liver and intestine, in which FXR activation leads to lower BA and cholesterol levels by reducing BAs synthesis through the inhibition of hepatic cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) and sterol 12α-hydroxylase (CYP8B1), and by enhancing cholesterol excretion through the activation of bile-salt transporter such as bile-salt export pump (BSEP), thereby playing a regulatory role linked to anti-inflammatory and metabolic benefits [139]. It has been shown that the administration of probiotic bacteria can be a preventive strategy to modulate cholesterol serum levels and related cardiovascular diseases. Several in vivo studies have confirmed that the reduction of cholesterol and triglyceride levels in animal models is mainly associated with the presence of microbial BSH ability [138,140,141]; this has also been confirmed by clinical trials which sought to evaluate the impact of BSH-active probiotic on cholesterol metabolism [142]. Among their biological roles, BAs act as signaling molecules in glucose homeostasis and energy expenditure via activation of TGR5 receptor that stimulate the browning of white adipose tissue, postprandial thermogenesis improving whole-body glucose and lipid metabolism [137,143]. It has also been reported that the activation of TGR5 is involved in innate immune responses [143]. A bile acid-adaptive immunity axis has been demonstrated, in which activation of the vitamin D receptor (VDR) by the secondary bile acid, lithocholic acid (LCA), directly mitigates the Th cell inflammation, thereby modulating the adaptive immune response, which is fundamental in all inflammatory conditions [143]. Besides immunity, the VDR receptor is involved in the regulation of many others biological functions such as cellular proliferation and differentiation, calcium homeostasis and xenobiotic detoxification [139]. Recently, it has been shown that unconjugated BAs can influence the regulation of host circadian gene expression, acting as microbial-derived regulators of circadian rhythm, whose alteration is known to be associated with obesity and metabolic dysfunctions [144]. Overall, the multiple biological roles of BA molecules reflect the intimate host–microbe crosstalk. Considering that fermented foods are rich in microbes that, once ingested, can actively contribute to host metabolism and homeostasis, microbial ability to modulate the profiles of BAs shows great promise in terms of food strategies to improve human health.
4.4. Antioxidant Properties
Nowadays, there is much interest in the effects of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and related oxidative stress that cause many alterations and inflammatory conditions in the gut. Diet, carrying both food and microbial components, is primarily responsible for the production of pro-oxidant and ROS precursor molecules in the gut environment. Recently, dietary interventions using bioactive antioxidants such as food extract or probiotic strains have been investigated as an innovative natural approach to treat oxidative stress disorders and related chronic and inflammatory diseases [145]. ROS such as hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), hydroxyl radical (•OH), and superoxide anion (•O2¯) are produced during cellular metabolism and are key factors in important processes such as cell signaling, ion transportation and gene expression [146]. However, ROS accumulation could lead to the oxidative injury of biomolecules including lipids and proteins. This oxidation damage is known to cause multiple associated diseases, so balance and maintenance of redox homeostasis are essential for maintaining correct cell functions. In particular, food-associated Lpb. plantarum strains have been widely investigated due to their antioxidant properties against ROS and free radicals. The mechanisms underlying the antioxidant activities of food-borne Lpb. plantarum, and other probiotic strains appear to be multifactorial. The production of antioxidant metabolites (such as folate, butyrate or glutathione), upregulation of antioxidant host genes (such as superoxide dismutase or catalase), downregulation of genes related with ROS production, or modulating intestinal microbiota are some of the existing mechanisms known in several probiotic strains. The antioxidant properties of Lpb. plantarum strains can be evaluated directly, against molecules and radicals, or quantified as oxidative stress in a cell model, like the dichlorofluorescein (DCF) assay [147].
Chemical assays to test the antioxidant activity of strains include 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical scavenging, hydroxyl radical scavenging (HRS) method and reducing power, among others. It is always recommended that antioxidant activity be evaluated using more than one method, and that the results be confirmed with an in vitro assay. Although correlation between chemical assays, in vitro approaches and confirmation of the in vivo activity cannot always be shown, it is better to perform this first screening to verify the antioxidant activity of particular strains. Xing and collaborators showed, by assessing that the antioxidant activity of a collection of lactobacilli strains, that Lpb. plantarum CCFM8661 displayed weak antioxidant activity in chemical assays, but proved its efficacy in inhibiting the radical-mediated damage on HepG2 cells [148]. Moreover, a study carried out with a collection of Lpb. plantarum and Lpb. paraplantarum strains isolated from fermented foods (khalpi, gundruk, sinki and bamboo) showed antioxidant activity by DPPH assay [149]. Lpb. plantarum K46 was able to tolerate hydrogen peroxide and exhibited good free radical scavenging activity [150]. The same properties were found for the strain DM5, which also showed strong antioxidant ability against hydroxyl radicals, DPPH activity, hydrogen peroxide resistance and inhibition of ascorbate [151]. Not only did the cells show antioxidant properties, but so too did heat-kill bacteria and cell-free extracts. Cell-free extracts of three Lpb. plantarum strains (C88, C10 and K25) isolated from traditional Chinese fermented foods showed strong hydroxyl radical scavenging activity [146], and both the supernatant and cell homogenate of Lpb. plantarum MA2, isolated from Tibetan kefir, exhibited glutathione peroxidase activity and superoxide dismutase activity [152]. Even though Lpb. plantarum does not have as complex a regulation system to defend against oxidation as eukaryotic cells, the presence of some enzymes such as nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH)-oxidase, superoxide dismutase, NADH peroxide and nonheme catalases is crucial when oxidative stress occurs [153]. Other studies have identified the EPS produced by LAB as being responsible for the antioxidant capacities of Lpb. plantarum strains [154].
Understanding the molecular mechanism behind the antioxidative properties of Lpb. plantarum and how microbe–host interactions can ameliorate oxidative inflammation is still an open challenge for researchers. Besides the direct neutralization of ROS, it has been shown that microbial cells can modulate or even block inflammatory pathways via modulation of ROS levels [155]. Recently, some Lpb. plantarum probiotic candidates, isolated from different fermented foods, were investigated for their antioxidant potential with a combined approach of in vitro chemical and cell-based assays [122]. Prete and coworkers found a potential dualistic effect of Lpb. plantarum in an intestinal cell model upon oxidative stress. In particular, their results suggested a preventive or protective effect of food-associated Lpb. plantarum strains based on the physiological status of the intestinal mucosa, i.e., either healthy or inflamed, suggesting an intimate and complex microbe–host interaction that goes beyond direct ROS neutralization [122]. Recent studies have noted that both commensal and probiotic microbes are directly associated with intestinal signaling via ROS modulation, and can influence different transduction pathways involved in restoring epithelial barrier function and gut inflammation [156,157], thereby providing evidence for the therapeutic use of food-associated Lpb. plantarum to ameliorate GI disorders related to oxidative and inflammatory stress.
4.5. Immune Modulation
One of the most attractive properties of commensal bacteria and probiotics is their contribution to host homeostasis by modulating the immune system. This modulation is driven by the production of immunoregulatory compounds and/or by direct stimulation of immune and epithelial cells [158]. Although the colonization of probiotics in the GI tract is transient, during their passage, bacteria are able to interact with both commensal microbes and epithelial cells. This brief contact allows probiotics and/or ingested bacteria to modulate the activity of epithelial cells, which, in turn, may activate immune cells, such as dendritic cells and macrophages [159]. Diverse effects have been associated with probiotics: increased secretory immunoglobulin A (sIgA) production, regulation of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines production, and modulation of the balance between T-helper (Th1, Th2) and regulatory T-cells (T-regs) [160].
Host intestinal and immune cells recognize commensal and foodborne bacteria through pattern recognition receptors (PRRs). In particular, the main receptors involved in the host–microbe crosstalk are TLRs and leucine-rich repeat containing receptors (NLRs). TLRs and NLRs recognizing microbial components are responsible for initiating the immune response [161]. TLRs are transmembrane receptors which can either be expressed on the cell surface or on intracellular organelles of immune and nonimmune mammalian cells, such as dendritic cells, natural killer cells, epithelial and endothelial cells, amongst others [162]. TLRs can recognize different components of the bacterial cell wall such as lipoteichoic acid (LTA) and lipopolysaccharides (LPS). In contrast, NOD1 and NOD2 (within the NLR family) act as cytoplasmic microbial sensors of intracellular bacteria, recognizing peptidoglycan [163].
Commensal and probiotic bacteria share the ability to interact with intestinal and immune cells, inducing the production of selected cytokines; food-borne Lpb. plantarum strains have been shown to possess the same ability. Lpb. plantarum strain 06CC2 isolated from Mongolian dairy products can increase the release of interleukin (IL)-12 in coculture with murine macrophages J7741.A. Moreover, the oral administration of the bacteria was shown to induce Th1 cytokine production, activating the immune response in normal mice [164]. In addition, pretreatment with some Lpb. plantarum strains isolated from different sources showed the ability to reduce IL-8 concentrations in inflamed colonic cells (NCM460) [121], as well as to modulate the IL-23/IL-17 axis [122]. Lpb. plantarum LC27, isolated from kimchi, was able to offset the ethanol-induced effects in macrophages, KATO III cells and mice by inhibiting the activation of NF-kB and the consequent release of IL-8 [165]. Vitali and colleagues determined the probiotic potential of several autochthonous lactic acid bacteria, in which Lpb. plantarum strains were encountered [166]. An immunomodulation assay showed that food-associated Lpb. plantarum strains were able to induce the release of cytokines in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PMBC). In particular, Lpb. plantarum POM42 was able to stimulate the largest number of cytokines with anti-inflammatory activity (IL-4, IL-1ra, IL-10 and IL-13) [166]. Preincubation of HT-29 cells with Lpb. plantarum strains FRP16, isolated from dairy products, was able to inhibit the production of IL-8 induced by Salmonella Typhimurium DT104 [167]. The capacity of Lpb. plantarum strains to modulate cytokine release was also observed when bacteria were heat-killed. Heat-killed Lpb. plantarum 137 isolated from a typical component of the Filipino diet induced the production of IL-12 and Interferon- γ (IFN-γ) by spleen cells in vitro [168].
In mice, treatment with Lpb. plantarum JLK0142, isolated from fermented dairy tofu was shown to increase the intestinal sIgA and the serum levels of IL-12 and Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α cytokines [169]. The same trend was observed in six-week-old BALB/c mice fed with Lpb. plantarum strains isolated from cheeses [170]. Consumption of Lpb. plantarum strains increased the phagocytic activity of peritoneal macrophages and the number of IgA-producing cells. In addition, a protective immune response was related with the consumption of Lpb. plantarum YU, isolated from traditional Japanese fermented foods [171]. As reported for other food-borne Lpb. plantarum strains, consumption of Lpb. plantarum YU increased IL-12 release and IgA activity, leading to enhancement of the Th1 immune response. Probiotic consumption has been linked with an increase of sIgA, one of the components of the humoral adaptative immune response. Production of IgA and further translocation to the intestinal lamina propria enhance the epithelial barrier by immune exclusion of pathogens [160]. Contact between bacteria and epithelial cells seems to be mediated by PRRs, in particular, by TLRs. As mentioned, TLRs are transmembrane receptors that respond to microbial surface-associated MAMPs. Once TLRs recognize bacteria, they are able to transduce this signal by recruitment of myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (Myd88), which, in turn, induces the Myd88-dependent signaling pathway for NF-kB and Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) activation [158]. The critical role of TLRs in the induction of immune responses has been proven. The Lpb. plantarum strain isolated from kimchi, CLP-0611, was shown to be capable of inhibiting IL-1β and IL-6 expression, as well as NF-KB and Activator protein-1 (AP1) activation in LPS-macrophages, and of inhibiting NF-kB activation in 2,4,6-trinitrobenzne sulfonic acid (TNBS)-induced colitis mice. Both results may suggest that the effects of Lpb. plantarum in modulating immune response is mediated by the regulation of the canonical TLR/NF-kB signaling pathway [172]. A study carried out by Ren and colleagues [173] showed that the stimulation of THP-1 by a collection of several food-associated Lpb. plantarum strains was TLR-dependent.
The effects on the immune system associated with food-borne Lpb. plantarum strains are diverse. Different biological responses after TLR-activation may be due to small differences in the composition and structural organization of the cell wall of the bacteria, along with EPS production [174]. What seems clear is that the immunoregulatory effects on gut homeostasis from probiotics or ingested bacteria are not the result of a single activation of a PRR, but rather, of a synergistic combination of TLR and NLR activation. Upregulation of TLRs by probiotics or commensal bacteria could be considered as a defense mechanism, because it has the potential to keep the immune system on alert. Increment of sIgA production, regulation of cytokine production and modulation of the balance between Th1, Th2 and regulatory T-cells seem to be the key factors in the mechanism of action of probiotics.
5. Clinical Studies
The health benefits of probiotics have to be demonstrated in at least one successful human trial supporting the health claim for which probiotic strains would be dispensed [13]. Following these criteria, a substantial body of evidence confirmed the successful use of diverse human probiotic Lpb. plantarum strains as a dietary intervention to prevent and/or ameliorate some widespread diseases, especially acute and chronic GI infections (i.e., C. difficile and H. pylori infections) [99,175], gut inflammatory syndrome (i.e., Irritable Bowel Disease (IBD) and Ulcerative Colitis) [176,177] cardiovascular diseases [178], hypercholesterolaemia and obesity [179,180], diabetes [181], gynaecological diseases [182] as well as colon cancer [183] and cognitive impairments [184].
Recently, Lpb. plantarum strains, isolated from a variety of fermented foods, have been applied in clinical studies as dietary interventions in both healthy and diseased subjects (Table 2). It is worth noting that the majority of Lpb. plantarum strains were isolated from ethnic traditional fermented foods, (such as kimchi, Taiwan mustard greens, Mongolian sour milk and dadih, an Indonesian traditional, spontaneously fermented buffalo milk), confirming the fundamental role of fermented foods in health promotion; the consumption of such foods in Western societies is, nowadays, is nearly lost.

Table 2.
Clinical studies of food-associated Lpb. plantarum strains showing efficacy for treatment of several disorders.
In particular, food-associated probiotic strains have been administrated either alone, as capsules or powder (i.e., Lpb. plantarum PS128, P8, DR7) or through probiotic formulations in combination with other probiotic strains belonging to different species (i.e., Latilactobacillus (Lat.) curvatus HY7601 and Lpb. plantarum KY1032, Lpb. plantarum UBLP-40 in UB0316 multispecies formulation), as well as within fermented food diets to synergistically enhance the beneficial effects (i.e., Lpb. plantarum C29 in fermented soybean powder, Lpb. plantarum YIT 0132 in fermented citrus juice). Various Lpb. plantarum strains have been successfully administrated in overweight subjects with hypertriglyceridaemia and body adiposity to investigate their triglyceride-lowering effects. Interestingly, a 12-week administration of two strains, Lat. curvatus HY7601 and Lpb. plantarum KY1032 (isolated from Korean traditional fermented cabbage), showed significant triglyceride-lowering effects through reductions in plasma metabolites, fatty acid primary amides and lysophosphatidyl choline (lysoPC) [185], and a subsequent increase in apolipoprotein A-V and LDL cholesterol [186] in overweight but nondiabetics adults (n = 92 and n = 128 respectively). In addition, evidence has been presented of body weight loss and reduction in adiposity after administration of Lat. curvatus HY7601 and Lpb. plantarum KY1032 in two human trials involving overweight nondiabetic adult patients with hypertriglyceridaemia [187,188]. Costabile and coworkers found a similar beneficial outcome of food-associated Lpb. plantarum ECGC 13110402, a strain selected for its notable BSH activity, in lowering cholesterol levels in a clinical study enrolling normal to mildly hypercholesterolaemic participants [189]. In line with the potential probiotic impact on metabolic syndrome, multistrain probiotic formulation UB0316, containing Lpb. plantarum UBLP-40, was recently applied as therapeutic intervention in patients affected by type-2 diabetes mellitus [190] and in a weight management clinical study [191].
Anti-inflammatory and positive modulation of the immune system are the main health claims regarding probiotic properties. Lpb. plantarum IS-10506, from danhi, was successfully administered as a dietary early intervention to stimulate humoral and intestinal immune response in healthy preschool children [192,193], as well as to treat children affected by atopic dermatitis, a chronic recurrent inflammatory skin disease characterized by an immunity dysregulation [194]. The capacity to ameliorate quality of life in patients affected by atopic dermatitis via inflammation reduction and the immunomodulatory effects (i.e., IgE attenuation, reduction in eosinophil count) of Lpb. plantarum CJLP133 and Lpb. plantarum YIT 0132, isolated from kimchi and other fermented foods has been also shown [195,196]. Lpb. plantarum YIT 0132, administrated in fruit juice, has also been applied in the treatment of allergic syndromes which are widespread in Japan, such as perennial allergic rhinitis and Japanese Cedar Pollinosis, both of which are characterized by acute and sometimes severe inflammation status [196,198].
Amelioration of oxidative stress and inflammation by different food-associated Lpb. plantarum strains, (Lpb. plantarum P8 and PS128) has been observed in an emerging research field aiming to investigate the role of probiotics in exercise physiology and endurance performance [199,200,201,203,204]. Huang and coworkers reported a clear alleviation of exercise-induced inflammation with enhanced exercise performance in triathletes, suggesting a potential ergogenic role of Lpb. plantarum PS128 in high intensity training lifestyles [200].
Finally, with emergent health claims based on the gut–brain axis, Lpb. plantarum strains from food origin have proven to be promising probiotic candidates with beneficial effects on brain health. The dairy isolate, Lpb. plantarum DR7, has been shown to be efficient in mental stress conditions by reducing anxiety and stress, improving cognitive functions via stimulation of dopamine and serotonin pathways [208,209]. Improvements of cognitive function with increased serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor were also observed after 12-week administration of Lpb. plantarum C29 (kimchi isolate) in combination with fermented soybean in a clinical study enrolling 100 adults with mild cognitive impairments [211]. Interestingly, a beneficial effect of Lpb. plantarum PS128 as a dietary intervention in children with autism spectrum disorder was recently reported [202].
Diverse food-associated Lpb. plantarum strains have proven to be a naturally safe and efficient strategy for disease prevention in healthy subjects, as well as suitable interventions for various pathological conditions, as already demonstrated by human strains of the same species, such as the well-documented Lpb. plantarum 299v and Lpb. plantarum TENSIA. For a number of these strains from food origin, beneficial effects have been documented with in vitro and in vivo studies, as well as human trials. However, doses, time of treatment, and, often, molecular mechanisms, have not yet been defined. Ongoing and future studies should evaluate the effectiveness of each probiotic, in terms of adequate doses and treatment time, for the amelioration of specific diseases, taking into account the strain specificity and not overlooking the understanding of the mode of action of the probiotic at a molecular level.
6. Conclusions
In this review, we summarized the latest in vitro, in vivo and clinical evidence for the health-promoting properties of food-borne Lpb. plantarum strains. As mentioned, such strains can have a positive impact on host health by exerting immunomodulatory, antioxidant and antigenotoxic properties, among others. As a result, the origin of microorganisms is becoming less of a criterion for probiotic selection, and new evidence points to fermented foods as a rich source of live and active bacteria. In particular, strains belonging to the species Lpb. plantarum, that can be found in different fermented foods (sourdhough, table olives, cheeses), have shown to exert in vitro anti-inflammatory and antioxidative properties similar to those isolated from the GI tract [121,122]. Additionally, bacteria directly isolated from fermented foods may have advantages in food making processes due to their long history of adaptation to fermentation environments, thereby overcoming technological obstacles associated with the use of difficult-to-handle probiotic bacteria.
However, the inherent variability amongst strains and the lack of conclusive and reproducible results is creating conflicts for industry and scientific partners, with food-borne strains falling into legislative voids. Moreover, in most cases, the precise mechanisms by which food-associated strains exert their mechanisms of action are not well elucidated. As proposed by other authors, the complexity of these mechanisms gives rise to incomprehension about whether these benefits are the result of a direct effect mediated by the cell surface or by the secondary effects of metabolites produced under a given set of forming conditions. This difficulty is exacerbated when the GI ecosystem comes into play. Thus, further in vitro, in vivo and clinical trials must to be performed in order to elucidate the nature of these complex networks. In order to solve these problems, the scientific community has proposed to move towards a precision probiotic tactic, designed according to target-based discovery strategies and person-centric trials. This strategy will deepen our understanding of the mechanistic activity and host response, which will help in the design of probiotics and functional microbes for specific therapeutic purposes [212].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.G.-G. and R.P.; writing—original draft preparation, N.G.-G. and R.P. writing—review and editing, N.B. and A.C.; supervision, N.B. and A.C.; funding acquisition, N.B. and A.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
“This research has received financial support from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under the Marie Skłodowska-Curie Grant Agreement 713714 ESR 07 (to N.G.G.) and was funded by the Italian Ministry of University and Research (National Interest Research Project PRIN 20152LFKAT).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Pasolli, E.; De Filippis, F.; Mauriello, I.E.; Cumbo, F.; Walsh, A.M.; Leech, J.; Cotter, P.D.; Segata, N.; Ercolini, D. Large-scale genome-wide analysis links lactic acid bacteria from food with the gut microbiome. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco, M.L.; Heeney, D.; Binda, S.; Cifelli, C.J.; Cotter, P.D.; Foligné, B.; Gänzle, M.; Kort, R.; Pasin, G.; Pihlanto, A.; et al. Health benefits of fermented foods: Microbiota and beyond. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2017, 44, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marco, M.L.; Hill, C.; Hutkins, R.; Slavin, J.; Tancredi, D.J.; Merenstein, D.; Sanders, M.E. Should There Be a Recommended Daily Intake of Microbes? J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 3061–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kok, C.R.; Hutkins, R. Yogurt and other fermented foods as sources of health-promoting bacteria. Nutr. Rev. 2018, 76, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezac, S.; Kok, C.R.; Heermann, M.; Hutkins, R. Fermented foods as a dietary source of live organisms. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Wittouck, S.; Salvetti, E.; Franz, C.M.A.P.; Harris, H.M.B.; Mattarelli, P.; O’Toole, P.W.; Pot, B.; Vandamme, P.; Walter, J.; et al. A taxonomic note on the genus Lactobacillus: Description of 23 novel genera, emended description of the genus Lactobacillus Beijerinck 1901, and union of Lactobacillaceae and Leuconostocaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 2782–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsetti, A.; Prete, R.; Garcia-Gonzalez, N. Lactic Acid Bacteria: Lactobacillus spp. Lactobacillus Plantarum; Reference Module in Food Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Behera, S.S.; Ray, R.C.; Zdolec, N. Lactobacillus plantarum with functional properties: An approach to increase safety and shelf-life of fermented foods. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 9361614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aponte, M.; Blaiotta, G.; Croce, F.L.; Mazzaglia, A.; Farina, V.; Settanni, L.; Moschetti, G. Use of selected autochthonous lactic acid bacteria for Spanish-style table olive fermentation. Food Microbiol. 2012, 30, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perpetuini, G.; Prete, R.; Garcia-Gonzalez, N.; Khairul Alam, M.; Corsetti, A. Table olives more than a fermented food. Foods 2020, 9, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization; World Health Organization. Probiotics in Food, Health and Nutritional Properties and Guidelines for Evaluation; FAO Food Nutrition: Rome, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. Expert consensus document. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binda, S.; Hill, C.; Johansen, E.; Obis, D.; Pot, B.; Sanders, M.E.; Tremblay, A.; Ouwehand, A.C. Criteria to qualify microorganisms as ”Probiotic” in foods and dietary supplements. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuraida, L. A review: Health promoting lactic acid bacteria in traditional Indonesian fermented foods. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2015, 4, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rychen, G.; Aquilina, G.; Azimonti, G.; Bampidis, V.; Bastos, M.L.; Bories, G.; Chesson, A.; Cocconcelli, P.S.; Flachowsky, G.; Gropp, J.; et al. Guidance on the characterisation of microorganisms used as feed additives or as production organisms. EFSA J. 2018, 16, e05206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seddik, H.A.; Bendali, F.; Gancel, F.; Fliss, I.; Spano, G.; Drider, D. Lactobacillus plantarum and its probiotic and food potentialities. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2017, 9, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadrasta, A.; Stanton, C.; Hill, C.; Fitzgerald, G.; Ross, R. Stress Responses of Lactic Acid Bacteria, 1st ed.; Papadimitriou, E.T.A.K., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Yu, Z.; Tian, F.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhai, Q.; Chen, W. Surface components and metabolites of probiotics for regulation of intestinal epithelial barrier. Microb. Cell Fact. 2020, 19, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odenwald, M.A.; Turner, J.R. The intestinal epithelial barrier: A therapeutic target? Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrien, M.; van Hylckama Vlieg, J.E. Fate, activity, and impact of ingested bacteria within the human gut microbiota. Trends Microbiol. 2015, 23, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleerebezem, M.; Boekhorst, J.; van Kranenburg, R.; Molenaar, D.; Kuipers, O.P.; Leer, R.; Tarchini, R.; Peters, S.A.; Sandbrink, H.M.; Fiers, M.W.; et al. Complete genome sequence of Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 1990–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evanovich, E.; de Souza Mendonça Mattos, P.J.; Guerreiro, J.F. Comparative Genomic Analysis of Lactobacillus plantarum: An Overview. Int. J. Genomics 2019, 2019, 4973214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siezen, R.J.; Tzeneva, V.A.; Castioni, A.; Wels, M.; Phan, H.T.; Rademaker, J.L.; Starrenburg, M.J.; Kleerebezem, M.; Molenaar, D.; van Hylckama Vlieg, J.E. Phenotypic and genomic diversity of Lactobacillus plantarum strains isolated from various environmental niches. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 758–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siezen, R.J.; Francke, C.; Renckens, B.; Boekhorst, J.; Wels, M.; Kleerebezem, M.; van Hijum, S.A. Complete resequencing and reannotation of the Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1 genome. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 195–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawley, A.B.; Henriksen, E.D.; Stout, E.; Brandt, K.; Barrangou, R. Characterizing the activity of abundant, diverse and active CRISPR-Cas systems in lactobacilli. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanilbaba, P.; Cakmak, G. Exopolysaccharides production by lactic acid bacteria. App. Microbiol. 2016, 2, 451–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelleher, P.; Murphy, J.; Mahony, J.; van Sinderen, D. Next-generation sequencing as an approach to dairy starter selection. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2015, 95, 545–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwodo, U.U.; Green, E.; Okoh, A.I. Bacterial exopolysaccharides: Functionality and prospects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 14002–14015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limoli, D.H.; Jones, C.J.; Wozniak, D.J. Bacterial extracellular polysaccharides in biofilm formation and function. Microbiol. Spectr. 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deo, D.; Davray, D.; Kulkarni, R. A Diverse repertoire of exopolysaccharide biosynthesis gene clusters in. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remus, D.M.; van Kranenburg, R.; van Swam, I.I.; Taverne, N.; Bongers, R.S.; Wels, M.; Wells, J.M.; Bron, P.A.; Kleerebezem, M. Impact of 4 Lactobacillus plantarum capsular polysaccharide clusters on surface glycan composition and host cell signaling. Microb. Cell Fact. 2012, 11, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.C.; Caggianiello, G.; van Swam, I.I.; Taverne, N.; Meijerink, M.; Bron, P.A.; Spano, G.; Kleerebezem, M. Strain-specific features of extracellular polysaccharides and their impact on Lactobacillus plantarum-host interactions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 3959–3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamontanara, A.; Caggianiello, G.; Orrù, L.; Capozzi, V.; Michelotti, V.; Bayjanov, J.R.; Renckens, B.; van Hijum, S.A.; Cattivelli, L.; Spano, G. Draft genome sequence of Lactobacillus plantarum Lp90 Isolated from wine. Genome Announc. 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, X.; Gu, Q.; Lou, X.Y.; Zhang, X.M.; Song, D.F.; Zhang, C. Comparative genomic analysis of Lactobacillus plantarum ZJ316 reveals its genetic adaptation and potential probiotic profiles. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2016, 17, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torino, M.I.; Font de Valdez, G.; Mozzi, F. Biopolymers from lactic acid bacteria. Novel applications in foods and beverages. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelin, J.; Kavitha, M. Exopolysaccharides from probiotic bacteria and their health potential. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 853–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayyash, M.; Abu-Jdayil, B.; Itsaranuwat, P.; Galiwango, E.; Tamiello-Rosa, C.; Abdullah, H.; Esposito, G.; Hunashal, Y.; Obaid, R.S.; Hamed, F. Characterization, bioactivities, and rheological properties of exopolysaccharide produced by novel probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum C70 isolated from camel milk. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 144, 938–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adesulu-Dahunsi, A.T.; Jeyaram, K.; Sanni, A.I.; Banwo, K. Production of exopolysaccharide by strains of Lactobacillus plantarum YP175 and OF101 isolated from traditional fermented cereal beverage. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Cui, Y.; Wang, X.; Yue, F.; Shan, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Yi, Y.; Lü, X. Purification, characterization and bioactivity of exopolysaccharides produced by Lactobacillus plantarum KX041. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 128, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, B.; Nampoothiri, K. Exposition of antitumour activity of a chemically characterized exopolysaccharide from a probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum MTCC 9510. Biologia 2013, 68, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Lindström, C.; Patel, A.; Prajapati, J.; Holst, O. Probiotic properties of exopolysaccharide producing lactic acid bacteria isolated from vegetables and traditional Indian fermented foods. Int. J. Fermented Foods 2012, 1, 87–101. [Google Scholar]
- Zacharof, M.; Lovitt, R. Bacteriocins produced by lactic acid bacteria a review article. APCBEE Proc. 2012, 2, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settanni, L.; Corsetti, A. Application of bacteriocins in vegetable food biopreservation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 121, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meade, E.; Slattery, M.A.; Garvey, M. Bacteriocins, potent antimicrobial peptides and the fight against multi drug resistant species: Resistance is futile? Antibiotics (Basel) 2020, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorov, S.D. Bacteriocins from Lactobacillus plantarum—Production, genetic organization and mode of action: Produção, organização genética e modo de ação. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2009, 40, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deegan, L.; Cotter, P.; Hill, C.; Ross, P. Bacteriocins: Biological tools for bio-preservation and shelf-life extension. Int. Dairy J. 2006, 16, 1058–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Sabo, S.; Vitolo, M.; González, J.M.D.; Oliveira, R.P.S. Overview of Lactobacillus plantarum as a promising bacteriocin producer among lactic acid bacteria. Food Res. Int. 2014, 64, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotter, P.D.; Hill, C.; Ross, R.P. Bacteriocins: Developing innate immunity for food. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florez, A.B.; Mayo, B. Genome analysis of Lactobacillus plantarum LL441 and genetic characterization of the locus for the lantibiotic plantaricin C. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holo, H.; Jeknic, Z.; Daeschel, M.; Stevanovic, S.; Nes, I.F. Plantaricin W from Lactobacillus plantarum belongs to a new family of two-peptide lantibiotics. Microbiology 2001, 147, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atrih, A.; Rekhif, N.; Milliere, J.; Lefebvre, G. Detection and characterisation of a bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus plantarum C19. J. Microbiol. 1993, 39, 1173–1179. [Google Scholar]
- Van Reenen, C.A.; Dicks, L.M.; Chikindas, M.L. Isolation, purification and partial characterization of plantaricin 423, a bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus plantarum. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1998, 84, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorov, S.D.; Perin, L.M.; Carneiro, B.M.; Rahal, P.; Holzapfel, W.; Nero, L.A. Safety of Lactobacillus plantarum ST8Sh and its bacteriocin. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2017, 9, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diep, D.B.; Myhre, R.; Johnsborg, O.; Aakra, A.; Nes, I.F. Inducible bacteriocin production in Lactobacillus is regulated by differential expression of the pln operons and by two antagonizing response regulators, the activity of which is enhanced upon phosphorylation. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 47, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enan, G.; Essaway, A.; Uyttendaele, M.; Debeverea, J. Antibacterial activity of Lactobacillus plantarum UG1 isolated from dry sausages: Characterisation, production, and bactericidal action of plantaricin UG1. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1996, 30, 189–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanatani, K.; Oshimura, M. Plasmid-associated bacteriocin production by a Lactobacillus plantarum strain. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1994, 58, 2084–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekhif, N.; Atrih, A.; Lefebvre, G. Activity of plantaricin SA6, a bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus plantarum SA6 isolated from fermented sausage. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1995, 78, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrmann, M.; Remiger, A.; Eijsink, V.; Vogel, R. A gene cluster encoding plantaricin 1.25 beta and other bacteriocin-like peptides in Lactobacillus plantarum TMW1.25. Biochem. Bioph. Acta Gene Struct. Expr. 2000, 1490, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricourt, B.; Barefoot, S.; Testin, R.; Hayasaka, S. Detection and activity of plantaricin F an antibacterial substance from Lactobacillus plantarum BF001 isolated from processed channel catfish. J. Food Protect. 1994, 57, 698–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, B.; Arca, P.; Mayo, B.; Suárez, J. Detection, purification and partial characterisation of plantaricin C, a bacteriocin produced by a Lactobacillus plantarum strain of dairy origin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 2158–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, D.L.; Brennan, L.; Meyer, H.E.; Lohaus, C.; Siethoff, C.; Costa, H.S.; Gonzalez, B.; Santos, H.; Suárez, J.E. Solution structure of plantaricin C, a novel lantibiotic. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 264, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rekhif, N.; Atrih, A.; Lefebvre, G. Characterisation and partial purification of plantaricin LC74, a bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus plantarum LC74. Biotechnol. Lett. 1994, 16, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.S.; Philip, K.; Ajam, N. Purification, characterization and mode of action of plantaricin K25 produced by Lactobacillus plantarum. Food Control 2016, 60, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorov, S.; Onno, B.; Sorokine, O.; Chobert, J.; Ivanova, I.; Dousset, X. Detection and characterisation of a novel antibacterial substance produced by Lactobacillus plantarum ST31 isolated from sourdough. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1999, 48, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.S.; Wang, Y.C.; Chow, Y.S.; Yanagida, F.; Liao, C.C.; Chiu, C.M. Purification and characterization of plantaricin Y, a novel bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus plantarum 510. Arch. Microbiol. 2014, 196, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Díaz, R.; Ruiz-Barba, J.L.; Cathcart, D.P.; Holo, H.; Nes, I.F.; Sletten, K.H.; Warner, P.J. Purification and partial amino acid sequence of plantaricin S, a bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus plantarum LPCO10, the activity of which depends on the complementary action of two peptides. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 4459–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, C.; Yu, J.; Lu, Z. Purification and characterization of plantaricin 163, a novel bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus plantarum 163 isolated from traditional Chinese fermented vegetables. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 11676–11682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Han, J.; Bie, X.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Lv, F. Purification and characterization of Plantaricin JLA-9: A Novel bacteriocin against Bacillus spp. produced by Lactobacillus plantarum JLA-9 from Suan-Tsai, a traditional Chinese fermented cabbage. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 2754–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersse, E.; Diep, D.; Nes, I.; Eijsink, V.; Nissen-Meyer, J. Antagonistic activity of Lactobacillus plantarum C11: Two new two-peptide bacteriocins, plantaricins EF and JK, and the induction factor plantaricin A. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 2269–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daeschel, M.; McKeneney, M.; McDonald, L. Bacteriocidal activity of Lactobacillus plantarum C-11. Food Microbiol. 1990, 7, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Gu, Q. Purification and characterisation of plantaricin ZJ008, a novel bacteriocin against Staphylococcus spp. from Lactobacillus plantarum ZJ008. Food Chem. 2014, 165, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.F.; Zhu, M.Y.; Gu, Q. Purification and characterization of Plantaricin ZJ5, a new bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus plantarum ZJ5. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Matsuda, T.; Ogawa, E.; Ogawa, H.; Kato, H.; Doi, U.; Nakamura, R. Plantaricin-149, a bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus plantarum NRIC 149. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 1994, 77, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, C.M.; Du Toit, M.; Olasupo, N.A.; Schillinger, U.; Holzapfel, W.H. Plantaricin D, a bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus plantarum BFE 905 ready-to-eat salad. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1998, 26, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourad, K.; Halima, Z.K. Detection and activity of plantaricin OL15 a bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus plantarum OL15 isolated from algerian fermented olives. Grasas Aceites 2005, 56, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Lin, Y.; Jie, Y.; Sun, M.; Zhang, B.; Bai, F.; Zhao, H.; Li, J. Purification, characterization, and action mechanism of plantaricin DL3, a novel bacteriocin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa produced by Lactobacillus plantarum DL3 from Chinese Suan-Tsai. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2018, 244, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Yi, H.; Han, X.; Chi, C. Identification and characterization of plantaricin Q7, a novel plantaricin produced by Lactobacillus plantarum Q7. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 71, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.S.; Meng, X.C.; Wang, H. Plantaricin MG active against Gram-negative bacteria produced by Lactobacillus plantarum KLDS1.0391 isolated from “Jiaoke”, a traditional fermented cream from China. Food Control 2010, 21, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shang, N.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, P. The complete genome sequence of Lactobacillus plantarum LPL-1, a novel antibacterial probiotic producing class IIa bacteriocin. J. Biotechnol. 2018, 266, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Xie, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, J.; Li, P. Purification and characterization of plantaricin LPL-1, a novel class IIa bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus plantarum LPL-1 isolated from fermented fish. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, R.; Li, P. Antibacterial mechanism of plantaricin LPL-1, a novel class IIa bacteriocin against Listeria monocytogenes. Food Control 2019, 97, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Yang, J.; Lu, X.; Lu, Z.; Bie, X.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, C.; Lu, F. Purification, characterization, and mode of action of plantaricin GZ1-27, a novel bacteriocin against Bacillus cereus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 4716–4724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Li, X.; Han, H.; Tao, Y. Purification and characterization of plantaricin SLG1, a novel bacteriocin produced by Lb. plantarum isolated from yak cheese. Food Control 2018, 84, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Hao, Y.; Zhong, S.; Liu, H.; Han, T.; Xie, Y. Isolation and partial characterization of a bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus plantarum BM-1 isolated from a traditionally fermented Chinese meat product. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 57, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, M.; Todorov, S.; Ivanova, I.; Belguesmia, Y.; Choiset, Y.; Rabesona, H.; Chobert, J.-M.; Haertlé, T.; Franco, B. Characterization of a two-peptide plantaricin produced by Lactobacillus plantarum MBSa4 isolated from Brazilian salami. Food Control 2016, 60, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinev, T.; Beev, G.; Tzanova, M.; Denev, S.; Dermendzhieva, D.; Stoyanova, A. Antimicrobial activity of Lactobacillus plantarum against pathogenic and food spoilage microorganisms: A review. Bulg. J. Vet. Med. 2018, 21, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tawaha, R.; Meng, C. Potential benefits of Lactobacillus plantarum as probiotic and its advantages in human health and industrial applications: A review. Adv. Environ. Biol. 2018, 12, 16–27. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.J.; Chen, Y.F.; Yang, H.J.; Yang, J.; Xue, J.G.; Li, C.K.; Kwok, L.Y.; Zhang, H.P.; Sun, T.S. Screening for Lactobacillus plantarum with potential inhibitory activity against enteric pathogens. Ann. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, M.P.; Silvain, A.; Normanno, G.; Grieco, F.; Drider, D.; Spano, G.; Fiocco, D. Use of Lactobacillus plantarum strains as a bio-control strategy against food-borne pathogenic microorganisms. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremonte, P.; Pannella, G.; Succi, M.; Tipaldi, L.; Sturchio, M.; Coppola, R.; Luongo, D.; Sorrentino, E. Antimicrobial activity of Lactobacillus plantarum strains isolated from different environments: A preliminary study. Int. Food Res. J. 2017, 24, 852–859. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, L.Y.J.; Chye, F.Y. Antagonistic effects of Lactobacillus plantarum 0612 on the adhesion of selected foodborne enteropathogens in various colonic environments. Food Control 2018, 91, 237–247. [Google Scholar]
- Bonatsou, S.; Tassou, C.C.; Panagou, E.Z.; Nychas, G.E. Table olive fermentation using starter cultures with multifunctional potential. Microorganisms 2017, 5, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, P.; Arena, M.P.; Fiocco, D.; Capozzi, V.; Drider, D.; Spano, G. Lactobacillus plantarum with broad antifungal activity: A promising approach to increase safety and shelf-life of cereal-based products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 247, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalié, D.; Deschamps, A.; Richard-Forget, F. Lactic acid bacteria–potential for control of mould growth and mycotoxins: A review. Food Control 2010, 21, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, E.H.; Yang, E.J.; Woo, E.R.; Chang, H.C. Purification and characterization of antifungal compounds from Lactobacillus plantarum HD1 isolated from kimchi. Food Microbiol. 2014, 41, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowley, S.; Mahony, J.; van Sinderen, D. Current perspectives on antifungal lactic acid bacteria as natural bio-preservatives. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 33, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galié, S.; García-Gutiérrez, C.; Miguélez, E.M.; Villar, C.J.; Lombó, F. Biofilms in the food industry: Health aspects and control methods. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Dhaka, P.; Vijay, D.; Vergis, J.; Mohan, V.; Kumar, A.; Kurkure, N.V.; Barbuddhe, S.B.; Malik, S.V.; Rawool, D.B. Antimicrobial effects of Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus acidophilus against multidrug-resistant enteroaggregative Escherichia coli. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2016, 48, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNicholl, A.G.; Molina-Infante, J.; Lucendo, A.J.; Calleja, J.L.; Pérez-Aisa, Á.; Modolell, I.; Aldeguer, X.; Calafat, M.; Comino, L.; Ramas, M.; et al. Probiotic supplementation with Lactobacillus plantarum and Pediococcus acidilactici for Helicobacter pylori therapy: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Helicobacter 2018, 23, e12529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onbas, T.; Osmanagaoglu, O.; Kiran, F. Potential properties of Lactobacillus plantarum F-10 as a bio-control strategy for wound infections. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 1110–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falagas, M.E.; Betsi, G.I.; Athanasiou, S. Probiotics for prevention of recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis: A review. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 58, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.-H.; Kim, Y.; Han, S.H.; Kim, J.-S.; Paek, N.-S.; So, J.-S. In vitro probiotic properties of vaginal Lactobacillus fermentum MG901 and Lactobacillus plantarum MG989 against Candida albicans. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2018, 228, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, B.R.; Park, G.-S.; Lee, Y.H.; Im, S.; Jeong, D.Y.; Kang, J. Whole genome analysis of Lactobacillus plantarum strains isolated from kimchi and determination of probiotic properties to treat mucosal infections by Candida albicans and Gardnerella vaginalis. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cenci, G.; Rossi, J.; Trotta, F.; Caldini, G. Lactic acid bacteria isolated from dairy products inhibit genotoxic effect of 4-nitroquinoline-1-oxide in SOS-chromotest. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 25, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felton, J.S.; Knize, M.G.; Wu, R.W.; Colvin, M.E.; Hatch, F.T.; Malfatti, M.A. Mutagenic potency of food-derived heterocyclic amines. Mutat. Res. 2007, 616, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, M.; Ambalam, P.; Kondepudi, K.K.; Pithva, S.; Kothari, C.; Patel, A.T.; Purama, R.K.; Dave, J.M.; Vyas, B.R. Potential of probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics for management of colorectal cancer. Gut Microbes 2013, 4, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Magueresse-Battistoni, B.; Labaronne, E.; Vidal, H.; Naville, D. Endocrine disrupting chemicals in mixture and obesity, diabetes and related metabolic disorders. World J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 8, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Gonzalez, N.; Prete, R.; Perugini, M.; Merola, C.; Battista, N.; Corsetti, A. Probiotic antigenotoxic activity as a DNA bioprotective tool: A minireview with focus on endocrine disruptors. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2020, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldini, G.; Trotta, F.; Villarini, M.; Moretti, M.; Pasquini, R.; Scassellati-Sforzolini, G.; Cenci, G. Screening of potential lactobacilli antigenotoxicity by microbial and mammalian cell-based tests. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2005, 102, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, M.L.; Chou, C.C. Mutagenicity and antimutagenic effect of soymilk fermented with lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006, 111, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.D.; Milner, J.A. Gastrointestinal microflora, food components and colon cancer prevention. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2009, 20, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federici, E.; Prete, R.; Lazzi, C.; Pellegrini, N.; Moretti, M.; Corsetti, A.; Cenci, G. Bacterial composition, genotoxicity, and cytotoxicity of fecal samples from individuals consuming omnivorous or vegetarian diets. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walia, S.; Keshani; Sood, S.; Kanwar, S.S. Exhibiotion of DNA-bioprotective activity by microflora of traditional fermented foods of North-Western Himalayas. Food Res. Int. 2014, 55, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prete, R.; Tofalo, R.; Federici, E.; Ciarrocchi, A.; Cenci, G.; Corsetti, A. Food-associated Lactobacillus plantarum and inhibit the genotoxic effect of 4-Nitroquinoline-1-oxide. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurhan, Ş.; Çakir, I. DNA-bioprotective effects of lactic acid bacteria against aflatoxin B1. Curr. Res. Nutr. Food Sci. J. 2016, 4, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartkiene, E.; Zavistanaviciute, P.; Lele, V.; Ruzauskas, M.; Bartkevics, V.; Bernatoniene, J.; Gallo, P.; Tenore, G.C.; Santini, A. Lactobacillus plantarum LUHS135 and paracasei LUHS244 as functional starter cultures for the food fermentation industry: Characterisation, mycotoxin-reducing properties, optimisation of biomass growth and sustainable encapsulation by using dairy by-products. LWT 2018, 93, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Q.; Yu, L.; Li, T.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Effect of dietary probiotic supplementation on intestinal microbiota and physiological conditions of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) under waterborne cadmium exposure. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2017, 110, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, L.; Ma, Y.; Huang, W.; Ling, Y.; Sun, L.; Wang, X.; Zeng, A.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Wang, C.; Wang, H. Dietary Lactobacillus plantarum ST-III alleviates the toxic effects of triclosan on zebrafish (Danio rerio) via gut microbiota modulation. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 84, 1157–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.-T.; Yang, C.-X.; Luo, B.-B.; Zhou, K.; Liu, S.-L. Efficiency of dairy strains of lactic acid bacteria to bind bisphenol A in phosphate buffer saline. Food Control 2017, 73, 1203–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinder, M.; Bisanz, J.E.; Burton, J.P.; Reid, G. Probiotic lactobacilli: A potential prophylactic treatment for reducing pesticide absorption in humans and wildlife. Benef. Microbes 2015, 6, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Gonzalez, N.; Prete, R.; Battista, N.; Corsetti, A. Adhesion properties of food-associated Lactobacillus plantarum strains on human intestinal epithelial cells and modulation of IL-8 release. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prete, R.; Garcia-Gonzalez, N.; Di Mattia, C.D.; Corsetti, A.; Battista, N. Food-borne Lactiplantibacillus plantarum protect normal intestinal cells against inflammation by modulating reactive oxygen species and IL-23/IL-17 axis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, J.Y. Bile acid metabolism and signaling. Compr. Physiol. 2013, 3, 1191–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urdaneta, V.; Casadesús, J. Interactions between bacteria and bile salts in the gastrointestinal and hepatobiliary tracts. Front. Med. 2017, 4, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Sun, K.; Wu, Z.; Yao, J.; Guo, B. All 4 bile salt hydrolase proteins are responsible for the hydrolysis activity in Lactobacillus plantarum ST-III. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, M622–M628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begley, M.; Hill, C.; Gahan, C.G. Bile salt hydrolase activity in probiotics. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 1729–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, S.L.; Gahan, C.G.M.; Joyce, S.A. Interactions between gut bacteria and bile in health and disease. Mol. Asp. Med. 2017, 56, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.B.; Yi, S.H.; Lee, B.H. Purification and characterization of three different types of bile salt hydrolases from Bifidobacterium strains. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishinaka, M.; Umeda, A.; Kuroki, S. High concentrations of conjugated bile acids inhibit bacterial growth of Clostridium perfringens and induce its extracellular cholylglycine hydrolase. Steroids 1994, 59, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijaya, A.; Hermann, A.; Abriouel, H.; Specht, I.; Yousif, N.M.; Holzapfel, W.H.; Franz, C.M. Cloning of the bile salt hydrolase (bsh) gene from Enterococcus faecium FAIR-E 345 and chromosomal location of bsh genes in food enterococci. J. Food Prot. 2004, 67, 2772–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begley, M.; Sleator, R.D.; Gahan, C.G.; Hill, C. Contribution of three bile-associated loci, bsh, pva, and btlB, to gastrointestinal persistence and bile tolerance of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 894–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, J.P.; Valeriano, V.D.; Kim, G.B.; Kang, D.K. Molecular cloning, characterization and comparison of bile salt hydrolases from Lactobacillus johnsonii PF01. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 114, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayashree, S.; Pooja, S.; Pushpanathan, M.; Rajendhran, J.; Gunasekaran, P. Identification and characterization of bile salt hydrolase genes from the genome of Lactobacillus fermentum MTCC 8711. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 174, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiaens, H.; Leer, R.J.; Pouwels, P.H.; Verstraete, W. Cloning and expression of a conjugated bile acid hydrolase gene from Lactobacillus plantarum by using a direct plate assay. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1992, 58, 3792–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, J.M.; Bongers, R.S.; de Vos, W.M.; Kleerebezem, M. Functional analysis of four bile salt hydrolase and penicillin acylase family members in Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 4719–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prete, R.; Long, S.L.; Gallardo, A.L.; Gahan, C.G.; Corsetti, A.; Joyce, S.A. Beneficial bile acid metabolism from Lactobacillus plantarum of food origin. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, C.; Gioiello, A.; Noriega, L.; Strehle, A.; Oury, J.; Rizzo, G.; Macchiarulo, A.; Yamamoto, H.; Mataki, C.; Pruzanski, M.; et al. TGR5-mediated bile acid sensing controls glucose homeostasis. Cell Metab. 2009, 10, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joyce, S.A.; MacSharry, J.; Casey, P.G.; Kinsella, M.; Murphy, E.F.; Shanahan, F.; Hill, C.; Gahan, C.G. Regulation of host weight gain and lipid metabolism by bacterial bile acid modification in the gut. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7421–7426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.Y.; Sheng, L. Regulation of bile acid receptor activity (☆). Liver Res. 2018, 2, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, S.A.; Shanahan, F.; Hill, C.; Gahan, C.G. Bacterial bile salt hydrolase in host metabolism: Potential for influencing gastrointestinal microbe-host crosstalk. Gut Microbes 2014, 5, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.C.; Luo, X.G.; Wang, C.X.; Ma, D.Y.; Wang, Y.; He, Y.Y.; Li, W.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, T.C. Cloning and analysis of bile salt hydrolase genes from Lactobacillus plantarum CGMCC No. 8198. Biotechnol. Lett. 2014, 36, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.L.; Tomaro-Duchesneau, C.; Martoni, C.J.; Prakash, S. Cholesterol lowering with bile salt hydrolase-active probiotic bacteria, mechanism of action, clinical evidence, and future direction for heart health applications. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2013, 13, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pols, T.W.H.; Puchner, T.; Korkmaz, H.I.; Vos, M.; Soeters, M.R.; de Vries, C.J.M. Lithocholic acid controls adaptive immune responses by inhibition of Th1 activation through the Vitamin D receptor. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindarajan, K.; MacSharry, J.; Casey, P.G.; Shanahan, F.; Joyce, S.A.; Gahan, C.G. Unconjugated bile acids influence expression of circadian genes: A potential mechanism for microbe-host crosstalk. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaretti, A.; di Nunzio, M.; Pompei, A.; Raimondi, S.; Rossi, M.; Bordoni, A. Antioxidant properties of potentially probiotic bacteria: In vitro and in vivo activities. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Huang, L.; Li, D.; Niu, C.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Q. Antioxidant activity of Lactobacillus plantarum strains isolated from traditional Chinese fermented foods. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 1914–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, G.; Gao, Y.; Tuo, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, F.; Jiang, S. Assessing and comparing antioxidant activities of lactobacilli strains by using different chemical and cellular antioxidant methods. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 10792–10806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, J.Y.; Song, G.P.; Deng, J.P.; Jiang, L.Z.; Xiong, P.; Yang, B.J.; Liu, S.S. Antitumor effects and mechanism of novel emodin rhamnoside derivatives against human cancer cells in vitro. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, S.M.; Aishwarya, S.; Halami, P.M. Discrimination and divergence among Lactobacillus plantarum-group (LPG) isolates with reference to their probiotic functionalities from vegetable origin. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 39, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valan Arasu, M.; Jung, M.W.; Ilavenil, S.; Jane, M.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, K.D.; Park, H.S.; Hur, T.Y.; Choi, G.J.; Lim, Y.C.; et al. Isolation and characterization of antifungal compound from Lactobacillus plantarum KCC-10 from forage silage with potential beneficial properties. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 115, 1172–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, D.; Goyal, A. Antioxidant activity and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) producing ability of probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum DM5 isolated from Marcha of Sikkim. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 61, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Xing, Z.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y. Molecular mechanisms and in vitro antioxidant effects of Lactobacillus plantarum MA2. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 1642–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higuchi, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kamio, Y. Molecular biology of oxygen tolerance in lactic acid bacteria: Functions of NADH oxidases and Dpr in oxidative stress. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2000, 90, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shao, C.; Liu, L.; Guo, X.; Xu, Y.; Lü, X. Optimization, partial characterization and antioxidant activity of an exopolysaccharide from Lactobacillus plantarum KX041. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 103, 1173–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanjundaiah, Y.S.; Wright, D.A.; Baydoun, A.R.; O’Hare, W.T.; Ali, Z.; Khaled, Z.; Sarker, M.H. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG conditioned media modulates acute reactive oxygen species and nitric oxide in J774 murine macrophages. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2016, 6, 68–75. [Google Scholar]
- Swanson, P.A., II; Kumar, A.; Samarin, S.; Vijay-Kumar, M.; Kundu, K.; Murthy, N.; Hansen, J.; Nusrat, A.; Neish, A.S. Enteric commensal bacteria potentiate epithelial restitution via reactive oxygen species-mediated inactivation of focal adhesion kinase phosphatases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 8803–8808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, J.D.; Reedy, A.R.; Wu, H.; Hinrichs, B.H.; Darby, T.M.; Addis, C.; Robinson, B.S.; Go, Y.-M.; Jones, D.P.; Jones, R.M. Proteomic analysis of microbial induced redox-dependent intestinal signaling. Redox Biol. 2019, 20, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaza-Diaz, J.; Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J.; Gil-Campos, M.; Gil, A. Mechanisms of action of probiotics. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, S49–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteagudo-Mera, A.; Rastall, R.A.; Gibson, G.R.; Charalampopoulos, D.; Chatzifragkou, A. Adhesion mechanisms mediated by probiotics and prebiotics and their potential impact on human health. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 6463–6472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado Galdeano, C.; Cazorla, S.I.; Lemme Dumit, J.M.; Vélez, E.; Perdigón, G. Beneficial effects of probiotic consumption on the immune system. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 74, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, R.S.; Ho, B.; Leung, B.P.; Ding, J.L. TLR cross-talk confers specificity to innate immunity. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 33, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hug, H.; Mohajeri, M.H.; La Fata, G. Toll-Like receptors: Regulators of the immune response in the human gut. Nutrients 2018, 10, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, R.; Warner, N.; Inohara, N.; Núñez, G. NOD1 and NOD2: Signaling, host defense, and inflammatory disease. Immunity 2014, 41, 898–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, S.; Kawahara, S.; Hidaka, M.; Yoshida, H.; Watanabe, W.; Takeshita, M.; Kikuchi, Y.; Bumbein, D.; Muguruma, M.; Kurokawa, M. Effects of oral administration of probiotics from Mongolian dairy products on the Th1 immune response in mice. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2013, 77, 1372–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, E.K.; Kang, G.-D.; Kim, W.-K.; Han, M.J.; Kim, D.-H. Lactobacillus plantarum LC27 and Bifidobacterium longum LC67 simultaneously alleviate ethanol-induced gastritis and hepatic injury in mice. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 38, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitali, B.; Minervini, G.; Rizzello, C.G.; Spisni, E.; Maccaferri, S.; Brigidi, P.; Gobbetti, M.; Di Cagno, R. Novel probiotic candidates for humans isolated from raw fruits and vegetables. Food Microbiol. 2012, 31, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, C.M.; Kostrzynska, M. Lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria attenuate the proinflammatory response in intestinal epithelial cells induced by Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Can. J. Microbiol. 2013, 59, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murosaki, S.; Yamamoto, Y.; Ito, K.; Inokuchi, T.; Kusaka, H.; Yoshikai, Y. Heat-killed Lactobacillus plantarum L-137 suppresses naturally fed antigen-specific IgE production by stimulation of IL-12 production in mice. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1998, 102, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, T.; Fang, X.; Min, W.; Yang, Z. Characterization and immunomodulatory activity of an exopolysaccharide produced by Lactobacillus plantarum JLK0142 isolated from fermented dairy tofu. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 115, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zago, M.; Fornasari, M.E.; Carminati, D.; Burns, P.; Suàrez, V.; Vinderola, G.; Reinheimer, J.; Giraffa, G. Characterization and probiotic potential of Lactobacillus plantarum strains isolated from cheeses. Food Microbiol. 2011, 28, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, T.; Hayashi, K.; Kosaka, A.; Kawashima, M.; Igarashi, T.; Tsutsui, H.; Tsuji, N.M.; Nishimura, I.; Hayashi, T.; Obata, A. Lactobacillus plantarum strain YU from fermented foods activates Th1 and protective immune responses. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2011, 11, 2017–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, S.E.; Han, M.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, D.H. Lactobacillus plantarum CLP-0611 ameliorates colitis in mice by polarizing M1 to M2-like macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 21, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Zhang, Q.; de Haan, B.J.; Zhang, H.; Faas, M.M.; de Vos, P. Identification of TLR2/TLR6 signalling lactic acid bacteria for supporting immune regulation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murofushi, Y.; Villena, J.; Morie, K.; Kanmani, P.; Tohno, M.; Shimazu, T.; Aso, H.; Suda, Y.; Hashiguchi, K.; Saito, T.; et al. The toll-like receptor family protein RP105/MD1 complex is involved in the immunoregulatory effect of exopolysaccharides from Lactobacillus plantarum N14. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 64, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujawa-Szewieczek, A.; Adamczak, M.; Kwiecień, K.; Dudzicz, S.; Gazda, M.; Więcek, A. The effect of Lactobacillus plantarum 299v on the incidence of Clostridium difficile infection in high risk patients treated with antibiotics. Nutrients 2015, 7, 10179–10188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorak, R.N.; Feagan, B.G.; Hotte, N.; Leddin, D.; Dieleman, L.A.; Petrunia, D.M.; Enns, R.; Bitton, A.; Chiba, N.; Paré, P.; et al. The probiotic VSL#3 has anti-inflammatory effects and could reduce endoscopic recurrence after surgery for Crohn’s disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 928–935.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barraza-Ortiz, D.A.; Pérez-López, N.; Medina-López, V.M.; Minero-Alfaro, J.I.; Zamarripa-Dorsey, F.; Fernández-Martínez, N.D.C.; Llorente-Ramón, A.; Ramos-Aguilar, G.A. Combination of a probiotic and an antispasmodic increases quality of life and reduces symptoms in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: A pilot study. Dig. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hütt, P.; Songisepp, E.; Rätsep, M.; Mahlapuu, R.; Kilk, K.; Mikelsaar, M. Impact of probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum TENSIA in different dairy products on anthropometric and blood biochemical indices of healthy adults. Benef. Microbes 2015, 6, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alisi, A.; Bedogni, G.; Baviera, G.; Giorgio, V.; Porro, E.; Paris, C.; Giammaria, P.; Reali, L.; Anania, F.; Nobili, V. Randomised clinical trial: The beneficial effects of VSL#3 in obese children with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 39, 1276–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosch, M.; Fuentes, M.C.; Audivert, S.; Bonachera, M.A.; Peiró, S.; Cuñé, J. Lactobacillus plantarum CECT 7527, 7528 and 7529: Probiotic candidates to reduce cholesterol levels. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miraghajani, M.; Dehsoukhteh, S.S.; Rafie, N.; Hamedani, S.G.; Sabihi, S.; Ghiasvand, R. Potential mechanisms linking probiotics to diabetes: A narrative review of the literature. Sao Paulo Med. J. 2017, 135, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicariotto, F.; Mogna, L.; Del Piano, M. Effectiveness of the two microorganisms Lactobacillus fermentum LF15 and Lactobacillus plantarum LP01, formulated in slow-release vaginal tablets, in women affected by bacterial vaginosis: A pilot study. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 48 (Suppl. 1), 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaźmierczak-Siedlecka, K.; Folwarski, M.; Skonieczna-Żydecka, K.; Ruszkowski, J.; Makarewicz, W. The use of Lactobacillus plantarum 299v (DSM 9843) in cancer patients receiving home enteral nutrition—Study protocol for a randomized, double-blind, and placebo-controlled trial. Nutr. J. 2020, 19, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudzki, L.; Ostrowska, L.; Pawlak, D.; Małus, A.; Pawlak, K.; Waszkiewicz, N.; Szulc, A. Probiotic Lactobacillus Plantarum 299v decreases kynurenine concentration and improves cognitive functions in patients with major depression: A double-blind, randomized, placebo controlled study. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2019, 100, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.Y.; Kim, M.; Ahn, Y.T.; Sim, J.H.; Choi, I.D.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, J.H. The triglyceride-lowering effect of supplementation with dual probiotic strains, Lactobacillus curvatus HY7601 and Lactobacillus plantarum KY1032: Reduction of fasting plasma lysophosphatidylcholines in nondiabetic and hypertriglyceridemic subjects. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 25, 724–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, H.Y.; Kim, M.; Chae, J.S.; Ahn, Y.T.; Sim, J.H.; Choi, I.D.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, J.H. Supplementation with two probiotic strains, Lactobacillus curvatus HY7601 and Lactobacillus plantarum KY1032, reduces fasting triglycerides and enhances apolipoprotein A-V levels in non-diabetic subjects with hypertriglyceridemia. Atherosclerosis 2015, 241, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, M.; Kim, M.; Kwak, J.H.; Lee, J.-W.; Ahn, Y.-T.; Sim, J.-H.; Lee, J.H. Supplementation with two probiotic strains, Lactobacillus curvatus HY7601 and Lactobacillus plantarum KY1032, reduced body adiposity and Lp-PLA2 activity in overweight subjects. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 19, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kang, M.; Yoo, H.J.; Kim, M.S.; Ahn, Y.T.; Sim, J.H.; Jee, S.H.; Lee, J.H. Effects of weight loss using supplementation with Lactobacillus strains on body fat and medium-chain acylcarnitines in overweight individuals. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costabile, A.; Buttarazzi, I.; Kolida, S.; Quercia, S.; Baldini, J.; Swann, J.R.; Brigidi, P.; Gibson, G.R. An in vivo assessment of the cholesterol-lowering efficacy of Lactobacillus plantarum ECGC 13110402 in normal to mildly hypercholesterolaemic adults. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madempudi, R.S.; Ahire, J.J.; Neelamraju, J.; Tripathi, A.; Nanal, S. Efficacy of UB0316, a multi-strain probiotic formulation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A double blind, randomized, placebo controlled study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudha, M.R.; Ahire, J.J.; Jayanthi, N.; Tripathi, A.; Nanal, S. Effect of multi-strain probiotic (UB0316) in weight management in overweight/obese adults: A 12-week double blind, randomised, placebo-controlled study. Benef. Microbes 2019, 10, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surono, I.S.; Martono, P.D.; Kameo, S.; Suradji, E.W.; Koyama, H. Effect of probiotic L. plantarum IS-10506 and zinc supplementation on humoral immune response and zinc status of Indonesian pre-school children. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2014, 28, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumo, P.D.; Bela, B.; Wibowo, H.; Munasir, Z.; Surono, I.S. IS-10506 supplementation increases faecal sIgA and immune response in children younger than two years. Benef. Microbes 2019, 10, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakoeswa, C.R.S.; Herwanto, N.; Prameswari, R.; Astari, L.; Sawitri, S.; Hidayati, A.N.; Indramaya, D.M.; Kusumowidagdo, E.R.; Surono, I.S. Lactobacillus plantarum IS-10506 supplementation reduced SCORAD in children with atopic dermatitis. Benef. Microbes 2017, 8, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Kim, B.; Ban, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, B.J.; Choi, B.S.; Hwang, S.; Ahn, K.; Kim, J. A randomized trial of Lactobacillus plantarum CJLP133 for the treatment of atopic dermatitis. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2012, 23, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harima-Mizusawa, N.; Kano, M.; Nozaki, D.; Nonaka, C.; Miyazaki, K.; Enomoto, T. Citrus juice fermented with Lactobacillus plantarum YIT 0132 alleviates symptoms of perennial allergic rhinitis in a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Benef. Microbes 2016, 7, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harima-Mizusawa, N.; Kamachi, K.; Kano, M.; Nozaki, D.; Uetake, T.; Yokomizo, Y.; Nagino, T.; Tanaka, A.; Miyazaki, K.; Nakamura, S. Beneficial effects of citrus jiuce fermented with Lactobacillus plantarum YIT0132 on atopic dermatitis: Results of daily intake by adult patients in two open trials. Biosci. Microbiota Food Health 2016, 35, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harima-Mizusawa, N.; Iino, T.; Onodera-Masuoka, N.; Kato-Nagaoka, N.; Kiyoshima-Shibata, J.; Gomi, A.; Shibahara-Sone, H.; Kano, M.; Shida, K.; Sakai, M.; et al. Beneficial effects of citrus juice fermented with Lactobacillus plantarum YIT 0132 on Japanese cedar pollinosis. Biosci. Microbiota Food Health 2014, 33, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.C.; Pan, C.H.; Wei, C.C.; Huang, H.Y. Lactobacillus plantarum PS128 improves physiological adaptation and performance in triathletes through gut microbiota modulation. Nutrients 2020, 12, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.Y.; Tsao, S.P. Long term supplementation of Lactobacillus plantarum PS128 attenuated high-intensity exercise induced acute-phase inflammation in triathletes. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2020, 4 (Suppl. 2), 1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.C.; Wei, C.C.; Huang, C.C.; Chen, W.L.; Huang, H.Y. The beneficial effects of Lactobacillus plantarum PS128 on high-intensity, exercise-induced oxidative stress, inflammation, and performance in triathletes. Nutrients 2019, 11, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.W.; Liong, M.T.; Chung, Y.E.; Huang, H.Y.; Peng, W.S.; Cheng, Y.F.; Lin, Y.S.; Wu, Y.Y.; Tsai, Y.C. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum PS128 on children with autism spectrum disorder in Taiwan: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Nutrients 2019, 11, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Z.; Kwok, L.; Ma, C.; Zhang, W.; Lv, Q.; Huang, W.; Zhang, H. Effect of oral consumption of probiotic Lactobacillus planatarum P-8 on fecal microbiota, SIgA, SCFAs, and TBAs of adults of different ages. Nutrition 2014, 30, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lew, L.C.; Hor, Y.Y.; Yusoff, N.A.A.; Choi, S.B.; Yusoff, M.S.B.; Roslan, N.S.; Ahmad, A.; Mohammad, J.A.M.; Abdullah, M.F.I.L.; Zakaria, N.; et al. Probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum P8 alleviated stress and anxiety while enhancing memory and cognition in stressed adults: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 2053–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.C.; Lee, M.C.; Lee, C.C.; Ng, K.S.; Hsu, Y.J.; Tsai, T.Y.; Young, S.L.; Lin, J.S.; Huang, C.C. Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum TWK10 on exercise physiological adaptation, performance, and body composition in healthy humans. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.C.; Hsu, Y.J.; Li, H.; Kan, N.W.; Chen, Y.M.; Lin, J.S.; Hsu, T.K.; Tsai, T.Y.; Chiu, Y.S.; Huang, C.C. Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum TWK10 on improving endurance performance in humans. Chin. J. Physiol. 2018, 61, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, H.X.; Yusoff, N.A.A.; Hor, Y.Y.; Lew, L.C.; Jaafar, M.H.; Choi, S.B.; Yusoff, M.S.B.; Wahid, N.; Abdullah, M.F.I.L.; Zakaria, N.; et al. Lactobacillus plantarum DR7 improved upper respiratory tract infections via enhancing immune and inflammatory parameters: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 4783–4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Chong, H.X.; Chung, F.Y.; Li, Y.; Liong, M.T. DR7 Modulated bowel movement and gut microbiota associated with dopamine and serotonin pathways in stressed adults. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, H.X.; Yusoff, N.A.A.; Hor, Y.Y.; Lew, L.C.; Jaafar, M.H.; Choi, S.B.; Yusoff, M.S.B.; Wahid, N.; Abdullah, M.F.I.L.; Zakaria, N.; et al. DR7 alleviates stress and anxiety in adults: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Benef. Microbes 2019, 10, 355–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashikawa, F.; Noda, M.; Awaya, T.; Nomura, K.; Oku, H.; Sugiyama, M. Improvement of constipation and liver function by plant-derived lactic acid bacteria: A double-blind, randomized trial. Nutrition 2010, 26, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, Y.H.; Park, S.; Paik, J.W.; Chae, S.W.; Kim, D.H.; Jeong, D.G.; Ha, E.; Kim, M.; Hong, G.; Park, S.H.; et al. Efficacy and safety of Lactobacillus plantarum C29-fermented soybean (DW2009) in individuals with mild cognitive impairment: A 12-week, multi-center, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Nutrients 2019, 11, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga, P.; Suez, J.; Derrien, M.; Elinav, E. Moving from probiotics to precision probiotics. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 878–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).