Time-Resolved Transcriptional Profiling of Epithelial Cells Infected by Intracellular Acinetobacter baumannii
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Cell Culture
2.2. Cell Culture and Infection
2.3. Flow Cytometry
2.4. Fluorescent Microscopy
2.5. RNA Isolation
2.6. Read Mapping and Differential Expression Analysis
2.7. Clustering and Functional Enrichment Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
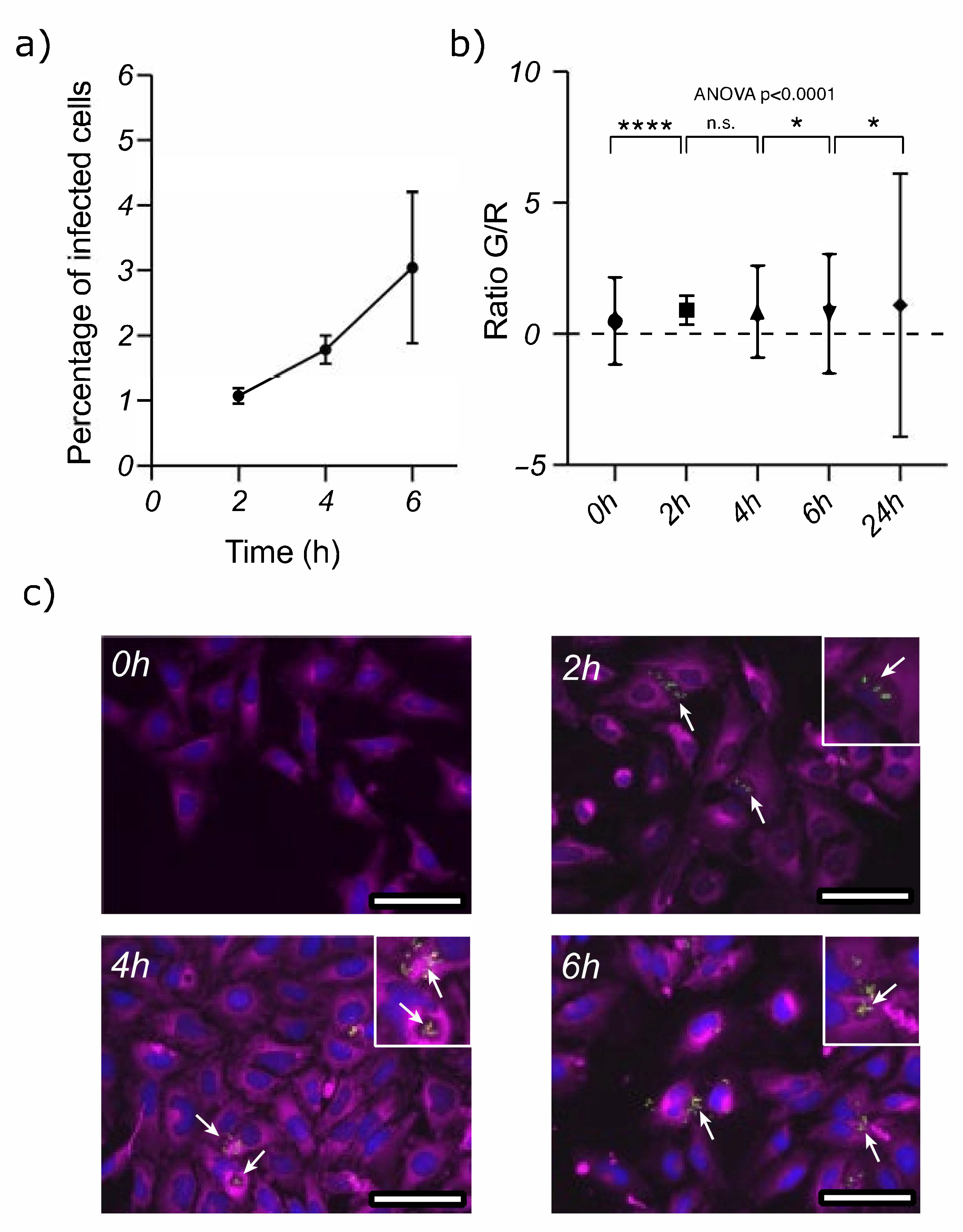
3.1. Acinetobacter baumannii Can Survive inside Epithelial Cells
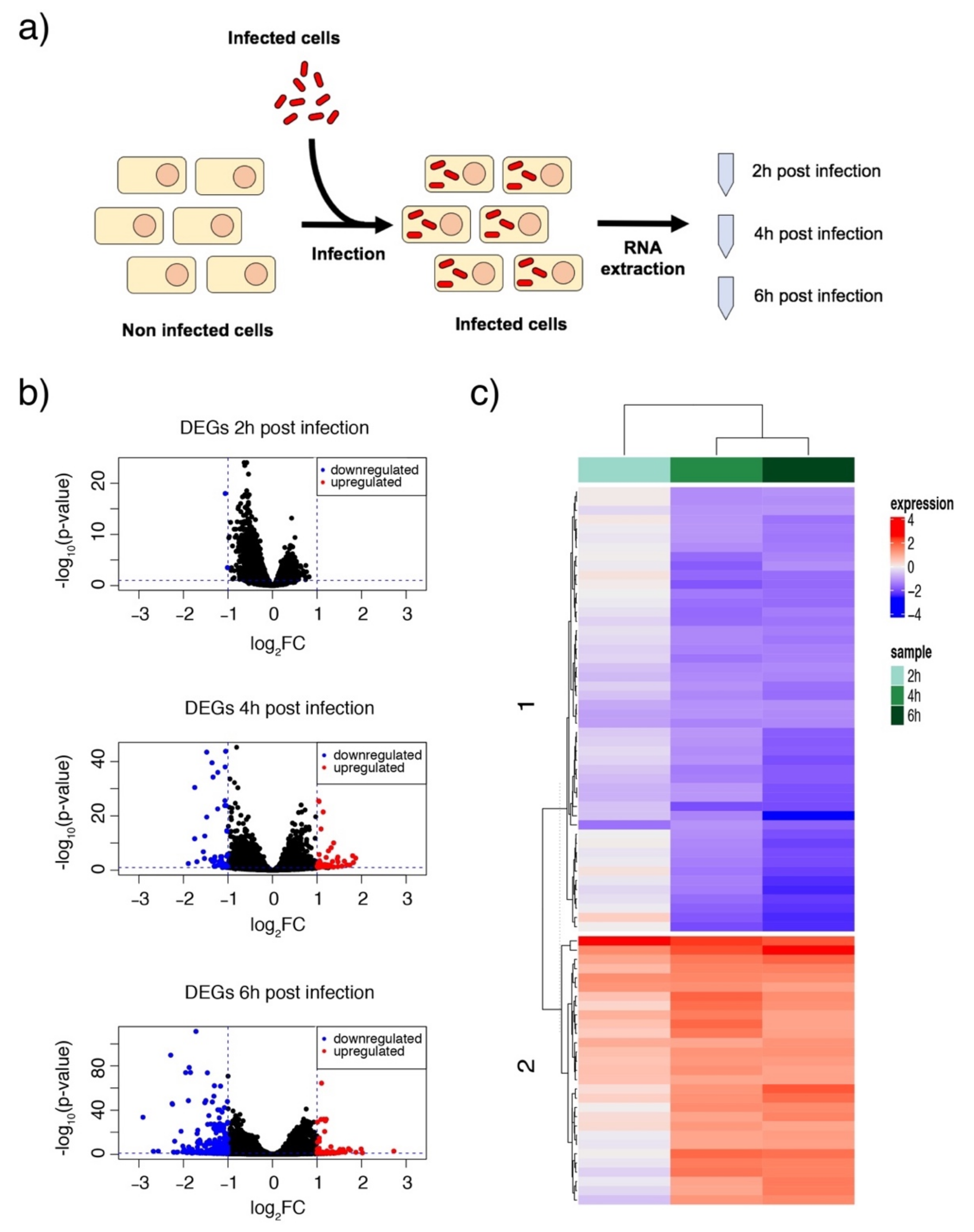
3.2. Acinetobacter baumannii Reorganizes the Cell Transcriptome after Intracellular Invasion
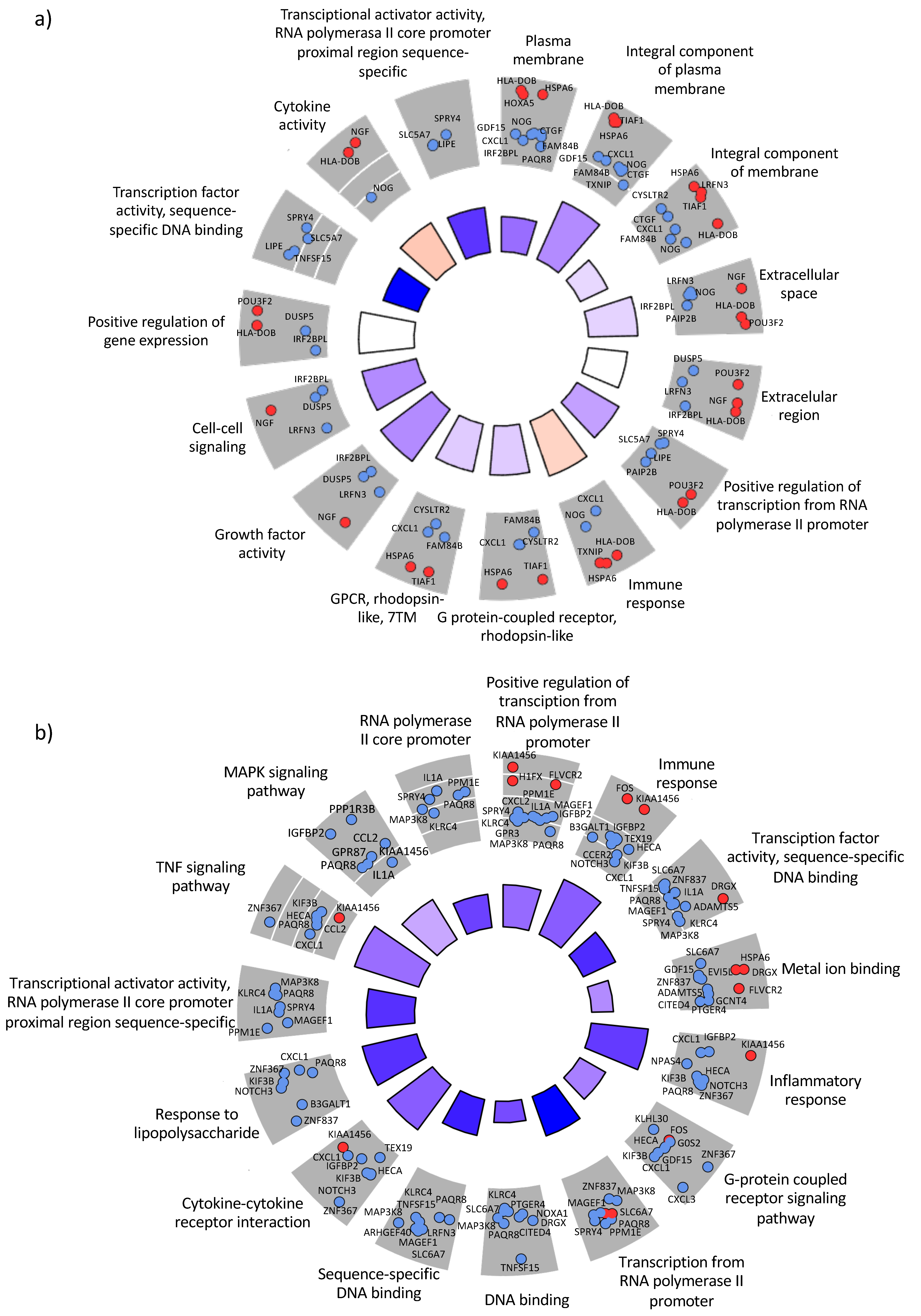
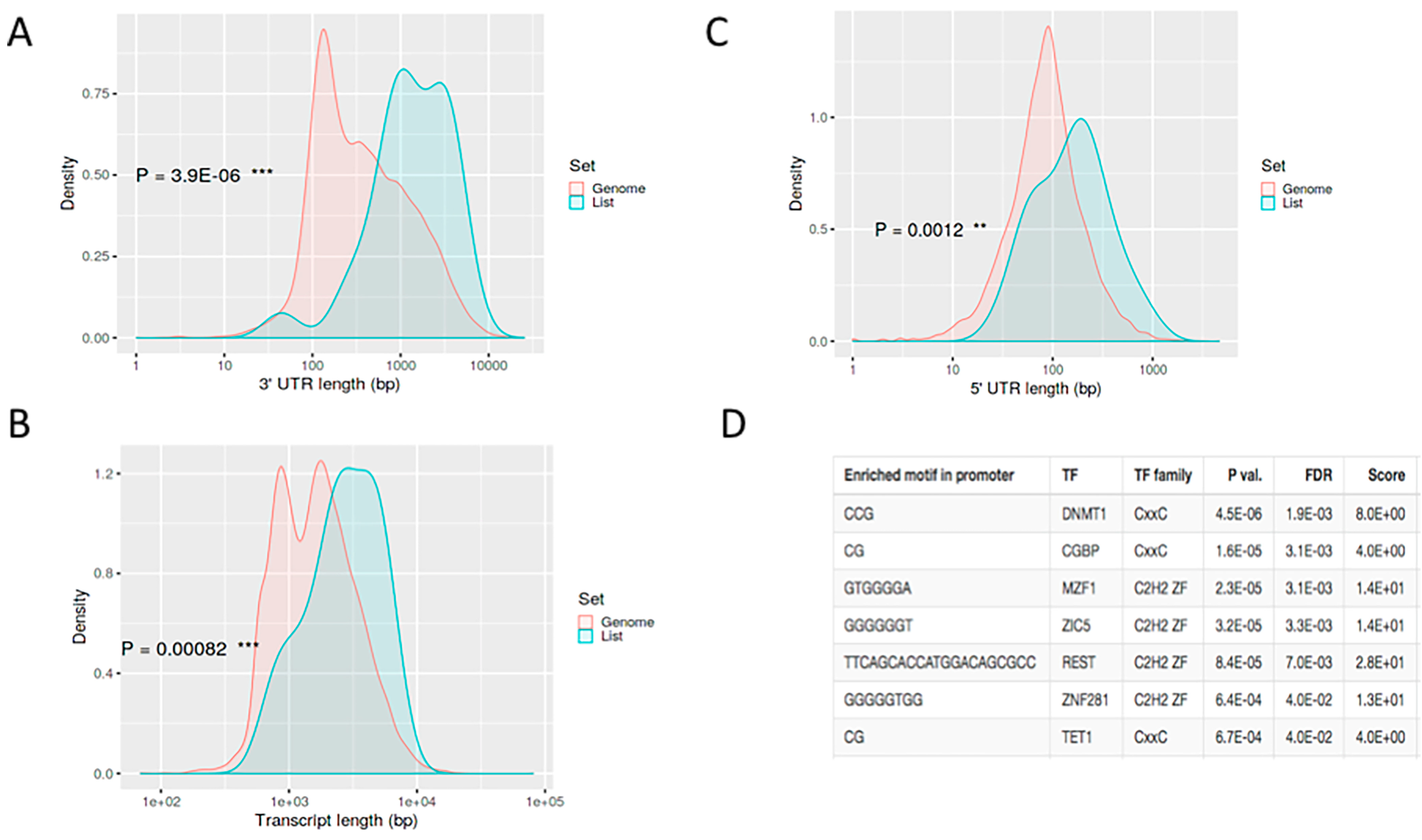
3.3. Regulation of Host Genes in Response to A. baumannii Infection
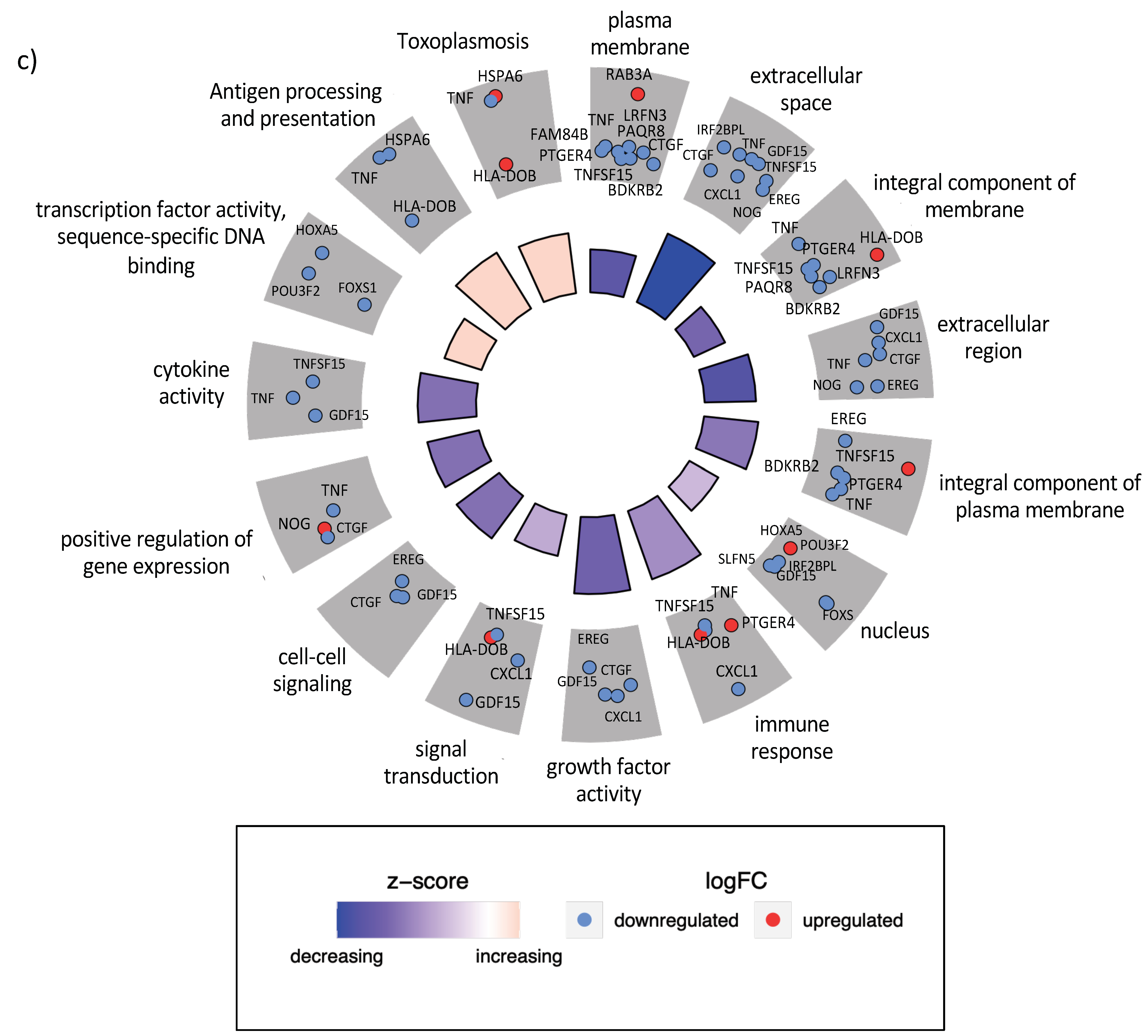
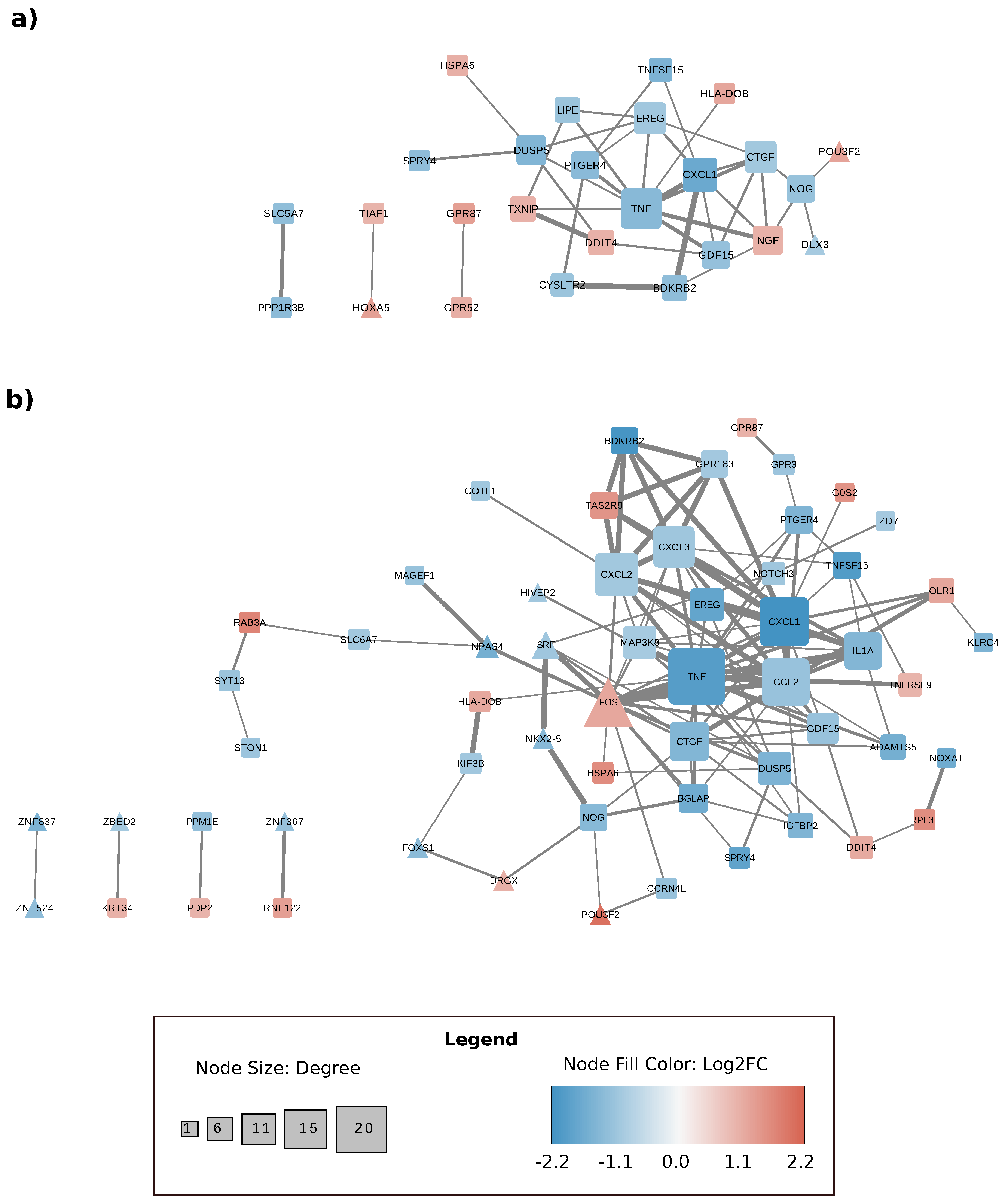
3.4. Gene Expression Changes Are Correlated at the Level of Protein–Protein Interactions
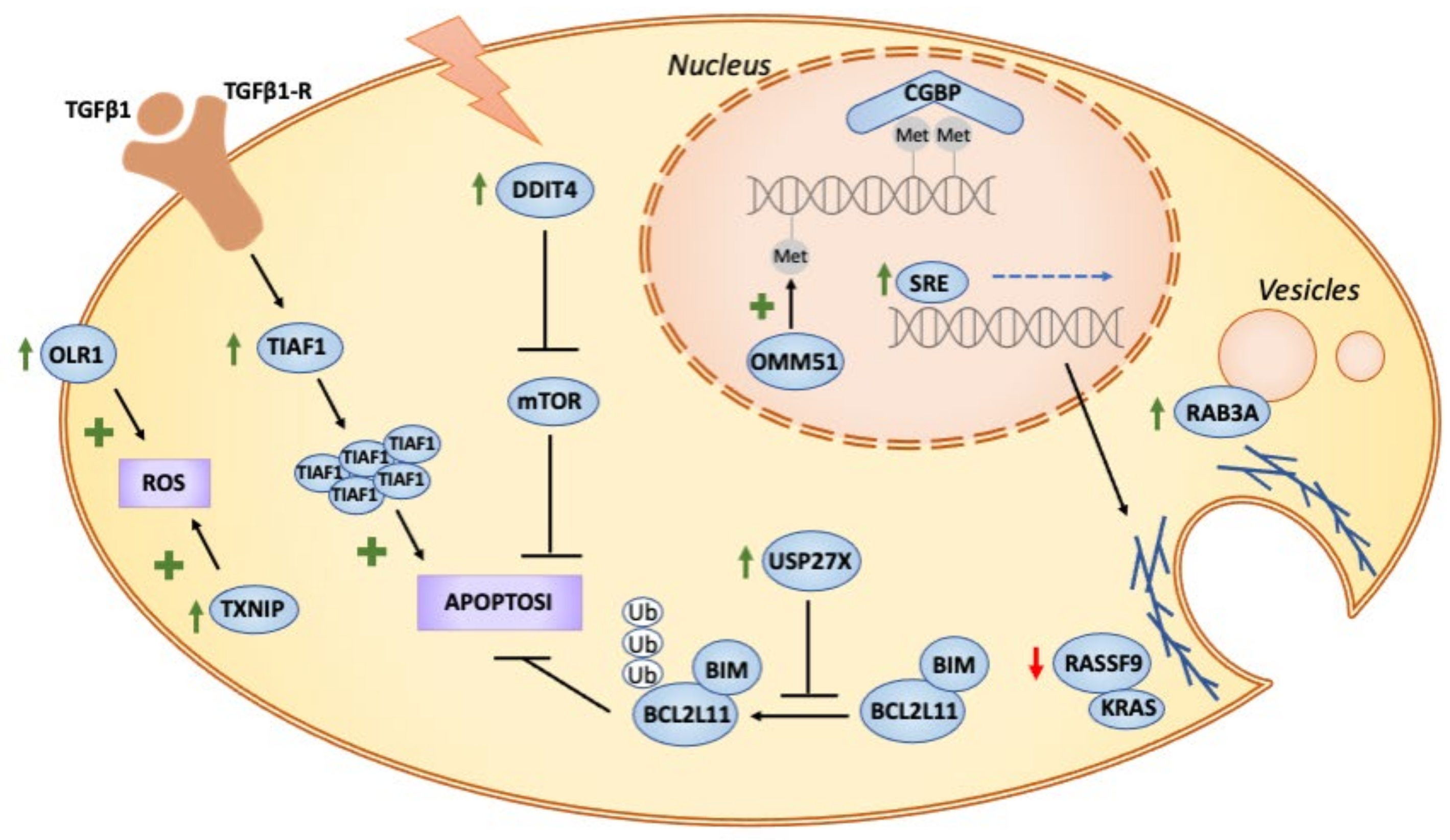
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Laxminarayan, R.; Duse, A.; Wattal, C.; Zaidi, A.K.M.; Wertheim, H.F.L.; Sumpradit, N.; Vlieghe, E.; Hara, G.L.; Gould, I.M.; Goossens, H.; et al. Antibiotic resistance—the need for global solutions. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 1057–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Certain, L.K.; Way, J.C.; Pezone, M.J.; Collins, J.J. Using Engineered Bacteria to Characterize Infection Dynamics and Antibiotic Effects In Vivo. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 22, 263–268.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cornejo, E.; Schlaermann, P.; Mukherjee, S. How to rewire the host cell: A home improvement guide for intracellular bacteria. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 216, 3931–3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Santajit, S.; Indrawattana, N. Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Resistance in ESKAPE Pathogens. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fournier, P.-E.; Vallenet, D.; Barbe, V.; Audic, S.; Ogata, H.; Poirel, L.; Richet, H.; Robert, C.; Mangenot, S.; Abergel, C.; et al. Comparative Genomics of Multidrug Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii. PLoS Genet. 2006, 2, e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coyne, S.; Guigon, G.; Courvalin, P.; Périchon, B. Screening and Quantification of the Expression of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Acinetobacter baumannii with a Microarray. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 54, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dijkshoorn, L.; Nemec, A.; Seifert, H. An increasing threat in hospitals: Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joly-Guillou, M.-L. Clinical impact and pathogenicity of Acinetobacter. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2005, 11, 868–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fleiszig, S.M.; Zaidi, T.S.; Pier, G.B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa invasion of and multiplication within corneal epithelial cells in vitro. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 4072–4077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwok, T.; Backert, S.; Schwarz, H.; Berger, J.; Meyer, T.F. Specific Entry of Helicobacter pylori into Cultured Gastric Epithelial Cells via a Zipper-Like Mechanism. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 2108–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruckdeschel, K.; Roggenkamp, A.; Lafont, V.; Mangeat, P.; Heesemann, J.; Rouot, B. Interaction of Yersinia enterocolitica with macrophages leads to macrophage cell death through apoptosis. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 4813–4821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chapartegui-González, I.; Lázaro-Díez, M.; Bravo, Z.; Navas, J.; Icardo, J.M.; Ramos-Vivas, J. Acinetobacter baumannii maintains its virulence after long-time starvation. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleg, A.Y.; Seifert, H.; Paterson, D.L. Acinetobacter baumannii: Emergence of a Successful Pathogen. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 21, 538–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, C.H.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, Y.C.; Park, T.I.; Lee, J.C. Acinetobacter baumannii invades epithelial cells and outer membrane protein A mediates interactions with epithelial cells. BMC Microbiol. 2008, 8, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.C.; Koerten, H.; Broek, P.V.D.; Beekhuizen, H.; Wolterbeek, R.; Barselaar, M.V.D.; Van Der Reijden, T.; Van Der Meer, J.; Van De Gevel, J.; Dijkshoorn, L. Adherence of Acinetobacter baumannii strains to human bronchial epithelial cells. Res. Microbiol. 2006, 157, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaddy, J.A.; Tomaras, A.P.; Actis, L.A. The Acinetobacter baumannii 19606 OmpA Protein Plays a Role in Biofilm Formation on Abiotic Surfaces and in the Interaction of This Pathogen with Eukaryotic Cells. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 3150–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, C.H.; Lee, E.Y.; Lee, Y.C.; Park, T.I.; Kim, H.J.; Hyun, S.H.; Kim, S.A.; Lee, S.-K.; Lee, J.C. Outer membrane protein 38 of Acinetobacter baumannii localizes to the mitochondria and induces apoptosis of epithelial cells. Cell. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 1127–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, A.C.; Hood, I.; Boyd, K.L.; Olson, P.D.; Morrison, J.M.; Carson, S.; Sayood, K.; Iwen, P.C.; Skaar, E.P.; Dunman, P.M. Inactivation of Phospholipase D Diminishes Acinetobacter baumannii Pathogenesis. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 1952–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weidensdorfer, M.; Ishikawa, M.; Hori, K.; Linke, D.; Djahanschiri, B.; Iruegas, R.; Ebersberger, I.; Riedel-Christ, S.; Enders, G.; Leukert, L.; et al. The Acinetobacter trimeric autotransporter adhesin Ata controls key virulence traits of Acinetobacter baumannii. Virulence 2019, 10, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. featureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raudvere, U.; Kolberg, L.; Kuzmin, I.; Arak, T.; Adler, P.; Peterson, H.; Vilo, J. g:Profiler: A web server for functional enrichment analysis and conversions of gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W191–W198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terskikh, A.V.; Fradkov, A.; Ermakova, G.; Zaraisky, A.; Tan, P.; Kajava, A.V.; Zhao, X.; Lukyanov, S.; Matz, M.; Kim, S.; et al. “Fluorescent Timer”: Protein That Changes Color with Time. Science 2000, 290, 1585–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claudi, B.; Spröte, P.; Chirkova, A.; Personnic, N.; Zankl, J.; Schürmann, N.; Schmidt, A.; Bumann, D. Phenotypic Variation of Salmonella in Host Tissues Delays Eradication by Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. Cell 2014, 158, 722–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vanderhoeven, J.P.; Bierle, C.J.; Kapur, R.P.; McAdams, R.M.; Beyer, R.P.; Bammler, T.K.; Farin, F.M.; Bansal, A.; Spencer, M.; Deng, M.; et al. Group B Streptococcal Infection of the Choriodecidua Induces Dysfunction of the Cytokeratin Network in Amniotic Epithelium: A Pathway to Membrane Weakening. PLOS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1003920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra-Millán, R.; Guerrero-Gómez, D.; Ayerbe-Algaba, R.; Pachón-Ibáñez, M.E.; Miranda-Vizuete, A.; Pachón, J.; Smani, Y. Intracellular Trafficking and Persistence of Acinetobacter baumannii Requires Transcription Factor EB. mSphere 2018, 3, e00106-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, N.-S.; Mattison, J.; Cao, H.; Pratt, N.; Zhao, Y.; Lee, C. Cloning and Characterization of a Novel Transforming Growth Factor-β1-Induced TIAF1 Protein That Inhibits Tumor Necrosis Factor Cytotoxicity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 253, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Q.; Hsu, L.-J.; Chou, P.-Y.; Chou, Y.-T.; Lu, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-A.; Chang, N.-S. Self-aggregating TIAF1 in lung cancer progression. Transl. Respir. Med. 2013, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Han, E.; Xing, Q.; Yan, J.; Arrington, A.; Wang, C.; Tully, D.; Kowolik, C.M.; Lu, D.M.; Frankel, P.H.; et al. Baicalein upregulates DDIT4 expression which mediates mTOR inhibition and growth inhibition in cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2015, 358, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coburn, J.; Gill, D.M. ADP-ribosylation of p21ras and related proteins by Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoenzyme S. Infect. Immun. 1991, 59, 4259–4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tiwari, V.; Tiwari, M.; Solanki, V. Polyvinylpyrrolidone-Capped Silver Nanoparticle Inhibits Infection of Carbapenem-Resistant Strain of Acinetobacter baumannii in the Human Pulmonary Epithelial Cell. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, B.S.; Kinsella, R.L.; Harding, C.M.; Feldman, M.F. The Secrets of Acinetobacter Secretion. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 532–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dramsi, S.; Cossart, P. Intracellular pathogens and the actin cytoskeleton. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1998, 14, 137–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, A.; García, F. Hijacking of eukaryotic functions by intracellular bacterial pathogens. Int. Microbiol. 2004, 7, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wilkie, G.S.; Dickson, K.S.; Gray, N.K. Regulation of mRNA translation by 5′- and 3′-UTR-binding factors. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2003, 28, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutay, N.; Ambite, I.; Hernandez, J.G.; Rydström, G.; Ragnarsdóttir, B.; Puthia, M.; Nadeem, A.; Zhang, J.; Storm, P.; Dobrindt, U.; et al. Bacterial control of host gene expression through RNA polymerase II. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 2366–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Pan, D.; Deng, A.-M.; Huang, F.; Sun, B.-L.; Yang, R.-G. DNA methyltransferases 1 and 3B are required for hepatitis C virus infection in cell culture. Virol. Rep. 2013, 441, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tolg, C.; Sabha, N.; Cortese, R.; Panchal, T.; Ahsan, A.; Soliman, A.T.; Aitken, K.J.; Petronis, A.; Bagli, D. Uropathogenic E. coli infection provokes epigenetic downregulation of CDKN2A (p16INK4A) in uroepithelial cells. Lab. Investig. 2011, 91, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Macho Rendón, J.; Lang, B.; Tartaglia, G.G.; Torrent Burgas, M. BacFITBase: A database to assess the relevance of bacterial genes during host infection. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D511–D516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Groot, N.S.; Torrent Burgas, M. Bacteria use structural imperfect mimicry to hijack the host interactome. PLoS Comput Biol. 2020, 16, e1008395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crua Asensio, N.; Muñoz Giner, E.; de Groot, N.; Torrent Burgas, M. Centrality in the host–pathogen interactome is associated with pathogen fitness during infection. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Groot, N.S.; Torrent Burgas, M. A Coordinated Response at The Transcriptome and Interactome Level is Required to Ensure Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Survival during Bacteremia. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Macho Rendón, J.; Lang, B.; Ramos Llorens, M.; Tartaglia, G.G.; Torrent Burgas, M. DualSeqDB: The host–pathogen dual RNA sequencing database for infection processes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D687–D693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Crua Asensio, N.; Macho Rendón, J.; Torrent Burgas, M. Time-Resolved Transcriptional Profiling of Epithelial Cells Infected by Intracellular Acinetobacter baumannii. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9020354
Crua Asensio N, Macho Rendón J, Torrent Burgas M. Time-Resolved Transcriptional Profiling of Epithelial Cells Infected by Intracellular Acinetobacter baumannii. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(2):354. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9020354
Chicago/Turabian StyleCrua Asensio, Nuria, Javier Macho Rendón, and Marc Torrent Burgas. 2021. "Time-Resolved Transcriptional Profiling of Epithelial Cells Infected by Intracellular Acinetobacter baumannii" Microorganisms 9, no. 2: 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9020354
APA StyleCrua Asensio, N., Macho Rendón, J., & Torrent Burgas, M. (2021). Time-Resolved Transcriptional Profiling of Epithelial Cells Infected by Intracellular Acinetobacter baumannii. Microorganisms, 9(2), 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9020354





