Extranodal NK/T-Cell Lymphoma, Nasal Type: Genetic, Biologic, and Clinical Aspects with a Central Focus on Epstein–Barr Virus Relation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Historical Context
3. Epidemiology
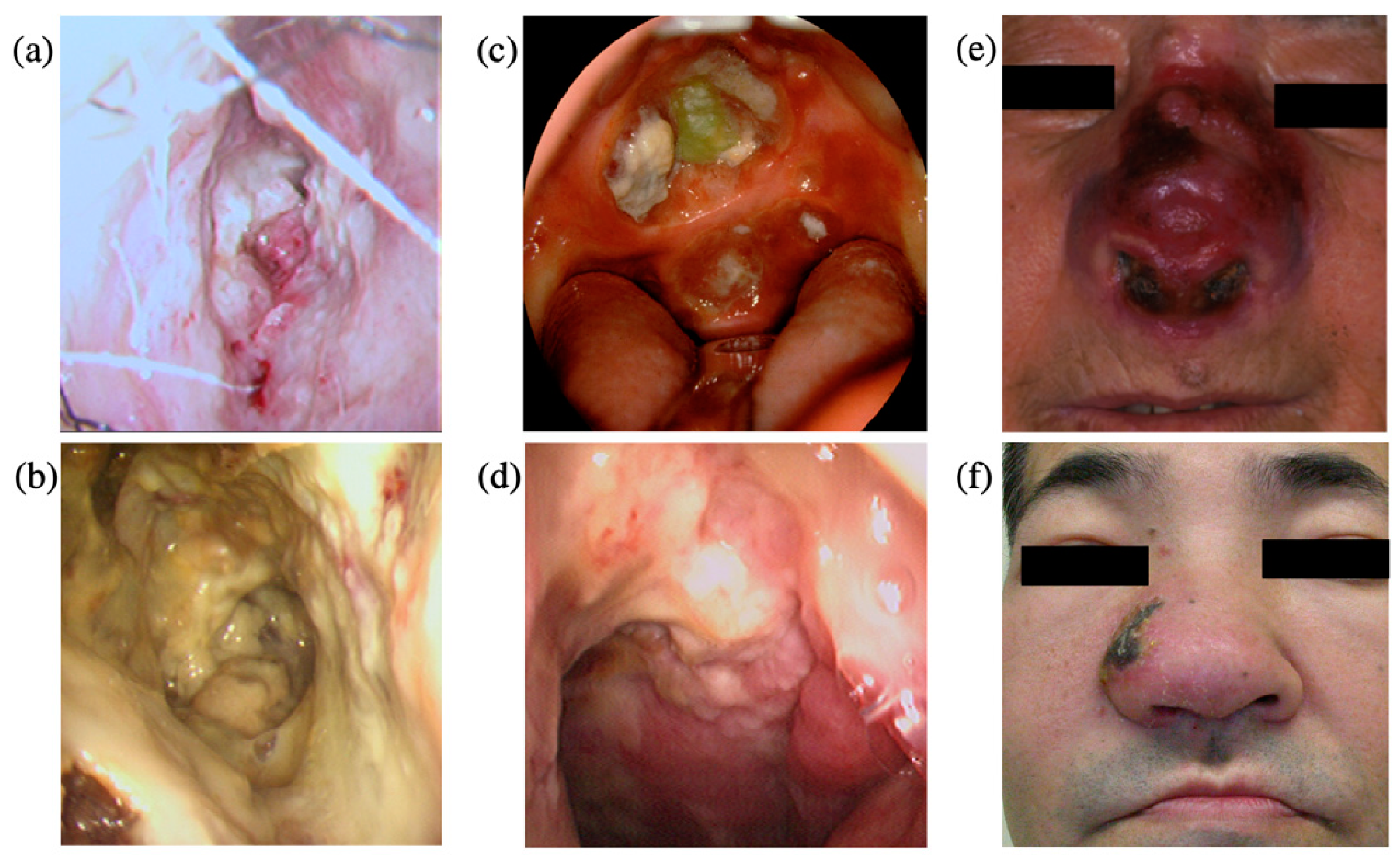
4. Clinical Features
5. Pathology
6. EBV Status
7. EBV Infection of T or NK Cells
8. Gene Mutations
9. Diagnosis by Using EBV Infection
10. Staging
11. Monitoring by Using EBV Infection
12. Proliferation and Invasion Factors
13. Involvement of EBV in Proliferation and Invasion Factors
14. Environmental Factors Affecting EBV Status
15. Therapy for Early Stage Extranodal NK/T-Cell Lymphoma, Nasal Type
16. Therapy for Advanced Stage Extranodal NK/T-Cell Lymphoma, Nasal Type
17. Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy with Concomitant Radiotherapy
18. Prospective Therapies
19. Prospective Therapies by Targeting EBV
20. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harabuchi, Y.; Yamanaka, N.; Kataura, A.; Imai, S.; Kinoshita, T.; Mizuno, F.; Osato, T. Epstein-Barr virus in nasal T-cell lymphomas in patients with lethal midline granuloma. Lancet 1990, 335, 128–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harabuchi, Y.; Imai, S.; Wakashima, J.; Hirao, M.; Kataura, A.; Osato, T.; Kon, S. Nasal T-cell lymphoma causally associated with Epstein-Barr virus: Clinicopathologic, phenotypic, and genotypic studies. Cancer 1996, 77, 2137–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Suh, C.; Park, Y.H.; Ko, Y.H.; Bang, S.M.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, D.H.; Huh, J.; Oh, S.Y.; Kwon, H.C.; et al. Extranodal natural killer T-cell lymphoma, nasal-type: A prognostic model from a retrospective multicenter study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 612–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aozasa, K.; Ohsawa, M.; Tajima, K.; Sasaki, R.; Maeda, H.; Matsunaga, T.; Friedmann, I. Nation-wide study of lethal mid-line granuloma in Japan: Frequencies of Wegener’s granulomatosis, polymorphic reticulosis, malignant lymphoma and other related conditions. Int. J. Cancer 1989, 44, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altemani, A.; Barbosa, A.C.; Kulka, M.; Takahashi, T.; Endo, L.; Vassallo, J.; Lorand-Metze, I. Characteristics of nasal T/NK-cell lymphoma among Brazilians. Neoplasma 2002, 49, 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Gaal, K.; Sun, N.C.; Hernandez, A.M.; Arber, D.A. Sinonasal NK/T-cell lymphomas in the United States. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2000, 24, 1511–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, R.W.; Devaney, K.; Ferlito, A.; Rinaldo, A.; Carbone, A. Sinonasal malignant lymphomas: A distinct clinicopathological category. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1999, 108, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanavaros, P.; Lescs, M.C.; Briere, J.; Divine, M.; Galateau, F.; Joab, I.; Bosq, J.; Farcet, J.P.; Reyes, F.; Gaulard, P. Nasal T-cell lymphoma: A clinicopathologic entity associated with peculiar phenotype and with Epstein-Barr virus. Blood 1993, 81, 2688–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamanaka, N.; Kataura, A.; Sambe, S.; Minase, T.; Ishii, Y. Midfacial T cell lymphoma: Characterization by monoclonal antibodies. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1985, 94, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Stein, H.; Banks, P.M.; Chan, J.K.; Cleary, M.L.; Delsol, G.; De Wolf-Peeters, C.; Falini, B.; Gatter, K.C.; et al. A revised European-American classification of lymphoid neoplasms: A proposal from the International Lymphoma Study Group. Blood 1994, 84, 1361–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eichel, B.S.; Harrison, E.G.; Devine, K.D.; Scanlon, P.W.; Brown, H.A. Primary lymphoma of the nose including a relationship to lethal midline granuloma. Am. J. Surg. 1966, 112, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emile, J.F.; Boulland, M.L.; Haioun, C.; Kanavaros, P.; Petrella, T.; Delfau-Larue, M.H.; Bensussan, A.; Farcet, J.P.; Gaulard, P. CD5-CD56+ T-cell receptor silent peripheral T-cell lymphomas are natural killer cell lymphomas. Blood 1996, 87, 1466–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagata, H.; Konno, A.; Kimura, N.; Zhang, Y.; Kimura, M.; Demachi, A.; Sekine, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Shimizu, N. Characterization of novel natural killer (NK)-cell and gammadelta T-cell lines established from primary lesions of nasal T/NK-cell lymphomas associated with the Epstein-Barr virus. Blood 2001, 97, 708–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kinney, M.C. The role of morphologic features, phenotype, genotype, and anatomic site in defining extranodal T-cell or NK-cell neoplasms. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1999, 111, S104–S118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, R.; Takeuchi, K.; Ohshima, K.; Nakamura, S. Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma: Diagnosis and treatment cues. Hematol. Oncol. 2008, 26, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harabuchi, Y.; Takahara, M.; Kishibe, K.; Moriai, S.; Nagato, T.; Ishii, H. Nasal natural killer (NK)/T-cell lymphoma: Clinical, histological, virological, and genetic features. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 14, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minarovits, J.; Hu, L.; Imai, S.; Harabuchi, Y.; Kataura, A.; Minarovits-Kormuta, S.; Osato, T.; Klein, G. Clonality, expression and methylation patterns of the Epstein-Barr virus genomes in lethal midline granulomas classified as peripheral angiocentric T cell lymphomas. J. Gen. Virol. 1994, 75, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harabuchi, Y.; Takahara, M.; Kishibe, K.; Nagato, T.; Kumai, T. Extranodal Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoma, Nasal Type: Basic Science and Clinical Progress. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, H.; Ogino, T.; Berger, C.; Kochli-Schmitz, N.; Nagato, T.; Takahara, M.; Nadal, D.; Harabuchi, Y. Clinical usefulness of serum EBV DNA levels of BamHI W and LMP1 for Nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma. J. Med. Virol. 2007, 79, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Ogawa, S.; Nomoto, Y. Treatment outcome of nasal NK-cell lymphoma: A case report of 12 consecutively-diagnosed cases and a review of the literature. J. Clin. Exp. Hematopathol. 2001, 41, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahara, M.; Nagato, T.; Kishibe, K.; Ueda, S.; Komabayashi, Y.; Yamashina, M.; Takahashi, K.; Harabuchi, Y. Novel treatment for early-stage nasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma: Intra-maxillary arterial infusion chemotherapy with concomitant radiotherapy. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 35, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, P. Photographs of a case of rapid destruction of the nose and face. J. Laryngol. Otol. 1897, 12, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, H.L. Lethal granulomatous ulceration, involving midline facial tissues. Ann. Otol. Rhino. Laryngol. 1949, 58, 1013–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harabuchi, Y.; Kataura, A.; Kobayashi, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Yamanaka, N.; Hirao, M.; Onodera, K.; Kon, S. Lethal midline granuloma (peripheral T-cell lymphoma) after lymphomatoid papulosis. Cancer 1992, 70, 835–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.S.; Chan, J.K.; Lo, S.T. Expression of natural killer cell markers in non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. Hum. Pathol. 1987, 18, 1257–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, Y.; Yamanaka, N.; Ogawa, K.; Yoshida, Y.; Takami, T.; Matsuura, A.; Isago, H.; Kataura, A.; Kikuchi, K. Nasal T-cell lymphoma as a type of so-called “lethal midline granuloma”. Cancer 1982, 50, 2336–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, F.C.; Srivastava, G.; Loke, S.L.; Fu, K.H.; Leung, B.P.; Liang, R.; Choy, D. Presence of Epstein-Barr virus DNA in nasal lymphomas of B and ‘T’ cell type. Hematol. Oncol. 1990, 8, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros, L.J.; Jaffe, E.S.; Chen, Y.Y.; Weiss, L.M. Localization of Epstein-Barr viral genomes in angiocentric immunoproliferative lesions. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1992, 16, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, L.M.; Gaffey, M.J.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Frierson, H.F. Frequency of Epstein-Barr viral DNA in “Western” sinonasal and Waldeyer’s ring non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1992, 16, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Song, B.; Fan, T.; Huang, C.; Xie, C.; Li, J.; Zhong, W.; Li, S.; Yu, J. Pathological and clinical characteristics of 1,248 non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas from a regional cancer hospital in Shandong, China. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2011, 12, 3055–3061. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vose, J.; Armitage, J.; Weisenburger, D.; International, T.C.L.P. International peripheral T-cell and natural killer/T-cell lymphoma study: Pathology findings and clinical outcomes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 4124–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudiger, T.; Weisenburger, D.D.; Anderson, J.R.; Armitage, J.O.; Diebold, J.; MacLennan, K.A.; Nathwani, B.N.; Ullrich, F.; Muller-Hermelink, H.K.; Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Classification, P. Peripheral T-cell lymphoma (excluding anaplastic large-cell lymphoma): Results from the Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Classification Project. Ann. Oncol. 2002, 13, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, M. Aggressive mature natural killer cell neoplasms: From epidemiology to diagnosis. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2013, 8, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haverkos, B.M.; Pan, Z.; Gru, A.A.; Freud, A.G.; Rabinovitch, R.; Xu-Welliver, M.; Otto, B.; Barrionuevo, C.; Baiocchi, R.A.; Rochford, R.; et al. Extranodal NK/T Cell Lymphoma, Nasal Type (ENKTL-NT): An Update on Epidemiology, Clinical Presentation, and Natural History in North American and European Cases. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2016, 11, 514–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hildesheim, A.; Apple, R.J.; Chen, C.J.; Wang, S.S.; Cheng, Y.J.; Klitz, W.; Mack, S.J.; Chen, I.H.; Hsu, M.M.; Yang, C.S.; et al. Association of HLA class I and II alleles and extended haplotypes with nasopharyngeal carcinoma in Taiwan. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2002, 94, 1780–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goldsmith, D.B.; West, T.M.; Morton, R. HLA associations with nasopharyngeal carcinoma in Southern Chinese: A meta-analysis. Clin. Otolaryngol. Allied Sci. 2002, 27, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niens, M.; Jarrett, R.F.; Hepkema, B.; Nolte, I.M.; Diepstra, A.; Platteel, M.; Kouprie, N.; Delury, C.P.; Gallagher, A.; Visser, L.; et al. HLA-A*02 is associated with a reduced risk and HLA-A*01 with an increased risk of developing EBV+ Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2007, 110, 3310–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coleman, C.B.; Wohlford, E.M.; Smith, N.A.; King, C.A.; Ritchie, J.A.; Baresel, P.C.; Kimura, H.; Rochford, R. Epstein-Barr virus type 2 latently infects T cells, inducing an atypical activation characterized by expression of lymphotactic cytokines. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 2301–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kimura, H. EBV in T-/NK-Cell Tumorigenesis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1045, 459–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamine, M.; Kishibe, K.; Takahara, M.; Nagato, T.; Ishii, H.; Bandoh, N.; Ogino, T.; Harabuchi, Y. Selected amino acid change encoding Epstein-Barr virus-specific T cell epitope of the LMP2A gene in Japanese nasal NK/T cell lymphoma patients. Intervirology 2007, 50, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamine, M.; Takahara, M.; Kishibe, K.; Nagato, T.; Ishii, H.; Bandoh, N.; Ogino, T.; Harabuchi, Y. Sequence variations of Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 gene in nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma. Virus Genes 2007, 34, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Wang, H.; Xie, K.; He, G.; Du, Z. Analysis of clinicopathological features and prognostic factors of 62 nasal NK/T-cell lymphomas. J. Clin. Otorhinolaryngol. 2007, 21, 932–934. [Google Scholar]
- Kojya, S.; Matsumura, J.; Ting, L.; Hongyo, T.; Inazawa, J.; Kirihata, M.; Aozasa, K. Familial nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma and pesticide use. Am. J. Hematol. 2001, 66, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, R.; Suzumiya, J.; Yamaguchi, M.; Nakamura, S.; Kameoka, J.; Kojima, H.; Abe, M.; Kinoshita, T.; Yoshino, T.; Iwatsuki, K.; et al. Prognostic factors for mature natural killer (NK) cell neoplasms: Aggressive NK cell leukemia and extranodal NK cell lymphoma, nasal type. Ann. Oncol. 2010, 21, 1032–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Li, P.; Zhao, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, F.; Yang, Y.Q.; Fang, F.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, W.Y.; et al. A clinical study of 115 patients with extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 20, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.M.; Park, Y.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, D.W.; Im, S.A.; Kim, T.Y.; Kim, C.W.; Heo, D.S.; Bang, Y.J.; et al. Local tumor invasiveness is more predictive of survival than International Prognostic Index in stage I(E)/II(E) extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Blood 2005, 106, 3785–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gualco, G.; Domeny-Duarte, P.; Chioato, L.; Barber, G.; Natkunam, Y.; Bacchi, C.E. Clinicopathologic and molecular features of 122 Brazilian cases of nodal and extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type, with EBV subtyping analysis. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2011, 35, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahara, M.; Kishibe, K.; Bandoh, N.; Nonaka, S.; Harabuchi, Y. P53, N- and K-Ras, and beta-catenin gene mutations and prognostic factors in nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma from Hokkaido, Japan. Hum. Pathol 2004, 35, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harabuchi, Y.; Kataura, A.; Imai, K. Circulating intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and its cellular expression in head and neck non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas, including lethal midline granuloma. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1996, 105, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaulard, P.; Henni, T.; Marolleau, J.P.; Haioun, C.; Henni, Z.; Voisin, M.C.; Divine, M.; Goossens, M.; Farcet, J.P.; Reyes, F. Lethal midline granuloma (polymorphic reticulosis) and lymphomatoid granulomatosis. Evidence for a monoclonal T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder. Cancer 1988, 62, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, T.Y.; Lee, H.T.; Chang, S.H. Nasal-type T/natural killer cell angiocentric lymphoma, Epstein-Barr virus-associated, and showing clonal T-cell receptor gamma gene rearrangement. Br. J. Dermatol. 1999, 140, 505–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, A.K.; Tao, Q.; Srivastava, G.; Ho, F.C. Nasal NK- and T-cell lymphomas share the same type of Epstein-Barr virus latency as nasopharyngeal carcinoma and Hodgkin’s disease. Int. J. Cancer 1996, 68, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Kim, Y.A.; Jeon, Y.K.; Park, S.S.; Heo, D.S.; Kim, C.W. Comparative analysis of NK/T-cell lymphoma and peripheral T-cell lymphoma in Korea: Clinicopathological correlations and analysis of EBV strain type and 30-bp deletion variant LMP1. Pathol. Int. 2003, 53, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutt-Fletcher, L.M. Epstein-Barr virus entry. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 7825–7832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borza, C.M.; Hutt-Fletcher, L.M. Alternate replication in B cells and epithelial cells switches tropism of Epstein-Barr virus. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tugizov, S.M.; Berline, J.W.; Palefsky, J.M. Epstein-Barr virus infection of polarized tongue and nasopharyngeal epithelial cells. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostopoulos, I.; Hummel, M.; Kreschel, C.; Stein, H. Morphology, immunophenotype, and distribution of latently and/or productively Epstein-Barr virus-infected cells in acute infectious mononucleosis: Implications for the interindividual infection route of Epstein-Barr virus. Blood 1995, 85, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hudnall, S.D.; Ge, Y.; Wei, L.; Yang, N.P.; Wang, H.Q.; Chen, T. Distribution and phenotype of Epstein-Barr virus-infected cells in human pharyngeal tonsils. Mod. Pathol. 2005, 18, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischer, E.; Delibrias, C.; Kazatchkine, M.D. Expression of CR2 (the C3dg/EBV receptor, CD21) on normal human peripheral blood T lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 1991, 146, 865–869. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Paterson, R.L.; Kelleher, C.; Amankonah, T.D.; Streib, J.E.; Xu, J.W.; Jones, J.F.; Gelfand, E.W. Model of Epstein-Barr virus infection of human thymocytes: Expression of viral genome and impact on cellular receptor expression in the T-lymphoblastic cell line, HPB-ALL. Blood 1995, 85, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischer, E.M.; Mouhoub, A.; Maillet, F.; Frémeaux-Bacchi, V.; Krief, C.; Gould, H.; Berrih-Aknin, S.; Kazatchkine, M.D. Expression of CD21 is developmentally regulated during thymic maturation of human T lymphocytes. Int. Immunol. 1999, 11, 1841–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Endo, R.; Yoshioka, M.; Ebihara, T.; Ishiguro, N.; Kikuta, H.; Kobayashi, K. Clonal expansion of multiphenotypic Epstein-Barr virus-infected lymphocytes in chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection. Med. Hypotheses 2004, 63, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohga, S.; Ishimura, M.; Yoshimoto, G.; Miyamoto, T.; Takada, H.; Tanaka, T.; Ohshima, K.; Ogawa, Y.; Imadome, K.; Abe, Y.; et al. Clonal origin of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-infected T/NK-cell subpopulations in EBV-positive T/NK-cell lymphoproliferative disorders of childhood. J. Clin. Virol. 2011, 51, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, N.A.; Coleman, C.B.; Gewurz, B.E.; Rochford, R. CD21 (Complement Receptor 2) Is the Receptor for Epstein-Barr Virus Entry into T Cells. J. Virol. 2020, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabiasco, J.; Vercellone, A.; Meggetto, F.; Hudrisier, D.; Brousset, P.; Fournié, J.J. Acquisition of viral receptor by NK cells through immunological synapse. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 5993–5998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.H.; Choi, J.; Ahn, Y.O.; Kim, T.M.; Heo, D.S. CD21-independent Epstein-Barr virus entry into NK cells. Cell Immunol. 2018, 327, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joly, E.; Hudrisier, D. What is trogocytosis and what is its purpose? Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tien, H.F.; Su, I.J.; Tang, J.L.; Liu, M.C.; Lee, F.Y.; Chen, Y.C.; Chuang, S.M. Clonal chromosomal abnormalities as direct evidence for clonality in nasal T/natural killer cell lymphomas. Br. J. Haematol. 1997, 97, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.F.; Chan, J.K.; Kwong, Y.L. Identification of del(6)(q21q25) as a recurring chromosomal abnormality in putative NK cell lymphoma/leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 1997, 98, 922–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siu, L.L.; Chan, V.; Chan, J.K.; Wong, K.F.; Liang, R.; Kwong, Y.L. Consistent patterns of allelic loss in natural killer cell lymphoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 157, 1803–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, H.S.; Su, I.J.; Lin, Y.C.; Chen, J.S.; Fang, S.Y. A 2.6 Mb interval on chromosome 6q25.2-q25.3 is commonly deleted in human nasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2003, 122, 590–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takakuwa, T.; Dong, Z.; Nakatsuka, S.; Kojya, S.; Harabuchi, Y.; Yang, W.I.; Nagata, S.; Aozasa, K. Frequent mutations of Fas gene in nasal NK/T cell lymphoma. Oncogene 2002, 21, 4702–4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, L.; Liang, A.C.; Lu, L.; Au, W.Y.; Kwong, Y.L.; Liang, R.H.; Srivastava, G. Frequent deletion of Fas gene sequences encoding death and transmembrane domains in nasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2002, 161, 2123–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, T.; Hongyo, T.; Syaifudin, M.; Nomura, T.; Dong, Z.; Shingu, N.; Kojya, S.; Nakatsuka, S.; Aozasa, K. Mutations of the p53 gene in nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma. Lab. Investig. 2000, 80, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoshida, Y.; Hongyo, T.; Jia, X.; He, Y.; Hasui, K.; Dong, Z.; Luo, W.J.; Ham, M.F.; Nomura, T.; Aozasa, K. Analysis of p53, K-ras, c-kit, and beta-catenin gene mutations in sinonasal NK/T cell lymphoma in northeast district of China. Cancer Sci. 2003, 94, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; Kremer, M.; Keller, G.; Nathrath, M.; Gamboa-Dominguez, A.; Meneses, A.; Luna-Contreras, L.; Cabras, A.; Hoefler, H.; Mohar, A.; et al. p53 Mutations in nasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma from Mexico: Association with large cell morphology and advanced disease. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 159, 2095–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongyo, T.; Hoshida, Y.; Nakatsuka, S.; Syaifudin, M.; Kojya, S.; Yang, W.I.; Min, Y.H.; Chan, H.; Kim, C.H.; Harabuchi, Y.; et al. p53, K-ras, c-kit and beta-catenin gene mutations in sinonasal NK/T-cell lymphoma in Korea and Japan. Oncol. Rep. 2005, 13, 265–271. [Google Scholar]
- Tse, E.; Kwong, Y.L. The diagnosis and management of NK/T-cell lymphomas. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 10, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheson, B.D.; Fisher, R.I.; Barrington, S.F.; Cavalli, F.; Schwartz, L.H.; Zucca, E.; Lister, T.A. Recommendations for initial evaluation, staging, and response assessment of Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma: The Lugano classification. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3059–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, K.I.; Chan, L.Y.; Chan, W.Y.; Johnson, P.J.; Lo, Y.M. Quantitative analysis of circulating cell-free Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DNA levels in patients with EBV-associated lymphoid malignancies. Br. J. Haematol. 2000, 111, 239–246. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, R.; Yamaguchi, M.; Izutsu, K.; Yamamoto, G.; Takada, K.; Harabuchi, Y.; Isobe, Y.; Gomyo, H.; Koike, T.; Okamoto, M.; et al. Prospective measurement of Epstein-Barr virus-DNA in plasma and peripheral blood mononuclear cells of extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Blood 2011, 118, 6018–6022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valadi, H.; Ekström, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjöstrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lötvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Komabayashi, Y.; Kishibe, K.; Nagato, T.; Ueda, S.; Takahara, M.; Harabuchi, Y. Circulating Epstein-Barr virus-encoded micro-RNAs as potential biomarkers for nasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 35, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagato, T.; Kobayashi, H.; Kishibe, K.; Takahara, M.; Ogino, T.; Ishii, H.; Oikawa, K.; Aoki, N.; Sato, K.; Kimura, S.; et al. Expression of interleukin-9 in nasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma cell lines and patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 8250–8257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moriai, S.; Takahara, M.; Ogino, T.; Nagato, T.; Kishibe, K.; Ishii, H.; Katayama, A.; Shimizu, N.; Harabuchi, Y. Production of interferon-{gamma}-inducible protein-10 and its role as an autocrine invasion factor in nasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 6771–6779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Komabayashi, Y.; Kishibe, K.; Nagato, T.; Ueda, S.; Takahara, M.; Harabuchi, Y. Downregulation of miR-15a due to LMP1 promotes cell proliferation and predicts poor prognosis in nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma. Am. J. Hematol. 2014, 89, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahara, M.; Nagato, T.; Komabayashi, Y.; Yoshino, K.; Ueda, S.; Kishibe, K.; Harabuchi, Y. Soluble ICAM-1 secretion and its functional role as an autocrine growth factor in nasal NK/T cell lymphoma cells. Exp. Hematol. 2013, 41, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumai, T.; Matsuda, Y.; Ohkuri, T.; Oikawa, K.; Ishibashi, K.; Aoki, N.; Kimura, S.; Harabuchi, Y.; Celis, E.; Kobayashi, H. c-Met is a novel tumor associated antigen for T-cell based immunotherapy against NK/T cell lymphoma. Oncoimmunology 2015, 4, e976077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagato, T.; Ueda, S.; Takahara, M.; Kishibe, K.; Komabayashi, Y.; Kumai, T.; Ohara, K.; Hirata-Nozaki, Y.; Harabuchi, S.; Hayashi, R.; et al. Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 and survivin as potential therapeutic targets against nasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Lab. Investig. 2019, 99, 612–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahara, M.; Kis, L.L.; Nagy, N.; Liu, A.; Harabuchi, Y.; Klein, G.; Klein, E. Concomitant increase of LMP1 and CD25 (IL-2-receptor alpha) expression induced by IL-10 in the EBV-positive NK lines SNK6 and KAI3. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 2775–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshino, K.; Kishibe, K.; Nagato, T.; Ueda, S.; Komabayashi, Y.; Takahara, M.; Harabuchi, Y. Expression of CD70 in nasal natural killer/T cell lymphoma cell lines and patients; its role for cell proliferation through binding to soluble CD27. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 160, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumai, T.; Nagato, T.; Kobayashi, H.; Komabayashi, Y.; Ueda, S.; Kishibe, K.; Ohkuri, T.; Takahara, M.; Celis, E.; Harabuchi, Y. CCL17 and CCL22/CCR4 signaling is a strong candidate for novel targeted therapy against nasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2015, 64, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishii, H.; Takahara, M.; Nagato, T.; Kis, L.L.; Nagy, N.; Kishibe, K.; Harabuchi, Y.; Klein, E. Monocytes enhance cell proliferation and LMP1 expression of nasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma cells by cell contact-dependent interaction through membrane-bound IL-15. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 130, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demoulin, J.B.; Renauld, J.C. Interleukin 9 and its receptor: An overview of structure and function. Int. Rev. Immunol. 1998, 16, 345–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Aozasa, K.; Oshimi, K.; Takada, K. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-encoded RNA promotes growth of EBV-infected T cells through interleukin-9 induction. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 5332–5337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marlin, S.D.; Springer, T.A. Purified intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) is a ligand for lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 (LFA-1). Cell 1987, 51, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, J.C.; Dummer, R.; Hartmann, A.A.; Burg, G.; Schmidt, R.E. Shedding of ICAM-1 from human melanoma cell lines induced by IFN-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Functional consequences on cell-mediated cytotoxicity. J. Immunol. 1991, 147, 4398–4401. [Google Scholar]
- Najjar, I.; Baran-Marszak, F.; Le Clorennec, C.; Laguillier, C.; Schischmanoff, O.; Youlyouz-Marfak, I.; Schlee, M.; Bornkamm, G.W.; Raphaël, M.; Feuillard, J.; et al. Latent membrane protein 1 regulates STAT1 through NF-kappaB-dependent interferon secretion in Epstein-Barr virus-immortalized B cells. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 4936–4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taub, D.D.; Lloyd, A.R.; Conlon, K.; Wang, J.M.; Ortaldo, J.R.; Harada, A.; Matsushima, K.; Kelvin, D.J.; Oppenheim, J.J. Recombinant human interferon-inducible protein 10 is a chemoattractant for human monocytes and T lymphocytes and promotes T cell adhesion to endothelial cells. J. Exp. Med. 1993, 177, 1809–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vockerodt, M.; Pinkert, D.; Smola-Hess, S.; Michels, A.; Ransohoff, R.M.; Tesch, H.; Kube, D. The Epstein-Barr virus oncoprotein latent membrane protein 1 induces expression of the chemokine IP-10: Importance of mRNA half-life regulation. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 114, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, K.M.; Izumi, K.M.; Kieff, E. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 is essential for B-lymphocyte growth transformation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 9150–9154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Liebowitz, D.; Kieff, E. An EBV membrane protein expressed in immortalized lymphocytes transforms established rodent cells. Cell 1985, 43, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöblom, A.; Nerstedt, A.; Jansson, A.; Rymo, L. Domains of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 (EBNA2) involved in the transactivation of the latent membrane protein 1 and the EBNA Cp promoters. J. Gen. Virol. 1995, 76 Pt 11, 2669–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kis, L.L.; Nishikawa, J.; Takahara, M.; Nagy, N.; Matskova, L.; Takada, K.; Elmberger, P.G.; Ohlsson, A.; Klein, G.; Klein, E. In vitro EBV-infected subline of KMH2, derived from Hodgkin lymphoma, expresses only EBNA-1, while CD40 ligand and IL-4 induce LMP-1 but not EBNA-2. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 113, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musso, T.; Calosso, L.; Zucca, M.; Millesimo, M.; Ravarino, D.; Giovarelli, M.; Malavasi, F.; Ponzi, A.N.; Paus, R.; Bulfone-Paus, S. Human monocytes constitutively express membrane-bound, biologically active, and interferon-gamma-upregulated interleukin-15. Blood 1999, 93, 3531–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Alvaro, I.; Domínguez-Jiménez, C.; Ortiz, A.M.; Núñez-González, V.; Roda-Navarro, P.; Fernández-Ruiz, E.; Sancho, D.; Sánchez-Madrid, F. Interleukin-15 and interferon-gamma participate in the cross-talk between natural killer and monocytic cells required for tumour necrosis factor production. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, R88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Kita, K.; Miwa, H.; Nishii, K.; Oka, K.; Ohno, T.; Shirakawa, S.; Fukumoto, M. Frequent expression of P-glycoprotein/MDR1 by nasal T-cell lymphoma cells. Cancer 1995, 76, 2351–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imashuku, S. Advances in the management of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Int. J. Hematol. 2000, 72, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Suzuki, R.; Kwong, Y.L.; Kim, W.S.; Hasegawa, Y.; Izutsu, K.; Suzumiya, J.; Okamura, T.; Nakamura, S.; Kawa, K.; et al. Phase I study of dexamethasone, methotrexate, ifosfamide, L-asparaginase, and etoposide (SMILE) chemotherapy for advanced-stage, relapsed or refractory extranodal natural killer (NK)/T-cell lymphoma and leukemia. Cancer Sci. 2008, 99, 1016–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Tobinai, K.; Oguchi, M.; Ishizuka, N.; Kobayashi, Y.; Isobe, Y.; Ishizawa, K.; Maseki, N.; Itoh, K.; Usui, N.; et al. Concurrent chemoradiotherapy for localized nasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma: An updated analysis of the Japan Clinical Oncology Group study JCOG0211. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 4044–4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Suzuki, R. JSH practical guidelines for hematological malignancies, 2018: II. Lymphoma-9. Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type (ENKL). Int. J. Hematol. 2019, 109, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCCN Guidelines T-Cell Lymphomas Version 1.2021. Available online: www.nccn.org/patients (accessed on 29 May 2021).
- Kim, T.M.; Kim, D.W.; Kang, Y.K.; Chung, J.; Song, H.S.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, B.S.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, H.; Yang, S.H.; et al. A phase II study of ifosfamide, methotrexate, etoposide, and prednisolone for previously untreated stage I/II extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type: A multicenter trial of the Korean Cancer Study Group. Oncologist 2014, 19, 1129–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Kwong, Y.L.; Kim, W.S.; Maeda, Y.; Hashimoto, C.; Suh, C.; Izutsu, K.; Ishida, F.; Isobe, Y.; Sueoka, E.; et al. Phase II study of SMILE chemotherapy for newly diagnosed stage IV, relapsed, or refractory extranodal natural killer (NK)/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type: The NK-Cell Tumor Study Group study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 4410–4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaccard, A.; Gachard, N.; Marin, B.; Rogez, S.; Audrain, M.; Suarez, F.; Tilly, H.; Morschhauser, F.; Thieblemont, C.; Ysebaert, L.; et al. Efficacy of L-asparaginase with methotrexate and dexamethasone (AspaMetDex regimen) in patients with refractory or relapsing extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, a phase 2 study. Blood 2011, 117, 1834–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Suzuki, R.; Oguchi, M. Advances in the treatment of extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Blood 2018, 131, 2528–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharfan-Dabaja, M.A.; Kumar, A.; Ayala, E.; Hamadani, M.; Reimer, P.; Gisselbrecht, C.; d’Amore, F.; Jantunen, E.; Ishida, T.; Bazarbachi, A.; et al. Clinical practice recommendations on indication and timing of hematopoietic cell transplantation in mature T CELL and NK/T cell lymphomas: An International collaborative effort on behalf of the guidelines committee of the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2017, 23, 1826–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Tobinai, K.; Oguchi, M.; Ishizuka, N.; Kobayashi, Y.; Isobe, Y.; Ishizawa, K.; Maseki, N.; Itoh, K.; Usui, N.; et al. Phase I/II study of concurrent chemoradiotherapy for localized nasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma: Japan Clinical Oncology Group study JCOG0211. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5594–5600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahara, M. nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma. Jpn. J. Rhinool. 2019, 58, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.H.; Bagot, M.; Pinter-Brown, L.; Rook, A.H.; Porcu, P.; Horwitz, S.M.; Whittaker, S.; Tokura, Y.; Vermeer, M.; Zinzani, P.L.; et al. Mogamulizumab versus vorinostat in previously treated cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (MAVORIC): An international, open-label, randomised, controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1192–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagato, T.; Ohkuri, T.; Ohara, K.; Hirata, Y.; Kishibe, K.; Komabayashi, Y.; Ueda, S.; Takahara, M.; Kumai, T.; Ishibashi, K.; et al. Programmed death-ligand 1 and its soluble form are highly expressed in nasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma: A potential rationale for immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2017, 66, 877–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwong, Y.L.; Chan, T.S.Y.; Tan, D.; Kim, S.J.; Poon, L.M.; Mow, B.; Khong, P.L.; Loong, F.; Au-Yeung, R.; Iqbal, J.; et al. PD1 blockade with pembrolizumab is highly effective in relapsed or refractory NK/T-cell lymphoma failing l-asparaginase. Blood 2017, 129, 2437–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schag, K.; Schmidt, S.M.; Müller, M.R.; Weinschenk, T.; Appel, S.; Weck, M.M.; Grünebach, F.; Stevanovic, S.; Rammensee, H.G.; Brossart, P. Identification of C-met oncogene as a broadly expressed tumor-associated antigen recognized by cytotoxic T-lymphocytes. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 3658–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mortenson, E.D.; Park, S.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, S.; Fu, Y.X. Effective anti-neu-initiated antitumor responses require the complex role of CD4+ T cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 1476–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumai, T.; Kobayashi, H.; Harabuchi, Y.; Celis, E. Peptide vaccines in cancer-old concept revisited. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2017, 45, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demachi-Okamura, A.; Ito, Y.; Akatsuka, Y.; Tsujimura, K.; Morishima, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Kuzushima, K. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) latent membrane protein-1-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes targeting EBV-carrying natural killer cell malignancies. Eur. J. Immunol. 2006, 36, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Nagato, T.; Takahara, M.; Sato, K.; Kimura, S.; Aoki, N.; Azumi, M.; Tateno, M.; Harabuchi, Y.; Celis, E. Induction of EBV-latent membrane protein 1-specific MHC class II-restricted T-cell responses against natural killer lymphoma cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fox, C.P.; Haigh, T.A.; Taylor, G.S.; Long, H.M.; Lee, S.P.; Shannon-Lowe, C.; O’Connor, S.; Bollard, C.M.; Iqbal, J.; Chan, W.C.; et al. A novel latent membrane 2 transcript expressed in Epstein-Barr virus-positive NK- and T-cell lymphoproliferative disease encodes a target for cellular immunotherapy. Blood 2010, 116, 3695–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Country | Japan | Japan | China | Korea | Korea | Brazil |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | 2019 | 2010 | 2008 | 2006 | 2005 | 2011 |
| Authors | Harabuchi et al. [18] | Suzuki et al. [44] | Wu et al. [45] | Lee et al. [3] | Kim et al. [46] | Gualco et al. [47] |
| Case number | 62 | 123 | 115 | 262 | 114 | 122 |
| Age | ||||||
| Range (mean) | 20–85 (53) | 14–89 (52) | (47) | 9–89 (45) | ||
| >60 | 22 (35%) | 20 (18%) | 55 (21%) | 20 (18%) | ||
| Sex | ||||||
| Male/Female | 43/19 | 81/42 | 78/29 | 170/92 | 72/42 | 85/37 |
| Clinical stage | ||||||
| I + II (%) | 57 (92%) | 84 (68%) | 87 (76%) | 200 (76%) | 114 (100%) | 25 (81%) |
| I/II/III/IV | 44/13/1/4 | 55/29/8/31 | 61/26/8/12 | 83/31/0/0 | 23/2/2/4 | |
| Symptom | ||||||
| Nasal obstruction | 49 (70%) | 84 (73%) | 97 (80%) | |||
| Bloody rhinorrhea | 29 (47%) | 50 (44%) | ||||
| B symptom | 32 (52%) | 56 (46%) | 57 (53%) | 92 (35%) | 35 (31%) | |
| Involved tissues | ||||||
| Nasal cavity | 60 (97%) | 111 (90%) | 115 (100%) | 73 (64%) | 97 (80%) | |
| Hard plate | 11 (18%) | 8 (7%) | 15 (13%) | |||
| Facial skin | 13 (21%) | 19 (15%) | ||||
| Pharynx | 13 (21%) | 28 (23%) | 27 (23%) | 21 (18%) | ||
| Lymph nodes | 10 (16%) | 31 (25%) | 21 (18%) | |||
| Skin | 9 (15%) | |||||
| Lung/Liver | 10 (16%) | 10 (8%) | 4 (2%) | |||
| Digestive tracts | 5 (8%) | 10 (4%) | ||||
| Bone marrow | 3 (5%) | 9 (7%) | 3 (3%) | 16 (6%) | ||
| Pathologic findings (Positive/Total cases) | ||||||
| CD3 | 25/47 (53%) | 68/86 (79%) | 105/108 (97%) | 104 (98%) | 116/122 (95%) | |
| CD43 | 31/35 (89%) | 15/17 (88%) | ||||
| CD45RO | 25/35 (71%) | 44/49 (90%) | 103/110 (94%) | 61/62 (98%) | ||
| CD20 | 0/59 (0%) | 1/14 (7%) | 0/115 (0%) | 0/106 (0%) | ||
| CD56 | 61/62 (98%) | 115/120 (96%) | 95/105 (91%) | 262 (100%) | 94/106 (89%) | 103/122 (84%) |
| CD16 | 5/11 (45%) | 9/40 (23%) | ||||
| EBER | 59/62 (95%) | 93/94 (99%) | 106/110 (96%) | 262 (100%) | 46/61 (75%) | 74/74 (100%) |
| LMP1 | 25/53 (47%) | 10/122 (8%) | ||||
| Gene rearrangement (Positive/Total cases) | ||||||
| B cell receptor | 0/34 (0%) | |||||
| T cell receptor | 12/34 (35%) | 7/74 (10%) |
| Case No | Age | Gender | Systemic Symtom | Performance Status | Clinical Stage | Lesion | LDH (IU/L) | sIL-2R (U/mL) | Radiation (Gy) | Response | EBV-DNA (Copy/mL) | Observation Period (Months) | Outcome | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Treatment | After Treatment | |||||||||||||
| 1 | 48 | Female | + | 1 | I | NC | 205 | 346 | 56 | CR | 391 | <100 | 111 | Disease free |
| 2 | 60 | Male | - | 0 | I | NC | 236 | 345 | 56 | CR | 149 | <100 | 107 | Disease free |
| 3 | 64 | Male | - | 0 | I | NC | 162 | 290 | 54 | CR | 120 | <100 | 107 | Disease free |
| 4 | 48 | Male | + | 1 | I | NC | 176 | 447 | 54 | CR | 1640 | <100 | 103 | Disease free |
| 5 | 40 | Female | + | 1 | I | NC | 144 | 604 | 54 | CR | 160 | <100 | 100 | Disease free |
| 6 | 70 | Male | - | 0 | I | NC | 152 | 528 | 54 | CR | 100 | <100 | 89 | Disease free |
| 7 | 21 | Male | + | 0 | I | NC | 177 | 529 | 54 | CR | 100 | <100 | 73 | Disease free |
| 8 | 63 | Male | - | 0 | I | NC | 151 | 530 | 54 | CR | <100 | <100 | 72 | Disease free |
| 9 | 58 | Male | - | 0 | II | NC | 765 | 2410 | 54 | CR | 270,000 | <100 | 68 | Disease free |
| 10 | 47 | Male | - | 0 | I | NC | 164 | 298 | 54 | CR | <100 | <100 | 48 | Disease free |
| 11 | 67 | Male | + | 0 | I | NC | 626 | 990 | 54 | CR | 62000 | <100 | 42 | Disease free |
| 12 | 21 | Male | + | 0 | II | NC | 205 | 406 | 54 | CR | 550 | <100 | 39 | Disease free |
| 13 | 67 | Male | - | 0 | I | NC | 293 | 580 | 54 | CR | 790 | <100 | 84 | Disease free |
| 14 | 79 | Male | - | 0 | I | NC | 193 | 452 | 54 | CR | <100 | <100 | 30 | Died with disease |
| 15 | 68 | Male | - | 0 | I | NC | 143 | 237 | 54 | CR | 150 | <100 | 48 | Disease free |
| 16 | 71 | Male | - | 0 | I | NC | 144 | 268 | 54 | CR | <100 | <100 | 40 | Alive with disease |
| 17 | 79 | Male | - | 0 | I | NC | 168 | 633 | 54 | CR | <100 | <100 | 36 | Disease free |
| 18 | 66 | Male | - | 0 | I | NC | 209 | 420 | 54 | CR | 450 | <100 | 26 | Disease free |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takahara, M.; Kumai, T.; Kishibe, K.; Nagato, T.; Harabuchi, Y. Extranodal NK/T-Cell Lymphoma, Nasal Type: Genetic, Biologic, and Clinical Aspects with a Central Focus on Epstein–Barr Virus Relation. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1381. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9071381
Takahara M, Kumai T, Kishibe K, Nagato T, Harabuchi Y. Extranodal NK/T-Cell Lymphoma, Nasal Type: Genetic, Biologic, and Clinical Aspects with a Central Focus on Epstein–Barr Virus Relation. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(7):1381. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9071381
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakahara, Miki, Takumi Kumai, Kan Kishibe, Toshihiro Nagato, and Yasuaki Harabuchi. 2021. "Extranodal NK/T-Cell Lymphoma, Nasal Type: Genetic, Biologic, and Clinical Aspects with a Central Focus on Epstein–Barr Virus Relation" Microorganisms 9, no. 7: 1381. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9071381
APA StyleTakahara, M., Kumai, T., Kishibe, K., Nagato, T., & Harabuchi, Y. (2021). Extranodal NK/T-Cell Lymphoma, Nasal Type: Genetic, Biologic, and Clinical Aspects with a Central Focus on Epstein–Barr Virus Relation. Microorganisms, 9(7), 1381. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9071381






