Lactobacillus plantarum TWK10 Improves Muscle Mass and Functional Performance in Frail Older Adults: A Randomized, Double-Blind Clinical Trial
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Subjects
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Maximum Handgrip Strength Test
2.5. Functional Performance
2.6. Body Composition and Bone Mass Density (BMD)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Subject Recruitment
3.2. Effect of TWK10 Supplementation on Elderly Grip Strength
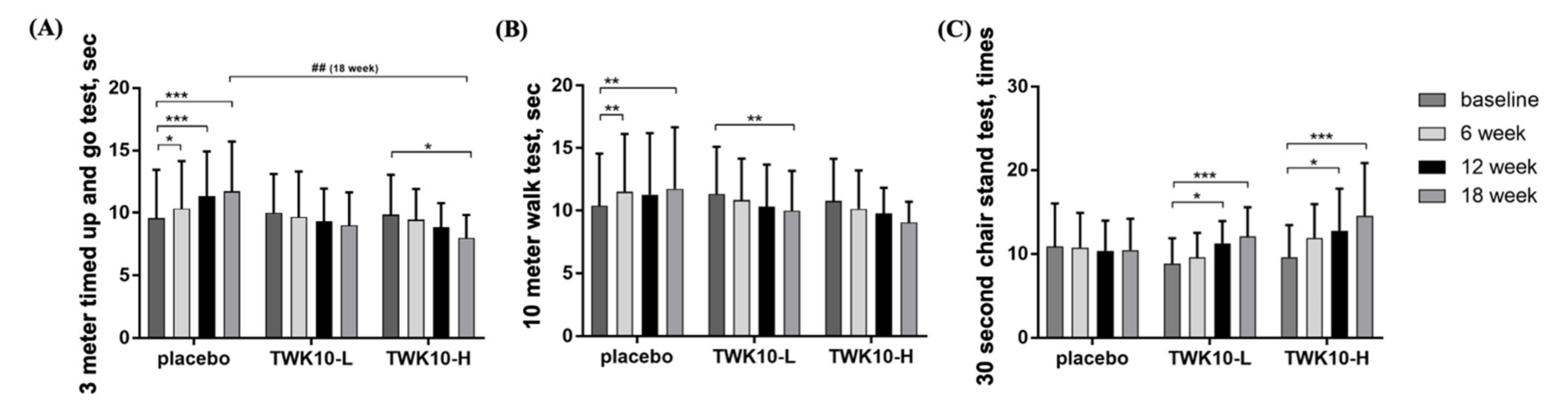
3.3. Effect of TWK10 Supplementation on Functional Performance of Elderly
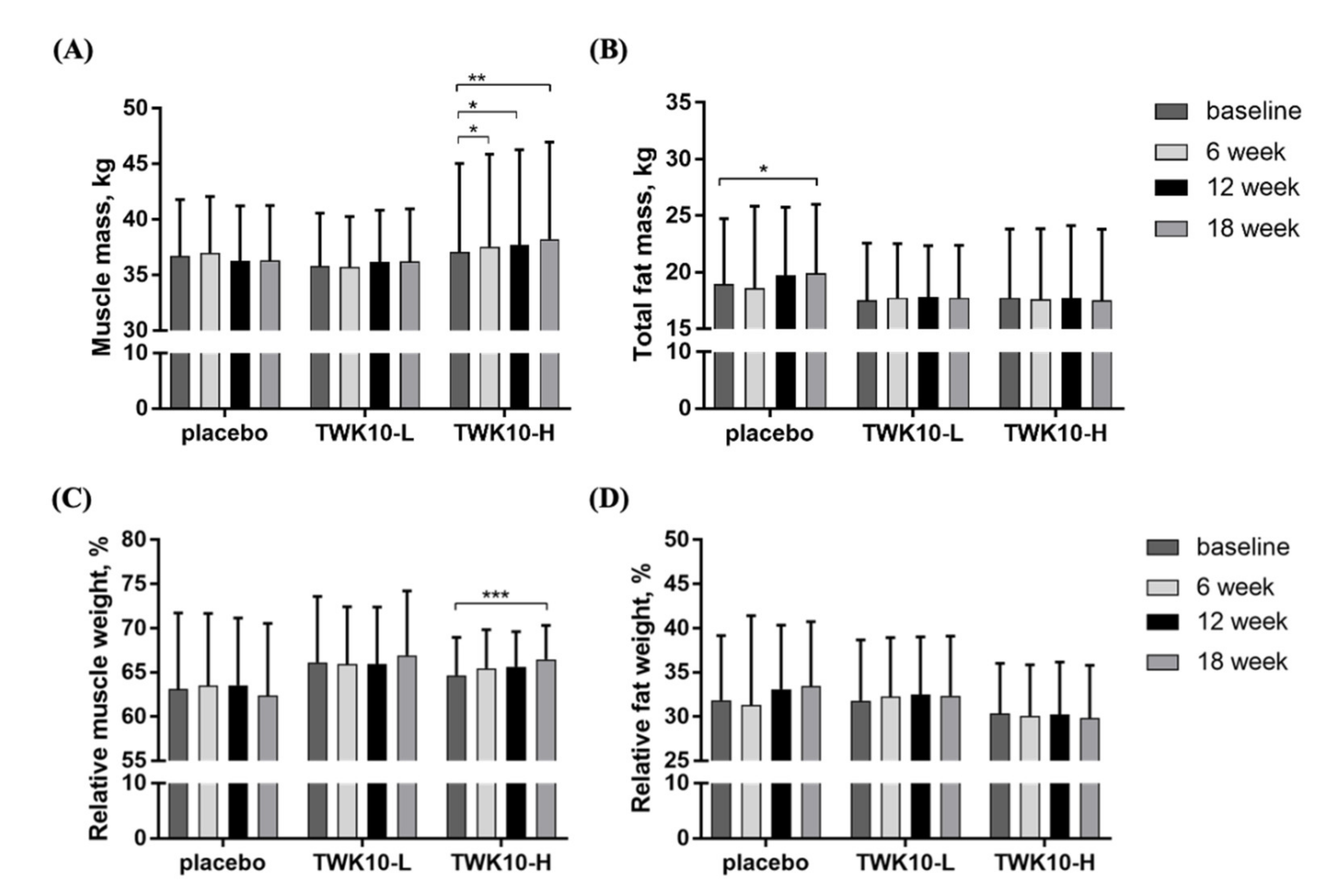
3.4. Effect of TWK10 Supplementation on Body Composition of the Elderly
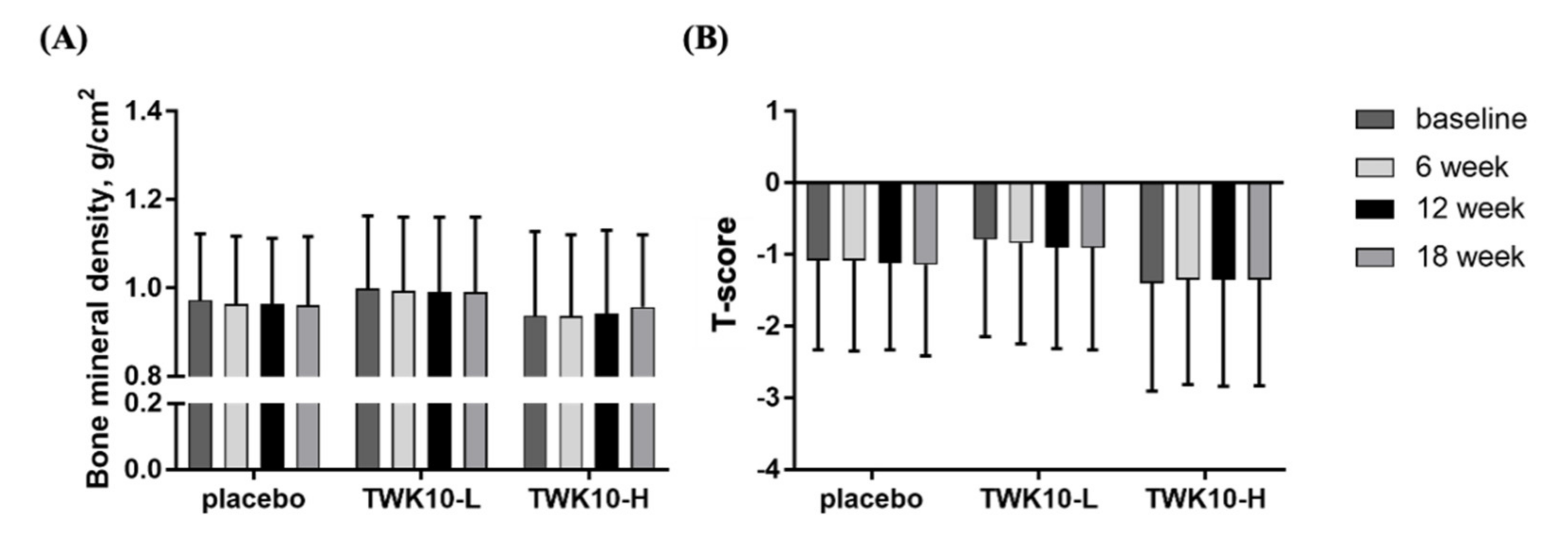
3.5. Effect of TWK10 Supplementation on Bone Mineral Density (BMD) of Elderly
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suzman, R.; Beard, J.R.; Boerma, T.; Chatterji, S. Health in an ageing world—What do we know? Lancet 2015, 385, 484–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzetti, E.; Calvani, R.; Tosato, M.; Cesari, M.; Di Bari, M.; Cherubini, A.; Collamati, A.; D’Angelo, E.; Pahor, M.; Bernabei, R.; et al. SPRINTT Consortium. Sarcopenia: An overview. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 29, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, A.; Dennison, E. Measuring the musculoskeletal aging phenotype. Maturitas 2016, 93, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenberg, I.H. Sarcopenia: Origins and clinical relevance. J. Nutr. 1997, 127, 990S–991S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Writing Group for the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People 2 (EWGSOP2), and the Extended Group for EWGSOP2. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mijnarends, D.M.; Schols, J.M.; Meijers, J.M.; Tan, F.E.; Verlaan, S.; Luiking, Y.C.; Morley, J.E.; Halfens, R.J. Instruments to assess sarcopenia and physical frailty in older people living in a community (care) setting: Similarities and discrepancies. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2015, 16, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clegg, A.; Young, J.; Iliffe, S.; Rikkert, M.O.; Rockwood, K. Frailty in elderly people. Lancet 2013, 381, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dent, E.; Morley, J.E.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Woodhouse, L.; Rodríguez-Mañas, L.; Fried, L.P.; Woo, J.; Aprahamian, I.; Sanford, A.; Lundy, J.; et al. Physical Frailty: ICFSR International Clinical Practice Guidelines for Identification and Management. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2019, 23, 771–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.H.; Liao, C.C.; Huang, C.H.; Tung, Y.T.; Chang, H.C.; Hsu, M.C.; Huang, C.C. Proteomics Analysis to Identify and Characterize the Biomarkers and Physical Activities of Non-Frail and Frail Older Adults. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 14, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eckardt, N. Lower-extremity resistance training on unstable surfaces improves proxies of muscle strength, power and balance in healthy older adults: A randomised control trial. BMC Geriatr. 2016, 16, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Naczk, M.; Marszalek, S.; Naczk, A. Inertial Training Improves Strength, Balance, and Gait Speed in Elderly Nursing Home Residents. Clin. Interv. Aging 2020, 15, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liguori, I.; Russo, G.; Aran, L.; Bulli, G.; Curcio, F.; Della-Morte, D.; Gargiulo, G.; Testa, G.; Cacciatore, F.; Bonaduce, D.; et al. Sarcopenia: Assessment of disease burden and strategies to improve outcomes. Clin. Interv. Aging 2018, 13, 913–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodrigo-Claverol, M.; Casanova-Gonzalvo, C.; Malla-Clua, B.; Rodrigo-Claverol, E.; Jové-Naval, J.; Ortega-Bravo, M. Animal-Assisted Intervention Improves Pain Perception in Polymedicated Geriatric Patients with Chronic Joint Pain: A Clinical Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landi, F.; Calvani, R.; Tosato, M.; Martone, A.M.; Ortolani, E.; Savera, G.; Sisto, A.; Marzetti, E. Anorexia of Aging: Risk Factors, Consequences, and Potential Treatments. Nutrients 2016, 8, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Huang, Y.; Yu, X. A Narrative Review of Gut-Muscle Axis and Sarcopenia: The Potential Role of Gut Microbiota. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, 14, 1263–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martí, J.M.; Martínez-Martínez, D.; Rubio, T.; Gracia, C.; Peña, M.; Latorre, A.; Moya, A.P.; Garay, C. Health and Disease Imprinted in the Time Variability of the Human Microbiome. mSystems 2017, 2, e00144–e00216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ticinesi, A.; Mancabelli, L.; Tagliaferri, S.; Nouvenne, A.; Milani, C.; Del Rio, D.; Lauretani, F.; Maggio, M.G.; Ventura, M.; Meschi, T. The Gut-Muscle Axis in Older Subjects with Low Muscle Mass and Performance: A Proof of Concept Study Exploring Fecal Microbiota Composition and Function with Shotgun Metagenomics Sequencing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations; World Health Organization. Health and Nutritional Properties of Probiotics in Food Including Powder Milk with Live Lactic Acid Bacteria; Joint FAO/WHO Expert Consultation: Córdoba, Argentina, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Van Tongeren, S.P.; Slaets, J.P.; Harmsen, H.J.; Welling, G.W. Fecal microbiota composition and frailty. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 6438–6442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaźmierczak-Siedlecka, K.; Folwarski, M.; Skonieczna-Żydecka, K.; Ruszkowski, J.; Makarewicz, W. The use of Lactobacillus plantarum 299v (DSM 9843) in cancer patients receiving home enteral nutrition—Study protocol for a randomized, double-blind, and placebo-controlled trial. Nutr. J. 2020, 19, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bested, A.C.; Logan, A.C.; Selhub, E.M. Intestinal microbiota, probiotics and mental health: From Metchnikoff to modern advances: Part II—Contemporary contextual research. Gut Pathog. 2013, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.M.; Wei, L.; Chiu, Y.S.; Hsu, Y.J.; Tsai, T.Y.; Wang, M.F.; Huang, C.C. Lactobacillus plantarum TWK10 Supplementation Improves Exercise Performance and Increases Muscle Mass in Mice. Nutrients 2016, 8, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.C.; Lee, M.C.; Lee, C.C.; Ng, K.S.; Hsu, Y.J.; Tsai, T.Y.; Young, S.L.; Lin, J.S.; Huang, C.C. Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum TWK10 on Exercise Physiological Adaptation, Performance, and Body Composition in Healthy Humans. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Koyanagi, A.; Smith, L.; Hu, L.; Colditz, G.A.; Toriola, A.T.; López Sánchez, G.F.; Vancampfort, D.; Hamer, M.; Stubbs, B.; et al. Hand grip strength and cognitive function among elderly cancer survivors. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira de Moraes Filho, A.; Chaves, S.N.; Martins, W.R.; Tolentino, G.P.; de Cássia Pereira Pinto Homem, R.; Landim de Farias, G.; Fischer, B.L.; Oliveira, J.A.; Pereira, S.K.A.; Vidal, S.E.; et al. Progressive Resistance Training Improves Bradykinesia, Motor Symptoms and Functional Performance in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Clin. Interv. Aging. 2020, 15, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krugh, M.; Langaker, M.D. Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Osawa, R.; Ikegami, S.; Horiuchi, H.; Tokida, R.; Kato, H.; Takahashi, J. Osteoporosis Detection by Physical Function Tests in Resident Health Exams: A Japanese Cohort Survey Randomly Sampled from a Basic Resident Registry. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, W.K.; Williams, J.; Atherton, P.; Larvin, M.; Lund, J.; Narici, M. Sarcopenia, dynapenia, and the impact of advancing age on human skeletal muscle size and strength—A quantitative review. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soysal, P.; Isik, A.T.; Carvalho, A.F.; Fernandes, B.S.; Solmi, M.; Schofield, P.; Veronese, N.; Stubbs, B. Oxidative stress and frailty: A systematic review and synthesis of the best evidence. Maturitas 2017, 99, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, D.; Jackson, T.; Sapey, E.; Lord, J.M. Frailty and sarcopenia: The potential role of an aged immune system. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 36, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesi, J.R.; Adams, D.H.; Fava, F.; Hermes, G.D.; Hirschfield, G.M.; Hold, G.; Quraishi, M.N.; Kinross, J.; Smidt, H.; Tuohy, K.M.; et al. The gut microbiota and host health: A new clinical frontier. Gut 2016, 65, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neis, E.P.; Dejong, C.H.; Rensen, S.S. The role of microbial amino acid metabolism in host metabolism. Nutrients 2015, 7, 2930–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dukes, A.; Davis, C.; El Refaey, M.; Upadhyay, S.; Mork, S.; Arounleut, P.; Johnson, M.H.; Hill, W.D.; Isales, C.M.; Hamrick, M.W. The aromatic amino acid tryptophan stimulates skeletal muscle IGF1/p70s6k/mTor signaling in vivo and the expression of myogenic genes in vitro. Nutrition 2015, 31, 1018–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bindels, L.B.; Delzenne, N.M. Muscle wasting: The gut microbiota as a new therapeutic target? Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 2186–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruta, H.; Yoshimura, Y.; Araki, A.; Kimoto, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Yamashita, H. Activation of AMP-Activated Protein Kinase and Stimulation of Energy Metabolism by Acetic Acid in L6 Myotube Cells. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leonel, A.J.; Alvarez-Leite, J.I. Butyrate: Implications for intestinal function. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2012, 15, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, M.E.; Bhattacharya, A.; Sataranatarajan, K.; Qaisar, R.; Sloane, L.; Rahman, M.M.; Kinter, M.; Van Remmen, H. The histone deacetylase inhibitor butyrate improves metabolism and reduces muscle atrophy during aging. Aging Cell 2015, 14, 957–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaudart, C.; Rolland, Y.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bauer, J.M.; Sieber, C.; Cooper, C.; Al-Daghri, N.; Araujo de Carvalho, I.; Bautmans, I.; Bernabei, R.; et al. Assessment of Muscle Function and Physical Performance in Daily Clinical Practice: A position paper endorsed by the European Society for Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis, Osteoarthritis and Musculoskeletal Diseases (ESCEO). Calcif. Tissue Int. 2019, 105, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.C.; Bohannon, R.W.; Kapellusch, J.; Washburn, D.; Li, X.; Yen, S.C.; Rahman, M.H. Between-side differences in hand-grip strength across the age span: Findings from 2011–2014 NHANES and 2011 NIH Toolbox studies. Laterality 2019, 24, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, F.S.; Gomes, G.A.; Neri, A.L.; Guariento, M.E.; Cintra, F.A.; Sousa Mda, L.; D’Elboux, M.J. Relationship between lower-limb muscle strength and frailty among elderly people. Sao Paulo Med. J. 2012, 130, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perera, S.; Patel, K.V.; Rosano, C.; Rubin, S.M.; Satterfield, S.; Harris, T.; Ensrud, K.; Orwoll, E.; Lee, C.G.; Chandler, J.M.; et al. Gait Speed Predicts Incident Disability: A Pooled Analysis. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2016, 71, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strandwitz, P. Neurotransmitter modulation by the gut microbiota. Brain Res. 2018, 1693, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, E.; Nieto, J.C.; Gely, C.; Vidal, S.; Pozuelo, M.; Poca, M.; Juárez, C.; Guarner, C.; Manichanh, C.; Soriano, G. Effect of a Multistrain Probiotic on Cognitive Function and Risk of Falls in Patients with Cirrhosis: A Randomized Trial. Hepatol. Commun. 2019, 3, 632–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lima, R.M.; de Oliveira, R.J.; Raposo, R.; Neri, S.G.R.; Gadelha, A.B. Stages of sarcopenia, bone mineral density, and the prevalence of osteoporosis in older women. Arch. Osteoporos. 2019, 14, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, B.R.; Andersen, H.E.; Haddock, B.; Hovind, P.; Schwarz, P.; Suetta, C. Prevalence of muscle dysfunction concomitant with osteoporosis in a home-dwelling Danish population aged 65–93 years—The Copenhagen Sarcopenia Study. Exp. Gerontol. 2020, 138, 110974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
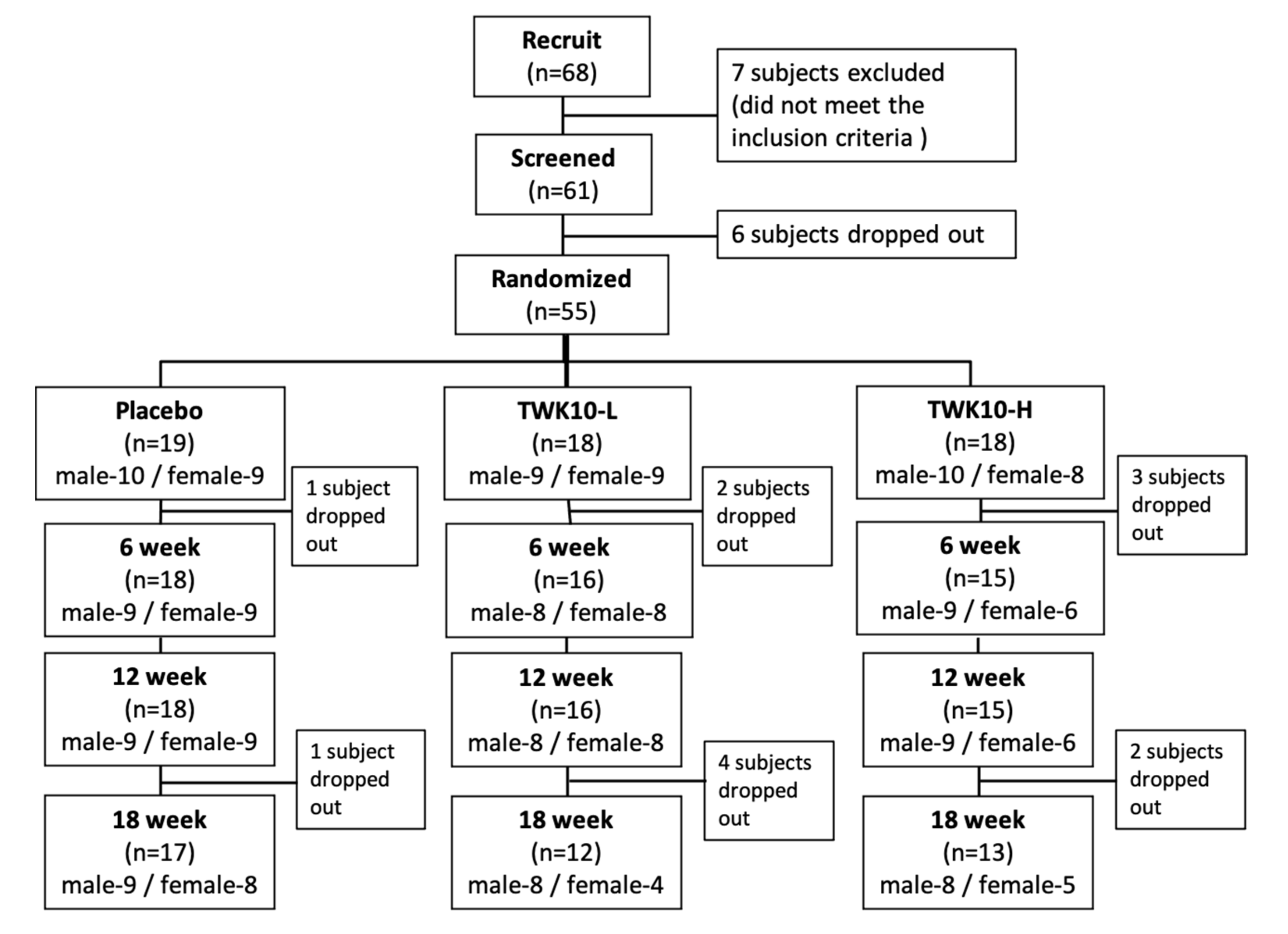

| Characters | Placebo (n = 17) | TWK10-L (n = 12) | TWK10-H (n = 13) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 75.2 ± 7.2 | 77.8 ± 7.2 | 80.5 ± 9.4 |
| Frailty (score) | 2.9 ± 1.3 | 3.0 ± 1.4 | 2.8 ± 1.3 |
| Height (cm) | 157.0 ± 7.8 | 155.0 ± 6.8 | 158.0 ± 7.1 |
| Weight (kg) | 58.9 ± 9.1 | 54.6 ± 8.5 | 57.7 ± 13.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, M.-C.; Tu, Y.-T.; Lee, C.-C.; Tsai, S.-C.; Hsu, H.-Y.; Tsai, T.-Y.; Liu, T.-H.; Young, S.-L.; Lin, J.-S.; Huang, C.-C. Lactobacillus plantarum TWK10 Improves Muscle Mass and Functional Performance in Frail Older Adults: A Randomized, Double-Blind Clinical Trial. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9071466
Lee M-C, Tu Y-T, Lee C-C, Tsai S-C, Hsu H-Y, Tsai T-Y, Liu T-H, Young S-L, Lin J-S, Huang C-C. Lactobacillus plantarum TWK10 Improves Muscle Mass and Functional Performance in Frail Older Adults: A Randomized, Double-Blind Clinical Trial. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(7):1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9071466
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Mon-Chien, Yu-Tsai Tu, Chia-Chia Lee, Shiow-Chwen Tsai, Han-Yin Hsu, Tsung-Yu Tsai, Te-Hua Liu, San-Land Young, Jin-Seng Lin, and Chi-Chang Huang. 2021. "Lactobacillus plantarum TWK10 Improves Muscle Mass and Functional Performance in Frail Older Adults: A Randomized, Double-Blind Clinical Trial" Microorganisms 9, no. 7: 1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9071466
APA StyleLee, M.-C., Tu, Y.-T., Lee, C.-C., Tsai, S.-C., Hsu, H.-Y., Tsai, T.-Y., Liu, T.-H., Young, S.-L., Lin, J.-S., & Huang, C.-C. (2021). Lactobacillus plantarum TWK10 Improves Muscle Mass and Functional Performance in Frail Older Adults: A Randomized, Double-Blind Clinical Trial. Microorganisms, 9(7), 1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9071466








