Predicted Cellular Interactors of the Endogenous Retrovirus-K Integrase Enzyme
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Database Curation
2.2. Protein Alignments and Eukaryotic Linear Motif Annotation
2.3. STRING Analysis and KEGG Pathways
3. Results
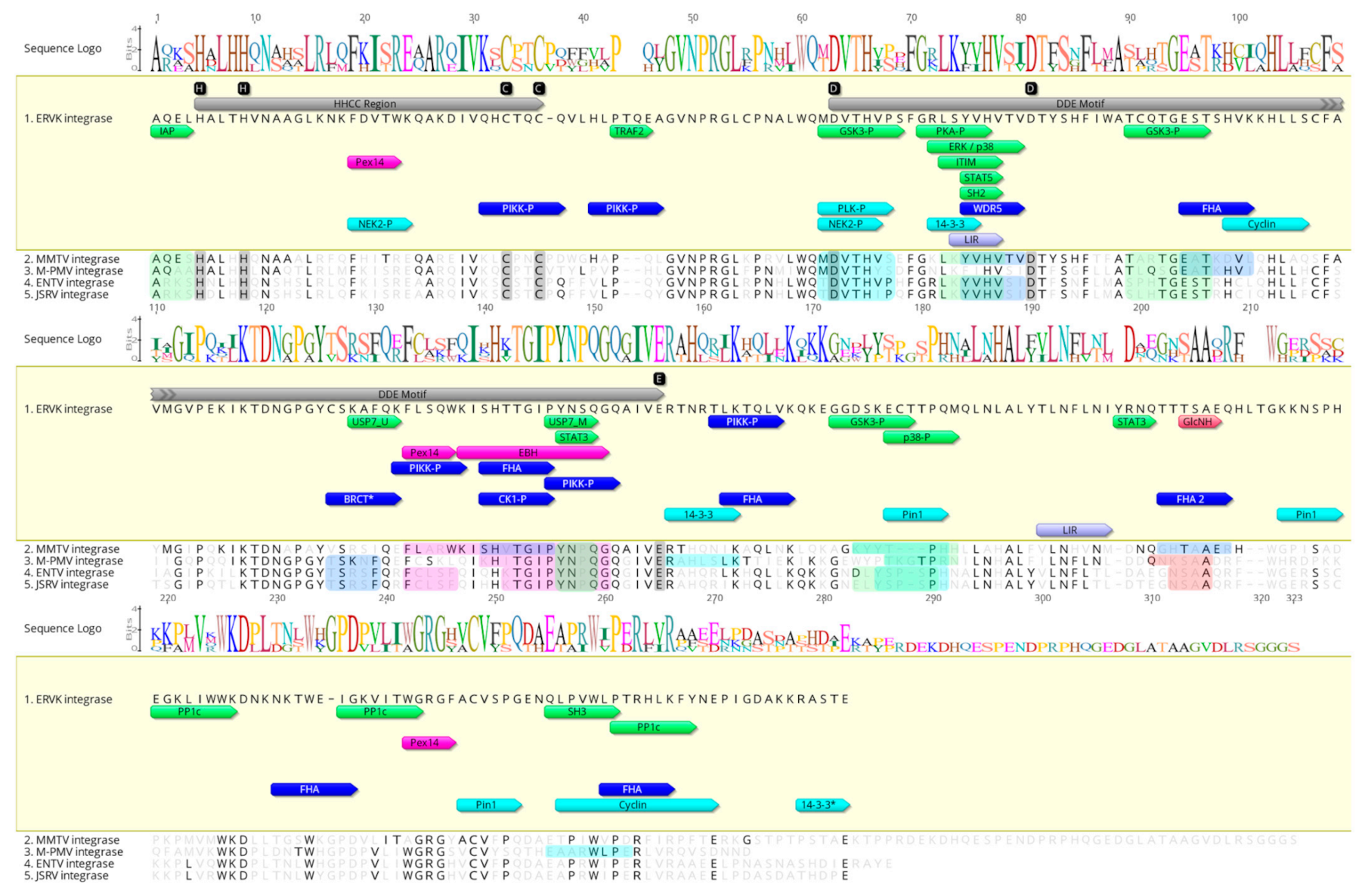
3.1. Characterization of Eukaryotic Linear Motifs in ERVK Integrase and Other Betaretroviral Integrases
3.2. Characterization of Eukaryotic Linear Motifs in ERVK Integrase and Other Endogenous Integrases
3.3. Unlike Similar Enzymes, the ERVK Integrase Contains Distinct ELM Signatures
3.3.1. ERVK Integrase has a High-Affinity BRCA1 Binding Site
3.3.2. ERVK Integrase C-Terminus Contains a 14-3-3 Binding RASTE Motif
3.3.3. ERVK Integrase Is Likely Post-Translationally Sumoylated
3.3.4. ERVK Integrase Exhibits Enhanced Interaction Potential with DDR Proteins
3.3.5. ERVK Integrase Contains Canonical Selective Autophagy Motifs
3.4. ERVK Interactome Reveals Association with a Diversity of Cellular Pathways
3.4.1. Many DNA Damage Response Proteins Are Potential ERVK Integrase Interactors
3.4.2. ERVK Integrase Likely Modulates Cell Cycle Pathways
3.4.3. Cell Signaling Pathways Associated with the ERVK Interactome
3.4.4. ERVK Integrase May Utilize Specific Cellular Transport Systems
3.5. Diseases and Pathways Implicated in the ERVK Integrase Interactome
3.5.1. Cancers
3.5.2. Neurological Disease
3.5.3. Diabetes
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Dedication
Appendix A
| Host | Species | Protein Name | Accession Number | Database | Percent Identity | E Value | Alignment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retroviridae—Betaretrovirus | |||||||
| Mus Musculus | Mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV) | MMTV strain BR6 Integrase, partial | 5CZ2_A | nr | 56.46% | 3.00 × 10−71 | |
| Unnamed protein product | CAA25954.1 | nr | 52.36% | 2.00 × 10−70 | |||
| Chain A. Integrase (Core model of the MMTV Intasome) | 3JCA_A | nr | 51.50% | 2.00 × 10−82 | |||
| Pr160 | NP_056880.1 | nr | 51.11% | 7.00 × 10−76 | |||
| Pr160 gag pro pol precursor | AAA46542.1 | nr | 51.11% | 7.00 × 10−76 | |||
| p30DU-p13PR-RT-IN | NP_955564.1 | nr | 51.11% | 2.00 × 10−76 | |||
| Gag-Pro-Pol polyprotein | P11283.2 | nr | 51.11% | 3.00 × 10−75 | |||
| MMTV putative integrase | AAC24859.1 | nr | 50.37% | 5.00 × 10−81 | |||
| Gag-Pol-Pro polyprotein, partial | BAA03767.1 | nr | 49.65% | 1.00 × 10−77 | |||
| Exogenous MMTV Gag-Pro-Pol | AAF31469.1 | nr | 49.65% | 4.00 × 10−76 | • | ||
| Endogenous MTV1 Gag-Pro-Pol | AAF31464.1 | nr | 49.65% | 4.00 × 10−76 | |||
| Capra hircus | Enzootic Nasal Tumor Virus (ENTV) | Pol protein, partial | AVG72436.1 | nr | 48.79% | 3.00 × 10−72 | |
| Pol protein, partial | AVG72437.1 | nr | 48.79% | 3.00 × 10−71 | |||
| Pol protein, partial | AVG72438.1 | nr | 48.79% | 7.00 × 10−71 | |||
| Pol protein, partial | AVG72441.1 | nr | 48.39% | 3.00 × 10−71 | |||
| Pol protein, partial | AVG72440.1 | nr | 48.39% | 4.00 × 10−71 | |||
| Pol protein, partial | AVG72435.1 | nr | 48.39% | 2.00 × 10−70 | |||
| Gag-Pro-Pol protein | QBP05340.1 | nr | 47.41% | 3.00 × 10−73 | |||
| Pol protein, partial | ANG58667.1 | nr | 47.41% | 2.00 × 10−72 | |||
| Pol protein | QEQ26602.1 | nr | 47.41% | 3.00 × 10−72 | |||
| Pol protein, partial | ANG58699.1 | nr | 47.41% | 2.00 × 10−71 | • | ||
| Pol protein, partial | ANG58695.1 | nr | 47.41% | 2.00 × 10−71 | |||
| Pol protein, partial | ANG58691.1 | nr | 47.41% | 2.00 × 10−71 | |||
| Pol protein, partial | ANG58679.1 | nr | 47.41% | 5.00 × 10−71 | |||
| Endogenous ENTV pol protein | QPG92760.1 | nr | 47.41% | 3.00 × 10−73 | |||
| Endogenous ENTV pol protein | QPG92768.1 | nr | 47.41% | 1.00 × 10−72 | |||
| Gag-Pro-Pol, partial | AOZ60515.1 | nr | 47.04% | 1.00 × 10−72 | |||
| Pol protein, partial | ANG58671.1 | nr | 47.04% | 1.00 × 10−71 | |||
| Pol protein, partial | ANG58683.1 | nr | 47.04% | 3.00 × 10−70 | |||
| Pol protein, partial | ANG58687.1 | nr | 47.04% | 2.00 × 10−71 | |||
| Pol protein, partial | ANG58663.1 | nr | 47.04% | 8.00 × 10−71 | |||
| Gag-Pro-Pol protein | ANC55859.1 | nr | 46.67% | 5.00 × 10−73 | |||
| Gag-Pro-Pol protein, partial | ADI50273.1 | nr | 46.67% | 4.00 × 10−72 | |||
| Gag-Pro-Pol protein, partial | AOZ60519.1 | nr | 46.67% | 7.00 × 10−72 | |||
| Pol protein, partial | ANG58675.1 | nr | 46.67% | 3.00 × 10−71 | |||
| Gag-Pro-Pol fusion, partial | NP_862833.2 | nr | 46.67% | 7.00 × 10−71 | |||
| Pol protein, partial | ANG58659.1 | nr | 46.10% | 1.00 × 10−72 | |||
| Macaca genus | Mason-Pfizer monkey virus (M-PMV) | Simian AIDS retrovirus SRV-1-Pol polyprotein | GNLJSA | nr | 48.30% | 2.00 × 10−70 | |
| Simian retrovirus SRV-5-Pol polyprotein | BBG56792.1 | nr | 47.57% | 5.00 × 10−71 | • | ||
| Simian retrovirus SRV-Y-Pol protein, partial | BAM71050.1 | nr | 47.57% | 2.00 × 10−70 | |||
| Ovis Aries | Jaagsiekte sheep retrovirus | Reverse transcriptase, partial | CAA77117.1 | nr | 46.67% | 5.00 × 10−75 | |
| Reverse transcriptase, partial | CAA77113.1 | nr | 46.67% | 2.00 × 10−74 | |||
| Pol protein | NP_041186.1 | nr | 46.30% | 1.00 × 10−70 | • | ||
| Species | Protein Name | Accession Number | Database | Percent Identity | E Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Homo sapiens | Human Endogenous Retrovirus K (HERV-K/ ERVK) | Pol/env ORF (bases 3878-8257) first start codon at 4172; Xxx; putative | AAA88033.1 | nr | 100.00% | 0 |
| Endogenous retrovirus group K member 10 Pol protein | P10266.2 | nr | 100.00% | 0 | ||
| Gag-Pro-Pol-Env protein | AAD51793.1 | nr | 100.00% | 0 | ||
| Pol protein, partial | CAA71417.1 | nr | 100.00% | 2.00 × 10−101 | ||
| Endogenous retrovirus group K member 11 Pol protein | Q9UQG0.2 | nr | 99.64% | 0 | ||
| Endogenous retrovirus group K member 7 Pol protein | P63135.1 | nr | 99.29% | 0 | ||
| Reverse transcriptase, partial | AGQ55918.1 | nr | 99.28% | 1.00 × 10−94 | ||
| Reverse transcriptase, partial | AGQ55922.1 | nr | 99.28% | 7.00 × 10−94 | ||
| Polymerase, partial | AAO27434.1 | nr | 99.27% | 0 | ||
| Gag-Pro-Pol protein | AAD51796.1 | nr | 99.17% | 5.00 × 10−161 | ||
| Endogenous retrovirus group K member 113 Pol protein | P63132.1 | nr | 98.21% | 0 | ||
| Polymerase, partial | AAK11553.1 | nr | 98.21% | 0 | ||
| Endogenous retrovirus group K member 6 Pol protein | Q9BXR3.2 | nr | 98.21% | 0 | ||
| Endogenous retrovirus group K member 8 Pol protein | P63133.1 | nr | 98.21% | 0 | ||
| Gag-Pro-Pol protein | AAD51797.1 | nr | 98.21% | 0 | ||
| Pol protein | CAA76885.1 | nr | 97.86% | 0 | ||
| Pol protein | CAA76879.1 | nr | 97.86% | 0 | ||
| Polymerase, partial | AAK11554.1 | nr | 97.86% | 0 | ||
| Reverse transcriptase, partial | AGQ55928.1 | nr | 97.84% | 6.00 × 10−93 | ||
| Reverse transcriptase, partial | AGQ55923.1 | nr | 97.84% | 8.00 × 10−93 | ||
| Reverse transcriptase, partial | AGQ55925.1 | nr | 97.83% | 2.00 × 10−92 | ||
| Reverse transcriptase, partial | AGQ55927.1 | nr | 97.83% | 3.00 × 10−92 | ||
| Reverse transcriptase, partial | AGQ55914.1 | nr | 97.76% | 6.00 × 10−89 | ||
| Pol protein | CAA76882.1 | nr | 97.50% | 0 | ||
| Endogenous retrovirus group K member 19 Pol protein | Q9WJR5.2 | nr | 97.50% | 0 | ||
| Endogenous retrovirus group K member 25 Pol protein | P63136.1 | nr | 97.50% | 0 | ||
| Pol protein | AAL60056.1 | nr | 97.30% | 1.00 × 10−152 | ||
| Reverse transcriptase, partial | AGQ55924.1 | nr | 97.12% | 2.00 × 10−92 | ||
| Reverse transcriptase, partial | AGQ55926.1 | nr | 97.10% | 9.00 × 10−92 | ||
| Reverse transcriptase, partial | AGQ55921.1 | nr | 97.10% | 9.00 × 10−92 | ||
| Reverse transcriptase, partial | AGQ55919.1 | nr | 97.10% | 1.00 × 10−91 | ||
| Pol/env protein, partial | AET81039.1 | nr | 96.97% | 1.00 × 10−81 | ||
| Reverse transcriptase, partial | AGQ55920.1 | nr | 96.38% | 2.00 × 10−91 | ||
| Pol protein | CAB56603.1 | nr | 90.13% | 2.00 × 10−132 | ||
| Endogenous retrovirus group K member 18 Pol protein | Q9QC07.2 | nr | 90.13% | 2.00 × 10−130 | ||
| hCG1808534 | EAW92672.1 | nr | 87.38% | 3.00 × 10−130 | ||
| Macaca fascicularis | PREDICTED: endogenous retrovirus group K member 8 Pol protein-like | XP_015309771.1 | nr | 83.77% | 2.00 × 10−127 | |
| Chlorocebus sabaeus | Pol protein, partial | BBC20786.1 | nr | 47.01% | 3.00 × 10−70 | |
| Oryctolagus cuniculus | PREDICTED: endogenous retrovirus group K member 8 Pol protein-like | XP_017205812.1 | nr | 49.82% | 1.00 × 10−76 | |
| Marmota marmota | PREDICTED: endogenous retrovirus group K member 11 Pol protein-like | XP_015349278.1 | nr | 47.96% | 4.00 × 10−71 | |
| Ochotona princeps | Uncharacterized protein LOC105942652 | XP_012786727.1 | nr | 47.33% | 1.00 × 10−70 | |
| Mus musculus (mouse) | Agouti-signaling protein isoform X1 | XP_017174599.2 | mo | 46.93% | 6.00 × 10−70 | |
| Contactin-5 isoform X2 | XP_036010832.1 | mo | 44.11% | 3.00 × 10−63 | ||
| Contactin-5 isoform X1 | XP_036010831.1 | mo | 44.11% | 4.00 × 10−63 | ||
| Contactin-5 isoform X3 | XP_036010833.1 | mo | 44.11% | 4.00 × 10−63 | ||
| Protein NYNRIN-like isoform X1 | XP_036020530.1 | mo | 30.15% | 9.00 × 10−14 | ||
| Uncharacterized protein Gm39701 | XP_011237194.2 | mo | 30.15% | 9.00 × 10−14 | ||
| Uncharacterized protein LOC118567641, partial | XP_036010828.1 | mo | 29.71% | 2.00 × 10−12 | ||
| Fukomys damarensis | Pol polyprotein | KFO35018.1 | nr | 45.14% | 1.00 × 10−71 | |
| Sus scrofa | TPA: uncharacterized protein | HCZ91355.1 | tsa | 61.54% | 2.00 × 10−65 | |
| TPA: uncharacterized protein | HDB33152.1 | tsa | 61.54% | 2.00 × 10−65 | ||
| Endogenous retrovirus group K member 11 Pol protein-like | HDB62800.1 | tsa | 60.66% | 2.00 × 10−17 | ||
| TPA: uncharacterized protein | HCZ89879.1 | tsa | 52.24% | 1.00 × 10−39 | ||
| Nuclear autoantigenic sperm protein isoform X4 | HDA97069.1 | tsa | 49.06% | 2.00 × 10−21 | ||
| Nuclear autoantigenic sperm protein isoform 2 | HCZ78574.1 | tsa | 48.86% | 5.00 × 10−15 | ||
| Nuclear autoantigenic sperm protein isoform 2 | HDB80991.1 | tsa | 48.42% | 7.00 × 10−17 | ||
| TPA: uncharacterized protein | HCZ87894.1 | tsa | 42.67% | 5.00 × 10−58 | ||
| TPA: uncharacterized protein | HDB20633.1 | tsa | 41.78% | 1.00 × 10−53 | ||
| TPA: uncharacterized protein | HDC25054.1 | tsa | 39.81% | 7.00 × 10−48 | ||
| TPA: uncharacterized protein | HDA81201.1 | tsa | 38.84% | 1.00 × 10−47 | ||
| Transmembrane protein 161B isoform X6-like | HDB13612.1 | tsa | 31.52% | 2.00 × 10−13 | ||
| TPA: uncharacterized protein | HDC69173.1 | tsa | 31.07% | 2.00 × 10−13 | ||
| TPA: uncharacterized protein | HDC69046.1 | tsa | 30.90% | 3.00 × 10−13 | ||
| Transmembrane protein 161B isoform X12-like | HDC79805.1 | tsa | 30.81% | 1.00 × 10−12 | ||
| Transmembrane protein 161B isoform X12-like | HDB85007.1 | tsa | 30.81% | 1.00 × 10−12 | ||
| Transmembrane protein 161B isoform X6-like | HDA96697.1 | tsa | 30.81% | 1.00 × 10−12 | ||
| Transmembrane protein 161B isoform X12-like | HDB79678.1 | tsa | 30.81% | 2.00 × 10−12 | ||
| Transmembrane protein 161B isoform X6 | HDB81123.1 | tsa | 30.77% | 1.00 × 10−11 | ||
| Transmembrane protein 161B isoform X6 | HDB82421.1 | tsa | 30.71% | 2.00 × 10−10 | ||
| TPA: uncharacterized protein | HDC70342.1 | tsa | 30.41% | 6.00 × 10−12 | ||
| TPA: uncharacterized protein | HDC70174.1 | tsa | 30.41% | 6.00 × 10−12 | ||
| TPA: uncharacterized protein | HDC69016.1 | tsa | 30.41% | 6.00 × 10−12 | ||
| putative protein-like | HDB95244.1 | tsa | 30.23% | 3.00 × 10−12 | ||
| TPA: uncharacterized protein | HDB49716.1 | tsa | 30.23% | 5.00 × 10−12 | ||
| TPA: uncharacterized protein | HDB49718.1 | tsa | 30.23% | 5.00 × 10−12 | ||
| TPA: uncharacterized protein | HDC70066.1 | tsa | 30.23% | 5.00 × 10−12 | ||
| TPA: uncharacterized protein | HDC69012.1 | tsa | 30.23% | 7.00 × 10−12 | ||
| TPA: uncharacterized protein | HDB50090.1 | tsa | 29.82% | 2.00 × 10−11 | ||
| TPA: uncharacterized protein | HDB54298.1 | tsa | 29.65% | 1.00 × 10−11 | ||
| Transmembrane protein 161B isoform X3-like | HDC79806.1 | tsa | 29.65% | 2.00 × 10−11 | ||
| Endogenous retrovirus group K member 25 Pol | HCZ79815.1 | tsa | 29.65% | 3.00 × 10−11 | ||
| Transmembrane protein 161B isoform X2-like | HDC79761.1 | tsa | 29.59% | 1.00 × 10−10 | ||
| Endogenous retrovirus group K member 25 Pol | HDA78544.1 | tsa | 29.24% | 4.00 × 10−11 | ||
| Endogenous retrovirus group K member 25 Pol | HDA79987.1 | tsa | 29.24% | 7.00 × 10−11 | ||
| TPA: uncharacterized protein | HDA79350.1 | tsa | 29.24% | 9.00 × 10−11 | ||
| Endogenous retrovirus group K member 25 Pol | HDA79988.1 | tsa | 29.24% | 9.00 × 10−11 | ||
| TPA: uncharacterized protein | HDA79349.1 | tsa | 29.24% | 1.00 × 10−10 | ||
| TPA: uncharacterized protein | HDC13198.1 | tsa | 29.24% | 1.00 × 10−10 | ||
| Transmembrane protein 161B isoform X6-like | HDB88647.1 | tsa | 29.07% | 3.00 × 10−11 | ||
| TPA: uncharacterized protein | HDA61679.1 | tsa | 29.07% | 5.00 × 10−11 | ||
| TPA: uncharacterized protein | HDB82700.1 | tsa | 29.07% | 1.00 × 10−10 | ||
| Equus asinus | PREDICTED: endogenous retrovirus group K member 8 Pol protein-like | XP_014715024.1 | nr | 56.46% | 3.00 × 10−95 | |
| Capra hircus | PREDICTED: LOW QUALITY PROTEIN: endogenous retrovirus group K member 18 Pol protein-like | XP_017905435.1 | nr | 47.41% | 3.00 × 10−71 | |
| Ovis aries | Pol protein | ABV71120.1 | nr | 47.04% | 2.00 × 10−72 | |
| Pol protein | ABV71104.1 | nr | 46.67% | 4.00 × 10−71 | ||
| Pol protein | ABV71084.1 | nr | 46.67% | 4.00 × 10−71 | ||
| Pol protein | ABV71074.1 | nr | 46.67% | 4.00 × 10−71 | ||
| Pol protein | ABV71079.1 | nr | 46.67% | 4.00 × 10−71 | ||
| Pol protein | ABV71069.1 | nr | 46.67% | 4.00 × 10−71 | ||
| Pol protein (endogenous virus) | AST51848.1 | nr | 46.67% | 5.00 × 10−71 | ||
| Pol protein | ABV71094.1 | nr | 46.30% | 2.00 × 10−70 | ||
| Species | Protein Name | Accession Number | Data base | Percent Identity | E Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Micrurus lemniscatus carvalhoi | Hypothetical protein, partial | LAA32932.1 | tsa | 58.47% | 2.00 × 10−40 |
| Hypothetical protein, partial | LAA32929.1 | tsa | 57.63% | 6.00 × 10−40 | |
| Hypothetical protein, partial | LAA32939.1 | tsa | 48.29% | 4.00 × 10−54 | |
| Hypothetical protein, partial | LAA32941.1 | tsa | 44.00% | 1.00 × 10−26 | |
| Zosterops borbonicus | Hypothetical protein HGM15179_011615 | TRZ15504.1 | nr | 46.97% | 3.00 × 10−71 |
| Zonotrichia albicollis | Uncharacterized protein LOC106629581 | XP_014125095.1 | nr | 46.24% | 1.00 × 10−71 |
| Micrurus corallinus | Hypothetical protein, partial | LAA64555.1 | tsa | 46.21% | 2.00 × 10−26 |
| Hypothetical protein, partial | LAA64556.1 | tsa | 45.08% | 2.00 × 10−21 | |
| Micrurus lemniscatus lemniscatus | Hypothetical protein, partial | LAA89554.1 | tsa | 44.57% | 4.00 × 10−18 |
| Hypothetical protein, partial | LAA89545.1 | tsa | 43.75% | 1.00 × 10−23 | |
| Bird metagenome | Gag-Pro-Pol polyprotein, partial | MBY11728.1 | tsa | 44.31% | 3.00 × 10−43 |
| Gallirallus okinawae | Hypothetical protein, partial | LAC45429.1 | tsa | 43.96% | 3.00 × 10−57 |
| Fundulus heteroclitus | Integrase core domain, partial | JAQ81073.1 | tsa | 35.05% | 2.00 × 10−11 |
| Danio rerio (zebrafish) | Uncharacterized protein LOC108190699 | XP_017212567.1 | mo | 33.64% | 4.00 × 10−12 |
| Uncharacterized protein K02A2.6-like | XP_021334762.1 | mo | 30.18% | 4.00 × 10−11 | |
| Uncharacterized protein K02A2.6-like | XP_017210639.2 | mo | 29.20% | 8.00 × 10−9 | |
| Uncharacterized protein LOC101886116 | XP_021327301.1 | mo | 28.47% | 1.00 × 10−5 | |
| Uncharacterized protein LOC110439859 | XP_021332670.1 | mo | 28.17% | 0.001 | |
| Uncharacterized protein K02A2.6-like | XP_003199161.1 | mo | 27.78% | 5.00 × 10−10 | |
| Uncharacterized protein K02A2.6-like | XP_002663225.3 | mo | 27.78% | 8.00 × 10−10 | |
| Uncharacterized protein LOC110438047 | XP_021323131.1 | mo | 26.43% | 0.006 | |
| Nothobranchius korthausae | Uncharacterized protein | SBQ67355.1 | tsa | 32.02% | 8.00 × 10−11 |
| Nothobranchius kadleci | Uncharacterized protein | SBP84572.1 | tsa | 32.00% | 8.00 × 10−11 |
| Nothobranchius furzeri | Uncharacterized protein | SBS54329.1 | tsa | 31.25% | 5.00 × 10−13 |
| Nothobranchius rachovii | Uncharacterized protein | SBS11479.1 | tsa | 30.07% | 2.00 × 10−10 |
| Species | Protein Name | Accession Number | Data base | Percent Identity | E Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Onchocerca flexuosa | Integrase core domain protein | OZC05619.1 | nr | 45.68% | 6.00 × 10−73 |
| Ixodes ricinus | Putative tf2-11 polyprotein | MXV00662.1 | tsa | 35.81% | 2.00 × 10−10 |
| Putative tick transposon, partial | JAP73380.1 | tsa | 30.67% | 1.00 × 10−11 | |
| Putative tick transposon, partial | JAR90689.1 | tsa | 30.67% | 6.00 × 10−11 | |
| Putative bell all, partial | JAA73039.1 | tsa | 30.00% | 2.00 × 10−10 | |
| Putative gypsy11-i sp, partial | JAP69562.1 | tsa | 30.00% | 2.00 × 10−10 | |
| Putative tick transposon, partial | JAR92200.1 | tsa | 28.06% | 4.00 × 10−13 | |
| Putative transposon tf2-9 polyprotein | MXV00940.1 | tsa | 27.37% | 9.00 × 10−13 | |
| Littorina littorea | Transposon Ty3-G Gag-Pol polyprotein | MBX96210.1 | tsa | 35.54% | 4.00 × 10−12 |
| Transposon Ty3-I Gag-Pol polyprotein | MBX97975.1 | tsa | 30.00% | 4.00 × 10−14 | |
| Ixodes scapularis | Putative tick transposon, partial | MOY42200.1 | tsa | 34.29% | 4.00 × 10−12 |
| Putative tick transposon, partial | MOY42203.1 | tsa | 32.67% | 2.00 × 10−13 | |
| Putative tick transposon, partial | MOY42202.1 | tsa | 32.67% | 7.00 × 10−13 | |
| Putative gypsy-17 ga-i, partial | MOY42236.1 | tsa | 31.09% | 2.00 × 10−12 | |
| Hypothetical protein, partial | MOY42219.1 | tsa | 30.00% | 6.00 × 10−11 | |
| Putative gypsy11-i sp, partial | MOY42209.1 | tsa | 29.17% | 7.00 × 10−12 | |
| Putative gypsy21-i sp, partial | MOY42223.1 | tsa | 29.17% | 8.00 × 10−12 | |
| Putative tick transposon, partial | MOY42227.1 | tsa | 28.50% | 4.00 × 10−13 | |
| Putative tick transposon, partial | MOY42214.1 | tsa | 28.25% | 9.00 × 10−11 | |
| Putative gypsy-27 xt-i, partial | MOY35588.1 | tsa | 26.44% | 1.00 × 10−10 | |
| Lygus hesperus | Retrotransposable element Tf2 protein type 3, partial | JAQ12551.1 | tsa | 33.58% | 6.00 × 10−13 |
| Uncharacterized protein | JAG20083.1 | tsa | 33.58% | 6.00 × 10−13 | |
| Hypothetical protein, partial CM83_13537, partial | JAG31779.1 | tsa | 29.93% | 5.00 × 10−11 | |
| Uncharacterized protein, partial K02A2.6, partial | JAG32119.1 | tsa | 28.87% | 1.00 × 10−11 | |
| Uncharacterized protein, partial K02A2.6, partial | JAG38901.1 | tsa | 26.82% | 8.00 × 10−12 | |
| Amblyomma sculptum | Putative gypsy-7 adi-i, partial | JAU00762.1 | tsa | 32.88% | 1.00 × 10−12 |
| Putative tick transposon, partial | JAU00733.1 | tsa | 30.00% | 2.00 × 10−10 | |
| Putative tick transposon, partial | JAU00744.1 | tsa | 30.00% | 2.00 × 10−10 | |
| Rhipicephalus microplus | Putative tick transposon | NIE47479.1 | tsa | 32.45% | 4.00 × 10−11 |
| Strongylocentrotus purpuratus | Integrase, catalytic core containing protein | MOS08875.1 | tsa | 32.19% | 2.00 × 10−16 |
| Integrase, catalytic core containing protein | MOS08729.1 | tsa | 32.03% | 7.00 × 10−13 | |
| Integrase, catalytic core containing protein | MOS14051.1 | tsa | 30.57% | 2.00 × 10−13 | |
| Reverse transcriptase domain-containing protein | MOS08491.1 | tsa | 30.57% | 2.00 × 10−13 | |
| Reverse transcriptase domain-containing protein | MOS11069.1 | tsa | 29.93% | 5.00 × 10−12 | |
| Integrase, catalytic core containing protein | MOS08728.1 | tsa | 29.76% | 2.00 × 10−10 | |
| Integrase, catalytic core containing protein | MOS08842.1 | tsa | 28.57% | 4.00 × 10−11 | |
| Integrase, catalytic core containing protein | MOS08745.1 | tsa | 24.12% | 2.00 × 10−10 | |
| Ornithodoros turicata | Putative transposon tf2-9 polyprotein | MBY06492.1 | tsa | 32.00% | 1.00 × 10−10 |
| Ornithodoros moubata | Esterase D, partial | JAW02195.1 | tsa | 29.86% | 2.00 × 10−10 |
| Photinus pyralis | Hypothetical protein | JAV53763.1 | tsa | 29.20% | 2.00 × 10−13 |
| Lepeophtheirus salmonis | Uncharacterized protein K02A2.6like, partial | CDW28658.1 | tsa | 28.28% | 1.00 × 10−10 |
| Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | Unnamed protein product | CAA30503.1 | nr-DM | 28.87% | 0.004 |
| Sd02026p | AAK84933.1 | nr-DM | 28.57% | 3.00 × 10−9 | |
| Blastopia polyprotein | CAA81643.1 | nr-DM | 28.19% | 2.00 × 10−9 | |
| Polyprotein | ACI62137.1 | nr-DM | 28.00% | 2.00 × 10−4 |
| Category | ELM | STRING Predicted Interactor (Gene Name) | Network |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cleavage | CLV_C14_Caspase3-7 | CASP3 | • |
| CASP7 | • | ||
| CLV_PCSK_KEX2_1 CLV_PCSK_PC1ET2_1 CLV_PCSK_SKI1_1 | PCSK1 | • | |
| PCSK2 | • | ||
| PCSK3 | • | ||
| PCSK4 | • | ||
| PCSK5 | • | ||
| PCSK6 | • | ||
| PCSK7 | • | ||
| PCSK8 | • | ||
| PCSK9 | • | ||
| Docking site | DOC_CYCLIN_RXL_1 | CCNA1 | • |
| CCNA2 | • | ||
| CCNB1 | • | ||
| CCNB2 | • | ||
| CCNB3 | • | ||
| CCNC | • | ||
| CCND1 | • | ||
| CCND2 | • | ||
| CCND3 | • | ||
| CCNE1 | • | ||
| CCNE2 | • | ||
| CCNF | • | ||
| CCNG1 | • | ||
| CCNG2 | • | ||
| CCNH | • | ||
| CCNI | • | ||
| CCNI2 | • | ||
| CCNJ | • | ||
| CCNJL | • | ||
| CCNK | • | ||
| CCNL1 | • | ||
| CCNL2 | • | ||
| CCNO | • | ||
| CCNP | • | ||
| CCNT1 | • | ||
| CCNT2 | • | ||
| CCNY | • | ||
| CCNYL1 | • | ||
| CNTD1 | • | ||
| DOC_MAPK_MEF2A_6 | MAPK1 | • | |
| MAPK3 | • | ||
| MAPK7 | • | ||
| MAPK11 | • | ||
| MAPK14 | • | ||
| DOC_PP1_RVXF_1 | PPP1CA | • | |
| PPP1CB | • | ||
| PPP1CC | • | ||
| PPP3CA | • | ||
| PPP3CB | • | ||
| PPP3CC | • | ||
| DOC_PP2B_LxvP_1 | PPP3R1 | • | |
| DOC_USP7_MATH_1 DOC_USP7_UBL2_3 | USP7 | • | |
| DOC_WW_Pin1_4 | PCIF1 | • | |
| PIN1 | • | ||
| SENP6 | • | ||
| Ligand | LIG_14-3-3_CanoR_1 LIG_14-3-3_CterR_2 | SFN | • |
| YWHAB | • | ||
| YWHAE | • | ||
| YWHAG | • | ||
| YWHAH | • | ||
| YWHAQ | • | ||
| YWHAZ | • | ||
| LIG_BIR_II_1 | BIRC2 | • | |
| BIRC3 | • | ||
| BIRC5 | • | ||
| BIRC6 | • | ||
| BIRC7 | • | ||
| NAIP | • | ||
| XIAP | • | ||
| LIG_BRCT_BRCA1_1 | BARD1 | • | |
| BRCA1 | • | ||
| CTDP1 | • | ||
| DNTT | • | ||
| ECT2 | • | ||
| LIG4 | • | ||
| MCPH1 | • | ||
| MDC1 | • | ||
| NBN | • | ||
| PARP1 | • | ||
| PARP4 | • | ||
| PAXIP1 | • | ||
| PES1 | • | ||
| RBPJ | • | ||
| REV1 | • | ||
| RFC1 | • | ||
| TOPBP1 | • | ||
| TP53BP1 | • | ||
| XRCC1 | • | ||
| LIG_FHA_1 LIG_FHA_2 | AGGF1 | • | |
| APLF | • | ||
| APTX | • | ||
| CEP170 | • | ||
| CEP170B | • | ||
| CHEK2 | • | ||
| CHFR | • | ||
| FHAD1 | • | ||
| FOXK1 | • | ||
| FOXK2 | • | ||
| KIF13A | • | ||
| KIF13B | |||
| KIF14 | • | ||
| KIF16B | |||
| KIF1A | • | ||
| KIF1B | • | ||
| KIF1C | |||
| MCRS1 | • | ||
| MDC1 | • | ||
| MKI67 | • | ||
| MLLT4 | • | ||
| NBN | • | ||
| PHF12 | • | ||
| PPP1R8 | • | ||
| RNF8 | • | ||
| SLC4A1AP | • | ||
| SLMAP | • | ||
| SNIP1 | • | ||
| STARD9 | • | ||
| TCF19 | • | ||
| TIFA | • | ||
| TIFAB | • | ||
| LIG_CSL_BTD_1 | CHEK2 | • | |
| MRC1 | • | ||
| RAD9A | • | ||
| XRCC1 | • | ||
| XRCC4 | • | ||
| LIG_LIR_Gen_1 LIG_LIR_Nem_4 | GABARAP | ||
| GABARAPL1 | |||
| GABARAPL2 | • | ||
| MAP1LC3A | |||
| MAP1LC3B | |||
| MAP1LC3B2 | • | ||
| MAP1LC3C | |||
| LIG_Pex14_1 | PEX13 | • | |
| PEX14 | • | ||
| LIG_SH2_PTP2 | PLCG1 | • | |
| PTPN11 | • | ||
| LIG_SH2_SRC | BLK | • | |
| FGR | • | ||
| FRK | • | ||
| FYN | • | ||
| HCK | • | ||
| LCK | • | ||
| LYN | • | ||
| SRC | • | ||
| YES1 | • | ||
| LIG_SH2_STAP1 | STAP1 | • | |
| LIG_TYR_ITIM | ABL1 | • | |
| ABL2 | • | ||
| FYN | • | ||
| LCK | • | ||
| MATK | • | ||
| PI3KCA | • | ||
| PLCG1 | • | ||
| SH2D1A | • | ||
| SHF | • | ||
| PTPN6 | • | ||
| PTPN11 | • | ||
| SRC | • | ||
| SYK | • | ||
| LIG_SH2_STAT3 | STAT3 | • | |
| LIG_SH2_STAT5 | STAT5A | • | |
| STAT5B | • | ||
| LIG_SH3_3 | ARHGEF7 | • | |
| CTTN | • | ||
| LIG_SxIP_EBH_1 | MAPRE1 | • | |
| MAPRE2 | • | ||
| MAPRE3 | • | ||
| LIG_TRAF2_1 | TRAF2 | • | |
| LIG_WD40_WDR5_VDV_2 | WDR5 | • | |
| Modification | MOD_CK1_1 | CSNK1A1 | • |
| MOD_CK2_1 | CSNK2A1 | • | |
| MOD_GSK3_1 | GSK3A | • | |
| GSK3B | • | ||
| MOD_N-GLC_1 | DDOST | • | |
| MOD_NEK2_1 | NEK2 | • | |
| MOD_PIKK_1 | ATM | • | |
| ATR | • | ||
| mTOR | • | ||
| PRKDC | • | ||
| SMG1 | • | ||
| TRRAP | • | ||
| MOD_PKA_2 | PAK1 | • | |
| PRKACA | • | ||
| PRKACB | • | ||
| PRKACG | • | ||
| PRKCA | • | ||
| PRKCB | • | ||
| PRKCE | • | ||
| PRKCG | • | ||
| PRKCH | • | ||
| PRKCI | • | ||
| PRKCQ | • | ||
| PRKCZ | • | ||
| MOD_Plk_1 MOD_Plk_4 | PLK1 | • | |
| PLK2 | • | ||
| PLK3 | • | ||
| PLK4 | • | ||
| MOD_ProDKin_1 | MAPK11 | • | |
| MAPK12 | |||
| MAPK13 | |||
| MAPK14 | • | ||
| MOD_SUMO_rev_2 | SUMO2 | • | |
| Targeting | TRG_ENDOCYTIC_2 | AP1M1 | • |
| AP2M1 | • | ||
| AP3M1 | • | ||
| AP3M2 | |||
| AP4M1 | • | ||
| AP5M1 | |||
| ARCN1 | |||
| FCHO1 | • | ||
| FCHO2 | • | ||
| SGIP1 | • | ||
| STON1 | • | ||
| STON2 | • | ||
| TRG_Pf-PMV_PEXEL_1 | None | ||
| KEGG Term ID | Term Description | Observed Gene Count | Background Gene Count | Strength | False Discovery Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hsa04218 | Cellular senescence | 28 | 156 | 1.27 | 2.30 × 10−23 |
| hsa05203 | Viral carcinogenesis | 29 | 183 | 1.21 | 3.47 × 10−23 |
| hsa04110 | Cell cycle | 25 | 123 | 1.32 | 2.38 × 10−22 |
| hsa04114 | Oocyte meiosis | 23 | 116 | 1.31 | 2.13 × 10−20 |
| hsa05169 | Epstein–Barr virus infection | 24 | 194 | 1.11 | 4.01 × 10−17 |
| hsa05205 | Proteoglycans in cancer | 23 | 195 | 1.08 | 4.79 × 10−16 |
| hsa04650 | Natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity | 19 | 124 | 1.2 | 3.96 × 10−15 |
| hsa04068 | FoxO signaling pathway | 19 | 130 | 1.18 | 7.58 × 10−15 |
| hsa04750 | Inflammatory mediator regulation of TRP channels | 17 | 92 | 1.28 | 8.12 × 10−15 |
| hsa05167 | Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection | 21 | 183 | 1.07 | 1.30 × 10−14 |
| hsa04720 | Long-term potentiation | 15 | 64 | 1.38 | 1.77 × 10−14 |
| hsa05161 | Hepatitis B | 19 | 142 | 1.14 | 2.19 × 10−14 |
| hsa05206 | MicroRNAs in cancer | 19 | 149 | 1.12 | 4.49 × 10−14 |
| hsa04370 | VEGF signaling pathway | 14 | 59 | 1.39 | 1.11 × 10−13 |
| hsa04660 | T cell receptor signaling pathway | 16 | 99 | 1.22 | 2.39 × 10−13 |
| hsa04012 | ErbB signaling pathway | 15 | 83 | 1.27 | 3.37 × 10−13 |
| hsa04611 | Platelet activation | 17 | 123 | 1.15 | 3.37 × 10−13 |
| hsa04921 | Oxytocin signaling pathway | 18 | 149 | 1.09 | 4.19 × 10−13 |
| hsa04115 | p53 signaling pathway | 14 | 68 | 1.33 | 4.53 × 10−13 |
| hsa05200 | Pathways in cancer | 29 | 515 | 0.76 | 6.20 × 10−13 |
| hsa05166 | HTLV-I infection | 21 | 250 | 0.94 | 1.82 × 10−12 |
| hsa04933 | AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications | 15 | 98 | 1.2 | 2.24 × 10−12 |
| hsa04510 | Focal adhesion | 19 | 197 | 1 | 2.57 × 10−12 |
| hsa04659 | Th17 cell differentiation | 15 | 102 | 1.18 | 3.46 × 10−12 |
| hsa05031 | Amphetamine addiction | 13 | 65 | 1.31 | 3.95 × 10−12 |
| hsa04728 | Dopaminergic synapse | 16 | 128 | 1.11 | 4.97 × 10−12 |
| hsa04658 | Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation | 14 | 88 | 1.21 | 7.29 × 10−12 |
| hsa05165 | Human papillomavirus infection | 22 | 317 | 0.85 | 1.27 × 10−11 |
| hsa04914 | Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation | 14 | 94 | 1.19 | 1.52 × 10−11 |
| hsa04310 | Wnt signaling pathway | 16 | 143 | 1.06 | 2.02 × 10−11 |
| hsa04390 | Hippo signaling pathway | 16 | 152 | 1.04 | 4.56 × 10−11 |
| hsa04062 | Chemokine signaling pathway | 17 | 181 | 0.99 | 5.10 × 10−11 |
| hsa04917 | Prolactin signaling pathway | 12 | 69 | 1.25 | 1.03 × 10−10 |
| hsa04662 | B cell receptor signaling pathway | 12 | 71 | 1.24 | 1.35 × 10−10 |
| hsa04919 | Thyroid hormone signaling pathway | 14 | 115 | 1.1 | 1.47 × 10−10 |
| hsa04064 | NF-kappa B signaling pathway | 13 | 93 | 1.16 | 1.57 × 10−10 |
| hsa04270 | Vascular smooth muscle contraction | 14 | 119 | 1.08 | 2.11 × 10−10 |
| hsa04360 | Axon guidance | 16 | 173 | 0.98 | 2.24 × 10−10 |
| hsa05162 | Measles | 14 | 133 | 1.04 | 7.76 × 10−10 |
| hsa05223 | Non-small cell lung cancer | 11 | 66 | 1.23 | 9.08 × 10−10 |
| hsa04666 | Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis | 12 | 89 | 1.14 | 1.18 × 10−9 |
| hsa04380 | Osteoclast differentiation | 13 | 124 | 1.03 | 3.48 × 10−9 |
| hsa01521 | EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance | 11 | 78 | 1.16 | 4.18 × 10−9 |
| hsa04010 | MAPK signaling pathway | 18 | 293 | 0.8 | 5.87 × 10−9 |
| hsa04931 | Insulin resistance | 12 | 107 | 1.06 | 7.37 × 10−9 |
| hsa04910 | Insulin signaling pathway | 13 | 134 | 1 | 7.61 × 10−9 |
| hsa04724 | Glutamatergic synapse | 12 | 112 | 1.04 | 1.14 × 10−8 |
| hsa04151 | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | 19 | 348 | 0.75 | 1.17 × 10−8 |
| hsa04912 | GnRH signaling pathway | 11 | 88 | 1.11 | 1.17 × 10−8 |
| hsa04664 | Fc epsilon RI signaling pathway | 10 | 67 | 1.19 | 1.30 × 10−8 |
| hsa04071 | Sphingolipid signaling pathway | 12 | 116 | 1.03 | 1.51 × 10−8 |
| hsa04722 | Neurotrophin signaling pathway | 12 | 116 | 1.03 | 1.51 × 10−8 |
| hsa01522 | Endocrine resistance | 11 | 95 | 1.08 | 2.24 × 10−8 |
| hsa04014 | Ras signaling pathway | 15 | 228 | 0.83 | 5.08 × 10−8 |
| hsa04210 | Apoptosis | 12 | 135 | 0.96 | 6.74 × 10−8 |
| hsa05152 | Tuberculosis | 13 | 172 | 0.89 | 1.01 × 10−7 |
| hsa04540 | Gap junction | 10 | 87 | 1.07 | 1.11 × 10−7 |
| hsa05221 | Acute myeloid leukemia | 9 | 66 | 1.15 | 1.42 × 10−7 |
| hsa05214 | Glioma | 9 | 68 | 1.13 | 1.74 × 10−7 |
| hsa05222 | Small cell lung cancer | 10 | 92 | 1.05 | 1.74 × 10−7 |
| hsa01524 | Platinum drug resistance | 9 | 70 | 1.12 | 2.13 × 10−7 |
| hsa04215 | Apoptosis—multiple species | 7 | 31 | 1.37 | 2.13 × 10−7 |
| hsa04926 | Relaxin signaling pathway | 11 | 130 | 0.94 | 3.72 × 10−7 |
| hsa04015 | Rap1 signaling pathway | 13 | 203 | 0.82 | 5.46 × 10−7 |
| hsa04960 | Aldosterone-regulated sodium reabsorption | 7 | 37 | 1.29 | 5.77 × 10−7 |
| hsa04668 | TNF signaling pathway | 10 | 108 | 0.98 | 6.23 × 10−7 |
| hsa04261 | Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes | 11 | 139 | 0.91 | 6.58 × 10−7 |
| hsa05145 | Toxoplasmosis | 10 | 109 | 0.98 | 6.58 × 10−7 |
| hsa04725 | Cholinergic synapse | 10 | 111 | 0.97 | 7.54 × 10−7 |
| hsa05120 | Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection | 8 | 66 | 1.1 | 1.53 × 10−6 |
| hsa04340 | Hedgehog signaling pathway | 7 | 46 | 1.2 | 1.97 × 10−6 |
| hsa04961 | Endocrine and other factor-regulated calcium reabsorption | 7 | 47 | 1.19 | 2.22 × 10−6 |
| hsa04066 | HIF-1 signaling pathway | 9 | 98 | 0.98 | 2.44 × 10−6 |
| hsa04520 | Adherens junction | 8 | 71 | 1.06 | 2.44 × 10−6 |
| hsa04916 | Melanogenesis | 9 | 98 | 0.98 | 2.44 × 10−6 |
| hsa05225 | Hepatocellular carcinoma | 11 | 163 | 0.84 | 2.56 × 10−6 |
| hsa04621 | NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | 11 | 166 | 0.83 | 2.99 × 10−6 |
| hsa05014 | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) | 7 | 50 | 1.16 | 2.99 × 10−6 |
| hsa05220 | Chronic myeloid leukemia | 8 | 76 | 1.04 | 3.62 × 10−6 |
| hsa05020 | Prion diseases | 6 | 33 | 1.27 | 4.44 × 10−6 |
| hsa04020 | Calcium signaling pathway | 11 | 179 | 0.8 | 5.69 × 10−6 |
| hsa04670 | Leukocyte transendothelial migration | 9 | 112 | 0.92 | 6.16 × 10−6 |
| hsa04726 | Serotonergic synapse | 9 | 112 | 0.92 | 6.16 × 10−6 |
| hsa04723 | Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling | 10 | 148 | 0.84 | 7.20 × 10−6 |
| hsa04727 | GABAergic synapse | 8 | 88 | 0.97 | 9.28 × 10−6 |
| hsa04934 | Cushing’s syndrome | 10 | 153 | 0.83 | 9.30 × 10−6 |
| hsa04924 | Renin secretion | 7 | 63 | 1.06 | 1.09 × 10−5 |
| hsa04024 | cAMP signaling pathway | 11 | 195 | 0.76 | 1.14 × 10−5 |
| hsa04657 | IL-17 signaling pathway | 8 | 92 | 0.95 | 1.20 × 10−5 |
| hsa04022 | cGMP-PKG signaling pathway | 10 | 160 | 0.81 | 1.28 × 10−5 |
| hsa04140 | Autophagy—animal | 9 | 125 | 0.87 | 1.28 × 10−5 |
| hsa04630 | Jak-STAT signaling pathway | 10 | 160 | 0.81 | 1.28 × 10−5 |
| hsa04713 | Circadian entrainment | 8 | 93 | 0.95 | 1.28 × 10−5 |
| hsa05146 | Amoebiasis | 8 | 94 | 0.94 | 1.32 × 10−5 |
| hsa05215 | Prostate cancer | 8 | 97 | 0.93 | 1.62 × 10−5 |
| hsa05231 | Choline metabolism in cancer | 8 | 98 | 0.92 | 1.72 × 10−5 |
| hsa04371 | Apelin signaling pathway | 9 | 133 | 0.84 | 1.94 × 10−5 |
| hsa04930 | Type II diabetes mellitus | 6 | 46 | 1.13 | 2.04 × 10−5 |
| hsa03450 | Non-homologous end-joining | 4 | 13 | 1.5 | 3.50 × 10−5 |
| hsa04072 | Phospholipase D signaling pathway | 9 | 145 | 0.81 | 3.61 × 10−5 |
| hsa05226 | Gastric cancer | 9 | 147 | 0.8 | 3.96 × 10−5 |
| hsa05210 | Colorectal cancer | 7 | 85 | 0.93 | 5.70 × 10−5 |
| hsa04217 | Necroptosis | 9 | 155 | 0.78 | 5.77 × 10−5 |
| hsa04730 | Long-term depression | 6 | 60 | 1.01 | 7.67 × 10−5 |
| hsa04925 | Aldosterone synthesis and secretion | 7 | 93 | 0.89 | 9.48 × 10−5 |
| hsa04530 | Tight junction | 9 | 167 | 0.74 | 9.70 × 10−5 |
| hsa05131 | Shigellosis | 6 | 63 | 0.99 | 9.70 × 10−5 |
| hsa05010 | Alzheimer’s disease | 9 | 168 | 0.74 | 9.98 × 10−5 |
| hsa05164 | Influenza A | 9 | 168 | 0.74 | 9.98 × 10−5 |
| hsa05160 | Hepatitis C | 8 | 131 | 0.8 | 0.00011 |
| hsa03440 | Homologous recombination | 5 | 40 | 1.11 | 0.00012 |
| hsa04922 | Glucagon signaling pathway | 7 | 100 | 0.86 | 0.00014 |
| hsa05140 | Leishmaniasis | 6 | 70 | 0.95 | 0.00016 |
| hsa05168 | Herpes simplex infection | 9 | 181 | 0.71 | 0.00016 |
| hsa04971 | Gastric acid secretion | 6 | 72 | 0.93 | 0.00018 |
| hsa04918 | Thyroid hormone synthesis | 6 | 73 | 0.93 | 0.00019 |
| hsa05133 | Pertussis | 6 | 74 | 0.92 | 0.0002 |
| hsa05212 | Pancreatic cancer | 6 | 74 | 0.92 | 0.0002 |
| hsa05224 | Breast cancer | 8 | 147 | 0.75 | 0.00021 |
| hsa04150 | mTOR signaling pathway | 8 | 148 | 0.75 | 0.00022 |
| hsa05110 | Vibrio cholerae infection | 5 | 48 | 1.03 | 0.00025 |
| hsa04810 | Regulation of actin cytoskeleton | 9 | 205 | 0.66 | 0.00037 |
| hsa04911 | Insulin secretion | 6 | 84 | 0.87 | 0.00037 |
| hsa05130 | Pathogenic Escherichia coli infection | 5 | 53 | 0.99 | 0.00037 |
| hsa04970 | Salivary secretion | 6 | 86 | 0.86 | 0.00041 |
| hsa05416 | Viral myocarditis | 5 | 56 | 0.96 | 0.00046 |
| hsa05032 | Morphine addiction | 6 | 91 | 0.83 | 0.00053 |
| hsa05213 | Endometrial cancer | 5 | 58 | 0.95 | 0.00053 |
| hsa04915 | Estrogen signaling pathway | 7 | 133 | 0.73 | 0.00063 |
| hsa05418 | Fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis | 7 | 133 | 0.73 | 0.00063 |
| hsa04213 | Longevity regulating pathway—multiple species | 5 | 61 | 0.93 | 0.00064 |
| hsa04550 | Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells | 7 | 138 | 0.72 | 0.00076 |
| hsa05211 | Renal cell carcinoma | 5 | 68 | 0.88 | 0.001 |
| hsa04920 | Adipocytokine signaling pathway | 5 | 69 | 0.87 | 0.0011 |
| hsa05219 | Bladder cancer | 4 | 41 | 1 | 0.0013 |
| hsa04211 | Longevity regulating pathway | 5 | 88 | 0.77 | 0.0029 |
| hsa04923 | Regulation of lipolysis in adipocytes | 4 | 53 | 0.89 | 0.0031 |
| hsa04120 | Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | 6 | 134 | 0.66 | 0.0033 |
| hsa04070 | Phosphatidylinositol signaling system | 5 | 97 | 0.72 | 0.0043 |
| hsa05034 | Alcoholism | 6 | 142 | 0.64 | 0.0043 |
| hsa05142 | Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis) | 5 | 101 | 0.71 | 0.005 |
| hsa04620 | Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | 5 | 102 | 0.7 | 0.0051 |
| hsa04932 | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) | 6 | 149 | 0.62 | 0.0053 |
| hsa05230 | Central carbon metabolism in cancer | 4 | 65 | 0.8 | 0.0059 |
| hsa03410 | Base excision repair | 3 | 33 | 0.97 | 0.0066 |
| hsa05143 | African trypanosomiasis | 3 | 34 | 0.96 | 0.0071 |
| hsa04622 | RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | 4 | 70 | 0.77 | 0.0075 |
| hsa05218 | Melanoma | 4 | 72 | 0.76 | 0.0081 |
| hsa05216 | Thyroid cancer | 3 | 37 | 0.92 | 0.0087 |
| hsa05202 | Transcriptional misregulation in cancer | 6 | 169 | 0.56 | 0.0091 |
| hsa04152 | AMPK signaling pathway | 5 | 120 | 0.63 | 0.0093 |
| hsa04962 | Vasopressin-regulated water reabsorption | 3 | 44 | 0.85 | 0.0132 |
| hsa05132 | Salmonella infection | 4 | 84 | 0.69 | 0.0132 |
| hsa03015 | mRNA surveillance pathway | 4 | 89 | 0.67 | 0.0157 |
| hsa04913 | Ovarian steroidogenesis | 3 | 49 | 0.8 | 0.0171 |
| hsa05030 | Cocaine addiction | 3 | 49 | 0.8 | 0.0171 |
| hsa03460 | Fanconi anemia pathway | 3 | 51 | 0.78 | 0.0187 |
| hsa05134 | Legionellosis | 3 | 54 | 0.76 | 0.0215 |
| hsa04137 | Mitophagy—animal | 3 | 63 | 0.69 | 0.0314 |
| hsa04714 | Thermogenesis | 6 | 228 | 0.43 | 0.0314 |
| hsa04927 | Cortisol synthesis and secretion | 3 | 63 | 0.69 | 0.0314 |
| hsa04976 | Bile secretion | 3 | 71 | 0.64 | 0.0413 |
| hsa04136 | Autophagy—other | 2 | 30 | 0.84 | 0.045 |
References
- Christiaansen, A.; Varga, S.M.; Spencer, J.V. Viral manipulation of the host immune response. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2015, 36, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McLean, J.E.; Ruck, A.; Shirazian, A.; Pooyaei-Mehr, F.; Zakeri, Z.F. Viral manipulation of cell death. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 198–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Etxebarria, K.; Sistiaga-Poveda, M.; Jugo, B.M. Endogenous retroviruses in domestic animals. Curr. Genom. 2014, 15, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Zhao, H.; Gong, Z.; Han, G.Z. Endogenous retroviruses of non-avian/mammalian vertebrates illuminate diversity and deep history of retroviruses. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, P.N.; Carnegie, P.R.; Martin, J.; Davari Ejtehadi, H.; Hooley, P.; Roden, D.; Rowland-Jones, S.; Warren, P.; Astley, J.; Murray, P.G. Demystified. Human endogenous retroviruses. Mol. Pathol. 2003, 56, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mayer, J.; Meese, E. Human endogenous retroviruses in the primate lineage and their influence on host genomes. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2005, 110, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohn, O.; Hanke, K.; Bannert, N. HERV-K(HML-2), the Best Preserved Family of HERVs: Endogenization, Expression, and Implications in Health and Disease. Front. Oncol. 2013, 3, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Downey, R.F.; Sullivan, F.J.; Wang-Johanning, F.; Ambs, S.; Giles, F.J.; Glynn, S.A. Human endogenous retrovirus K and cancer: Innocent bystander or tumorigenic accomplice? Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Douville, R.; Liu, J.; Rothstein, J.; Nath, A. Identification of active loci of a human endogenous retrovirus in neurons of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 69, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manghera, M.; Ferguson-Parry, J.; Douville, R.N. TDP-43 regulates endogenous retrovirus-K viral protein accumulation. Neurobiol. Dis. 2016, 94, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manghera, M.; Ferguson-Parry, J.; Lin, R.; Douville, R.N. NF-kappaB and IRF1 Induce Endogenous Retrovirus K Expression via Interferon-Stimulated Response Elements in Its 5′ Long Terminal Repeat. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 9338–9349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arru, G.; Mameli, G.; Deiana, G.A.; Rassu, A.L.; Piredda, R.; Sechi, E.; Caggiu, E.; Bo, M.; Nako, E.; Urso, D.; et al. Humoral immunity response to human endogenous retroviruses K/W differentiates between amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and other neurological diseases. Eur. J. Neurol. 2018, 25, e1076–e1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romer, C. Viruses and Endogenous Retroviruses as Roots for Neuroinflammation and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 648629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenig, M. HERVs, immunity, and autoimmunity: Understanding the connection. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vincendeau, M.; Gottesdorfer, I.; Schreml, J.M.; Wetie, A.G.; Mayer, J.; Greenwood, A.D.; Helfer, M.; Kramer, S.; Seifarth, W.; Hadian, K.; et al. Modulation of human endogenous retrovirus (HERV) transcription during persistent and de novo HIV-1 infection. Retrovirology 2015, 12, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pilie, P.G.; Tang, C.; Mills, G.B.; Yap, T.A. State-of-the-art strategies for targeting the DNA damage response in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 81–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penndorf, D.; Witte, O.W.; Kretz, A. DNA plasticity and damage in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neural Regen. Res. 2018, 13, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.B.; Almeida, S.; Lopez-Gonzalez, R. Dysregulated molecular pathways in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-frontotemporal dementia spectrum disorder. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 2931–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessl, J.J.; Kutluay, S.B.; Townsend, D.; Rebensburg, S.; Slaughter, A.; Larue, R.C.; Shkriabai, N.; Bakouche, N.; Fuchs, J.R.; Bieniasz, P.D.; et al. HIV-1 Integrase Binds the Viral RNA Genome and Is Essential during Virion Morphogenesis. Cell 2016, 166, 1257–1268.e1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lesbats, P.; Engelman, A.N.; Cherepanov, P. Retroviral DNA Integration. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 12730–12757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daniel, R.; Kao, G.; Taganov, K.; Greger, J.G.; Favorova, O.; Merkel, G.; Yen, T.J.; Katz, R.A.; Skalka, A.M. Evidence that the retroviral DNA integration process triggers an ATR-dependent DNA damage response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 4778–4783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Skalka, A.M.; Katz, R.A. Retroviral DNA integration and the DNA damage response. Cell Death Differ. 2005, 12 (Suppl. S1), 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bray, S.; Turnbull, M.; Hebert, S.; Douville, R.N. Insight into the ERVK Integrase—Propensity for DNA Damage. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kitamura, Y.; Ayukawa, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Kanda, T.; Yoshiike, K. Human endogenous retrovirus K10 encodes a functional integrase. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 3302–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Maele, B.; Busschots, K.; Vandekerckhove, L.; Christ, F.; Debyser, Z. Cellular co-factors of HIV-1 integration. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2006, 31, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christ, F.; Debyser, Z. The LEDGF/p75 integrase interaction, a novel target for anti-HIV therapy. Virology 2013, 435, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Studamire, B.; Goff, S.P. Interactions of host proteins with the murine leukemia virus integrase. Viruses 2010, 2, 1110–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jayappa, K.D.; Ao, Z.; Wang, X.; Mouland, A.J.; Shekhar, S.; Yang, X.; Yao, X. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 employs the cellular dynein light chain 1 protein for reverse transcription through interaction with its integrase protein. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 3497–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryan, E.L.; Hollingworth, R.; Grand, R.J. Activation of the DNA Damage Response by RNA Viruses. Biomolecules 2016, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, Y.; Craigie, R. The road to chromatin—Nuclear entry of retroviruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Chew, M.L. Role of host-encoded proteins in restriction of retroviral integration. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daniel, R.; Greger, J.G.; Katz, R.A.; Taganov, K.D.; Wu, X.; Kappes, J.C.; Skalka, A.M. Evidence that stable retroviral transduction and cell survival following DNA integration depend on components of the nonhomologous end joining repair pathway. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 8573–8581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turlure, F.; Devroe, E.; Silver, P.A.; Engelman, A. Human cell proteins and human immunodeficiency virus DNA integration. Front. Biosci. 2004, 9, 3187–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cooper, A.; Garcia, M.; Petrovas, C.; Yamamoto, T.; Koup, R.A.; Nabel, G.J. HIV-1 causes CD4 cell death through DNA-dependent protein kinase during viral integration. Nature 2013, 498, 376–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mourad, R.; Ginalski, K.; Legube, G.; Cuvier, O. Predicting double-strand DNA breaks using epigenome marks or DNA at kilobase resolution. Genome Biol. 2018, 19, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stetson, D.B.; Ko, J.S.; Heidmann, T.; Medzhitov, R. Trex1 prevents cell-intrinsic initiation of autoimmunity. Cell 2008, 134, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Scadden, D.T.; Crumpacker, C.S. Primitive hematopoietic cells resist HIV-1 infection via p21. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ran, X.; Ao, Z.; Olukitibi, T.; Yao, X. Characterization of the Role of Host Cellular Factor Histone Deacetylase 10 during HIV-1 Replication. Viruses 2019, 12, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, H.; Mano, M.; Braga, L.; Naseem, A.; Marini, B.; Vu, D.M.; Collesi, C.; Meroni, G.; Lusic, M.; Giacca, M. Cellular TRIM33 restrains HIV-1 infection by targeting viral integrase for proteasomal degradation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulder, L.C.; Chakrabarti, L.A.; Muesing, M.A. Interaction of HIV-1 integrase with DNA repair protein hRad18. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 27489–27493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Maele, B.; Debyser, Z. HIV-1 integration: An interplay between HIV-1 integrase, cellular and viral proteins. AIDS Rev. 2005, 7, 26–43. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Anisenko, A.N.; Knyazhanskaya, E.S.; Zalevsky, A.O.; Agapkina, J.Y.; Sizov, A.I.; Zatsepin, T.S.; Gottikh, M.B. Characterization of HIV-1 integrase interaction with human Ku70 protein and initial implications for drug targeting. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BLAST. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/BLAST/ (accessed on 12 July 2021).
- Rosindell, J.; Harmon, L.J. OneZoom: A fractal explorer for the tree of life. PLoS Biol. 2012, 10, e1001406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Wang, J.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Geer, R.C.; Gonzales, N.R.; Gwadz, M.; Hurwitz, D.I.; Marchler, G.H.; Song, J.S.; et al. CDD/SPARCLE: The conserved domain database in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D265–D268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, M.; Gouw, M.; Michael, S.; Sámano-Sánchez, H.; Pancsa, R.; Glavina, J.; Diakogianni, A.; Valverde, J.A.; Bukirova, D.; Čalyševa, J.; et al. ELM-the eukaryotic linear motif resource in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D296–D306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.M.; Liou, Y.C. Gears-In-Motion: The Interplay of WW and PPIase Domains in Pin1. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramos, F.; Villoria, M.T.; Alonso-Rodriguez, E.; Clemente-Blanco, A. Role of protein phosphatases PP1, PP2A, PP4 and Cdc14 in the DNA damage response. Cell Stress 2019, 3, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knippschild, U.; Kruger, M.; Richter, J.; Xu, P.; Garcia-Reyes, B.; Peifer, C.; Halekotte, J.; Bakulev, V.; Bischof, J. The CK1 Family: Contribution to Cellular Stress Response and Its Role in Carcinogenesis. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fry, A.M.; O’Regan, L.; Sabir, S.R.; Bayliss, R. Cell cycle regulation by the NEK family of protein kinases. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 4423–4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Sharma, G.; Chakraborty, C.; Sharma, A.R.; Kim, J. Regulatory functional territory of PLK-1 and their substrates beyond mitosis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 37942–37962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinhardt, H.C.; Yaffe, M.B. Phospho-Ser/Thr-binding domains: Navigating the cell cycle and DNA damage response. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 563–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Long, J.E. STAT3 roles in viral infection: Antiviral or proviral? Future Virol. 2018, 13, 557–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rani, A.; Murphy, J.J. STAT5 in Cancer and Immunity. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2016, 36, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, K.; Mahajan, N.P. Cross talk of tyrosine kinases with the DNA damage signaling pathways. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 10588–10601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teyra, J.; Huang, H.; Jain, S.; Guan, X.; Dong, A.; Liu, Y.; Tempel, W.; Min, J.; Tong, Y.; Kim, P.M.; et al. Comprehensive Analysis of the Human SH3 Domain Family Reveals a Wide Variety of Non-canonical Specificities. Structure 2017, 25, 1598–1610.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lalaoui, N.; Vaux, D.L. Recent advances in understanding inhibitor of apoptosis proteins. F1000Research 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, L.; Voss, C.; Wang, F.; Liu, J.; Li, S.S. A Comprehensive Immunoreceptor Phosphotyrosine-based Signaling Network Revealed by Reciprocal Protein-Peptide Array Screening. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2015, 14, 1846–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beurel, E.; Grieco, S.F.; Jope, R.S. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK3): Regulation, actions, and diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 148, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Canovas, B.; Nebreda, A.R. Diversity and versatility of p38 kinase signalling in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 346–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covill-Cooke, C.; Toncheva, V.S.; Kittler, J.T. Regulation of peroxisomal trafficking and distribution. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 1929–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Wittmann, T. + TIPs: SxIPping along microtubule ends. Trends Cell Biol. 2012, 22, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.Y.; Guo, X. Adaptor protein complexes and intracellular transport. Biosci. Rep. 2014, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egea, P.F. Crossing the Vacuolar Rubicon: Structural Insights into Effector Protein Trafficking in Apicomplexan Parasites. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matic, I.; Schimmel, J.; Hendriks, I.A.; van Santen, M.A.; van de Rijke, F.; van Dam, H.; Gnad, F.; Mann, M.; Vertegaal, A.C. Site-specific identification of SUMO-2 targets in cells reveals an inverted SUMOylation motif and a hydrophobic cluster SUMOylation motif. Mol. Cell 2010, 39, 641–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamborlini, A.; Coiffic, A.; Beauclair, G.; Delelis, O.; Paris, J.; Koh, Y.; Magne, F.; Giron, M.L.; Tobaly-Tapiero, J.; Deprez, E.; et al. Impairment of human immunodeficiency virus type-1 integrase SUMOylation correlates with an early replication defect. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 21013–21022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X. SUMO-Mediated Regulation of Nuclear Functions and Signaling Processes. Mol. Cell 2018, 71, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quek, H.; Lim, Y.C.; Lavin, M.F.; Roberts, T.L. PIKKing a way to regulate inflammation. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2018, 96, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penalosa-Ruiz, G.; Bousgouni, V.; Gerlach, J.P.; Waarlo, S.; van de Ven, J.V.; Veenstra, T.E.; Silva, J.C.R.; van Heeringen, S.J.; Bakal, C.; Mulder, K.W.; et al. WDR5, BRCA1, and BARD1 Co-regulate the DNA Damage Response and Modulate the Mesenchymal-to-Epithelial Transition during Early Reprogramming. Stem Cell Rep. 2019, 12, 743–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wheatley, S.P.; Altieri, D.C. Survivin at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2019, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fang, Y.; Zhang, X. Targeting NEK2 as a promising therapeutic approach for cancer treatment. Cell Cycle 2016, 15, 895–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Carcer, G. The Mitotic Cancer Target Polo-Like Kinase 1: Oncogene or Tumor Suppressor? Genes 2019, 10, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Grevenynghe, J.; Cubas, R.A.; DaFonseca, S.; Metcalf, T.; Tremblay, C.L.; Trautmann, L.; Sekaly, R.P.; Schatzle, J.; Haddad, E.K. Foxo3a: An integrator of immune dysfunction during HIV infection. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2012, 23, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aloni-Grinstein, R.; Charni-Natan, M.; Solomon, H.; Rotter, V. p53 and the Viral Connection: Back into the Future (double dagger). Cancers 2018, 10, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, J.; Moyes, D.L.; Tavassoli, M.; Naglik, J.R. The Role of ErbB Receptors in Infection. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 942–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanizadeh, S.; Hasanvand, B.; Esmaeil Lashgarian, H.; Almasian, M.; Goudarzi, G. Interaction of viral oncogenic proteins with the Wnt signaling pathway. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2018, 21, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martini, W.; Rahman, R.; Ojegba, E.; Jungwirth, E.; Macias, J.; Ackerly, F.; Fowler, M.; Cottrell, J.; Chu, T.; Chang, S.L. Kinases: Understanding Their Role in HIV Infection. World J. AIDS 2019, 9, 142–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medders, K.E.; Kaul, M. Mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 in HIV infection and associated brain injury. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2011, 6, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saez-Cirion, A.; Manel, N. Immune Responses to Retroviruses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 36, 193–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.H.; Sun, S.C. Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor-Associated Factor Regulation of Nuclear Factor kappaB and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathways. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehlig, A.; Molina, A.; Rodrigues-Ferreira, S.; Honore, S.; Nahmias, C. Regulation of end-binding protein EB1 in the control of microtubule dynamics. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 2381–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cao, H.; Orth, J.D.; Chen, J.; Weller, S.G.; Heuser, J.E.; McNiven, M.A. Cortactin is a component of clathrin-coated pits and participates in receptor-mediated endocytosis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 2162–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zare, M.; Mostafaei, S.; Ahmadi, A.; Azimzadeh Jamalkandi, S.; Abedini, A.; Esfahani-Monfared, Z.; Dorostkar, R.; Saadati, M. Human endogenous retrovirus env genes: Potential blood biomarkers in lung cancer. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 115, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergallo, M.; Montanari, P.; Mareschi, K.; Merlino, C.; Berger, M.; Bini, I.; Dapra, V.; Galliano, I.; Fagioli, F. Expression of the pol gene of human endogenous retroviruses HERV-K and -W in leukemia patients. Arch. Virol 2017, 162, 3639–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Hong, Z.; Liu, H.; Chen, X.; Ding, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, F.; Yuan, Y. Human Endogenous Retroviruses-K (HML-2) Expression Is Correlated with Prognosis and Progress of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 8201642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Soto, C.; Jiang, X.; An, Z.; Zheng, W.J. Human Endogenous Retroviruses in Glioblastoma Multiforme. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dembny, P.; Newman, A.G.; Singh, M.; Hinz, M.; Szczepek, M.; Kruger, C.; Adalbert, R.; Dzaye, O.; Trimbuch, T.; Wallach, T.; et al. Human endogenous retrovirus HERV-K(HML-2) RNA causes neurodegeneration through Toll-like receptors. JCI Insight 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeong, B.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Carp, R.I.; Kim, Y.S. The prevalence of human endogenous retroviruses in cerebrospinal fluids from patients with sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J. Clin. Virol. 2010, 47, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovo, P.A.; Rabbone, I.; Tinti, D.; Galliano, I.; Trada, M.; Dapra, V.; Cerutti, F.; Bergallo, M. Enhanced expression of human endogenous retroviruses in new-onset type 1 diabetes: Potential pathogenetic and therapeutic implications. Autoimmunity 2020, 53, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, M.J.; Speake, C.; Gersuk, V.H.; Nguyen, Q.A.; O’Brien, K.K.; Odegard, J.M.; Buckner, J.H.; Greenbaum, C.J.; Chaussabel, D.; Nepom, G.T. Low HERV-K(C4) copy number is associated with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2014, 63, 1789–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dickerson, F.; Rubalcaba, E.; Viscidi, R.; Yang, S.; Stallings, C.; Sullens, A.; Origoni, A.; Leister, F.; Yolken, R. Polymorphisms in human endogenous retrovirus K-18 and risk of type 2 diabetes in individuals with schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2008, 104, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinek, O.; Kramna, L.; Odeh, R.; Alassaf, A.; Ibekwe, M.A.U.; Ahmadov, G.; Elmahi, B.M.E.; Mekki, H.; Lebl, J.; Abdullah, M.A. Eukaryotic viruses in the fecal virome at the onset of type 1 diabetes: A study from four geographically distant African and Asian countries. Pediatr. Diabetes 2021, 22, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piekna-Przybylska, D.; Sharma, G.; Maggirwar, S.B.; Bambara, R.A. Deficiency in DNA damage response, a new characteristic of cells infected with latent HIV-1. Cell Cycle 2017, 16, 968–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, D.; Lopez, A.; Sandoval, C.; Nichols Doyle, R.; Fregoso, O.I. HIV Vpr Modulates the Host DNA Damage Response at Two Independent Steps to Damage DNA and Repress Double-Strand DNA Break Repair. mBio 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, H.; Guo, X.; Ho, Y.K.; Pasupala, N.; Engstrom, H.A.A.; Semmes, O.J.; Giam, C.Z. RNF8 Dysregulation and Down-regulation During HTLV-1 Infection Promote Genomic Instability in Adult T-Cell Leukemia. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luftig, M.A. Viruses and the DNA Damage Response: Activation and Antagonism. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2014, 1, 605–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hristova, D.B.; Lauer, K.B.; Ferguson, B.J. Viral interactions with non-homologous end-joining: A game of hide-and-seek. J. Gen. Virol. 2020, 101, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, D.H.; Yaffe, M.B. 14-3-3 proteins, FHA domains and BRCT domains in the DNA damage response. DNA Repair 2009, 8, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pancholi, N.J.; Price, A.M.; Weitzman, M.D. Take your PIKK: Tumour viruses and DNA damage response pathways. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zimmerman, E.S.; Chen, J.; Andersen, J.L.; Ardon, O.; Dehart, J.L.; Blackett, J.; Choudhary, S.K.; Camerini, D.; Nghiem, P.; Planelles, V. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Vpr-mediated G2 arrest requires Rad17 and Hus1 and induces nuclear BRCA1 and gamma-H2AX focus formation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 9286–9294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shukrun, M.; Jabareen, A.; Abou-Kandil, A.; Chamias, R.; Aboud, M.; Huleihel, M. HTLV-1 Tax oncoprotein inhibits the estrogen-induced-ER alpha-Mediated BRCA1 expression by interaction with CBP/p300 cofactors. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, K.G.; Lal, S.K. The Multifarious Role of 14-3-3 Family of Proteins in Viral Replication. Viruses 2020, 12, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Jubb, H.; Blundell, T.L. Phosphopeptide interactions with BRCA1 BRCT domains: More than just a motif. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2015, 117, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clapperton, J.A.; Manke, I.A.; Lowery, D.M.; Ho, T.; Haire, L.F.; Yaffe, M.B.; Smerdon, S.J. Structure and mechanism of BRCA1 BRCT domain recognition of phosphorylated BACH1 with implications for cancer. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2004, 11, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Cui, L.; Zeng, Y.; Song, W.; Gaur, U.; Yang, M. 14-3-3 Proteins Are on the Crossroads of Cancer, Aging, and Age-Related Neurodegenerative Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morales, D.; Skoulakis, E.C.; Acevedo, S.F. 14-3-3s are potential biomarkers for HIV-related neurodegeneration. J. Neurovirol. 2012, 18, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roskoski, R., Jr. RAF protein-serine/threonine kinases: Structure and regulation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 399, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wang, J.Y.; Parker, L.L. Detection of early Abl kinase activation after ionizing radiation by using a peptide biosensor. ChemBioChem Eur. J. Chem. Biol. 2012, 13, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, S.D.S.; Leontyev, D.; Nicoletti, P.; Binnington, B.; Kozlowski, H.N.; Ostrowski, M.; Cochrane, A.; Branch, D.R.; Wong, R.W. Targeting ABL1 or ARG Tyrosine Kinases to Restrict HIV-1 Infection in Primary CD4+ T-Cells or in Humanized NSG Mice. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2019, 82, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, D.; Tanaka, M.; Matsuzaki, T.; Izumo, K.; Nakano, N.; Matsuura, E.; Saito, M.; Nagai, M.; Horiuchi, M.; Utsunomiya, A.; et al. Inhibition of ABL1 tyrosine kinase reduces HTLV-1 proviral loads in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskaran, R.; Escobar, S.R.; Wang, J.Y. Nuclear c-Abl is a COOH-terminal repeated domain (CTD)-tyrosine (CTD)-tyrosine kinase-specific for the mammalian RNA polymerase II: Possible role in transcription elongation. Cell Growth Differ. 1999, 10, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schlatterer, S.D.; Acker, C.M.; Davies, P. c-Abl in neurodegenerative disease. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2011, 45, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, B.W.; Jeong, Y.E.; Wong, M.; Martin, L.J. DNA damage accumulates and responses are engaged in human ALS brain and spinal motor neurons and DNA repair is activatable in iPSC-derived motor neurons with SOD1 mutations. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2020, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Mani, A.M.; Wu, Z.H. DNA damage-induced nuclear factor-kappa B activation and its roles in cancer progression. J. Cancer Metastasis Treat. 2017, 3, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, S.; Xue, Y.; Tang, S.; Yao, J.; Du, R.; Yang, P.; Chen, X. 14-3-3 epsilon dynamically interacts with key components of mitogen-activated protein kinase signal module for selective modulation of the TNF-alpha-induced time course-dependent NF-kappaB activity. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 3465–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennington, K.L.; Chan, T.Y.; Torres, M.P.; Andersen, J.L. The dynamic and stress-adaptive signaling hub of 14-3-3: Emerging mechanisms of regulation and context-dependent protein-protein interactions. Oncogene 2018, 37, 5587–5604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saha, R.N.; Jana, M.; Pahan, K. MAPK p38 regulates transcriptional activity of NF-kappaB in primary human astrocytes via acetylation of p65. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 7101–7109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Y.; Ao, Z.; Wang, B.; Jayappa, K.D.; Yao, X. Host protein Ku70 binds and protects HIV-1 integrase from proteasomal degradation and is required for HIV replication. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 17722–17735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Llano, M.; Delgado, S.; Vanegas, M.; Poeschla, E.M. Lens epithelium-derived growth factor/p75 prevents proteasomal degradation of HIV-1 integrase. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 55570–55577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manganaro, L.; Lusic, M.; Gutierrez, M.I.; Cereseto, A.; Del Sal, G.; Giacca, M. Concerted action of cellular JNK and Pin1 restricts HIV-1 genome integration to activated CD4+ T lymphocytes. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quy, V.C.; Carnevale, V.; Manganaro, L.; Lusic, M.; Rossetti, G.; Leone, V.; Fenollar-Ferrer, C.; Raugei, S.; Del Sal, G.; Giacca, M.; et al. HIV-1 integrase binding to its cellular partners: A perspective from computational biology. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 3412–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, Y.; Ryo, A. Pinning down viral proteins: A new prototype for virus-host cell interaction. Front. Microbiol. 2010, 1, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nieto-Torres, J.L.; Leidal, A.M.; Debnath, J.; Hansen, M. Beyond Autophagy: The Expanding Roles of ATG8 Proteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leymarie, O.; Lepont, L.; Berlioz-Torrent, C. Canonical and Non-Canonical Autophagy in HIV-1 Replication Cycle. Viruses 2017, 9, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicencio, E.; Beltran, S.; Labrador, L.; Manque, P.; Nassif, M.; Woehlbier, U. Implications of Selective Autophagy Dysfunction for ALS Pathology. Cells 2020, 9, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, Y.; Taguchi, K.; Tanaka, M. Ubiquitin, Autophagy and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Cells 2020, 9, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrini, S.; Gorgoulis, V.G.; Halazonetis, T.D. Genomic instability--an evolving hallmark of cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Curle, A.J.; Haider, A.M.; Balmus, G. The role of DNA damage response in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Essays Biochem. 2020, 64, 847–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Song, H.; Croteau, D.L.; Akbari, M.; Bohr, V.A. Genome instability in Alzheimer disease. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2017, 161, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madabhushi, R.; Pan, L.; Tsai, L.H. DNA damage and its links to neurodegeneration. Neuron 2014, 83, 266–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malaspina, A.; Kaushik, N.; de Belleroche, J. A 14-3-3 mRNA is up-regulated in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis spinal cord. J. Neurochem. 2000, 75, 2511–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hermeking, H. The 14-3-3 cancer connection. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 931–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, L.J. p53 is abnormally elevated and active in the CNS of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurobiol. Dis. 2000, 7, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozaki, T.; Nakagawara, A. Role of p53 in Cell Death and Human Cancers. Cancers 2011, 3, 994–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koul, H.K.; Pal, M.; Koul, S. Role of p38 MAP Kinase Signal Transduction in Solid Tumors. Genes Cancer 2013, 4, 342–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Vandoorne, T.; Steyaert, J.; Staats, K.A.; Van Den Bosch, L. The multifaceted role of kinases in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Genetic, pathological and therapeutic implications. Brain 2020, 143, 1651–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Guan, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Meng, F.; Wang, X.; Gao, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, F.; Zhou, S.; et al. Potential Roles of the WNT Signaling Pathway in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Cells 2021, 10, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menck, K.; Heinrichs, S.; Baden, C.; Bleckmann, A. The WNT/ROR Pathway in Cancer: From Signaling to Therapeutic Intervention. Cells 2021, 10, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manigrasso, M.B.; Juranek, J.; Ramasamy, R.; Schmidt, A.M. Unlocking the biology of RAGE in diabetic microvascular complications. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 25, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, V.; Fleming, T.; Terjung, S.; Gorzelanny, C.; Gebhardt, C.; Agrawal, R.; Mall, M.A.; Ranzinger, J.; Zeier, M.; Madhusudhan, T.; et al. Homeostatic nuclear RAGE-ATM interaction is essential for efficient DNA repair. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 10595–10613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, R.; Yamagishi, S. AGE-RAGE system and carcinogenesis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 940–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derk, J.; MacLean, M.; Juranek, J.; Schmidt, A.M. The Receptor for Advanced Glycation Endproducts (RAGE) and Mediation of Inflammatory Neurodegeneration. J. Alzheimers Dis. Parkinsonism 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaposhnikov, M.; Proshkina, E.; Shilova, L.; Zhavoronkov, A.; Moskalev, A. Lifespan and Stress Resistance in Drosophila with Overexpressed DNA Repair Genes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garinis, G.A.; van der Horst, G.T.; Vijg, J.; Hoeijmakers, J.H. DNA damage and ageing: New-age ideas for an age-old problem. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelman, A.N. Multifaceted HIV integrase functionalities and therapeutic strategies for their inhibition. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 15137–15157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cherepanov, P. LEDGF/p75 interacts with divergent lentiviral integrases and modulates their enzymatic activity in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anisenko, A.; Kan, M.; Shadrina, O.; Brattseva, A.; Gottikh, M. Phosphorylation Targets of DNA-PK and Their Role in HIV-1 Replication. Cells 2020, 9, 1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos da Silva, E.; Shanmugapriya, S.; Malikov, V.; Gu, F.; Delaney, M.K.; Naghavi, M.H. HIV-1 capsids mimic a microtubule regulator to coordinate early stages of infection. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e104870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, D.S.; Rosa, M.T.; Vieira, C.; Loreto, E.L.S. Oxidative and radiation stress induces transposable element transcription in Drosophila melanogaster. J. Evol. Biol. 2021, 34, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salces-Ortiz, J.; Vargas-Chavez, C.; Guio, L.; Rech, G.E.; Gonzalez, J. Transposable elements contribute to the genomic response to insecticides in Drosophila melanogaster. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2020, 375, 20190341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| ELM Motif | ELM Accession | Alignment Notation | Integrase | Conservation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERVK | MMTV | M-PMV | ENTV | JSRV | |||||
| Cleavage and degradation | CLV_C14_Caspase3-7 | ELME000321 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0.4 | |
| CLV_PCSK_KEX2_1 | ELME000108 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | ||
| CLV_NRD_NRD_1 | ELME000102 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.6 | ||
| CLV_PCSK_PC1ET2_1 | ELME000100 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | ||
| CLV_PCSK_SKI1_1 | ELME000146 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0.8 | ||
| DEG_APCC_DBOX_1 | ELME000231 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.2 | ||
| Docking | DOC_CKS1_1 | ELME000358 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | |
| DOC_CYCLIN_RxL_1 | ELME000106 | Cyclin | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0.4 | |
| DOC_MAPK_gen_1 | ELME000233 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.6 | ||
| DOC_MAPK_MEF2A_6 | ELME000432 | ERK/p38 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.8 | |
| DOC_PP1_RVXF_1 | ELME000137 | PP1c | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.0 | |
| DOC_PP2B_LxvP_1 | ELME000367 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.4 | ||
| DOC_PP4_FxxP_1 | ELME000477 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.6 | ||
| DOC_USP7_MATH_1 | ELME000239 | USP7_M | 1 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0.8 | |
| DOC_USP7_UBL2_3 | ELME000394 | USP7_U | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.4 | |
| DOC_WW_Pin1_4 | ELME000136 | Pin1 | 3 | 6 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1.0 | |
| Ligand | LIG_14-3-3_CanoR_1 | ELME000417 | 14-3-3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1.0 |
| LIG_14-3-3_CterR_2 | ELME000418 | 14-3-3 * | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | |
| LIG_Actin_WH2_2 | ELME000313 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.6 | ||
| LIG_APCC_ABBA_1 | ELME000435 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | ||
| LIG_BIR_II_1 | ELME000285 | IAP | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.0 | |
| LIG_BIR_III_4 | ELME000293 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.2 | ||
| LIG_BRCT_BRCA1_1 | ELME000197 | BRCT | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.8 | |
| LIG_BRCT_BRCA1_2 | ELME000198 | BRCT1 * | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | |
| LIG_CSL_BTD_1 | ELME000410 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.4 | ||
| LIG_EH1_1 | ELME000148 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0.4 | ||
| LIG_eIF4E_1 | ELME000317 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | ||
| LIG_FHA_1 | ELME000052 | FHA | 5 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0.8 | |
| LIG_FHA_2 | ELME000220 | FHA 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.6 | |
| LIG_LIR_Apic_2 | ELME000369 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0.8 | ||
| LIG_LIR_Gen_1 | ELME000368 | LIR | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | |
| LIG_MAD2 | ELME000167 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.2 | ||
| LIG_NRBOX | ELME000045 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.2 | ||
| LIG_LIR_Nem_3 | ELME000370 | 0 | 6 | 7 | 1 | 4 | 0.8 | ||
| LIG_Pex14_1 | ELME000080 | Pex14 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | |
| LIG_Pex14_2 | ELME000328 | Pex14 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.0 | |
| LIG_PTB_Apo_2 | ELME000122 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0.4 | ||
| LIG_PTB_Phospho_1 | ELME000095 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.2 | ||
| LIG_RPA_C_Fungi | ELME000382 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.6 | ||
| LIG_SH2_CRK | ELME000458 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | ||
| LIG_SH2_NCK_1 | ELME000474 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | ||
| LIG_SH2_PTP2 | ELME000083 | SH2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.8 | |
| LIG_SH2_SRC | ELME000081 | SH2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.0 | |
| LIG_SH2_STAP1 | ELME000465 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.4 | ||
| LIG_SH2_STAT3 | ELME000163 | STAT3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.0 | |
| LIG_SH2_STAT5 | ELME000182 | STAT5 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1.0 | |
| LIG_SH3_1 | ELME000005 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | ||
| LIG_SH3_3 | ELME000155 | SH3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.0 | |
| LIG_SH3_4 | ELME000156 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.2 | ||
| LIG_SxIP_EBH_1 | ELME000254 | EBH | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1.0 | |
| LIG_TRAF2_1 | ELME000117 | TRAF2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.8 | |
| LIG_TYR_ITIM | ELME000020 | ITIM | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.0 | |
| LIG_Vh1_VBS_1 | ELME000438 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.2 | ||
| LIG_WD40_WDR5_VDV_2 | ELME000365 | WDR5 | 2 | 10 | 3 | 8 | 9 | 1.0 | |
| LIG_WW_3 | ELME000135 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | ||
| Modification | MOD_CDK_SPK_2 | ELME000429 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | |
| MOD_CDK_SPxK_1 | ELME000153 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | ||
| MOD_CK1_1 | ELME000063 | CK1-P | 1 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 1.0 | |
| MOD_CK2_1 | ELME000064 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.6 | ||
| MOD_Cter_Amidation | ELME000093 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | ||
| MOD_GlcNHglycan | ELME000085 | GlyNH | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1.0 | |
| MOD_GSK3_1 | ELME000053 | GSK3-P | 3 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1.0 | |
| MOD_NEK2_1 | ELME000336 | NEK2-P | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 1.0 | |
| MOD_NEK2_2 | ELME000337 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | ||
| MOD_N-GLC_1 | ELME000070 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0.6 | ||
| MOD_PIKK_1 | ELME000202 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.4 | ||
| MOD_PKA_1 | ELME000008 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | ||
| MOD_PKA_2 | ELME000062 | PKA-P | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0.8 | |
| MOD_Plk_1 | ELME000442 | PLK-P | 4 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1.0 | |
| MOD_Plk_4 | ELME000444 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.4 | ||
| MOD_ProDKin_1 | ELME000159 | p38-P | 3 | 6 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1.0 | |
| MOD_SUMO_rev_2 | ELME000393 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.4 | ||
| Target | TRG_ENDOCYTIC_2 | ELME000120 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1.0 | |
| TRG_Pf-PMV_PEXEL_1 | ELME000462 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.0 | ||
| ELM Motif | ELM Accession | ERVK Integrase (Homo sapiens) | ERVK-8 Pol protein-Like (Macaca fascicularis) | Pol Protein (Chlorocebus sabaeus) | Pol Protein (Fukomys darmarensis) | Putative Protein (Ochonta princeps) | ERVK-8 pol Protein-Like (Equus asinus) | ERVK-18 pol Protein-Like (Capra hircus) | Pol Protein (Ovis aries) | Putative Protein (Zonotrichia albicollis) | Putative Protein (Zosterops borbonicus) | Integrase (Onchocerca flexuosa) | Motif conservation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cleavage | CLV_C14_Caspase3-7 | ELME000321 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 |
| CLV_NRD_NRD_1 | ELME000102 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.2 | |
| CLV_PCSK_KEX2_1 | ELME000108 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.3 | |
| CLV_PCSK_PC1ET2_1 | ELME000100 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.3 | |
| CLV_PCSK_SKI1_1 | ELME000146 | 5 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 7 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 0.8 | |
| Degradation | DEG_APCC_DBOX_1 | ELME000231 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.1 |
| DEG_MDM2_SWIB_1 | ELME000184 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | |
| Docking | DOC_CKS1_1 | ELME000358 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.5 |
| DOC_CYCLIN_RxL_1 | ELME000106 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 0.7 | |
| DOC_MAPK_DCC_7 | ELME000433 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.2 | |
| DOC_MAPK_gen_1 | ELME000233 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 0.8 | |
| DOC_MAPK_HePTP_8 | ELME000434 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.1 | |
| DOC_MAPK_MEF2A_6 | ELME000432 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 0.8 | |
| DOC_PP1_RVXF_1 | ELME000137 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.7 | |
| DOC_PP2A_B56_1 | ELME000425 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | |
| DOC_PP2B_LxvP_1 | ELME000367 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | |
| DOC_PP2B_PxIxI_1 | ELME000237 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | |
| DOC_PP4_FxxP_1 | ELME000477 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0.6 | |
| DOC_USP7_MATH_1 | ELME000239 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 0.9 | |
| DOC_USP7_MATH_2 | ELME000240 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | |
| DOC_USP7_UBL2_3 | ELME000394 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0.4 | |
| DOC_WW_Pin1_4 | ELME000136 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 0.8 | |
| Ligand | LIG_14-3-3_CanoR_1 | ELME000417 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1.0 |
| LIG_14-3-3_CterR_2 | ELME000418 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | |
| LIG_Actin_WH2_2 | ELME000313 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | |
| LIG_APCC_ABBA_1 | ELME000435 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | |
| LIG_BIR_II_1 | ELME000285 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.0 | |
| LIG_BIR_III_4 | ELME000293 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | |
| LIG_BRCT_BRCA1_1 | ELME000197 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0.5 | |
| LIG_BRCT_BRCA1_2 | ELME000198 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | |
| LIG_CSL_BTD_1 | ELME000410 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.5 | |
| LIG_deltaCOP1_diTrp_1 | ELME000459 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | |
| LIG_EH1_1 | ELME000148 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.3 | |
| LIG_eIF4E_1 | ELME000317 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.2 | |
| LIG_FHA_1 | ELME000052 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 0.8 | |
| LIG_FHA_2 | ELME000220 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.5 | |
| LIG_LIR_Apic_2 | ELME000369 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0.8 | |
| LIG_LIR_Gen_1 | ELME000368 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0.8 | |
| LIG_LIR_Nem_3 | ELME000370 | 6 | 5 | 7 | 6 | 7 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 6 | 1.0 | |
| LIG_LYPXL_S_1 | ELME000294 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.1 | |
| LIG_PCNA_PIPBox_1 | ELME000140 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | |
| LIG_PCNA_yPIPBox_3 | ELME000482 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.3 | |
| LIG_Pex14_1 | ELME000080 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0.4 | |
| LIG_Pex14_2 | ELME000328 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.9 | |
| LIG_PTB_Apo_2 | ELME000122 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0.5 | |
| LIG_PTB_Phospho_1 | ELME000095 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.4 | |
| LIG_REV1ctd_RIR_1 | ELME000450 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | |
| LIG_RPA_C_Fungi | ELME000382 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.3 | |
| LIG_SH2_CRK | ELME000458 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0.5 | |
| LIG_SH2_GRB2like | ELME000084 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.1 | |
| LIG_SH2_NCK_1 | ELME000474 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0.5 | |
| LIG_SH2_PTP2 | ELME000083 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0.7 | |
| LIG_SH2_SRC | ELME000081 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0.8 | |
| LIG_SH2_STAP1 | ELME000465 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.6 | |
| LIG_SH2_STAT3 | ELME000163 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.7 | |
| LIG_SH2_STAT5 | ELME000182 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 1.0 | |
| LIG_SH3_3 | ELME000155 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 1.0 | |
| LIG_SUMO_SIM_par_1 | ELME000333 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0.4 | |
| LIG_SxIP_EBH_1 | ELME000254 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.6 | |
| LIG_TRAF2_1 | ELME000117 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.6 | |
| LIG_TRAF6 | ELME000133 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | |
| LIG_TRFH_1 | ELME000249 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.1 | |
| LIG_TYR_ITIM | ELME000020 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0.7 | |
| LIG_UBA3_1 | ELME000395 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.2 | |
| LIG_Vh1_VBS_1 | ELME000438 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.4 | |
| LIG_WD40_WDR5_VDV_1 | ELME000364 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.1 | |
| LIG_WD40_WDR5_VDV_2 | ELME000365 | 2 | 10 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 10 | 10 | 12 | 1.0 | |
| LIG_WW_3 | ELME000135 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | |
| Modification | MOD_CDK_SPK_2 | ELME000429 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.3 |
| MOD_CDK_SPxxK_3 | ELME000428 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0.4 | |
| MOD_CK1_1 | ELME000063 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 0.9 | |
| MOD_CK2_1 | ELME000064 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.6 | |
| MOD_CMANNOS | ELME000160 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | |
| MOD_Cter_Amidation | ELME000093 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | |
| MOD_GlcNHglycan | ELME000085 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 0.9 | |
| MOD_GSK3_1 | ELME000053 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 0.9 | |
| MOD_NEK2_1 | ELME000336 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1.0 | |
| MOD_NEK2_2 | ELME000337 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0.5 | |
| MOD_N-GLC_1 | ELME000070 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0.6 | |
| MOD_N-GLC_2 | ELME000079 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.3 | |
| MOD_PIKK_1 | ELME000202 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0.6 | |
| MOD_PK_1 | ELME000065 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.3 | |
| MOD_PKA_1 | ELME000008 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.4 | |
| MOD_PKA_2 | ELME000062 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0.8 | |
| MOD_Plk_1 | ELME000442 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1.0 | |
| MOD_Plk_4 | ELME000444 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0.7 | |
| MOD_ProDKin_1 | ELME000159 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 0.9 | |
| MOD_SUMO_for_1 | ELME000002 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | |
| MOD_SUMO_rev_2 | ELME000393 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | |
| Targeting | TRG_ENDOCYTIC_2 | ELME000120 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1.0 |
| TRG_LysEnd_APsAcLL_1 | ELME000149 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0.2 | |
| TRG_NLS_MonoExtC_3 | ELME000278 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | |
| TRG_Pf-PMV_PEXEL_1 | ELME000462 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.0 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Benoit, I.; Brownell, S.; Douville, R.N. Predicted Cellular Interactors of the Endogenous Retrovirus-K Integrase Enzyme. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9071509
Benoit I, Brownell S, Douville RN. Predicted Cellular Interactors of the Endogenous Retrovirus-K Integrase Enzyme. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(7):1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9071509
Chicago/Turabian StyleBenoit, Ilena, Signy Brownell, and Renée N. Douville. 2021. "Predicted Cellular Interactors of the Endogenous Retrovirus-K Integrase Enzyme" Microorganisms 9, no. 7: 1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9071509
APA StyleBenoit, I., Brownell, S., & Douville, R. N. (2021). Predicted Cellular Interactors of the Endogenous Retrovirus-K Integrase Enzyme. Microorganisms, 9(7), 1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9071509






