Molecular Phylogeny of Unicellular Marine Coccoid Green Algae Revealed New Insights into the Systematics of the Ulvophyceae (Chlorophyta)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cultures and Light Microscopy
2.2. DNA Extraction, PCR, Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analyses
2.3. Secondary Structure Analyses for Species Delimitation and Distribution Pattern
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Phylogeny of the Ulvophyceae Based on SSU rDNA Sequences
3.2. ITS-2 Secondary Structures and the Usage of ITS-2/CBC Approach for Species Delineation
3.3. Distribution of Desmochloris, Chlorocystis and Sykidion Using BLASTn Search Algorithm
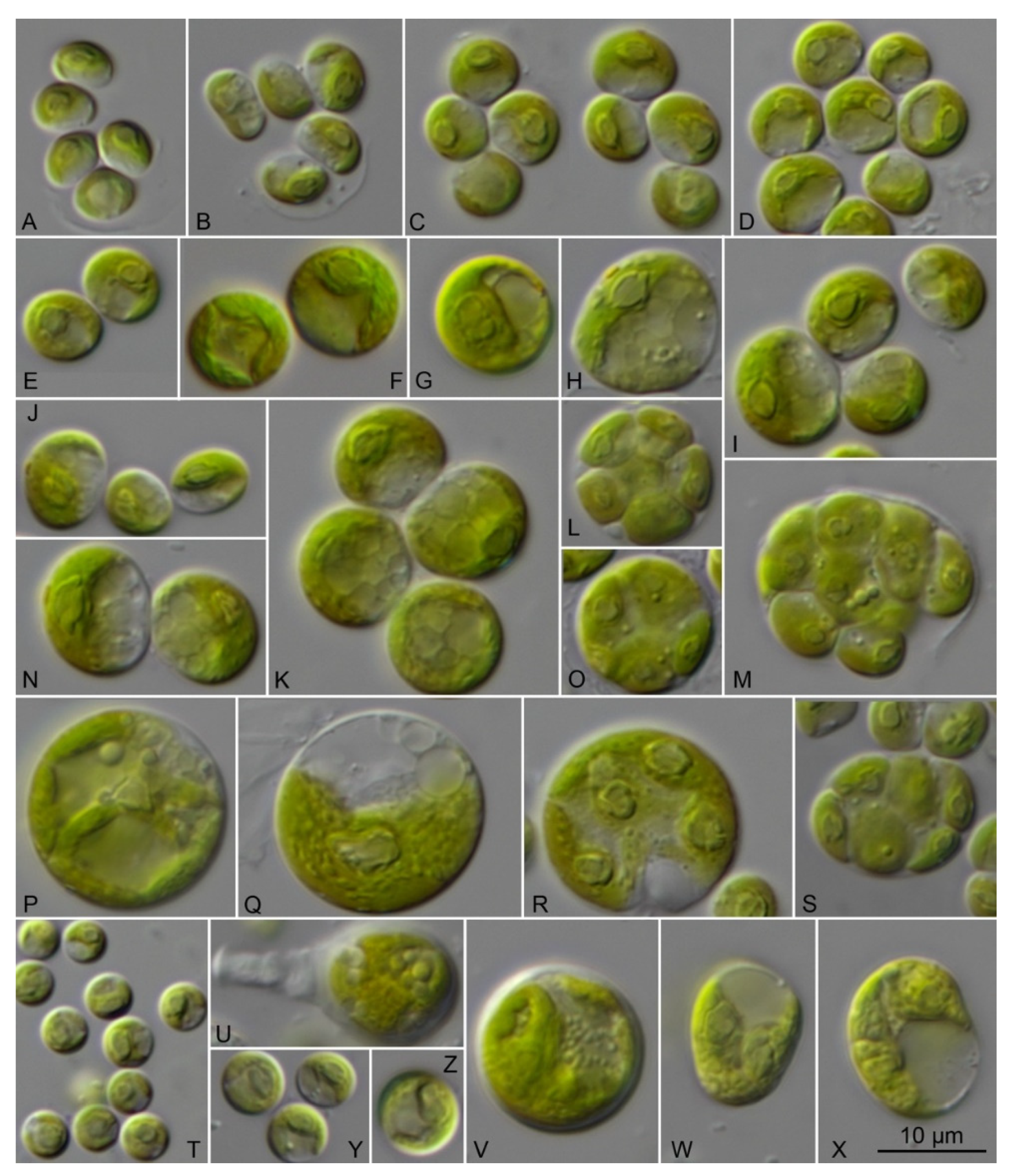
3.4. Morphology of the Investigated Strains
4. Discussion
4.1. Two Different Concepts: The Classes Ulvophyceae sensu Mattox and Stewart and Codiolo-phyceae sensu Kornmann and Their Subdivision into Orders
4.2. Diversity and Systematics of Marine Coccoid Green Algae
4.3. Taxonomic Revisions and Diagnoses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Friedl, T. The evolution of the green algae. In Origins of Algae and Their Plastids; Bhattacharya, D., Ed.; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 1997; pp. 87–101. [Google Scholar]
- Pröschold, T.; Leliaert, F. Systematics of the green algae: Conflict of classic and modern approaches. In Unravelling the Algae: The Past, Present, and Future of the Algae Systematics; Brodie, J., Lewis, J., Eds.; Taylor and Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2007; pp. 123–153. [Google Scholar]
- Komárek, J.; Fott, B. Chlorophyceae (Grünalgen) Ordnung: Chlorococcales. In Das Phytoplankton des Süßwassers 7. Teil, 1. Hälfte; Huber-Pestalozzi, G., Ed.; Schweizerbart: Stuttgart, Germany, 1983; pp. 1–1044. [Google Scholar]
- Huss, V.A.R.; Frank, C.; Hartmann, E.C.; Hirmer, M.; Kloboucek, A.; Seidel, B.M.; Wenzeler, P.; Kessler, E. Biochemical taxonomy and molecular phylogeny of the genus Chlorella Sensu Lato. J. Phycol. 1999, 35, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kessler, E.; Schäfer, M.; Hümmer, C.; Kloboucek, A.; Huss, V.A.R. Physiological, biochemical, and molecular characters for the taxonomy of the subgenera of Scenedesmus (Chlorococcales, Chlorophyta). Bot. Acta 1997, 110, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darienko, T.; Rad-Menéndez, C.; Campbell, C.; Pröschold, T. Are there any true marine Chlorella species? Molecular phylogenetic assessment and ecology of marine Chlorella-like organisms, including description of Droopiella gen. nov. Syst. Biodivers. 2019, 17, 811–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darienko, T.; Lukesova, A.; Pröschold, T. The polyphasic approach revealed new species of Chloroidium (Trebouxiophyceae, Chlorophyta). Phytotaxa 2018, 372, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, L.A.; Wilcox, L.W.; Fuerst, P.A.; Floyd, G.L. Concordance of molecular and ultrastructural data in the study of zoosporic chlorococcalean green algae. J. Phycol. 1992, 28, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattox, K.R.; Stewart, K.D. Classification of the green algae: A concept based on comparative cytology. In The Systematics of Green Algae; Irvine, D.E.G., John, D.M., Eds.; Systematics Association 27; Academic Press: London, UK, 1984; pp. 29–72. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, S.; Himizu, A.; Lewis, L.A.; Floyd, G.L.; Fuerst, P.A. Pseudoneochloris marina (Chlorophyta), a new coccoid ulvophycean alga, and its phylogenetic position inferred from morphological and molecular data. J. Phycol. 2000, 36, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, E.P. On a new genus and species of unicellular algae, living on the filaments of Rhizoclonium casparyi. Trans. Roy. Ir. Acad. 1881, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Wille, N. Studien über Chlorophyceen I–VII. Videnskap. Skr. Math. Naturvid. Kl. 1901, 1900, 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Guillard, R.R.L.; Bold, H.C.; MacEntee, F.J. Four new unicellular chlorophycean algae from mixohaline habitats. Phycologia 1975, 14, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Kuroda, N.; Maiwa, F. Phylogenetic status of Helicodictyon planctonicum and Desmochloris halophila gen. et comb. nov. and the definition of the class Ulvophyceae (Chlorophyta). Phycologia 2001, 40, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darienko, T.; Friedl, T.; Pröschold, T. Desmochloris mollenhauerii–A new terrestrial ulvophycean algae from south-west African soils (Molecular phylogeny and systematics of terrestrial Ulvophyceae I.). Algol. Stud. 2009, 129, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornmann, P.; Sahling, P.-H. Meeresalgen von Helgoland: Ergänzung. Helgol. Meeresunters. 1983, 36, 1–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornmann, P. Codiolophyceae, a new class of Chlorophyta. Helgol. Wiss. Meeresunters. 1973, 25, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kornmann, P. Phylogenetische Beziehungen in der Grünalgengattung Acrosiphonia. Helgol. Wiss. Meeresunters. 1970, 21, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kornmann, P. Les sporophytes vivant en endophyte de quelques Acrosiphoniacées et leurs rapports biologiques et taxo-nomiques. Mém. Soc. Bot. Fr. 1972, 1972, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.C. Studies on the life histories of marine algae. I. Codiolum petrocelidis and Spongomorpha coalita. Bull. Torrey Bot. Club 1959, 86, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornmann, P. Die Entwicklung von Codiolum gregarium A. Braun. Helgol. Wiss. Meeresunters. 1961, 7, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kornmann, P. Über Codiolum und Urospora. Helgol. Wiss. Meeresunters. 1961, 8, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kornmann, P. Über Spongomorpha lanosa und ihre Sporophytenformen. Helgol. Wiss. Meeresunters. 1961, 7, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kornmann, P. Zur Biologie von Spongomorpha aeruginosa (Linnaeus) van den Hoek. Helgol. Wiss. Meeresunters. 1964, 11, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornmann, P. Die Entwicklung von Monostroma grevillei. Helgol. Wiss. Meeresunters. 1962, 8, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kornmann, P. Die heterogene Gattung Gomontia I. Der sporangiale Anteil, Codiolum polyrhizum. Helgol. Wiss. Meeresunters. 1959, 6, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodel, A. Die Kraushaar-Alge Ulothrix zonata. Ihre geschlechtliche und ungeschlechtliche Fortpflanzung. Jahrb. Wiss. Bot. 1876, 10, 1–136. [Google Scholar]
- Kornmann, P. Advances in marine phycology on the basis of cultivation. Helgol. Wiss. Meeresunters. 1970, 20, 39–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Kelly, C.J.; Floyd, G.L. Correlations among patterns of sporangial structure and development, life histories, and ultrastructural features in the Ulvophyceae. In The Systematics of Green, Algae; Irvine, D.E.G., John, D.M., Eds.; Systematics Association 27; Academic Press: London, UK, 1984; pp. 121–156. [Google Scholar]
- Zechman, F.W.; Theriot, E.C.; Zimmer, E.A.; Chapman, R.L. Phylogeny of the Ulvophyceae (Chlorophyta): Cladistic analysis of nuclear-encoded rRNA sequence data. J. Phycol. 1990, 26, 700–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Nakayama, T. Ultrastructure and phylogenetic relationships of the unicellular green algae Ignatius tetrasporus and Pseudocharacium americanum (Chlorophyta). Phycol. Res. 2007, 55, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaloud, P.; Rindi, F.; Boedecker, C.; Leliaert, F. Chlorophyta: Ulvophyceae. In Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa 13; Büdel, B., Gärtner, G., Krienitz, L., Schagerl, M., Eds.; Springer Spektrum: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 1–288. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, S.; Li, Z.; Zhang, F.; Xiao, Y.; Cheng, H. Symbiochlorum hainanensis gen. et sp. nov. (Ulvophyceae, Chlorophyta) isolated from bleached corals living in the South China Sea. J. Phycol. 2018, 54, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlösser, U.G. Additions to the culture collections of algae since 1994. Bot. Acta 1997, 110, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlösser, U.G. SAG-Sammlung von Algenkulturen at the University of Göttingen. Bot. Acta 1994, 107, 424–429. [Google Scholar]
- Swofford, D.L. PAUP* Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (*and Other Methods), Version 4.0b10; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; Van Der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jow, H.; Hudelot, C.; Rattray, M.; Higgs, P. Bayesian phylogenetics using an RNA substitution model applied to early mammalian evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2002, 19, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgs, P.; Jameson, D.; Jow, H.; Rattray, M. The evolution of tRNA-Leu genes in animal mitochondrial genomes. J. Mol. Evol. 2003, 57, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hudelot, C.; Gowri-Shankar, V.; Jow, H.; Rattray, M.; Higgs, P. RNA-based phylogenetic methods: Application to mammalian mitochondrial RNA sequences. Mol. Phylogen. Evol. 2003, 28, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gibson, A.; Gowri-Shankar, V.; Higgs, P.; Rattray, M. A comprehensive analysis of mammalian mitochondrial genome base composition and improved phylogenetic methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Telford, M.J.; Wise, M.J.; Gowri-Shankar, V. Consideration of RNA secondary structure significantly improves likelihood-based estimates of phylogeny: Examples from the bilateria. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuker, M. Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acid Res. 2003, 31, 3406–3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darienko, T.; Pröschold, T. Toward a monograph of non-marine Ulvophyceae using an integrative approach (Molecular phylogeny and systematics of terrestrial Ulvophyceae II). Phytotaxa 2017, 324, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, M.; Posada, D.; Crandall, K.A. TCS: A computer program to estimate gene genealogies. Mol. Ecol. 2000, 9, 1657–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clement, M.; Snell, Q.; Walker, P.; Posada, D.; Crandall, K. TCS: Estimating gene genealogies. Parallel Distr. Process. Symp. Internat. Proc. 2002, 2, 184. [Google Scholar]
- Leigh, J.W.; Bryant, D. POPART: Full-feature software for haplotype network construction. Meth. Ecol. Evol. 2015, 6, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, J.A. New records of marine algae from Peru. Bot. Marina 1991, 34, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, J.A.; Braga, M. Halochlorococcum operculatum Kornmann et Sahling (Chlorophyta): New records from Brazil, Australia and South Africa. Hoehnea 1992, 19, 129–133. [Google Scholar]
- Sluiman, H.J. The green algal class Ulvophyceae. An ultrastructural survey and classification. Crypt. Bot. 1989, 1, 83–94. [Google Scholar]
- Floyd, G.L.; O‘Kelly, C.J. Phylum Chlorophyta: Class Ulvophyceae. In Handbook of Protoctista; Margulis, L., Corliss, J.O., Melkonian, M., Chapman, D.J., Eds.; Jones and Bartlett: Boston, MA, USA, 1990; pp. 617–635. [Google Scholar]
- Friedl, T. Evolution of the polyphyletic genus Pleurastrum (Chlorophyta): Inferences from nuclear-encoded ribosomal DNA sequences and motile cell ultrastructure. Phycologia 1996, 35, 456–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Hoek, C.; Stam, W.T.; Olsen, J.L. The emergence of a new chlorophytan system, and Dr. Kornmann’s contribution thereto. Helgol. Meeresunters. 1988, 42, 339–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van den Hoek, C.; Mann, D.G.; Jahns, H.M. Algae. An Introduction to Phycology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Cocquyt, E.; Verbruggen, H.; Leliaert, F.; De Clerck, O. Evolution and cytological diversification of the green seaweeds (Ulvophyceae). Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 2052–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leliaert, F.; Smith, D.R.; Moreau, H.; Herron, M.D.; Verbruggen, H.; Delwiche, C.F.; De Clerck, O. Phylogeny and molecular evolution of the green algae. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2012, 31, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skaloud, P.; Kalina, T.; Nemjova, K.; De Clerck, O.; Leliaert, F. Morphology and phylogenetic position of the freshwater green microalgae Chlorochytrium (Chlorophyceae) and Scotinosphaera (Scotinosphaerales, ord. nov., Ulvophyceae). J. Phycol. 2013, 49, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leliaert, F.; López-Bautista, J.M. The chloroplast genomes of Bryopsis plumosa and Tydemania expeditiones (Bryopsidales, Chlorophyta): Compact genomes and genes of bacterial origin. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 204. [Google Scholar]
- Turmel, M.; Otis, C.; Lemieux, C. Mitochondrion-to-chloroplast DNA transfers and intragenomic proliferation of chloroplast group II introns in Gloeotilopsis green algae (Ulotrichales, Ulvophyceae). Genome Biol. Evol. 2016, 8, 2789–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turmel, M.; Otis, C.; Lemieux, C. Divergent copies of the large inverted repeat in the chloroplast genomes of ulvophycean green algae. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Del Cortona, A.; Jackson, C.J.; Bucchini, F.; Van Bel, M.; D’hondt, S.; Škaloud, P.; Delwiche, C.W.; Knoll, A.H.; Raven, J.A.; Verbruggen, H.; et al. Neoproterozoic origin and multiple transitions to macroscopic growth in green seaweeds. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 2551–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulbrandsen, Ø.S.; Andresen, I.J.; Krabberød, A.K.; Bråte, J.; Shalchian-Tabrizi, K. Phylogenomic analysis restructures the Ulvophyceae. J. Phycol. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Dangeard, P.J.L. Sur deux Chlorococcales marines. Botaniste 1965, 48, 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Dangeard, P.J.L. Sur cinq espéces d‘Ulvella. Botaniste 1965, 48, 45–64. [Google Scholar]
- Bliding, C. A critical survey of European taxa in Ulvales. I. Capsosiphon Percursaria Blidingia Enteromorpha. Opera Bot. 1963, 8, 1–160. [Google Scholar]
- Bliding, C. A critical survey of European taxa in Ulvales. II. Ulva Ulvaria Monostroma Kornmannia. Bot. Notiser. 1968, 121, 535–629. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, E.P. On a new species of parasitic green algae belonging to the genus Chlorochytrium of Cohn. Trans. Roy. Ir. Acad. 1877, 26, 355–368. [Google Scholar]
- Guiry, M.D. Validation of some invalid names for green algae introduced by P.J.L. Dangeard. Not. Algarum 2017, 42, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann, W. Helgoländer Meeresalgen. I–VI. Wiss. Meeresunters. 1925, 16, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Lagerheim, G. Om Chlorochytrium cohnii Wright och dess förhållende till nästående arter. Öfvers. K. Ventensk. Akad. Förh. Stockh. 1884, 7, 91–97. [Google Scholar]
- Burrows, E.M. Seaweeds of the British Isles. Volume 2 Chlorophyta; Natural History Museum: London, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Reinhard, L. Algologische Untersuchungen. 1. Materialien zur Morphologie und Systematik der Algen des Schwarzen Meeres; Gesellschaft Naturforscher: Odessa, Ukraine, 1885. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Printz, H. Die Algenvegetation des Trondhjemsfjordes. Skr. Norske Vidensk. Akad. 1926, 1926, 1–274. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, G.T. New or little known unicellular algae. I. Chlorocystis Cohnii. Bot. Gaz. 1900, 30, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, N.L. New Pacific coast marine algae. I. Univ. Calif. Publ. Bot. 1917, 6, 377–416. [Google Scholar]
- West, J.A.; Smith, C.M.; McBride, D.L. Observations on the marine unicellular endophyte Chlorochytrium porphyrae (Chlorophyceae). Bot. Marina 1988, 31, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanic, L.A.; Lindstrom, S.C. Life history and systematic studies of Pseudothrix borealis gen. et sp. nov. (= North Pacific Capsosiphon groenlandicus, Ulotrichaceae, Chlorophyta). Algae 2008, 23, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





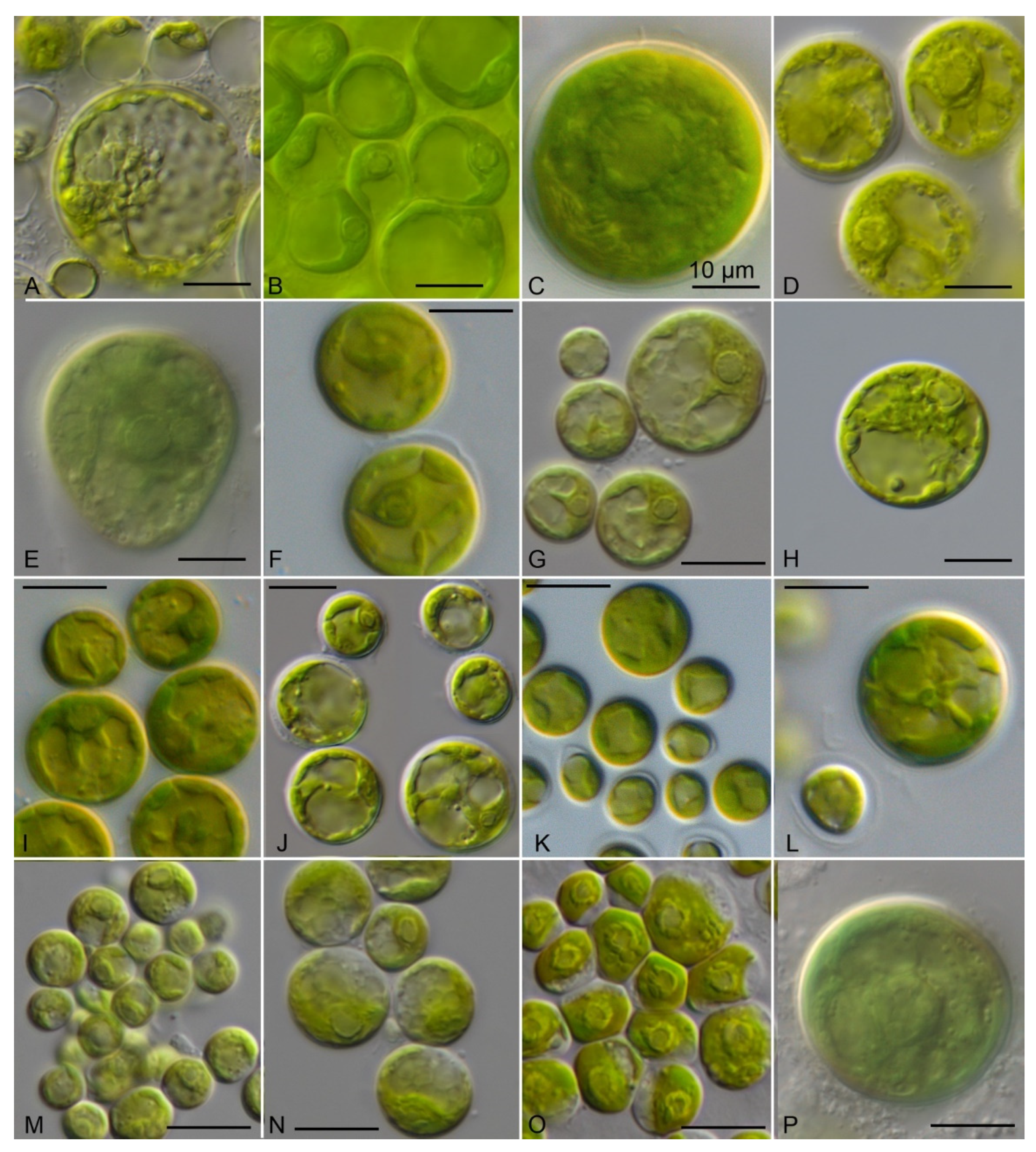
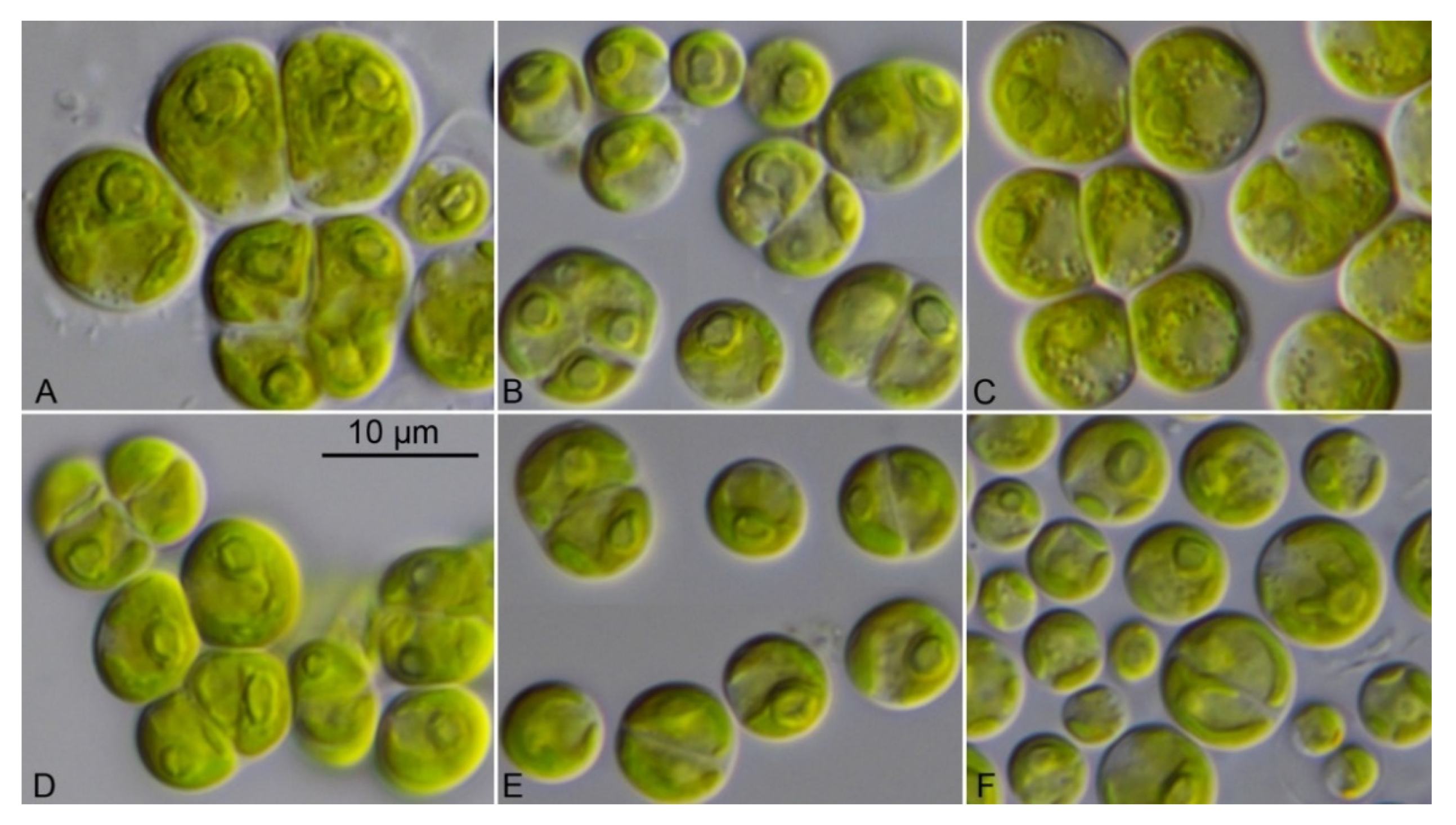


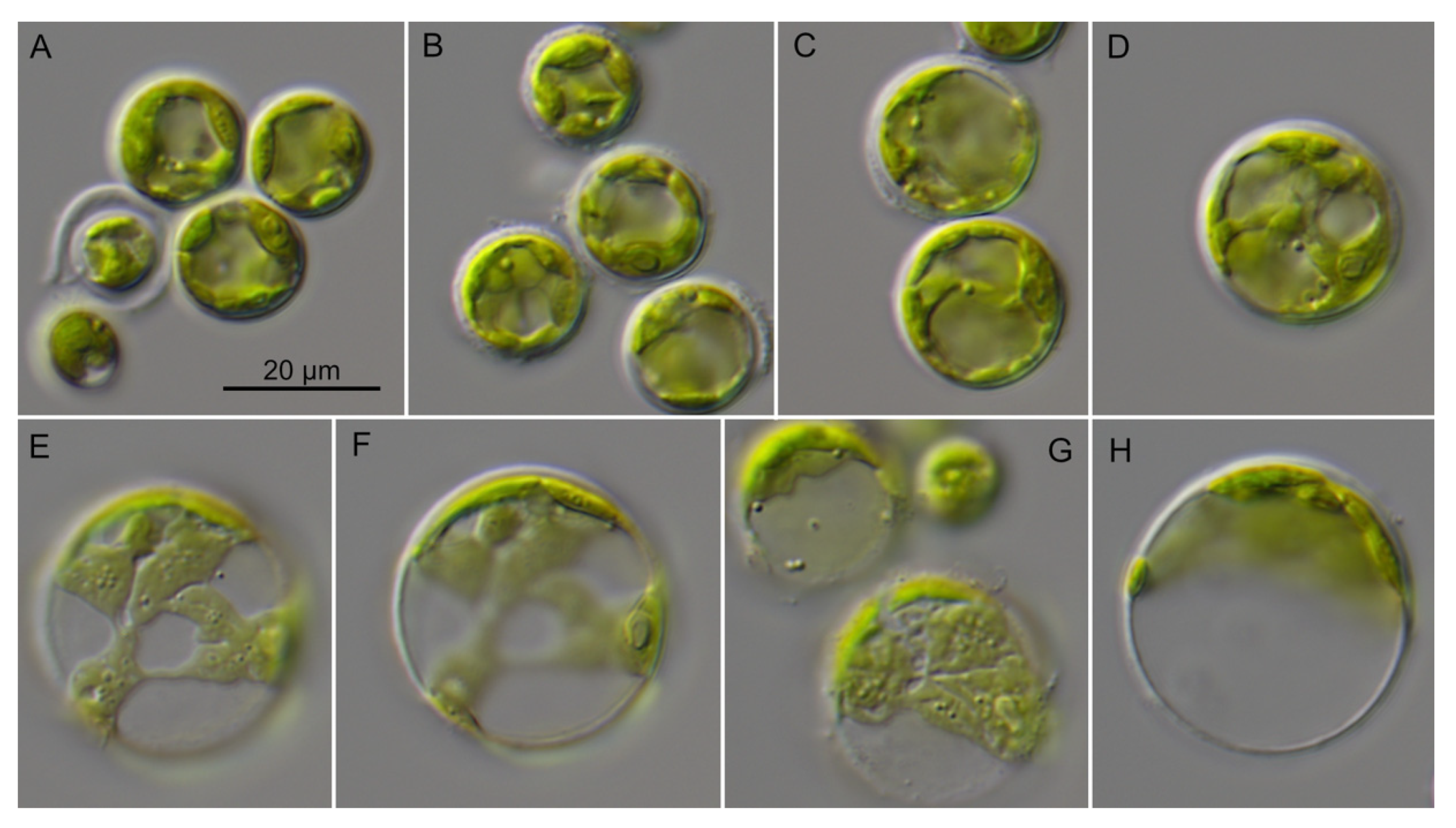
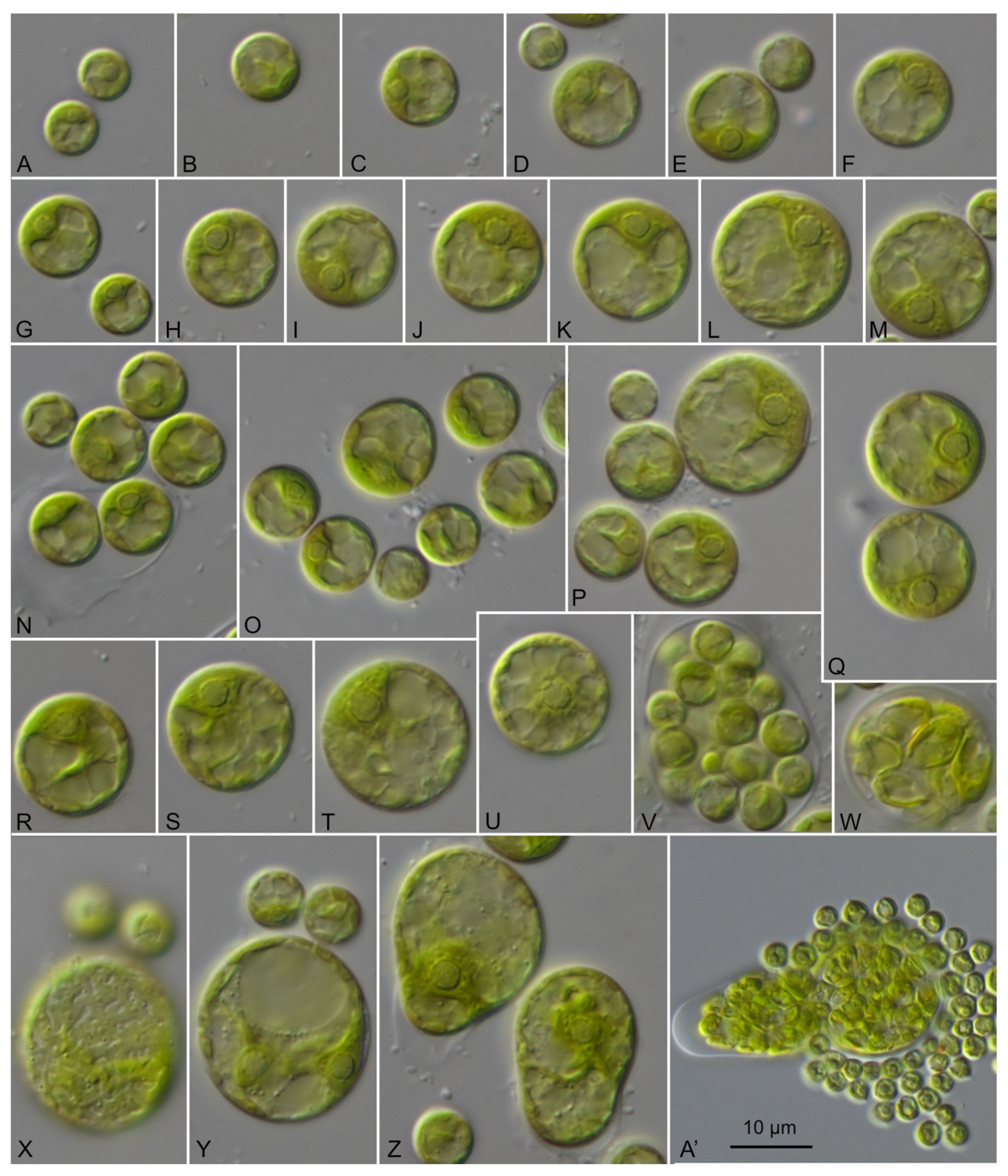

| Strain | Species | Origin | Accession 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chlorocystis | |||
| SAG 9.90 | C. cohnii | Germany, Helgoland, from tube jelly of colony-forming Berkelya rutilans | MW714132 |
| SCCAP K-0421 | C. cohnii | Greenland, Godthåbsfjorden, Kapisillit, endophyte on Polysiphonia violacea | MW714133 |
| SAG 8.86 | C. dangeardii | UK, North Wales, oyster breeding tank at Conway | MW714140 |
| CCAP 233/1 2 | C. dangeardii | France, Ulva culture from Soulac | MW714142 |
| CCAP 211/25 | C. dangeardii | UK, England, Cornwall, Henn Point, Tamar Estuary | MW714141 |
| SAG 12.90 | C. dilatatum | Germany, Helgoland, littoral rock pool | MW714139 |
| CCAP 6005/4 | C. john-westii | Brazil, São Paulo, Ilha do Cardoso, Rio Pereque, endophyte in Bostrychia calliptera | MW714146 |
| CCAP 6005/5 | C. john-westii | Australia, Queensland, Gladstone, endophyte in Bostrychia moritziana | MW714147 |
| CCAP 6005/10 | C. john-westii | Peru, Tumbes, Puerto Pizzaro, endophyte in Bostrychia radicans | MW714143 |
| CCAP 6005/11 | C. john-westii | Australia, Queensland, Bowling Green Bay, endophyte in Bostrychia bispora | MW714144 |
| CCAP 6005/12 | C. john-westii | Australia, Queensland, Bowling Green Bay, endophyte in Bostrychia moritziana | MW714145 |
| CCAP 6005/13 | C. john-westii | Madagascar, Chenal d’Ampanarata, Belo sur Mer, epiphyte on Bostrychia pinnata | MK541803 |
| UTEX 2846 | C. john-westii | Brazil, Maranhão, Parra Açu, endophyte in Bostrychia montagnei | MW714148 |
| CCAP 6005/6 | C. moorei | Germany, Helgoland, epiphyte on Blidingia minima | MW714137 |
| CCMP 2288 | C. moorei | USA, Washingtion, Friday Harbor, San Juan Isand | MW714138 |
| SAG 11.90 | C. operculatum | Germany, Helgoland from oyster-shell in a littoral pool | MW714136 |
| SAG 19.92= CCMP 435 2 | C. operculatum | France, Ulva culture from Soulac | MW714134 MW714135 |
| Desmochloris | |||
| CCAP 6006/5 | D. edaphica | Ukraine, Snake Island, Black Sea, soil | MW714127 |
| CCAP 6006/6 | D. edaphica | Chile, Atacama, biological soil crust | MW714128 |
| CCAP 6006/1 | D. halophila | USA, MA, Martha’s Vineyard, Great Pond | FM882216 |
| SAG 2565 | D. halophila | Germany, Island Rügen, the coast of the Baltic Sea, sand dunes | MH703754 |
| SAG 2397 | D. halophila | Germany, Franconian Alb, Deinschwanger Bach, biofilm on rock surface | MW714126 |
| CCAP 6006/4 | D. halophila | Chile, Atacama, soil | MW714125 |
| CCAP 6006/2 | D. mollenhaueri | South Africa, Flaminkvlakte, Van Rhynsdorp, biological soil crust | FM882217 |
| CCAP 6006/3 | D. mollenhaueri | South Africa, Groot Derm-Yellow Dune 10, biological soil crust | FM882218 |
| CCAP 6006/7 | D. mollenhaueri | South Africa, Koeroegap Vlakte, biological soil crust | MW714129 |
| CCAP 6006/8 | D. mollenhaueri | Chile, Atacama, biological soil crust | MW714130 |
| CCAP 6006/9 | D. mollenhaueri | Chile, Atacama, biological soil crust | MW714131 |
| Sykidion | |||
| CCMP 258 | S. droebakense | Canada, BC, Vancouver Island, from South Long Beach | MW714151 |
| CCMP 438 3 | S. droebakense | Antarctica, from Palmer Station | MW714152 |
| CCMP 257 | S. dyeri | USA, CT, Milford, from tank | MW714150 |
| UTEX 1445 | S. marina | origin unknown | MW714149 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Darienko, T.; Rad-Menéndez, C.; Campbell, C.N.; Pröschold, T. Molecular Phylogeny of Unicellular Marine Coccoid Green Algae Revealed New Insights into the Systematics of the Ulvophyceae (Chlorophyta). Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1586. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9081586
Darienko T, Rad-Menéndez C, Campbell CN, Pröschold T. Molecular Phylogeny of Unicellular Marine Coccoid Green Algae Revealed New Insights into the Systematics of the Ulvophyceae (Chlorophyta). Microorganisms. 2021; 9(8):1586. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9081586
Chicago/Turabian StyleDarienko, Tatyana, Cecilia Rad-Menéndez, Christine N. Campbell, and Thomas Pröschold. 2021. "Molecular Phylogeny of Unicellular Marine Coccoid Green Algae Revealed New Insights into the Systematics of the Ulvophyceae (Chlorophyta)" Microorganisms 9, no. 8: 1586. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9081586
APA StyleDarienko, T., Rad-Menéndez, C., Campbell, C. N., & Pröschold, T. (2021). Molecular Phylogeny of Unicellular Marine Coccoid Green Algae Revealed New Insights into the Systematics of the Ulvophyceae (Chlorophyta). Microorganisms, 9(8), 1586. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9081586






