Potential Zoonotic Pathovars of Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli Detected in Lambs for Human Consumption from Tierra del Fuego, Argentina
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
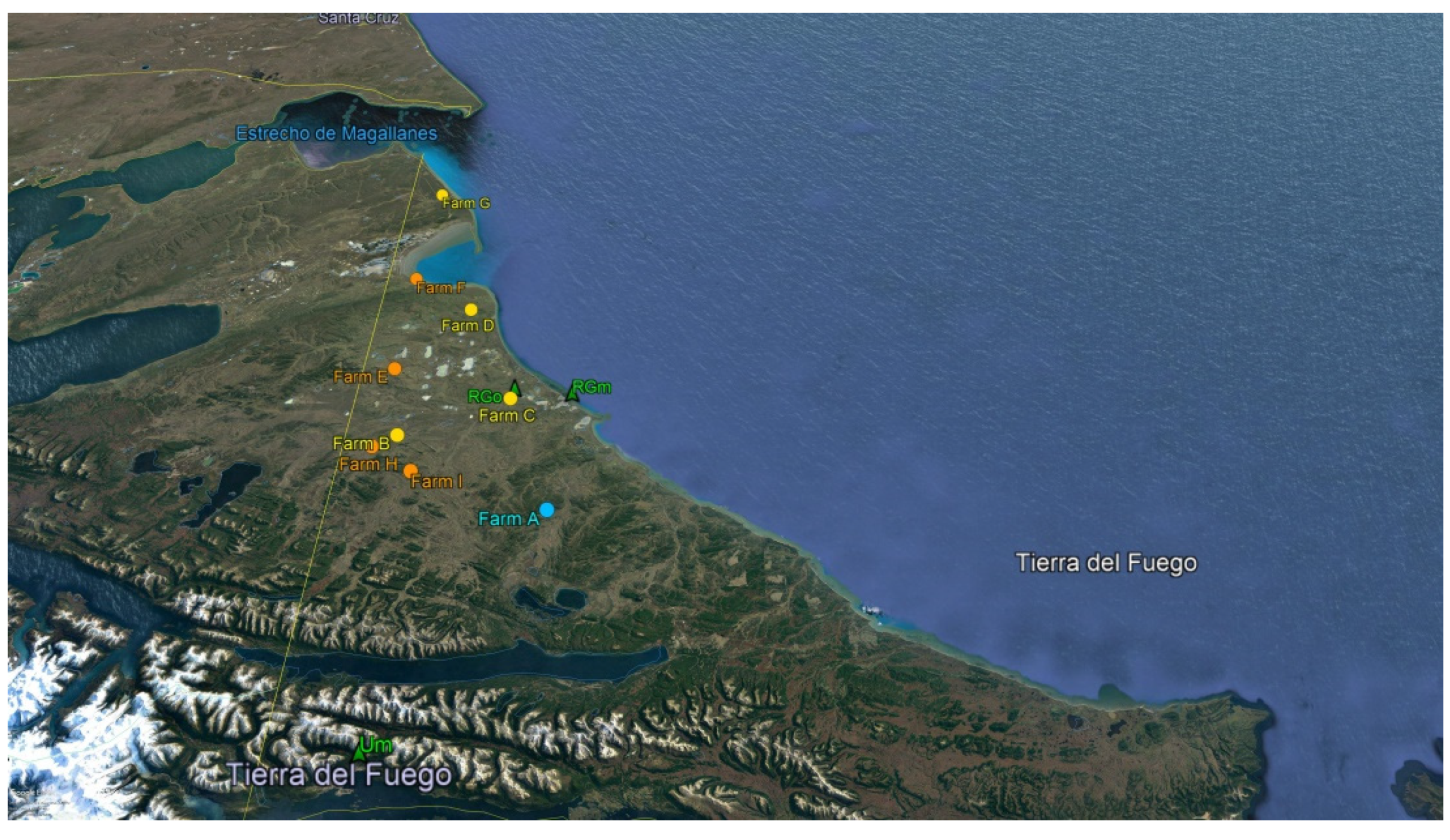
2.1. Samples
2.2. Detection and Isolation of DEC
2.3. Biochemical Identification and Characterization of DEC
2.4. Serotyping of DEC
2.5. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.6. Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis (PFGE)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Williams, N.D.; Torres, A.G.; Lloyd, S.J. Evolution and epidemiology of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli. In Pathogenic Escherichia coli in Latin America, 1st ed.; Torres, A.G., Ed.; Bentham Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 8–24. [Google Scholar]
- Miliwebsky, E.; Deza, N.; Chinen, I.; Martinez Espinosa, E.; Gomez, D.; Pedroni, E.; Caprile, L.; Bashckier, A.; Manfredi, E.; Leotta, G.; et al. Prolonged fecal shedding of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli among children attending day-care centers. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2007, 39, 90–92. [Google Scholar]
- Zota, C.M.; Chinen, I.; Lavayén, S.; Cepeda, M.; Deza, N.; Morvay, L.; Carbonari, C.; Rearte, A.; Rivas, M. Portación de Escherichia coli en convivientes de casos de síndrome urémico hemolítico. Salud(i)Ciencia 2015, 21, 136–141. Available online: https://ine.gov.ar/documentos/publicaciones/034.pdf (accessed on 7 August 2021).
- Ministerio de Salud Argentina. BIV 2021, N559, in press. Available online: https://bancos.salud.gob.ar/bancos/materiales-para-equipos-de-salud/soporte/boletines-epidemiologicos (accessed on 26 June 2021).
- Rivero, M.A.; Paccussi, J.A.; Rodríguez, E.M.; Parma, A.E. Seasonal variation of HUS occurrence and VTEC infection in children with acute diarrhea from Argentina. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 31, 1131–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabulsi, L.R.; Keller, R.; Gomez, T.A.T. Typical and atypical enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, A.G. Escherichia coli in Latin America—A One Health multidisciplinary approach. Pathog. Dis. 2017, 75, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldir, P.E.; Navarro-García, F. Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli (EAEC). In Escherichia coli in the Americas; Torres, A.G., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 27–58. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro-García, F. Escherichia coli O104:H4 pathogenesis: An Enteroaggregative E. coli/Shiga Toxin-Producing E. coli explosive cocktail of high virulence. Microbiol. Spectr. 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miliwebsky, E.; Deza, N.; Zolezzi, G.; Baschkier, A.; Carbonari, C.C.; Manfredi, E.; D’Astek, B.A.; Chinen, I.; Rivas, M. Manual de Procedimientos: Escherichia coli Productor de Toxina Shiga en el Marco de la Detección de E.coli diarreigénico. 2019. Available online: http://sgc.anlis.gob.ar/handle/123456789/2307 (accessed on 6 June 2021).
- Carbonari, C.C.; Ricciardi, M.; Rodríguez Calvo, A.; Montes, A.; Deza, N.L.; Conde Valentino, M.A.; Zolezzi, G.; Baschkier, A.; Vago, M.; Acosta, D.; et al. An Stx-EAEC O59:NM[H19] strain isolated from an hemolytic uremic syndrome case in Argentina. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2019, 52, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consejo Federal de Inversiones. Cadena de Valor de la Carne Bovina en la Provincial de Tierra de Fuego. Available online: http://biblioteca.cfi.org.ar/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2016/04/item-d_-tdf.pdf (accessed on 16 April 2019).
- Dean, A.G.; Sullivan, K.M.; Soe, M.M. OpenEpi: Open Source Epidemiologic Statistics for Public Health, Version. Available online: www.OpenEpi.com (accessed on 7 August 2021).
- Ballem, A.; Gonc¸alves, S.; Garcia-Meniño, I.; Flament-Simon, S.C.; Blanco, J.E.; Fernandes, C.; Saavedra, M.J.; Pinto, C.; Oliveira, H.; Blanco, J.; et al. Prevalence and serotypes of Shiga toxinproducing Escherichia coli (STEC) in dairy cattle from Northern Portugal. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0244713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leotta, G.; Chinen, I.; Epszteyn, S.; Miliwebsky, E.; Melamed, I.C.; Motter, M.; Ferrer, M.; Marey, E.; Rivas, M. Validación de una técnica de PCR múltiple para la detección de Escherichia coli productor de toxina Shiga. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2005, 37, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blanco, M.; Schumacher, S.; Tasara, T.; Zweifel, C.; Blanco, J.E.; Dahbi, G.; Blanco, J.; Stephan, R. Serotypes, intimin variants and other virulence factors of eae positive Escherichia coli strains isolated from healthy cattle in Switzerland. Identification of a new intimin variant gene (eae-2). BMC Microbiol. 2005, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boisen, N.; Scheutz, F.; Rasko, D.A.; Redman, J.C.; Persson, S.; Simon, J.; Kotloff, K.L.; Levine, M.M.; Sow, S.; Tamboura, B.; et al. Genomic characterization of enteroaggregative Escherichia coli of children in Mali. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 205, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieler, L.H.; Semmler, T.; Eichhorn, I.; Antao, E.M.; Kinnemann, B.; Geue, L.; Karch, H.; Guenther, S.; Bethe, A. No evidence of the Shiga toxin-producing E. coli O104:H4 outbreak strain or enteroaggregative E. coli (EAEC) found in cattle faeces in northern Germany, the hostpot of the 2011 HUS outbreak area. Gut Pathog. 2011, 3, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- MacFaddin, J.F. Pruebas Bioquímicas Para la Identificación de Bacterias de Importancia Clínica, 3rd ed.; Médica Panamericana Ed: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2003; pp. 54–421. [Google Scholar]
- Scheutz, F.; Teel, L.D.; Beutin, L.; Pierard, D.; Buvens, G.; Karch, H.; Mellmann, A.; Caprioli, A.; Tozzoli, R.; Morabito, S.; et al. Multicenter evaluation of a sequence-based protocol for subtyping Shiga toxins and standardizing Stx nomenclature. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 2951–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paton, A.W.; Paton, J.C. Direct detection and characterization of Shiga toxigenic Escherichia coli by multiplex PCR for stx1, stx 2, eae, ehxA, and saa. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gunzburg, S.T.; Tornieporth, N.G.; Riley, L.W. Identification of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli by PCR-based detection of thebundle—forming pilus gene. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 1375–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edwards, P.R.; Ewing, W.H. Edwards and Ewing’s Identification of Enterobacteriaceae, 4th ed.; Elsevier Science Publishing Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Orskov, F.; Orskov, I. Serotyping of Escherichia coli. In Methods in Microbiology; Bergan, T., Ed.; Academic Press Ltd.: London, UK, 1984; Volume 14, pp. 3–112. [Google Scholar]
- Beutin, L.; Kong, K.; Feng, L.; Wang, Q.; Krause, G.; Leomil, L.; Jin, Q.; Wang, L. Development of PCR assays targeting the genes involved in synthesis and assembly of the new Escherichia coli O174 and O177 O antigens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 5143–5149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cundon, C.; Marey, E.; Roldán, F.; Canosa Montero, C.S.; Navarro, A.; Gadea, P.; Blanco Crivelli, X.; Babich, J.; Rocchi, D.; Kiernicki, M.C.; et al. Preliminary detection and characterization of Escherichia coli O174 Shiga toxin-producing. Senasa 2015, 8, 52–63. [Google Scholar]
- Di Rienzo, J.A.; Casanoves, F.; Balzarini, M.G.; González, L.; Tablada, M.; Robledo, C.W.; Infostat Version 2016e. Grupo Infostat. 2016; Universidad Nacional de Córdoba, Argentina. Available online: https://www.infostat.com.ar/ (accessed on 7 August 2021).
- McCarthy, S.C.; Burgess, C.M.; Fanning, S.; Duffy, G. An overview of Shiga-toxin producing Escherichia coli carriage and prevalence in the ovine meat production chain. Foodborne Pathg. Dis. 2021, 18, 147–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batisti, A.; Lovari, S.; Franco, A.; Di Egidio, A.; Tozzoli, R.; Caprioli, A.; Morabito, S. Prevalence of Escherichia coli O157 in lambs at slaughter in Rome, central Italy. Epidemiol. Infect. 2006, 134, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudva, I.T.; Hatfield, P.G.; Hovde, C.J. Escherichia coli O157:H7 in microbial flora of sheep. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 34, 431–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rey, J.; Blanco, J.E.; Blanco, M.; Mora, A.; Dahbi, G.; Alonso, J.M.; Hermoso, M.; Hermoso, J.; Alonso, M.P.; Usera, M.A.; et al. Serotypes, phage types and virulence genes of Shiga-producing Escherichia coli isolated from sheep in Spain. Vet. Microbiol. 2003, 94, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.R.; Brooks, H.J.L.; O’Brien, R. Prevalence of Shiga toxin-producing and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli marker genes in diarrhoeic stools in a New Zealand catchment area. J. Clin. Pathol. 2017, 70, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, C.A.; De, J.; Bertoldi, B.; Dunn, L.; Chapin, T.; Jay-Russell, M.; Danyluk, M.D.; Schneider, K.R. Prevalence and concentration of stx+ E. coli and E. coli O157 in bovine manure from Florida farms. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beutin, L.; Geier, D.; Steinrück, H.; Zimmermann, S.; Scheutz, F. Prevalence and some properties of Verotoxin (Shiga-like toxin) producing Escherichia coli in seven different species of healthly domestic animals. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1993, 31, 2483–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martins, F.H.; Guth, B.E.C.; Piazza, R.M.; Cardoso Leao, S.; Ludovico, A.; Ludovico, M.S.; Dahbi, G.; Marzoa, J.; Mora, A.; Blanco, J.; et al. Diversity of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in sheep flocks of Paraná State, southern Brazil. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 175, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orden, J.A.; Ruiz-Santa-Quiteria, J.A.; Blanco, M.; Blanco, J.E.; Mora, A.; Cid, D.; González, E.A.; Blanco, J.; De la Fuente, R. Prevalence and characterization of Vero cytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli isolated from diarrhoeic and healthy sheep and goats. Epidemiol. Infect. 2003, 130, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buvens, G.; De Rauw, K.; Roisin, S.; Vanfraechem, G.; Denis, O.; Jacobs, F.; Scheutz, F.; Pierard, D. Verocytotoxin-Producing Escherichia coli O128ab:H2 bacteremia in a 27-year-old male with hemolytic-uremic syndrome. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 1633–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brett, K.N.; Ramachandran, V.; Hornitzky, M.A.; Bettelheim, K.A.; Walker, M.J.; Djordjevic, S.P. stx1c is the most common Shiga toxin 1 subtype among Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli isolated from sheep but not among isolates from cattles. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 926–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rivas, M.; Miliwebsky, E.; Chinen, I.; Roldán, C.D.; Balbi, L.; García, B.; Fiorilli, G.; Sosa-Estani, S.; Kincaid, J.; Rangel, J.; et al. Characterization and epidemiologic subtyping of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli strains isolated from hemolytic uremic syndrome and diarrhea cases in Argentina. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2006, 3, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oderiz, S.; Leotta, G.A.; Galli, L. Detección y caracterización de Escherichia coli productor de toxina Shiga en niños atendidos en un hospital pediátrico interzonal de la ciudad de La Plata. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2018, 50, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manandhar, R.; Bettiol, S.S.; Bettelheim, K.A.; Goldsmid, J.M. Isolation of verotoxigenic Escherichia coli from the Tasmanian environment. Comp. Immunol Microbiol Infect. Dis. 1997, 20, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornitzky, M.A.; Vanselow, B.A.; Walker, K.; Bettelheim, K.A.; Corney, B.; Gill, P.; Bailey, G.; Djordjevic, P. Virulence properties and serotypes of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli from healthy Australian cattle. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 6439–6445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Montero, D.A.; Velasco, J.; Del Canto, F.; Puente, J.L.; Padola, N.L.; Rasko, D.A.; Farfán, M.; Salazar, J.C.; Vidal, R. Locus of adhesion and autoaggregation (LAA), a pathogenicity island present in emerging Shiga Toxin-producing Escherichia coli strains. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vettorato, M.P.; de Castro, A.F.P.; Cergole-Novella, M.C.; Camargo, F.L.L.; Irino, K.; Guth, B.E.C. Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli and atypical enteropathogenic Escherichia coli strains isolated from healthy sheep of different populations in Sao Paulo, Brazil. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 49, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanbarpour, R.; Askari, N.; Ghorbanpour, M.; Tahamtan, Y.; Mashayekhi, K.; Afsharipour, N.; Darijani, N. Genotypic analysis of virulence genes and antimicrobial profile of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli isolated from diseased lambs in Iran. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2017, 49, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazato, G.; Gyles, C.; Ziebell, K.; Keller, R.; Trabulsi, L.R.; Gomes, T.A.T.; Irino, K.; Da Silveira, W.D.; De Castro, A.F.P. Attaching and effacing Escherichia coli isolated from dogs in Brazil: Characteristics and serotypic relationship to human enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC). Vet. Microbiol. 2004, 101, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröhlicher, E.; Krause, G.; Zweifel, C.; Beutin, L.; Stephan, R. Characterization of attaching and effacing Escherichia coli (AEEC) isolated from pigs and sheep. BMC Microbiol. 2008, 8, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blanco, M.; Blanco, J.E.; Dahbi, G.; Alonso, M.P.; Mora, A.; Coira, M.A.; Madrid, C.; Juárez, A.; Bernárdez, M.I.; González, E.A.; et al. Identification of two new intimin types in atypical enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Int. Microbiol. 2006, 9, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blanco Crivelli, X.; Bonino, M.P.; Von Wernich Castillo, P.; Navarro, A.; Degregorio, O.; Bentancor, A. Detection and characterization of enteropathogenic and Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli strains in Rattus spp. from Buenos Aires. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sheng, H.; Duan, M.; Hunter, S.S.; Minnich, S.A.; Settles, M.L.; New, D.D.; Chase, J.R.; Fagnan, M.W.; Hovde, C.J. High-Quality complete genome sequences of three bovine Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli O177:H- (fliCH25) isolates harboring virulent stx2 and multiple plasmids. Genome Announc. 2018, 15, e01592-17. [Google Scholar]
- Wani, S.A.; Hussai, I.; Beg, S.A.; Rather, M.A.; Kabli, Z.A.; Mir, M.A.; Nishikawa, Y. Diarrhoeagenic Escherichia coli and salmonellae in calves and lambs in Kashmir: Absence, prevalence and antibiogram. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2013, 32, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uber, A.P.; Trabulsi, L.R.; Irino, K.; Beutin, L.; Ghilardi, A.C.; Gomes, T.A.; Liberatone, A.M.A.; de Castro, A.F.; Elias, W.P. Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli from humans and animals differ in major phenotypical traits and virulence genes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 256, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dubreil, J.D. EAST1 toxin: An enigmatic molecule associated with sporadic episodes of diarrhea in humans and animals. J. Microbiol. 2019, 57, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puño-Sarmiento, J.; Medeiros, L.; Chiconi, C.; Martins, F.; Pelayo, J.; Rocha, S.; Blanco, J.; Blanco, M.; Zanutto, M.; Kobayaski, R.; et al. Detection of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli strains isolated from dogs and cats in Brazil. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 166, 676–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oporto, B.; Ocejo, M.; Alkorta, M.; Marimón, J.M.; Montes, M.; Hurtado, A. Zoonotic approach to Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli: Integrated analysis of virulence and antimicrobial resistance in ruminants and humans. Epidemiol. Infect. 2019, 147, e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Serotype | n | stx1 | stx2 | rfbO157 | eae | saa | bfpA | ehxA | Pathovar | Farm | Slaughterhouse | Lamb ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2:H40 | 1 | − | − | − | + | − | − | EPEC | A | Um | OV38 | |
| O32:H8 | 1 | − | − | − | + | − | − | EPEC | A | Um | OV5 | |
| O56:H6 | 1 | − | − | − | + | − | − | EPEC | A | Um | OV52 | |
| O70:HNT | 1 | stx1c | stx2b | − | − | − | − | STEC | A | Um | OV91 | |
| O81:HNT | 1 | stx1c | stx2b | − | − | − | + | STEC | I | RGm | OV419 | |
| O81:H21 | 1 | stx1c | stx2b | − | − | − | + | STEC | A | Um | OV89 | |
| O102:H6 | 1 | stx1c | stx2b | − | − | − | + | STEC | A | Um | OV81 | |
| O108:H21 | 1 | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | EPEC | A | Um | OV36 |
| O128ab:H2 | 3 | stx1c | − | − | − | − | + | STEC | A | Um | OV53/OV54/OV75 | |
| − | 1 | stx1c | − | − | − | − | − | STEC | A | Um | OV68 | |
| − | 1 | stx1c | − | − | − | − | − | STEC | G | RGo | OV388 | |
| − | 1 | stx1c | stx2b | − | − | − | + | STEC | A | Um | OV61 | |
| O174:H8 | 1 | stx1c | stx2b | − | − | − | − | STEC | A | Um | OV94 | |
| O174:HNT | 1 | − | stx2b | − | − | − | + | STEC | A | Um | OV80 | |
| O177:H25 | 1 | − | − | − | + | − | − | + | EPEC | G | RGo | OV398 |
| O177:H25 | 1 | − | − | − | + | − | − | + | EPEC | G | RGm | OV437 |
| Total | 18 | 11 | 7 | − | 6 | − | 10 | − | − | − | − |
| Serotype | Pathovar | AMC | S | CTX | AZT | CAZ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O32:H8 | aEPEC | s | s | R | s | s |
| O56:H6 | aEPEC | s | r | s | s | s |
| O70:HNT | STEC | s | r | s | s | s |
| O81:HNT | STEC | R | s | s | s | s |
| O81:H21 | STEC | s | r | R | r | s |
| O108:H21 | aEPEC | r | s | s | s | s |
| O128ab:H2 | STEC | r | s | s | s | s |
| STEC | R | r | s | s | s | |
| STEC | r | s | s | s | s | |
| STEC | r | s | s | s | s | |
| O174:H8 | STEC | s | R | s | s | R |
| O177:H25 | aEPEC | r | s | s | s | s |
| aEPEC | r | s | r | s | s |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blanco Crivelli, X.; Bonino, M.P.; Sanin, M.S.; Petrina, J.F.; Disalvo, V.N.; Massa, R.; Miliwebsky, E.; Navarro, A.; Chinen, I.; Bentancor, A. Potential Zoonotic Pathovars of Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli Detected in Lambs for Human Consumption from Tierra del Fuego, Argentina. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9081710
Blanco Crivelli X, Bonino MP, Sanin MS, Petrina JF, Disalvo VN, Massa R, Miliwebsky E, Navarro A, Chinen I, Bentancor A. Potential Zoonotic Pathovars of Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli Detected in Lambs for Human Consumption from Tierra del Fuego, Argentina. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(8):1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9081710
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlanco Crivelli, Ximena, María Paz Bonino, Mariana Soledad Sanin, Juan Facundo Petrina, Vilma Noelia Disalvo, Rosana Massa, Elizabeth Miliwebsky, Armando Navarro, Isabel Chinen, and Adriana Bentancor. 2021. "Potential Zoonotic Pathovars of Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli Detected in Lambs for Human Consumption from Tierra del Fuego, Argentina" Microorganisms 9, no. 8: 1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9081710
APA StyleBlanco Crivelli, X., Bonino, M. P., Sanin, M. S., Petrina, J. F., Disalvo, V. N., Massa, R., Miliwebsky, E., Navarro, A., Chinen, I., & Bentancor, A. (2021). Potential Zoonotic Pathovars of Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli Detected in Lambs for Human Consumption from Tierra del Fuego, Argentina. Microorganisms, 9(8), 1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9081710






