Haemogregarines and Criteria for Identification
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Levine, N.D. Taxonomy of the Sporozoa. J. Parasitol. 1970, 56, 208–209. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, A.J.; Johnston, M.R.L. The biology of some intraerythrocytic parasites of fishes, amphibian and reptiles. Adv. Parasitol. 2000, 45, 1–107. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adl, S.M.; Simpson, A.G.B.; Lane, C.E.; Lukeš, J.; Bass, D.; Bowser, S.S.; Brown, M.W.; Burki, F.; Dunthorn, M.; Hampl, V.; et al. The revised classification of eukaryotes. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2012, 59, 429–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hossen, M.S.; Bandyopadhyay, P.K.; Gürelli, G. On the occurrence of a Haemogregarinae (Apicomplexa) parasite from freshwater turtles of South 24 Parganas, West Bengal, India. Tutkiye Parazitol. Derg. 2013, 37, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Telford, S.R. Hemoparasites of the Reptilia: Color Atlas and Text; CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Levine, N.D. Some corrections in Haemogregarine (Apicomplexa: Protozoa) Nomenclature. J. Protozool. 1982, 29, 601–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danilewsky, B. Die Hematozoen der Kaltblüter. Arch. Mikr. Anat. 1885, 24, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labbé, A. Recherches zoologiques et biologiques sur les parasites endoglobulaires du sang des Vertébrés. Arch. Zool. Exp. Gen. 1894, 2, 55–258. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, W.W. Hepatozoon perniciosum n. g. n. sp., a haemogregarines pathogenic for white rats: With a brief description of the sexual cycle in the intermediate host a mite (Laelaps echidninus Berlese). Hyg. Lab. Bull. (Washington) 1908, 46, 51–123. [Google Scholar]
- Lainson, R. On Cyrilia gomesi (Neiva and Pinto, 1926) gen. nov. (Haemogregarinidae) and Trypanosoma bourouli Neiva and Pinto. In the fish Synbranchus marmoratus: Simultaneous transmission by the leech Haementeria lutzi. In Parasitological Topics; Special Publication; Canning, E.U., Ed.; Society of Protozoologists, Inc.: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1981; Volume 1, pp. 150–158. [Google Scholar]
- Barta, J.R. Phylogenetic analysis of the Class Sporozoa (Phylum Apicomplexa Levine 1970): Evidence for the independent evaluation of heteroxenous life cycles. J. Parasitol. 1989, 75, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.H.H.; Mansour, N.S. The haemogregarines complex (an analytical systematic review). Bull. Fac. Pharm. Cairo Univ. (BFPC) 1959, 35, 39–52. [Google Scholar]
- Wenyon, C.M. Protozoology; Bailliere, Tindall and Cox: London, UK, 1926; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Petit, G.; Landau, I.; Baccam, D.; Lainson, R. Description et cycle biologique d’Hemolivia stellate n. g., n. sp., hémogregarine de crapauds Brésiliens. [Desription and life cycle of Hemolivia stellate n.g., n. sp., a haemogregarines of Brazilian toads]. Ann. Parasitol. Hum. Comp. 1990, 65, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Široký, P.; Kamler, M.; Modrý, D. Long-term occurrence of Hemolivia cf. mauritanica (Apicomplexa: Adeleina: Haemogregarinidae) in the captive Testudo marginata (Reptilia: Testudinidae): Evidence for cyclic merogony? J. Parasitol. 2004, 90, 1391–1393. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson, E.R. Parasites and parasitic diseases of reptiles. In Infectious Diseases and Pathology of Reptiles: Color Atlas and Text; Jacobson, E.R., Ed.; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; pp. 579–580. [Google Scholar]
- Pineda-Catalan, O.; Perkins, S.L.; Peirce, M.A.; Engstrand, R.; Garcia-Davila, C.; Pinedo-Vasquez, M.; Aguirre, A.A. Revision of hemoproteid genera and description and redescription of two species of chelonian hemoproteid parasites. J. Parasitol. 2013, 99, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haklová-Kočíková, B.; Hižňanová, A.; Majláth, I.; Račka, K.; Harris, D.G.; Földvári, G. Molecular characterization of Karyolysus– a neglected but common parasite infecting some European lizards. Parasite. Vector. 2014, 7, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barta, J.R.; Ogedengbe, J.D.; Martin, D.S.; Smith, T.G. Phylogenetic position of the adeleorinid coccidia (Myzozoa, Apicomplexa, Coccidia, Eucoccidiorida, Adeleorina) inferred using 18S rDNA sequences. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2012, 59, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujvari, B.; Madsen, T.; Olsson, M. High prevalence of Hepatozoon spp. (Apicomplexa, Hepatozoidae) infection in water pythons (Liasis fuscus) from tropical Australia. J. Parasitol. 2004, 90, 670–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, A.J.; Origgi, F.C.; Wellehan, J.F.X., Jr. Molecular diagnostics. In Infectious Diseases and Pathology of Reptiles: Color Atlas and Text; Jacobson, E.R., Ed.; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; pp. 351–380. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, D.J.; Maia, J.P.M.C.; Perera, A. Molecular characterization of Hepatozoon species in reptiles from the Seychelles. J. Parasitol. 2011, 97, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvořáková, N.; Kvičerova, J.; Papousek, I.; Javanbakht, H.; Tiar, G.; Kami, H.G. Haemogregarines from western Palaearctic freshwater turtles (genera Emys, Mauremys) are conspecifi c with Haemogregarina stepanowi Danilewsky, 1885. Parasitology 2014, 141, 522–530. [Google Scholar]
- Jòzsef, Ö.; Darko, M.; Milos, V.; Bojan, G.; Jevrosima, S.; Dejan, K.; Sanja, A.-K. Cytological and molecular identification of Haemogregarina stepanowi in blood samples of the European pond turtle (Emys orbicularis) from quarantine at Belgrade Zoo. Acta Vet.-Beograd 2015, 65, 443–453. [Google Scholar]
- O’Donoghue, P. Haemoprotozoa: Making biological sense of molecular. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2017, 6, 241–256. [Google Scholar]
- Kvičerová, J.; Hypša, V.; Pakandl, M. Phylogenetic relationships among Eimeria spp. (Apicomplexa, Eimeriidae) infecting rabbits: Evolutionary significance of biological and morphological features. Parasitology 2008, 135, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, M.; Jeong, A.; Kim, S.I.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, H.; Kimura, J.; Agatsuma, T.; Sakai, H.; Yanai, T. The first report of Hepatozoon species infection in leopard cats (Prionailurus bengalensis) in Korea. J. Parasitol. 2010, 96, 437–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawar, R.M.; Poornachandar, A.; Srinivas, P.; Rao, K.R.; Lakshmikantan, U.; Shivaji, S. Molecular characterization of Hepatozoon spp. infection in endangered Indian wild felids and canids. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 186, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Baki, A.S.; Al-Quraishy, S.; Zhang, J.Y. Redescription of Haemogregarina garnhami (Apicomplexa: Adeleorina) from the blood of Psammophis schokari (Serpentes: Colubridae) as Hepatozoon garnhami n. comb. based on molecular, morphometric and morphologic characters. Acta Parasitol. 2014, 59, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, C.A.; Lawton, S.P.; Davies, A.J.; Smit, N.J. Reassignment of the land tortoise haemogregarine Haemogregarina fitzimonsi Dias 1953 (Adeleorina: Haemogregarinidae) to the genus Hepatozoon Miller 1908 (Adeleorina: Hepatozoidae) based on parasite morphology, life cycle and phylogenetic analysis of 18S rDNA sequence fragments. Parasitology 2014, 141, 1611–1620. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, C.A.; Netherlands, E.C.; Smit, N.J. Redescription, molecular characterisation and taxonomic re-evaluation of a unique African monitor lizard haemogregarine Karyolysus paradoxa (Dias, 1954) n. comb. (Karyolysidae). Parasit. Vectors. 2016, 9, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cook, C.A.; Netherlands, E.C.; Van As, J.; Smit, N.J. Two new species of Hepatozoon (Apicomplexa: Hepatozoidae) parasitizing species of Philothamnus (Ophidia: Colubridae) from South Africa. Folia Parasitol. 2018, 65, 004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osimani, J.J. Haemogregarina triatomae n. sp. from a South American lizard, Tupinambis teguixin transmitted by the Reduviid Triatoma rebrovaria. J. Parasite. 1942, 28, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telford, S.R., Jr.; Ernst, J.A.; Clark, A.M.; Butler, J.F. Hepatozoon sauritus: A polytopic haemogregarine of three genera and four species of snakes in North Florida, with specific identity verified from genome analysis. J. Parasitol. 2004, 90, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbert, J.D.K.; Godfrey, S.; Bull, C.M.; Menz, I. Developmental stages and molecular phylogeny of Hepatozoon tuatarae, a parasite infecting the New Zealand tuatara, Sphenodon punctatus and the tick, Amblyomma sphenodonti. Int. J. Parasitol. 2010, 40, 1311–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddall, M.E.; Desser, S.S. Merogonic development of Haemogregarina balli (Apicomplexa: Adeleina: Haemogregarinidae) in the leech Placobdella ornate (Glossiphoniidae), its transmission to a chelonian intermediate host and phylogenetic implications. J. Parasitol. 1991, 77, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvořáková, N.; Kvičerová, J.; Hostovský, M.; Široký, P. Haemogregarines of freshwater turtles from Southeast Asia with a description of Haemogregarina sacaliae sp. n. and a redescription of Haemogregarina pellegrini Laveran and Pettit, 1910. Parasitology 2015, 142, 816–826. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamoto, W.; Silva, A.J.; Machado, P.E.; Padovani, C.R.; Januario, S.A.; De Abreu, M.E. Leukocytes and Cyrilia gomesi (blood parasite) in Synbranchus marmoratus Bloch, 1975 (Pisces, Synbranchidae) from the Biriqui region of Sao Paulo (Brazil). Rev. Bras. Biol. 1991, 51, 755–761. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, A.J.; Eiras, J.C.; Austin, R.T.E. Investigations into the transmission of Haemogregarina bigemina Laveran and Mesnil, 1901 (Apicomplexa: Adeleorina) between intertidal fishes in Portugal. J. Fish. Dis. 1994, 17, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lom, J.; Tomas, K.; Dykova, I. Haemogregarina vltavensis, new species from perch (Perca fluviatilis) in Czechoslovakia. Syst. Parasitol. 1989, 13, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.P.; Hendrickson, G.L. Haematozoa of fishes in Humboldt Bay, California. J. Wildl. Dis. 1991, 27, 701–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, A.J.; Smit, N.J. The life cycle of Haemogregarina bigemina (Adeleina: Haemogregarinidae) in South African hosts. Folia Parasit. 2001, 48, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacLean, S.A.; Davies, A.J. Prevalence and development of intraleucocytic haemogregarines from northwest and northeast Atlantic mackerel, Scomber scombrus L. J. Fish. Dis. 1990, 13, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, P.M.; Smit, N.J.; Seddon, A.M.; Wertheim, D.F.; Davies, A.J. A new fish haemogregarine from South Africa and its suspected dual transmission with trypanosomes by a marine leech. Folia Parasit. 2006, 53, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Curtis, L.M.; Grutter, A.S.; Smit, N.J.; Davies, A.J. Gnathia aureamaculosa, a likely definitive host of Haemogregarina balistapi and potential vector for Haemogregarina bigemina between fishes of the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.; Araújo, M.L.G.; Pantoja-Lima, J.; Aride, P.; Tavares-Dias, M.; Brinn, R.P.; Marcon, J.L. Cyrilia sp. (Apicomplexa: Haemogregarinidae) in the Amazonian freshwater stingray Potamotrygon wallacei (cururu stingray) in different hydrological phases of the Rio Negro. Rev. Bras. Biol. 2016, 77, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Esteves-Silva, P.H.; da Silva, M.R.L.; O’Dwyer, L.H.; Tavares-Dias, M.; Viana, L.A. Haemogregarina daviesensis sp. nov. (Apicomplexa: Haemogregarinidae) from South American lungfish Lepidosiren paradoxa (Sarcopterygii: Lepidosirenidae) in the eastern Amazon region. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 2773–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awerenzew, S. Parasiten aus dem Blute von Rana nuti. Arch. Protistenk. 1941, 95, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Ball, G.H. Some blood sporozoans from East African reptiles. J. Protozool. 1967, 14, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, R. Studies on the anuran blood parasites of sub-Himalayan West Bengal, India. J. Beng. Nat. Hist. Soc. 1992, 11, 4–8. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, T.G.; Desser, S.S.; Martin, D.S. The development of Hepatozoon sipedon n. sp. (Apicomplexa: Adeleina: Hepatozoidae) in its natural host, the northern water snake (Nerodia sipedon sipedon), its culicine vectors (Culex pipiens and Culex territans) and its intermediate host, the northern leopard frog (Rana pipiens). Parasitol. Res. 1994, 80, 559–568. [Google Scholar]
- Desser, S.S.; Hong, H.; Martin, D.S. The life history, ultrastructure and experimental transmission of Hepatozoon catesbiana n. comb., an apicomplexan parasite of the bullfrog, Rana catesbeiana and the mosquito, Culex territans in Algonquin Park, Ontario. J. Parasitol. 1995, 81, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lainson, R.; Paperna, I.; Naiff, R.D. Development of Hepatozoon caimani (Carini, 1909) Pessôa, de Biasi & de Souza, 1972 in the Caiman c. Crocodilus, the frog Rana catesbeiana and the mosquito Culex fatigans. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo. Cruz. 2003, 98, 103–113. [Google Scholar]
- Conradie, R.; Cook, C.A.; Preez, L.H.; Jordaan, A.; Netherlands, E.C. Ultrastructural comparison of Hepatozoon ixoxo and Hepatozoon theileri (Adeleorina: Hepatozoidae), parasitising South African anurans. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2017, 64, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netherlands, E.C.; Cook, C.A.; Du Preez, L.H.; Vanhove, M.P.M.; Brendonck, L.; Smit, N.J. Monophyly of the species of Hepatozoon (Adeleorina: Hepatozoidae) parasitizing (African) anurans, with the description of three new species from hyperoliid frogs in South Africa. Parasitology 2018, 145, 1039–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robin, L.A. Cycle évolutif d’un Hepatozoon de Greko verticillatus. Ann. Inst. Pasteur. 1936, 56, 376–394. [Google Scholar]
- Garnham, P.C.C.C. A haemogregarines in Argas brumpti. Riv. Parasitol. 1954, 15, 425–435. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, J.E.; Wagner, E.D. Hepatozoon sauromali sp. n., a haemogregarines from the Chuckwalla (Sauromalus spp.) with notes on the life history. J. Parasitol. 1964, 50, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwasila, M. Haemogregarina sp. (Apicomplexa: Adeleorina) from the gecko Tarentola annularis in the Sudan: Fine structure and life-cycle trials. Parasitol. Res. 1989, 75, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, B.; Desser, S.S. Developmental stages of Hepatozoon lygosomarum (Dore 1919) comb. N. (Protozoa, Haemogregarinidae), a parasite of a new Zealand skink, Leiolopisma nigriplamtare. J. Parasitol. 1981, 67, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saratchandra, B. Two new haemogregarines, Haemogregarina waltairensis n. sp. from Calotes versicolor (Daudin) and H. ganapatii n. sp. from Lissemys punctata granosa (Shoepff). Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Anim. Sci.) 1981, 90, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashtar, A.-R.; Abdel-Ghaffar, F.; Shazly, M.A. Developmental stages of Hepatozoon gracilis (Wenyon, 1909) comb. Nov., a parasite of the Egyptian Skink, Mabuya quinquetaeniata. Parasitol. Res. 1987, 73, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, V.; Galdón, M.A. Haemogregarine blood parasites in the lizards Podarcis bocagei (Seoane) and P. carbonelli (Pérez-Mellado) (Sauria: Lacertidae) from NW Portugal. Syst. Parasitol. 2010, 75, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Baki, A.S.; Al-Quraishy, S. Morphological characteristics of a new species of Haemogregarina Danilewsky, 1885 (Apicomplexa: Adeleorina) in naturally infected Acanthodactylus boskianus (Daudin) (Sauria: Lacertidae) in Egypt. Syst. Parasitol. 2012, 82, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, I.D.; Harris, D.J.; Rosado, D.; Tavares, I.; Maia, J.P.; Salvi, D.; Perera, A. Consequences of haemogregarine infection on the escape distance in the lacertid lizard, Podarcis vaucheri. Acta Herpetol. 2014, 9, 119–123. [Google Scholar]
- Rabie, S.A.H.; Hussein, A.-N.A. A description of Haemogregarina species naturally infecting white-spotted gecko (Tarentola annularis) in Qena, Egypt. J. Egypt Soc. Parasitol. 2014, 44, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou Shafeey, H.; Mohamadain, H.S.; Abdel-Gaber, R.; Emara, N.M. Haemogregarines infecting reptiles in Egypt: 1- Blood and Merogenic stages of Haemogregarine sp. infecting the skink Scincus scincus. Egypt J. Exp. Biol. (Zool.) 2019, 15, 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Zechmeisterová, K.; De Bellocq, J.G.; Široký, P. Diversity of Karyolysus and Schellackia from the Iberian lizard Lacerta schreiberi with sequence data from engorged ticks. Parasitology 2019, 146, 1690–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ball, G.H.; Oda, S.N. Sexual stages in the life history of the haemogregarines Hepatozoon rarefaciens (Sambon and Seligmann 1907). J. Protozool. 1971, 18, 697–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, N.F. Morphological, experimental and taxonomic studies on protozoan blood parasite of Egyptian reptiles. Ph.D. Thesis, Ain Shams University, Cairo, Egypt, 1974; 220p. [Google Scholar]
- Ball, G.H.; Chao, J.; Telford, S.R. Hepatozoon fusifex sp. n. a haemogregarine from the Boa constrictor producing marked morphological changes in the infected erythrocytes. J. Parasitol. 1969, 55, 800–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashtar, A.R.; Boules, R.; Mehlhorn, H. Hepatozoon aegypti nov. sp. 1- Life cycle. Z. Parasitenkd. 1984, 70, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowichik, A.; Lanners, H.N.; Lowrie, R.C.; Meiners, N.E. Gametogenesis and sporogony of Hepatozoon mocassinin (Apicomplexa: Adeleina: Hepatozoidae) in an experimental mosquito host, Aedes aegypti. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 1993, 40, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Ghaffar, F.A.; Bashtar, A.R.; Shazly, M.A. Life cycle of Hepatozoon seurati comb. Nov. 1- Gamogony and sporogony inside the vector, Culex pipiens molestus. J. Egypt Ger. Soc. Zool. 1991, 3, 211–226. [Google Scholar]
- Bashtar, A.R.; Abdel-Ghaffar, F.A.; Shazly, M.A. Life cycle of Hepatozoon mehlhorni sp. nov. in the viper Echis carinatus and the mosquito Culex pipiens. Parasitol. Res. 1991, 77, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashtar, A.R.; Shazly, M.A.; Ahmed, A.K.; Fayed, H.M. Life cycle of Hepatozoon matruhensis comb. nov. 1- Blood stages and merogony inside the snake Psammophis schokari. J. Egypt Ger. Soc. Zool. 1994, 14, 117–131. [Google Scholar]
- Shazly, M.A.; Ahmed, A.K.; Bashtar, A.R.; Fayed, H.M. Life cycle of Hepatozoon matruhensis comb. nov. 2. Gamogony and sporogony inside the vector Culex pipiens molestus. J. Egypt Ger. Soc. Zool. 1994, 14, 323–340. [Google Scholar]
- Saoud, M.; Ramadan, N.; Mohammed, S.; Fawzi, S. On two new haemogregarines (Protozoa: Apicomplexa) from Colubrid and Elapidae snakes in Egypt. Qatar Univ. Sci. J. 1996, 16, 127–139. [Google Scholar]
- Sloboda, M.; Kamler, M.; Bulantová, J.; Votýpka, J.; Modrý, D. A new species of Hepatozoon (Apicomplexa: Adeleorina) from Python regius (Serpentes:Pythonidae) and its experimental transmission by a mosquito vector. J. Parasitol. 2007, 93, 1189–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Farraj, S. Light and electron microscopic study on a haemogregarine species infecting the viper Cerastes cerastes gasperitti from Saudi Arabia. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2008, 11, 1414–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjadi, S.S.; Javanbakht, H. Study of blood parasites of the three snake species in Iran: Natrix natrix, Natrix tessellate and Zamenis longissimus (Colubridae). J. Genet. Resour. 2017, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Haleem, H.M.; Mansour, L.; Holal, M.; Qasem, M.A.; Al-Quraishy, S.; Abdel-Baki, A.S. Molecular characterisation of Hepatozoon aegypti Bashtar, Boulos & Mehlhorn, 1984 parasitising the blood of Spalerosophis diadema (Serpentes: Colubridae). Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 3119–3125. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Robertson, M. Studies on Ceylon haematozoa. II- Notes on the life cycle of Haemogregarina nicoriae. Q. J. Microsc. Sci. 1910, 55, 741–762. [Google Scholar]
- Siddall, M.E.; Desser, S.S. Ultrastructure of gametogenesis and sporogony of Haemogregarina (sensu lato) myoxoxephali (Apicomplexa: Adeleina) in the Marine Leech Malmianta scorpii. J. Protozool. 1992, 39, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, J.C. Hepatozoon mauritanicum (Et. Et Ed. Sergent, 1904) n. comb., parasite de Testudo graeca: Redescription de la sporogone chez Hyalomma aegyptium et de la schizogonie tissularie d’apres le material d’E. Brump. Ann. Parasitol. Hum. Comp. 1973, 48, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Acholonu, A.D. Haemogregarina pseudemydis n sp (Apicomplexa: Haemogregarinidae) and Pirhemocyton chelonarum n. sp. in turtles from Louisiana. J. Protozool. 1947, 21, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, K.K. Erythrocytic Schizogony in Haemogregarina gangetica of a River Turtle, Trionyx gangeticus Cuvier. Proc. Zool. Soc. (Calcutta) 1981, 32, 141–143. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, J.Y.; Chen, C.H. Six new species of Haemogregarina from chinese turtles. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 1990, 14, 129–137. [Google Scholar]
- Mihalca, A.D.; Achelăriţei, D.; Popescu, P. Haemoparasites of the genus Haemogregarina in a population of european pond turtles (Emys orbicularis) from Drăgăşani, Vâlcea county, Romania. Rev. Sci. Parasitol. 2002, 3, 22–27. [Google Scholar]
- Paperna, I. Hemolivia mauritanica (Haemogregarindae: Apicomplex) infection in the tortoise Testudo graeca in the Near East with data on sporogonous development in the tick vector Hyalomna aegyptium. Parasite 2006, 13, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Široký, P.; Mikulíček, P.; Jandzik, D.; Kami, H.; Mihalca, A.; Rouag, R.; Kamler, M.; Schneider, C.; Zaruba, M.; Modrý, D. Co-distribution pattern of a haemogregarine Hemolivia mauritanica (Apicomplexa: Haemogregarinidae) and its vector Hyalomma aegyptium (Metastigmata: Ixodidae). J. Parasitol. 2009, 95, 728–733. [Google Scholar]
- Telford, S.R., Jr.; Norton, T.M.; Moler, P.E.; Jensen, J.B. A new Haemogregarina species of the alligator snapping turtle, Macrochelys temminckii (Testudines: Chelydridae), in Georgia and Florida that produces macromeronts in circulating erythrocytes. J. Parasitol. 2009, 95, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, D.J.; Graciá, E.; Jorge, F.; Maia, J.P.M.C.; Perera, A.; Carretero, M.A.; Giménez, A. Molecular detection of Hemolivia (Apicomplexa: Haemogregarinidae) from ticks of North African Testudo graeca (Testudines: Testudinidae) and an estimation of their phylogenetic relationships using 18S rRNA sequences. Comp. Parasitol. 2013, 80, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossow, J.A.; Hernandez, S.M.; Sumner, S.M.; Altman, B.R.; Crider, C.G.; Gammage, M.B.; Segal, K.M.; Yabsley, M.J. Haemogregarine infections of three species of aquatic freshwater turtles from two sites in Costa Rica. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2013, 2, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soares, P.; de Brito, E.S.; Paiva, F.; Pavan, D.; Viana, L.A. Haemogregarina spp. in a wild population from Podocnemis unifilis Troschel, 1848 in the Brazilian Amazonia. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 4499–4503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molla, S.H.; Bandyopadhyay, P.K.; Gürelli, G. Description of a new Haemogregarine, Haemogregarina sundarbanensis n. sp. (Apicomplexa: Haemogregarinidae) from Mud Turtle of Sundarban Regions, West Bengal, India. Turkiye. Parazitol. Derg. 2015, 39, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picelli, A.M.; Carvalho, A.V.; Viana, L.A.; Malvasio, A. Prevalence and parasitemia of Haemogregarina sp. in Podocnemis expansa (Testudines: Podocnemididae) from the Brazilian Amazon. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2015, 24, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arizza, V.; Sacco, F.; Russo, D.; Scardino, R.; Arculeo, M.; Vamberger, M.; Marrone, F. The good, the bad, and the ugly: Emys trinacris, Placobdella costata and Haemogregarina stepanowi in Sicily (Testudines, Annelida and Apicomplexa). Folia Parasit. 2016, 63, 029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakhshandehroo, E.; Sharifiyazdi, H.; Ahmadi, A. Morphological and molecular characterisation of Haemogregarina sp. (Apicomplexa: Adeleina: Haemogregarinidae) from the blood of the Caspian freshwater turtle Mauremys caspica (Gmelin) (Geoemydidae) in Iran. Syst. Parasitol. 2016, 93, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhaboubi, A.R.; Pollard, D.A.; Holman, P.J. Molecular and morphological characterization of a haemogregarine in the alligator snapping turtle, Macrochelys temminckii (Testudines: Chelydridae). J. Parasitol. 2017, 116, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goes, V.C.; Brito, E.S.; Valadao, R.M.; Gutierrez, C.O.; Picelli, A.M.; Viana, L.A. Haemogregarine (Apicomplexa: Adeleorina) infection in Vanderhaege’s toadheaded turtle, Mesoclemmys vanderhaegei (Chelidae), from a Brazilian Neotropical savanna region. Folia Parasitol. 2018, 65, 012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Úngari, L.P.; Santos, A.L.Q.; O’Dwyer, L.H.; da Silva, M.R.L.; Santos, T.C.R.; da Cunha, M.J.R.; de Melo Costa Pinto, R.; Cury, M.C. Molecular characterization and identification of Hepatozoon species Miller, 1908 (Apicomplexa: Adeleina: Hepatozoidae) in captive snakes from Brazil. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 3857–3865. [Google Scholar]
- Börner, C. Untersuchungen über Hämospridien. I-Ein Beitrag zur kenntnis des genus Haemogregarina Danilewsky. Z. Wiss. Zool. Abt. A 1901, 69, 398–416. [Google Scholar]
- Pessôa, S.B.; De Biasi, P. Nota taxonomica sobre cistos esporôgônicos de algumas espécies de Hepatozoon (Sporozoa, Haemogregarinidae) parasites de serpents brasileiras. Mem. Inst. Butantan (Sâo Paulo) 1973, 37, 299–307. [Google Scholar]
- Hoare, C.A. On protozoal blood parasites collected in Uganda with an account of the life cycle of the croccdile haemogregarines. Parasitology 1932, 24, 210–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, L.A.; Marques, E.J. Haemogregarine parasites (Apicomplexa: Hepatozoidae) in Caiman crocodilus yacare (Crocodilia: Alligatoridae) from Pantanal, Corumba, MS, Brazil. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2005, 14, 173–175. [Google Scholar]
- Viana, L.A.; Paiva, F.; Coutinho, M.E.; Lourenço-de-Oliveira, R. Hepatozoon caimani (Apicomplexa: Hepatozoidae) in Wild Caiman, Caiman yacare, from the Pantanal region, Brazil. J. Parasitol. 2010, 96, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, G.F.; Earle, R.A.; Penzhorn, B. Ornithodoros peringueyi (Argasidae) and Xenopsylla trispinis (Siphonaptera), probable intermediate hosts of Hepatozzon atticoare of the South African Cliff swallow, Hirundo spilodera. Can. J. Zool. 1992, 70, 188–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, G.F.; Earle, R.A. New species of Haemoproteus, Hepatozoon and Leucocytozoon from South African birds. S. Afr. J. Wildl. Res. 1992, 22, 114–118. [Google Scholar]
- Desser, S.S. Tissue “Cyst” of Hepatozoon griseisciuri in the Grey Squirrel, Sciurus carolinensis: The significance of these cysts in species of Hepatozoon. J. Parasitol. 1990, 76, 257–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göbel, E.; Krampitz, H.E. Histologische Untersuchungean zur Gamogonie und Sporogonie von Hepatozoon erhardovae in experimental infizierten rattenflohen (Xenopsylla cheopis). Z. Parasitenkd. 1982, 67, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, C. Über die Bedeutung von Laelaps agilis CL Koch 1836 (Mosostigmata: Parasitiformae) fur die Ubertragung von Hepatozoon sylvatici Coles 1914 (Sporozoa: Haemogregarinidae). Z. Parasitenkd. 1977, 53, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forlano, M.D.; Teixeira, K.R.S.; Scolfield, A.; Elisei, C.; Yotoko, K.S.C.; Fernandes, K.R.; Linhares, G.F.C.; Ewing, S.A.; Massard, C.L. Molecular characterization of Hepatozoon sp. from Brazilian dogs and its phylogenetic relationship with other Hepatozoon spp. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 145, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otranto, D.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Weigl, S.; Latrofa, M.S.; Stanneck, D.; Decaprariis, D.; Capelli, G.; Baneth, G. Diagnosis of Hepatozoon canis in young dogs by cytology and PCR. Parasite. Vector. 2011, 4, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baneth, G.; Sheiner, A.; Eyal, O.; Hahn, S.; Beaufils, J.P.; Anug, Y.; Talmi-Frank, D. Redescription of Hepatozoon felis (Apicomplexa: Hepatozoidae) based on phylogenetic analysis, tissue and blood form morphology, and possible transplacental transmission. Parasite. Vector. 2013, 6, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramos, C.A.N.; Babo-Terra, V.J.; Pedroso, T.C.; Filho, A.F.S.; Araújo, F.R.; Cleveland, H.P.K. Molecular identification of Hepatozoon canis in dogs from Campo Grande, Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil. Braz. J. Vet. Parasitol. Jaboticabal 2015, 24, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paiz, L.M.; Silva, R.C.; Satake, F.; Fraga, T.L. Hematological disorders detected in dogs infected by Hepatozoon canis in a municipality in Mato Grosso do Sul State, Brazil. Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec. 2016, 68, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, K.C.M.; Fernandes, M.P.; Herrera, H.M.; Benevenute, J.L.; Santos, F.M.; Rocha, F.L.; Barreto, W.T.G.; Macedo, G.C.; Campos, J.B.; Martins, T.F.; et al. Molecular detection of Hepatozoon spp. in domestic dogs and wild mammals in southern Pantanal, Brazil with implications in the transmission route. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 237, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhusri, B.; Sariya, L.; Mongkolphan, C.; Suksai, P.; Kaewchot, S.; Changbunjong, T. Molecular characterization of Hepatozoon felis in Rhipicephalus sanguineus ticks infested on captive lions (Panthera leo). J. Parasit. Dis. 2017, 41, 903–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitkova, B.; Hrazdilova, K.; Novotna, M.; Jurankova, J.; Hofmannova, L.; Forejtek, P.; Modry, D. Autochthonous Babesia canis, Hepatozoon canis and imported Babesia gibsoni infection in dogs in the Czech Republic. Vet. Med. 2017, 62, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barati, A.; Razmi, G.R. A parasitologic and molecular survey of Hepatozoon canis infection in stray dogs in northeastern Iran. J. Parasitol. 2018, 104, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuna, G.E.; Bakırcı, S.; Dinler, C.; Battal, G.; Ulutaş, B. Molecular Identification and Clinicopathological Findings of Hepatozoon sp. Infection in a Cat: First Report from Turkey. Turkiye Parazitol. Derg. 2018, 42, 286–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attipa, C.; Maguire, D.; Solano-Gallego, L.; Szladovits, B.; Barker, E.N.; Farr, A.; Baneth, G.; Tasker, S. Hepatozoon canis in three imported dogs: A new tickborne disease reaching the United Kingdom. Vet. Rec. 2018, 183, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harris, D.J.; Sergiadou, D.; Halajian, A.; Swanepoel, L.; Roux, F. Molecular screening indictes high prevalence and mixed infections of Hepatozoon parasites in wild felines from South Africa. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 2020, 91, a2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van As, M.; Netherlands, E.C.; Smit, N.J. Molecular characterization and morphological description of two new species of Hepatozoon Miller, 1908 (Apicomplexa: Adeleorina: Hepatozoidae) infecting leukocytes of African leopards Panthera pardus pardus (L.). Parasite. Vector. 2020, 13, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baticados, A.M.; Baticados, W.N.; Carlos, E.T.; Carlos, S.M.; Villarba, L.A.; Subiaga, S.G.; Magcalas, J.M. Parasitological detection and molecular evidence of Hepatozoon canis from canines in Manila, Philippines. Vet. Med. Res. Rep. 2011, 1, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bray, R.S. A check-list of the parasitic protozoa of West Africa with some notes on their classification. Bull. Inst. Fr. Afr. Noire. 1964, 26, 238–315. [Google Scholar]
- Yanai, T.; Tomita, A.; Masegi, T.; Ishikawa, K.; Iwasaki, T.; Yamazoe, K.; Ueda, K. Histopathologic features of naturally occurring hepatozoonosis in wild martens (Martes melampus) in Japan. J. Wildl. Dis. 1996, 31, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saoud, M.F.A.; Ramadan, N.F.; Mohammed, S.H.; Fawzi, S.M. Haemogregarines of geckos in Egypt, together with a description of Haemogregarina helmymohammedi n. sp. Qatar Univ. Sci. J. 1995, 15, 131–146. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, T.G.; Desser, S.S. Ultrastructural features of cystic and merogonic stages of Hepatozoon sipedon (Apicomplexa: Adeleorina) in northern leopard frogs (Rana pipiens) and northern water snakes (Narodia sipedon) from Ontario, Canada. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 1998, 45, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadler, S.A.; Miller, J.H. A redescription of Hepatozoon mocassini (Laveran, 1902) n. comb. from Agkistrodon piscivorus leucostoma Troost 1836. J. Protozool. 1984, 31, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Baki, A.S.; Mansour, L.; Al-Malki, E.S.; Al-Quraishy, S.; Abdel-Halim, H.M. Morphometric and molecular characterisation of Hepatozoon bashtari n. sp. in painted saw-scaled viper, Echis coloratus (Ophidia, Viperidae). Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 3793–3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, A.N.A. Light and transmission electron microscopic studies of a haemogregarine in naturally infected fan-footed gecko (Ptyodactylus hasselquistii ). Parasitol. Res. 2006, 98, 468–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichenow, E. Karyolysus lacerate, ein wirtwechselndes Coccidium der Eidechse Laverta muralis und der Milbe Liponyssus saurarum. Arb. Gesundh. Amt. Berl. 1913, 45, 317–363. [Google Scholar]
- Honigberg, B.M.; Chairman of Committee. A revised classification of the phylum Protozoa. J. Protozool. 1964, 11, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubini, D.S.; Paduan, K.S.; Perez, R.R.; Ribolla, P.E.M.; O’Dwyer, L.H. Molecular characterization of feline Hepatozoon species from Brazil. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 137, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortuño, A.; Castella, J.; Criado-Fornelio, A.; Buling, A.; Barba-Carretero, J.C. Molecular detection of a Hepatozoon species in stray cats from a feline colony in North-eastern Spain. Vet. J. 2008, 177, 134–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilcins, I.E.; Ujvari, B.; Old, J.M.; Deane, E. Molecular and morphological description of a Hepatozoon species in reptiles and their ticks in the Northern Territory, Australia. J. Parasitol. 2009, 95, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maia, J.P.M.C.; Perera, A.; Harris, D.J. Molecular survey and microscopic examination of Hepatozoon Miller, 1908 (Apicomplexa: Adeleorina) in lacertid lizards from the western Mediterranean. Folia Parasitol. 2012, 59, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tomé, B.M.; Maia, J.P.M.C.; Harris, D.J. Molecular assessment of apicomplexan parasites in the snake Psammophis from north Africa: Do multiple parasite lineages reflect the final vertebrate host diet? J. Parasitol. 2013, 99, 883–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xavier, R.; Severino, R.; Pérez-Losada, M.; Gestal, C.; Freitas, R.; Harris, D.J.; Verissino, A.; Rosado, D.; Cable, J. Phylogenetic analysis of apicomplexan parasites infecting commercially valuable species from the North-East Atlantic reveals high levels of diversity and insights into the evolution of the group. Parasite. Vector. 2018, 11, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waeschenbach, A.; Webster, B.L.; Bray, R.A.; Littlewood, D.T.J. Added resolution among ordinal level relationships of tapeworms (Platyhelminthes: Cestoda) with complete small and large subunit nuclear ribosomal RNA genes. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2007, 45, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.S.; Saeed, M.A.; Rashid, I.; Ashraf, K.; Shehzad, W.; Traub, R.J.; Baneth, G.; Jabbar, A. Molecular characterization of Hepatozoon canis from farm dogs in Pakistan. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 1131–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, P.M.; Smit, N.J. Molecular insights into the identification and phylogenetics of the cosmopolitan marine fish blood parasite, Haemogregarina bigemina (Adeleorina: Haemogregarinidae). Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites. Wildl. 2019, 8, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordmeyer, S.C.; Henry, G.; Guerra, T.; Rodriquez, D.; Forstner, M.R.J.; Hahn, D. Identification of blood parasites in individuals fromsix families of freshwater turtles. Chelonian Conserv. Biol. 2020, 19, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, J.S.; Van Den Bussche, R.A.; Ewing, S.A. Phylogenetic relationships of Hepatozoon (Apicomplexa Adeleorina) based on molecular, morphologic, and life-cycle characters. J. Parasitol. 2000, 86, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, S.L.; Keller, A.K. Phylogeny of nuclear small subunit rRNA genes of haemogregarines amplified with specific primers. J. Parasitol. 2001, 87, 870–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inokuma, H.; Okuda, M.; Ohno, K.; Shimoda, K.; Onishi, T. Analysis of the 18S rRNA gene sequence of a Hepatozoon detected in two Japanese dogs. Vet. Parasitol. 2002, 106, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criado-Fornelio, A.; Buling, A.; Cunha-Filho, N.A.; Ruas, J.L.; Farias, N.A.; Rey-Valeiron, C.; Pingret, J.L.; Etievant, M.; Barba-Carretero, M.J.C. Development and evaluation of a quantitative PCR assay for detection of Hepatozoon sp. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 150, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabar, M.D.; Altet, L.; Francino, O.; Sánchez, A.; Ferrer, L.; Roura, X. Vector-borne infections in cats: Molecular study in Barcelona area (Spain). Vet. Parasitol. 2008, 151, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kledmanee, K.; Suwanpakdee, S.; Krajangwong, S.; Chatsiriwech, J.; Suksai, P.; Suwannachat, P.; Sariya, L.; Buddhirongawatr, R.; Charoonrut, P.; Chaichoun, K. Development of multiplex polymerase chain reaction for detection of Ehrlichia canis, Babesia spp. and Hepatozoon canis in canine blood. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2009, 40, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Zintl, A.; Finnerty, E.J.; Murphy, T.M.; De Waal, T.; Gray, J.S. Babesias of red deer (Cervus elaphus) in Ireland. Vet. Res. 2011, 42, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hodžić, A.; Alić, A.; Fuehrer, H.P.; Harl, J.; Wille-Piazzai, W.; Duscher, G.G. A molecular survey of vector-borne pathogens in red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) from Bosnia and Herzegovina. Parasite. Vector. 2015, 8, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
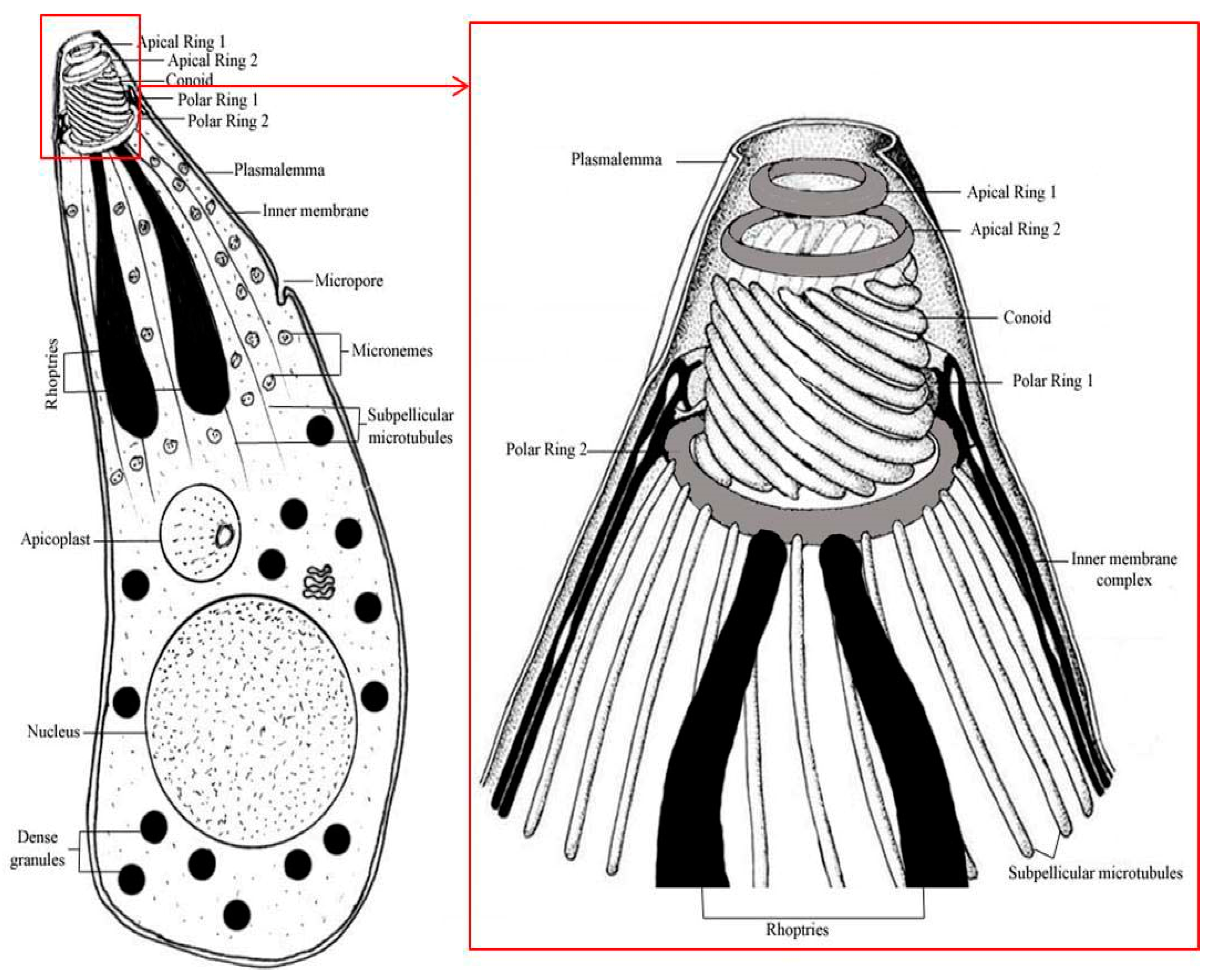


| Comparable Features | Karyolysis | Haemogregarina | Cryilia | Hepatozoon | Haemolivia |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conoid present | In all non-gametes | In all non-gametes | In all non-gametes | In all non-gametes | In all non-gametes |
| Crystalloid bodies +/- | ? | + | ? | + | + (fragmented) |
| Merogeny +/- | + Intra-cellular | + Intra-cellular | + Intra-cellular | + Intra-cellular | + Intra-cellular |
| Micropores +/- | + | + | + | + | + |
| Mitochondria. | Cristate | Cristate | Cristate | Cristate | Cristate |
| Mitosis | Centriolar | Centriolar | ? | Centriolar | Centriolar |
| Amylopectin granules +/- | + | - | - | + | + |
| Polar ring complex +/- | + | + | + | + | + |
| Gametogenesis | Extra-cellular | Extra-cellular | Extra-cellular | Extra-cellular | Intra-cellular |
| No. of microgametes/each microgamont | 2 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 2–4 |
| Gamonts | Anisogamous | Anisogamous | Anisogamous | Anisogamous | Anisogamous |
| Syzygy | + | + | + | + | + |
| Zygote | Non-motile | Non-motile | Non-motile | Non-motile | Non-motile |
| Sporogony | Extra-cellular | Extra-cellular | Extra-cellular | Extra-cellular | Intra-cellular |
| Persistent cysts +/- | - | - | - | + | + |
| No. of flagella/microgametes | 1 | 1 | Absent | 1 | ? |
| Arrangement of flagella in microgametes | Terminal | Terminal | ? | Terminal | Terminal |
| No. of sporozoites/oocyst | 20–30 | 8 | >20 | 4–16 | 10–25 |
| Species of Haemogregarines | The Vertebrate Host | Site of Merogony | Invertebrate Vector | Site of Gamogony and Sporogony | Locality | Authors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cyrilia gomesi | Synbranchus marmoratus | Leucocytes | Haementeria lutzi | Stomach | Sao Paulo, Brazil | Nakamoto et al. [38] |
| Haemogregarina bigemina | Lipophrys folis and Coryphoblrnnius galerita | Blood cells | Gnathia maxillaris | Hindgut | Portugal Atlantic west coast | Davies et al. [39] |
| Haemogregarina vltavensis | Perca fluviatilis | Intra-erythrocytic gamonts are only described | -- | -- | Czechoslovakia | Lom et al. [40] |
| Haemogregarina leptocotti | Leptocottus armatus | Blood cells | -- | -- | California USA | Hill and Hendrickson [41] |
| Haemogregarina roelofsi | Sebastes melanops | Blood cells | -- | -- | California USA | Hill and Hendrickson [41] |
| Haemogregarina bigemina | Clinus superciliosus and Clinus cottoides | Intra-erythrocytic | Gnathia africana | -- | South Africa | Davies and Smit [42] |
| Haemogregarine sp. | Scomber scombrus L. | Leucocytes | -- | -- | Northwest and Northeast Atlantic ocean | Maclean and Davies [43] |
| Haemogregarina curvata | Clinus cottoides, Parablennius cornutus | Intra-erythrocytic | Zeylanicobdella arugamensis | Host gut tissue | South Africa | Hayes et al. [44] |
| Haemogregarina balistapi | Rhinecanthus aculeatus | Intra-erythrocytic | Gnathia aureamaculosa | Host gut tissue | Great Barrier Reef, Australia | Curtis et al. [45] |
| Cyrilia sp. | Potamotrygon wallacei | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Rio Negri | Oliveira et al. [46] |
| Haemogregarina daviesensis | Lepidosiren paradoxa | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Eastern Amazon region | Esteves-Silva et al. [47] |
| Species of Haemogregarines | The Vertebrate Host | Site of Merogony | Invertebrate Vector | Site of Gamogony and Sporogony | Locality | Authors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudohaemogregarina nutti | Rana nutti | Erythrocytes and liver | -- | -- | Germany | Awerenzew [48] |
| Haemogregarina theileri | Rana angloensis | Erythrocytes and liver | -- | -- | Njoro, Kenya | Ball [49] |
| Haemolivia stellate | Brazilian toads | Liver | Ticks | Gut wall | Brazil | Petit et al. [14] |
| Haemogregarina nucleobisecans | Bufo himalayanus | Erythrocytes and liver | -- | -- | India | Ray [50] |
| Hepatozoon sipedon | Nerodia sipedon and Rana pipiens | Various internal organs | Culex pipiens and Culex territans | Hemocoel | Ontario, Canada | Smith et al. [51] |
| Hepatozoon catesbianae | Rana catesbeiana | Erythrocytes and liver | Culex territans | Malpighian tubules | Ontario, Canada | Desser et al. [52] |
| Hepatozoon caimani | Rana catesbeiana | Intra-erythrocytic | Culex fatigans | Extra-erythrocytic gametocytes | State of Mato Grosso | Lainson et al. [53] |
| Hepatozoon theileri | Amietia quecketti | Intra-erythrocytic gamonts are only described | -- | -- | South Africa | Conradie et al. [54] |
| Hepatozoon involucrum | Hyperolius marmoratus | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa | Netherlands et al. [55] |
| Hepatozoon tenuis | Afrixalus fornasinii | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa | Netherlands et al. [55] |
| Hepatozoon thori | Hyperolius marmoratus | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa | Netherlands et al. [55] |
| Species of Haemogregarines | The Vertebrate Host | Site of Merogony | Invertebrate Vector | Site of Gamogony and Sporogony | Locality | Authors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hepatozoon mesnili | Gecko verticillatus | Endothelial cells of all host organs | Culex fatigans and Aedes albopictus | Stomach | Saigon | Robin [56] |
| Haemogregarina triatomae | Tupinambis teguixin | Liver and lung | Triatoma subrovaria | Intestine | South America | Osimani [33] |
| Hepatozoon argantis | Agama mossambica | Liver | Argas brumpti | Gut and homocoelomic cavity | East Africa, Mossambic | Garnham [57] |
| Hepatozoon sauromali | Sauromalus sp. | Liver | Ophionyssus sp. | Hemocoel | -- | Lewis and Wagner [58] |
| Haemogregarina sp. | Tarentola annularis | Lung | -- | -- | Sudan | Elwasila [59] |
| Hepatozoon lygosomarum | Leiolopisma nigriplantare | Liver and spleen | Ophionissus saurarum | Wall of the gut caeca | Canterbury, New Zealand | Allison and Desser [60] |
| Haemogregarina waltairensis | Calotes versicolor | Peripheral blood, liver, lung, and bone marrow | -- | -- | India | Saratchandra [61] |
| Hepatozoon gracilis | Mabuya quinquetaeniata | Liver | Culex pipienis molesus | Hemocoel | Giza, Egypt | Bashtar et al. [62] |
| Haemogregarina sp. | Podarcis bocagei and Podarcis carbonelli | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | NW Portugal | Roca and Galdón [63] |
| Haemogregarina ramadani | Acanthodactylus boskianus | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Giza, Egypt | Abdel-Baki and Al-Quraishy [64] |
| Hepatozoon sp. | Podarcis vaucheri | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Oukaimeden | Moreira et al. [65] |
| Haemogregarina sp. | Tarentola annularis | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Qena, Egypt | Rabie and Hussein [66] |
| Karyolysus lacazei Karyolysus sp. Karyolysus latus | Lacerta agilis Zootoca vivipara Podarcis muralis | Intra-erythrocytic | Ophionyssus saurarum and Ixodes ricinus | Poland, Slovakia | Haklová-Kočíková et al. [18] | |
| Karyolysus paradoxa | Varanus albigularis, Varanus niloticus | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Ndumo Game Reserve, South Africa | Cook et al. [31] |
| Haemogregarina daviesensis | Lepidosiren paradoxa | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Eastern Amazon region | Esteves-Silva et al. [47] |
| Haemogregarina sp. | Scincus scincus | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | South Sinai, Egypt | Abou Shafeey et al. [67] |
| Karyolysus lacazei | Lacerta schreiberi | Intra-erythrocytic | Ixodes ricinus | -- | Czech Republic | Zechmeisterová et al. [68] |
| Species of Haemogregarines | The Vertebrate Host | Site of Merogony | Invertebrate Vector | Site of Gamogony and Sporogony | Locality | Authors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hepatozoon rarefaciens | Drymachon corais | Lung | Culex tarsalis, Anopheles albintarus, Aedes sierrensis | Hemocoel | California, USA | Ball and Oda [69] |
| Haemogregarnia matruhensis | Psammophis schokari | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Egypt | Ramadan [70] |
| Hepatozoon fusifex | Boa constrictor | Lung | Culex tarsalis | Hemocoel | USA | Ball et al. [71] |
| Hepatozoon aegypti | Spalerosophis diadema | Lung | Culex pipiens molestus | Hemocoel | Egypt | Bashtar et al. [72] |
| Hepatozoon mocassini | Agkistrodon piscivorus leucostoma | Liver parenchyma cells | Aedes aegypti | Hemocoel | Louisiana, USA | Lowichik et al. [73] |
| Hepatozoon seurati | Cerastes cerastes | Liver, lung, and spleen | Culex pipiens molestus | Hemocoel | Aswan, Egypt | Abdel-Ghaffar et al. [74] |
| Hepatozoon mehlhorni | Echis carinatus | Liver, lung, and spleen | Culex pipiens molestus | Hemocoel | Siwah and Baharia Oasis, Egypt | Bashtar et al. [75] |
| Hepatozoon matruhensis | Psammophis schokari | Liver and lung | Culex pipiens molestus | Hemocoel | Faiyum, Ismailia, Egypt | Bashtar et al. [76] |
| Hepatozoon ghaffari | Cerastes vipera | Liver, lung, and spleen | Culex pipiens molestus | Hemocoel | Aswan, Egypt | Shazly et al. [77] |
| Hepatozoon sipedon | Nerodia sipedon and Rana pipiens | Liver and internal organs | Culex pipiens, and Culex territans | Hemocoel | Ontario, Canada | Smith et al. [51] |
| Haemogregarnia garnhami | Psammophis schokari | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Egypt | Saoud et al. [78] |
| Hepatozoon ayorgbor | Python regius | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Ghana | Sloboda et al. [79] |
| Haemogregarnia sp. | Cerastes cerastes gasperetti | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Jizan, Saudi Arabia | Al-Farraj [80] |
| Hepatozoon garnhami | Psammophis schokari | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Riyadh, Saudi Arabia | Abdel-Baki et al. [29] |
| Hepatozoon sp. | Zamenis longissimus | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Iran | Sajjadi and Javanbakht [81] |
| Hepatozoon aegypti | Spalerosophis diadema | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Riyadh, Saudi Arabia | Abdel-Haleem et al. [82] |
| Species of Haemogregarines | The Vertebrate Host | Site of Merogony | Invertebrate Vector | Site of Gamogony and Sporogony | Locality | Authors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hemogregarina nicoriae | Nicoria trijuga | Circulating blood and lung | Ozobranchus shipleyi | Intestinal epithelium | Ceylon | Robertson [83] |
| Haemogregarina balli | Chelydra serpentine serpentina | Lacunar endothelial cells, liver, lung, and spleen | Placobdella ornata | Gastric and intestinal caeca | Ontario, Canada | Siddall and Desser [84] |
| Hepatozoon mauritanicum | Testudo graeca | Endothelial cells of all host organs as liver, lung, spleen … etc | Hyalomma aegyptium | The intestinal epithelium of the tick | -- | Michel [85] |
| Haemogregarina pseudomydis | Pseudemys scripta elegans | Leucocytes and Erythrocytes | Placobdella parasitica | The intestinal epithelium of the leech | Louisiana, USA | Acholonu [86] |
| Haemogregarina gangetica (=H. simondi) | Trionyx gangeticus | Erythrocytes and lung | -- | -- | India | Misra [87] |
| Haemogregarina ganapatii | Lissemys punctata granosa | Peripheral blood and Liver and lung | -- | -- | India | Saratchandra [61] |
| Haemogregarina sinensis | Trionyx sinensis | Erythrocytes and Kupffer’s cells of the liver | Mooreotorix cotylifer | Gastric and intestinal caeca of the leech | China | Chai and Chen [88] |
| Haemogregarina sp. | Emys orbicularis | Intra-erythrocytic | Placobdella costata | -- | Romania | Mihalca et al. [89] |
| Haemolivia mauritanica | Testudo graeca | Intra-erythrocytic | Hyalomna aegyptium | Gut cells | Israel | Paperna [90] |
| Haemolivia mauritanica | Tortoises | Intra-erythrocytic | Hyalomma aegyptium | -- | Western Palaearctic realm | Široký et al. [91] |
| Haemogregarina macrochelysi | Macrochelys temminckii | Intra-erythrocytic | Leech | -- | Georgia and Florida | Telford et al. [92] |
| Haemogregarina stepanowi | Emys orbicularis, Mauremys caspica, M. rivulata, M. leprosa | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Western Palaearctic | Dvořáková et al. [23] |
| Haemogregarina sp. | Lissemys punctata and Geoclemys hamiltonii | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | West Bengal, India | Hossen et al. [4] |
| Haemolivia mauritanica | Testudo graeca and Testudo marginata | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | North African | Harris et al. [93] | |
| Haemogregarina sp. | Rhinoclemmys funera and Kinosternon leucostomum | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Costa Rica | Rossow et al. [94] |
| Haemogregarina sp. | Podocnemis unifilis | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Brazilian Amazonia | Soares et al. [95] |
| Haemogregarina sundarbanensis | Lissemys punctata | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | West Bengal, India | Molla et al. [96] |
| Haemogregarina stepanowi | Emys orbicularis | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Belgrade Zoo | Jòzsef et al. [24] |
| Haemogregarina sp. | Podocnemis expansa | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Araguaia River Basin, Brazil | Picelli et al. [97] |
| Haemogregarina sacaliae Haemogregarina pellegrini | Cuora galbinifrons, Leucocephalon yuwonoi, Malayemys subtrijuga, Platysternon megacephalum, | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Southeast Asia | Dvořáková et al. [37] |
| Haemogregarina fitzsimonsi Haemogregarina parvula | Land tortorise, Stigmochelys pardalis | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | South African | Cook et al. [31] |
| Haemogregarina stepanowi | Emys trinacris | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Sicily | Arizza et al. [98] |
| Haemogregarina sp. | Mauremys caspica | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Iran | Rakhshandehroo et al. [99] |
| Haemogregarina sp. | Macrochelys temminckii | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Caldwell Zoo, Texas | Alhaboubi et al. [100] |
| Haemogregarina sp. | Mesoclemmys vanderhaegei | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Brazil | Goes et al. [101] |
| Haemogregarina podocnemis | Podocnemis Unifilis | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Brazil | Úngari et al. [102] |
| Species of Haemogregarines | The Vertebrate Host | Site of Merogony | Invertebrate Vector | Site of Gamogony and Sporogony | Locality | Authors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Haemogregarina crocodilinorum | Alligator mississippiensis | Intra-erythrocytic | Placobdella multilineata | Intestinal epithelial cells of the leech | Southern USA includes Arkansas, Carolina, and Florida | Börner [103] |
| Haemogregarina caimani (= Hepatozoon caimani) | Caiman latirostris | Intra-erythrocytic | Culex dolosus | Hemocoel | Brazil | Pessôa and de Biasi [104] |
| Haemogregarina pettiti (=Hepatozoon pettiti Hoare 1932) | Crocodilus niloticus | Erythrocytes and liver | Glossina palpalis | Intestine | Uganda, Senegal, West Africa | Hoare [105] |
| Hepatozoon sp. | Caiman c. yacare | Intra-erythrocytic | Phaeotabanus fervens | Intestine | Pantanal | Viana and Marques [106] |
| Hepatozoon caimani | Caiman yacare | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Pantanal region, Brazil | Viana et al. [107] |
| Species of Haemogregarines | The Vertebrate Host | Site of Merogony | Invertebrate Vector | Site of Gamogony and Sporogony | Locality | Authors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hepatozoon atticorae | Hirundo spilodera | Intra-erythrocytic | Ornithodoros peringueyi and Xenopsylia trispinis | Hemolymph | South Africa, South America, Jamaica, Europea | Bennett et al. [108] |
| Hepatozoon prionopis | Prionops plumatus | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Transvaal, South Africa | Bennett and Earle [109] |
| Hepatozoon lanis | Lanius collaris | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | South Africa | Bennett et al. [108] |
| Hepatozoon malacotinus | Dryoscopus cubla | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | South Africa | Bennett et al. [108] |
| Hepatozoon numidis | Numida meleagris | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | South Africa | Bennett et al. [108] |
| Hepatozoon pittae | Pitta arcuate | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Sabah | Bennett et al. [108] |
| Hepatozoon estrildus | Lonchura cucullata | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Zambia | Bennett et al. [108] |
| Hepatozoon sylvae | Parisoma subcaeruleum | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | South Africa | Bennett et al. [108] |
| Hepatozoon zosteropis | Zosterops pallida | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | South Africa | Bennett et al. [108] |
| Hepatozoon passeris | Sporopipes squamifrons | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Botswana, South Africa | Bennett et al. [108] |
| Species of Haemogregarines | The Vertebrate Host | Site of Merogony | Invertebrate Vector | Site of Gamogony and Sporogony | Locality | Authors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hepatozoon perniciosum | Laboratory white rats | The liver | Echinolaelaps echidninus | Stomach | Washington, USA | Miller [9] |
| Hepatozoon griseisciuri | Sciurus carolinensis | Bone marrow, liver, lung, and spleen (with intra-leucocytic gametocytes) | Euhaemogamasus ambulans, Echinolaelaps echidninus and Haemogamasus reidi | Stomach | Washington, Marland, Georgia, USA | Desser [110] |
| Hepatozoon erhardovae | Clethrionomys glareolus | Lung | Xenopsylla cheopis, Ctenophthalmus agyrtes, C. assimilis and Nosopsyllus fasciatus | Stomach and fat-body cells | Munich, Germany | Göbel and Krampitz [111] |
| Hepatozoon sylvatici | Apodemus sylvaticus and Apodemus flavicollis | Bone marrow and liver | Laelaps agilis | Stomach | Austria | Frank [112] |
| Hepatozoon sp. | Dogs | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Brazil | Forlano et al. [113] |
| Hepatozoon canis | Dogs | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Italy | Otranto et al. [114] |
| Hepatozoon felis | Cats | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | India | Baneth et al. [115] |
| Hepatozoon canis | Dogs | Intra-erythrocytic | Rhipicephalus sanguineus | -- | Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil | Ramos et al. [116] |
| Hepatozoon canis | Dogs | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Central-western Brazil | Paiz et al. [117] |
| Hepatozoon sp. | Cerdocyon thous, Nasua nasua, Leopardus pardalis, Canis familiaris, Thrichomys fosteri, Oecomys mamorae, Clyomys laticeps, Thylamys macrurus, Monodelphis domestics | Intra-erythrocytic | Amblyomma sculptum, A. parvum, A. tigrinum, Rhipicephalus microplus, R. sanguineus, A. auricularium | -- | Brazil | De Sousa et al. [118] |
| Hepatozoon felis | Panthera leo | -- | Rhipicephalus sanguineus | -- | Thailand | Bhusri et al. [119] |
| Hepatozoon canis | Dogs | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Czech Republic | Mitkova et al. [120] |
| Hepatozoon felis | Dogs | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Northeastern Iran | Barati and Razmi [121] |
| Hepatozoon sp. | Cats | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Turkey | Tuna et al. [122] |
| Hepatozoon canis | Dogs | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | United Kingdom | Attipa et al. [123] |
| Hepatozoon felis | Felis silvestris, Caracal caracal, Panthera pardus, P. leo, Leptailurus serval | Muscle and Liver | -- | -- | Limpopo and Mpumalanga | Harris et al. [124] |
| Hepatozoon luiperdjie | Panthera pardus | Leukocytes | -- | -- | Limpopo Province, South Africa | Van As et al. [125] |
| Hepatozoon canis | Dogs | Intra-erythrocytic | -- | -- | Manila, Philippines | Baticados et al. [126] |
| Primer Set | Primer Sequence | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| 4558F | 5′- GCT AAT ACA TGA GCA AAA TCT CAA -3ʹ | Mathew et al. [146] |
| 2733R | 5′- CGG AAT TAA CCA GAC AAA T -3ʹ | |
| 2867F | 5′- AAC CTG GTT GAT CCT GCC AG -3′ | Mathew et al. [146] |
| 2868R | 5′- TGA TCC TTC TGC AGG TTC ACC TAC -3′ | |
| HEMO1 | 5′ - TAT TGG TTT TAA GAA CTA ATT TTA TGA TTG - 3′ | Perkins and Keller [147] |
| HEMO2 | 5′ - CTT CTC CTT CCT TTA AGT GAT AAG GTT CAC - 3′ | |
| HepF | 5′- ATA-CAT-GAG-CAA-AAT-CTC-AAC -3′ | Inokuma et al. [148] |
| HepR | 5′- CTT-ATT-ATT-CCA-TGC-TGC-AG -3′ | |
| HepF300 | 5′- GTTTCTGACCTATCAGCTTTCGAC -3ʹ | Ujvari et al. [20] |
| HepR900 | 5′- CAAATCTAAGAATTTCACCTCTGAC -3ʹ | |
| HEP-1 | 5′- CGC GAA ATT ACC CAA TT -3′ | Criado-Fornelio et al. [149] |
| HEP-2 | 5′- CAG ACC GGT TAC TTT YAG CAG -3′ | |
| Piroplasmid-F | 5′- CCA GCA GCC GCG GTA ATT -3ʹ | Tabar et al. [150] |
| Piroplasmid-R | 5′- CTT TCG CAG TAG TTY GTC TTT AAC AAA TCT -3ʹ | |
| EF | 5′-GAA ACT GCG AAT GGC TCA TT-3′ | Kvičerová et al. [26] |
| ER | 5′-CTT GCG CCT ACT AGG CAT TC-3′ | |
| Hep-001F | 5′- CCT GGC TAT ACA TGA GCA AAA TCT CAA CTT -3′ | Kledmanee et al. [151] |
| Hep-737R | 5′- CCA ACT GTC CCT ATC AAT CAT TAA AGC -3′ | |
| BTH-1F | 5′- CCT GAG AAA CGG CTA CCA CAT CT -3′ | Zintl et al. [152] |
| BTH-1R | 5′- TTG CGA CCA TAC TCC CCC CA -3′ | |
| GF2 | 5′- GTC TTG TAA TTG GAA TGA TGG -3′ | Hodžić et al. [153] |
| GR2 | 5′- CCA AAG ACT TTG ATT TCT CTC -3′ | |
| Haemog11_F | 5′- ATT GGA GGG CAA GTC TGG TG -3ʹ | Rakhshandehroo et al. [99] |
| Haemog11_R | 5′- GCG TTA GAC ACG CAA AGT CT -3ʹ | |
| HemoFN | 5′- CCG TGG TAA TTC TAG AGC TAA TAC ATG AGC -3′ | Alhaboubi et al. [100] |
| HemoRN | 5′- GAT AAG GTT TAC GAA ACT TTC TAT ATT TA -3′ |
| Parasites | Hosts | Accession Number in GenBank |
|---|---|---|
| Haemogregarina podocnemis | Podocnemis unifilis | MF476203.1 - MF476205.1 |
| Haemogregarina pellegrini | Platysternon megacephalum | KM887509.1 |
| Malayemys subtrijuga | KM887508.1 | |
| Haemogregarina sacaliae | Sacalia quadriocellata | KM887507.1 |
| Haemogregarina stepanowi | Emys orbicularis | MT345287.1 |
| Mauremys leprosa | MT345284.1 - MT345286.1, KX691418.1, KX691417.1 | |
| Emys orbicularis | KT749877.1, KF257928.1 | |
| Mauremys leprosa | KF257929.1 | |
| Mauremys rivlata | KF257927.1 | |
| Mauremys caspica | KF257926.1, KF992697.1 | |
| Haemogregarina bigemina | Lipophrys pholis | MK393799.1 - MK393801.1 |
| Haemogregarina balli | Chelydra serpentine | HQ224959.1 |
| Hepatozoon fitzsimonsi | Kinixys zombensis | KR069084.1 |
| Chersina angulate | KJ702453.1 | |
| Hepatozoon ursi | Ursus thibetanus japonicus | EU041718.1, AB586028.1, LC431855.1 - LC431853.1 |
| Melursus ursinus | HQ829437.1 - HQ829429.1 | |
| Hepatozoon seychellensis | Gradisonia alternans | KF246566.1, KF246565.1, |
| Hepatozoon ayorgbor | Apodemus sylvaticus | KT274177.1, KT274178.1 |
| Ctenophthalmus agyrtes | KJ634066.1 | |
| Python regius | EF157822.1 | |
| Rhombomys opimus | MW342705.1 | |
| Hepatozoon musa | Crotalus durissus | MF497763.1 - MF497767.1 |
| Philodryas natterei | KX880079.1 | |
| Hepatozoon involucrum | Hyperolius marmoratus | MG041591.1 - MG041594.1 |
| Ursus arctos | MN150506.1 - MN150504.1 | |
| Hepatozoon clamatae | Rana pipiens | MN310689.1 |
| Hepatozoon catesbianae | Rana clamitans | MN244529.1, MN244528.1, AF040972.1, |
| Hepatozoon aegypti | Spalerosophis diadema | MH198742.1 |
| Hepatozoon martis | Martes foina | MG136688.1, MG136687.1 |
| Hepatozoon procyonis | Nasua nasua | MF685386.1 - MF685409.1 |
| Hepatozoon griseisciuri | Scinurus carolinensis | MK452389.1, MK452388.1, MK452253.1, MK452252.1, |
| Hepatozoon sciuri | Scinus vulgaris | MN104636.1 - MN104640.1, |
| Hepatozoon americanum | Canis familiaris | AF206668.1, KU729739.1 |
| Hepatozoon ingwe | Panthera pardus pardus | MN793001.1, MN793000.1 |
| Hepatozoon theileri | Amietia quecketti | KP119773.1, KX512804.1, KJ599676.1, |
| Amietia delalandii | MG041605.1 | |
| Hepatozoon caimani | Caiman crocodilus yacare | MF322538.1, MF322539.1 |
| Caiman crocodilus | MF435046.1 - MF435049.1 | |
| Hepatozoon silvestris | Felis silvestris silvestris | KX757032.1 |
| Felis catus | MH078194.1, KY649445.1 | |
| Hepatozoon tenuis | Afrixalus fornasini | MG041595.1 - MG041599.1 |
| Hepatozoon thori | Hyperolius argus | MG041600.1 - MG041603.1 |
| Hepatozoon ixoxo | Amietophrynus maculatus | KP119772.1 |
| Hepatozoon luiperdjie | Panthera pardus pardus | MN793002.1 - MN793004.1, |
| Hepatozoon cuestensis | Crotalus durissus | MF497769.1, MF497770.1 |
| Hepatozoon sipedon | Snakes | AF110249.1 - AF110241.1 |
| Hepatozoon erhardovae | Megabothris turbidus | KJ608372.1 |
| Hepatozoon domerguei | Furcifer sp. | KM234649.1 - KM234646.1 |
| Hepatozoon tuatarae | Sphenodon punctatus | GU385473.1 - GU385470.1 |
| Hepatozoon cf. ophisauri | Rhombomys opimus | MW256822.1 |
| Hepatozoon colubri | -- | MN723844.1 |
| Hepatozoon canis | Amblyomma cajennense | KT215377.1 - KT215353.1 |
| Amblyomma sculptum | KP167594.1 | |
| Tapir tapir | MT458172.1 | |
| Haemaphysalis longicornis | MT107092.1 - MT107097.1, MT107087.1 - MT107089.1, LC169075.1 | |
| Haemaphysalis concinna | KC509532.1 - KC509527.1 | |
| Rhipicephalus sanguineus | MH595911.1 - MH595892.1, MG807347.1, KY056823.1, MG241229.1, KT587790.1, KT587789.1, KY196999.1, KY197000.1 - KY197002.1, JQ867389.1, MN207197.1 | |
| Rhipicephalus microplus | HQ605710.1 | |
| Rhipicephalus decoloratus | MN294724.1 | |
| Canis lupus familiaris | MH615003.1, EU289222.1, DQ071888.1, MK910141.1 - MK910144.1, MK757793.1 - MK757815.1, MN791089.1, MN791088.1, MN393913.1, MN393910.1, MK645971.1 - MK645946.1, MK214285.1 - MK214282.1, MG254613.1 - MG254622.1, MK091084.1 - MK091092.1, KY940658.1, MG772658.1, MG254573.1 - MG254611.1, KY021176.1 - KY021184.1, MG496257.1, MG496273.1, MG062866.1, MG076961.1, MG209580.1 - MG209594.1, KX588232.1, KU729737.1, KU729738.1, KY026191.1, KY026192.1, KX880502.1 - KX880506.1, KX761384.1, KU232309.1, KU232310.1, KT736298.1, LC012839.1 - LC012821.1, LC053450.1, JX976545.1, JN584478.1 - JN584475.1, JF459994.1, GQ176285.1, EU571737.1, EF650846.1, MW019643.1 - MW019630.1, MT909554.1, MT081051.1, MT081050.1, MT821184.1, MT499356.1 - MT499354.1, MT754266.1, LC556379.1, MT433126.1 - MT433121.1 | |
| Lycalopex vetulus | AY150067.2, MT458173.1 | |
| Kinixys species | MT704950.1 | |
| Lycalopex gymnocercus | KX816958.1 | |
| Didelphis albiventris | KY392884.1, KY392885.1 | |
| Canis aureus | KF322145.1, KC886721.1, KC886729.1 - KC886733.1, KJ868814.1, KJ572977.1 - KJ572975.1, KJ634654.1, JX466886.1 - JX466880.1, | |
| Felis catus | KY469446.1, MN689671.1 - MN689661.1 | |
| Vulpes vulpes | KF322141.1-KF322144.1, KC886720.1 - KC886728.1, MK757741.1 - MK757792.1, MN103520.1, MN103519.1, MH699884.1 - MH699892.1, MG077084.1 - MG077087.1, KY693670.1, KJ868819.1 - KJ868815.1, KU893118.1 - KU893127.1, KM096414.1 - KM096411.1, KJ572979.1, KJ572978.1, EU165370.1, GU376458.1 - GU376446.1, DQ869309.1, AY731062.1, MW295531.1, MN463026.1 - MN463021.1 | |
| Ixodes ricinus | KU597235.1 - KU597242.1, KC584780.1 | |
| Hydrochoerus hydrochaeris | KY965141.1 - KY965144.1 | |
| Cuon alpinus | HQ829448.1 - HQ829438.1, MK144332.1 | |
| Dermacentor reticulatus | KC584777.1 - KC584773.1 | |
| Pseudalopex gymnocercus | AY471615.1, AY461376.1, AY461375.1 | |
| Panthera leo | MT814748.1 | |
| Panthera tigris | MT232064.1 - MT232062.1 | |
| Camelus dromedrius | MN989311.1 | |
| Hepatozoon apri | Sus scrofa leucomystax | LC314791.1 |
| Amietophrynus gutturalis | KP119771.1 | |
| Amietophrynus garmani | KP119770.1, | |
| Sclerophrys maculata | KX512803.1 | |
| Sclerophrys pusilla | MG041604.1 | |
| Hepatozoon cf. felis | Felis catus | MK301457.1 - MK301462.1, MK724001.1, MG386482.1 - MG386484.1, KY649442.1 - KY649444.1, AY628681.1, AY620232.1 |
| Felis silvestris silvestris | KX757033.1, MT210593.1 - MT210598.1, | |
| Puma concolor | MT458171.1 | |
| Eira barbara | MT458170.1 | |
| Lycalopex gymnocercus | HQ020489.1 | |
| Leopardus pardalis | KY684005.1 | |
| Asiatic lion | KX017290.1 | |
| Prionailurus bengalensis | AB771577.1 - AB771501.1, GQ377218.1 - GQ377216.1 | |
| Prionailurus iriomotensis | AB636287.1 - AB636285.1 | |
| Panthera onca | KU232302.1 - KU232308.1 | |
| Panthera tigris | MT645336.1, MT634695.1 | |
| Rhipicephalus sanguineus | JQ867388.1 | |
| Eurasian lynx | MN905025.1, MN905023.1, MN905027.1 | |
| Haemolivia parvula | Kinixys zombensis | KR069083.1, KR069082.1 |
| Haemolivia stellata | Amblyomma dissimile | MH196477.1 - MH196482.1, MH196475 |
| Amblyomma rotundatum | KP881349.1 | |
| Haemolivia mariae | Egernia stokesii | KF992712.1, KF992711.1 |
| Tiliqua rugosa | JN211118.1, HQ224961.1 | |
| Haemolivia mauritanica | Hyalomma aegyptium | MH618775.1, MN463032.1, MN463031.1, MW092781.1 - MW092776.1, MK918611.1 - MK918608.1, MH497199.1 - MH497190.1, MH975037.1, MH975031.1, MH975026.1, MH975025.1, |
| Hyalomma sp. | MF383512. - MF383506.1, | |
| Haemolivia mauritanica | Canis lupus familiaris | KP719092.1 |
| Testudo marginata | KF992710.1, KF992699.1 | |
| Testudo graeca | KF992709.1 - KF992698.1, MH975039.1 - MH975032.1, MH975030.1 - MH975027.1, MH975024.1 - MH975021.1, | |
| Karyolysus paradoxa | Varanus albigularis | KX011039.1, KX011040.1 |
| Karyolysus cf. lacazei | Ixodes ricinus | MK497254.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Quraishy, S.; Abdel-Ghaffar, F.; Dkhil, M.A.; Abdel-Gaber, R. Haemogregarines and Criteria for Identification. Animals 2021, 11, 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11010170
Al-Quraishy S, Abdel-Ghaffar F, Dkhil MA, Abdel-Gaber R. Haemogregarines and Criteria for Identification. Animals. 2021; 11(1):170. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11010170
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Quraishy, Saleh, Fathy Abdel-Ghaffar, Mohamed A. Dkhil, and Rewaida Abdel-Gaber. 2021. "Haemogregarines and Criteria for Identification" Animals 11, no. 1: 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11010170
APA StyleAl-Quraishy, S., Abdel-Ghaffar, F., Dkhil, M. A., & Abdel-Gaber, R. (2021). Haemogregarines and Criteria for Identification. Animals, 11(1), 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11010170






