The Occurrence of Quill Mites (Arachnida: Acariformes: Syringophilidae) on Bee-Eaters (Aves: Coraciiformes: Meropidae: Merops) of Two Sister Clades
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Species Composition
3.2. Systematics
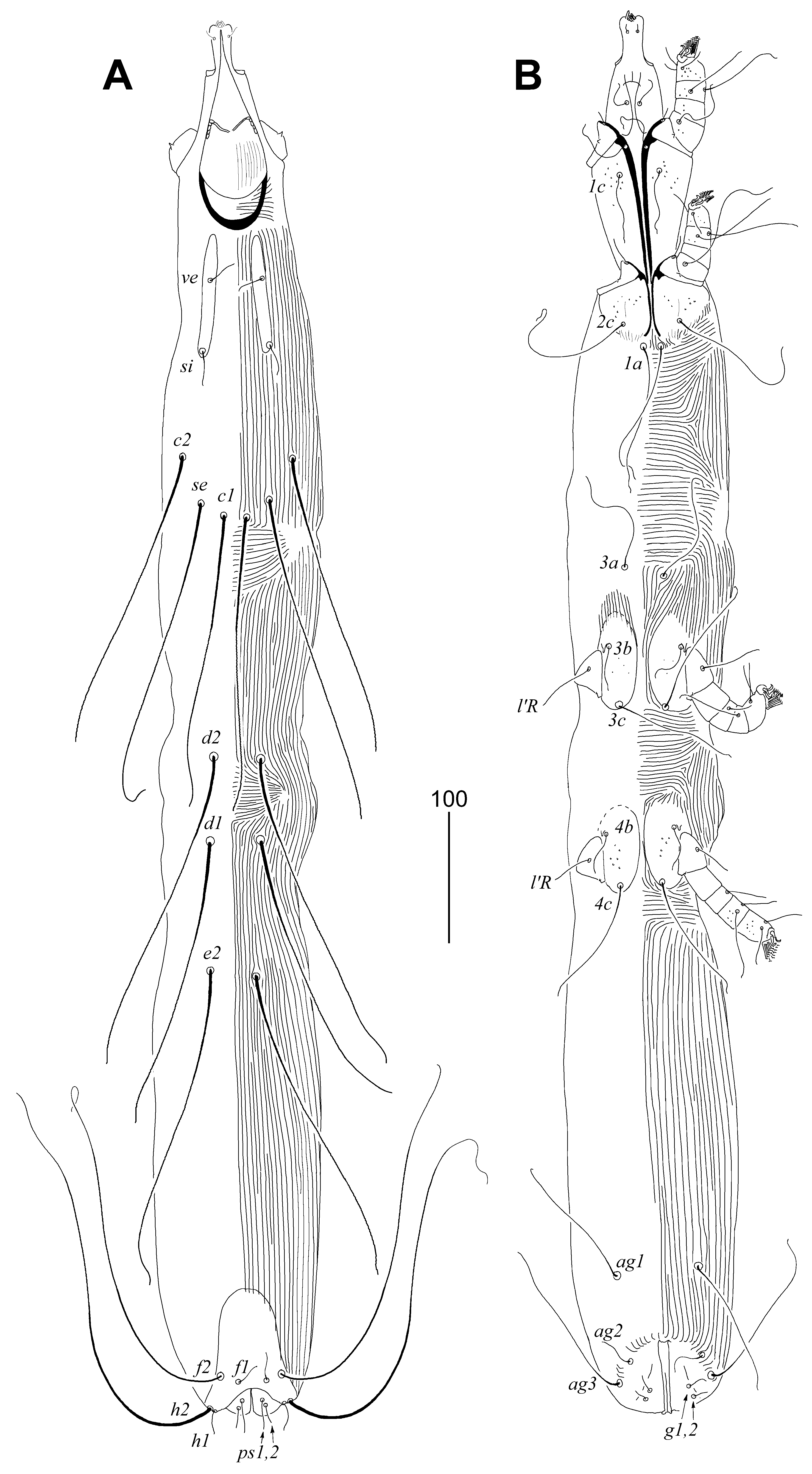
3.2.1. Peristerophila mayri Skoracki and Hromada sp. n.
Female, Heteromorphic Form, Holotype
Homeomorphic Female and Male
Type Material
Type Material Deposition
Additional Material
Habitat
Etymology
Differential Diagnosis
3.2.2. Peristerophila meropis (Skoracki, Hromada et Sikora, 2017)
Hosts and Distribution
Habitat
New Material Examined
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zmudzinski, M.; Skoracki, M.; Sikora, B. An updated checklist of quill mites of the family Syringophilidae (Acariformes: Prostigmata). Figshare. Dataset. 2021. Available online: https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.16529574.v1 (accessed on 20 October 2021).
- Kethley, J.B. A revision of the family Syringophilidae (Prostigmata: Acarina). Contrib. Am. Entomol. Inst. 1970, 6, 1–76. [Google Scholar]
- Skoracki, M. Quill mites (Acari: Syringophilidae) of the Palaearctic region. Zootaxa 2011, 2840, 1–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skoracki, M.; Glowska, E.; Bochkov, A.V. Phylogeny of quill mites of the family Syringophilidae (Acari: Prostigmata) based on their external morphology. Eur. J. Entomol. 2013, 110, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skoracki, M.; Sikora, B.; Spicer, G.S. A review of the subfamily Picobiinae Johnston and Kethley, 1973 (Acariformes: Prostigmata: Syringophilidae). Zootaxa 2016, 4113, 1–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, C.H. Family Meropidae (bee-eaters). In Handbook of the Birds of the World, 1st ed.; del Hoyo, J., Elliot, A., Sargatal, J., Eds.; Mousebirds to Hornbills: Lynx Ediciones, Barcelona, Spain, 2001; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Clements, J.F.; Schulenberg, T.S.; Iliff, M.J.; Roberson, D.; Fredericks, T.A.; Sullivan, B.L.; Wood, C.L. The eBird/Clements Checklist of Birds of the World. Ver. 2020. Available online: http://www.birds.cornell.edu/clementschecklist/download/ (accessed on 20 October 2021).
- Winkler, D.W.; Billerman, S.M.; Lovette, I.J. Bee-eaters (Meropidae). In Birds of the World, version: 1.0; Billerman, S.M., Keeney, B.K., Rodewald, P.G., Eds.; Cornell Lab of Ornithology: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2020; Available online: https://doi.org/10.2173/bow.meropi1.01 (accessed on 30 October 2021).
- Marks, B.D.; Weckstein, J.; Moyle, R.G. Molecular phylogenetics of the bee-eaters (Aves: Meropidae) based on nuclear and mitochondrial DNA sequence data. Mol. Phyl. Evol. 2007, 45, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro de Melo Moura, C.; Bastian, H.V.; Bastian, A.; Wang, E.; Wang, X.; Wink, M.; Wink, M. Pliocene origin, ice ages and postglacial population expansion have influenced a panmictic phylogeography of the European Bee-Eater Merops apiaster. Diversity 2019, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skoracki, M.; Dabert, J. Syringophilopsis albicollisi, a new species of the quill mite of the family Syringophilidae Lavoipierre, 1953 (Acari: Prostigmata). Acarina 2000, 8, 59–63. [Google Scholar]
- Skoracki, M.; Dabert, J. The quill mites of the genus Syringophilopsis Kethley, 1970 (Acari, Syringophilidae) from African birds. Acarina 2001, 9, 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Skoracki, M.; Hromada, M.; Sikora, B. Castosyringophilus meropis sp. n. (Acariformes: Syringophilidae)—A new quill mite species parasitising the world population of Merops apiaster Linnaeus (Coraciiformes: Meropidae). Folia Parasitol. 2017, 64, 024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skoracki, M.; Hromada, M.; Kaszewska, K.; Sikora, B. Females of the quill mite genera Peristerophila and Castosyringophilus (Acariformes: Syringophilidae) are two morphological forms: ontogenetic and population evidences. Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2020, 25, 1803–1820. [Google Scholar]
- Grandjean, F. Les segments postlarvaires de l’hysterosoma chez les oribates (Acariens). Bull. Soc. Zool. France 1939, 64, 273–284. [Google Scholar]
- Kethley, J.B. Acarina: Prostigmata (Actinedida). In Soil Biology Guide; Dindal, D.L., Ed.; Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 667–754. [Google Scholar]
- Grandjean, F. Observations sure les Acariens de la famille des Stigmaeidae. Archiv. Sci. Phys. Nat. 1944, 26, 103–131. [Google Scholar]
- Jetz, W.; Thomas, G.H.; Joy, J.B.; Hartmann, K.; Mooers, A.O. The global diversity of birds in space and time. Nature 2012, 491, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Møller, A.P.; Díaz, M.; Flensted-Jensen, E.; Grim, T.; Ibáñez-Álamo, J.D.; Jokimäki, J. Urbanized birds have superior establishment success in novel environments. Oecologia 2015, 178, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mikula, P.; Morelli, F.; Lučan, R.K.; Jones, D.N.; Tryjanowski, P. Bats as prey of diurnal birds: A global perspective. Mamm. Rev. 2016, 46, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hromada, M.; Klimovicova, M.; Unsoeld, M.; Skoracki, M. Host-parasite relationships in the system composed by cuckoos and quill mites. Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2016, 21, 528–536. [Google Scholar]
- Skoracki, M.; Sikora, B.; Jerzak, L.; Hromada, M. Tanopicobia gen. nov., a new genus of quill mites, its phylogenetic placement in the subfamily Picobiinae (Acariformes: Syringophilidae) and picobiine relationships with avian hosts. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0225982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, A.J.; Rambaut, A. BEAST: Bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rambaut, A. FigTree v1.4.4. 2018. Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/ (accessed on 20 May 2021).
- BirdLife International and Nature Serve. Bird Species Distribution Maps of the World; BirdLife International: Cambridge, UK; NatureServe: Arlington, TX, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Vuilleumier, F. Ernst Mayr’s biogeography: A lifetime of study. Ornithol. Monogr. 2005, 58, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayr, E. Populations, Species, and Evolution: An Abridgment of Animal Species and Evolution; Belknap Press of Harvard University Press: London, UK, 1970; p. 453. [Google Scholar]
- Skoracki, M.; Hromada, M.; Sikora, B. Quill mites of the family Syringophilidae (Acariformes: Prostigmata) parasitizing coraciiform birds (Aves: Coraciiformes). Zootaxa 2020, 4802, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahrenholz, H. Ectoparasiten und Abstammungslehre. Zool. Anz. 1913, 41, 371–374. [Google Scholar]
- Eichler, W. Wirtsspezifitat und stammesgeschichtliche Gleichlaufigkeit bei Parasiten im allgemeinen und bei Mallophagen im besonderen. Zool. Anz. 1941, 132, 254–262. [Google Scholar]
- Sibley, C.G.; Ahlquist, J.E. Phylogeny and Classification of Birds; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 1990; pp. xxiii + 976. [Google Scholar]
- Sibley, C.G.; Monroe, B.L., Jr. Distribution and Taxonomy of Birds of the World; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 1990; p. 1111. [Google Scholar]
- Sibley, C.G.; Monroe, B.L., Jr. A Supplement to Distribution and Taxonomy of Birds of the World; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 1993; p. 108. [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson, E.C. The Howard & Moore Complete Checklist of the Birds of the World, 3rd ed.; Christopher Helm: London, UK, 2003; p. 1039. [Google Scholar]
- Collar, N.J. Species limits in some Philippine birds including the Greater Flameback Chrysocolaptes lucidus. Forktail 2011, 27, 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Del Hoyo, J.; Collar, N.J.; Christie, D.A.; Elliott, A.; Fishpool, L.D.C. HBW and Bird Life International Illustrated Checklist of the Birds; Lynx Ediciouns: Barcelona, Spain, 2016; Volume 1, p. 904. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.H.; Tu, F.Y.; Murphy, R.W. Analysis of the complete mitogenome of Oriental turtle dove (Streptopelia orientalis) and implications for species divergence. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2016, 65, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Hoyo, J.; Collar, N.; Kirwan, G.M. Rufous-crowned Bee-eater (Merops americanus). In Birds of the World, version: 1.0; del Hoyo, J., Elliott, A., Sargatal, J., Christie, D.A., de Juana, E., Eds.; Cornell Lab of Ornithology: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2020; Available online: https://doi.org/10.2173/bow.rucbee1.01 (accessed on 30 October 2021).
- Fry, H.; Boesman, P.F.D. Blue-tailed Bee-eater (Merops philippinus). In Birds of the World, version: 1.0; del Hoyo, J., Elliott, A., Sargatal, J., Christie, D.A., de Juana, E., Eds.; Cornell Lab of Ornithology: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2020; Available online: https://doi.org/10.2173/bow.btbeat1.01 (accessed on 30 October 2021).
- Woodall, P.F. Collared Kingfisher (Todiramphus chloris). In Birds of the World, version: 1.0; Billerman, S.M., Keeney, B.K., Rodewald, P.G., Schulenberg, T.S., Eds.; Cornell Lab of Ornithology: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2020; Available online: https://doi.org/10.2173/bow.colkin1.01 (accessed on 30 October 2021).
- Skoracki, M.; Kosicki, J.Z.; Kwiecinski, Z. Distribution of the parasitic mite Bubophilus aegolius sp. n. (Acariformes: Syringophilidae) on the Boreal Owl Aegolius funereus (L) (Strigiformes: Strigidae) and the low effectiveness of infestation. Eur. Zool. J. 2021, 88, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaszewska-Gilas, K.; Kosicki, J.Z.; Hromada, M.; Skoracki, M. Global studies of the host-parasite relationships between ectoparasitic mites of the family Syringophilidae and birds of the order Columbiformes. Animals 2021, 11, 3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoracki, M.; Hromada, M.; Prevuznakova, P.; Wamiti, W. Mites of the family Syringophilidae (Acariformes: Cheyletoidea) parasitizing waxbills of the genus Estrilda (Passeriformes: Estrildidae). Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2019, 24, 1799–1808. [Google Scholar]
- Skoracki, M.; Hromada, M.; Zmudzinski, M.; Unsoeld, M.; Sikora, B. Parasitic quill mites of the family Syringophilidae (Acariformes: Prostigmata) associated with Sub Saharan Sunbirds (Passeriformes: Nectariniidae): Species composition and host-parasite relationships. J. Med. Entomol. 2018, 55, 1464–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossi, A.; Proctor, H. The distribution of quill mites (Betasyringophiloidus seiuri) among flight feathers of the ovenbird (Seiurus aurocapilla). J. Parasitol. 2020, 106, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoracki, M.; Michalik, J.; Sikora, B. Prevalence and habitat preference of quill mites (Acari, Syringophilidae) parasitizing forest passerine birds in Poland. Acta Parasitol. 2010, 55, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skirnisson, K.; Nielsen, Ó.K. Quill mite infestation of rock ptarmigan Lagopus muta (Aves: Phasianidae) in relation to year and host age, sex, body condition, and density. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 2643–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
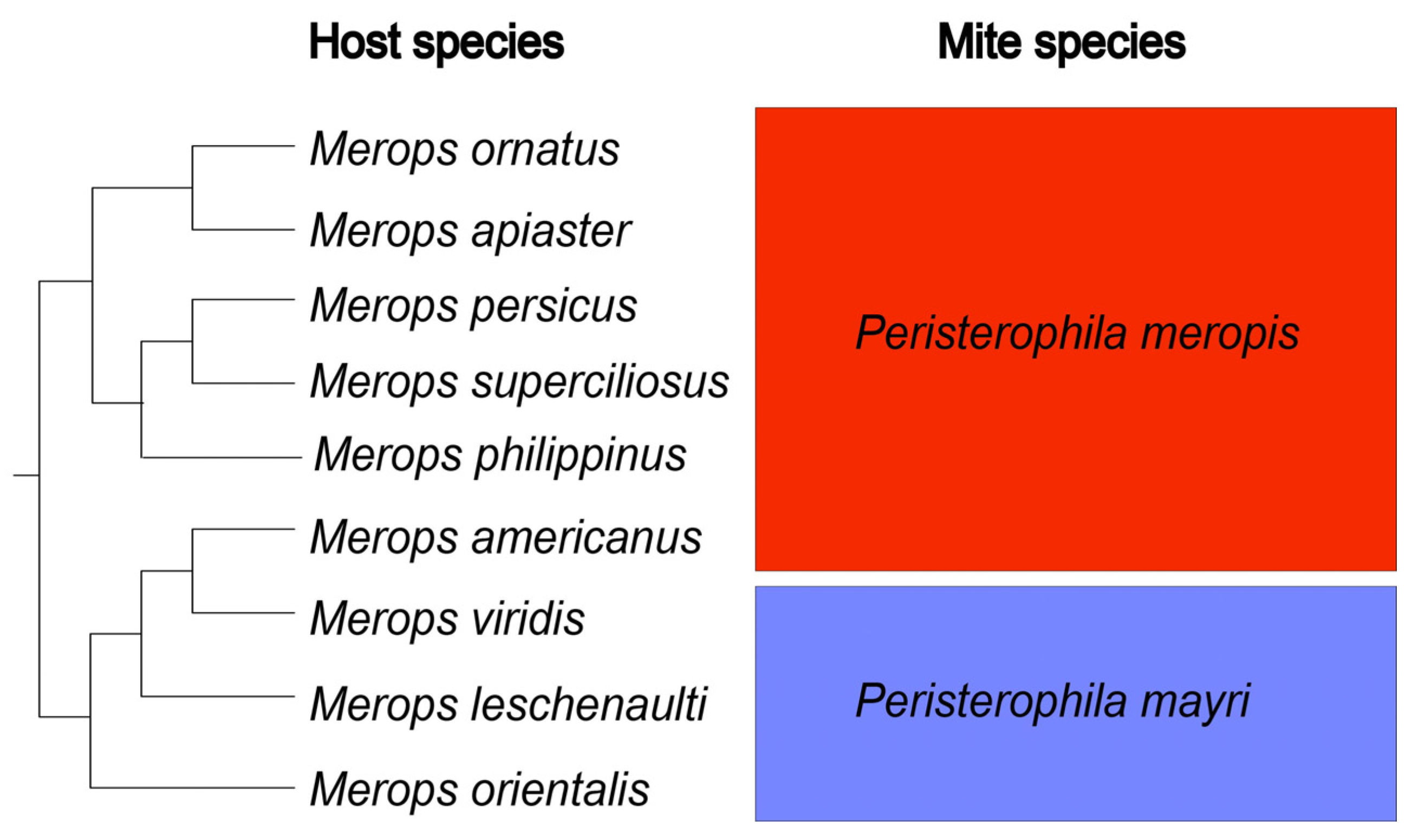


| Peristerophila Quill Mite Species | Merops Hosts | Origin of Host Specimens (Collection) | Host Examined/Infested; Index of Prevalence (IP); Confidence Interval 95% - Sterne (CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| P. meropis | M. ornatus | Papua New Guinea (ZSM) | 25/4; IP 16.0%; CI 5.7–35.7 |
| P. meropis | M. apiaster(*) | Spain, France, Gibraltar, Italy, Macedonia, Romania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Greece, Turkey, Russia, Azerbaijan, Pakistan, Morocco, Tanzania, Kenya (ZSM, NMK) | 75/22; IP 29.3%; CI 20–40 |
| P. meropis | M. persicus | Sudan, Tanzania, Liberia, Senegal, Kenya, D.R. Congo (ZSM, RMCA) | 68/10; IP 14.7%; CI 7.8–25.6 |
| P. meropis | M. superciliosus | Egypt, Tanzania (ZSM, RMCA) | 34/13; IP 38.2%; CI 23.2–56.0 |
| P. meropis | M. philippinus | Thailand, Sri Lanka, Indonesia (ZSM, NMP) | 8/3; IP 37.5%; CI 11.1–71.1 |
| P. meropis | M. americanus | Philippines: Luzon (ZFMK) | 8/3; IP 37.5%; CI 11.1–71.1 |
| P. mayri sp. n. | M. viridis | Philippines: Luzon (ZSM) | 10/1; IP 10.0%; CI 0.5–44.7 |
| P. mayri sp. n. | M. leschenaulti | Nepal, Sri Lanka (ZSM) | 13/2; IP 15.4%; CI 2.8–43.4 |
| P. mayri sp. n. | M. orientalis | Sri Lanka (ZSM) | 32/1; IP 3.1%; CI 0.2–16.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skoracki, M.; Kosicki, J.Z.; Sikora, B.; Töpfer, T.; Hušek, J.; Unsöld, M.; Hromada, M. The Occurrence of Quill Mites (Arachnida: Acariformes: Syringophilidae) on Bee-Eaters (Aves: Coraciiformes: Meropidae: Merops) of Two Sister Clades. Animals 2021, 11, 3500. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11123500
Skoracki M, Kosicki JZ, Sikora B, Töpfer T, Hušek J, Unsöld M, Hromada M. The Occurrence of Quill Mites (Arachnida: Acariformes: Syringophilidae) on Bee-Eaters (Aves: Coraciiformes: Meropidae: Merops) of Two Sister Clades. Animals. 2021; 11(12):3500. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11123500
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkoracki, Maciej, Jakub Z. Kosicki, Bozena Sikora, Till Töpfer, Jan Hušek, Markus Unsöld, and Martin Hromada. 2021. "The Occurrence of Quill Mites (Arachnida: Acariformes: Syringophilidae) on Bee-Eaters (Aves: Coraciiformes: Meropidae: Merops) of Two Sister Clades" Animals 11, no. 12: 3500. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11123500
APA StyleSkoracki, M., Kosicki, J. Z., Sikora, B., Töpfer, T., Hušek, J., Unsöld, M., & Hromada, M. (2021). The Occurrence of Quill Mites (Arachnida: Acariformes: Syringophilidae) on Bee-Eaters (Aves: Coraciiformes: Meropidae: Merops) of Two Sister Clades. Animals, 11(12), 3500. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11123500







