The Characteristics and Distribution of α2D-, α2B- and α2C-Adrenoceptor Subtypes in Goats
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
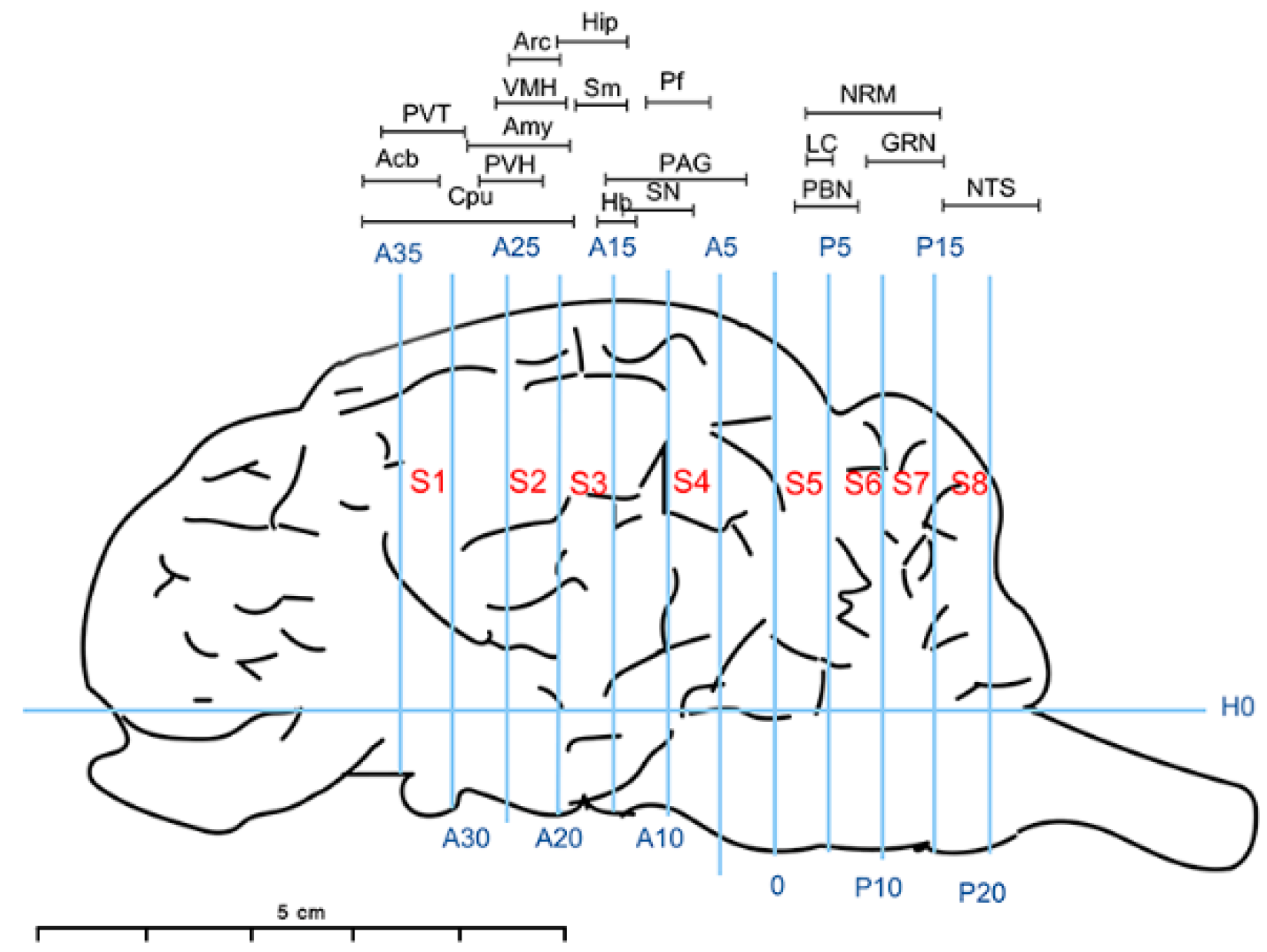
2.1. Animal Preparation
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Catheter Implantation Procedure
2.4. Antibody Preparation
2.5. Nociception Threshold Determination
2.6. Measurement of Physiological Indices
2.7. Sample Collection
2.8. RNA Isolation and Real-Time Quantitative PCR
2.9. Protein Separation and Western Blot Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
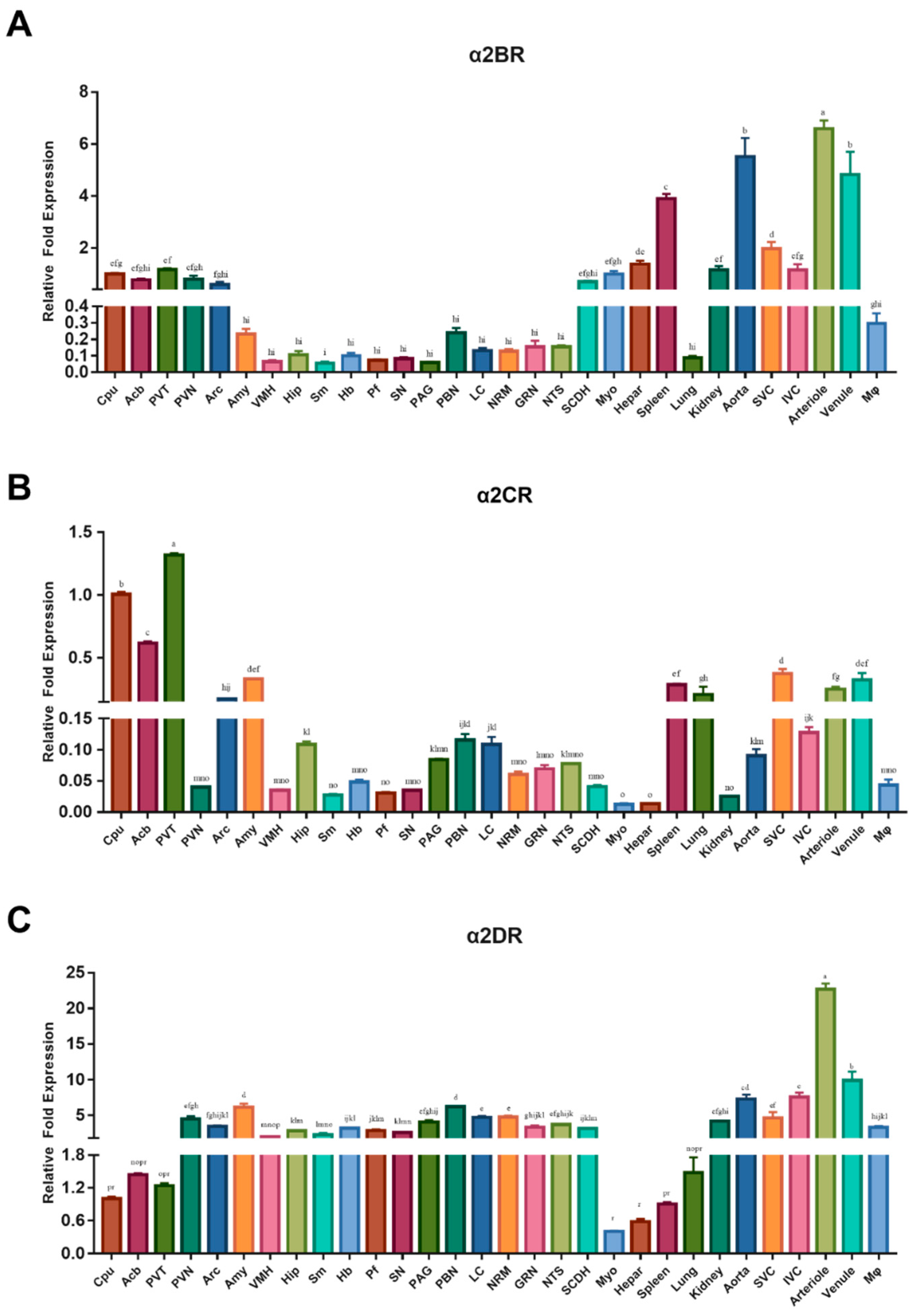
3.1. Real-Time Quantitative PCR Analyses of α2DR, α2BR and α2CR mRNA Abundance in Selected CNS Nuclei and Regions, as well as Peripheral Tissues
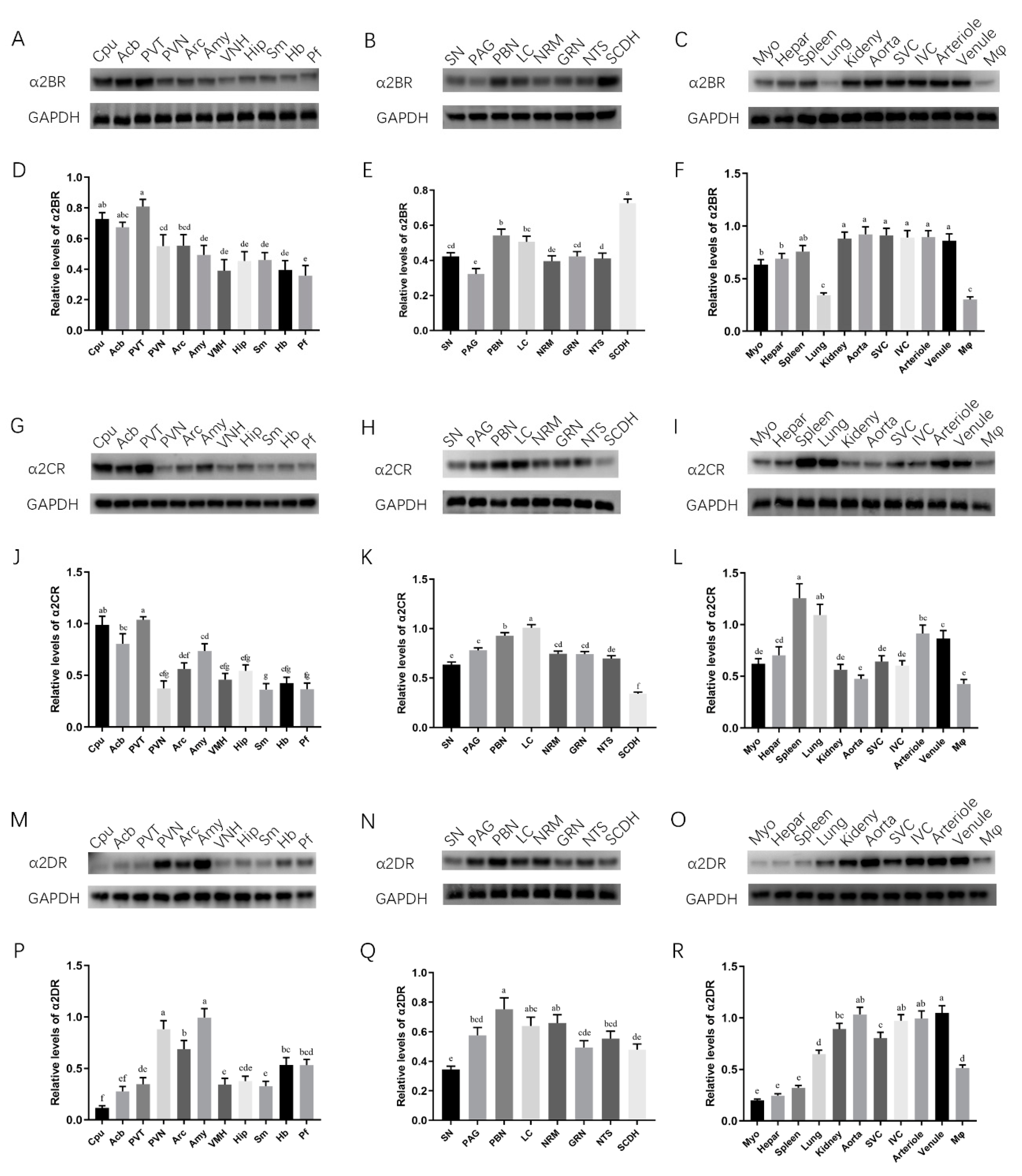
3.2. Western Blot Analyses of α2DR, α2BR and α2CR mRNA Abundances in Selected CNS Nuclei and Regions, as well as Peripheral Tissues
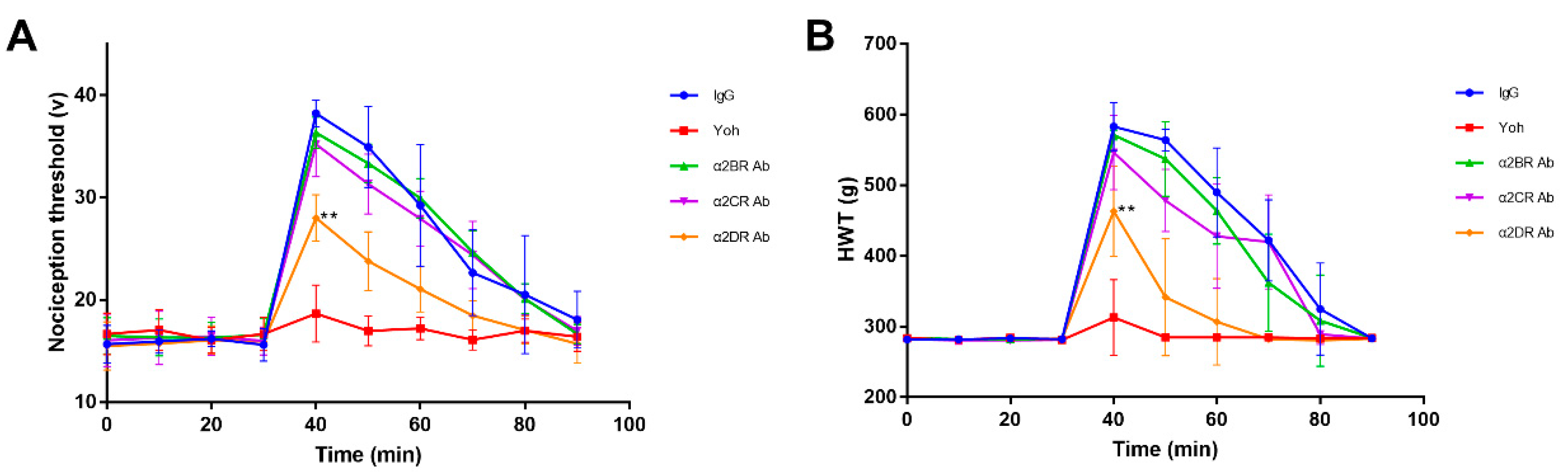
3.3. α2R-Mediated Analgesia in the Goat Spinal Cord
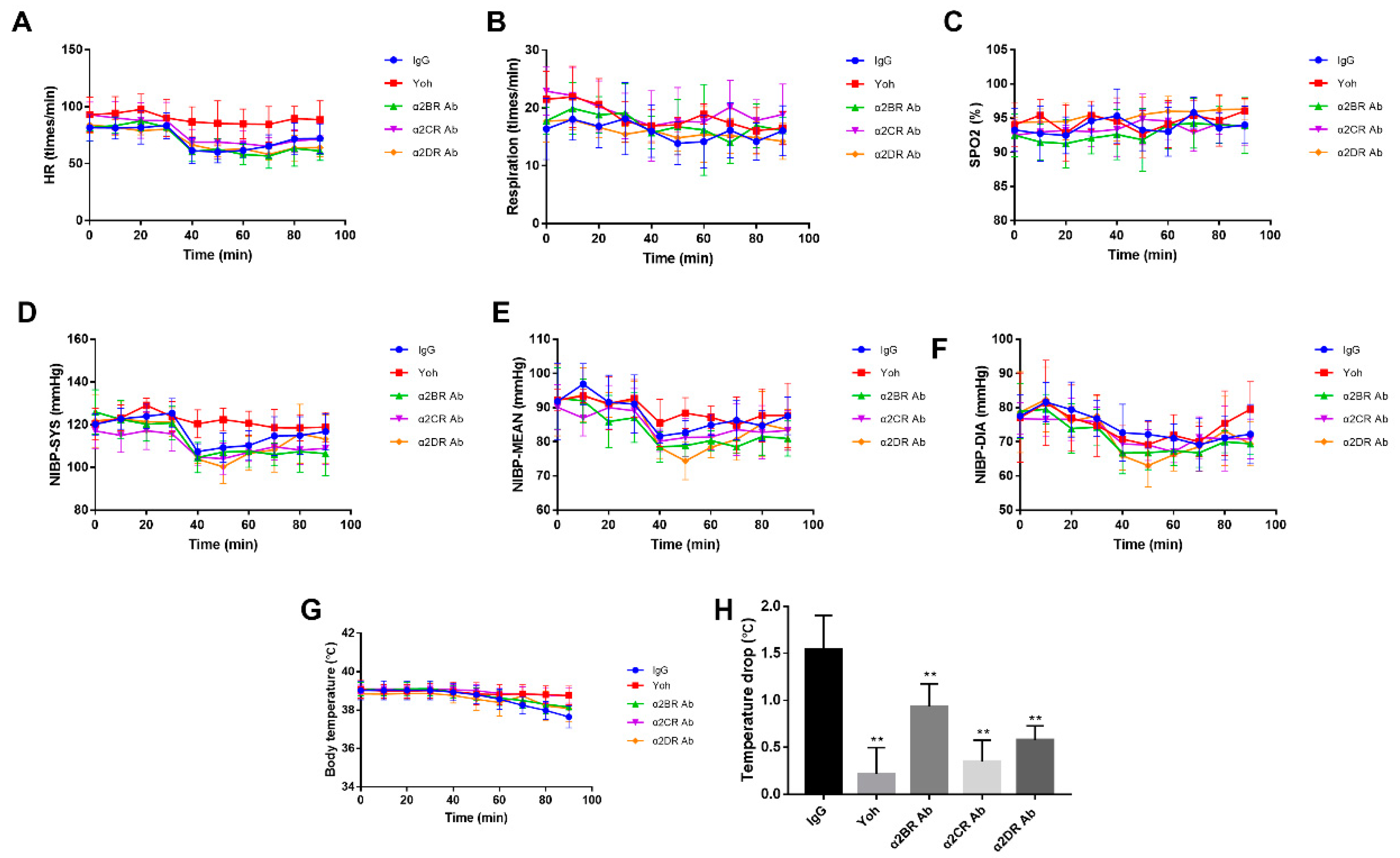
3.4. Effect of α2Rs Expressed in the Spinal Cord on Physiological Indices of Goats
3.5. α2R-Mediated Analgesia in the Goat Brain
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| α2BR Ab | α2BR antibody; |
| α2CR Ab | α2CR antibody; |
| α2DR Ab | α2DR antibody; |
| Acb | nucleus accumbens; |
| Amy | amygdala; |
| Arc | arcuate nucleus; |
| Cpu | caudate putamen nucleus; |
| GRN | gigantocellular reticular nucleus; |
| Hb | habenular nucleus; |
| Hip | hippocampus; |
| HWT | hindlimb withdrawal threshold; |
| IgG | nonspecific immunoglobulin; |
| IVC | inferior vena cava; |
| LC | locus coeruleus; |
| Mφ | blood mononuclear macrophages; |
| Myo | myocardium; |
| NRM | nucleus raphe magnus; |
| NTS | nucleus of the solitary tract; |
| PBN | parabrachial nucleus; |
| Pf | parafascicular nucleus; |
| PAG | periaqueductal gray; |
| PVN | hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus; |
| PVT | paraventricular thalamus; |
| SCDH | spinal cord L4-L6 dorsal horn; |
| Sm | thalamic nucleus submedius; |
| SN | substantia nigra; |
| SVC | superior vena cava; |
| VMH | ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus; |
| Yoh | yohimbine |
References
- Bantel, C.; Maze, M.; Stone, L.; Wilcox, G. Alpha(α) 2-Adrenergic Agonists in Pain Treatment. In Encyclopedia of Pain; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 58–61. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, A.K.; Cheung, C.W.; Chong, Y.K. Alpha-2 agonists in acute pain management. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2010, 11, 2849–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKelvey, D.; Hollingshead, K.W. Veterinary Anesthesia and Analgesia, 3rd ed.; Mosby: St Louis, MO, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, Z.; Ding, M.-X.; Hu, M.-L. A review on the current use of alpha2 agonists in small ruminants. Kafkas Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2014, 20, 633–639. [Google Scholar]
- Carroll, G.L.; Hartsfield, S.M. General anesthetic techniques in ruminants. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 1996, 12, 627–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, M.D. A review of the physiological effects of alpha2-agonists related to the clinical use of medetomidine in small animal practice. Can. Vet. J. Rev. Vet. Can. 2003, 44, 885–897. [Google Scholar]
- McCallum, J.B.; Boban, N.; Hogan, Q.; Schmeling, W.T.; Kampine, J.P.; Bosnjak, Z.J. The Mechanism of [alpha] 2-Adrenergic Inhibition of Sympathetic Ganglionic Transmission. Anesth. Analg. 1998, 87, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajkowski, J.; Kubiak, P.; Aston-Jones, G. Locus coeruleus activity in monkey: Phasic and tonic changes are associated with altered vigilance. Brain Res. Bull. 1994, 35, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzori, M.; Cuevas-Olguin, R.; Esquivel-Rendon, E.; Garcia-Oscos, F.; Salgado-Delgado, R.C.; Saderi, N.; Miranda-Morales, M.; Treviño, M.; Pineda, J.C.; Salgado, H. Locus ceruleus norepinephrine release: A central regulator of CNS spatio-temporal activation? Front. Synaptic Neurosci. 2016, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaksh, T.L.; Pogrel, J.W.; Lee, Y.W.; Chaplan, S.R. Reversal of nerve ligation-induced allodynia by spinal alpha-2 adrenoceptor agonists. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1995, 272, 207–214. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.B.; Lin, Q.; Willis, W.D. Involvement of alpha-2 adrenoceptors in the periaqueductal gray-induced inhibition of dorsal horn cell activity in rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1996, 278, 125–135. [Google Scholar]
- Herbert, H.; Flügge, G. Distribution of alpha 2-adrenergic binding sites in the parabrachial complex of the rat. Anat. Embryol. 1995, 192, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijeysundera, D.N.; Bender, J.S.; Beattie, W.S. Alpha-2 adrenergic agonists for the prevention of cardiac complications among patients undergoing surgery. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2009, 7, CD004126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bylund, D.B. Subtypes of alpha 2-adrenoceptors: Pharmacological and molecular biological evidence converge. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988, 9, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonneaux, V.; Ebadi, M.; Bylund, D.B. Identification and characterization of alpha 2D-adrenergic receptors in bovine pineal gland. Mol. Pharmacol. 1991, 40, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Celly, C.; Mcdonell, W.; Young, S.; Black, W. The comparative hypoxaemic effect of four α2 adrenoceptor agonists (xylazine, romifidine, detomidine and medetomidine) in sheep. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 1997, 20, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ongioco, R.R.; Richardson, C.D.; Rudner, X.L.; Stafford-Smith, M.; Schwinn, D.A. Alpha2-adrenergic receptors in human dorsal root ganglia: Predominance of alpha2b and alpha2c subtype mRNAs. Anesthesiology 2000, 92, 968–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giron, L.T., Jr.; McCann, S.A.; Crist-Orlando, S.G. Pharmacological characterization and regional distribution of alpha-noradrenergic binding sites of rat spinal cord. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1985, 115, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kästner, S.B. A2-agonists in sheep: A review. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2006, 33, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.Y.; Ding, Y.; Cui, L.Y.; Hu, M.L.; Ding, M.X. The Expression Patterns of c-Fos and c-Jun Induced by Different Frequencies of Electroacupuncture in the Brain. Evid. Based Complementary Altern. Med. Ecam 2015, 2015, 343682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphries, S.A.; Long, N.R.; Johnson, M.H. Iontophoretically applied potassium ions as an experimental pain stimulus for investigating pain mechanisms. Percept. Psychophys. 1994, 56, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Spadavecchia, C.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Andersen, O.K.; Spadavecchia, L.; Doherr, M.; Schatzmann, U. Comparison of nociceptive withdrawal reflexes and recruitment curves between the forelimbs and hind limbs in conscious horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2003, 64, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, F.G. Advances in the Knowledge of the α 2-Adrenergic Agonists Action Mechanisms in Domestic Animals: Clinical Implications and Future Perspectives. In Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association World Congress Proceedings, Mexico City, Mexico, 11–14 May 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, J.K.; Pearson, W.R.; Lynch, K.R. Molecular characterization of α1-and α2-adrenoceptors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1991, 12, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosin, D.L.; Talley, E.M.; Lee, A.; Stornetta, R.L.; Gaylinn, B.D.; Guyenet, P.G.; Lynch, K.R. Distribution of α2C-adrenergic receptor-like immunoreactivity in the rat central nervous system. J. Comp. Neurol. 1996, 372, 135–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffolo, R.R., Jr.; Nichols, A.; Stadel, J.; Hieble, J. Pharmacologic and therapeutic applications of alpha2-adrenoceptor subtypes. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1993, 33, 243–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, L.; Altman, J.D.; Kobilka, B.K. Two functionally distinct α 2-adrenergic receptors regulate sympathetic neurotransmission. Nature 1999, 402, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsook, D.; Upadhyay, J.; Chudler, E.H.; Becerra, L. A key role of the basal ganglia in pain and analgesia—insights gained through human functional imaging. Mol. Pain 2010, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogon, I.; Takebayashi, T.; Iwase, T.; Emori, M.; Tanimoto, K.; Miyakawa, T.; Terashima, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Tohse, N.; Yamashita, T. Sympathectomy and sympathetic blockade reduce pain behavior via alpha-2 adrenoceptor of the dorsal root ganglion neurons in a lumbar radiculopathy model. Spine 2015, 40, E1269–E1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Micheli, L.; Crocetti, L.; Paola Giovannoni, M.; Vergelli, C.; Ghelardini, C. α2 adrenoceptor: A target for neuropathic pain treatment. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelman, E.; Marsala, C. Efficacy of adding clonidine to intrathecal morphine in acute postoperative pain: Meta-analysis. Br. J. Anaesth. 2013, 110, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavin, K.; Colgan, M.-P.; Moore, D.; Shanik, G.; Docherty, J. α2C-adrenoceptors mediate contractile responses to noradrenaline in the human saphenous vein. Naunyn Schmiedeberg‘s Arch. Pharmacol. 1997, 355, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Warner, R.; Brune, M.; DeBernardis, J. Calcium-induced vasocontractions after alpha-2 adrenergic receptor activation in the dog saphenous vein: Comparison to calcium-induced contractions after potassium-depolarization. Gen. Pharmacol. Vasc. Syst. 1990, 21, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regitz-Zagrosek, V.; Hocher, B.; Bettmann, M.; Brede, M.; Hadamek, K.; Gerstner, C.; Lehmkuhl, H.B.; Hetzer, R.; Hein, L. Alpha2C-adrenoceptor polymorphism is associated with improved event-free survival in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Eur. Heart 2006, 27, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, X.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Lv, X.; Lu, D.; Wang, H. Yohimbine Promotes Cardiac NE Release and Prevents LPS-Induced Cardiac Dysfunction via Blockade of Presynaptic α 2A-Adrenergic Receptor. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63622. [Google Scholar]
- Pypendop, B.H.; Verstegen, J.P. Hemodynamic effects of medetomidine in the dog: A dose titration study. Vet. Surg. 1998, 27, 612–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertovaara, A.; Almeida, A. Descending inhibitory systems. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2006, 81, 179–192. [Google Scholar]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Pan, D.; Ding, M.; Ding, Y. The Characteristics and Distribution of α2D-, α2B- and α2C-Adrenoceptor Subtypes in Goats. Animals 2022, 12, 664. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12050664
Xu M, Zhang Q, Wang Q, Pan D, Ding M, Ding Y. The Characteristics and Distribution of α2D-, α2B- and α2C-Adrenoceptor Subtypes in Goats. Animals. 2022; 12(5):664. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12050664
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Ming, Qiulin Zhang, Qi Wang, Di Pan, Mingxing Ding, and Yi Ding. 2022. "The Characteristics and Distribution of α2D-, α2B- and α2C-Adrenoceptor Subtypes in Goats" Animals 12, no. 5: 664. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12050664
APA StyleXu, M., Zhang, Q., Wang, Q., Pan, D., Ding, M., & Ding, Y. (2022). The Characteristics and Distribution of α2D-, α2B- and α2C-Adrenoceptor Subtypes in Goats. Animals, 12(5), 664. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12050664





