Combined Effects of Temperature and Dietary Lipid Level on Body Composition, Growth, and Freshness Profile in European Seabass, Dicentrarchus labrax
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish and Rearing Conditions
2.2. Experimental Diets
2.3. Fish Sampling and Storage
2.4. Composition Analysis
2.5. Growth Performance
2.6. Freshness Profile
2.6.1. Sensorial Analysis
2.6.2. Physical Analysis
2.6.3. Microbiological Analysis
2.7. Taxonomic Profiling of the Skin Microbiome by 16S rRNA Gene Metabarcoding Sequencing
2.8. Data Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Compositional Analysis
3.2. Growth Evaluation and Condition Index
3.3. Sensorial Analysis
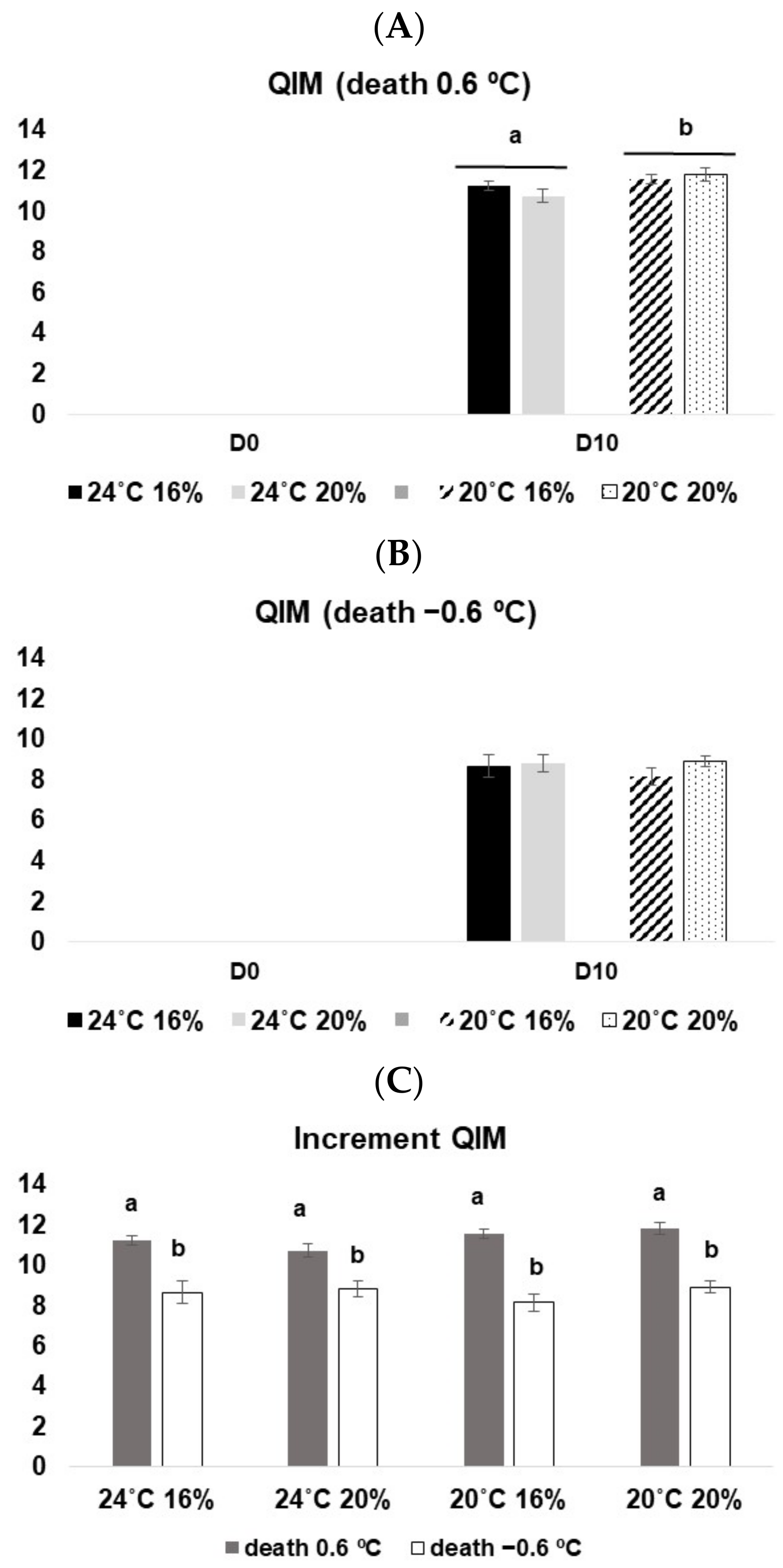
3.3.1. Quality Index Method (QIM)
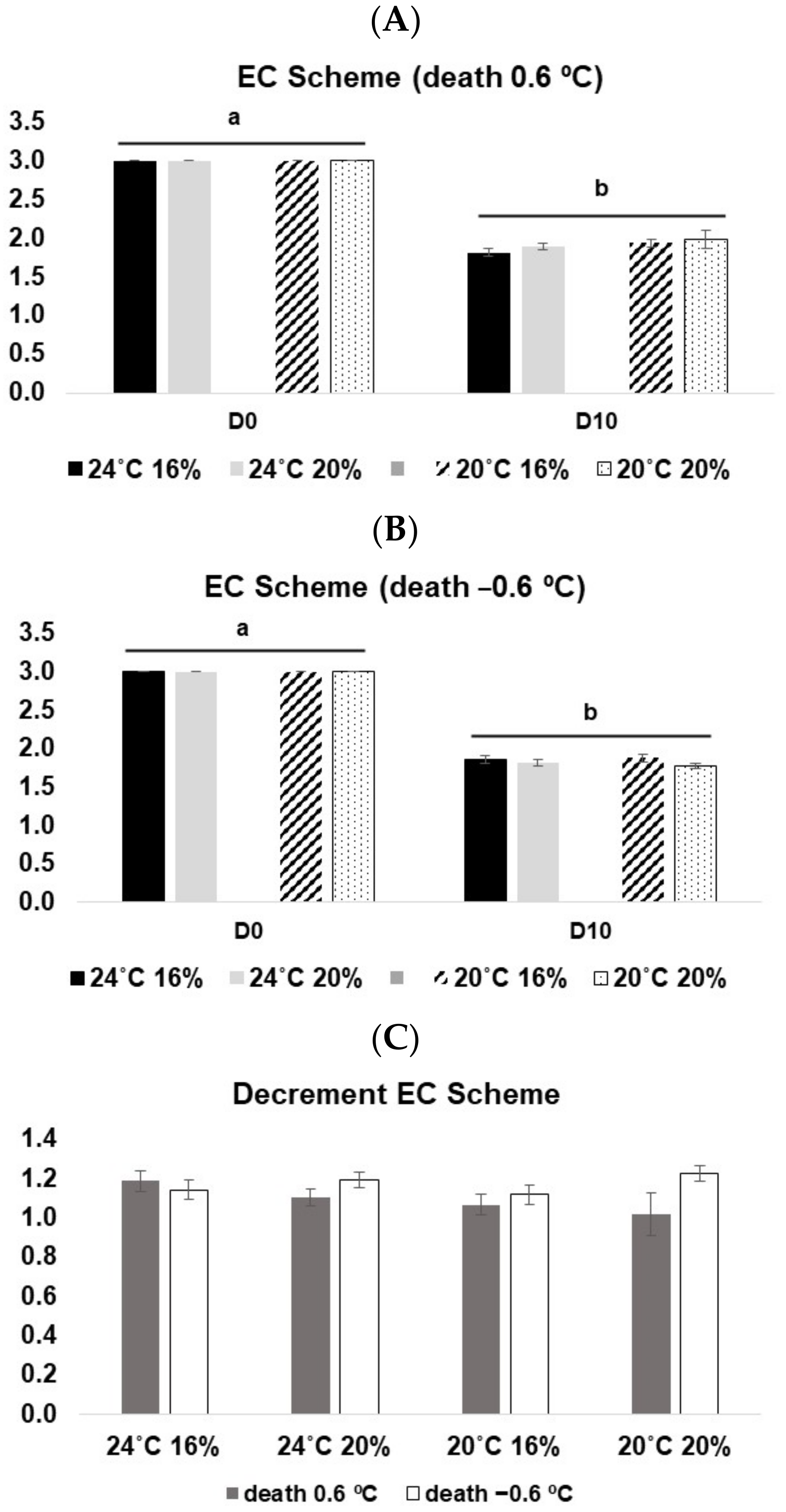
3.3.2. EC Scheme
3.3.3. Physical Analysis (Torrymeter—TRM)
3.3.4. Microbiological Analysis
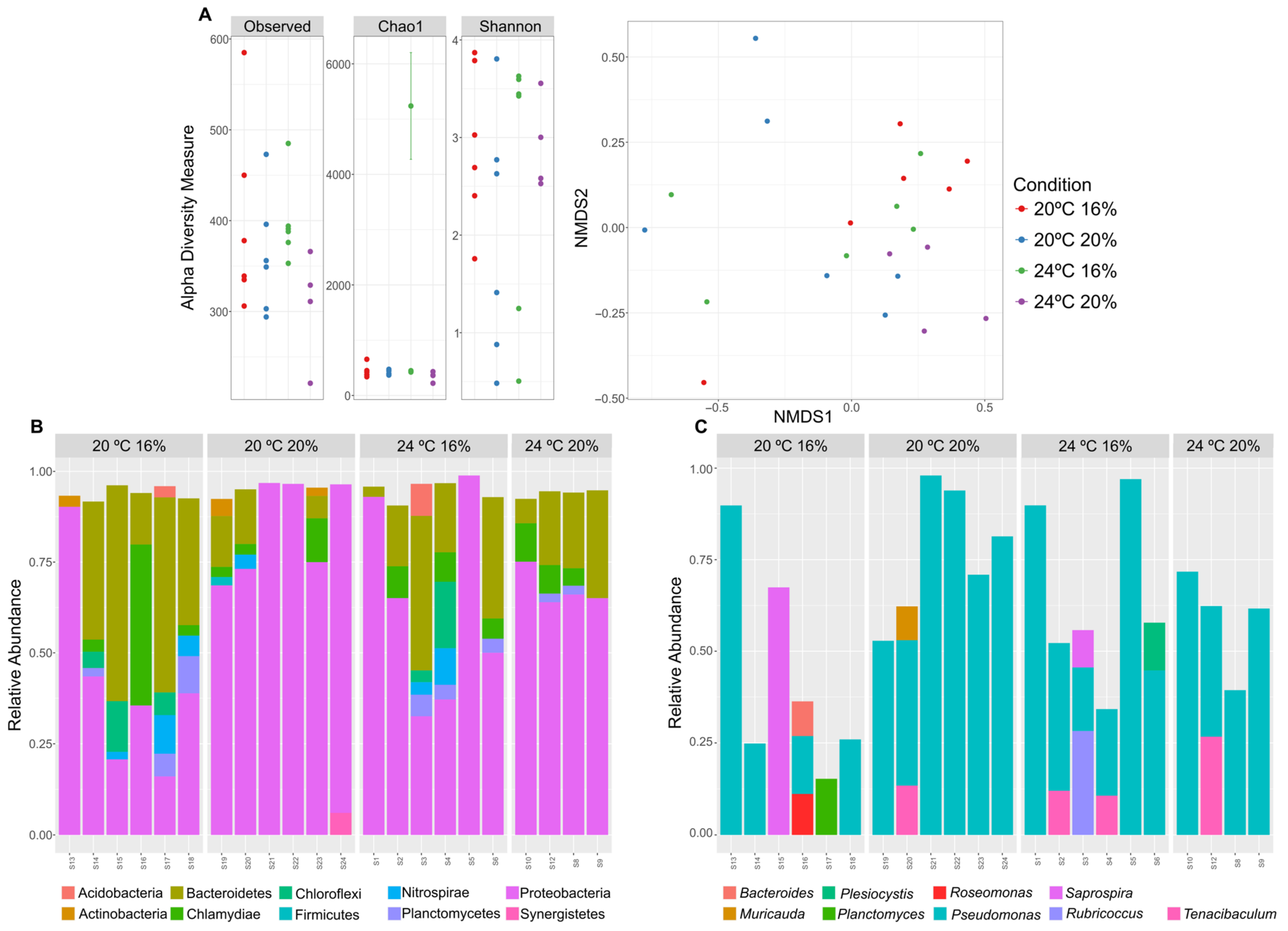
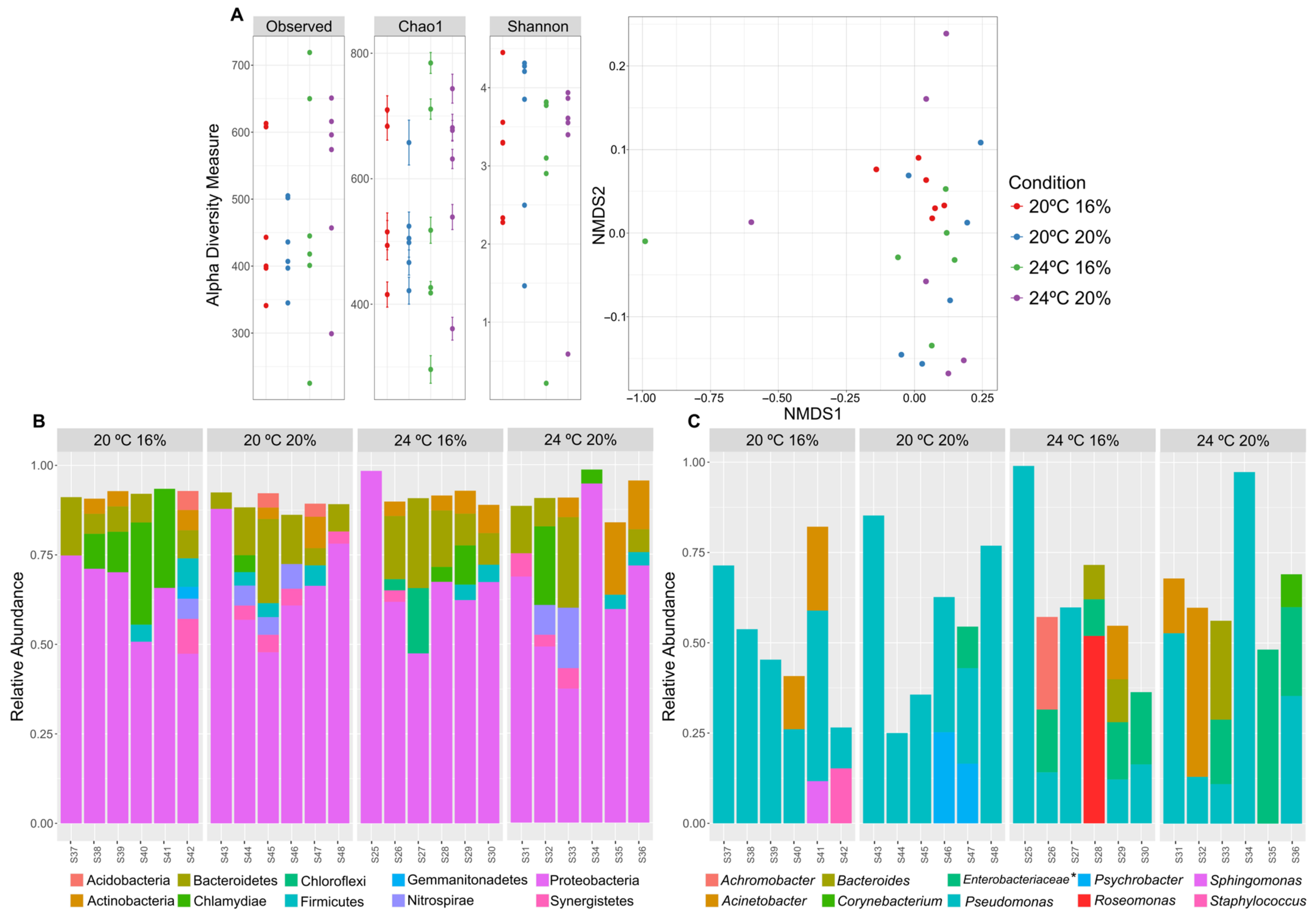
3.4. Taxonomic Profiling of the Skin Microbiome by 16S rRNA Gene Metabarcoding Sequencing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Pachauri, R.K., Meyer, L.A., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ficke, A.; Myrick, C.; Hansen, L. Potential impacts of global climate change on freshwater fisheries. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish 2007, 71, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portner, H.O.; Farrell, A.P. Physiology and climate change. Science 2008, 322, 690–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeppesen, E.; Meerhoff, M.; Holmgren, K.; Gonzalez-Bergonzoni, I.; Teixeira-de Mello, F.; Declerck, S.A.J.; De Meester, L.; Sondergaard, M.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Bjerring, R.; et al. Impacts of climate warming on lake fish community structure and potential effects on ecosystem function. Hydrobiologia 2010, 646, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.S. Digestive functions in teleost fishes. In Fish Nutrition; Halver, E., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 331–421. [Google Scholar]
- Tidwell, J.H.; Coyle, S.D.; Bright, L.A.; VanArnum, A.; Yasharian, D. Effect of water temperature on growth, survival and biochemical composition of largemouth bass Micropterus salmoides. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2003, 34, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Jérez, J.J.; Hernández-Herrero, M.M.; Roig-Sagués, A.X. New methods to determine fish freshness in research and industry. In Global Quality Assessment in Mediterranean Aquaculture; CIHEAM: Zaragoza, Spain, 2000; pp. 63–69, (Cahiers Options Mediterranean’s; n. 51). Workshop of the CIHEAM Networks on Technology of Aquaculture in the Mediterranean (TECAM) and Socio-Economic and Legal aspects of Aquaculture in the Mediterranean, 1999/11/29–1999/12/01, Barcelona. (In Spainish) [Google Scholar]
- Pal, M.; Ketema, A.; Anberber, M.; Mulu, S.; Dutta, Y. Microbial quality of fish and fish products. Beverage Food World 2016, 43, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Esteves, E.; Aníbal, J. Sensory evaluation of seafood freshness using the quality index method: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Food Micro. 2021, 337, 108934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, A.; Vaz-Pires, P. Quality index method (QIM):development of a sensorial scheme for common octopus (Octopus vulgaris). Food Control 2004, 15, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakar, P.K.; Vatsa, S.; Srivastav, P.P.; Pathak, S.S. A comprehensive review on freshness of fish and assessment: Analytical methods and recent innovations. Food Res. Inter. 2020, 133, 109157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, R.; Gibson, D.M.; Jason, A.C.; Sanders, H.R. Comparison of methods of freshness assessment of wet fish. II. Instrumental and chemical assessment of boxed experimental fish. J. Food Technol. 1976, 11, 73–89. [Google Scholar]
- Oehlenschläger, J. Seafood Quality Assessment. In Seafood Processing: Technology, Quality and Safety; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 359–386. ISBN 9781118346174. [Google Scholar]
- Volckaert, F.; Batargias, C.; Canario, A.; Chatziplis, D.; Chistiakov, D.; Haley, C.; Libertini, A.; Tsigenopoulos, C. European Sea Bass. In Genome Mapping and Genomics in Fishes and Aquatic Animals; Kocher, T.D., Kole, C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 2, pp. 117–133. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, A.K.; Dasan, A.F.; Rasoloniriana, R.; Pipralia, N.; Blust, R.; de Boeck, G. Hypo-osmotic stress-induced physiological and ion-osmoregulatory responses in European seabass are modulated differentially by nutritional status. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2015, 181, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collares-Pereira, M.J.; Alves, M.J.; Ribeiro, F.; Domingos, I.; Almeida, P.R.; Costa, L.; Gante, H.; Filipe, A.F.; Aboim, M.A.; Rodrigues, P.M.; et al. Guia Dos Peixes de Água Doce e Migradores de Portugal Continental; Afrontamento, E., Ed.; Edições Afrontamento: Porto, Portugal, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Ruzafa, A.; Marcos, C. Ecology and Distribution of Dicentrarchus labrax (Linnaeus 1758). In Biology of European Sea Bass, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 3–26. [Google Scholar]
- Claireaux, G.; Lagardère, J.P. Influence of temperature, oxygen and salinity on the metabolism of the European seabass. J. Sea Res. 1999, 42, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, N.; Wang, H.P.; Yao, H.; Shen, Z.G.; Shaheen, A.A.; Abou-ElGheit, E.N. Expression of Hsp 70, Igf1, and three oxidative stress biomarkers in response to handling and salt treatment at different water temperatures in yellow perch, Perca flavescens. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sampaio, E.; Lopes, A.R.; Francisco, S.; Paula, J.R.; Pimentel, M.; Maulvault, A.L.; Repolho, T.; Grilo, T.F.; Pousão-Ferreira, P.; Marques, A.; et al. Ocean acidification dampens warming and contamination effects on the physiological stress response of a commercially important fish. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 618, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.J.; Kunzmann, A.; Bogner, M.; Meyer, A.; Thiele, R.; Slater, M.J. Metabolic and molecular stress responses of European seabass, Dicentrarchus labrax at low and high temperature extremes. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 112, 106118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, B.D.; Connell, S.D.; Findlay, H.S.; Tait, K.; Widdicombe, S.; Mieszkowska, N. Ocean acidification and rising temperatures may increase biofilm primary productivity but decrease grazer consumption. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 20120438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zampacavallo, G.; Scappini, F.; Mecatti, M.; Lurzan, F.; Mosconi, G.; Poli, B.M. Study on methods to decrease the stress at slaughter in farmed seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2003, 2 (Suppl. 1), 616–618. [Google Scholar]
- Sansuwan, K.; Kovitvadhia, S.; Thongprajukaew, K.; Ozório, R.O.A.; Somsue, P.; Kovitvadhi, U. Microwave irradiation and pelleting method affected feed chemical composition, and growth performance and feed utilization of sex-reversed Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 1836–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alasalvar, K.; Taylor, D.A.; Öksüz, A.; Shahidi, F.; Alexis, M. Comparison of freshness quality of cultured and wild sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). J. Food Sci. 2002, 67, 3220–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howgate, P.A.J.; Whittle, K.J. Multilingual Guide to EC Freshness Grades for Fishery Products; Torry Research Station, Food Safety Directorate, Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food: Aberdeen, WA, USA, 1992.
- Bernardi, D.C.; Mársico, E.T.; Freitas, M.Q. Quality Index Method (QIM) to assess the freshness and shelf life of fish. Braz. Arch. Biol. Tech. 2013, 56, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, R.M.; Capell, C.J.; Vaz-Pires, P. Combined treatments to extend the shelf-life of fresh fish. In Minimal Processing of Foods and Process Optimization—An Interface; Singh, R.P., Oliveira, F., Eds.; CRC Press, Inc.: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1994; pp. 233–241. ISBN 0-8493-7903-2. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, M.; Moss, M.O. Microbiology of Primary Food Commodities (chapter 5), Fish. In Food Microbiology; RSC Publishing: London, UK, 1995; pp. 119–124. ISBN 0-85404-509-0. [Google Scholar]
- Silva-Brito, F.; Alexandrino, D.A.; Jia, Z.; Mo, Y.; Kijjoa, A.; Abreu, H.; Carvalho, M.F.; Ozório, R.; Magnoni, L. Fish performance, intestinal bacterial community, digestive function and skin and fillet attributes during cold storage of gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) fed diets supplemented with Gracilaria by-products. Aquaculture 2021, 541, 736808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zar, J. Biostatistical Analysis, 4th ed.; Prentice-Hall International: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gram, L.; Trolle, G.; Huss, H.H. Detection of specific spoilage bacteria from fish stored at low (0 °C) and high (20 °C) temperatures. Int. J. Food Microb. 1987, 4, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gram, L.; Huss, H.H. Microbiological spoilage of fish and fish products. Int. J. Food Microb. 1996, 33, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gram, L.; Dalgaard, P. Fish spoilage bacteria—Problems and solutions. Curr. Opin. Biotechno. 2002, 13, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, G. Fish: Microbiological spoilage and safety. Food Sci. Technol. 1991, 5, 166–173. [Google Scholar]
- Jobling, M.; Bendiksen, E.A. Dietary lipids and temperature interact to influence tissue fatty acid compositions of Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L., parr. Aquac. Res. 2003, 34, 1423–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Yoo, J.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Park, E.J.; Lee, H.J. Ameliorative effects of black ginseng on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in free fatty acid-induced HepG2 cells and high-fat/high-fructose diet-fed mice. J. Ginseng Res. 2020, 44, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katersky, R.S.; Carter, C.G. High growth efficiency occurs over a wide temperature range for juvenile barramundi Lates calcarifer fed a balanced diet. Aquaculture 2007, 272, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Xu, X.; Kestemont, P. Effect of temperature and feeding frequency on growth performances, feed efficiency and body composition of pikeperch juveniles (Sander lucioperca). Aquaculture 2009, 289, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Xu, N.; Liu, Y.; Du, J.; Xiang, X.; Xu, D.; Liu, Q.; Yin, Z.; Li, J.; Mai, K.; et al. Effect of dietary bile acid on the growth performance, body composition, antioxidant resposnses and expresson of lipid metabolis-related genes of juvenile large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) fed high-lipid diets. Aquaculture 2020, 518, 734768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, A.G.; Loughland, I.; Seebacher, F. What do warming waters mean for fish physiology and fisheries? Fish Biol. 2020, 97, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Ham, E.H.; Berntssen, M.H.G.; Imsland, A.K.; Parpoura, A.C.; Bonga, S.E.W.; Stefansson, S.O. The influence of temperature and ration on growth, feed conversion, body composition and nutrient retention of juvenile turbot (Scophalmus maximus). Aquaculture 2003, 217, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Person-Le Ruyet, J.; Mahé, K.; Le Bayon, N.; Le Delliou, H. Effects of temperature on growth and metabolism in a Mediterranean population of European seabass, Dicentrarchus labrax. Aquaculture 2004, 237, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cardoso, P.G.; Gonçalves, O.; Carvalho, M.F.; Ozório, R.; Vaz-Pires, P. Seasonal evaluation of freshness profile of commercially important fish species. Foods 2021, 10, 1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordóñes-Grande, B.; Guerreiro, P.M.; Sanahuja, I.; Fernandez-Alacid, L. Environmental salinity modifies mucus exudation and energy use in European seabass juveniles. Animals 2021, 11, 1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatsos, I.N.; Kotzamanis, Y.; Henry, M.; Angelidis, P.; Alexis, M.N. Monitoring stress in fish by applying image analysis to their skin mucous cells. Eur. J. Histochem. 2010, 54, e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| 24 °C 16% | 24 °C 20% | 20 °C 16% | 20 °C 20% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Body Weight (IBW) | 60.54 ± 4.93 | 56.66 ± 2.64 | 60.55 ± 3.84 | 60.69 ± 2.86 |
| Final Body Weight (FBW) | 141.98 ± 13.77 | 136.71 ± 6.15 | 129.53 ± 13.05 | 133.97 ± 8.35 |
| Weight gain (WG) | 81.44 ± 8.91 | 80.05 ± 3.63 | 68.88 ± 10.34 | 73.28 ± 5.64 |
| Feed Conversion Ratio (FCR) | 1.36 ± 0.16 | 1.46 ± 0.01 | 1.41 ± 0.16 | 1.46 ± 0.11 |
| Daily Growth Index (DGI) | 2.30 ± 0.12 a | 2.34 ± 0.04 a | 2.01 ± 0.21 b | 2.12 ± 0.09 b |
| Protein Efficiency Ratio (PER) | 1.46 ± 0.16 | 1.36 ± 0.05 | 1.37 ± 0.29 | 1.4 ± 0.08 |
| Condition Index (CI) | 1.2 ± 0.09 | 1.2 ± 0.13 | 1.2 ± 0.13 | 1.2 ± 0.14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cardoso, P.G.; Gonçalves, O.; Cavalheri, T.; Amorim, V.E.; Cao, W.; Alexandrino, D.A.M.; Jia, Z.; Carvalho, M.F.; Vaz-Pires, P.; Ozório, R.O.A. Combined Effects of Temperature and Dietary Lipid Level on Body Composition, Growth, and Freshness Profile in European Seabass, Dicentrarchus labrax. Animals 2023, 13, 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13061068
Cardoso PG, Gonçalves O, Cavalheri T, Amorim VE, Cao W, Alexandrino DAM, Jia Z, Carvalho MF, Vaz-Pires P, Ozório ROA. Combined Effects of Temperature and Dietary Lipid Level on Body Composition, Growth, and Freshness Profile in European Seabass, Dicentrarchus labrax. Animals. 2023; 13(6):1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13061068
Chicago/Turabian StyleCardoso, Patrícia G., Odete Gonçalves, Thais Cavalheri, Vânia E. Amorim, Weiwei Cao, Diogo A. M. Alexandrino, Zhongjun Jia, Maria F. Carvalho, Paulo Vaz-Pires, and Rodrigo O. A. Ozório. 2023. "Combined Effects of Temperature and Dietary Lipid Level on Body Composition, Growth, and Freshness Profile in European Seabass, Dicentrarchus labrax" Animals 13, no. 6: 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13061068
APA StyleCardoso, P. G., Gonçalves, O., Cavalheri, T., Amorim, V. E., Cao, W., Alexandrino, D. A. M., Jia, Z., Carvalho, M. F., Vaz-Pires, P., & Ozório, R. O. A. (2023). Combined Effects of Temperature and Dietary Lipid Level on Body Composition, Growth, and Freshness Profile in European Seabass, Dicentrarchus labrax. Animals, 13(6), 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13061068










