Genome Sequence Comparisons between Small and Large Colony Phenotypes of Equine Clinical Isolates of Arcanobacterium hippocoleae
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacteria Isolation and Identification
2.2. Bacterial Genomic DNA Extraction and Analysis
2.3. MinION Sequence Library Preparation and Sequencing
2.4. DNA Sequence Assembly and Analysis
2.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Bacteriology
3.2. Run Summary and Genome Assembly Statistics
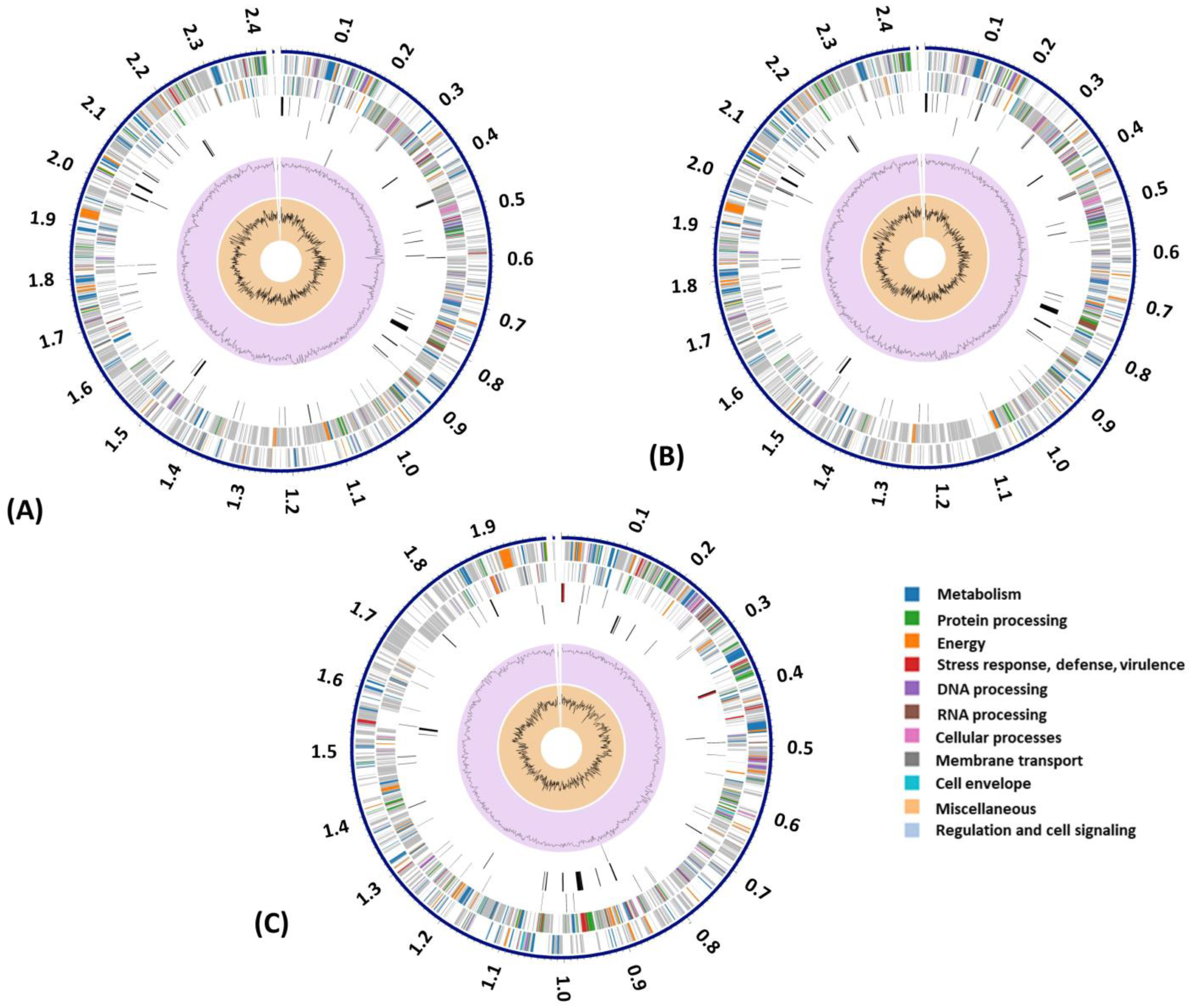
3.3. Genome Annotation and Subsystem Analysis
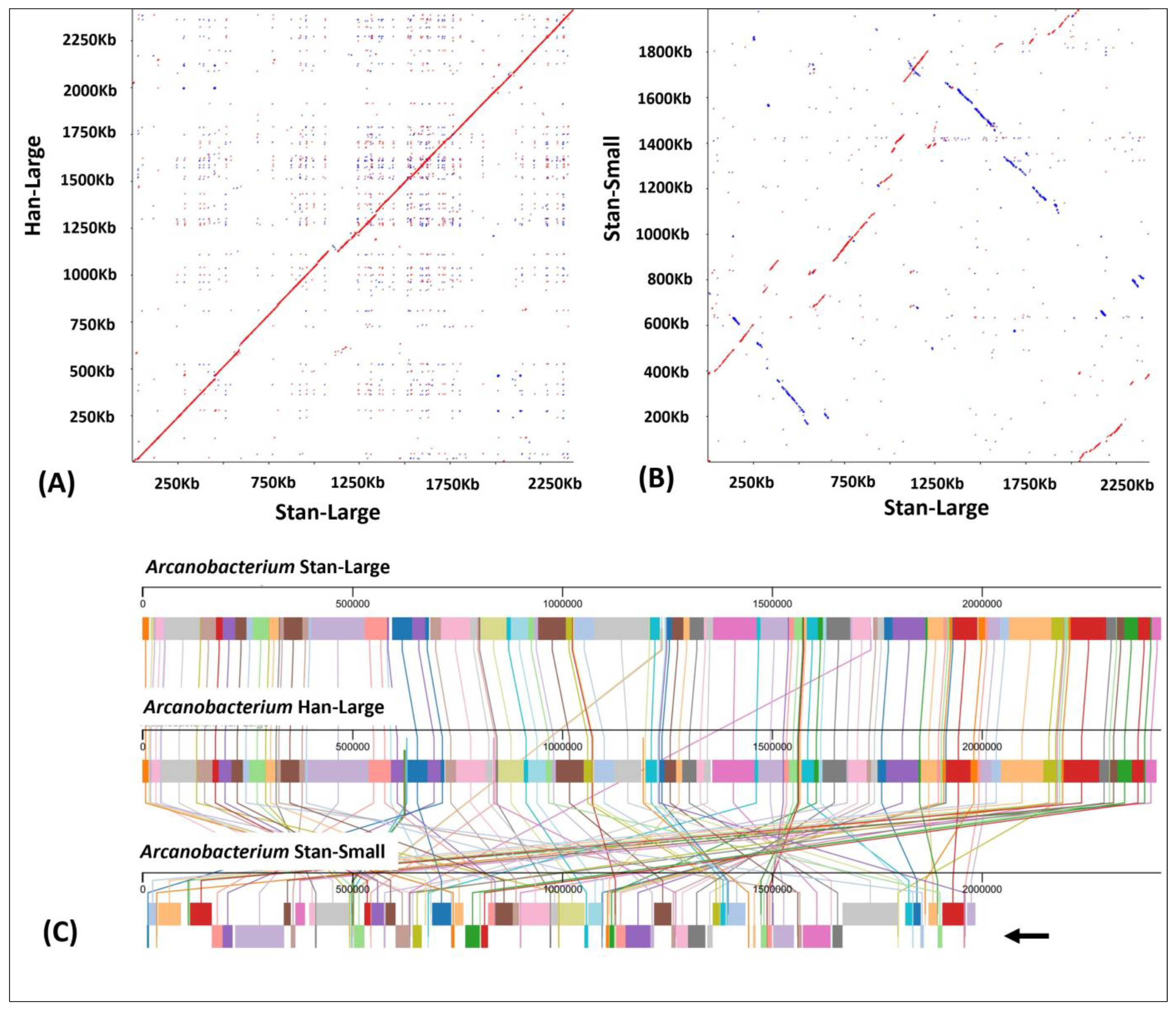
3.4. Dot-Plot Analysis and Whole Genome Alignment
3.5. Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) Genes and Potential Drug Targets
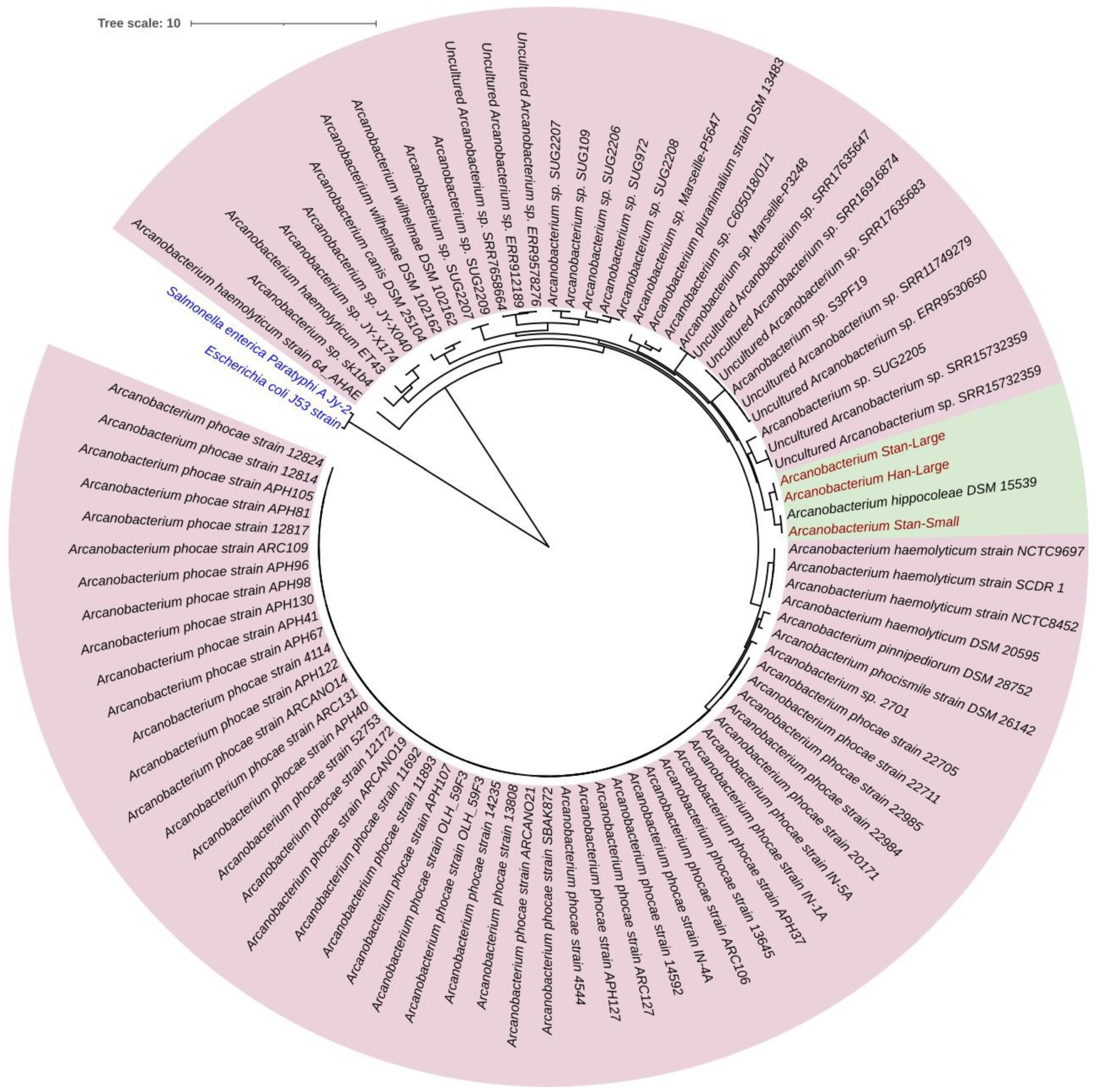
3.6. Sequence Comparison and Phylogenetic Tree Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoyles, L.; Falsen, E.; Foster, G.; Rogerson, F.; Collins, M.D. Arcanobacterium hippocoleae sp. nov., from the vagina of a horse. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2002, 52 Pt 2, 617–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, H.; Archambault, M.; Prescott, J.F. 16S ribosomal RNA sequence-based identification of veterinary clinical bacteria. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2003, 15, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bemis, D.A.; Bryant, M.J.; Kania, S.A.; Newman, S.J. Isolation of Arcanobacterium hippocoleae from a case of placentitis and stillbirth in a mare. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2008, 20, 688–691, Erratum in J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2009, 21, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickhorst, J.P.; Sammra, O.; Hassan, A.A.; Alssashen, M.; Lämmler, C.; Prenger-Berninghoff, E.; Erhard, M.; Metzner, M.; Paschertz, K.; Timke, M.; et al. Identification of Arcanobacterium hippocoleae by MALDI-TOF MS analysis and by various genotypical properties. Res. Vet. Sci. 2017, 115, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pégné, J.C.; Duquesne, F.; Laugier, C.; Lequeux, G.; Petry, S. Isolation and comparison of Arcanobacterium hippocoleae isolates from the genital tract of 15 mares. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 228, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, R. Unexplained infertility, endometriosis, and fibroids. BMJ 2003, 327, 721–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holyoak, G.R.; Premathilake, H.U.; Lyman, C.C.; Sones, J.L.; Gunn, A.; Wieneke, X.; DeSilva, U. The healthy equine uterus harbors a distinct core microbiome plus a rich and diverse microbiome that varies with geographical location. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heil, B.A.; van Heule, M.; Thompson, S.K.; Kearns, T.A.; Oberhaus, E.L.; King, G.; Daels, P.; Dini, P.; Sones, J.L. Effect of Sampling Method on Detection of the Equine Uterine Microbiome during Estrus. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barba, M.; Martínez-Boví, R.; Quereda, J.J.; Mocé, M.L.; Plaza-Dávila, M.; Jiménez-Trigos, E.; Gómez-Martín, Á.; González-Torres, P.; Carbonetto, B.; García-Roselló, E. Vaginal Microbiota Is Stable throughout the Estrous Cycle in Arabian Maress. Animals 2020, 10, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Heule, M.; Monteiro, H.F.; Bazzazan, A.; Scoggin, K.; Rolston, M.; El-Sheikh Ali, H.; Weimer, B.C.; Ball, B.; Daels, P.; Dini, P. Characterization of the equine placental microbial population in healthy pregnancies. Theriogenology 2023, 206, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckers, K.F.; Gomes, V.C.L.; Crissman, K.R.; Liu, C.C.; Schulz, C.J.; Childers, G.W.; Sones, J.L. Metagenetic Analysis of the Pregnant Microbiome in Horses. Animals 2023, 13, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmogorov, M.; Yuan, J.; Lin, Y.; Pevzner, P.A. Assembly of long, error-prone reads using repeat graphs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Yuan, J.; Kolmogorov, M.; Shen, M.W.; Chaisson, M.; Pevzner, P.A. Assembly of long error-prone reads using de Bruijn graphs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E8396–E8405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, A.; Saveliev, V.; Vyahhi, N.; Tesler, G. QUAST: Quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, D.H.; Imelfort, M.; Skennerton, C.T.; Hugenholtz, P.; Tyson, G.W. CheckM: Assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chklovski, A.; Parks, D.H.; Woodcroft, B.J.; Tyson, G.W. CheckM2: A rapid, scalable and accurate tool for assessing microbial genome quality using machine learning. Nat. Methods 2023, 20, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Ouk Kim, Y.; Park, S.C.; Chun, J. OrthoANI: An improved algorithm and software for calculating average nucleotide identity. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 1100–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling, A.E.; Mau, B.; Perna, N.T. progressiveMauve: Multiple genome alignment with gene gain, loss and rearrangement. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattam, A.R.; Davis, J.J.; Assaf, R.; Boisvert, S.; Brettin, T.; Bun, C.; Conrad, N.; Dietrich, E.M.; Disz, T.; Gabbard, J.L.; et al. Improvements to PATRIC, the all-bacterial Bioinformatics Database and Analysis Resource Center. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D535–D542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, R.K.; Bartels, D.; Best, A.A.; DeJongh, M.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Formsma, K.; Gerdes, S.; Glass, E.M.; Kubal, M.; et al. The RAST Server: Rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overbeek, R.; Olson, R.; Pusch, G.D.; Olsen, G.J.; Davis, J.J.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Gerdes, S.; Parrello, B.; Shukla, M.; et al. The SEED and the Rapid Annotation of microbial genomes using Subsystems Technology (RAST). Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D206–D214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brettin, T.; Davis, J.J.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Gerdes, S.; Olsen, G.J.; Olson, R.; Overbeek, R.; Parrello, B.; Pusch, G.D.; et al. RASTtk: A modular and extensible implementation of the RAST algorithm for building custom annotation pipelines and annotating batches of genomes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.J.; Wattam, A.R.; Aziz, R.K.; Brettin, T.; Butler, R.; Butler, R.M.; Chlenski, P.; Conrad, N.; Dickerman, A.; Dietrich, E.M.; et al. The PATRIC Bioinformatics Resource Center: Expanding data and analysis capabilities. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D606–D612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.J.; Gerdes, S.; Olsen, G.J.; Olson, R.; Pusch, G.D.; Shukla, M.; Vonstein, V.; Wattam, A.R.; Yoo, H. PATtyFams: Protein Families for the Microbial Genomes in the PATRIC Database. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Abraham, D.; Wattam, A.R.; Wilson, M.J.; Shukla, M.; Yoo, H.S.; Sobral, B.W. Curation, integration and visualization of bacterial virulence factors in PATRIC. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zheng, D.; Liu, B.; Yang, J.; Jin, Q. VFDB 2016: Hierarchical and refined dataset for big data analysis—10 years on. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D694–D697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cock, P.J.; Antao, T.; Chang, J.T.; Chapman, B.A.; Cox, C.J.; Dalke, A.; Friedberg, I.; Hamelryck, T.; Kauff, F.; Wilczynski, B.; et al. Biopython: Freely available Python tools for computational molecular biology and bioinformatics. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1422–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, A.; Hoover, P.; Rougemont, J. A rapid bootstrap algorithm for the RAxML Web servers. Syst. Biol. 2008, 57, 758–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schomburg, I.; Chang, A.; Ebeling, C.; Gremse, M.; Heldt, C.; Huhn, G.; Schomburg, D. BRENDA, the enzyme database: Updates and major new developments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, D431–D433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M. KEGG as a reference resource for gene and protein annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D457–D462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houghton, J.; Townsend, C.; Williams, A.R.; Rodgers, A.; Rand, L.; Walker, K.B.; Böttger, E.C.; Springer, B.; Davis, E.O. Important role for Mycobacterium tuberculosis UvrD1 in pathogenesis and persistence apart from its function in nucleotide excision repair. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 2916–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.W.; Faisal, S.M.; Chandra, S.; McDonough, S.P.; Moreira, M.A.; Scaria, J.; Chang, C.F.; Bannantine, J.P.; Akey, B.; Chang, Y.F. Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of the Mycobacterium avium subsp paratuberculosis attenuated mutants against challenge in a mouse model. Vaccine 2012, 30, 3015–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Selby, C.P.; Adar, S.; Adebali, O.; Sancar, A. Molecular mechanisms and genomic maps of DNA excision repair in Escherichia coli and humans. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 15588–15597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bijlsma, J.J.; Lie-A-Ling, M.; Nootenboom, I.C.; Vandenbroucke-Grauls, C.M.; Kusters, J.G. Identification of loci essential for the growth of Helicobacter pylori under acidic conditions. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 182, 1566–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, S.A.; Blaser, M.J. Isolation of the Helicobacter pylori recA gene and involvement of the recA region in resistance to low pH. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 2185–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, M.N.; Ferguson, R.J.; Li, Y.H.; Cvitkovitch, D.G. uvrA is an acid-inducible gene involved in the adaptive response to low pH in Streptococcus mutans. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 5964–5973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeb, A.T.M.; Al-Rubeaan, K.A.; Mani, B.; Tayeb, H.T. Osteomyelitis infection caused by Arcanobacterium haemolyticum in a diabetic patient: A first case report. IDCases 2021, 24, e01139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Gorski, L.; Reynolds, J.; Orozco, E.; Fielding, S.; Park, Y.H.; Borucki, M.K. Role of uvrA in the growth and survival of Listeria monocytogenes under UV radiation and acid and bile stress. J. Food Prot. 2006, 69, 3031–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, F.; Khanduja, J.S.; Bortoluzzi, A.; Houghton, J.; Sander, P.; Güthlein, C.; Davis, E.O.; Springer, B.; Böttger, E.C.; Relini, A.; et al. The biological and structural characterization of Mycobacterium tuberculosis UvrA provides novel insights into its mechanism of action. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 7316–7328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambir, M.; Ivanova, L.B.; Bryksin, A.V.; Godfrey, H.P.; Cabello, F.C. Functional analysis of Borrelia burgdorferi uvrA in DNA damage protection. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2011, 317, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, R.L.; Gunn, A.J.; Stephen, C.P.; Ip, H.; Brookes, V.J. Assessment of uterine luminal pH in mares and the effect of dilute vinegar lavage on uterine luminal pH and endometrial health. Theriogenology 2018, 117, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, H.J.; Pearce, D.M.; Glenn, S.; Taylor, C.M.; Kuhn, M.; Sonenshein, A.L.; Andrew, P.W.; Roberts, I.S. Characterization of relA and codY mutants of Listeria monocytogenes: Identification of the CodY regulon and its role in virulence. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 63, 1453–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, S.M.; Chen, J.W.; Yan, F.; Chen, T.T.; Useh, N.M.; Yan, W.; Guo, S.; Wang, S.J.; Glaser, A.L.; McDonough, S.P.; et al. Evaluation of a Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis leuD mutant as a vaccine candidate against challenge in a caprine model. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2013, 20, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khare, S.; Hondalus, M.K.; Nunes, J.; Bloom, B.R.; Garry Adams, L. Mycobacterium bovis DeltaleuD auxotroph-induced protective immunity against tissue colonization, burden and distribution in cattle intranasally challenged with Mycobacterium bovis Ravenel S. Vaccine 2007, 25, 1743–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patton, T.G.; Rice, K.C.; Foster, M.K.; Bayles, K.W. The Staphylococcus aureus cidC gene encodes a pyruvate oxidase that affects acetate metabolism and cell death in stationary phase. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 56, 1664–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Moussa, S.H.; Targy, N.M.; Bose, J.L.; George, N.M.; Gries, C.; Lopez, H.; Zhang, L.; Bayles, K.W.; Young, R.; et al. Active Bax and Bak are functional holins. Genes. Dev. 2011, 25, 2278–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.J.; Qu, M.D.; Roberts, E.; Burne, R.A.; Rice, K.C. Identification of the Streptococcus mutans LytST two-component regulon reveals its contribution to oxidative stress tolerance. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, A.; Kambara, K.; Meyer, H.; Stenz, L.; Bonetti, E.J.; Girard, M.; Lalk, M.; Francois, P.; Schrenzel, J. GdpS contributes to Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation by regulation of eDNA release. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 304, 284–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matson, E.G.; Thompson, M.G.; Humphrey, S.B.; Zuerner, R.L.; Stanton, T.B. Identification of genes of VSH-1, a prophage-like gene transfer agent of Brachyspira hyodysenteriae. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 5885–5892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, A.S.; Zhaxybayeva, O.; Beatty, J.T. Gene transfer agents: Phage-like elements of genetic exchange. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Han-Large | Stan-Large | Stan-Small | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Annotated Genome Features | |||
| CDS | 3234 | 2941 | 2399 |
| Repeat regions | 67 | 85 | 53 |
| tRNA | 46 | 46 | 45 |
| rRNA | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Partial CDS | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Protein Features | |||
| Hypothetical proteins | 1799 | 1614 | 1126 |
| Proteins with functional assignments | 1435 | 1327 | 1273 |
| Proteins with EC number assignments | 652 | 597 | 590 |
| Proteins with GO assignments | 552 | 507 | 493 |
| Proteins with pathway assignments | 474 | 436 | 421 |
| Proteins with PATRIC genus-specific family (PLfam) assignments | 732 | 704 | 654 |
| Proteins with PATRIC cross-genus family (PGfam) assignments | 1151 | 1073 | 973 |
| PGFam | Align. Score | Align. Length | Mean Sqr Freq | Prop Gaps | Product Used in the Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PGF_02704551 | 22.49 | 1601 | 0.562 | 0.171 | DNA-directed RNA polymerase beta’ subunit (EC 2.7.7.6) rpoB |
| PGF_10049811 | 18.27 | 1050 | 0.564 | 0.111 | Protein translocase subunit SecA |
| PGF_05195027 | 16.30 | 496 | 0.732 | 0.033 | ATP synthase beta chain (EC 3.6.3.14) atpB |
| PGF_09939762 | 13.87 | 593 | 0.570 | 0.149 | SSU ribosomal protein S1p |
| PGF_10149521 | 12.57 | 439 | 0.600 | 0.052 | Glucose-1-phosphate adenylyltransferase (EC 2.7.7.27) glgC |
| PGF_00421792 | 12.25 | 501 | 0.547 | 0.083 | DNA repair protein RadA |
| PGF_00007028 | 12.10 | 551 | 0.515 | 0.135 | Ribosome LSU-associated GTP-binding protein HflX |
| PGF_00007012 | 11.98 | 421 | 0.584 | 0.139 | GTP-binding and nucleic acid-binding protein YchF |
| PGF_01937476 | 11.83 | 756 | 0.430 | 0.211 | BioD-like N-terminal domain/Phosphate acetyltransferase (EC 2.3.1.8) PTA |
| PGF_03004613 | 10.20 | 488 | 0.462 | 0.107 | Histidyl-tRNA synthetase (EC 6.1.1.21) HisRS |
| PGF_00634936 | 10.17 | 412 | 0.501 | 0.153 | Protein QmcA (possibly involved in integral membrane quality control) QmcA |
| PGF_00912265 | 10.07 | 449 | 0.475 | 0.139 | tRNA-dihydrouridine synthase DusB |
| PGF_04505269 | 10.01 | 322 | 0.558 | 0.165 | SSU ribosomal protein S2p (SAe) |
| PGF_00016431 | 9.86 | 228 | 0.653 | 0.043 | LSU ribosomal protein L3p (L3e) |
| PGF_02390924 | 9.86 | 367 | 0.515 | 0.099 | 16S rRNA (cytosine(1402)-N(4))-methyltransferase (EC 2.1.1.199) rsmH |
| PGF_04521913 | 9.75 | 561 | 0.412 | 0.146 | UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-tripeptide--D-alanyl-D-alanine ligase (EC 6.3.2.10) murF |
| PGF_00049896 | 9.48 | 237 | 0.616 | 0.088 | SSU ribosomal protein S5p (S2e) |
| PGF_07063065 | 9.28 | 508 | 0.412 | 0.249 | Transcription termination protein NusA |
| PGF_06162930 | 9.16 | 581 | 0.380 | 0.181 | UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine--D-glutamate ligase (EC 6.3.2.9) murD |
| PGF_00419915 | 9.15 | 294 | 0.533 | 0.089 | 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate hydroxymethyltransferase (EC 2.1.2.11) panB |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ayalew, L.E.; Mekuria, Z.H.; Despres, B.; Saab, M.E.; Ojha, S. Genome Sequence Comparisons between Small and Large Colony Phenotypes of Equine Clinical Isolates of Arcanobacterium hippocoleae. Animals 2024, 14, 1609. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14111609
Ayalew LE, Mekuria ZH, Despres B, Saab ME, Ojha S. Genome Sequence Comparisons between Small and Large Colony Phenotypes of Equine Clinical Isolates of Arcanobacterium hippocoleae. Animals. 2024; 14(11):1609. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14111609
Chicago/Turabian StyleAyalew, Lisanework E., Zelalem H. Mekuria, Beatrice Despres, Matthew E. Saab, and Shivani Ojha. 2024. "Genome Sequence Comparisons between Small and Large Colony Phenotypes of Equine Clinical Isolates of Arcanobacterium hippocoleae" Animals 14, no. 11: 1609. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14111609
APA StyleAyalew, L. E., Mekuria, Z. H., Despres, B., Saab, M. E., & Ojha, S. (2024). Genome Sequence Comparisons between Small and Large Colony Phenotypes of Equine Clinical Isolates of Arcanobacterium hippocoleae. Animals, 14(11), 1609. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14111609





