Comparative Nutritional and Histological Analysis of Malabar Red Snapper (Lutjanus malabaricus) and Asian Seabass (Lates calcarifer)
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
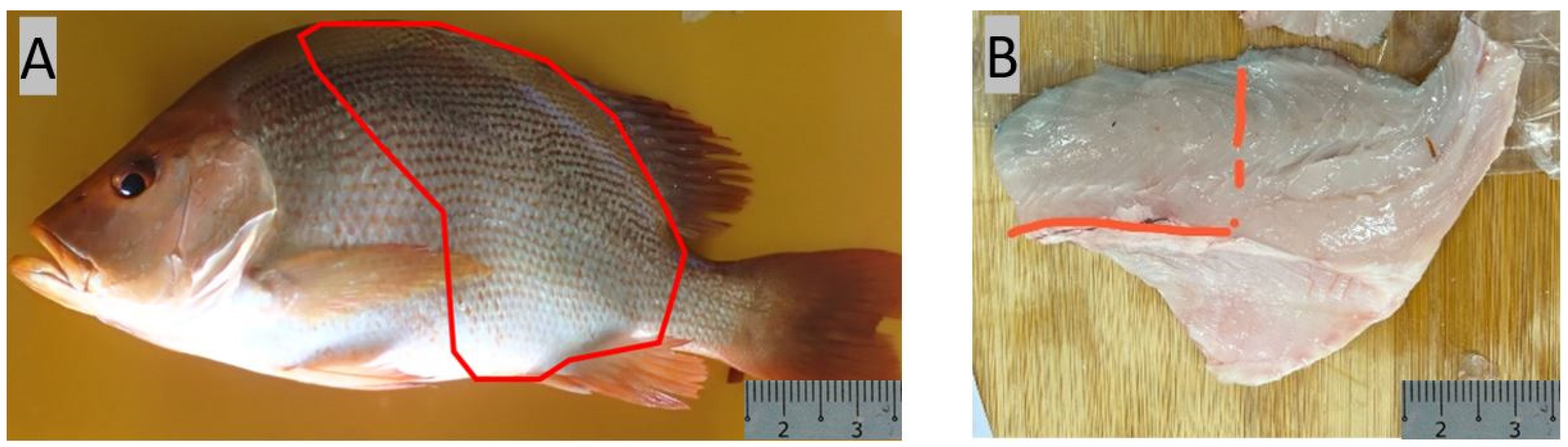
2.2. Sampling for Histological Analysis and Nutritional Profiling
2.3. Histological Analysis
2.4. Proximate Composition of Fish Fillet and Feed
2.4.1. Fillet Fatty Acid Extraction and Analysis
2.4.2. Fillet Moisture, Protein and Ash Analyses
2.4.3. Feed Crude Fat, Moisture, Protein and Ash Analyses
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
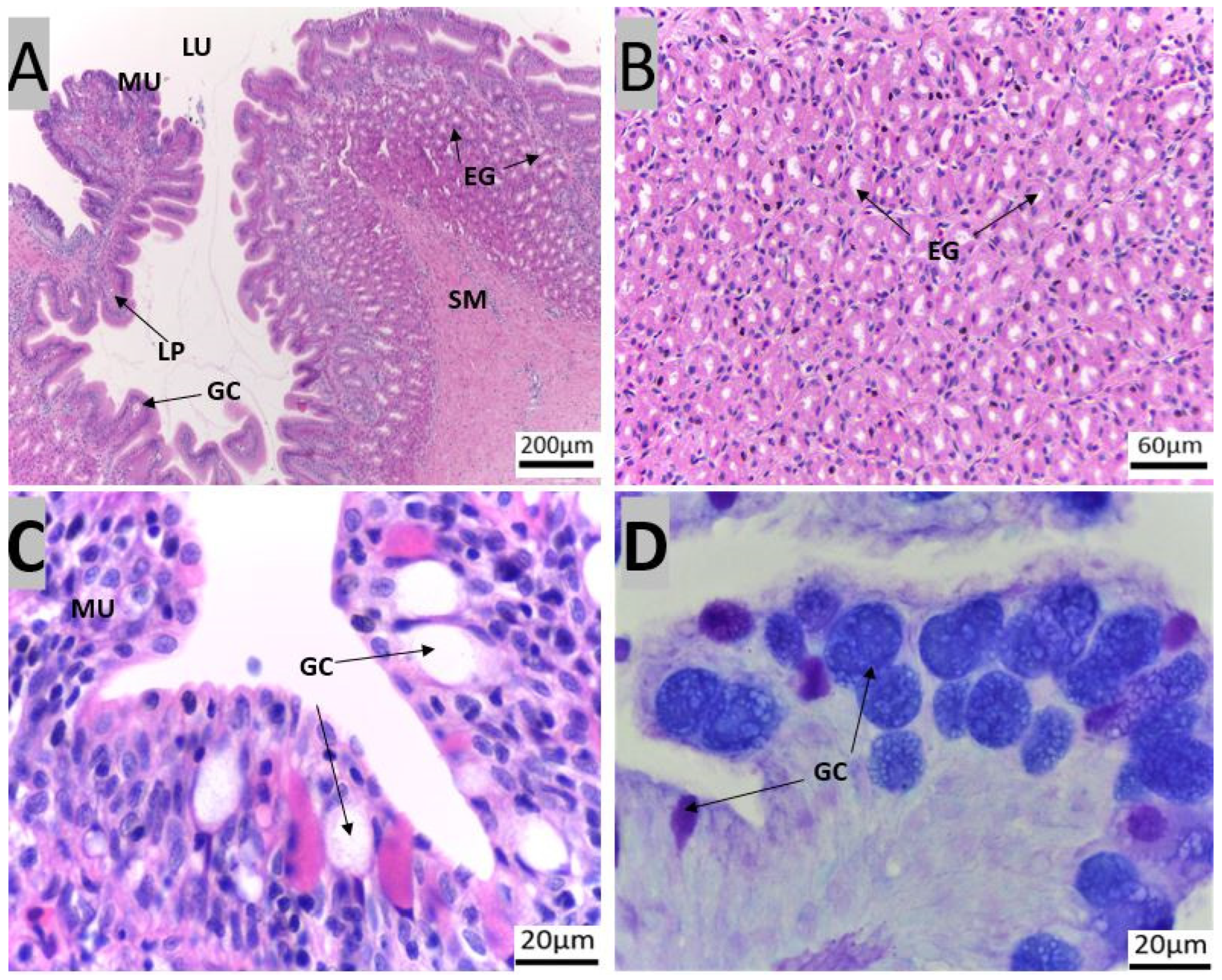
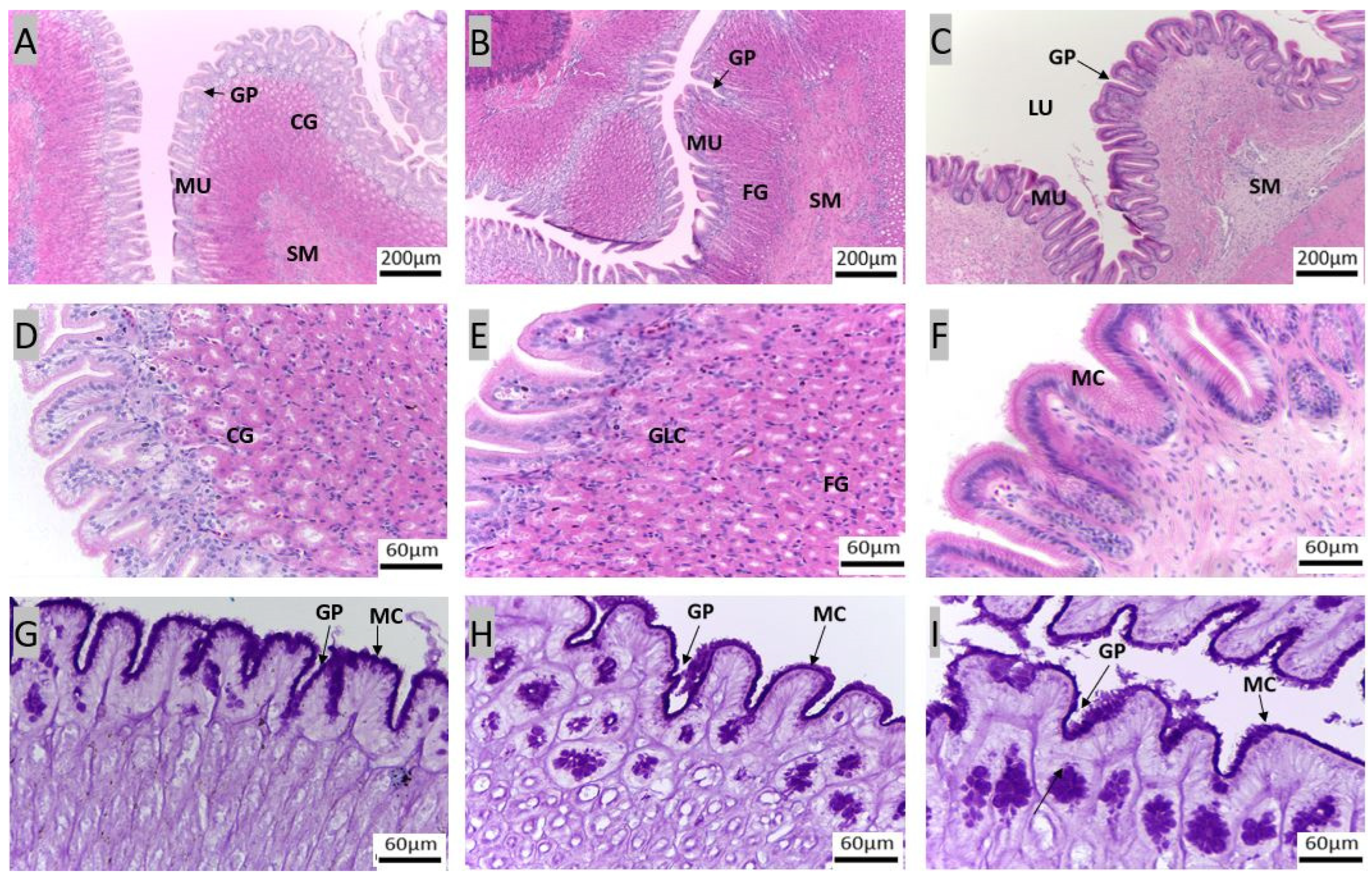
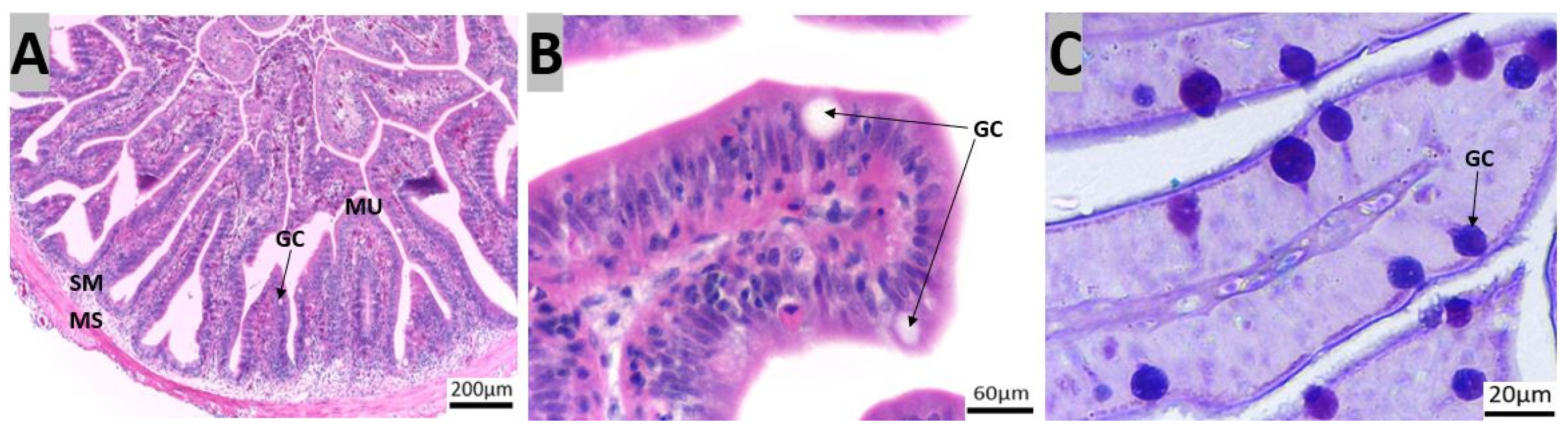
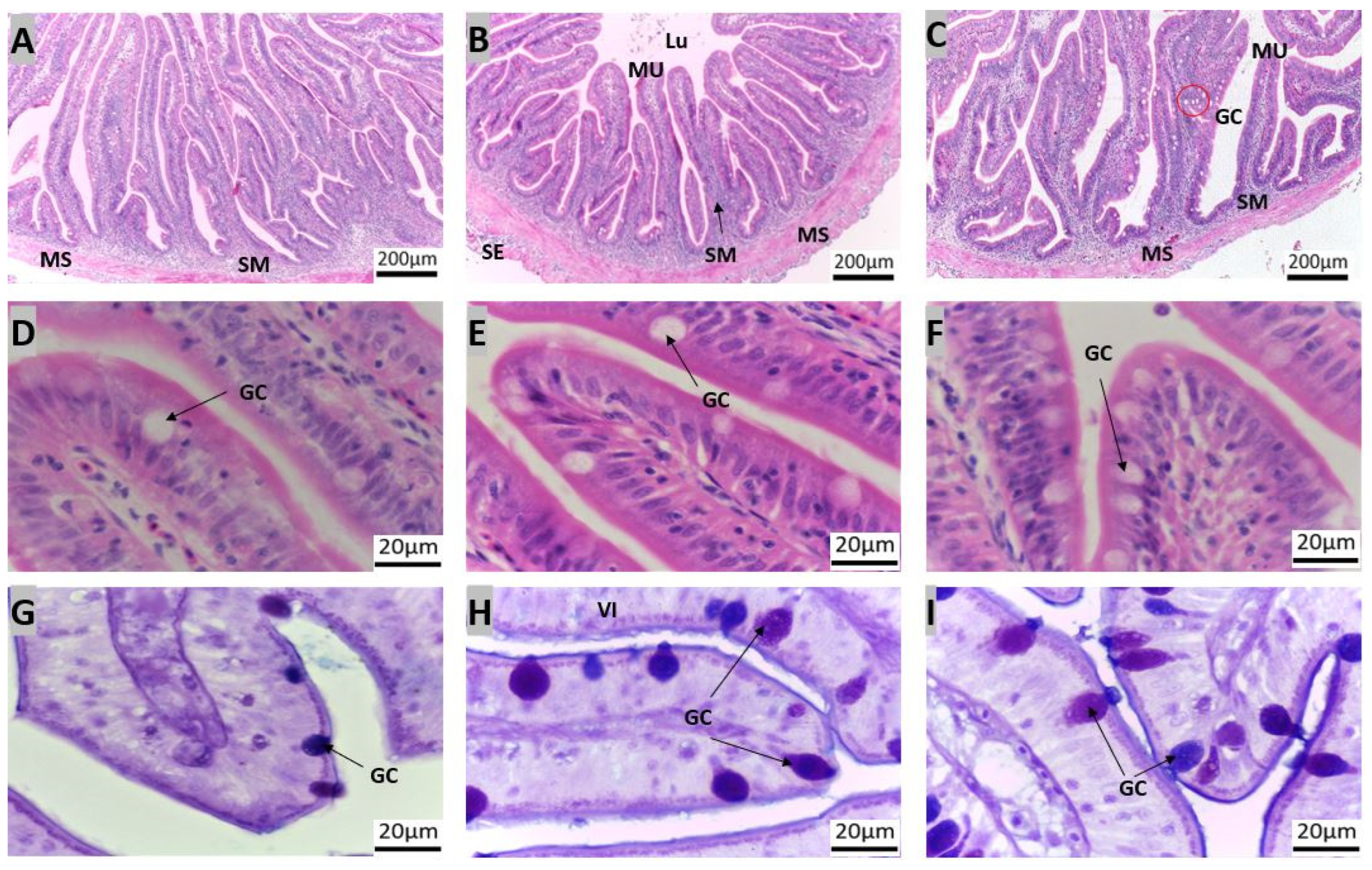
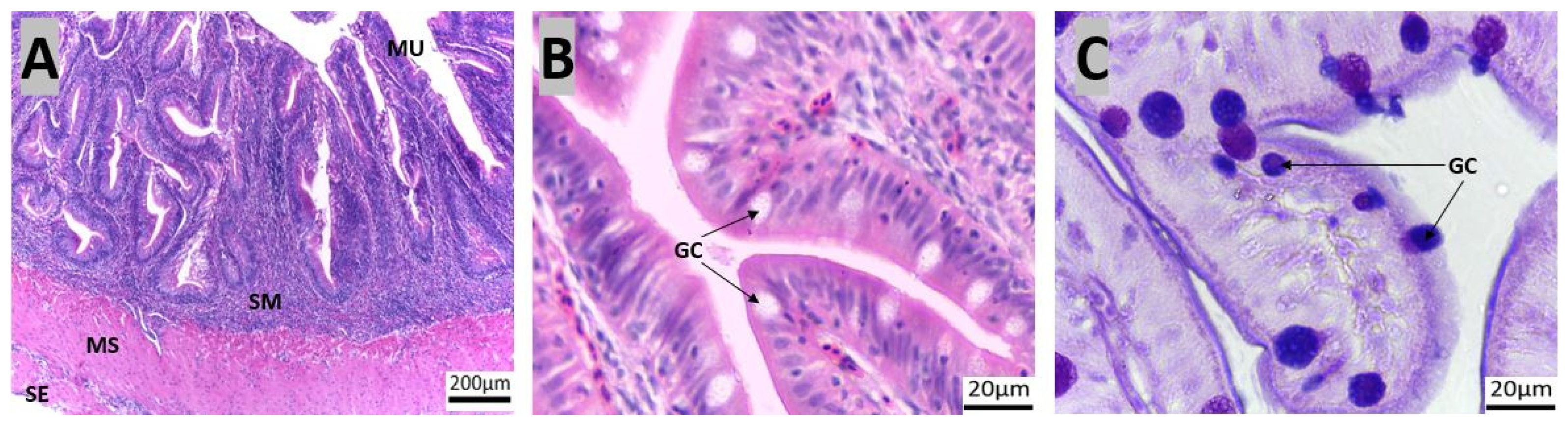
3.1. Morpho-Histological Analysis of the Gastrointestinal Tract of Red Snapper
3.2. Nutritional Profile Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Protective Components of the Gastrointestinal Tract of Red Snapper
4.2. Components of the Gastrointestinal Tract Crucial for Digestion and Nutrient Absorption
4.3. Fatty Acid Profile in the Fillet of Red Snapper
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022. Towards Blue Transformation; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vij, S.; Kuhl, H.; Kuznetsova, I.S.; Komissarov, A.; Yurchenko, A.A.; Van Heusden, P.; Singh, S.; Thevasagayam, N.M.; Prakki, S.R.; Purushothaman, K.; et al. Chromosomal-level assembly of the Asian Seabass genome using long sequence reads and multi-layered scaffolding. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1005954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vij, S.; Purushothaman, K.; Gopikrishna, G.; Lau, D.; Saju, J.M.; Shamsudheen, K.V.; Kumar, K.V.; Basheer, V.S.; Gopalakrishnan, A.; Hossain, M.S.; et al. Barcoding of Asian seabass across its geographic range provides evidence for its bifurcation into two distinct species. Front. Mar. Sci. 2014, 1, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vij, S.; Purushothaman, K.; Sridatta, P.S.R.; Jerry, D.R. Transcriptomic analysis of gill and kidney from Asian Seabass (Lates calcarifer) acclimated to different salinities reveals pathways involved with euryhalinity. Genes 2020, 11, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safiin, N.S.Z.; Ching, F.F.; Shapawi, R. Successful co-feeding of Asian Seabass, Lates calcarifer larvae with palm oil-based microdiets and live feeds. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2022, 6, 836275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durmus, M. Fish oil for human health: Omega-3 fatty acid profiles of marine seafood species. J. Food Technol. 2018, 39, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özogul, Y.; Özogul, F. Fatty acid profiles of commercially important fish species from the Mediterranean, Aegean and Black Seas. Food Chem. 2007, 100, 1634–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, R.M.; Petenuci, M.E.; Maistrovicz, F.C.; Galuch, M.B.; Montanher, P.F.; Pizzo, J.S.; Gualda, I.P.; Visentainer, J.V. Lipid profile and fatty acid composition of marine fish species from Northeast coast of Brazil. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 1177–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canan, B.; do Nascimento, W.S.; da Silva, N.B.; Chellappa, S. Morphohistology of the digestive tract of the damsel fish Stegastes fuscus (Osteichthyes: Pomacentridae). Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 787316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuthe, G.E.; Bhomela, B. Morphology, histology and histochemistry of the digestive tract of the Banded tilapia, Tilapia sparrmanii (Perciformes: Cichlidae). Zoologia 2021, 37, e51043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moawad, U.K.; Awaad, A.S.; Tawfiek, M.G. Histomorphological, histochemical, and ultrastructural studies on the stomach of the adult African catfish (Clarias gariepinus). J. Microsc. Ultrastruct. 2017, 5, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raji, A.r.; Norouzi, E. Histological and histochemical study on the alimentary canal in Walking catfish (Claris batrachus) and piranha (Serrasalmus nattereri). Iran. J. Vet. Med. 2010, 11, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOAA. Red Snapper. 2024. Available online: https://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/species/red-snapper (accessed on 22 January 2024).
- Ngoh, S.Y.; Tan, D.; Shen, X.; Kathiresan, P.; Jiang, J.; Liew, W.C.; Thevasagayam, N.M.; Kwan, H.Y.; Saju, J.M.; Prakki, S.R.; et al. Nutrigenomic and nutritional analyses reveal the effects of pelleted feeds on Asian Seabass (Lates calcarifer). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Kamath, S. Comparative anatomy of digestive system of some commercially important fishes. Online Int. Interdiscip. Res. J. 2014, IV. [Google Scholar]
- Nasruddin, N.S.; Azmai, M.N.; Ismail, A.; Saad, M.Z.; Daud, H.M.; Zulkifli, S.Z. Histological features of the gastrointestinal tract of wild Indonesian shortfin eel, Anguilla bicolor bicolor (McClelland, 1844), captured in Peninsular Malaysia. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 312670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhukova, K.; Stroganov, A.N. Anatomy of the digestive system of lumpfish (Cyclopterus lumpus) as an adaptation to puffing behavior. Anat. Rec. 2022, 305, 1732–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alabssawy, A.N.; Khalaf-Allah, H.M.M.; Gafar, A.A. Anatomical and histological adaptations of digestive tract in relation to food and feeding habits of lizardfish, Synodus variegatus (Lacepède, 1803). Egypt J. Aquat. Res. 2019, 45, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purushothaman, K.; Lau, D.; Saju, J.M.; Musthaq Sk, S.; Lunny, D.P.; Vij, S.; Orbán, L. Morpho-histological characterisation of the alimentary canal of an important food fish, Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer). PeerJ 2016, 4, e2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, A.; Tao, S.; Goh, Y.J.; Chaganty, V.; See, K.; Purushothaman, K.; Orbán, L.; Mathuru, A.S.; Wohland, T.; Winkler, C. A Neurexin2aa deficiency results in axon pathfinding defects and increased anxiety in zebrafish. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2021, 29, 3765–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purushothaman, K.; Tan, J.K.H.; Lau, D.; Saju, J.M.; Thevasagayam, N.M.; Wee, C.L.; Vij, S. Feed restriction modulates growth, gut morphology and gene expression in Zebrafish. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itani, K.; Marcussen, C.; Rocha, S.D.C.; Kathiresan, P.; Mydland, L.T.; Press, C.M.; Xie, Z.; Tauson, A.H.; Øverland, M. Effect of Cyberlindnera jadinii yeast on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, and gut health of broiler chickens from 1 to 34 d of age. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 103127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, S.D.C.; Morales-Lange, B.; Montero, R.; Teklay Okbayohanese, D.; Kathiresan, P.; McLean Press, C.; Torunn Mydland, L.; Øverland, M. Norway spruce extracts (NSEs) as bioactive compounds in novel feeds: Effect on intestinal immune-related biomarkers, morphometry and microbiota in Atlantic salmon pre-smolts. J. Funct. Foods 2023, 111, 105888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooft, J.M.; Montero, R.; Morales-Lange, B.; Blihovde, V.F.; Purushothaman, K.; Press, C.M.; Mensah, D.D.; Agboola, J.O.; Javed, S.; Mydland, L.T.; et al. Paecilomyces variotii (PEKILO®) in novel feeds for Atlantic salmon: Effects on pellet quality, growth performance, gut health, and nutrient digestibility and utilization. Aquaculture 2024, 589, 740905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Fallon, J.V.; Busboom, J.R.; Nelson, M.L.; Gaskins, C.T. A direct method for fatty acid methyl ester synthesis: Application to wet meat tissues, oils, and feedstuffs. J. Anim. Sci. 2007, 85, 1511–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sáez-Plaza, P.; Navas, M.J.; Wybraniec, S.; Michałowski, T.; Asuero, A.G. An Overview of the Kjeldahl Method of Nitrogen Determination. Part II. Sample Preparation, Working Scale, Instrumental Finish, and Quality Control. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2013, 43, 224–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horwitz, W.; Latimer, G.W. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 18th ed.; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hayden, B.; Palomares, M.L.D.; Smith, B.E.; Poelen, J.H. Biological and environmental drivers of trophic ecology in marine fishes—A global perspective. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, F.; Zhang, L.; Limbu, S.M.; Yin, H.; Xie, Y.; Yang, Z.; Shang, Z.; Kong, L.; Rong, H. A comparison of digestive strategies for fishes with different feeding habits: Digestive enzyme activities, intestinal morphology, and gut microbiota. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 13, e10499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aragão, C.; Gonçalves, A.T.; Costas, B.; Azeredo, R.; Xavier, M.J.; Engrola, S. Alternative Proteins for Fish Diets: Implications beyond Growth. Animals 2022, 12, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geyikoglu, F.; Vuraler, Ö.; Temelli, A. Histological, histochemical and ultrastructural investigations on the esophagus of juvenile Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Turk. J. Zool. 2004, 28, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, A.P.C.; Pereira, R.T.; Rosa, P.V. Morphology of the digestive system in carnivorous freshwater dourado Salminus brasiliensis. J. Fish. Biol. 2021, 99, 1222–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, H.M.; Wright, G.M.; Goff, G.P. A study of the posterior esophagus in the winter flounder, Pleuronectes americanus, and the yellowtail flounder, Pleuronectes ferruginea: Morphological evidence for pregastric digestion? Can. J. Zool. 1994, 72, 1191–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Hernández, M.P.; Lozano, M.T.; Elbal, M.T.; Agulleiro, B. Development of the digestive tract of sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L). Light and electron microscopic studies. Anat. Embryol. 2001, 204, 39–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbal, M.T.; García Hernández, M.P.; Lozano, M.T.; Agulleiro, B. Development of the digestive tract of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.). Light and electron microscopic studies. Aquaculture 2004, 234, 215–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrassón, M.; Grau, A.; Dopazo, L.R.; Crespo, S. A histological, histochemical and ultrastructural study of the digestive tract of Dentex dentex (Pisces, Sparidae). Histol. Histopathol. 2006, 21, 579–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahlmann, C.; Gu, J.; Kortner, T.M.; Lein, I.; Krogdahl, Å.; Bakke, A.M. Ontogeny of the digestive system of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.) and effects of soybean meal from start-feeding. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Bailey, D.; Yang, P.; Kim, E.; Que, J. The development and stem cells of the esophagus. Development 2021, 148, dev.193839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Beasley, A.; Hu, Y.; Chen, X. A Zebrafish model for studies on esophageal epithelial biology. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, G.C. Mucins and the Microbiome. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2020, 89, 769–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, M.R.F.; de Oliveira Souza, H.; de Souza, V.L.; de Azevedo, A.; Goitein, R.; Nobre, A.D. Morphological and anatomical characterization of the digestive tract of Centropomus parallelus and C. undecimalis. Acta Sci. Biol. Sci. 2013, 35, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.H. The Esophageal Squamous Epithelial Cell-Still a Reasonable Candidate for the Barrett’s Esophagus Cell of Origin? Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 4, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marco, G.; Cappello, T.; Maisano, M. Histomorphological Changes in Fish Gut in Response to Prebiotics and Probiotics Treatment to Improve Their Health Status: A Review. Animals 2023, 13, 2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bocina, I.; ŠantiĆ, Ž.; RestoviĆ, I.; TopiĆ, S. Histology of the digestive system of the garfish Belone belone (Teleostei: Belonidae). Eur. Zool. J. 2017, 84, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, H.T.; Shao, X.; Krogdahl, Å.; Kortner, T.M.; Lein, I.; Kousoulaki, K.; Lie, K.K.; Sæle, Ø. Intestinal function of the stomachless fish, ballan wrasse (Labrus bergylta). Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjakasy, J.M.; Day, R.D.; Kemp, A.; Tibbetts, I.R. Functional morphology of digestion in the stomachless, piscivorous needlefishes Tylosurus gavialoides and Strongylura leiura ferox (Teleostei: Beloniformes). J. Morphol. 2009, 270, 1155–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Løkka, G.; Austbø, L.; Falk, K.; Bjerkås, I.; Koppang, E.O. Intestinal morphology of the wild Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). J. Morphol. 2013, 274, 859–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.J.; Wang, W.M. Histology and mucin histochemistry of the digestive tract of yellow catfish, Pelteobagrus fulvidraco. Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2009, 38, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.K.; Chakrabarti, P. Histological, surface ultrastructural, and histochemical study of the stomach of red piranha, Pygocentrus nattereri (Kner). Fish. Aquat. Life 2015, 23, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, J.; Smyth, H.D.C.; Ghosh, D. Physicochemical properties of mucus and their impact on transmucosal drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 532, 555–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørensen, S.L.; Ghirmay, A.; Gong, Y.; Dahle, D.; Vasanth, G.; Sørensen, M.; Kiron, V. Growth, chemical composition, histology and antioxidant genes of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) fed whole or pre-processed nannochloropsis oceanica and Tetraselmis sp. Fishes 2021, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buddington, R.K.; Diamond, J.M. Aristotle revisited: The function of pyloric caeca in fish. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 8012–8014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refstie, S.; Landsverk, T.; Bakke-McKellep, A.M.; Ringø, E.; Sundby, A.; Shearer, K.D.; Krogdahl, Å. Digestive capacity, intestinal morphology, and microflora of 1-year and 2-year old Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) fed standard or bioprocessed soybean meal. Aquaculture 2006, 261, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, D.M.; Xie, C.X.; Zhang, H.J.; Liu, H.P. Digestive enzymes along digestive tract of a carnivorous fish Glyptosternum maculatum (Sisoridae, Siluriformes). J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2011, 95, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resende, A.C.; Severo-Neto, F.; Carvalho, F.R. Diet composition, conditionfactor and intestinal coefficient of the fish Astyanax lineatus reflect the anthropogenic effects on streams in central Brazil. Oecol. Aust. 2022, 26, 592–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.L.d.; Arantes, F.P.; Pessali, T.C.; Santos, J.E.d. Morphological, Histological and Histochemical Analysis of the Digestive Tract of Trachelyopterusstriatulus (Siluriformes: Auchenipteridae); Sociedade Brasileira de Zoologia: Curitiba, Brazil, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Weatherley, A.H.; Gill, H.S.; Casselman, J.M. The Biology of Fish Growth; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Breccia, A.; Palmieri, M.-A.; Di-Yorio, M.-P.; Battista, A.-G.; Vissio, P.-G.; Pérez-Sirkin, D.-I. Anatomy and histology of the digestive tract and immunolocalization of Npy in the fish Cichlasoma dimerus (Cichliformes: Cichlidae). Rev. Biol. Trop. 2022, 70, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarasquete, C.; Gisbert, E.; Ribeiro, L.; Vieira, L.; Dinis, M.T. Glyconjugates in epidermal, branchial and digestive mucous cells and gastric glands of gilthead sea bream, Sparus aurata, Senegal sole, Solea senegalensis and Siberian sturgeon, Acipenser baeri development. Eur. J. Histochem. 2001, 45, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yashpal, M.; Kumari, U.; Mittal, S.; Mittal, A.K. Histochemical characterization of glycoproteins in the buccal epithelium of the catfish, Rita rita. Acta Histochem. 2007, 109, 285–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krogdahl, Å.; Sundby, A.; Holm, H. Characteristics of digestive processes in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Enzyme pH optima, chyme pH, and enzyme activities. Aquaculture 2015, 449, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Du, J.; Lam, S.H.; Mathavan, S.; Matsudaira, P.; Gong, Z. Morphological and molecular evidence for functional organization along the rostrocaudal axis of the adult zebrafish intestine. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, R.T.; Nebo, C.; de Paula Naves, L.; Fortes-Silva, R.; Regina Cardoso de Oliveira, I.; Paulino, R.R.; Drummond, C.D.; Rosa, P.V. Distribution of goblet and endocrine cells in the intestine: A comparative study in Amazonian freshwater Tambaqui and hybrid catfish. J. Morphol. 2020, 281, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, D.M.; Abd-Elhafez, E.A.; Hassan, A.H. Histology, histochemistery and surface architecture of the rectum of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). J. Adv. Microsc. 2017, 12, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, K.A.; Mohamed, A.Z.; Jamilah, B. Fatty acids in fish and beef and their nutritional values: A review. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2009, 7, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Carta, G.; Murru, E.; Banni, S.; Manca, C. Palmitic acid: Physiological role, metabolism and nutritional implications. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, T.; Amalina, R.; Bachok, Z. Variation in fatty acid composition of the bigeye snapper Lutjanus lutjanus collected in coral reef habitats of the Malaysian South China Sea. J. Biol. Res. 2015, 22, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, M.D.; Kitts, D.D. Evaluating nutritional quality of pacific fish species from fatty acid signatures. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahena, F.; Zaidul, I.; Jinap, S.; Saari, N.; Jahurul, H.; Abbas, K.; Norulaini, N. PUFAs in fish: Extraction, fractionation, importance in health. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2009, 8, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dighriri, I.M.; Alsubaie, A.M.; Hakami, F.M.; Hamithi, D.M.; Alshekh, M.M.; Khobrani, F.A.; Dalak, F.E.; Hakami, A.A.; Alsueaadi, E.H.; Alsaawi, L.S.; et al. Effects of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Brain Functions: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e30091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, I.J.; Eilertsen, K.E.; Otnæs, C.H.A.; Mæhre, H.K.; Elvevoll, E.O. An update on the content of fatty acids, dioxins, PCBs and heavy metals in farmed, escaped and wild Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) in Norway. Foods 2020, 9, 1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chee, W.-L.; Turchini, G.M.; Teoh, C.-Y.; Ng, W.-K. Dietary arachidonic acid and the impact on growth performance, health and tissues fatty acids in Malabar red snapper (Lutjanus malabaricus) fingerlings. Aquaculture 2020, 519, 734757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recommendations, N.N. Fat and Fatty Acids. 2023. Available online: https://pub.norden.org/nord2023-003/fat-and-fatty-acids.html (accessed on 22 January 2023).
- Ahmed, I.; Jan, K.; Fatma, S.; Dawood, M.A.O. Muscle proximate composition of various food fish species and their nutritional significance: A review. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 106, 690–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emmanuel, B.; Oshionebo, C.; Aladetohun, N. Comparative analysis of the proximate compositions of Tarpon atlanticus and Clarias gariepinus from culture systems in South-Western Nigeria. Afr. J. Food Agric. Nutr. Dev. 2011, 11, 5344–5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayanda, I.O.; Ekhator, U.I.; Bello, O.A. Determination of selected heavy metal and analysis of proximate composition in some fish species from Ogun River, Southwestern Nigeria. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Species | Body Weight (BW) g | Standard Length (SL) cm | Total Length (TL) cm | Intestinal Length (IL) cm | Intestinal Coefficient (IC) cm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Red Snapper | 52.09 ± 6.45 | 12.00 ± 0.73 | 14.07 ± 0.92 | 15.41 ± 2.27 | 1.29 ± 0.17 |
| Asian Seabass | 15.30 ± 3.30 | 7.80 ± 0.86 | 9.60 ± 1.00 | 8.90 ± 0.90 | 1.14 ± 0.04 |
| Organ | Region | Goblet Cell Number |
|---|---|---|
| Intestine | Anterior | 197 ± 15 a |
| Mid | 254 ± 16 b | |
| Posterior | 334 ± 30 c | |
| Rectum | 507 ± 24 d |
| RS | ASB | RS | ASB | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nutrient Composition | Mean | Mean | SD | SD |
| % in dry matter | ||||
| Moisture | 6.80 | 8.83 | 3.74 | 0.60 |
| Crude protein | 24.6 | 23.5 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Ash R | 6.23 | 4.92 | 0.26 | 0.42 |
| Fatty acid composition (% of total fatty acids) | ||||
| Methyl butyric acid C4:0 R | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.00 |
| Methyl hexanoic acid C6:0 A | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Methyl octanoic acid C8:0 A | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| Methyl lauric acid C12:0 A | 0.16 | 0.33 | 0.02 | 0.04 |
| Methyl tridecanoic C13 R | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| Methyl myristic acid C14:0 R | 2.24 | 1.72 | 0.22 | 0.26 |
| Methyl pentadecanoic acid C15:0 R | 0.24 | 0.20 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| Methyl palmitic acid C16:0 | 23.03 | 22.88 | 0.47 | 0.59 |
| Methyl heptadecanoic acid C17:0 R | 0.33 | 0.26 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| Methyl stearic acid C18:0 | 8.55 | 9.33 | 0.51 | 0.52 |
| Methyl arachidic acid C20:0 R | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| Methyl heneicosanoic acid C21:0 R | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Methyl behenic acid C22:0 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Methyl lignoceric acid C24:0 R | 0.12 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.01 |
| ƩSFA | 35.19 | 35.17 | 1.38 | 1.51 |
| Methyl myristoleic acid C14:1 R | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Methyl cis-10 pentadecenoic acid C15:1 A | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.01 |
| Methyl palmitoleic acid C16:1 R | 2.92 | 2.43 | 0.26 | 0.32 |
| Methyl cis-10 heptadecenoic acid C17:1 A | 0.04 | 0.19 | 0.05 | 0.00 |
| Methyl trans-9 eladic acid C18:1n9t | 0.36 | 0.40 | 0.04 | 0.02 |
| Methyl cis-9 oleic acid C18:1n9c A | 21.76 | 24.40 | 0.93 | 1.22 |
| Methyl cis-11-eicosenoic acid C20:1n9 R | 0.32 | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| Methyl erucic acid C22:1n9 R | 0.11 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Methyl nervonic acid C24:1n9 | 0.39 | 0.18 | 0.01 | 0.08 |
| ƩMUFA | 25.96 | 27.86 | 1.33 | 1.70 |
| Methyl linolelaidic acid C18:2n6t | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Methyl linoleic acid C18:2n6c R | 15.25 | 13.10 | 0.35 | 1.13 |
| Methyl gamma-linolenic acid C18:3n6 A | 0.22 | 0.55 | 0.02 | 0.12 |
| Methyl alpha-linolenic acid C18:3n3 R | 0.93 | 0.76 | 0.07 | 0.09 |
| Methyl cis-11,14-eicosadienoic acid C20:2 R | 0.75 | 0.53 | 0.03 | 0.04 |
| Methyl cis-8,11,14-eicosatrienoic acid C20:3n6 A | 0.38 | 0.78 | 0.02 | 0.18 |
| Methyl cis-11,14,17-eicosatrienoic acid C20:3n3 R | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| Methyl cis-5, 8, 11, 14-eicosatetraenoic acid C20:4n6 A | 2.74 | 3.68 | 0.29 | 0.49 |
| Methyl cis-13, 16- docosadienoic acid C22:2 R | 0.26 | 0.19 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| Methyl cis-5, 8, 11, 14, 17-eicosapentaenoic acid C20:5n3 | 2.97 | 2.80 | 0.15 | 0.29 |
| Methyl cis-4, 7, 10, 13, 16,19-docosahexaenoic acid C22:6n3 | 13.42 | 11.24 | 1.27 | 1.65 |
| ƩPUFA | 36.98 | 33.67 | 2.24 | 4.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Purushothaman, K.; Ho Jia Wen, R.; bin Mohamed, M.H.; Rwei Qing, S.D.T.; Heng Wuan, L.; Liang, B.; Thanh Vu, N.; Voigtmann, M.; McLean Press, C.; Loo, G.; et al. Comparative Nutritional and Histological Analysis of Malabar Red Snapper (Lutjanus malabaricus) and Asian Seabass (Lates calcarifer). Animals 2024, 14, 1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14121803
Purushothaman K, Ho Jia Wen R, bin Mohamed MH, Rwei Qing SDT, Heng Wuan L, Liang B, Thanh Vu N, Voigtmann M, McLean Press C, Loo G, et al. Comparative Nutritional and Histological Analysis of Malabar Red Snapper (Lutjanus malabaricus) and Asian Seabass (Lates calcarifer). Animals. 2024; 14(12):1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14121803
Chicago/Turabian StylePurushothaman, Kathiresan, Rachel Ho Jia Wen, Muhammad Hazim bin Mohamed, Saraphina Dianne Tneo Rwei Qing, Lee Heng Wuan, Bing Liang, Nguyen Thanh Vu, Michael Voigtmann, Charles McLean Press, Grace Loo, and et al. 2024. "Comparative Nutritional and Histological Analysis of Malabar Red Snapper (Lutjanus malabaricus) and Asian Seabass (Lates calcarifer)" Animals 14, no. 12: 1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14121803
APA StylePurushothaman, K., Ho Jia Wen, R., bin Mohamed, M. H., Rwei Qing, S. D. T., Heng Wuan, L., Liang, B., Thanh Vu, N., Voigtmann, M., McLean Press, C., Loo, G., Bisa, S., Domingos, J. A., Jerry, D. R., & Vij, S. (2024). Comparative Nutritional and Histological Analysis of Malabar Red Snapper (Lutjanus malabaricus) and Asian Seabass (Lates calcarifer). Animals, 14(12), 1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14121803






