Simple Summary
Many transitions of sex determination and sex chromosomes are found in amphibians. However, there is still controversy about how frequently such transitions have occurred. We carried out genotyping-by-sequencing and bioinformatics analyses on two closely related frogs (Nanorana quadranus and Quasipaa yei). The results show that both species involve male heterogamety concerning chromosome 1 and suggest that this chromosome would have been independently co-opted for sex determination in deeply divergent groups of anurans.
Abstract
Sex determination is remarkably diverse, with frequent transitions between sex chromosomes, in amphibians. Under these transitions, some chromosomes are more likely to be recurrently co-opted as sex chromosomes, as they are often observed across deeply divergent taxa. However, little is known about the pattern of sex chromosome evolution among closely related groups. Here, we examined sex chromosome and sex determination in two spiny frogs, Nanorana quadranus and Quasipaa yei. We conducted an analysis of genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) data from a total of 34 individuals to identify sex-specific makers, with the results verified by PCR. The results suggest that chromosome 1 is a homologous sex chromosome with an XY pattern in both species. This chromosome has been evolutionarily conserved across these closely related groups within a period of time. The DMRT1 gene is proposed to be implicated in homology across two distantly related spiny frog species as a putative candidate sex-determining gene. Harboring the DMRT1 gene, chromosome 1 would have been independently co-opted for sex determination in deeply divergent groups of anurans.
1. Introduction
In sharp contrast with mammals and birds, most amphibians are homomorphic with little-differentiated sex chromosomes in both sexes, and sex determination mechanisms are labile and diverse [1,2,3]. Indeed, most of the sex determination mechanisms reported in vertebrates, such as the XX/XY male heterogametic system in mammals and the ZZ/ZW female heterogametic system in birds, have been revealed in amphibians, and different sex-determination systems can even coexist in species of the same genus or in one species with different geographic populations [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11]. Some recent research explains this diversity by sex chromosome transition in which sex-determining genes are translocated or replaced by another gene from a different chromosome [12,13,14,15]. The sex-determining locus is often found on nonhomologous chromosomes in some closely related species, and it can even exhibit variation within a single species [8,16]. By placing the sex-determining systems for each species onto a phylogenetic tree, high frequency transitions have been detected in some clades of amphibians [17,18,19].
However, although sex chromosomes transitions have occurred multiple times in amphibians, they have not been randomly selected. Some empirical evidence indicates that some chromosomes seem to be recurrently co-opted (i.e., recruited) for sex chromosomes [20,21]. On the basis of sex linkage and karyotypic data, 7 out of all 13 pairs of chromosomes have been predicted to be candidate sex chromosomes (Chrs) in true frogs (i.e., Chrs 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, and 9) [22,23,24,25,26,27]. Jeffries et al. (2018) identified sex-determining system and sex chromosomes in 28 species of true frogs by using restriction-site associated DNA sequencing (RAD-seq) [18]. They found that at least 13 turnover events among 28 species. Of 13 events, only 5 pairs of chromosomes are used as sex chromosomes, with 3 of them having emerged multiple times as sex chromosomes, whereas other 2 chromosomes never appeared as such. In pipid frogs, at least seven independently evolved sex determination mechanisms have been described across both ZZ/ZW and XX/XY [28,29]. Coincidentally, there are also five pairs of chromosomes used as sex chromosomes in pipid frogs based on the genomic location of Xenopus tropicalis [29].
Why are some chromosomes more likely to be recurrently co-opted for sex chromosomes? One possible explanation is that they harbor a series of particular genes that play key roles in sex determination [30,31,32,33]. The DMW gene (DMRT1 paralog) identified in X. laevis was the only master sex determining gene known within the entire amphibian group [34]. Recently, the newly uncovered structural X/Y variation in the 5′-regulatory region of the BOD1L gene in Bufo viridis indicated a Y-specific candidate sex determination locus in amphibians [35]. Several sex-linked genes that have been linked to gonadal differentiation in different frogs have been identified on certain chromosomes [27,30,31,32,33]. Among the genes implicated in feminization, we find CYP19, SF1, FOXL2, SOX3, etc., while genes associated with masculinization include DMRT1, AMH, AR, CYP17, and so on. In frogs, these potential candidates with gene ontology related to sex determination/ sex differentiation, seemingly limited to few chromosomes out of the complement of 13 haploid sets, are DMRT1 and AMH on Chr 1; FGF9, AMHR2 and RSPO1 on Chr2; CYP19 and FOXL2 on Chr 3; SOX3, SF, and AR on Chr 7; and CYP17 on Chr 9 [19,27].
However, highly frequent transitions are limited to a few frog groups, mostly emerging across deeply divergent taxa like families or genera except across ranid and pipid species [18,29,36]. We need more data, especially between closely related groups to understand the pattern of sex chromosomes evolution in amphibians. Spiny frogs, belonging to the tribe Paini in the family Dicroglossidae, live mostly in swift boulder-strewn streams in the mountains of South and Southeast Asia. Most male frogs are characterized by keratinized spines on the chest, belly, or other parts of their bodies. This tribe consists of two main radiations, corresponding to the genera Nanorana and Quasipaa, which diverged 27 million years ago [37]. In this study, we identified sex-specific markers via genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) in two spiny frogs, Nanorana quadranus and Quasipaa yei, to investigate the sex chromosomes and sex-linkage genes. We used these spiny frog species to address two questions: (1) Is there homology between sex determination in these closely related genera? If yes, these chromosomes are evolutionarily conserved or recurrently co-opted? (2) Are there candidate sex-determining genes involved in homology? And here, are these particular genes evolutionarily conserved or not?
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Preparation
A combined sample of 15 individuals comprising 7 females and 8 males were collected for N. quadranus, whereas a total of 19 individuals consisting of 9 females and 10 males were collected for Q. yei in 2019 (Supplementary File S1). The physiological sex of samples was determined by their secondary sexual characteristics and histology. The swelled vent above the anus in adult males was thought to be a unique structure and a kind of secondary sexual characteristic in N. quadranus and Q. yei. In addition, keratinized spines near the anus are often found in adult males of Q. yei [38]. Muscular tissues were taken from both females and males and stored in 95% ethanol for subsequent analysis. Of these, 31 samples were used for PCR verification.
The frog sampling procedure was permitted and approved by the local ethics committee for Animal Care and Use Committee of Chengdu Institute of Biology (CIB), Chinese Academy of Sciences (Permit Number: CIB-2017009).
2.2. Genomic Library Preparation
Genomic DNA was isolated from muscle tissues using a Qiagen® DNeasy Blood and Tissue Kit (QIAGEN, Valencia, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions for animal tissue extraction. Briefly, the muscle tissues (500 mg) were frozen in liquid nitrogen, milled to powder, and then digested with proteinase K at 56 °C for 1 h. Genomic DNA was purified from 20 mg of tissue powder using a DNeasy Blood & Tissue Kit (QIAGEN, Valencia, CA, USA), and eluted in 100 µL of RNase-free water. Genomic libraries were constructed following Elshire et al. [39]. Initially, genomic DNA was digested with MseI restriction enzymes (New England Biolabs, NEB, Ipswich, MA, USA) at 37 °C, and individual barcodes were ligated to the restriction sites. Subsequently, the DNA samples were purified using a Gel Extraction Kit (QIAGEN, Valencia, CA, USA), and DNA fragments of approximately 300–350 bp were excised from agarose gels. Furthermore, the prepared library was sequenced on the Illumina NovaSeq6000 platform at Novogene Bioinformatics Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China (www.novogene.cn; accessed on 15 December 2019) using a 150 bp paired-end protocol. In the end, the original sequences, also known as raw data, were obtained.
2.3. Filtering and SNP Calling
The software package Stacks-2.41 was chosen for GBS data analysis due to its versatility and capacity to handle substantial de novo GBS datasets [40]. Initially, we employed the process_radtag tool within Stacks-2.41 to clean the raw GBS data, eliminating low-quality reads such as those missing the restriction site. Following this, we executed the de novo_map function of the Stacks program. In this stage, we utilized three critical parameters: the minimum depth of coverage (m, −m = 2), the maximum number of allowed mismatches within stacks (alleles) for an individual (M, −M = 2), and the maximum number of mismatches permitted between individuals (n, −n = 1).
2.4. Screening Sex-Linked Markers
Sex-linked markers are typically found on the heterogametic sex chromosome: Y-chromosome markers in species where males are heterogametic and W-chromosome markers in species where females are heterogametic. For screening sex-linked markers, particularly in the context of the XY sex-determination system, we used two approaches in accordance with Brelsford et al. [41]. The first approach is based on sex differences in heterozygosity. A locus was deemed sex-linked if it exhibited homozygosity in half of the females and heterozygosity in at least half of the male samples. The second approach is based on sex-specific loci that only appear in one sex. Loci are considered Y-specific if they are completely absent in females and present in at least half of males. It is important to note that these methods are generally reversed when applying them to species with a ZW sex-determination system. Additionally, we employed a bespoke R script, using R-4.1.1 (R Core Team 2022) [42,43], to identify sex-linked loci through association analysis of the output generated by Stacks.
2.5. Confirmation of Sex-Specific Markers
To eliminate false positives from the identified potential sex-linked markers, a two-step process was implemented. Initially, we used a Linux grep command to remove any putative sex-limited GBS tags that were present in the original read files of the opposite sex. Next, we utilized BLAST 2.12.0+ to further filter out false positives [44], creating a local BLAST database from the population.sample.fa file produced by Stacks. We then aligned the sex-linked loci identified by our R script to this database using BLAST 2.12.0+ [44]. Putative sex-linked loci with the highest match scores were considered significant and retained if their E-value was equal to or less than 1 × 10−10. For instance, in the context of the XY system, if a sex-linked locus aligned homogeneously with the female sequence and heterogeneously with the male sequence, it was considered a true positive and retained (the criteria were reversed for the ZW system).
2.6. PCR Validation
PCR and gel electrophoresis assays were designed for validating the confirmed sex-linked markers that were truly sex-linked. We designed two types of primers to perform PCR verification. Taking XY systems as an example, first, several reads exhibited multiple SNP sites. During primer design, both upstream and downstream primers were targeted at these two SNP sites, with the male SNP being designated as the first base at the 3′ end of the primer sequence. The second method involved designing primers based on male-specific sequences. Male-specific sequences refer to those that exist only in the male genome (Y chromosome). Therefore, by directly designing primers based on male-specific sequences, we amplified bands that are specific to males. The PCR products were separated by electrophoresis (1.5%), and we expected that a band could be seen in males rather than in females (see details in Figure S1).
2.7. Assigning Sex-Linked Markers onto Sex Chromosome
Based on the close phylogenetic relationships, the Quasipaa spinosa genome and the Nanorana parkeri genome were selected as the reference genomes [45,46]. We used the direct mapping method to determine the chromosomal location of sex-linked markers. The sex-linked markers were directly mapped to the reference genome using BLAST [44] to determine relative positions of the sex-linked markers on the reference genome. The top matches with e-values of no more than 1 × 10−10 were retained.
2.8. Predicting the Sex-Linked Markers Involved in Genes for Sex Determination
Amphibians have highly diverse sex-determining modes, but the molecular mechanisms of sex determination are still unclear. According to previous research, candidate sex-determining genes in amphibians were compared, including AMH, AMHR2, AR, CYP17, CYP19A1, RSPO1, BOD1L, DMRT1, FOXL2, SOX3, and SF1. To verify whether the obtained sex-linked markers serve as candidate sex-determining genes, an indirect approach was utilized.
The initial step involved aligning the coding sequences of the candidate sex-determining genes with the reference genome to locate their positions. Subsequently, we extended and trimmed the alignment regions and aligned them with the sex-linked loci to determine whether any sex-linked loci were located within those regions. Here, the Q. spinosa and N. parkeri genomes were selected as reference genomes based on their close phylogenetic relationships [45,46].
3. Results
3.1. GBS Data Analyses and SNP Calling
A combined total of 34,134,552,576 raw Illumina sequencing reads were acquired from a genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) library prepared for 10 male and 9 female individuals of the species Q. yei. For N. quadranus, a total of 22,175,915,040 raw Illumina bases were obtained from a GBS library constructed for eight male and seven female N. quadranus individuals. Following the removal of low-quality sequences using the process_radtags tool, a total of 56,309,046,030 reads were retained for both species (Supplementary Table S1). Subsequently, the Stacks de novo_map pipeline was applied for SNP discovery, resulting in the identification of a catalogue comprising 1,260,290 SNPs across the populations of these two species.
3.2. Sex-Linked Marker Screening
The method based on heterozygosity differences revealed the presence of 33 sex-linked SNPs (located on 26 GBS tags) exhibiting an XY pattern in N. quadranus and 907 sex-linked SNPs (located on 630 GBS-tags) displaying an XY pattern in Q. yei. Notably, no sex-linked SNP displaying the ZW pattern was detected in either of these species. Leveraging the sex-limited occurrence approach, 267 male-limited GBS tags were identified in N. quadranus, while 1148 male-limited and 10 female-limited GBS tags were identified in Q. yei. In aggregate, a total of 2365 putative sex-linked markers were identified in these two species using the aforementioned approaches (Supplementary Tables S2 and S7).
3.3. Validation of the Sex-Linked Markers
The screening process for sex-linked markers within our GBS datasets revealed markers exhibiting the anticipated XY or ZW patterns, suggesting the possibility of false positives. Following the elimination of false positives using BLAST, we identified 28 sex-linked loci (located on 24 GBS tags) and 66 sex-specific sequences with an XY pattern, resulting in a total of 94 confirmed sex-linked markers for N. quadranus. For Q. yei, a total of 598 sex-linked markers and 489 sex-specific markers were identified through this process. Ultimately, it was verified that N. quadranus and Q. yei exhibit an XY sex-determination system (Supplementary Tables S3 and S7).
As with the SNP-based analysis, we found no male specific GBS tag shared between the species.
3.4. PCR Validation
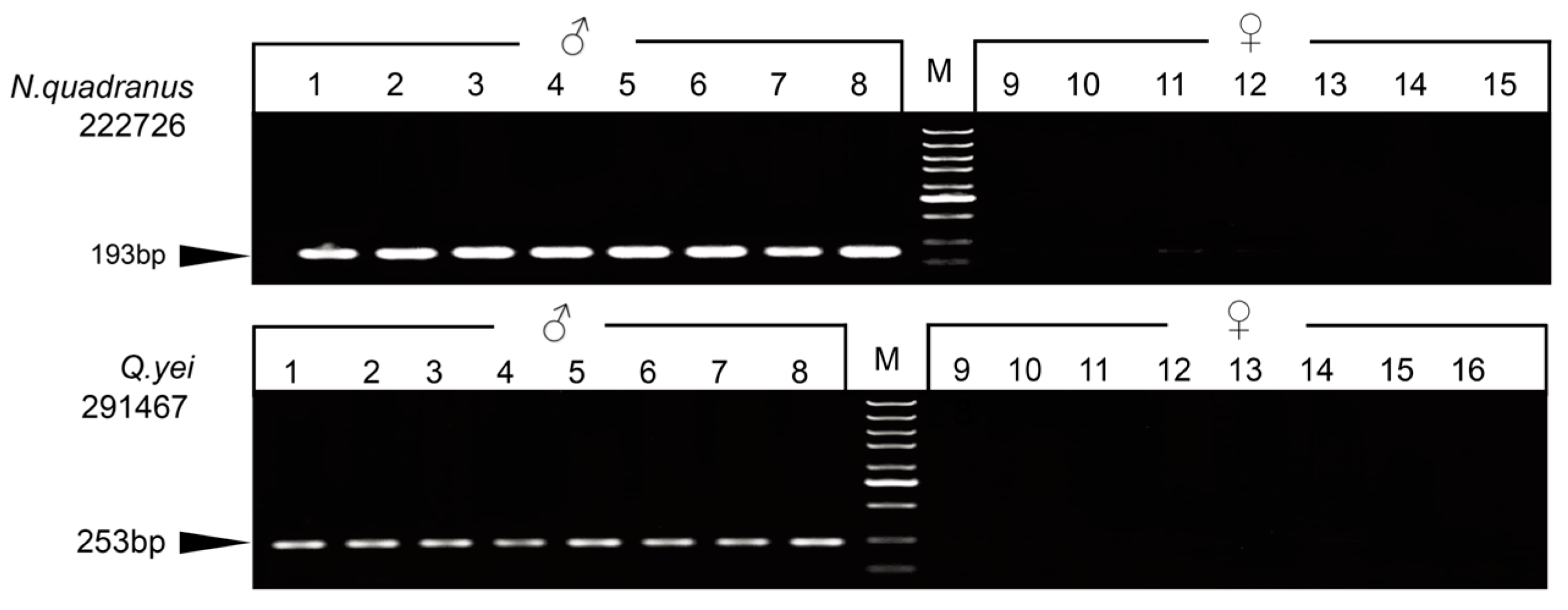
For each species, we randomly selected some markers, which were validated to design two types of primers for the PCR test. Three markers were successfully detected by agarose gel electrophoresis after amplification, and only males exhibited bands. Ultimately, one sex-linked marker was validated for Q. yei, and two sex-linked ones were validated for N. quadranus (Figure 1 and Figure S2, Supplementary Tables S4 and S7).
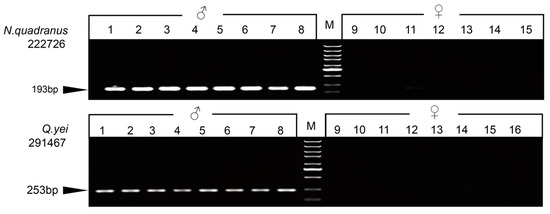
Figure 1.
Gel electrophoresis showing the PCR amplification of markers 22276 (N. quadranus) and 291467 (Q. yei). The locus ID is indicated to the left. ‘M’ indicates a DNA marker. Black arrows indicate the PCR product size.
3.5. Identifying the Sex Chromosome
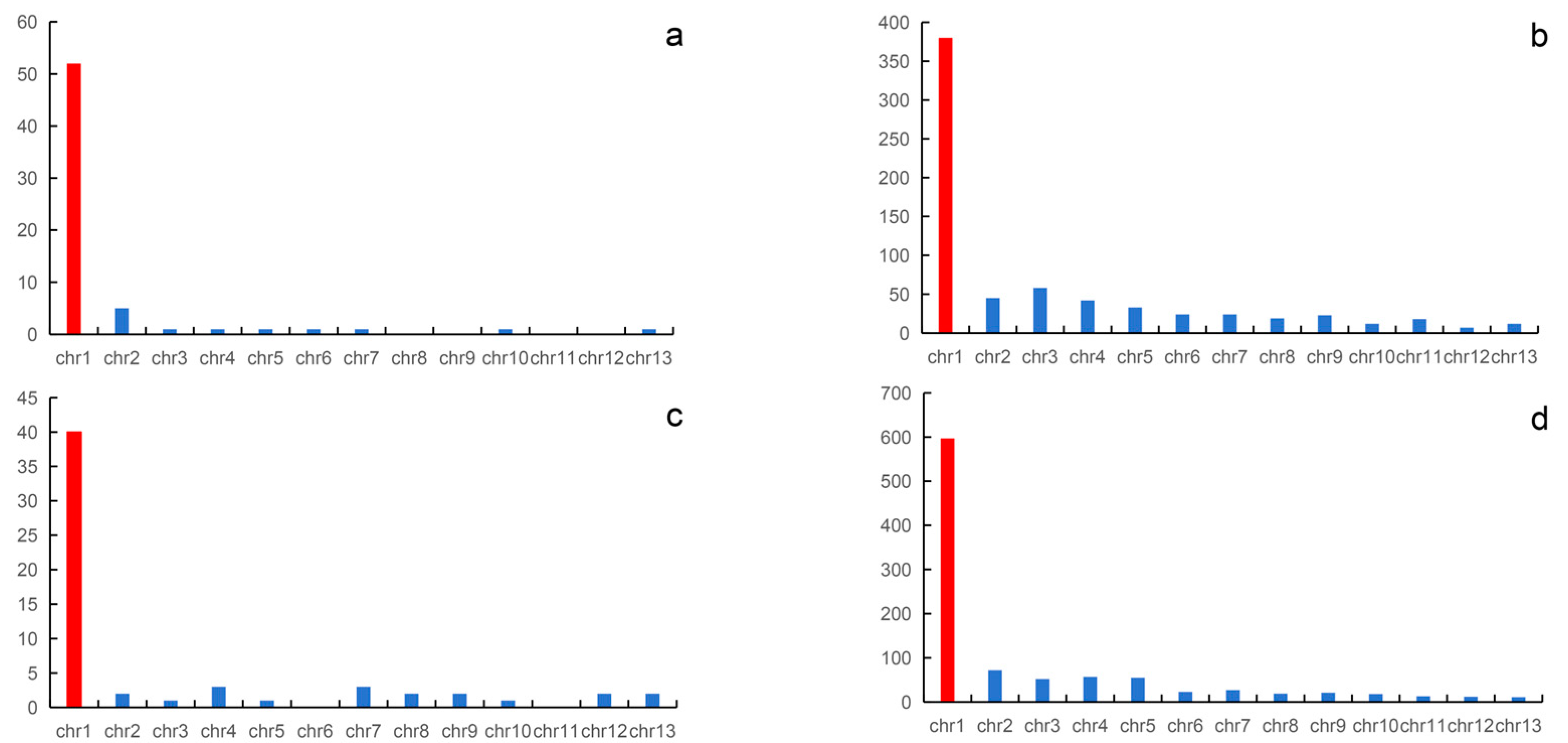
In this study, we directly mapped all sex-linked markers to the genome of Q. spinosa and N. parkeri. In N. quadranus, a total of 59 sex-linked markers were mapped to the genome of Q. spinosa, with 40 out of the 59 (68%) sex-linked markers being successfully mapped to chromosome 1; the remaining markers are distributed across the remaining 12 pairs of chromosomes. For Q. yei, a total of 981 sex-linked markers were successfully mapped to the genome of Q. spinosa, and 597 out of 981 (60.9%) of the sex-linked markers could be mapped to chromosome 1. The remaining 39.1% of the markers are scattered across the remaining 12 pairs of chromosomes.
Using the N. parkeri genome as a reference genome, out of the 94 confirmed sex-linked markers of the N. quadranus, 64 sex-linked markers were successfully aligned to the reference genome, while the remaining markers could not be successfully aligned. Of the 64 sex-linked markers that were aligned successfully, 54 sex-linked markers concentrate on chromosome 1. For Q. yei, out of 1087 sex-linked markers, 697 sex-linked markers were successfully aligned to the N. parkeri reference genome. Among the 697 sex-linked markers successfully aligned, 50% of the markers are concentrated on chromosome 1, while the remaining markers are distributed across other chromosomes, ranging from 1% to 8%.
The reasons for the unsuccessful alignment of sex-linked markers may be that these markers are noncoding genes, exhibit significant differences, or lack homologous sequences in the reference genome. Regardless of using the genome of Q. spinosa or N. parkeri as the reference genome, the sex-linked markers of N. quadranus and Q. yei are both concentrated on chromosome 1. These findings indicated that in N. quadranus and Q. yei, chromosomes 1 might function as the sex chromosome pair, containing a collection of sex-linked loci (Figure 2 and Figure 3, Supplementary Tables S5–S7).
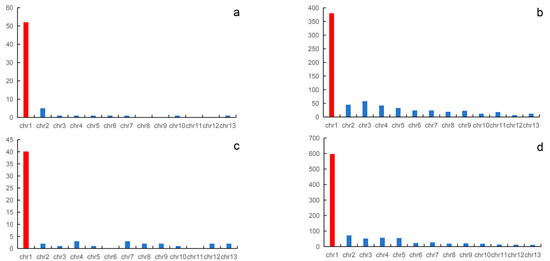
Figure 2.
Mapping of the sex-linked markers of N. quadranus and Q. yei to the reference genome. The sex-linked markers of N. quadranus and Q. yei are mapped to the N. parkeri genome (a,b). The sex-linked markers of N. quadranus and Q. yei are mapped to the Q. spinosa genome (c,d), respectively. The red columns indicate sex chromosomes.
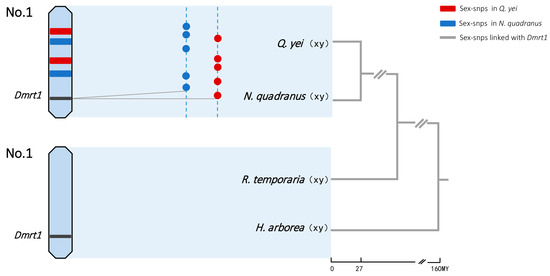
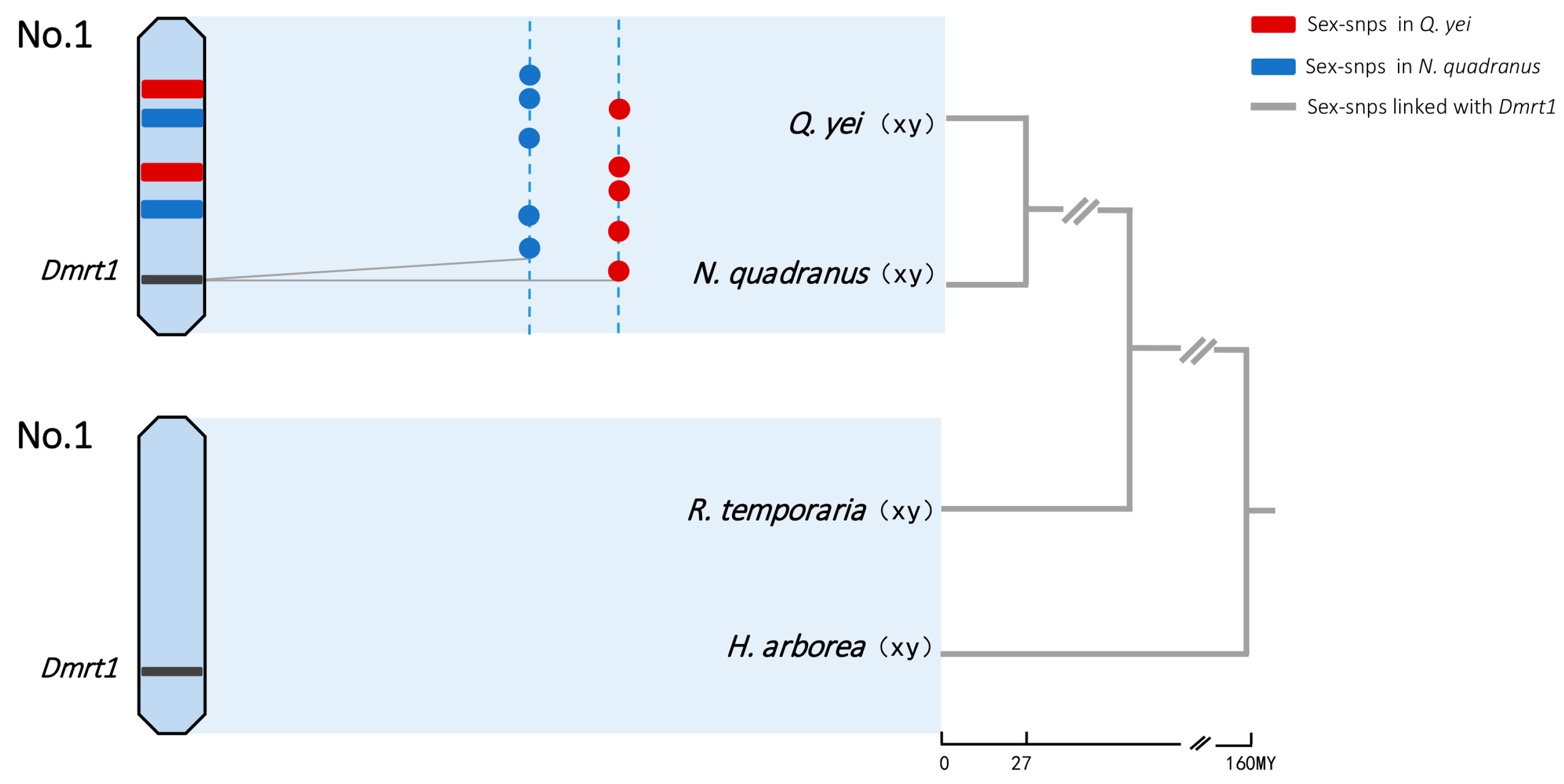
Figure 3.
Sex chromosomes and sex-linked genes in four frogs. Sex-determination system and sex-chromosome identities were from GBS data in N. quadranus and Q. yei (the majority of sex-linked markers mapped to chromosome 1 of Q. spinosa and N. parkeri: see detail in Figure S2, Supplementary Tables S4 and S6) and from the literature in R. temporaria and H. arborea [36,47]. Chromosome 1 harbors the candidate gene Dmrt1 for sex determination in four frogs. The dotted lines represent the sex chromosome for each species, and colored dots show sex-linked SNPs in N. quadranus (blue) and Q. yei (red). Sex-linked SNPs are randomly located, and there was no shared XY site found. The grey solid lines show that several sex-linked SNPs were mapped to the Dmrt1 gene. Tree topology and approximate divergence times (My) were adapted using a combination of data from Che et al. (2010), Yuan et al. (2019) [37,48] and http://timetree.org (accessed on 4 February 2024).
3.6. Identifying Potential Sex-Determining Genes
Based on the indirect method, only the DMRT1 gene of G. ruguosa is located on chromosome 1 of the reference genome. The remaining candidate sex-determining genes either failed to align to the reference genome or were aligned to multiple chromosomes.
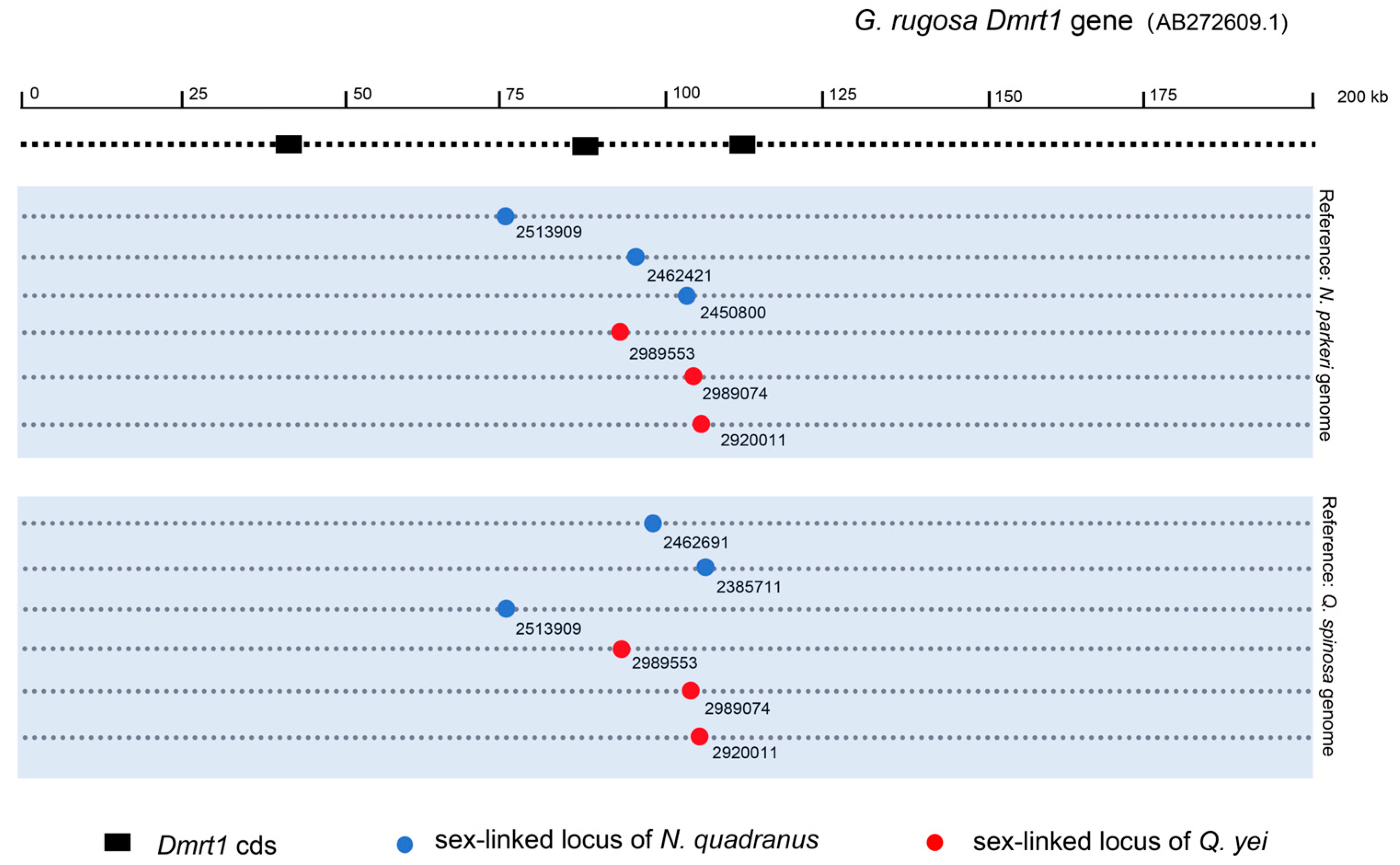
By using the Q. spinosa genome as a reference genome, it was found that both N. quadranus (CLoci_2513909, 2462691, 2385711) and Q. yei (CLoci_2989553, 2989074, 2920011) possess three sex-linked markers positioned within the alignment region of DMRT1 on the reference genome. Conversely, upon utilizing the N. parkeri genome, it was revealed that N. quadranus contains three sex-linked markers (CLoci_2513909, 2462421, 2450800), while Q. yei exhibited same markers (CLoci_2989553, 2989074, 2920011) situated in the alignment region of DMRT1 on the reference genome (Figure 4; see details in Supplementary Tables S9 and S10.
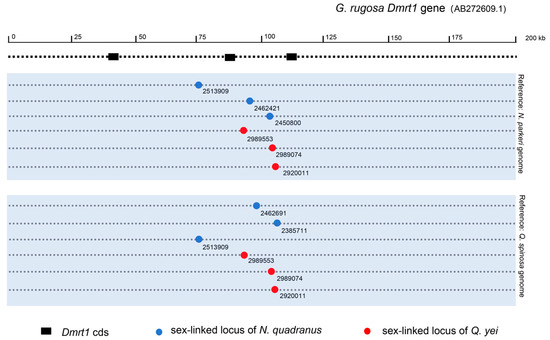
Figure 4.
The mapping of sex-linked locus of N. quadranus and Q. yei on DMRT1 gene of G. rugosa. Circles indicate sex-linked loci of N. quadranus and Q. yei, and dashed lines indicate the relative alignment region of the DMRT1 gene of G. ruguosa in the reference genome. The blue background sections display the reference genomes utilized for screening sex-linked loci.
Taking into account the accumulated evidence, we propose that DMRT1 is the most probable candidate sex-determining gene in N. quadranus and Q. yei.
4. Discussion
4.1. Sex Determination Is Limited to Homologous Chromosomes
Our results show that the majority of sex-linked markers with male heterogamety from both spiny frogs were mapped to the genome of Q. spinosa as well as N. parkeri, both corresponding to chromosome 1 (Figure 2 and Figure 3, Supplementary Tables S5–S7). Chromosome 1 was then co-opted as the sex chromosome with an XY system in both species. And thus, the sex determination was limited to homologous chromosomes in two distant spiny frogs, where they belong to closely related genera, Quasipaa and Nanorana, diverged 27 million years ago [37].
Chromosome 1 turns out to be sex-linked one in these two closely related genera, Quasipaa and Nanorana. In fact, our additional examinations revealed a consistent XY system in other investigated species, with chromosome pair 1 being shared in these species of Quasipaa and Nanorana (Xia, Xiao, Zeng, unpublished). Thus, our findings so far support that the species from Quasipaa and Nanorana retain an ancestral sex chromosome pair, which has been evolutionarily conserved for 27 million years.
Many investigated cases in frogs show that the species of closely related groups shared the same sex-linked chromosome pair. In the European tree frog clade, including four species of the Hyla arborea group, the Tyrrhenian Hyla sarda, and the Middle Eastern Hyla savignyi, all species share the same sex chromosome pair within approximately 11 M years [49,50,51]. The largest chromosome pair with an XY system was retained in all diploid species of the Bufo viridis subgroup, including B. siculus, B. shaartusiensis, B. balearicus, B. turanensis, B. variabilis, B. viridis, and probably B. boulengeri [52]. Similarly, chromosome 5 was sex-limited with male heterogamety across at least eight species of the western clade of torrent frog Amolops within approximately 31 M years [53]. In such cases, transitions of sex chromosomes have happened infrequently across closely related species or groups, and they would then have been evolutionarily conserved within a period of time.
Moreover, species sharing a homologous sex chromosome pair have been discovered even across deeply divergent groups. Chromosome 1 was proved to be extensively conserved synteny across four anuran families (Pipidae, Ranidae, Hylidae, and Bufonidae) within approximately 210 million years [36]. This chromosome appears to be sex-linked across the species of some anuran families, i.e., Ranidae, and Hylidae [36,51], which now extends to spiny frogs of the family Dicroglossidae (this study). The more plausible explanation may be that this chromosome has independently evolved sex linkage multiple times in these groups over more than 160 million years (http://timetree.org; accessed on 4 February 2024). Through sex chromosome transitions have been found in many deeply divergent clades in amphibians, the high frequency of transitions in closely related genera or species is not common, except in some ranid and pipid species [17,19]. For example, within the genus Rana, sex chromosome transitions have happened multiple times, and chromosome 1 (corresponding to Xenopus tropicalis chromosome 1) has been recurrently co-opted as the sex chromosome in at least eight species [18]. In this situation, the possibility that species from these different families retain an ancestral sex chromosome pair might be excluded. When sex chromosome transitions are frequently biased toward certain chromosomes, this bias would become a self-reinforcing evolutionary process. When a chromosome has been sex-linked in the past, it might have accumulated genes likely to be concerned with sexually antagonistic effects, which could then make it more likely to recapture the role of a sex chromosome in a turnover event [54,55]. Thus, chromosome 1 being homologous sex-linked has been recurrently co-opted as the sex chromosome across these families.
Notably, despite very few cases, sex chromosomes seem to be evolutionarily conserved among closely related groups within a period of time. Across deeply divergent clades when estimated on a large evolutionary scale of taxa, considering the high frequency of sex chromosome transitions, some chromosomes are more likely to have been recurrently co-opted for sex chromosomes.
4.2. Sex Determination May Pertain to the DMRT1 Gene
In the present study, the transcription factor DMRT1 of the frog G. rugosa was the gene that was identified that matched with sex-linkage markers in both spiny species investigated (Figure 3 and Figure 4, Supplementary Tables S8–S10). Furthermore, there is no other candidate gene that was found involving in these sex-linked markers in both species. The DMW gene (DMRT1 paralog) is the only one detected gene among potential candidates known in frogs [34]. Thus, the candidate sex-determining genes would be involved in the homology between two distant spiny frogs.
The DMRT1 gene is possibly harbored by chromosome 1, which was found to be sex-linked in both spiny frogs of the family Dicroglossidae (Figure 3 and Figure 4, Supplementary Tables S8–S10). This corresponds to the records in Rana frogs of the Ranidae and Hyla tree frogs of the Hylidae, where sex-linked DMRT1 has been suggested to be located on chromosome 1 [36,49,51,56]. Ranid frogs together with those of the Rhacophoridae and Mantellidae, have been grouped into the sister clade of Dicroglossidae, which diverged 75 million years ago [48]. Accordingly, considerable synteny is shown among frog genomes, despite long periods of independent evolution [45,57,58]. The DMRT1 gene would then have the same chromosomal location across three families over more than 160 million years (Figure 3) (http://timetree.org; accessed on 4 February 2024) [48].
What might have predisposed chromosome 1 to repeatedly evolving sex linkage in these deeply divergent taxa? The presence of the DMRT1 gene might be a good explanation. This gene appears to concern the male differentiation pathway throughout the whole animal kingdom, from flies to mammals. The DMRT1 gene or its paralogs determine sex in birds, medaka fish, and African clawed frogs, making it an appealing candidate gene for sex determination in species where it is sex-linked. Harboring the DMRT1 gene, chromosome 1 would have been independently co-opted for sex determination in deeply divergent groups over a long period of time.
5. Conclusions
XY sex-determination systems were detected in both N. quadranus and Q. yei species by GBS and verified by PCR. The results of mapping sex-linked markers onto the genome of Q. spinosa suggest that chromosome 1 serves as a sex chromosome in both species. This finding indicates that this chromosome seems to be evolutionarily conserved across these closely related groups over 27 million years. The transcription factor DMRT1 was found to be a putative candidate sex-determining gene implicated in homology in two distantly related spiny species. Furthermore, harboring the DMRT1 gene, chromosome 1 has been independently co-opted for sex determination in deeply divergent groups over a long period of time. The patterns of sex chromosome evolution in spiny frogs imply that transitions are not highly frequent in many groups of frogs.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ani14131849/s1, File S1: Specimen information and location data; Figure S1: Primer design for sex-linked markers; Figure S2: Gel electrophoresis showing the PCR amplification of markers 446253 (N. quadranus); Table S1: Quality summary of Q. yei and N. quadranus per GBS sequencing; Table S2: Detailed information of all putatively sex-linked markers screened from N. quadranus and Q. yei; Table S3: Confirmed sex-linked makers after the elimination of false positives; Table S4: Primer sequences of sex-linked markers isolated from N. quadranus and Q. yei; Table S5: The results of mapping sex-linked markers onto to the genome of Q. spinosa; Table S6: The results of mapping sex-linked markers onto to the genome of N. parkeri; Table S7. Details of sequencing datasets for N. quadransua and Q. yei analyses; Table S8: BLAST results of candidate sex-determining genes to the reference genome; Table S9. Mapping the sex-linked loci to the alignment region of DMRT1 in the genome of Q. spinosa; Table S10. Mapping the sex-linked loci to the alignment region of DMRT1 in the genome of N. parkeri.
Author Contributions
X.Z. and Y.X. (Yun Xia) designed the study; laboratory work was performed by Y.X. (Yu Xiao) and G.L.; analyses were performed by Y.X. (Yun Xia), Y.X. (Yu Xiao) and W.L.; Y.X. (Yu Xiao) and X.Z. wrote the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Second Tibetan Plateau Scientific Expedition and Research (STEP) program (grant No. 2019QZKK0501), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 32170419 and No. 32270448), and the Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Province (2022NSFSC1756).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was permitted and approved by the local ethics committee for Animal Care and Use Committee of Chengdu Institute of Biology (CIB), Chinese Academy of Sciences (Permit Number: CIB-2017009).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting the results of this study can be found in the manuscript. The raw sequence data obtained in this study were deposited in the China National Center for Bioinformation and are publicly accessible at CRA015437.
Acknowledgments
We thank Ziwen Wang and Jun Ping for their help with data analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Beukeboom, L.W.; Perrin, N. Evolution of Sex Determination; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bachtrog, D.; Mank, J.E.; Peichel, C.L.; Kirkpatrick, M.; Otto, S.P.; Ashman, T.L.; Hahn, M.W.; Kitano, J.; Mayrose, I.; Ming, R.; et al. Tree of Sex Consortium. Sex determination: Why so many ways of doing it? PLoS Biol. 2014, 12, e1001899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M. Sex determination in amphibians. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2009, 20, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, M.; Steinlein, C.; Bogart, J.P.; Feichtinger, W.; León, P.; La Marca, E.; Díaz, L.M.; Sanz, A.; Chen, S.H.; Hedges, S.B. The chromosomes of terraranan frogs. Insights into vertebrate cytogenetics. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2010, 130–131, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, M.; Steinlein, C. Sex chromosomes, sex-linked genes, and sex determination in the vertebrate class amphibia. EXS 2001, 91, 143–176. [Google Scholar]
- Malcom, J.W.; Kudra, R.S.; Malone, J.H. The sex chromosomes of frogs: Variability and tolerance offer clues to genome evolution and function. J. Genom. 2014, 20, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, Y.; Nishida, C.; Takagi, C.; Igawa, T.; Ueno, N.; Sumida, M.; Matsuda, Y. Extraordinary diversity in the origins of sex chromosomes in anurans inferred from comparative gene mapping. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2015, 145, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, I. An evolutionary witness: The frog Rana rugosa underwent change of heterogametic sex from XY male to ZW female. Sex. Dev. 2007, 1, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, N.; Vuille, Y.; Brelsford, A.; Merilä, J.; Perrin, N. The genetic contribution to sex determination and number of sex chromosomes vary among populations of common frogs (Rana temporaria). Heredity 2016, 117, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furman, B.L.S.; Cauret, C.M.S.; Knytl, M.; Song, X.Y.; Premachandra, T.; Ofori-Boateng, C.; Jordan, D.C.; Horb, M.E.; Evans, B.J. A frog with three sex chromosomes that co-mingle together in nature: Xenopus tropicalis has a degenerate W and a Y that evolved from a Z chromosome. PLoS Genet. 2020, 16, e1009121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.Y.; Furman, B.L.S.; Premachandra, T.; Knytl, M.; Cauret, C.M.S.; Wasonga, D.V.; Measey, J.; Dworkin, I.; Evans, B.J. Sex chromosome degeneration, turnover, and sex-biased expression of sex-linked transcripts in African clawed frogs (Xenopus). Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2021, 376, 20200095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, A.S. Moving up the hierarchy: A hypothesis on the evolution of a genetic sex determination pathway. Bioessays 1995, 17, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schartl, M. Sex chromosome evolution in non-mammalian vertebrates. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2004, 14, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volff, J.N.; Nanda, I.; Schmid, M.; Schartl, M. Governing sex determination in fish: Regulatory putsches and ephemeral dictators. Sex. Dev. 2007, 1, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, J.A. How to evolve new vertebrate sex determining genes. Dev. Dyn. 2013, 242, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlesworth, D.; Mank, J.E. The birds and the bees and the flowers and the trees: Lessons from genetic mapping of sex determination in plants and animals. Genetics 2010, 186, 9–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillis, D.M.; Green, D.M. Evolutionary changes of heterogametic sex in the phylogenetic history of amphibians. J. Evol. Biol. 1990, 3, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffries, D.L.; Lavanchy, G.; Sermier, R.; Sredl, M.J.; Miura, I.; Borzée, A.; Barrow, L.N.; Canestrelli, D.; Crochet, P.A.; Dufresnes, C.; et al. A rapid rate of sex-chromosome turnover and non-random transitions in true frogs. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.J.; Veltsos, P. The diversity and evolution of sex chromosomes in frogs. Genes. 2021, 12, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall Graves, J.A.; Peichel, C.L. Are homologies in vertebrate sex determination due to shared ancestry or to limited options? Genome Biol. 2010, 11, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Meally, D.; Ezaz, T.; Georges, A.; Sarre, S.D.; Graves, J.A. Are some chromosomes particularly good at sex? insights from amniotes. Chromosome Res. 2012, 20, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, D.A.; Richards, C.M.; Frost, J.S.; Camozzi, A.M.; Kunz, B.J. Genetic mapping in amphibians. Isozymes Curr. Top. Biol. Med. Res. 1983, 10, 287–311. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, D.A.; Richards, C.M. Two sex-linked loci in the leopard frog, Rana pipiens. Genetics 1983, 103, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumida, M.; Nishioka, M. A pronounced sex difference when two linked loci of the Japanese brown frog Rana japonica are recombined. Biochem. Genet. 1994, 32, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumida, M.; Nishioka, M. Sex-linked genes and linkage maps in amphibians. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2000, 126, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Xia, Y.; Yue, B.S.; Zeng, X.M. Assigning the Sex-Specific Markers via Genotyping-by-Sequencing onto the Y Chromosome for a torrent frog Amolops mantzorum. Genes 2020, 11, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, I. Sex determination and sex chromosomes in amphibia. Sex. Dev. 2017, 11, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roco, Á.S.; Olmstead, A.W.; Degitz, S.J.; Amano, T.; Zimmerman, L.B.; Bullejos, M. Coexistence of Y, W, and Z sex chromosomes in Xenopus tropicalis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E4752–E4761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauret, C.M.S.; Gansauge, M.T.; Tupper, A.S.; Furman, B.L.S.; Knytl, M.; Song, X.Y.; Greenbaum, E.; Meyer, M.; Evans, B.J. Developmental Systems drift and the drivers of sex chromosome evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 799–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, I.; Ohtani, H.; Nakamura, M.; Ichikawa, Y.; Saitoh, K. The origin and differentiation of the heteromorphic sex chromosomes Z, W, X, and Y in the frog Rana rugosa, inferred from the sequences of a sex-linked gene, ADP/ATP translocase. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1998, 15, 1612–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Uno, Y.; Nishida, C.; Yoshimoto, S.; Ito, M.; Oshima, Y.; Yokoyama, S.; Nakamura, M.; Matsuda, Y. Diversity in the origins of sex chromosomes in anurans inferred from comparative mapping of sexual differentiation genes for three species of the Raninae and Xenopodinae. Chromosome Res. 2008, 16, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, Y.; Kato, T.; Wang, D.; Murakami, T.; Matsuda, Y.; Nagahama, Y.; Nakamura, M. Promoter activity and chromosomal location of the Rana rugosa P450 aromatase (CYP19) gene. Zoolog Sci. 2006, 23, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, N.; Maruo, K.; Haraguchi, S.; Uno, Y.; Oshima, Y.; Tsutsui, K.; Matsuda, Y.; Do Rego, J.L.; Pelletier, G.; Vaudry, H.; et al. Immunohistochemical detection and biological activities of CYP17 (P450c17) in the indifferent gonad of the frog Rana rugosa. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 112, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, S.; Okada, E.; Umemoto, H.; Tamura, K.; Uno, Y.; Nishida-Umehara, C.; Matsuda, Y.; Takamatsu, N.; Shiba, T.; Ito, M. A W-linked DM-domain gene, DM-W, participates in primary ovary development in Xenopus laevis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2469–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhl, H.; Tan, W.H.; Klopp, C.; Kleiner, W.; Koyun, B.; Ciorpac, M.; Feron, R.; Knytl, M.; Kloas, W.; Schartl, M.; et al. A candidate sex determination locus in amphibians which evolved by structural variation between X- and Y-chromosomes. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brelsford, A.; Stöck, M.; Betto-Colliard, C.; Dubey, S.; Dufresnes, C.; Jourdan-Pineau, H.; Rodrigues, N.; Savary, R.; Sermier, R.; Perrin, N. Homologous sex chromosomes in three deeply divergent anuran species. Evolution. 2013, 67, 2434–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, J.; Zhou, W.W.; Hu, J.S.; Yan, F.; Papenfuss, T.J.; Wake, D.B.; Zhang, Y.P. Spiny frogs (Paini) illuminate the history of the Himalayan region and Southeast Asia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13765–13770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, L.; Hu, S.Q.; Ye, C.Y.; Huang, Y. Fauna sinica. Amphibia, Anura Ranidae; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2009; Volume 3. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Elshire, R.J.; Glaubitz, J.C.; Sun, Q.; Poland, J.A.; Kawamoto, K.; Buckler, E.S.; Mitchell, S.E. A robust, simple genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) approach for high diversity species. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catchen, J.M.; Amores, A.; Hohenlohe, P.; Cresko, W.; Postlethwait, J.H. Stacks: Building and genotyping Loci de novo from short-read sequences. G3 2011, 1, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brelsford, A.; Lavanchy, G.; Sermier, R.; Rausch, A.; Perrin, N. Identifying Homomorphic Sex Chromosomes from Wild-Caught adults with limited genomic resources. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2017, 17, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statisticalcomputing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. 2022. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 16 June 2021).
- Stovall, W.R.; Taylor, H.R.; Black, M.; Grosser, S.; Rutherford, K.; Gemmell, N.J. Genetic sex assignment in wild populations using genotyping-by-sequencing data: A statistical threshold approach. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2018, 18, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Schwartz, S.; Wagner, L.; Miller, W. A greedy algorithm for aligning DNA sequences. J. Comput. Biol. 2000, 7, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.X.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Ming, Y.; Jian, J.B.; Jiang, S.J.; Zhang, D.D.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zheng, S.J.; Fang, X.D.; Yang, Y.L.; et al. A chromosomal level genome sequence for Quasipaa spinosa (Dicroglossidae) reveals chromosomal evolution and population diversity. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2022, 22, 1545–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.T.; Sun, Y.B.; Gao, W.; Long, C.B.; Yang, C.H.; Yang, X.W.; Zhang, Y.; Lan, X.Q.; Huang, S.; Jin, J.Q.; et al. The highest-elevation frog provides insights into mechanisms and evolution of defenses against high UV radiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2212406119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brelsford, A.; Dufresnes, C.; Perrin, N. Trans-species variation in Dmrt1 is associated with sex determination in four European tree-frog species. Evolution 2016, 70, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.Y.; Zhang, B.L.; Raxworthy, C.J.; Weisrock, D.W.; Hime, P.M.; Jin, J.Q.; Lemmon, E.M.; Lemmon, A.R.; Holland, S.D.; Kortyna, M.L.; et al. Natatanuran frogs used the Indian Plate to step-stone disperse and radiate across the Indian Ocean. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2019, 6, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufresnes, C.; Borzée, A.; Horn, A.; Stöck, M.; Ostini, M.; Sermier, R.; Wassef, J.; Litvinchuck, S.N.; Kosch, T.A.; Waldman, B.; et al. Sex-Chromosome homomorphy in palearctic tree frogs results from both turnovers and X-Y recombination. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 2328–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufresnes, C.; Brelsford, A.; Baier, F.; Perrin, N. When sex chromosomes recombine only in the heterogametic sex: Heterochiasmy and heterogamety in Hyla tree frogs. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brelsford, A.; Dufresnes, C.; Perrin, N. High-density sex-specific linkage maps of a European tree frog (Hyla arborea) identify the sex chromosome without information on offspring sex. Heredity 2016, 116, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamschick, S.; Rozenblut-Kościsty, B.; Bonato, L.; Dufresnes, C.; Lymberakis, P.; Kloas, W.; Ogielska, M.; Stöck, M. Sex chromosome conservation, DMRT1 phylogeny and gonad morphology in diploid Palearctic green toads (Bufo viridis subgroup). Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2014, 144, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, J.; Xia, Y.; Ran, J.H.; Zeng, X.M. Heterogeneous evolution of sex chromosomes in the torrent frog Genus Amolops. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaser, O.; Grossen, C.; Neuenschwander, S.; Perrin, N. Sex-chromosome turnovers induced by deleterious mutation load. Evolution. 2013, 67, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Doorn, G.S.; Kirkpatrick, M. Turnover of sex chromosomes induced by sexual conflict. Nature 2007, 449, 909–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toups, M.A.; Rodrigues, N.; Perrin, N.; Kirkpatrick, M. A reciprocal translocation radically reshapes sex-linked inheritance in the common frog. Mol. Ecol. 2019, 28, 1877–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.B.; Xiong, Z.J.; Xiang, X.Y.; Liu, S.P.; Zhou, W.W.; Tu, X.L.; Zhong, L.; Wang, L.; Wu, D.D.; Zhang, B.L.; et al. Whole-genome sequence of the Tibetan frog Nanorana parkeri and the comparative evolution of tetrapod genomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E1257–E1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomar, G.; Ahmad, F.; Vasemägi, A.; Matsuba, C.; Nicieza, A.G.; Cano, J.M. Comparative high-density linkage mapping reveals conserved genome structure but variation in levels of heterochiasmy and location of recombination cold spots in the common frog. G3 2017, 7, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).