Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Immunosuppression in Tiger Pufferfish (Takifugu rubripes) under Cryptocaryon irritans Infection
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. RNA Isolation, Library Construction and Sequencing
2.3. Differential Expression Analysis and Functional Enrichment
2.4. Key DEGs Screening and Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network
2.5. Comparison of DEGs and Candidate Genes in QTL Regions
2.6. Processing of PacBio Full-Length Sequencing Data
2.7. Isoforms Annotation and Structure Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Overview of the PacBio Sequencing Data
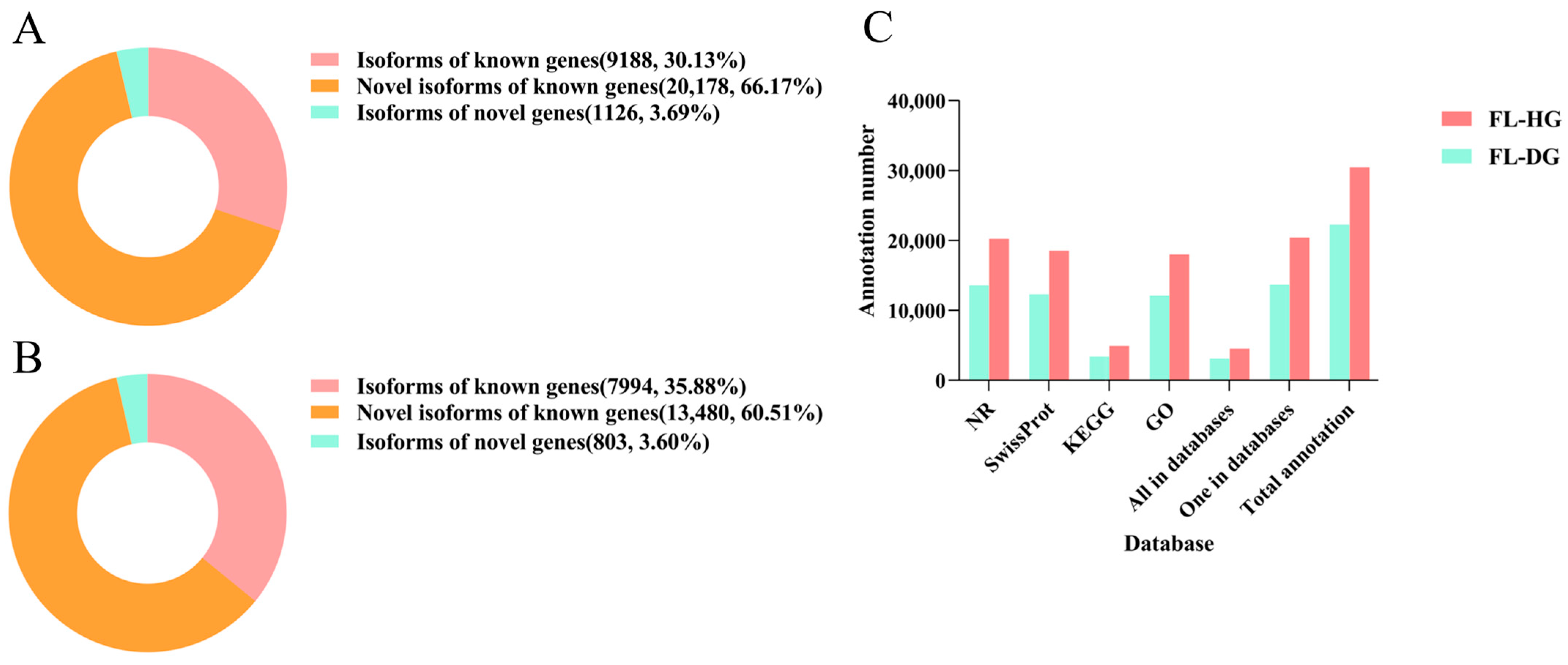
3.2. Functional Annotation of the Transcripts
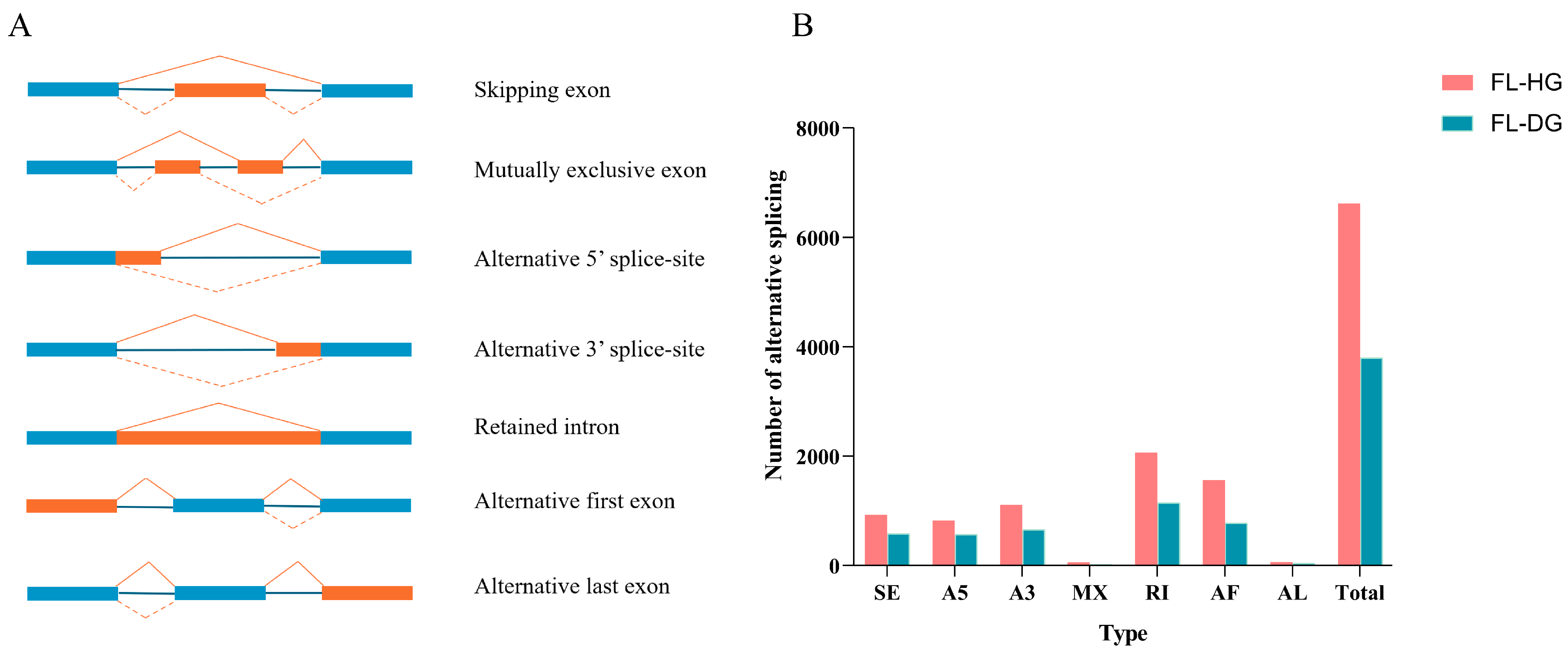
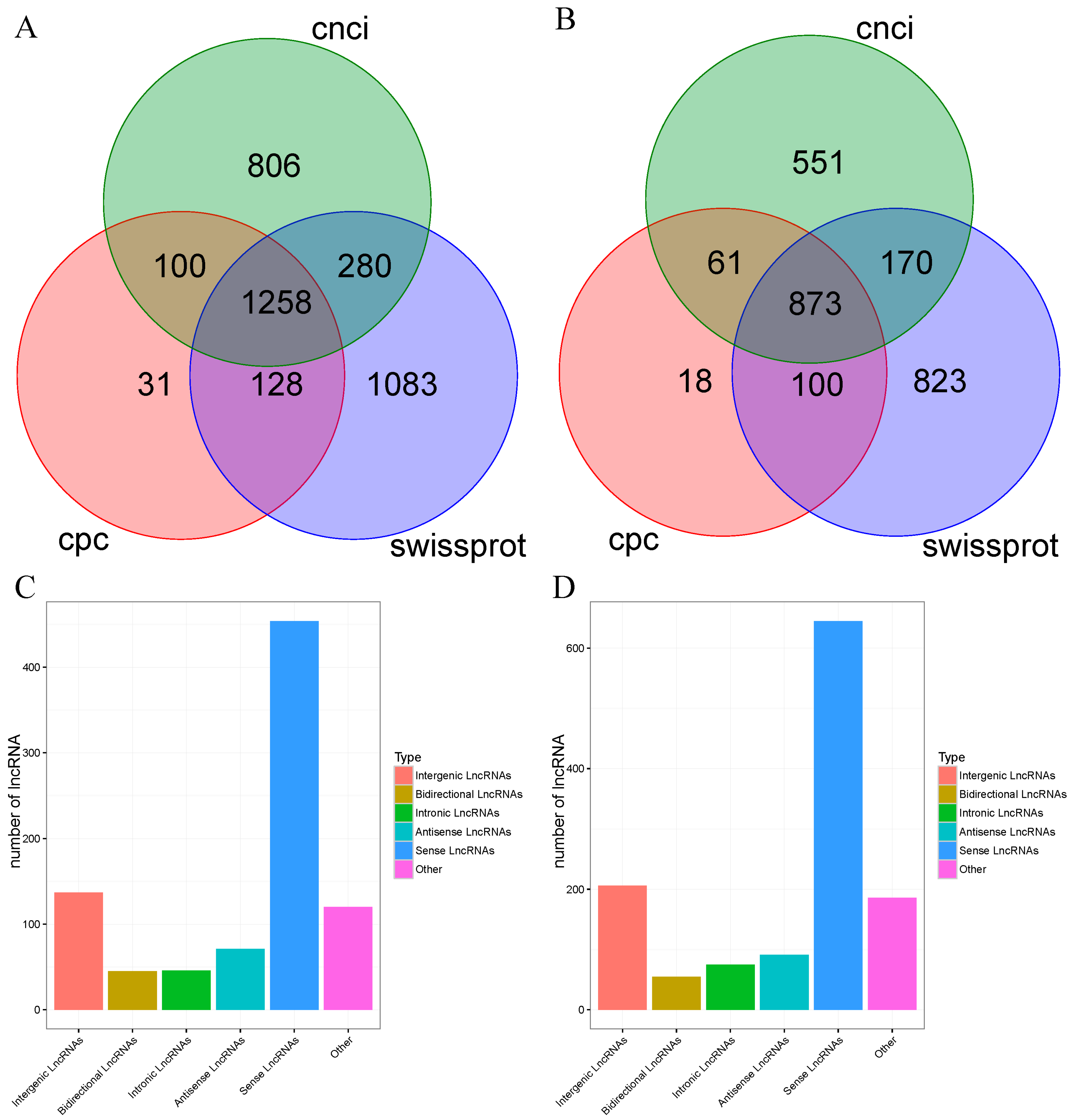
3.3. Alternative Splicing (AS) and lncRNA Analysis
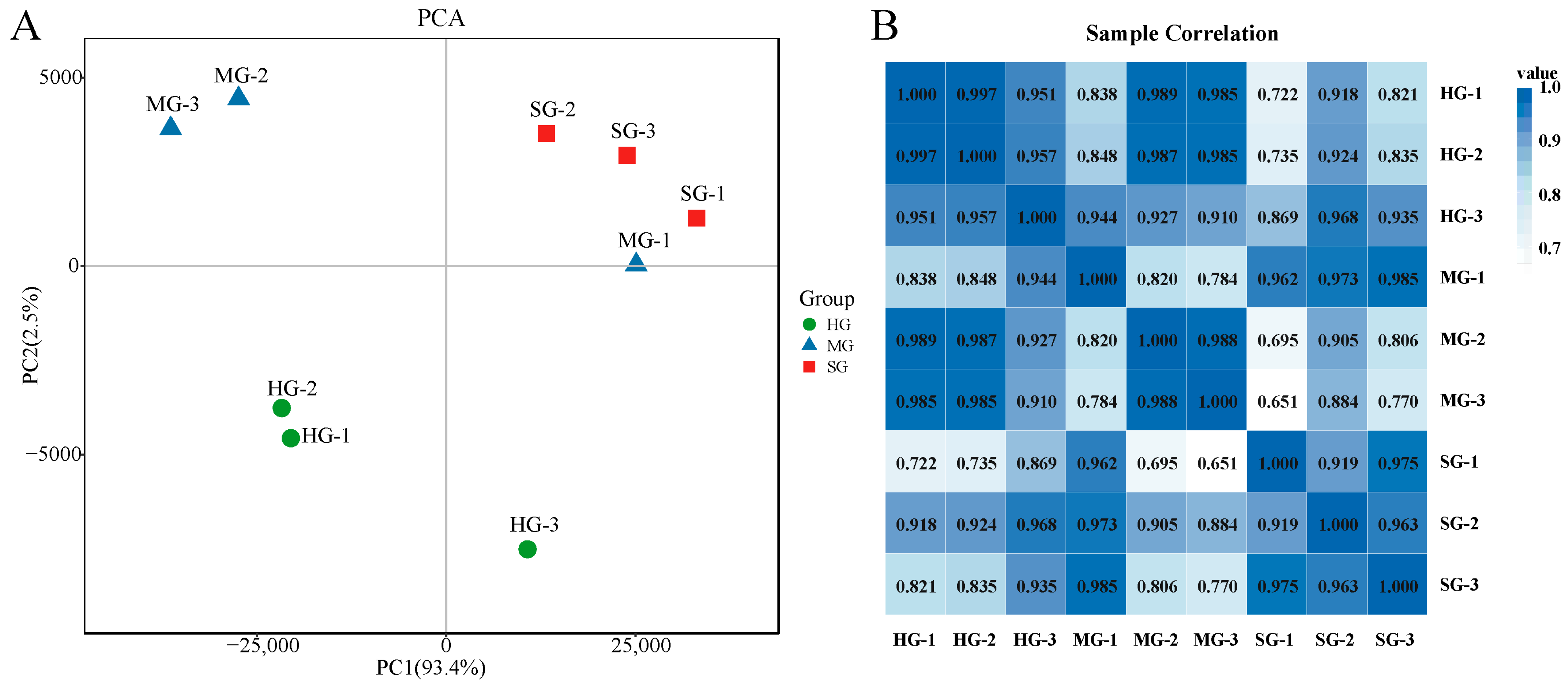
3.4. Quality Assessment of Short-Read Sequencing Data
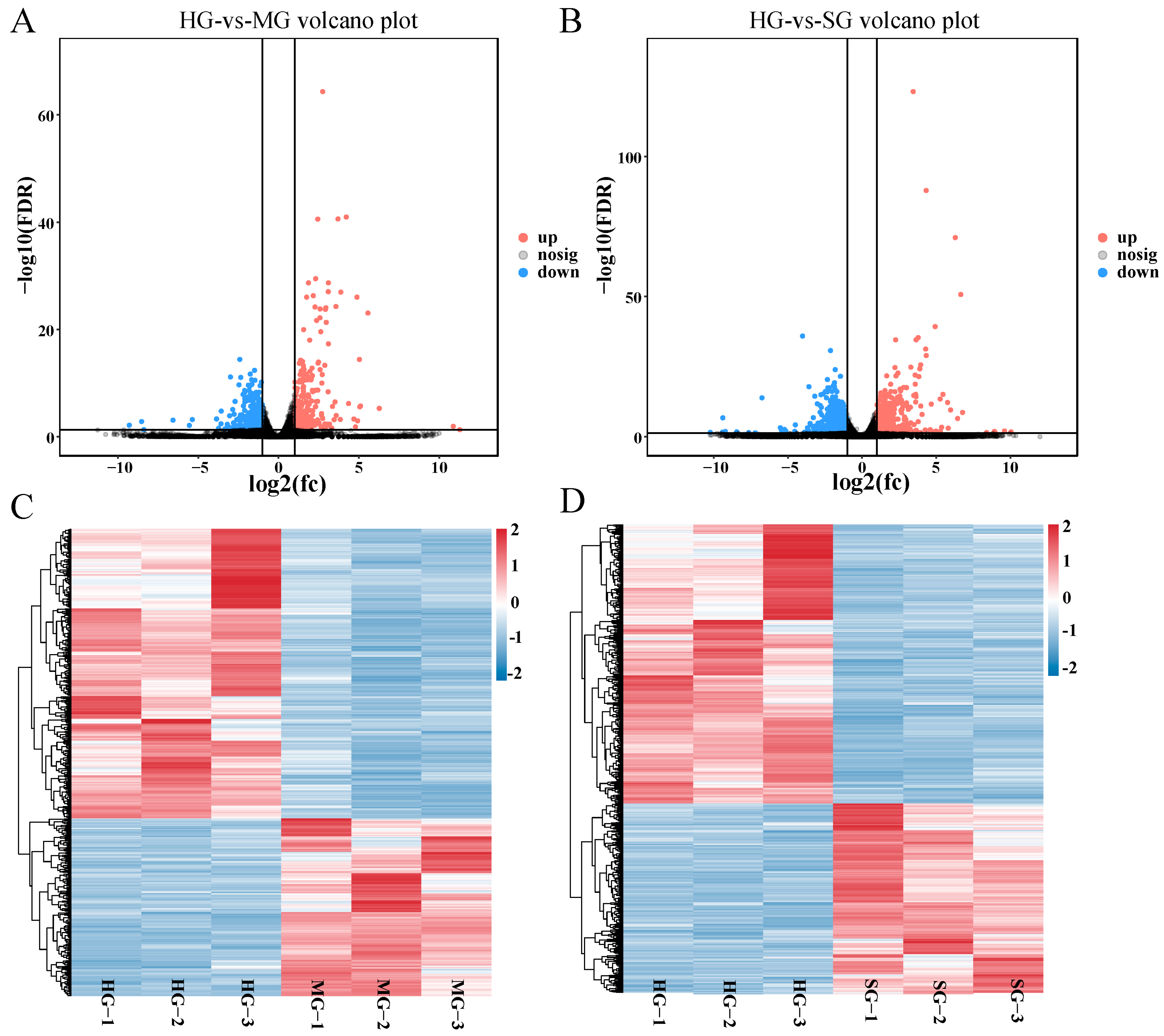
3.5. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes
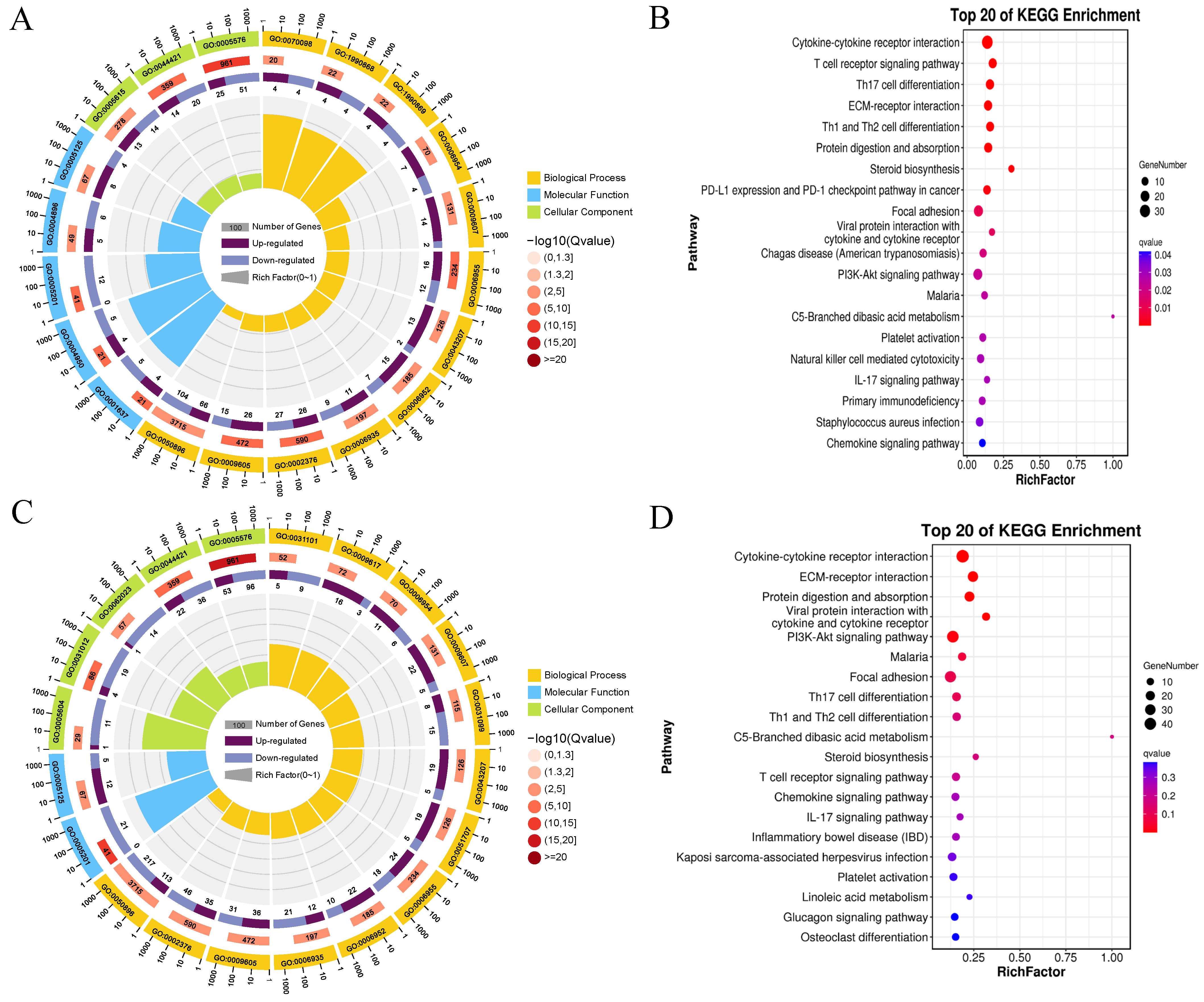
3.6. Functional Analysis of DEGs
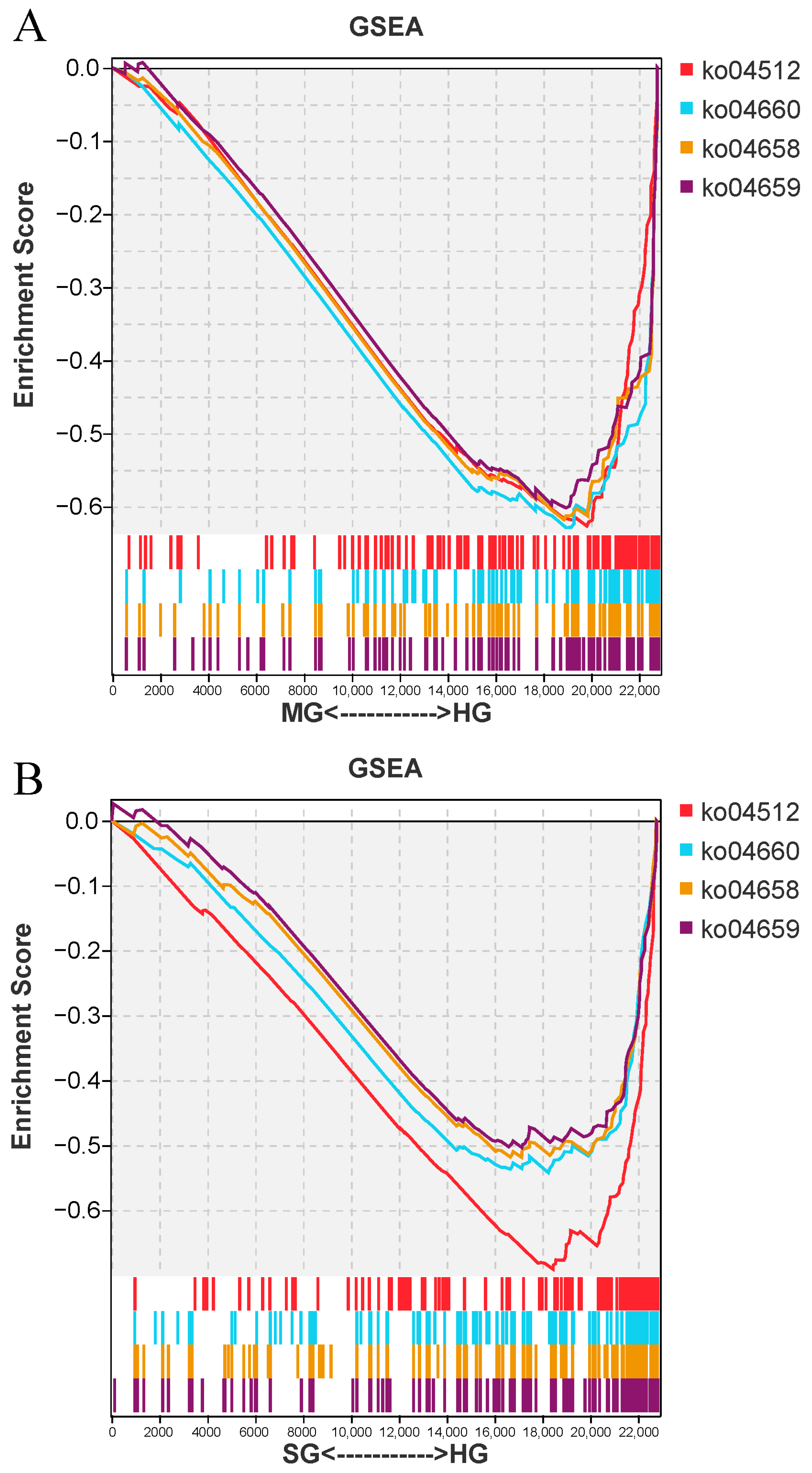
3.7. GSEA Enrichment Analysis
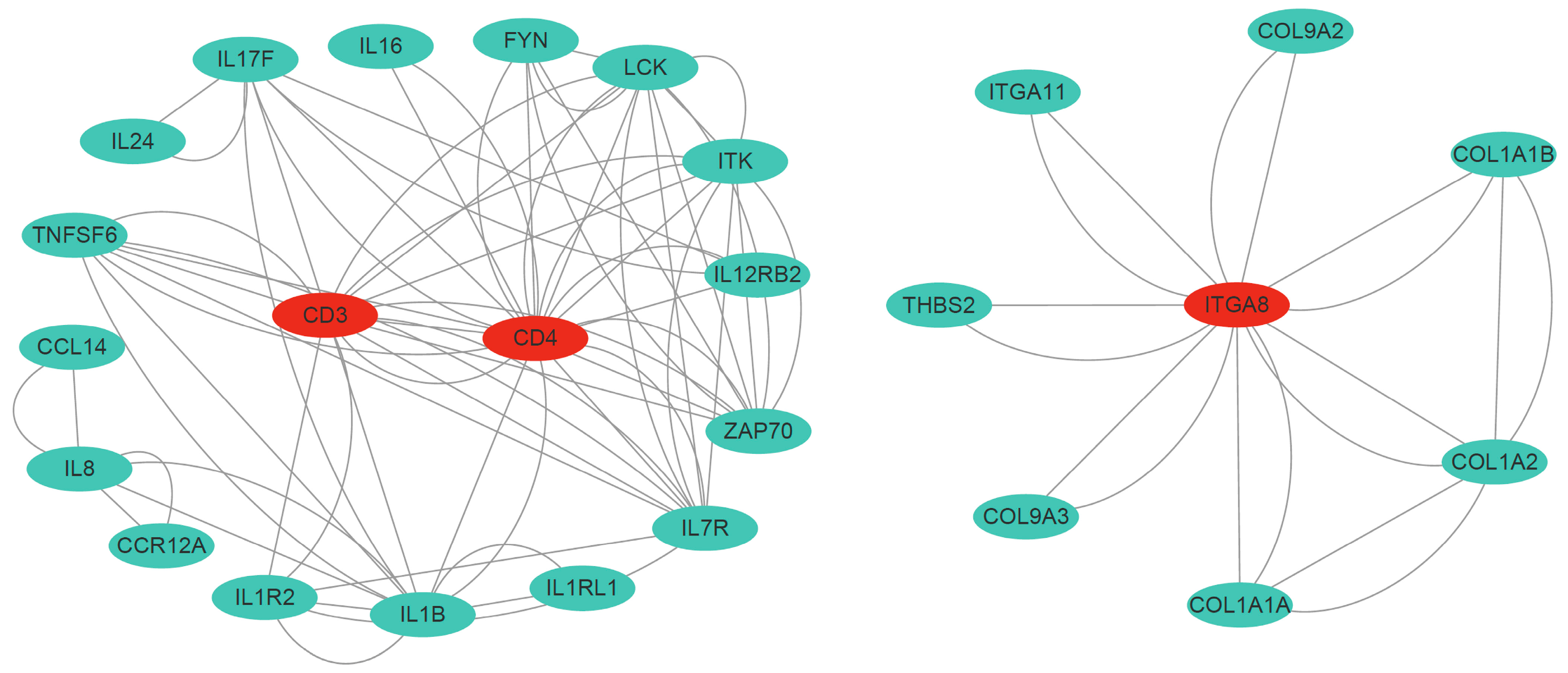
3.8. Immune-Related DEGs and Protein–Protein Interaction Networks
3.9. Overlapping Genes between DEGs and Candidate Genes in QTLs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brenner, S.; Elgar, G.; Sandford, R.; Macrae, A.; Venkatesh, B.; Aparicio, S. Characterization of the pufferfish (fugu) genome as a compact model vertebrate genome. Nature 1993, 366, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.Z.; Shen, X.Y.; Gong, Q.L.; Yang, G.P.; Gu, Q.Q. Identification of sex markers by cDNA-AFLP in Takifugu rubripes. Aquaculture 2006, 257, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; Bao, M.X.; Shang, F.Q.; Wei, R.J.; Liu, F.J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.L. Comparative transcriptome profiling and functional analysis in the blood of tiger puffer (Takifugu rubripes) in response to acute hypoxia. Aquac. Rep. 2023, 30, 101618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tun, T.; Ogawa, K.; Wakabayashi, H. Pathological changes induced by three myxosporeans in the intestine of cultured tiger puffer, Takifugu rubripes (Temminck and Schlegel). J. Fish Dis. 2002, 25, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.Y.; Xia, Y.Q.; Cheng, J.X.; Liu, P.F. Tandem mass tag (TMT) quantitative proteomics and phosphoproteomic of Takifugu rubripes infected with Cryptocaryon irritans. Comp. Biochem. Phys. D 2023, 48, 101124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pironet, F.; Jones, J. Treatments for ectoparasites and disease in captive western Australian dhufish. Aquac. Int. 2000, 8, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Xia, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, P.; Liu, Y. Transcriptome analysis in Takifugu rubripes and Dicentrarchus labrax gills during Cryptocaryon irritans infection. J. Fish Dis. 2021, 44, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.Q.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.Y.; Cheng, J.X.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.X.; Liu, P.F. DNA methylation analysis reveals potential mechanism in Takifugu rubripes against Cryptocaryon irritans infection. Mar. Biotechnol. 2024, 26, 288–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutz, K.O.; Heilkenbrinker, A.; Lönne, M.; Walter, J.G.; Stahl, F. Transcriptome analysis using next-generation sequencing. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2013, 24, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Nutiu, R.; Moffat, J.; Blencowe, B.J. SnapShot: High-throughput sequencing applications. Cell 2021, 146, 1044–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoo, C.K.; Abdul-Murad, A.M.; Kua, B.C.; Mohd-Adnan, A. Cryptocaryon irritans infection induces the acute phase response in Lates calcarifer: A transcriptomic perspective. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 33, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Gao, Q.; Tang, B.; Sun, P.; Han, K.; Huang, W. Transcriptome and analysis on the complement and coagulation cascades pathway of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) to ciliate ectoparasite Cryptocaryon irritans infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 50, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.Q.; Zhou, T.; Zhao, J.; Chen, B.H.; Pu, F.; Bai, Y.L.; Wu, Y.D.; Chen, L.; Shi, Y.; Ke, Q.Z.; et al. Transcriptome analysis reveals the temporal gene expression patterns in skin of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) in response to Cryptocaryon irritans infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 99, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Li, J.J.; Li, S.; Liu, H.H.; Xu, D.D.; Chi, C.F.; Zheng, L.B. Transcriptomic analysis of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) reveals the suppression of the inflammatory response from Cryptocaryon irritans infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 144, 109258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Du, J.J.; Li, Y.W.; Ma, P.; Hu, Y.Z.; Li, A.X. Transcriptome analysis provides insights into molecular immune mechanisms of rabbitfish, Siganus oramin against Cryptocaryon irritans infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 88, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.F.; Xia, Y.; Hua, X.T.; Fan, K.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y. Quantitative proteomic analysis in serum of Takifugu rubripes infected with Cryptocaryon irritans. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 104, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Yu, Y.; Liu, X.; Lei, Y.; Zhou, S.; Xie, X.; Jin, S.; Qian, D.; Yin, F. Transcriptomic analysis of Nibea albiflora skin in response to infection by Cryptocaryon irritans. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 98, 819–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Kong, J.D.; Huang, J.S.; Zhou, L.Y.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Miao, R.J.; Yin, F. Integration of metabolomic and transcriptomic analyses to characterize the influence of the gill metabolism of Nibea albiflora on the response to Cryptocaryon irritans infection. Vet. Parasitol. 2021, 298, 109533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoads, A.; Au, K.F. PacBio sequencing and its applications. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2015, 13, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.Z.; Zhang, H.X.; Kohnen, M.V.; Prasad, K.V.S.K.; Gu, L.F.; Reddy, A.S.N. Analysis of transcriptome and epitranscriptome in plants using PacBio Iso-Seq and nanopore-based direct RNA sequencing. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomopoulos, S.; Bayega, A.; Fahiminiya, S.; Djambazian, H.; Berube, P.; Ragoussis, J. Methodologies for transcript profiling using long-read technologies. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, N.; Antonio, F.; Kent, B.; Sadler, K.C.; Sealfon, S.C.; Walsh, M.J.; Elena, Z. High resolution annotation of zebrafish transcriptome using long-read sequencing. Genome Res. 2018, 28, 1415–1425. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Wen, H.B.; Xu, D.P.; Lv, G.H.; Zhou, Y.F. PacBio full-length and Illumina transcriptomes of the gill reveal the molecular response of Corbicula fluminea under aerial exposure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Pan, L.; Tong, R.; Li, Y.; Tian, Y.; Li, D.; Si, L. PacBio full length transcript sequencing and Illumina transcriptome insight into immune defense mechanism of Litopenaeus vannamei under ammonia-N stress. Aquaculture 2021, 536, 736457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, S.C.; Li, Y.Q.; Li, X.C.; Cao, M.; Yang, N. A novel full-length transcriptome resource from multiple immune-related tissues in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) using Pacbio SMART sequencing. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 129, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. Fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertea, M.; Kim, D.; Pertea, G.M.; Leek, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. Transcript-level expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with HISAT, StringTie and Ballgown. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 1650–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertea, M.; Pertea, G.M.; Antonescu, C.M.; Chang, T.C.; Mendell, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Lander, E.S. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel1, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga1, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski1, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fraslin, C.; Chi, Y.; Mukiibi, R.; Hu, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, W.; Li, W.; Houston, D.R.; Robledo, D.; et al. A newly developed 20k SNP array reveals QTLs for disease resistance to Cryptocaryon Irritans in tiger pufferfish (Takifugu Rubripes). preprint, 2024. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=4853888 (accessed on 4 June 2024). [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Minimap2: Pairwise alignment for nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3094–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamancos, G.P.; Pagès, A.; Trincado, J.L.; Bellora, N.; Eyras, E. Leveraging transcript quantification for fast computation of alternative splicing profiles. RNA 2015, 21, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, Z.Q.; Liu, X.Q.; Zhao, S.Q.; Wei, L.; Gao, G. CPC: Assess the protein-coding potential of transcripts using sequence features and support vector machine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W345–W349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Luo, H.; Bu, D.; Zhao, G.; Yu, K.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Chen, R.; Zhao, Y. Utilizing sequence intrinsic composition to classify protein-coding and long non-coding transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlin, H.; Piccinini, A.M. A complex interplay between the extracellular matrix and the innate immune response to microbial pathogens. Immunology 2018, 155, 186–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenzi, H.L.; Lenzi, J.A.; Kerr, I.B.; Antunes, S.L.; Mota, E.M.; Oliveira, D.N. Extracellular matrix in parasitic and infectious diseases. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 1991, 86, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Steukers, L.; Glorieux, S.; Vandekerckhove, A.P.; Favoreel, H.W.; Nauwynck, H.J. Diverse microbial interactions with the basement membrane barrier. Trends Microbiol. 2012, 20, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofat, N.; Wait, R.; Robertson, S.D.; Baines, D.L.; Baker, E.H. Interaction between extracellular matrix molecules and microbial pathogens: Evidence for the missing link in autoimmunity with rheumatoid arthritis as a disease model. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 5, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Sun, M.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Kong, M.; Wang, Y.; Song, J.; Zhang, Q.; He, Y.; Qi, J. Whole transcriptome analysis provides new insight on immune response mechanism of golden pompano (Trachinotus ovatus) to Amyloodinium ocellatum infestation. Aquaculture 2022, 560, 738396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Jiang, L.; Huang, W.; Li, X.; Yuan, L.; Jiang, J.; Zhou, S.; Wang, Y.; Xie, J. Investigating the interplay between Cryptocaryon irritans ectoparasite infection and the immune responses of the head kidney in silver pomfret (Pampus argenteus). Aquaculture 2023, 575, 739780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pribila, J.T.; Quale, A.C.; Mueller, K.L.; Shimizu, Y. Integrins and T cell-mediated immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 22, 157–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medzhitov, R. Origin and physiological roles of inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borish, L.C.; Steinke, J.W. Cytokines and chemokines. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 111, S460–S475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.H.; Secombes, C.J. The cytokine networks of adaptive immunity in fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 1703–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, P.H.; Moses, A.; Früh, K. Evasion of adaptive and innate immune response mechanisms by γ-herpesviruses. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2013, 3, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C. Cytokine regulation and function in T cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 39, 51–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, T.; Shibasaki, Y.; Matsuura, Y. T cells in fish. Biology 2015, 4, 640–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laing, K.J.; Hansen, J.D. Fish T cells: Recent advances through genomics. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 1282–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckheeram, R.V.; Zhou, R.; Verma, A.D.; Xia, B. CD4+T Cells: Differentiation and functions. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 925135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.M.; Duan, Y.M.; Wu, Y.H.; Yang, D.S.; An, J. A novel integrated metabolism-immunity gene expression model predicts the prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma patients. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 728368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haskó, G.; Kuhel, D.G.; Marton, A.; Nemeth, Z.H.; Deitch, E.A.; Szabó, C. Spermine differentially regulates the production of interleukin-12 p40 and interleukin-10 and suppresses the release of the T helper 1 cytokine interferon-gamma. Shock 2000, 14, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azeredo, R.; Perez-Sanchez, J.; Sitja-Bobadilla, A.; Fouz, B.; Tort, L.; Aragao, C.; Costas, B. European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) immune status and disease resistance are impaired by arginine dietary supplementation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.W.; Hojer, C.D.; Zhou, M.J.; Wu, X.M.; Wuster, A.; Lee, W.P.; Yaspan, B.L.; Chan, A.C. Regulation of T cell receptor signaling by DENND1B in TH2 cells and allergic disease. Cell 2016, 164, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.F.; Wang, Z.J.; Chen, X.L.; Peng, X.; Nie, Q.H. CircNFIC balances inflammation and apoptosis by sponging miR-30e-3p and regulating DENND1B expression. Genes 2021, 12, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid-Hempel, P. Immune defence, parasite evasion strategies and their relevance for ‘macroscopic phenomena’ such as virulence. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2009, 364, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velavan, T.P.; Ojurongbe, O. Regulatory T cells and parasites. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 520940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maizels, R.M.; McSorley, H.J. Regulation of the host immune system by helminth parasites. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donelson, J.E. Antigenic variation and the African trypanosome genome. Acta Trop. 2003, 85, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.L.; Liu, Y.; Qu, A.; Wang, J.Y.; Zhao, J.; Ke, Q.Z.; Chen, X.T.; Pu, F.; Wu, L.N.; Xu, P.; et al. Dual RNA-seq reveals a host-pathogen interaction transcriptional regulation pattern between Cryptocaryon irritans and large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Aquaculture 2023, 565, 739104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Subjects | Data | Number | |
|---|---|---|---|
| FL-HG | FL-DG | ||
| Subreads | Total base | 58,401,291,009 | 44,613,937,642 |
| Subreads number | 26,318,483 | 21,660,262 | |
| Average length | 2219 | 2059 | |
| N50 | 2395 | 2211 | |
| Number of CCS | Number of CCS reads | 786,806 | 609,313 |
| FLNC reads number | 704,548 (89.55%) | 505,811 (83.01%) | |
| Mean length of FLNC | 2410 | 2130 | |
| Number of isoforms | HQ isoform number | 47,307 | 34,413 |
| HQ isoform mapped to genome | Unique mapped (%) | 35,931 (75.95%) | 25,614 (74.43%) |
| Multiple mapped (%) | 385 (0.81%) | 271 (0.79%) | |
| Unmapped (%) | 10,991 (23.23%) | 8528 (24.78%) | |
| ID | Description | Abbreviation | Log2 Fold Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HG vs. MG | HG vs. SG | |||
| Chemokines and Chemokine Receptors | ||||
| ENSTRUG00000010223 | C-C chemokine receptor type 12a | CCR12A | 2.69 | 1.82 |
| ENSTRUG00000019936 | C-C chemokine receptor type 7 | CCR7 | −2.21 | −1.59 |
| ENSTRUG00000027740 | C-C chemokine receptor type 9-like | CCR9A | −1.17 | −1.26 |
| ENSTRUG00000023885 | C-C chemokine receptor type 9b | CCR9B | −2.09 | −2.36 |
| ENSTRUG00000029174 | C-C motif chemokine 14-like | CCL14 | −1.91 | −2.07 |
| ENSTRUG00000020129 | Interleukin 1 receptor type 2 | IL1R2 | 1.88 | 2.55 |
| ENSTRUG00000016002 | Interleukin 1 beta | IL1B | 1.78 | 3.00 |
| ENSTRUG00000023550 | Interleukin 1 receptor type 1-like | IL1RL1 | 1.70 | 1.47 |
| ENSTRUG00000026338 | Interleukin 7 receptor | IL7R | −1.80 | −2.00 |
| ENSTRUG00000006788 | Interleukin 8 | IL8 | 2.58 | 3.78 |
| ENSTRUG00000018372 | Interleukin-12 receptor subunit beta-2-like | IL12RB2 | −1.34 | −1.19 |
| ENSTRUG00000033166 | Interleukin 16 | IL16 | −1.08 | −1.03 |
| ENSTRUG00000020732 | Interleukin 17F-like | IL17F | −1.67 | −1.53 |
| ENSTRUG00000006725 | Interleukin-24-like | IL24 | 2.67 | 2.84 |
| ENSTRUG00000021770 | Interleukin-6 receptor subunit beta-like | IL6RB | 1.25 | 1.38 |
| ENSTRUG00000017328 | TNF receptor superfamily member 21 | TNFRSF21 | −1.45 | −1.25 |
| ENSTRUG00000021595 | Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 6-like | TNFSF6 | −1.43 | −1.28 |
| ECM-receptor interaction | ||||
| ENSTRUG00000031037 | Thrombospondin 2 | THBS2 | −2.46 | −2.78 |
| ENSTRUG00000029497 | Laminin subunit alpha 5 | LAMA5 | −1.91 | −2.07 |
| ENSTRUG00000013059 | Integrin subunit alpha 8 | ITGA8 | −1.27 | −1.40 |
| ENSTRUG00000016742 | Integrin subunit alpha 11 | ITGA11 | −1.24 | −1.77 |
| ENSTRUG00000013913 | Collagen alpha-1a(I) chain-like | COL1A1A | −1.45 | −2.18 |
| ENSTRUG00000007520 | Collagen alpha-1b(I) chain-like | COL1A1B | −1.31 | −2.13 |
| ENSTRUG00000015407 | Collagen alpha-2(I) chain | COL1A2 | −1.25 | −2.03 |
| ENSTRUG00000010345 | Collagen alpha-1(II) chain | COL2A1 | −2.81 | −3.58 |
| ENSTRUG00000006672 | Collagen alpha-3(IX) chain | COL9A3 | −1.79 | −1.63 |
| ENSTRUG00000015261 | Collagen alpha-2(IX) chain | COL9A2 | −1.57 | −1.47 |
| T/B cell activation and proliferation | ||||
| ENSTRUG00000010193 | Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit delta | PIK3CD | −1.01 | −1.09 |
| ENSTRUG00000003538 | FYN proto-oncogene, Src family tyrosine kinase | FYN | −1.06 | −1.16 |
| ENSTRUG00000006051 | Zeta chain of T cell receptor associated protein kinase 70 | ZAP70 | −1.39 | −1.45 |
| ENSTRUG00000004669 | LCK proto-oncogene, Src family tyrosine kinase | LCK | −1.30 | −1.48 |
| ENSTRUG00000003789 | CD3 gamma/delta | CD3 | −1.48 | −1.28 |
| ENSTRUG00000010854 | T-cell surface glycoprotein CD4 | CD4 | −1.76 | −2.34 |
| ENSTRUG00000004405 | IL2-inducible T-cell kinase | ITK | −1.23 | −1.39 |
| ENSTRUG00000018363 | Nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 2-like | NFATC2 | −1.16 | −1.51 |
| ENSTRUG00000021189 | Interferon regulatory factor 4-like | IRF4A | −1.20 | −1.23 |
| ENSTRUG00000022517 | Forkhead box P3b | FOXP3B | −2.10 | −2.07 |
| ENSTRUG00000018285 | Transcription factor Maf-like | MAF | −1.28 | −1.04 |
| ID | Description | Symbol | Log2 Fold Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HG vs. MG | HG vs. SG | |||
| ENSTRUG00000003741 | NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase subunit B6 | NDUFB6 | - | 1.06 |
| ENSTRUG00000005382 | PRELI domain containing 1 | PRELID1 | - | 1.07 |
| ENSTRUG00000001507 | Spermine oxidase | SMOX | 1.74 | 1.95 |
| ENSTRUG00000005070 | Solute carrier family 25 member 40 | SLC25A40 | - | 1.24 |
| ENSTRUG00000017613 | DENN domain-containing protein 1B-like | DENND1B | - | −1.16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chi, Y.; Mukiibi, R.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, W.; Robledo, D.; Chen, S.; Li, Y. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Immunosuppression in Tiger Pufferfish (Takifugu rubripes) under Cryptocaryon irritans Infection. Animals 2024, 14, 2058. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14142058
Chi Y, Mukiibi R, Zhang H, Zhang H, Li W, Robledo D, Chen S, Li Y. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Immunosuppression in Tiger Pufferfish (Takifugu rubripes) under Cryptocaryon irritans Infection. Animals. 2024; 14(14):2058. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14142058
Chicago/Turabian StyleChi, Yong, Robert Mukiibi, Hongxiang Zhang, Haien Zhang, Weidong Li, Diego Robledo, Songlin Chen, and Yangzhen Li. 2024. "Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Immunosuppression in Tiger Pufferfish (Takifugu rubripes) under Cryptocaryon irritans Infection" Animals 14, no. 14: 2058. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14142058
APA StyleChi, Y., Mukiibi, R., Zhang, H., Zhang, H., Li, W., Robledo, D., Chen, S., & Li, Y. (2024). Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Immunosuppression in Tiger Pufferfish (Takifugu rubripes) under Cryptocaryon irritans Infection. Animals, 14(14), 2058. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14142058






