Food Safety: Pathological and Biochemical Responses of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) to Parasitological Infestation and Heavy Metals Pollution in Aquaculture System, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Fish Sampling
2.2. Physicochemical Properties of Water
2.3. Fish Health Assessment
2.3.1. Fish Physical Examination
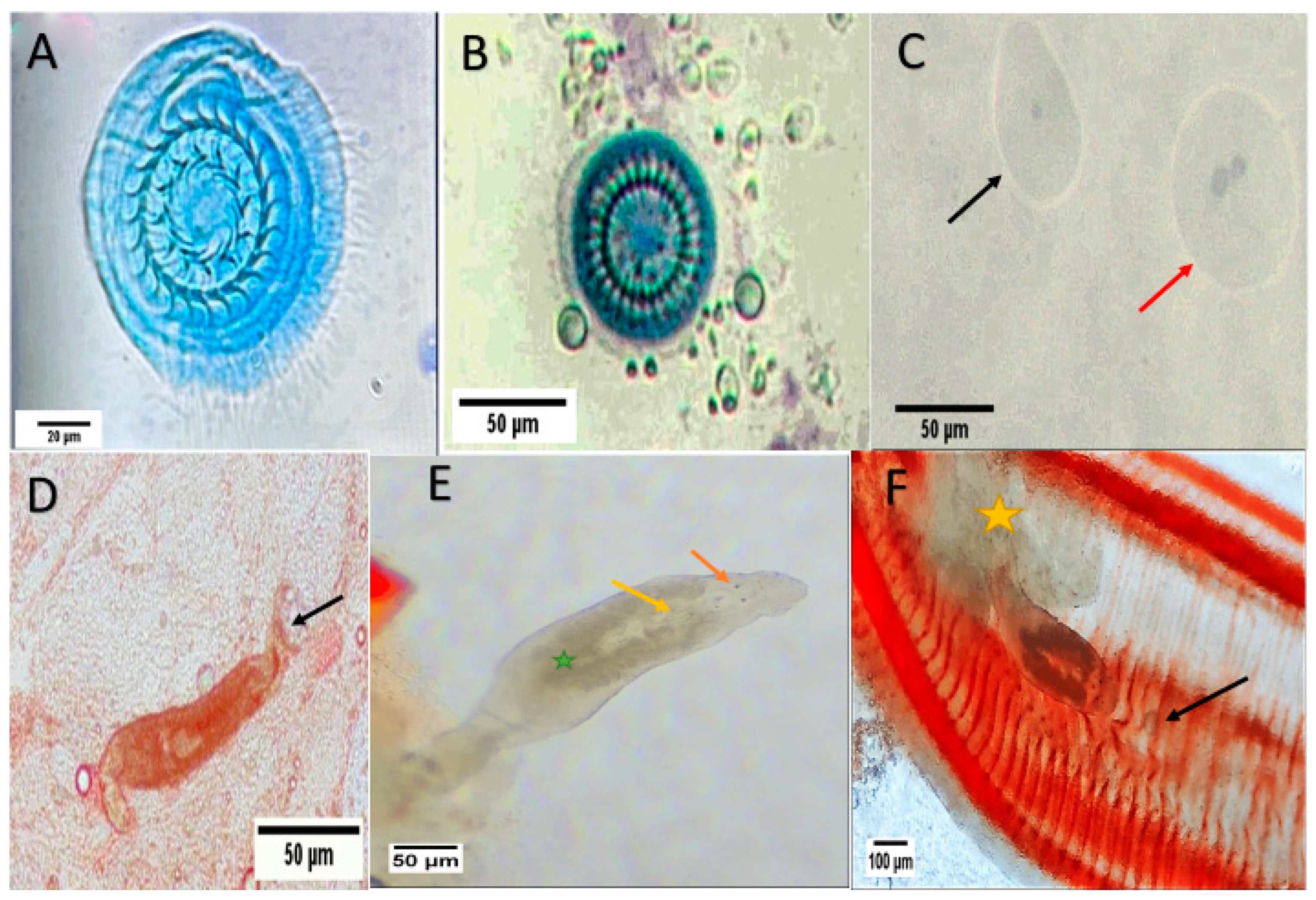
2.3.2. Parasites Identification
2.3.3. Haematological and Biochemical Analyses
2.3.4. Histopathological Studies
2.3.5. Heavy Metal Bioaccumulation in Fish Tissue
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Aquaculture Water Quality
3.2. Fish Parasites Assemblage
3.3. Haematological and Biochemical Analysis
3.3.1. Haematological Parameters
3.3.2. Biochemical Parameters
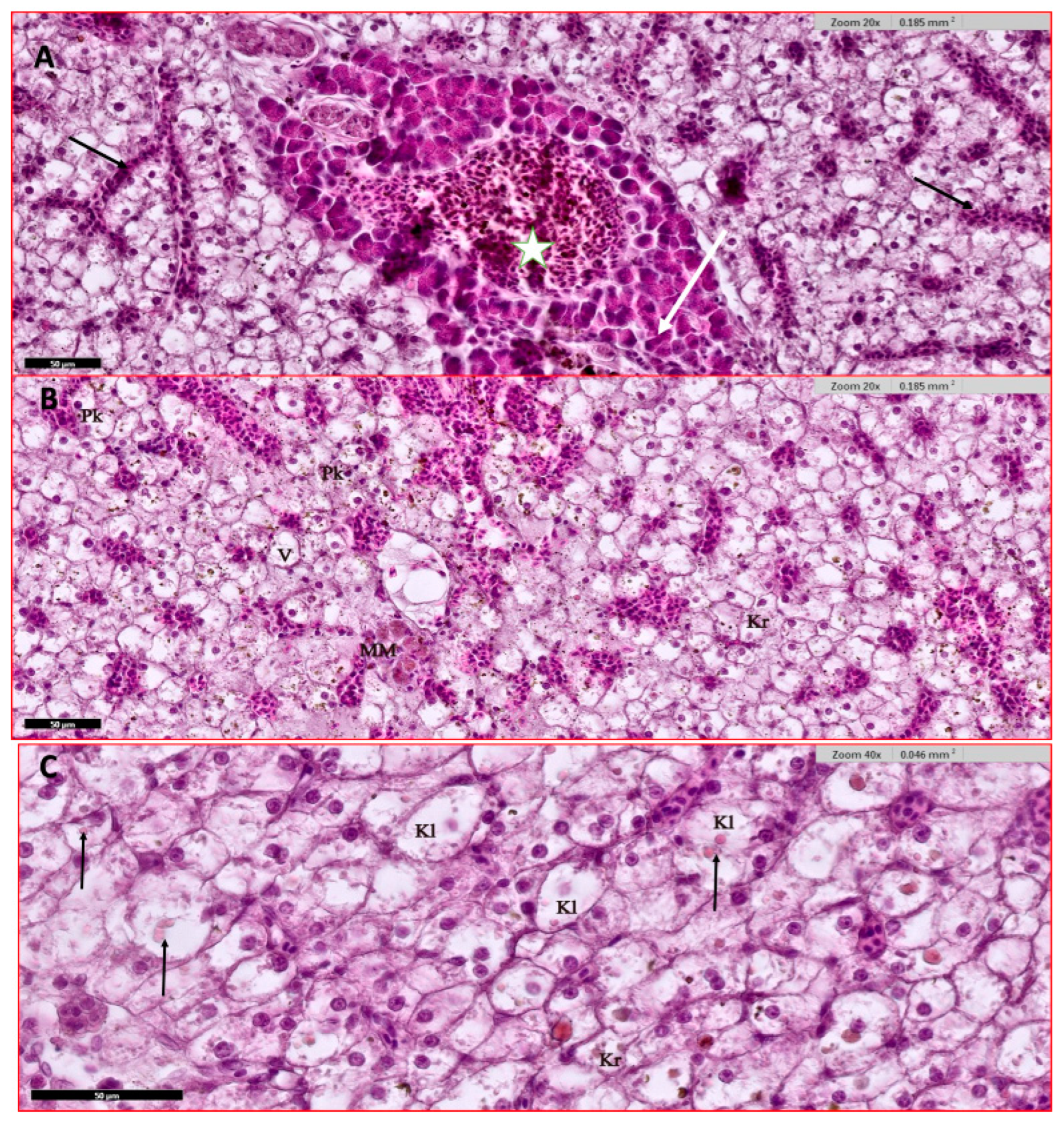
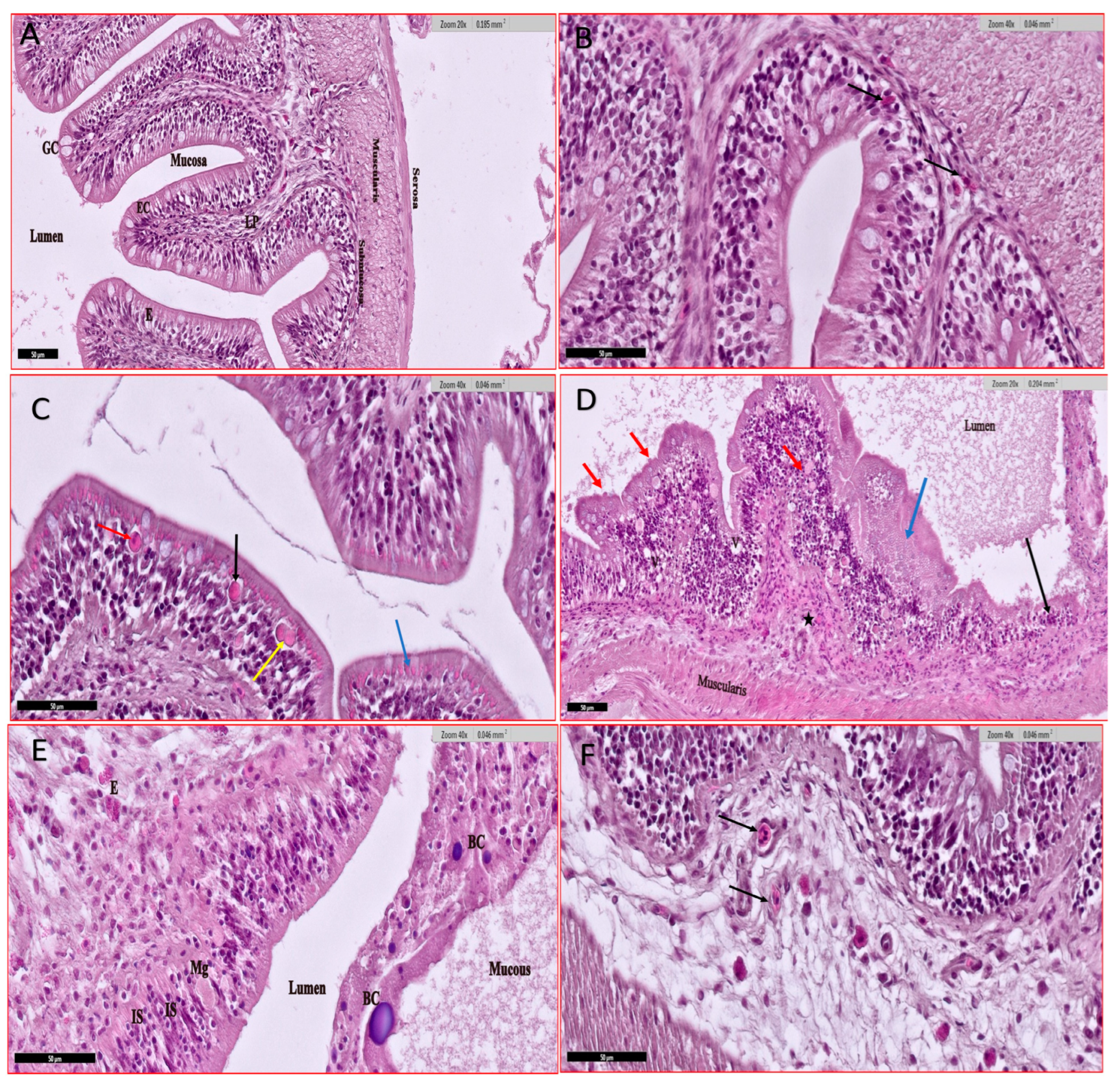
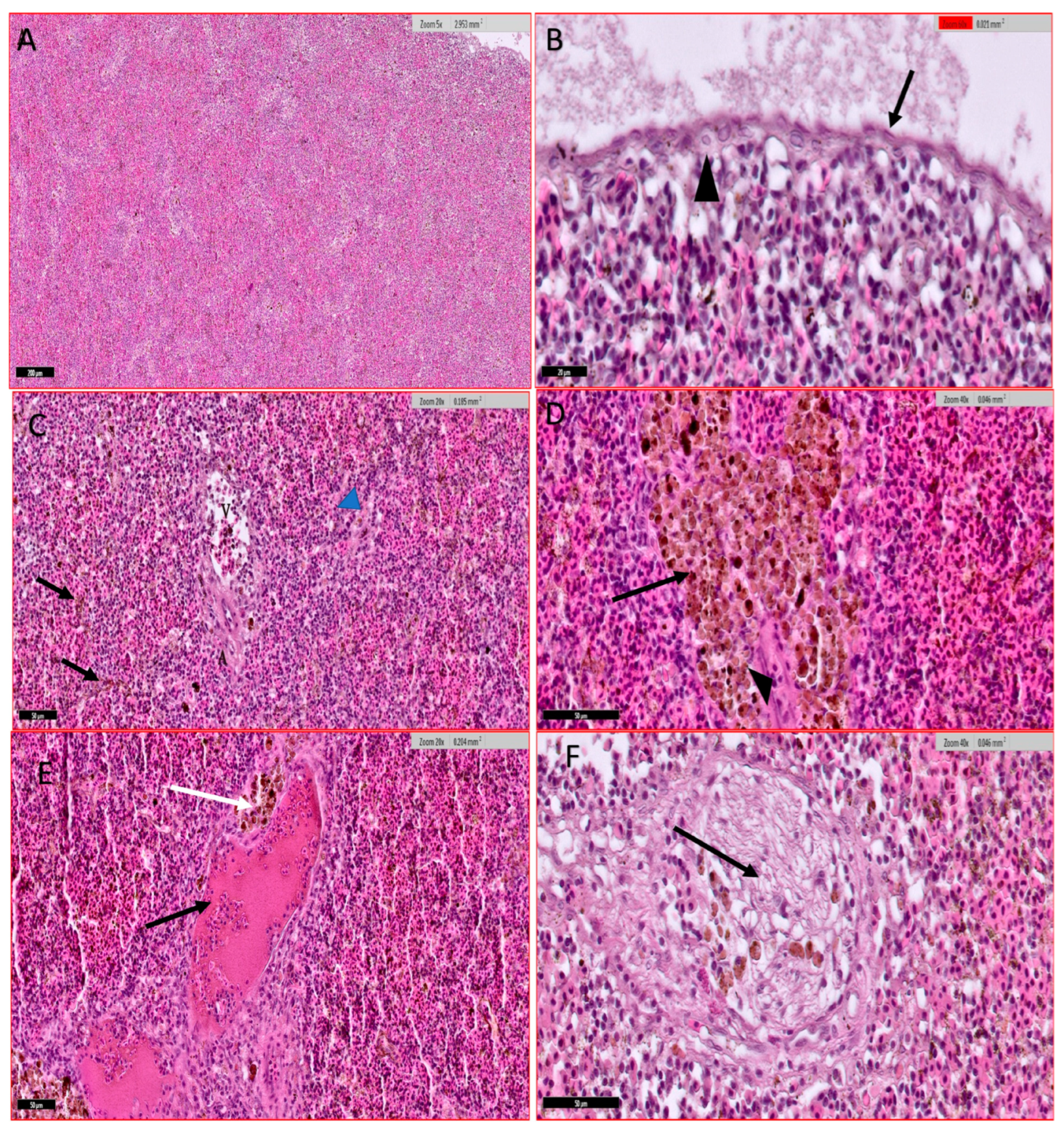
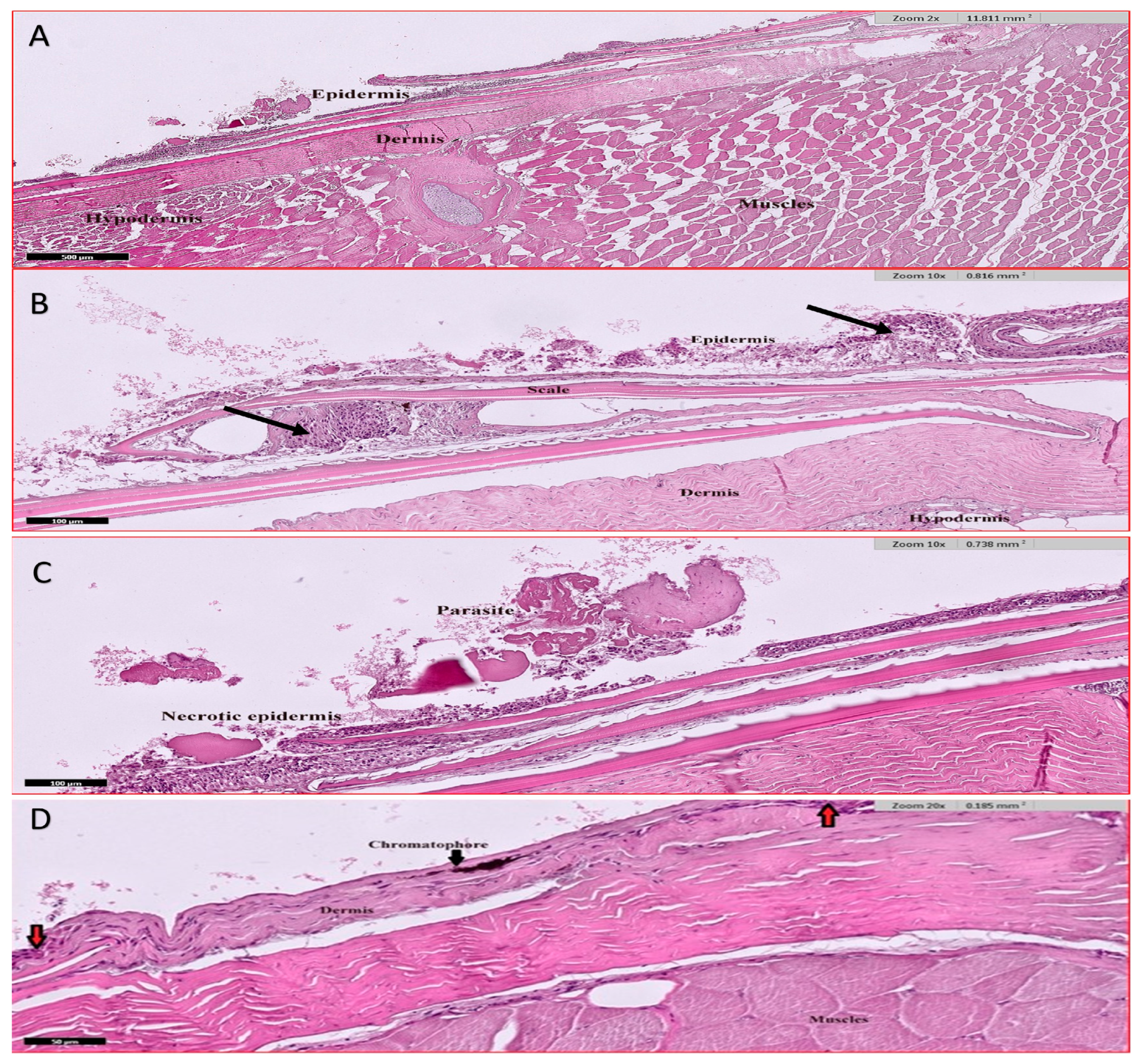
3.4. Histological Studies
3.4.1. Liver and Hepatopancreas
3.4.2. Gills
3.4.3. Intestine
3.4.4. Spleen
3.4.5. Skin
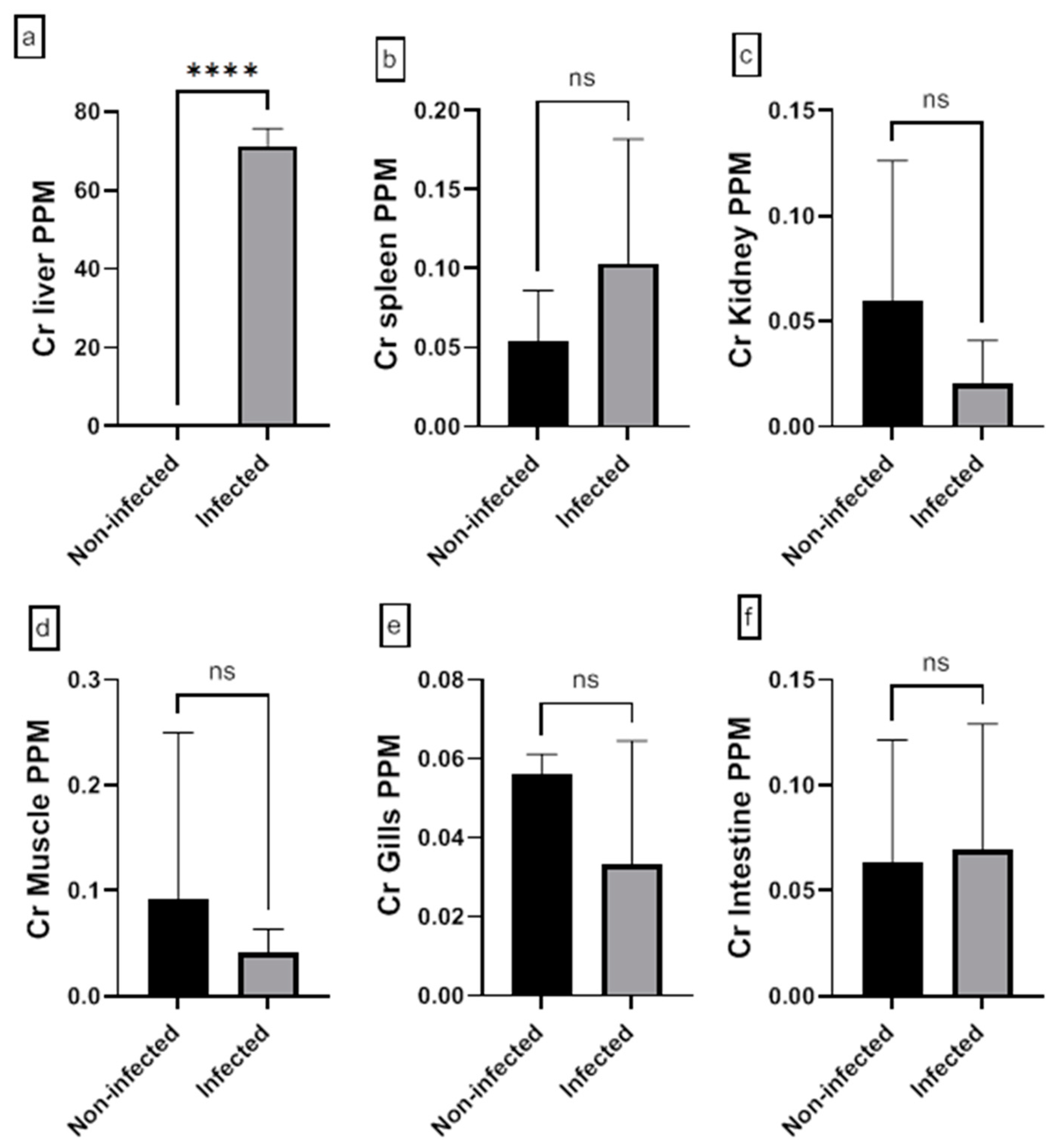
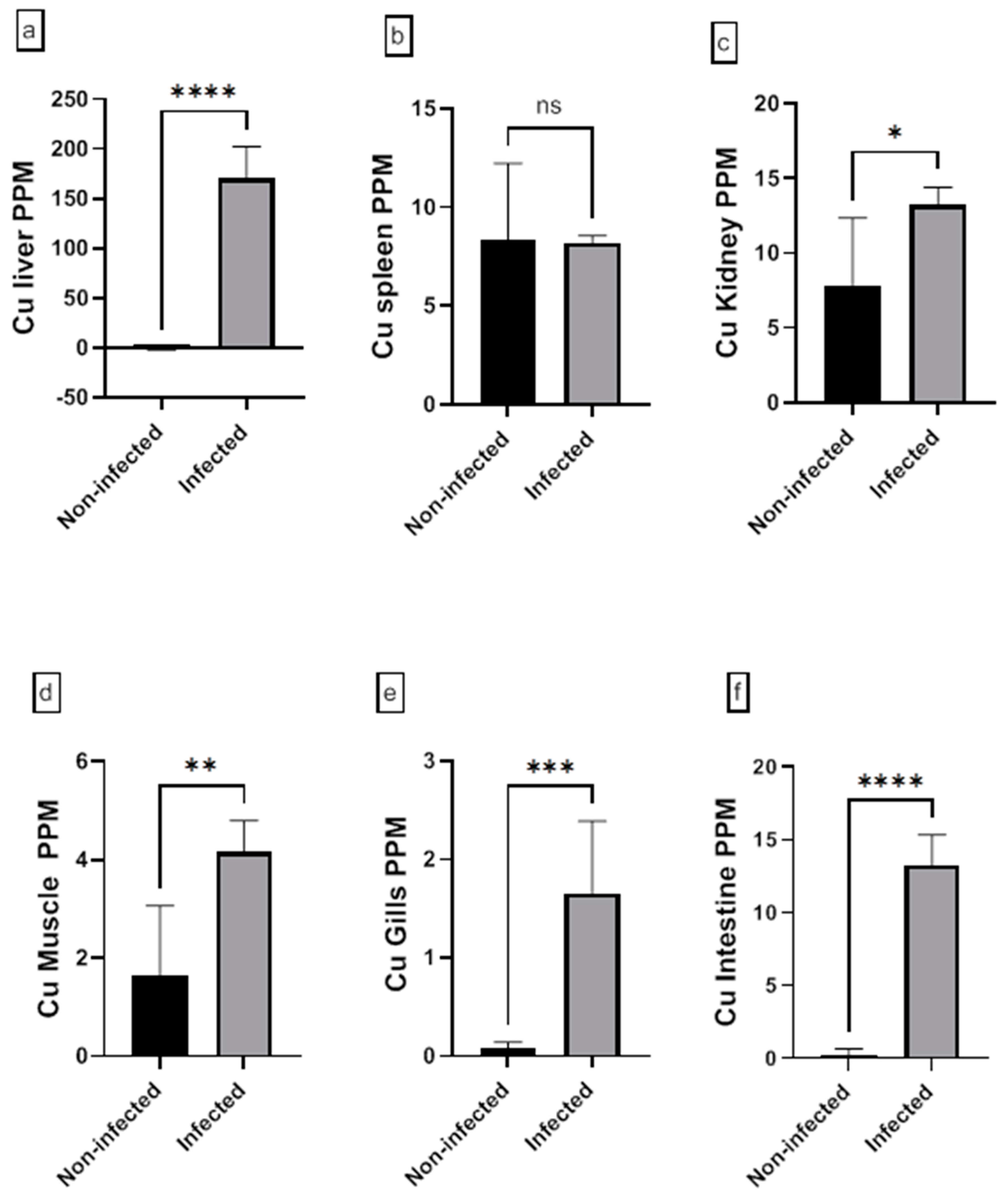
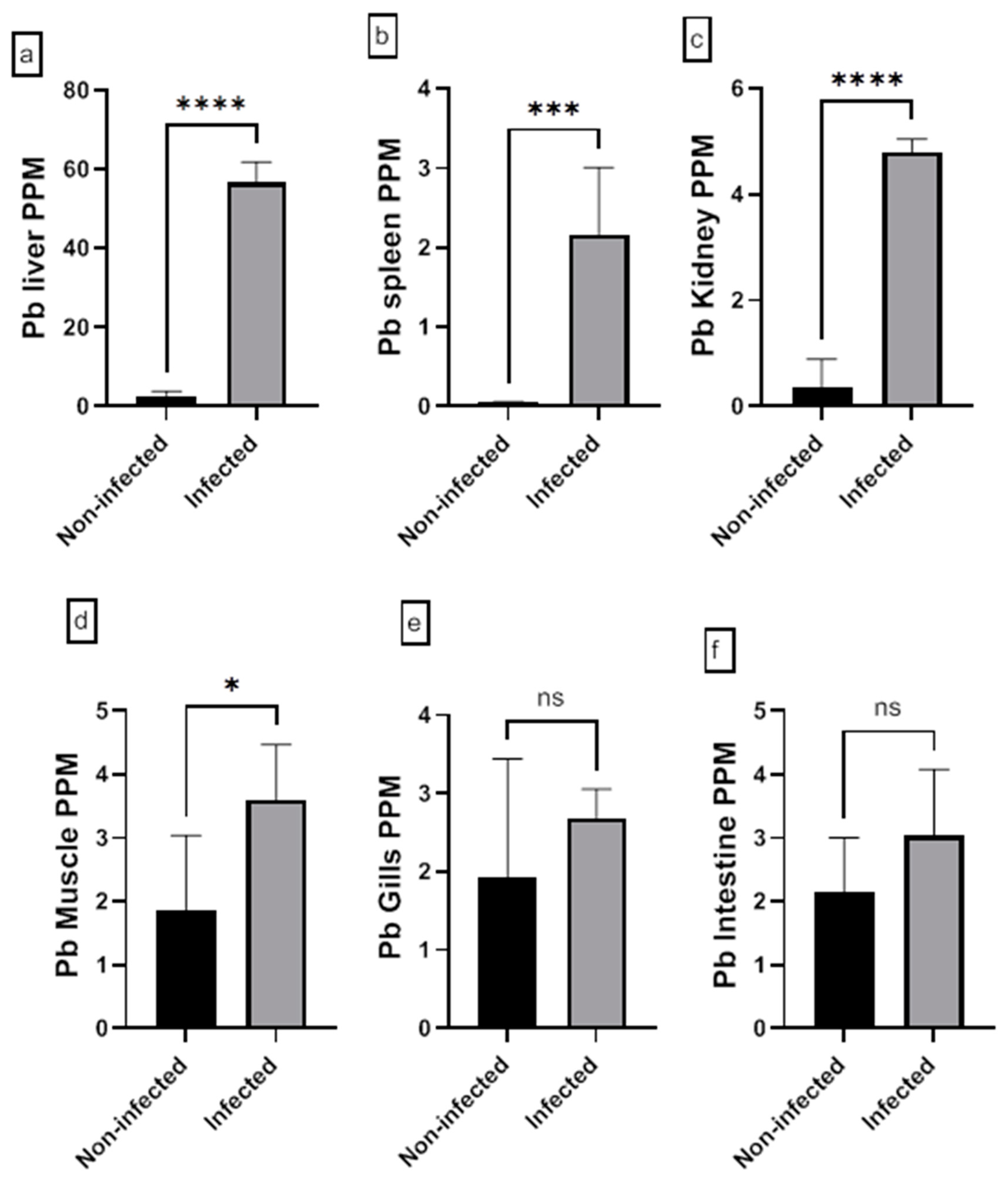
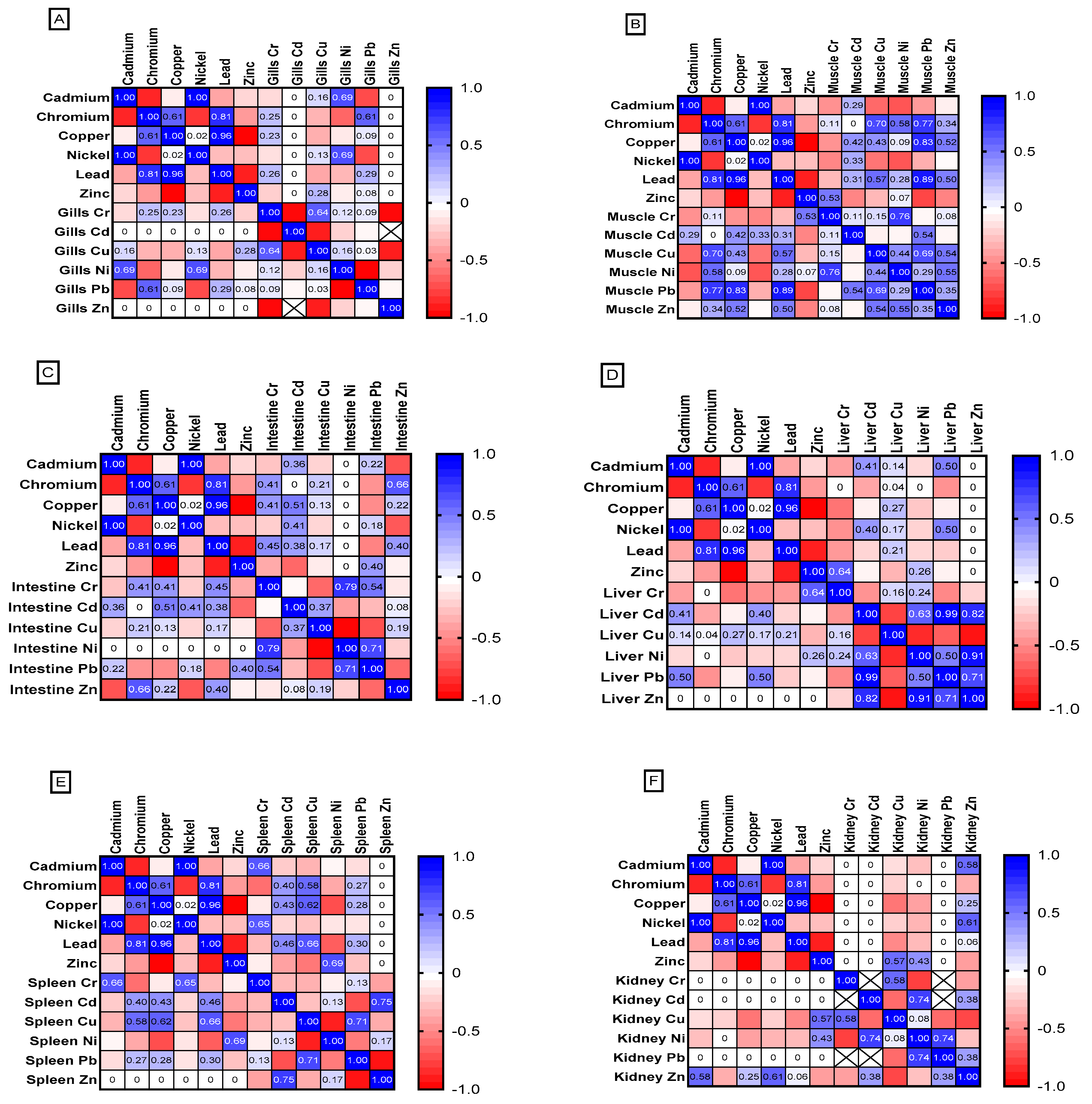
3.5. Analysis of Heavy Metal in Fish Tissue
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Awuchi, C.G.; Chukwu, C.N.; Iyiola, A.O.; Noreen, S.; Morya, S.; Adeleye, A.O.; Twinomuhwezi, H.; Leicht, K.; Mitaki, N.B.; Okpala, C.O.R. Bioactive Compounds and Therapeutics from Fish: Revisiting Their Suitability in Functional Foods to Enhance Human Wellbeing. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 3661866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalili Tilami, S.; Sampels, S. Nutritional Value of Fish: Lipids, Proteins, Vitamins, and Minerals. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2017, 26, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabu, E.; Rajagopalsamy, C.B.T.; Ahilan, B.; Jeevagan, I.J.M.A.; Renuhadevi, M. Tilapia—An Excellent Candidate Species for World Aquaculture: A Review. Annu. Res. Rev. Biol. 2019, 31, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garlock, T.; Asche, F.; Anderson, J.; Ceballos-Concha, A.; Love, D.C.; Osmundsen, T.C.; Pincinato, R.B.M. Aquaculture: The missing contributor in the food security agenda. Glob. Food Secur. 2022, 32, 100620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, L. Assessing the Contribution of Aquaculture to Food Security: A Survey of Methodologies; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Abd-Elrahman, S.M.; Gareh, A.; Mohamed, H.I.; Alrashdi, B.M.; Dyab, A.K.; El-Khadragy, M.F.; Khairy Elbarbary, N.; Fouad, A.M.; El-Gohary, F.A.; Elmahallawy, E.K.; et al. Prevalence and Morphological Investigation of Parasitic Infection in Freshwater Fish (Nile tilapia) from Upper Egypt. Animals 2023, 13, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes-Trujillo, A.; Mendoza-Carranza, M. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the relationship between farm management, water quality and pathogen outbreaks in tilapia culture. J. Fish Dis. 2022, 45, 1529–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiona, O.O.; Anifowose, A.J.; Awojide, S.H.; Adebisi, O.C.; Adesina, B.T.; Ipinmoroti, M.O. Histopathological biomarking changes in the internal organs of Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and catfish (Clarias gariepinus) exposed to heavy metals contamination from Dandaru pond, Ibadan, Nigeria. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2019, 13, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhiee, E.Y.; Elbialy, Z.I.; Saad, A.H.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Aboubakr, M.; El-Nagar, S.H.; El-Diasty, E.M.; Salah, A.S.; Saad, H.M.; Fadl, S.E. The impact of Moringa oleifera on the health status of Nile tilapia exposed to aflatoxicosis. Aquaculture 2021, 533, 736110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Li, Z.; Hassan, S.; Ahmad, S.; Guo, X.; Wanghe, K.; Nabi, G. Heavy metals bioaccumulation and subsequent multiple biomarkers based appraisal of toxicity in the critically endangered Tor putitora. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 228, 113032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahboub, H.H.; Beheiry, R.R.; Shahin, S.E.; Behairy, A.; Khedr, M.H.E.; Ibrahim, S.M.; Elshopakey, G.E.; Daoush, W.M.; Altohamy, D.E.; Ismail, T.A.; et al. Adsorptivity of mercury on magnetite nano-particles and their influences on growth, economical, hemato-biochemical, histological parameters and bioaccumulation in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquat. Toxicol. 2021, 235, 105828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaçar, E. Heavy metal concentrations in various tissues of two fish species from Damsa Dam Lake (Turkey) and associated health risk assessment. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2024, 81, 127339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Moselhy, K.M.; Othman, A.I.; Abd El-Azem, H.; El-Metwally, M.E.A. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in some tissues of fish in the Red Sea, Egypt. Egypt. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2014, 1, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Singh, S.; Jain, A.; Yadav, S.; Dubey, A.; Trivedi, S.P. A review on heavy metal-induced toxicity in fishes: Bioaccumulation, antioxidant defense system, histopathological manifestations, and transcriptional profiling of genes. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2024, 83, 127377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevcikova, M.; Modrá, H.; Slaninova, A.; Svobodova, Z. Metals as a cause of oxidative stress in fish: A review. Vet. Med. 2011, 56, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishaq, S.; Jabeen, G.; Arshad, M.; Kanwal, Z.; Un Nisa, F.; Zahra, R.; Shafiq, Z.; Ali, H.; Samreen, K.B.; Manzoor, F. Heavy metal toxicity arising from the industrial effluents repercussions on oxidative stress, liver enzymes and antioxidant activity in brain homogenates of Oreochromis niloticus. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriel, U.U.; Ezeri, G.N.O.; Opabunmi, O.O. Influence of sex, source, health status and acclimation on the haematology of Clarias gariepinus (Burch, 1822). Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2004, 3, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabner, D.; Rothe, L.; Sures, B. Parasites and Pollutants: Effects of Multiple Stressors on Aquatic Organisms. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2023, 42, 1946–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sures, B.; Nachev, M.; Selbach, C.; Marcogliese, D.J. Parasite responses to pollution: What we know and where we go in ‘Environmental Parasitology’. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaleghzadeh-Ahangar, H.; Malek, M.; McKenzie, K. The parasitic nematodes Hysterothylacium sp. type MB larvae as bioindicators of lead and cadmium: A comparative study of parasite and host tissues. Parasitology 2011, 138, 1400–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nachev, M.; Schertzinger, G.; Sures, B. Comparison of the metal accumulation capacity between the acanthocephalan Pomphorhynchus laevis and larval nematodes of the genus Eustrongylides sp. infecting barbel (Barbus barbus). Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehana, E.-S.E.; Khafaga, A.F.; Elblehi, S.S.; Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Naiel, M.A.E.; Bin-Jumah, M.; Othman, S.I.; Allam, A.A. Biomonitoring of Heavy Metal Pollution Using Acanthocephalans Parasite in Ecosystem: An Updated Overview. Animals 2020, 10, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, B.M.; Avenant-Oldewage, A. Parasites and pollution: The effectiveness of tiny organisms in assessing the quality of aquatic ecosystems, with a focus on Africa. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 18742–18769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, M.; Haseli, M.; Mobedi, I.; Ganjali, M.; MacKenzie, K.J.P. Parasites as heavy metal bioindicators in the shark Carcharhinus dussumieri from the Persian Gulf. Parasitology 2007, 134, 1053–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Pérez, V.J.; Ángeles-Hernández, J.C.; Vega-Sánchez, V.; Zepeda-Velázquez, A.P.; Añorve-Morga, J.; Ponce-Noguez, J.B.; Reyes-Rodríguez, N.E.; De-La-Rosa-Arana, J.L.; Ramírez-Paredes, J.G.; Gómez-De-Anda, F.R. Prevalence of Parasitic Infections with Zoonotic Potential in Tilapia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Animals 2022, 12, 2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SPA. Report: Saudi Arabia’s Fish Farm Production Soars by 56.4%. 2024. Available online: https://www.spa.gov.sa/en/N2184324 (accessed on 7 October 2024).
- Rice, E.W.; Bridgewater, L.; Association, A.P.H.; Association, A.W.W.; Federation, W.E. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pandiyan, J.; Mahboob, S.; Govindarajan, M.; Al-Ghanim, K.A.; Ahmed, Z.; Al-Mulhm, N.; Jagadheesan, R.; Krishnappa, K. An assessment of level of heavy metals pollution in the water, sediment and aquatic organisms: A perspective of tackling environmental threats for food security. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 1218–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Safety and Quality of Water Used in Food Production and Processing: Meeting Report; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Alhassan, E.; Osei, S.; Ampofo-Yeboah, A.; Dandi, S. Prevalence of Endoparasites and Haematology in Redbelly Tilapia from a Shallow Tropical Reservoir in Ghana. Tanzan. J. Sci. 2023, 49, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiyu, M.; Gebreselassie, H.; Haftu, M. Prevalence of Internal Nematode Parasites of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Fish Species caught from Southwestern Part of Lake Tana, Central Gondar, Ethiopia. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2020, 11, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, X.Z.; Cobcroft, J.; Hutson, K.S. Chapter Three—Fish ectoparasite detection, collection and curation. In Advances in Parasitology; Rollinson, D., Stothard, R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 105–157. [Google Scholar]
- El-Khayat, H.M.M.; Sayed, S.S.M.; Mohammed, W.A.; Sadek, A.-S.M. Protozoan and helminths infestation of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus and its correlation with certain water quality variables along river Nile in the area of Greater Cairo. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 345, 123459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, A.; Abbas, F.; Hafeez-Ur-Rehman, M.; Khan, B.N.; Aihetasham, A.; Amin, I.; Hmidullah; Mothana, R.A.; Alharbi, M.S.; Khan, I.; et al. Parasite Diversity in a Freshwater Ecosystem. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran-Duy, A.; Schrama, J.W.; van Dam, A.A.; Verreth, J.A.J. Effects of oxygen concentration and body weight on maximum feed intake, growth and hematological parameters of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Aquaculture 2008, 275, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witeska, M.; Kondera, E.; Ługowska, K.; Bojarski, B. Hematological methods in fish—Not only for beginners. Aquaculture 2022, 547, 737498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancroft, J.D.; Layton, C. 10—The hematoxylins and eosin. In Bancroft’s Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques, 8th ed.; Suvarna, S.K., Layton, C., Bancroft, J.D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, M.; Elbayoumi, Z.; Khader, R.; Elbagory, A. Assessment of Heavy Metal Concentration in Fish Meat of Wild and Farmed Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus), Egypt. Alex. J. Vet. Sci. 2018, 57, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łuczyńska, J.; Pietrzak-Fiećko, R.; Purkiewicz, A.; Łuczyński, M.J. Assessment of Fish Quality Based on the Content of Heavy Metals. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munguti, J.M.; Nairuti, R.; Iteba, J.O.; Obiero, K.O.; Kyule, D.; Opiyo, M.A.; Abwao, J.; Kirimi, J.G.; Outa, N.; Muthoka, M.; et al. Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus Linnaeus, 1758) culture in Kenya: Emerging production technologies and socio-economic impacts on local livelihoods. Aquac. Fish Fish. 2022, 2, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulei, I.R.; Mbuthia, P.G.; Waruiru, R.M.; Nyaga, P.N.; Mutoloki, S.; Evensen, Ø. Management Practices, Farmers’ Knowledge of Diseased Fish, and Their Occurrence in Fish Farms in Nyeri County, Kenya. Vet. Med. Int. 2021, 2021, 8896604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridha, M. Comparative study of growth performance of three strains of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, L. at two stocking densities. Aquac. Res. 2005, 37, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridha, M.; Saheb, A.; Hossain, M.; El-Dakour, S. Effect of Probiotics and Dietary Levels of Protein on Growth, Muscle Quality and Expression of Some Immune Genes in the Head Kidney of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). J. Mar. Sci. Res. Oceanogr. 2023, 6, 174–187. [Google Scholar]
- Rebouças, V.T.; dos Santos Lima, F.R.; de Holanda Cavalcante, D.; do Carmo e Sá, M.V. Reassessment of the suitable range of water pH for culture of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus L. in eutrophic water. Acta Scientiarum. Anim. Sci. 2016, 38, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, R.; Masood, Z.; Ul Hassan, H.; Khan, W.; Mushtaq, S.; Ali, A.; Gul, Y.; Jafari, H.; Habib, A.; Ishaq Ali Shah, M.; et al. Growth performance, haematological assessment and chemical composition of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (Linnaeus, 1758) fed different levels of Aloe vera extract as feed additives in a closed aquaculture system. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanbo, W.; Wenju, Z.; Weifen, L.; Zirong, X. Acute toxicity of nitrite on tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) at different external chloride concentrations. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2006, 32, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, C.E.; Tucker, C.; McNevin, A.; Bostick, K.; Clay, J. Indicators of Resource Use Efficiency and Environmental Performance in Fish and Crustacean Aquaculture. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2007, 15, 327–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.E.; Tucker, C.S.; Somridhivej, B. Alkalinity and Hardness: Critical but Elusive Concepts in Aquaculture. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2016, 47, 6–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Cao, J.; Qin, X.; Qiu, W.; Mei, J.; Xie, J. Toxic Effects on Bioaccumulation, Hematological Parameters, Oxidative Stress, Immune Responses and Tissue Structure in Fish Exposed to Ammonia Nitrogen: A Review. Animals 2021, 11, 3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stentiford, G.D.; Neil, D.M.; Peeler, E.J.; Shields, J.D.; Small, H.J.; Flegel, T.W.; Vlak, J.M.; Jones, B.; Morado, F.; Moss, S.; et al. Disease will limit future food supply from the global crustacean fishery and aquaculture sectors. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2012, 110, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiazon, K.M.A. Updates on Aquatic Parasites in Fisheries: Implications to Food Safety, Food Security and Environmental Protection. J. Coast. Zone Manag. 2015, 18, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, H.N.; Balian, S.C.; Relvas, R.S.; Soares, H.S.; Queiroz, M.R.; Martins, M.L.; Cardoso, P.H.M. Parasitological diagnosis in ornamental freshwater fish from different fish farmers of five Brazilian states. Braz. J. Biol. 2023, 83, e270067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, E.; Mohamed Al Tayip, A.; Khaleel Abd Elghaffar Nasr, S.; Mohamed Sayed, G.; Elkamel, A.A. Acanthogyrus Tilapiae Infections in Wild and Cultured Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Assiut Vet. Med. J. 2017, 63, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinsanya, B.; Emmanuel, A.; Dada, E.O.; Saliu, J.; Olasehinde, G.; Patrick Omoregie, I. Accumulation of PCBs and Infections of Parasitic helminthes in Synodontis filamentosus (Boulenger, 1901) and Tilapia zillii (Gervais, 1848) of Epe Lagoon, Lagos, Nigeria. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2020, 24, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bekele, J.; Hussien, D. Prevalence of Internal Parasites of Oreochromis niloticus and Clarias gariepinus Fish Species in Lake Ziway, Ethiopia. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2015, 6, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britton, J.R.; Harper, D.M. Length–weight relationships of fish species in the freshwater rift valley lakes of Kenya. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2006, 22, 334–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assen, A.A. Prevalence of Internal Parasitic Helminthes Infected Oreochromis niloticus (Nile tilapia), Clarias gariepinus (African catfish) and Cyprinus carpio (Common carp) in Lake Lugo (Hayke), Northeast Ethiopia. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2019, 5, 233. [Google Scholar]
- Jerônimo, G.T.; da Cruz, M.G.; Bertaglia, E.d.A.; Furtado, W.E.; Martins, M.L. Fish parasites can reflect environmental quality in fish farms. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 14, 1558–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baidoo, K.; Abobi, S.; Agbeko, E. Ecto-parasites Infestation of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in Concrete Ponds in Tamale, Ghana. Aquac. Int. 2015, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojwala, R.A.; Otachi, E.O.; Kitaka, N.K. Effect of water quality on the parasite assemblages infecting Nile tilapia in selected fish farms in Nakuru County, Kenya. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 3459–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suliman, E.A.M.; Al-Harbi, A.H. Prevalence and seasonal variation of ectoparasites in cultured Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus in Saudi Arabia. J. Parasit. Dis. 2016, 40, 1487–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mortuza, M.G.; Al-Misned, F.A. Prevalence of ectoparasites in carp fry and fingerlings of Rajshahi district, Bangladesh. J. Parasit. Dis. 2015, 39, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ihsan, B.; Sitinjak, R.S. Prevalence of Ectoparasites in Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in Tarakan. J. Med. Vet. 2023, 6, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfaye, A.; Teklu, A.; Bekelle, T.; Tkue, T.; Kebede, E.; Gebretsadik, T.; Berhe, N. A survey on occurrence of internal and external fish parasites and causes of fish population reduction in Lake Hashenge, Tigray, Ethiopia. Ethiop. Vet. J. 2017, 21, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Long, J.H.; Hale, M.E.; McHenry, M.J.; Westneat, M.W. Functions of Fish Skin: Flexural Stiffness and Steady Swimming of Longnose Gar Lepisosteus osseus. J. Exp. Biol. 1996, 199, 2139–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noga, E.J. Review Article: Skin Ulcers in Fish: Pfiesteria and Other Etiologies. Toxicol. Pathol. 2000, 28, 807–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebastião, F.A.; Nomura, D.; Sakabe, R.; Pilarski, F. Hematology and Productive Performance of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Naturally Infected With Flavobacterium columnare. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2011, 42, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herczeg, D.; Ujszegi, J.; Kásler, A.; Holly, D.; Hettyey, A. Host-multiparasite interactions in amphibians: A review. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romansic, J.M.; Johnson, P.T.J.; Searle, C.L.; Johnson, J.E.; Tunstall, T.S.; Han, B.A.; Rohr, J.R.; Blaustein, A.R. Individual and combined effects of multiple pathogens on Pacific treefrogs. Oecologia 2011, 166, 1029–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okon, E.M.; Okocha, R.C.; Taiwo, A.B.; Michael, F.B.; Bolanle, A.M. Dynamics of co-infection in fish: A review of pathogen-host interaction and clinical outcome. Fish Shellfish Immunol. Rep. 2023, 4, 100096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pigeault, R.; Cozzarolo, C.S.; Choquet, R.; Strehler, M.; Jenkins, T.; Delhaye, J.; Bovet, L.; Wassef, J.; Glaizot, O.; Christe, P. Haemosporidian infection and co-infection affect host survival and reproduction in wild populations of great tits. Int. J. Parasitol. 2018, 48, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshath, A.A.; Rajan, A.P.; Vimal, S.; Prabhakaran, V.-S.; Ganesan, R. Bacterial Pathogenesis in Various Fish Diseases: Recent Advances and Specific Challenges in Vaccine Development. Vaccines 2023, 11, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandford, M.I.; Taylor-Brown, A.; Schlacher, T.A.; Nowak, B.; Polkinghorne, A. Epitheliocystis in fish: An emerging aquaculture disease with a global impact. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quezada-Rodriguez, P.R.; Taylor, R.S.; Downes, J.; Egan, F.; White, S.; Brenan, A.; Rigby, M.; Nowak, B.F.; Ruane, N.M.; Wynne, J.W. Prevalence of epitheliocystis in freshwater Atlantic salmon reared in flow-through and recirculation aquaculture systems. J. Fish Dis. 2022, 45, 1721–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, A.J.; Hassan, A.H.; Kadhim, K.H.; Kadhim, K.K. The immunity function of rodlet cells in the intestine of Binni fish (Mesopotamichthys sharpeyi). J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 2022, 9, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silphaduang, U.; Colorni, A.; Noga, E.J. Evidence for widespread distribution of piscidin antimicrobial peptides in teleost fish. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2006, 72, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitjà-Bobadilla, A.; Estensoro, I.; Pérez-Sánchez, J. Immunity to gastrointestinal microparasites of fish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 64, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnár, K.; Ostoros, G.; Dunams-Morel, D.; Rosenthal, B.M. Eimeria that infect fish are diverse and are related to, but distinct from, those that infect terrestrial vertebrates. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2012, 12, 1810–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiras, J.C.; Pavanelli, G.C.; Takemoto, R.M.; Nawa, Y. An Overview of Fish-borne Nematodiases among Returned Travelers for Recent 25 Years-Unexpected Diseases Sometimes Far Away from the Origin. Korean J. Parasitol. 2018, 56, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padrilah, S.N.; Ahmad, S.A.; Yasid, N.A.; Sabullah, M.K.; Daud, H.M.; Khalid, A.; Shukor, M.Y. Toxic effects of copper on liver and cholinesterase of Clarias gariepinus. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 22510–22523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sures, B. Host–parasite interactions in polluted environments. J. Fish Biol. 2008, 73, 2133–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmat, R.; Fayyaz, S.; Kazi, N.; Mahmood, S.J.; Uddin, F. Natural Bioremediation of Heavy Metals Through Nematode Parasite of Fish. Biotechnology 2008, 7, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, A.; Câmara, N.; Sierra, E.; Arbelo, M.; Bernaldo de Quirós, Y.; Jepson, P.D.; Deaville, R.; Díaz-Delgado, J.; Suárez-Santana, C.; Castro, A.; et al. Cetacean Intracytoplasmic Eosinophilic Globules: A Cytomorphological, Histological, Histochemical, Immunohistochemical, and Proteomic Characterization. Animals 2023, 13, 2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-L.; Chen, H.-C. Effects of gallium on common carp (Cyprinus carpio): Acute test, serum biochemistry, and erythrocyte morphology. Chemosphere 2003, 53, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghawri, A.; Nashaat, M. Molecular Identification of Enterogyrus sp. Parasite (Dactylogyridae: Ancyrocephalinae) and its Impact on the Health Status of the Red tilapia (Oreochromis sp.) in Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2022, 26, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinel, N.C.; Bolnick, D.I. Melanomacrophage Centers as a Histological Indicator of Immune Function in Fish and Other Poikilotherms. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo Ismael, A.; Elgohary, M.; Tanekhy, M.; Gaafar, A.; Alsenosy, A.e.; Elbialy, A.; Abaza, S.; Soliman, M. Efficacy of Dietary Probiotic Supplementation with Inclusion of Q Z Toss™ on Nile tilapia. Damanhour J. Vet. Sci. 2019, 3, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waly, D.; Muthupandian, A.; Fan, C.-W.; Anzinger, H.; Magor, B.G. Immunoglobulin VDJ repertoires reveal hallmarks of germinal centers in unique cell clusters isolated from zebrafish (Danio rerio) lymphoid tissues. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1058877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ŞAhan, A.; Duman, S. Influence of \beta-1,3/1,6 glucan applications on some non-specific cellular immune response and haematologic parameters of healthy Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L., 1758). Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2010, 34, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Eissa, I.A.M.; Abdeen, A.; Abdel-Latif, H.M.R.; Ismail, M.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Hassan, A.M. Lycopene and resveratrol ameliorate zinc oxide nanoparticles-induced oxidative stress in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 69, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoseinifar, S.H.; Yousefi, S.; Van Doan, H.; Ashouri, G.; Gioacchini, G.; Maradonna, F.; Carnevali, O. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Defense in Fish: The Implications of Probiotic, Prebiotic, and Synbiotics. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2020, 29, 198–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, M.M.; El-Gameel, S.M.; Ismael, E. Evaluation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α); gamma interferon (IFN-γ) genes and oxidative stress in sheep: Immunological responses induced by Oestrus ovis (Diptera: Oestridae) infestation. J. Parasit. Dis. 2020, 44, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, J.; Secombes, C.J. The Function of Fish Cytokines. Biology 2016, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Water Quality Parameters | ||
| Water Parameters (n = 6) | Mean ± SD | Standard Limits by WHO Guidelines |
| pH (unit) | 6.57 ± 0.22 | 5.5 to 9.5 |
| Salinity (g/L) | 0.88 ± 0.55 | 0.5 to 2.5 |
| Electrical Conductivity (µS/cm) | 1160 ± 520.5 | 100 to 2000 |
| Total Dissolve Solids (mg/L) | 777.5 ± 347.1 * | <400 |
| Ammonia (mg/L) | 6.83 ± 1.51 * | 1.5 |
| Nitrate (mg/L) | 1.93 ± 1.17 | 0.2 to 219 |
| Nitrite (mg/L) | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 3 |
| Total Alkalinity (mg/L) | 77.00 ± 20.63 * | 20 |
| Total Hardness (mg/L) | 291.7 ± 256.0 * | 50–100 |
| Phosphate (mg/L) | 0.68 ± 0.24 * | 0.4–0.5 |
| Sulfate (mg/L) | 72.92 ± 71.31 | No health-based guideline value |
| Chlorine (mg/L) | 0.13 ± 0.12 | 5 |
| Water heavy metal concentrations | ||
| Heavy metal (PPM) (n = 6) | Mean ±SD | Standard limits by WHO guidelines |
| Cr | 0.37 ± 0.04 * | 0.05 |
| Cd | 0.08 ± 0.04 * | 0.005 |
| Cu | 1.11 ± 0.08 | 1.5 |
| Ni | 0.35 ± 0.19 * | 0.07 |
| Pb | 0.427 ± 0.29 * | 0.05 |
| Zn | 4.18 ± 1.47 | 5.0 |
| Variable | Non-Infected (n = 81) | Infected (n = 30) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | |||
| No. Male | 51 (62.96%) | 27 (90%) | p = 0.0051 |
| No. Female | 30 (37.04%) | 3 (10%) | |
| Weight (g) | |||
| Total Average | 216.9 ± 65.52 | 157.0 ± 62.71 | p < 0.0001 |
| Male | 218.2 ± 66.56 | 161.9 ± 64.33 a | p = 0.0004 a |
| Female | 214.8 ± 64.77 | 113.3 ± 5.77 b | p = 0.0112 b |
| Weight Classes (g) | |||
| I (70–100 g) | 3 (3.70%) | 0 | p = 0.67 |
| II (110–200 g) | 46 (56.79%) | 21 (70%) | |
| III (210–300 g) | 28 (34.57%) | 9 (30%) | |
| IV (>310 g) | 4 (4.94%) | 0 | |
| Length (cm) | |||
| Total Average | 23.65 ± 2.935 | 20.72 ± 1.893 | p < 0.0001 |
| Male | 23.61 ± 2.505 | 20 ± 1 a | p < 0.0001 a |
| Female | 23.73 ± 3.596 | 20.17 ± 1.893 b | p = 0.0256 b |
| Length classes (cm) | |||
| I (<18 cm) | 1 (1.23%) | 0 | p = 0.6858 |
| II (18–28 cm) | 79 (97.53%) | 30 (100%) | |
| III (>28 cm) | 1 (1.23%) | 0 | |
| Parasite | Site of Infection | Incidence (n = 30) | Prevalence (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protozoan (Trichodina truttae) | Skin/Gills | 3 | 10 |
| Protozoan (Trichodina heterodentata) | Skin | 1 | 3.3 |
| Protozoan (Ichthyophthirius multifiliis) | Skin | 1 | 3.3 |
| Monogenean (Dactylogyrus spp.) | Skin/Gills | 18 | 60 |
| Monogenean (Cichlidogyrus tilapiae) | Gills | 2 | 6.7 |
| Mesomycetozoea (Icthyophonus hoferi) | Kidney/Spleen | 1 | 3.3 |
| Coccidian protozoa | Intestine | 1 | 3.3 |
| Nematode (Capillaria spp.) | Intestine | 3 | 10 |
| Trematode (Monogeneans) | Protozoa | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dactylogyrus spp. | Cichlidogyrus tilapiae | Trichodina spp. | Icthyophthirius multifiliis | |
| Gender | ||||
| Male | 16 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| Female | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Weight (g) | ||||
| I (70–100 g) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| II (110–200 g) | 10 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| III (210–300 g) | 8 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| Length (cm) | ||||
| I (<18 cm) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| II (18–28 cm) | 18 | 2 | 4 | 1 |
| III (>28 cm) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Mesomycetozoea | Protozoa | Nematodes | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ichthyophonus hoferi | Coccidian | Capillaria spp. | |
| Gender | |||
| Male | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| Female | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Weight (g) | |||
| 70–100 g | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 110–200 g | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| 210–300 g | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Length (cm) | |||
| <18 cm | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 18–28 cm | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| >28 cm | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Parameter | Non-Infected Fish | Infected Fish | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| WBC (103/uL) | 12.96± 2.675 | 33.17 ± 1.260 | **** |
| Neutrophils (103/uL) | 1.66 ± 0.332 | 1.85 ± 0.249 | ns |
| Lymphocytes (103/uL) | 6.80 ± 0.194 | 7.23 ± 0.787 | ns |
| Monocytes 103/uL | 0.566 ± 0.533 | 2.42 ± 0.388 | **** |
| Eosinophils (103/uL) | 0.008 ± 0.011 | 0.48 ± 0.1909 | *** |
| Basophil (103/uL) | 0.821 ± 0.575 | 0.84 ± 0.724 | ns |
| RBC (106/uL) | 5.23 ± 0.430 | 1.470 ± 0.287 | **** |
| HGB (g/dL) | 8.367 ± 1.527 | 5.700 ± 0.971 | ** |
| HCT (%) | 39.80 ± 1.230 | 32.05 ± 5.542 | ** |
| MCV (fL) | 185.8 ± 2.872 | 166.8 ± 5.095 | **** |
| MCH (pg) | 36.87 ± 2.333 | 30.75 ± 1.861 | *** |
| MCHC (g/dL) | 24.37 ± 2.002 | 18.58 ± 1.132 | **** |
| PLT count (103/uL) | 16.00 ± 2.966 | 27.00 ± 1.789 | **** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alsulami, M.N.; Baowidan, S.K.; Aljarari, R.M.; Albohiri, H.H.; Khan, S.A.; Elkhawass, E.A. Food Safety: Pathological and Biochemical Responses of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) to Parasitological Infestation and Heavy Metals Pollution in Aquaculture System, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Animals 2025, 15, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15010039
Alsulami MN, Baowidan SK, Aljarari RM, Albohiri HH, Khan SA, Elkhawass EA. Food Safety: Pathological and Biochemical Responses of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) to Parasitological Infestation and Heavy Metals Pollution in Aquaculture System, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Animals. 2025; 15(1):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15010039
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlsulami, Muslimah N., Sarah Khaled Baowidan, Rabab M. Aljarari, Haleema H. Albohiri, Samar A. Khan, and Elham Ali Elkhawass. 2025. "Food Safety: Pathological and Biochemical Responses of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) to Parasitological Infestation and Heavy Metals Pollution in Aquaculture System, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia" Animals 15, no. 1: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15010039
APA StyleAlsulami, M. N., Baowidan, S. K., Aljarari, R. M., Albohiri, H. H., Khan, S. A., & Elkhawass, E. A. (2025). Food Safety: Pathological and Biochemical Responses of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) to Parasitological Infestation and Heavy Metals Pollution in Aquaculture System, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Animals, 15(1), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15010039







