Outbreak of Respiratory Disease Due to Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus with Concomitant Infections by Histophilus somni and Pasteurella multocida in Adult Dairy Cows and Calves from Southern Brazil
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Geographical Location, Clinical Presentation, and Sampling
2.2. Histopathological Evaluations and Immunohistochemical Detection of BRSV Antigens
2.3. Molecular Detection of Infectious Agents Associated with Respiratory Disease of Cattle
2.4. Sanger Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
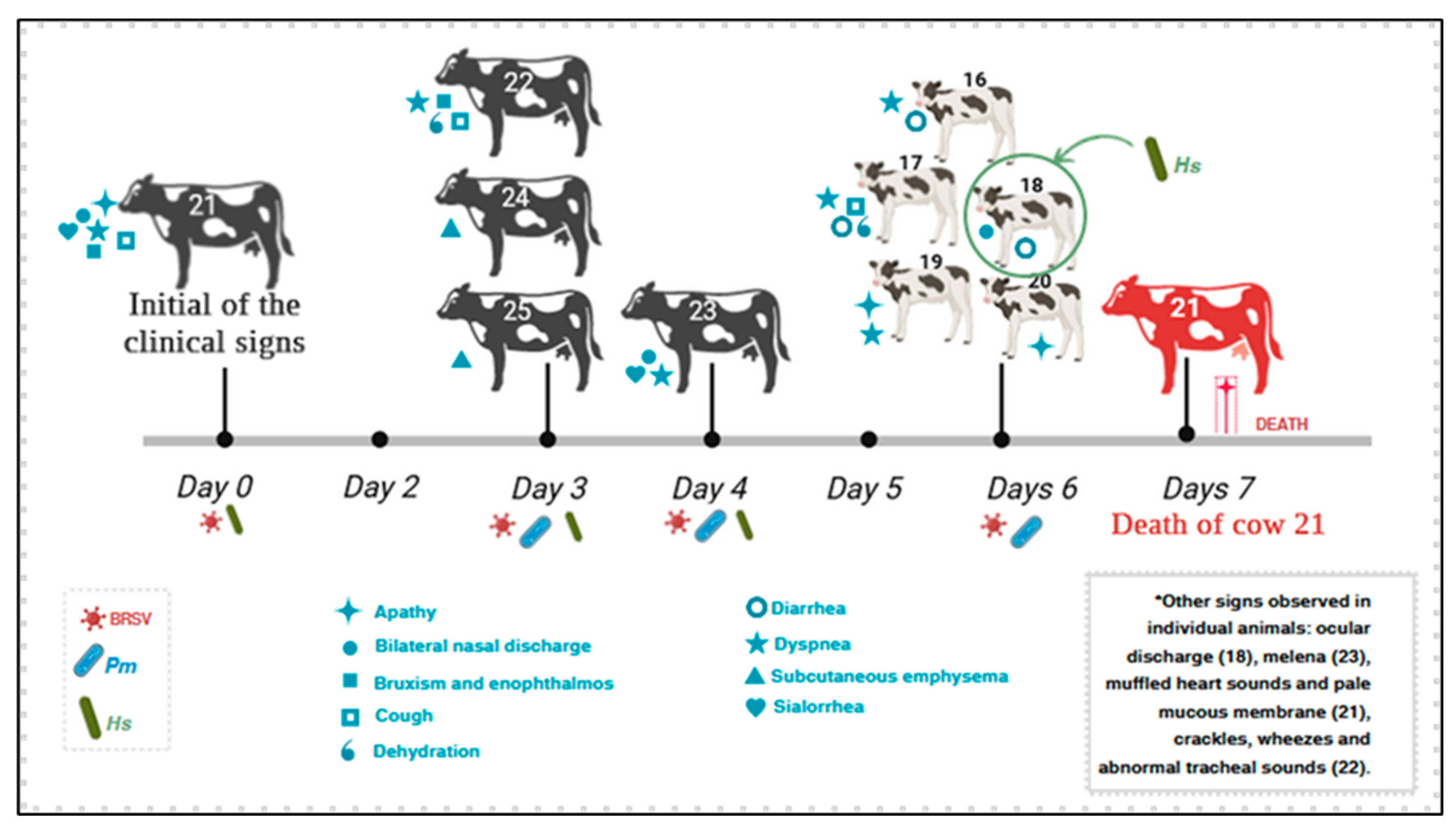
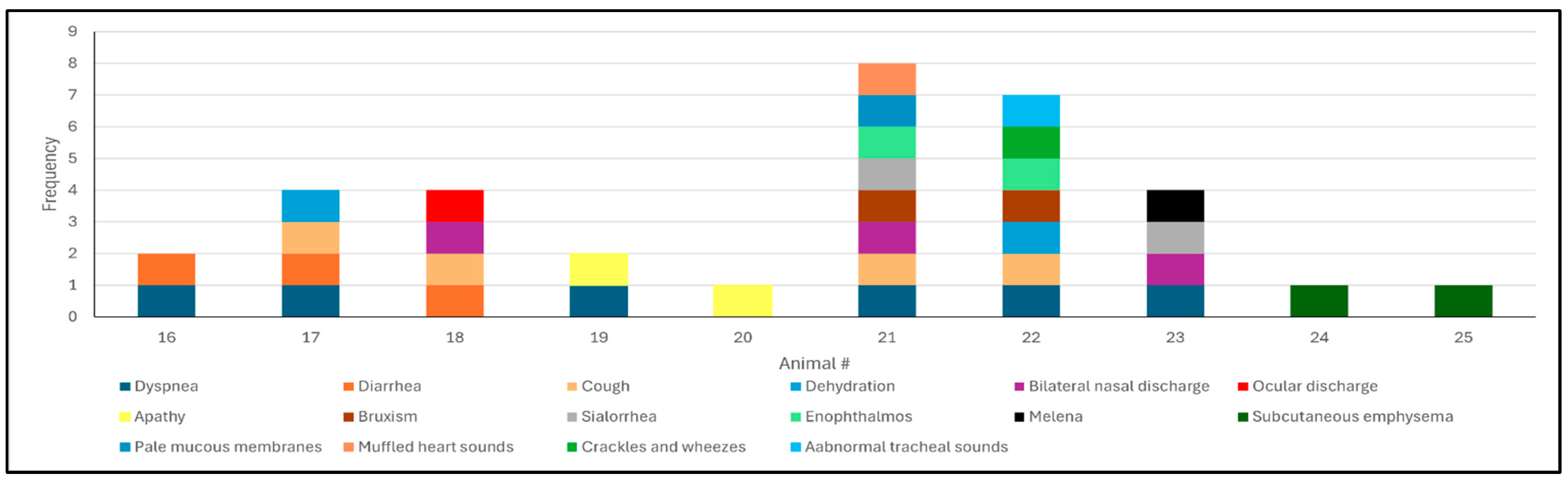
3.1. Epidemiological Data and Clinical Findings
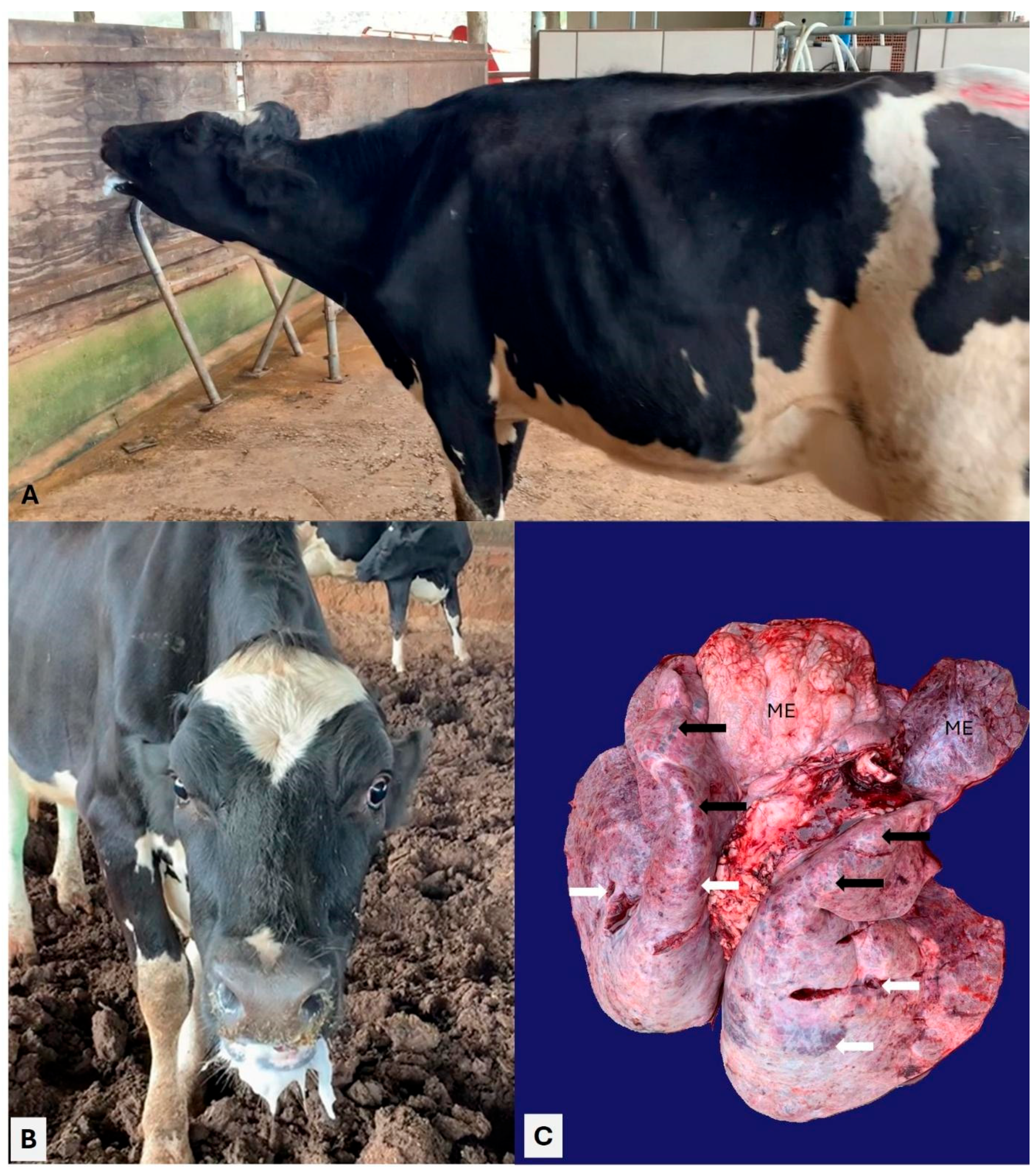
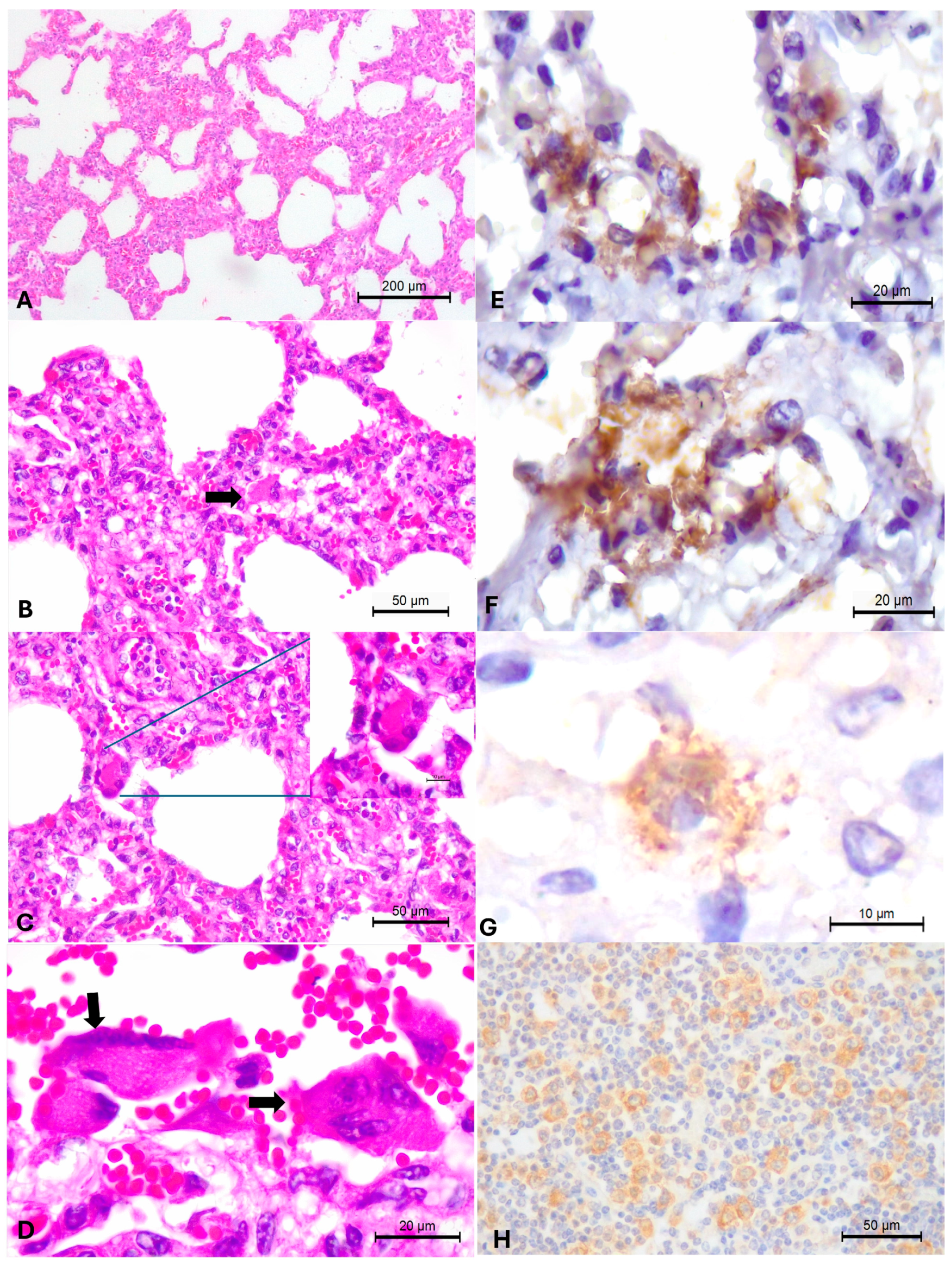
3.2. Pathological Observations
3.3. Immunohistochemical Identification of BRSV Antigens
3.4. Molecular Detection of Infectious Agents of BRD by Multiplex qPCR
3.5. Simultaneous Infections Detected in Adult Dairy Cows and Calves with BRD
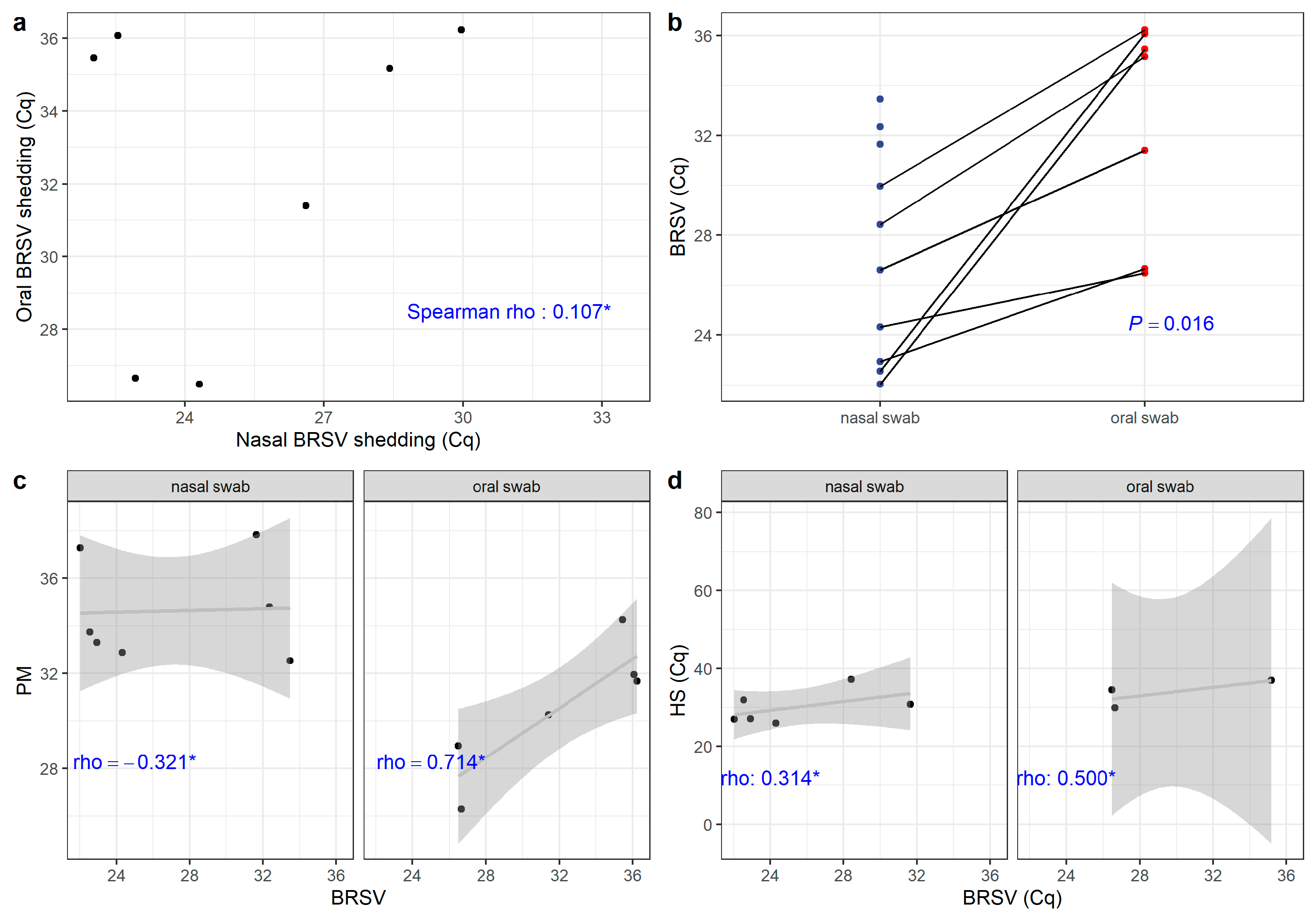
3.6. Statistical Correlations Between Nasal and Oral Shedding of the Infectious Disease Pathogens Identified in Cattle with Respiratory Disease
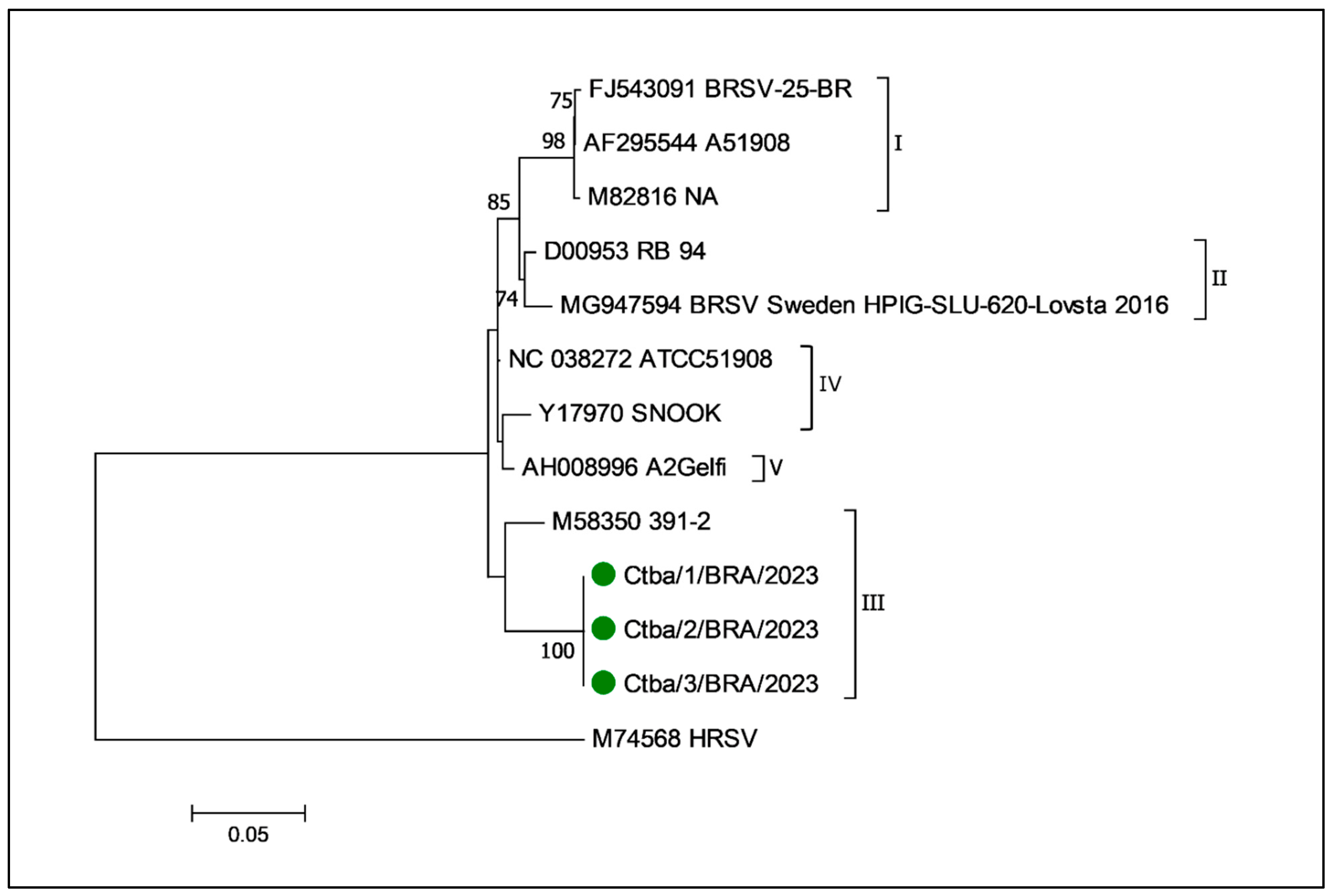
3.7. Molecular Characterization of BRSV and Phylogenetic Analysis of the BRSV Fusion Protein Gene
4. Discussion
4.1. Adverse Environmental Conditions and Management Practices Were Possible Triggers for This Outbreak
4.2. Simultaneous Infections Are Frequent in Outbreaks of Bovine Respiratory Disease
4.3. BRSV Shedding in Nasal and Oral Samples
4.4. Phylogenetic Relationships of the BRSV Fusion Protein Gene
4.5. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fulton, R.W. Bovine Respiratory Disease Research (1983–2009). Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2009, 10, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, V.L.; Brodersen, B.W. Respiratory Disease Diagnostics of Cattle. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food. Anim. Pract. 2010, 26, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro, M.M.; de Oliveira, T.E.S.; Headley, S.A. Bovine Respiratory Disease in Brasil: A Short Review. Semin-Cienc. Agrar. 2021, 42, 2081–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.A.; Step, D.L.; Woolums, A.R. Bovine Respiratory Disease: Looking Back and Looking Forward, What Do We See? Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food. Anim. Pract. 2020, 36, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headley, S.A.; Dall Agnol, A.M.; Bessegato, J.A.; Frucchi, A.P.S.; Maturana, É.F.L.; Rodrigues, R.V.; Xavier, A.A.C.; Alfieri, A.F.; Alfieri, A.A. Association of Ovine Gammaherpesvirus 2 with an Outbreak of Acute Respiratory Disease in Dairy Cattle. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). 2025. Available online: https://ictv.global/taxonomy/ (accessed on 8 October 2025).
- Sarmiento-Silva, R.E.; Nakamura-Lopez, Y.; Vaughan, G. Epidemiology, Molecular Epidemiology and Evolution of Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus. Viruses 2012, 4, 3452–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valarcher, J.F.; Ttaylor, G. Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection. Vet. Res. 2007, 38, 153–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, I.P.D.; Simanke, A.T.; Jost, H.C.; Hötzel, I.; Dal Soglio, A.; Moojen, V. Detection of Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Calves of Rio Grande Do Sul, Brazil. Cienc. Rural 1993, 23, 389–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campalans, J.B.; Arns, C.W. Serological Evidence of Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Brazil. Virus Rev. Res. 1997, 2, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, I.B.A.L.; de Medeiros, A.S.R.; Arns, C.W.; Samara, S.I. Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus Seroprevalence and Risk Factors in Non-Vaccinated Dairy Cattle Herds in Brazil. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshitani, G.D.; Camilo, S.L.O.; Fritzen, J.T.T.; Oliveira, M.V.; Lorenzetti, E.; Lisbôa, J.A.N.; Alfieri, A.F.; Alfieri, A.A. Serological Profile for Major Respiratory Viruses in Unvaccinated Cows from High-Yielding Dairy Herds. Animals 2024, 14, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padalino, B.; Cirone, F.; Zappaterra, M.; Tullio, D.; Ficco, G.; Giustino, A.; Ndiana, L.A.; Pratelli, A. Factors Affecting the Development of Bovine Respiratory Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study in Beef Steers Shipped From France to Italy. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 627894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, R.E.; McGill, J.L.; Pillatzki, A.E.; Palmer, M.V.; Ackermann, M.R. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection in Cattle. Vet. Pathol. 2014, 51, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- İnce, Ö.B.; Şevik, M.; Özgür, E.G.; Sait, A. Risk Factors and Genetic Characterization of Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus in the Inner Aegean Region, Turkey. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2022, 54, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidokhti, M.R.M.; Tråvén, M.; Fall, N.; Emanuelson, U.; Alenius, S. Reduced Likelihood of Bovine Coronavirus and Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection on Organic Compared to Conventional Dairy Farms. Vet. J. 2009, 182, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, L.E. Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus (BRSV): A Review. Acta Vet. Scand. 2000, 41, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spilki, F.R.; Arns, C.W. Vírus Respiratório Sincicial Bovino. Acta Sci. Vet. 2008, 36, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Shao, Z.; Dai, G.; Li, X.; Xiang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, G. Pathogenic Infection Characteristics and Risk Factors for Bovine Respiratory Disease Complex Based on the Detection of Lung Pathogens in Dead Cattle in Northeast China. J. Dairy Sci. 2023, 106, 589–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leme, R.A.; Dall Agnol, A.M.; Balbo, L.C.; Pereira, F.L.; Possatti, F.; Alfieri, A.F.; Alfieri, A.A. Molecular Characterization of Brazilian Wild-Type Strains of Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus Reveals Genetic Diversity and a Putative New Subgroup of the Virus. Vet. Q. 2020, 40, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Affonso, I.B.; De Souza, A.; Martini, M.C.; Dos Santos, M.M.A.B.; Spilki, F.R.; Arns, C.W.; Samara, S.I. Detection of an Untyped Strain of Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus in a Dairy Herd. Semin-Cienc. Agrar. 2014, 35, 2539–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giammarioli, M.; Mangili, P.; Nanni, A.; Pierini, I.; Petrini, S.; Pirani, S.; Gobbi, P.; De Mia, G.M. Highly Pathogenic Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus Variant in a Dairy Herd in Italy. Vet. Med. Sci. 2020, 6, 740–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferella, A.; Streitenberger, N.; Pérez Aguirreburualde, M.S.; Dus Santos, M.J.; Fazzio, L.E.; Quiroga, M.A.; Zanuzzi, C.N.; Asin, J.; Carvallo, F.; Mozgovoj, M.V.; et al. Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection in Feedlot Cattle Cases in Argentina. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2023, 35, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, P.V.; Mota, R.A.; Brito, M.F.; Corbellini, L.G.; Driemeier, D.; Souza, M.I.d. Infecção Natural Pelo Vírus Sincicial Respiratório Bovino (BRSV) No Estado de Alagoas. Pesqui. Vet. Bras. 2000, 20, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, L.E.; Tegtmeier, C.; Pedersen, E. Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus (BRSV) Pneumonia in Beef Calf Herds Despite Vaccination. Acta Vet. Scand. 2001, 42, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arns, C.W.; Campalans, J.; Costa, S.C.B.; Domingues, H.G.; D’Arce, R.C.F.; Almeida, R.S. Characterization of Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus Isolated in Brazil. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2003, 36, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headley, S.A.; Okano, W.; Balbo, L.C.; Marcasso, R.A.; Oliveira, T.E.; Alfieri, A.F.; Negri Filho, L.C.; Michelazzo, M.Z.; Rodrigues, S.C.; Baptista, A.L.; et al. Molecular Survey of Infectious Agents Associated with Bovine Respiratory Disease in a Beef Cattle Feedlot in Southern Brazil. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2018, 30, 249–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritzen, J.T.T.; Yasumitsu, C.Y.; Silva, I.V.; Lorenzetti, E.; Alfieri, A.F.; Alfieri, A.A. Respiratory Illness in Young and Adult Cattle Caused by Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus Subgenotype 2b in Singular and Mixed Bacterial Infection in a BVDV-Vaccinated Dairy Herd. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2024, 55, 4139–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driemeier, D.; Gomes, M.J.P.; Moojen, V.; Arns, C.W.; Vogg, G.; Kessler, L.; Costa, U.M. da Manifestação Clínico-Patológica de Infecção Natural Pelo Vírus Respiratório Sincicial Bovino (BRSV) Em Bovinos de Criação Extensiva No Rio Grande Do Sul, Brasil. Pesqui. Vet. Bras. 1997, 17, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, E.F.; Weiblen, R.; Medeiros, M.; Botton, S.A.; Irigoyen, L.F.; Driemeier, D.; Schuch, L.F.; Moraes, E.M. A Retrospective Search for Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus (BRSV) Antigens in Histological Specimens by Immunofluorescence and Immunohistochemistry. Pesqui. Vet. Bras. 2000, 20, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (IBGE). 2025. Available online: https://www.ibge.gov.br/cidades-e-estados/pr/senges.html (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Oliveira, V.H.; Dall Agnol, A.; Fritzen, J.T.; Lorenzetti, E.; Alfieri, A.; Alfieri, A. Microbial Diversity Involved in the Etiology of a Bovine Respiratory Disease Outbreak in a Dairy Calf Rearing Unit. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 101494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, T.E.S.; Scuisato, G.S.; Pelaquim, I.F.; Cunha, C.W.; Cunha, L.S.; Flores, E.F.; Pretto-Giordano, L.G.; Lisbôa, J.A.N.; Alfieri, A.A.; Saut, J.P.E.; et al. The Participation of a Malignant Catarrhal Fever Virus and Mycoplasma Bovis in the Development of Single and Mixed Infections in Beef and Dairy Cattle With Bovine Respiratory Disease. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 691448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thonur, L.; Maley, M.; Gilray, J.; Crook, T.; Laming, E.; Turnbull, D.; Nath, M.; Willoughby, K. One-Step Multiplex Real Time RT-PCR for the Detection of Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus, Bovine Herpesvirus 1 and Bovine Parainfluenza Virus 3. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decaro, N.; Elia, G.; Campolo, M.; Desario, C.; Mari, V.; Radogna, A.; Colaianni, M.L.; Cirone, F.; Tempesta, M.; Buonavoglia, C. Detection of Bovine Coronavirus Using a TaqMan-Based Real-Time RT-PCR Assay. J. Virol. Methods 2008, 151, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, C.W.; Otto, L.; Taus, N.S.; Knowles, D.P.; Li, H. Development of a Multiplex Real-Time PCR for Detection and Differentiation of Malignant Catarrhal Fever Viruses in Clinical Samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 2586–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimoto, M.; Tsuchiaka, S.; Rahpaya, S.S.; Hasebe, A.; Otsu, K.; Sugimura, S.; Kobayashi, S.; Komatsu, N.; Nagai, M.; Omatsu, T.; et al. Development of a One-Run Real-Time PCR Detection System for Pathogens Associated with Bovine Respiratory Disease Complex. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2017, 79, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstock, D.; Bhudevi, B.; Castro, A.E. Single-Tube Single-Enzyme Reverse Transcriptase PCR Assay for Detection of Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus in Pooled Bovine Serum. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Du, J.; Tian, Z.; Niu, Q.; Huang, D.; Wang, J.; Luo, J.; Liu, G.; Yin, H. A SYBR Green I–Based Quantitative RT-PCR Assay for Bovine Ephemeral Fever Virus and Its Utility for Evaluating Viral Kinetics in Cattle. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2020, 32, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilcek, S.; Elvander, M.; Ballagi-Pordany, A.; Belak, S. Development of Nested PCR Assays for Detection of Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Clinical Samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1994, 32, 2225–2231, Erratum in J. Clin. Microbiol. 1994, 32, 2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodoridis, A.; Coetzer, J.A. Subcutaneous and Pulmonary Emphysema as Complications of Bovine Ephemeral Fever. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 1979, 46, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Nei, M. Estimation of the Number of Nucleotide Substitutions in the Control Region of Mitochondrial DNA in Humans and Chimpanzees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1993, 10, 512–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A User-Friendly Biological Sequence Alignment Editor and Analysis Program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Makoschey, B.; Berge, A.C. Review on Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus and Bovine Parainfluenza—Usual Suspects in Bovine Respiratory Disease—A Narrative Review. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirie, H.M.; Petrie, L.; Pringle, C.R.; Allen, E.M.; Kennedy, G.J. Acute Fatal Pneumonia in Calves Due to Respiratory Syncytial Virus. Vet. Rec. 1981, 108, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caswell, J.L.; Hewson, J.; Slavić, D.; DeLay, J.; Bateman, K. Laboratory and Postmortem Diagnosis of Bovine Respiratory Disease. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food. Anim. Pract. 2012, 28, 419–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolums, A.R. Feedlot Acute Interstitial Pneumonia. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food. Anim. Pract. 2015, 31, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urso, P.M.; Turgeon, A.; Ribeiro, F.R.B.; Smith, Z.K.; Johnson, B.J. Review: The Effects of Dust on Feedlot Health and Production of Beef Cattle. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2021, 49, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saa, L.R.; Perea, A.; Jara, D.V.; Arenas, A.J.; Garcia-Bocanegra, I.; Borge, C.; Carbonero, A. Prevalence of and Risk Factors for Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus (BRSV) Infection in Non-Vaccinated Dairy and Dual-Purpose Cattle Herds in Ecuador. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2012, 44, 1423–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicoski, L.M.; Fritzen, J.T.T.; Lorenzetti, E.; da Costa, A.R.; Moro, E.; de Carvalho, E.R.; Alfieri, A.F.; Alfieri, A.A. Serological Profile of Respiratory Viruses in Unvaccinated Steers upon Their Arrival at Brazilian Feedlot Facilities. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2023, 54, 3237–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachowicz-Wolak, A.; Klimowicz-Bodys, M.D.; Płoneczka-Janeczko, K.; Bednarski, M.; Dyba, K.; Knap, P.; Rypuła, K. Simultaneous Presence of Antibodies against Five Respiratory Pathogens in Unvaccinated Dairy Calves from South-Western Poland. Animals 2024, 14, 2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panciera, R.J.; Confer, A.W. Pathogenesis and Pathology of Bovine Pneumonia. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food. Anim. Pract. 2010, 26, 191–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haydock, L.A.J.; Fenton, R.K.; Sergejewich, L.; Squires, E.J.; Caswell, J.L. Acute Interstitial Pneumonia and the Biology of 3-Methylindole in Feedlot Cattle. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2022, 23, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorden, S.D.; Kerr, R.W.; Janzen, E.D. Interstitial Pneumonia in Feedlot Cattle: Concurrent Lesions and Lack of Immunohistochemical Evidence for Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2000, 12, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, R.C.; Sorensen, N.J.; Payton, M.E.; Confer, A.W. Comparative Histopathology of Bovine Acute Interstitial Pneumonia and Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus-Associated Interstitial Pneumonia. J. Comp. Pathol. 2022, 192, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagea, M.I.; Bateman, K.G.; Van Dreumel, T.; McEwen, B.J.; Carman, S.; Archambault, M.; Shanahan, R.A.; Caswell, J.L. Diseases and Pathogens Associated with Mortality in Ontario Beef Feedlots. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2006, 18, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkouiten, S.; Gautret, P.; Belhouchat, K.; Drali, T.; Nougairede, A.; Salez, N.; Memish, Z.A.; Al Masri, M.; Raoult, D.; Brouqui, P.; et al. Comparison of Nasal Swabs with Throat Swabs for the Detection of Respiratory Viruses by Real-Time Reverse Transcriptase PCR in Adult Hajj Pilgrims. J. Infect. 2015, 70, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.; Ahmed, J.A.; Eidex, R.B.; Nyoka, R.; Waiboci, L.W.; Erdman, D.; Tepo, A.; Mahamud, A.S.; Kabura, W.; Nguhi, M.; et al. Comparison of Nasopharyngeal and Oropharyngeal Swabs for the Diagnosis of Eight Respiratory Viruses by Real-Time Reverse Transcription-PCR Assays. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Agent | Primer/ Probe | DNA Sequence (5′-3′) Probe Labels | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| F | GGTCAAACTAAATGACACTTTCAACAAG | ||
| BRSV 1 | R | AGCATACCACACAACTTATTGAGATG | [34] |
| P | TGATACAGGTGACAA | ||
| F | TGTGGACCTAAACCTCACGGT | ||
| BoAHV1 2 | R | GTAGTCGAGCAGACCCGTGTC | [34] |
| P | AGGACCGCGAGTTCTTGCCGC | ||
| F | TGATTGGATGTTCGGGAGTGA | ||
| BPIV3 3 | R | AGAATCCTTTCCTCAATCCTGATATACT | [34] |
| P | TACAATCGAGGATCTTGTTCA | ||
| F | CTGGAAGTTGGTGGAGTT | ||
| BCoV 4 | R | ATTATCGGCCTAACATACATC | [35] |
| P | CCTTCATATCTATACACATCAAGTTGTT | ||
| F | CACACCCAACTGGAGTATGAC | ||
| OvGHV2 5 | R | ATGTTGTAGTGGGGCCAGTC | [36] |
| P | ATGTGCGCTTCGACCCTC | ||
| Histophilus somni | F | AAGGCCTTCGGGTTGTAAAG | |
| R | CCGGTGCTTCTTCTGTGATTAT | [37] | |
| P | CGGTGATGAGGAAGGCGATTAG | ||
| Pasteurella multocida | F | GGGCTTGTCGGTAGTCTTT | |
| R | CGGCAAATAACAATAAGCTGAGTA | [37] | |
| P | CGGCGCAACTGATTGGACGTTATT | ||
| Mannheimia haemolytica | F | ATTAGTGGGTTGTCCTGGTTAG | |
| R | GCGTGATTTCGGTTCAGTTG | [37] | |
| P | CTGAACCAACACGAGTAGTCGCTGC | ||
| Mycoplasma bovis | F | TCAAGGAACCCCACCAGAT | |
| R | AGGCAAAGTCATTTCTAGGTGCAA | [37] | |
| P | TGGCAAACTTACCTATCGGTGACCCT |
| Animal | Age (Months) | Rectal Temperature | Biological Sample | qPCR Threshold Cycle (Cq) by Sample | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β-Actin 1 | BRSV 2 | HS 3 | PM 4 | ||||
| 16 | 3 | 38.6 °C | nasal swab | 21.74 | 26.61 | ND | ND |
| oral swab | 32.42 | 31.4 | ND | 30.26 | |||
| 17 | 2 | 37.9 °C | nasal swab | 22.92 | 29.96 | ND | ND |
| oral swab | 29.67 | 36.23 | ND | 31.67 | |||
| 18 | 2.5 | 38.8 °C | nasal swab | 23.09 | 31.64 | 30.72 | 37.83 |
| oral swab | 26.18 | ND | 28.89 | 31.24 | |||
| 19 | 5.5 | 38.4 °C | nasal swab | 20.84 | 33.46 | ND | 32.53 |
| oral swab | 36.33 | ND | ND | 35.77 | |||
| 20 | 2.6 | 38.8 °C | nasal swab | 16.29 | 32.34 | ND | 34.79 |
| oral swab | 32.79 | ND | ND | 27.99 | |||
| 21 a | 41 | 37.7 °C | nasal swab | 18.49 | 28.42 | 37.15 | ND |
| oral swab | 33.21 | 35.17 | 36.89 | ND | |||
| lung | 25.07 | 27.03 | ND | ND | |||
| trachea | 24.99 | 30.24 | ND | ND | |||
| heart, kidney, liver | 25 | ND | ND | ND | |||
| 22 | 50 | 37.2 °C | nasal swab | 21.04 | 24.31 | 25.97 | 32.88 |
| oral swab | 31.07 | 26.49 | 34.41 | 28.95 | |||
| 23 | 48 | 37.8 °C | nasal swab | 20.02 | 22.93 | 27.07 | 33.31 |
| oral swab | 27.69 | 26.66 | 29.85 | 26.3 | |||
| 24 | 52 | 37.1 °C | nasal swab | 18.97 | 22.03 | 27 | 37.29 |
| oral swab | 30.77 | 35.46 | ND | 34.25 | |||
| 25 | 49 | 41 °C | nasal swab | 22.26 | 22.55 | 31.88 | 33.75 |
| oral swab | 32.90 | 36.07 | ND | 31.95 | |||
| Animal | Type of Sample | Type of Infection | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | Oral | ||||
| 16 | BRSV | BRSV + PM | BRSV + PM | ||
| 17 | BRSV | BRSV + PM | BRSV + PM | ||
| 18 | BRSV + HS | HS + PM | BRSV + HS + PM | ||
| 19 | BRSV + PM | PM | BRSV + PM | ||
| 20 | BRSV + PM | PM | BRSV + PM | ||
| 21 | BRSV | BRSV + HS | BRSV + HS | ||
| 22 | BRSV + HS + PM | BRSV + HS + PM | BRSV + HS + PM | ||
| 23 | BRSV + HS + PM | BRSV + HS + PM | BRSV + HS + PM | ||
| 24 | BRSV + HS | BRSV + PM | BRSV + HS + PM | ||
| 25 | BRSV + HS + PM | BRSV + PM | BRSV + HS + PM | ||
| Nasal Cq values (average) | Oral Cq values (average) | ||||
| BRSV | 22.03–33.46 (27.43) | 26.49–36.23 (32.68) | |||
| Histophilus somni | 25.97–31.88 (29.96) | 28.89–36.89 (32.51) | |||
| Pasteurella multocida | 32.53–34.79 (34.62) | 26.3–35.77 (30.93) | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perotta, J.H.; Silva, I.V.; Rodriguez, M.C.; Joineau, M.E.G.; Tschá, M.K.; de Sousa, R.S.; Dall Agnol, A.M.; Silva, F.H.P.; Buczinski, S.; Headley, S.A.; et al. Outbreak of Respiratory Disease Due to Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus with Concomitant Infections by Histophilus somni and Pasteurella multocida in Adult Dairy Cows and Calves from Southern Brazil. Animals 2025, 15, 3015. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15203015
Perotta JH, Silva IV, Rodriguez MC, Joineau MEG, Tschá MK, de Sousa RS, Dall Agnol AM, Silva FHP, Buczinski S, Headley SA, et al. Outbreak of Respiratory Disease Due to Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus with Concomitant Infections by Histophilus somni and Pasteurella multocida in Adult Dairy Cows and Calves from Southern Brazil. Animals. 2025; 15(20):3015. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15203015
Chicago/Turabian StylePerotta, João Henrique, Isabela Vaz Silva, Maria Constanza Rodriguez, Mara Eliza Gasino Joineau, Marcel Kruchelski Tschá, Renato Silva de Sousa, Alais Maria Dall Agnol, Flávia Helena Pereira Silva, Sébastien Buczinski, Selwyn Arlington Headley, and et al. 2025. "Outbreak of Respiratory Disease Due to Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus with Concomitant Infections by Histophilus somni and Pasteurella multocida in Adult Dairy Cows and Calves from Southern Brazil" Animals 15, no. 20: 3015. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15203015
APA StylePerotta, J. H., Silva, I. V., Rodriguez, M. C., Joineau, M. E. G., Tschá, M. K., de Sousa, R. S., Dall Agnol, A. M., Silva, F. H. P., Buczinski, S., Headley, S. A., & Barros Filho, I. R. d. (2025). Outbreak of Respiratory Disease Due to Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus with Concomitant Infections by Histophilus somni and Pasteurella multocida in Adult Dairy Cows and Calves from Southern Brazil. Animals, 15(20), 3015. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15203015







