Survival Strategies and Color Preferences of Mandarin Fish (Siniperca chuatsi) and Mud Carp (Cirrhinus molitorella): Implications for Aquaculture
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish Maintaince
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Experimental Methods
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
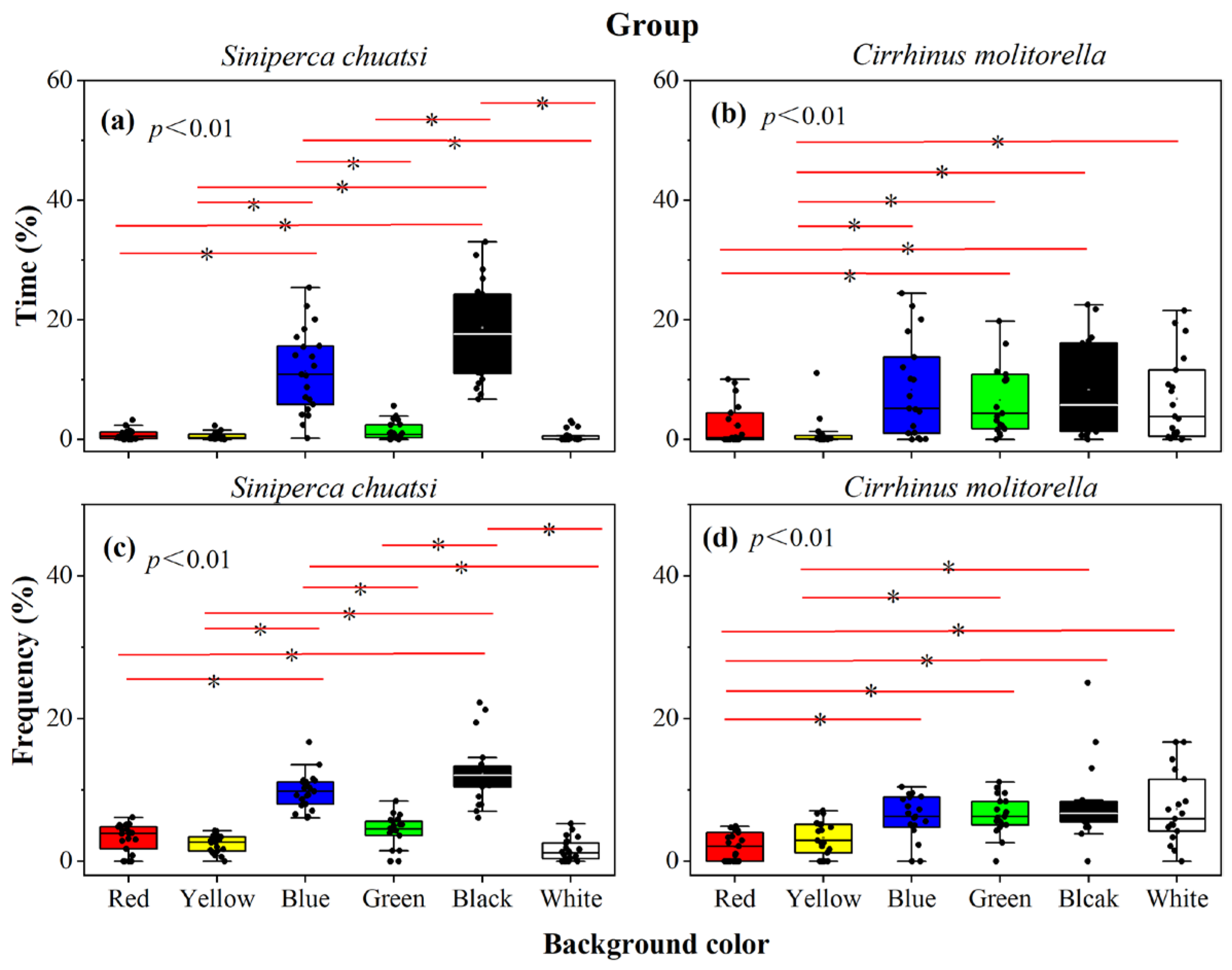
3.1. Preference of Individual Siniperca Chuatsi and Cirrhinus Molitorella
3.2. Preference of Siniperca Chuatsi and Cirrhinus Molitorella
4. Discussion
4.1. Habitat Coloration Selection of Siniperca Chuatsi
4.2. Habitat Coloration Selection of Cirrhinus Molitorella
4.3. Future Consideration
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Species | Red | Yellow | Blue | Green | Black | White | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (%) | Siniperca chuatsi | Singleton | 5.08 ± 1.27% | 2.24 ± 0.36% | 33.78 ± 3.70% | 5.96 ± 0.97% | 47.10 ± 4.39% | 5.85 ± 1.63% |
| Group | 0.80 ± 0.18% | 0.54 ± 0.13% | 11.42 ± 1.51% | 1.36 ± 0.34% | 18.63 ± 1.77% | 0.59 ± 0.21% | ||
| Cirrhinus molitorella | Singleton | 7.59 ± 2.94% | 3.91 ± 1.66% | 37.07 ± 9.50% | 3.93 ± 1.64% | 22.33 ± 8.10% | 25.17 ± 6.80% | |
| Group | 2.37 ± 0.79% | 1.03 ± 0.59% | 8.28 ± 1.86% | 6.61 ± 1.30% | 8.28 ± 1.77% | 6.77 ± 1.63% | ||
| Visit frequency (%) | Siniperca chuatsi | Singleton | 9.54 ± 1.28% | 8.74 ± 1.01% | 28.35 ± 2.51% | 13.37 ± 1.42% | 33.0 1± 3.18% | 6.99 ± 1.12% |
| Group | 3.21 ± 0.44% | 2.37 ± 0.27% | 9.80 ± 0.55% | 4.11 ± 0.51% | 12.32 ± 0.93% | 1.53 ± 0.34% | ||
| Cirrhinus molitorella | Singleton | 8.19 ± 3.01% | 5.71 ± 2.01% | 37.07 ± 9.50% | 7.53 ± 2.77% | 20.56 ± 6.94% | 27.07 ± 5.83% | |
| Group | 2.03 ± 0.44% | 3.27 ± 0.55% | 6.16 ± 0.69% | 6.48 ± 0.62% | 8.07 ± 1.23% | 7.32 ± 1.13% | ||
References
- Broom, D.M. Animal welfare: Concepts and measurement. J. Anim. Sci. 1991, 69, 4167–4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiber, A.; Stomp, M.; Rouby, M.; Ferreira, V.H.B.; Bégout, M.L.; Benhaïm, D.; Labbé, L.; Tocqueville, A.; Levadoux, M.; Calandreau, L.; et al. Cognitive Enrichment to Increase Fish Welfare in Aquaculture: A Review. Aquaculture 2023, 575, 739654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, M.O.; Rey Planellas, S.; Yang, Y.; Phillips, C.; Descovich, K. Emerging Indicators of Fish Welfare in Aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 14, 343–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, N.; Shiller, D. Engage with Animal Welfare in Conservation. Science 2020, 369, 629–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.X.; Gong, W.A.; Wang, L.Y.; Xia, J.G.; Fu, S.J. Color and illumination intensity in aquaculture environment on personality of cichlids. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2024, 5, 780–786. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.H.; Li, D.P. Review in the effects of aquaculture facility space on fish welfare. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2025, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; He, Y.; Wang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Mo, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, W. A Global Synthesis of Environmental Enrichment Effect on Fish Stress. Fish Fish. 2025, 26, 131–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreck, C.; Contreras-Sanchez, W.F.T.; Schreck, C.; Contreras-Sanchez, W.F.T. Effects of Stress on Fish Reproduction, Gamete Quality, and Progeny. In Reproductive Biotechnology in Finfish Aquaculture; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 3–24. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.J.; Paull, G.C.; Tyler, C.R. Improving zebrafish laboratory welfare and scientific research through understanding their natural history. Biol. Rev. 2022, 97, 1038–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blewett, T.A.; Binning, S.A.; Weinrauch, A.M.; Ivy, C.M.; Rossi, G.S.; Borowiec, B.G.; Lau, G.Y.; Overduin, S.L.; Aragao, I.; Norin, T. Physiological and behavioural strategies of aquatic animals living in fluctuating environments. J. Exp. Biol. 2022, 225, jeb242503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, P.J. Fish welfare: Current issues in aquaculture. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2007, 104, 199–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arechavala-Lopez, P.; Cabrera-Álvarez, M.J.; Maia, C.M.; Saraiva, J.L. Environmental enrichment in fish aquaculture: A review of fundamental and practical aspects. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 14, 704–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.X.; Ulgiati, S.; Yang, Z.F.; Chen, B. Emergy evaluation and economic analysis of three wetland fish farming systems in Nansi Lake area, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.F.; Oku, H.; Ogata, H.Y.; Liu, J.; He, X.J.A.R. Weaning Chinese perch Siniperca chuatsi (Basilewsky) onto artificial diets based upon its specific sensory modality in feeding. Aquac. Res. 2001, 32, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Xiong, F.; Wang, K.; Chang, Y. Status of research on Yangtze fish biology and fisheries. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2009, 85, 337–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milstein, A.; Wahab, M.A.; Rahman, M.M. Environmental effects of common carp Cyprinus carpio (L.) and mrigal Cirrhinus mrigala (Hamilton) as bottom feeders in major Indian carp polycultures. Aquac. Res. 2002, 33, 1103–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horváth, L.; Kovács, É.; Csorbai, B.; Hegyi, Á.; Lefler, K.; Müller, T.; Urbányi, B. Carp breeding in the Carpathian Basin with a sustainable utilization of renewable natural resources. Life 2022, 12, 1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costedoat, C.; Chappaz, R.; Barascud, B.; Guillard, O.; Gilles, A. Heterogeneous colonization pattern of European Cyprinids, as highlighted by the dace complex (Teleostei: Cyprinidae). Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2006, 41, 127–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Liere, L.; Gulati, R.D. Restoration and recovery of shallow eutrophic lake ecosystems in The Netherlands: Epilogue. Hydrobiologia 1992, 233, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, Q.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Mou, C.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, H.; Du, J.; Yang, X.; Liang, X.; et al. Study on the Adaptive Regulation of Light on the Stress Response of Mandarin Fish (Siniperca chuatsi) with Re-Feeding after Starvation. Animals 2023, 13, 2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, F.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, Y.; Ma, H.; Sun, Y. Preference of juvenile tiger puffer for light spectrum and tank colours based on different body size and breeding background. Animal 2023, 17, 101021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Bao, J.; Zhang, C.; Mi, X.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, H.; Twardek, W.M.; Cooke, S.J.; Duan, M. Group size influences light-emitting diode light colour and substrate preference of David’s Schizothoracin (Schizothorax davidi): Relevance for design of fish passage facilities. River Res. Appl. 2022, 38, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colson, V.; Ferreira, V.H.B.; Luchiari, A.C.; Valotaire, C.; Borel, F.; Bugeon, J.; Prigent, S.; Dickel, L.; Calandreau, L.; Guesdon, V. Loss of light colour preference after chronic embryonic stress in rainbow trout fry: A novel and potential indicator of fish welfare? Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2021, 239, 105335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Q.; Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Bao, J.; Lyu, H.; Duan, M. Shy and bold fish have the same preference for light color selection. Animals 2024, 14, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chi, L.; Tian, H.; Meng, L.; Zheng, J.; Gao, X.; Liu, Y. Colour preferences of juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Physiol. Behav. 2016, 156, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjernsmo, K.; Merilaita, S. Background choice as an anti-predator strategy: The roles of background matching and visual complexity in the habitat choice of the least killifish. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 279, 4192–4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almazán-Rueda, P.; Schrama, J.W.; Verreth, J.A. Behavioural responses under different feeding methods and light regimes of the african catfish (Clarias gariepinus) juveniles. Aquaculture 2004, 231, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, B.; Yu, L.; Wang, F. Shelter color selection of juvenile swimming crabs (Portunus trituberculatus). Fishes 2022, 7, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapunda, J.; Mtolera, M.S.P.; Yahya, S.A.S.; Ngo, V.M.; Golan, M. Light colour affect the survival rate, growth performance, cortisol level, body composition, and digestive enzymes activities of different snubnose pompano (Trachinotus blochii (Lacépède, 1801) Larval Stages. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 21, 100804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, J.; An, D.; Li, L.; Dong, Y.; Gao, Q.; Dong, S. The effects of blue and red light color combinations on the growth and immune performance of juvenile steelhead trout, oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 24, 101156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, X.; Lin, T.; Zhang, D.; Zou, X. The consistent background color preference highlights the personality in the lined seahorse, Hippocampus erectus. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 939749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, M.; Merilaita, S. Animal camouflage: Current issues and new perspectives. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, M. Predator perception and the interrelation between different forms of protective coloration. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2007, 274, 1457–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gall, M.P.; Davies-Colley, R.J.; Merrilees, R.A. Exceptional visual clarity and optical purity in a sub-alpine lake. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2013, 58, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffney, L.P.; Franks, B.; Weary, D.M.; von Keyserlingk, M.A. Coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch) prefer and are less aggressive in darker environments. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, S.C.J.; Patman, J.; Lutnesky, M.M.F. Water clarity affects collective behavior in two cyprinid fishes. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2021, 75, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Escobedo, R.; Sire, C.; Theraulaz, G. Computational and robotic modeling reveal parsimonious combinations of interactions between individuals in schooling fish. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2020, 16, e1007194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannomiya, N.; Tian, Y.J.; Nakamine, H. Emergence of cooperation in fish behavior models. Trans. Soc. Instrum. Control. Eng. 1999, 35, 1370–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ward, A.J.; Sumpter, D.J.; Couzin, I.D.; Hart, P.J.; Krause, J. Quorum decision-making facilitates information transfer in fish shoals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 6948–6953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, M.R.; Cummings, J.M.; Cabe, A.R.; Hulthén, K.; Peterson, M.N.; Langerhans, R.B. Natural and anthropogenic sources of habitat variation influence exploration behaviour, stress response, and brain morphology in a coastal fish. J. Anim. Ecol. 2021, 90, 2446–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, N.; Parikh, K.; Kenney, J.W. Beyond bold versus shy: Zebrafish exploratory behavior falls into several behavioral clusters and is influenced by strain and sex. Biol.s Open 2022, 11, bio059443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attwell, J.R.; Ioannou, C.C.; Reid, C.R.; Herbert-Read, J.E. Fish avoid visually noisy environments where prey targeting is reduced. Am. Nat. 2021, 198, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eterovick, P.C.; Mendes, I.S.; Kloh, J.S.; Pinheiro, L.T.; Václav, A.B.H.P.; Santos, T.; Gontijo, A.S.B. Tadpoles respond to background colour under threat. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosetto, L.; Hart, N.S.; Ryan, L.A. Dazzling damselfish: Investigating motion dazzle as a defence strategy in humbug damselfish (Dascyllus aruanus). PeerJ 2024, 12, e18152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newport, C.; Green, N.F.; McClure, E.C.; Osorio, D.C.; Vorobyev, M.; Marshall, N.J.; Cheney, K.L. Fish use colour to learn compound visual signals. Anim. Behav. 2017, 125, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.X.; Zhang, J.H.; Gong, W.A.; Fu, S.J. Labidochromis caeruleus cichlid preference for background colour varied between individuals and groups but did not vary for body colour of other fish. J. Ethol. 2024, 42, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
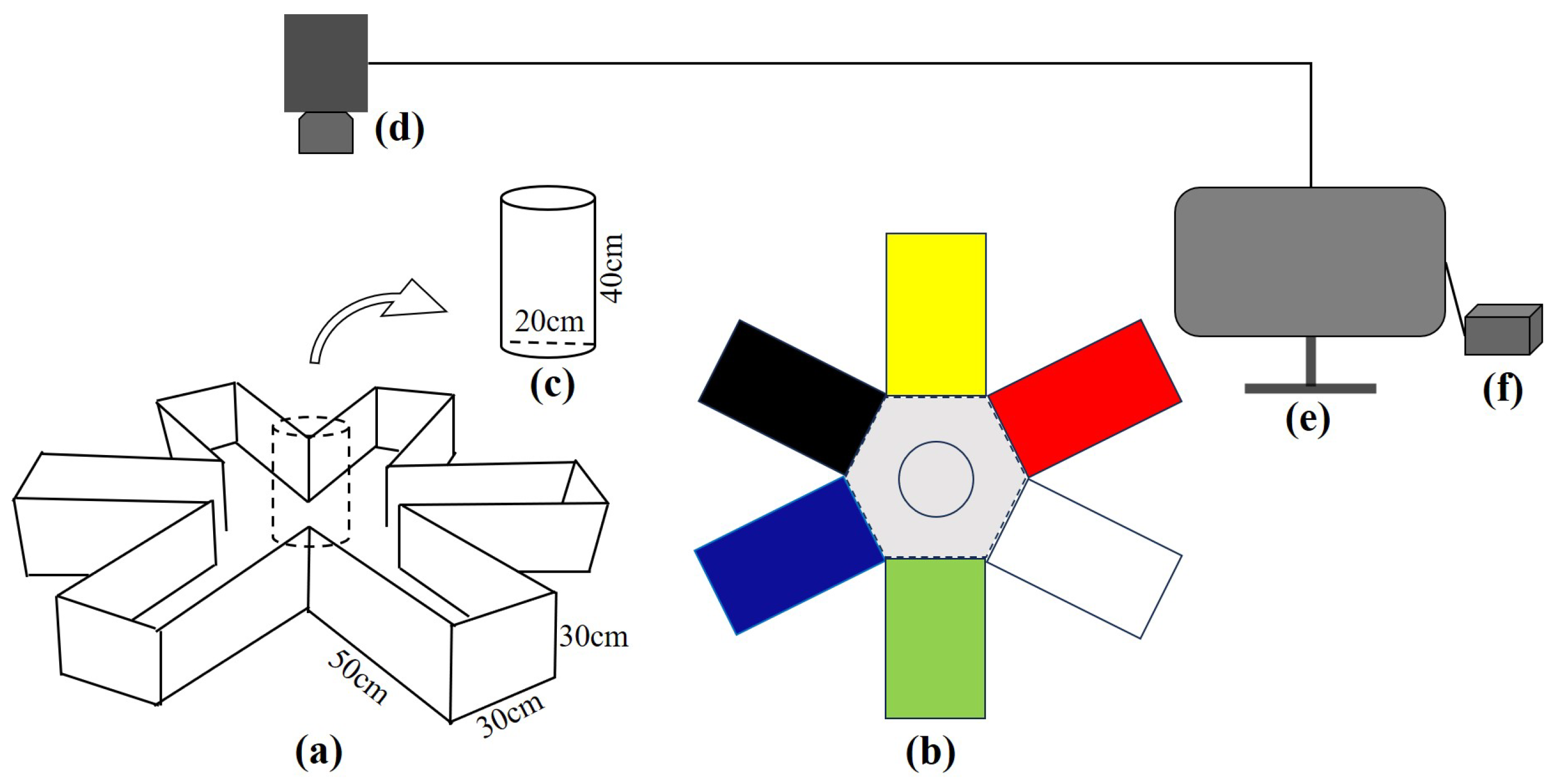

| Fish | Number of Trials | Total Number | Standard Length/cm | Weight/g | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Siniperca chuatsi | Singleton | 40 | 40 | 18.8 ± 1.8 | 173.9 ± 49.4 |
| Group | 21 | 63 | 18.5 ± 1.8 | 166.4 ± 46.6 | |
| Cirrhinus molitorella | Singleton | 20 | 20 | 4.9 ± 0.8 | 1.7 ± 1.0 |
| Group | 19 | 57 | 5.4 ± 1.1 | 2.5 ± 1.5 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiang, M.; Wei, N.; Liu, H.; Liao, M.; Meng, Z.; Li, X. Survival Strategies and Color Preferences of Mandarin Fish (Siniperca chuatsi) and Mud Carp (Cirrhinus molitorella): Implications for Aquaculture. Animals 2025, 15, 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15040557
Xiang M, Wei N, Liu H, Liao M, Meng Z, Li X. Survival Strategies and Color Preferences of Mandarin Fish (Siniperca chuatsi) and Mud Carp (Cirrhinus molitorella): Implications for Aquaculture. Animals. 2025; 15(4):557. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15040557
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiang, Miao, Nian Wei, Haoran Liu, Mulan Liao, Zihao Meng, and Xuemei Li. 2025. "Survival Strategies and Color Preferences of Mandarin Fish (Siniperca chuatsi) and Mud Carp (Cirrhinus molitorella): Implications for Aquaculture" Animals 15, no. 4: 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15040557
APA StyleXiang, M., Wei, N., Liu, H., Liao, M., Meng, Z., & Li, X. (2025). Survival Strategies and Color Preferences of Mandarin Fish (Siniperca chuatsi) and Mud Carp (Cirrhinus molitorella): Implications for Aquaculture. Animals, 15(4), 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15040557








