Oyster Reefs Are Reservoirs for Potential Pathogens in a Highly Disturbed Subtropical Estuary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites
2.2. Sample Collection and Processing
2.3. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.4. Bioinformatics and Statistical Analyses
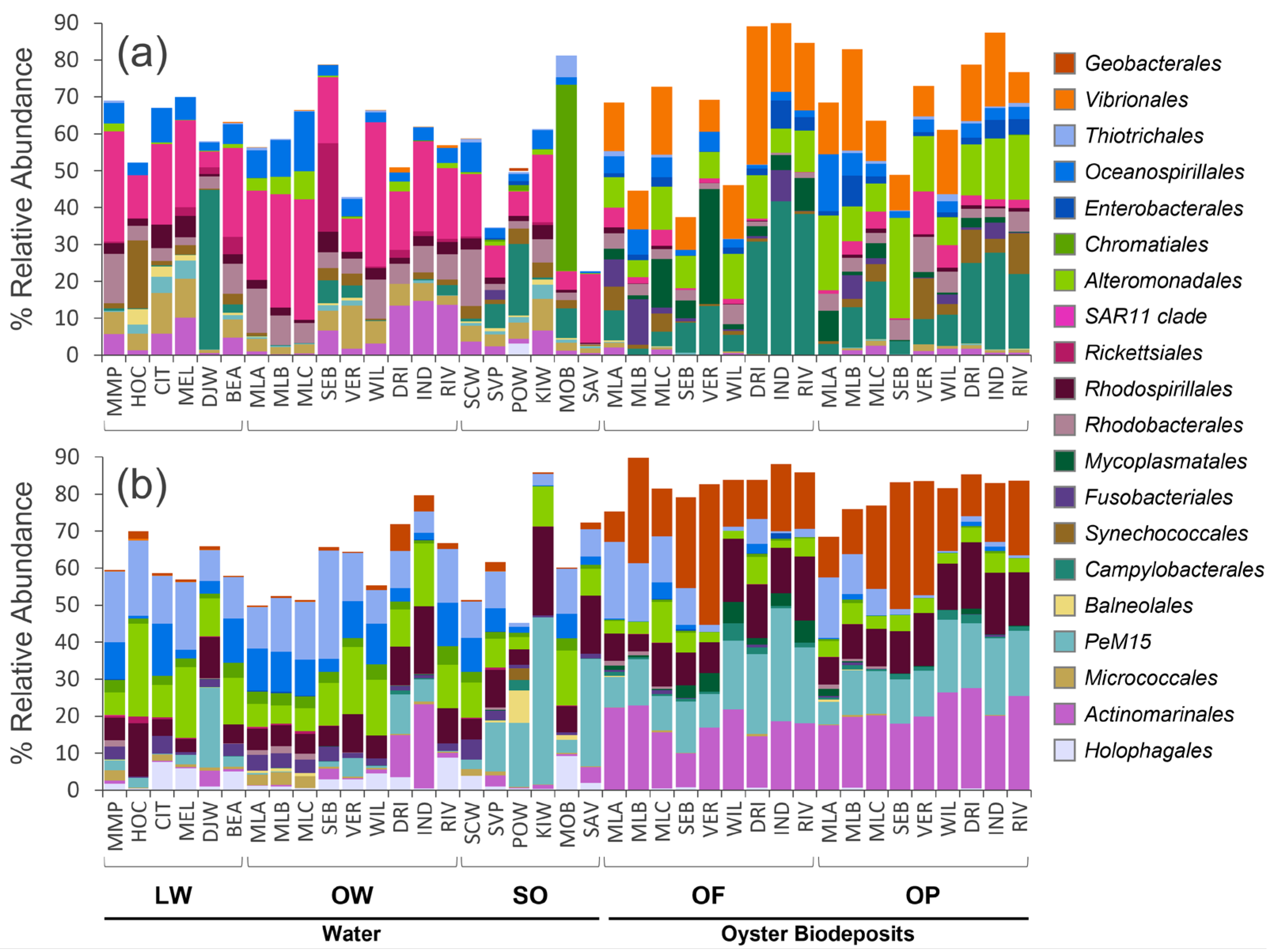
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Freeman, L.A.; Corbett, D.R.; Fitzgerald, A.M.; Lemley, D.A.; Quigg, A.; Steppe, C.N. Impacts of urbanization and development on estuarine ecosystems and water quality. Estuar. Coast. 2019, 42, 1821–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrigan, P.J.; Stegeman, J.J.; Fleming, L.E.; Allemand, D.; Anderson, D.M.; Backer, L.C.; Brucker-Davis, F.; Chevalier, N.; Corra, L.; Czerucka, D.; et al. Human health and ocean pollution. Ann. Glob. Health 2020, 86, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, J.; Rhodes, M.; Sturgis, B.; Wood, B. Influence of environmental gradients on the abundance and distribution of Mycobacterium spp. in a coastal lagoon estuary. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7378–7384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janda, J.M.; Abbott, S.L. The genus Aeromonas: Taxonomy, pathogenicity, and infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 35–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderpour, A.; Mohd Nasori, K.N.; Chew, L.L.; Chong, V.C.; Thong, K.L.; Chai, L.C. Detection of multiple potentially pathogenic bacteria in matang mangrove estuaries, Malaysia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 83, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochsenkühn, M.A.; Fei, C.; Bayaara, O.; Romeo, E.; Amosa, P.; Idaghdour, Y.; Goldstein, G.; Bromage, T.G.; Amin, S.A. Microbial contamination survey of environmental fresh and saltwater resources of Upolu Island, Samoa. Environments 2021, 8, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooban, B.; Fitzhenry, K.; O’Connor, L.; Miliotis, G.; Joyce, A.; Chueiri, A.; Farrell, M.L.; DeLappe, N.; Tuohy, A.; Cormican, M.; et al. A longitudinal survey of antibiotic-resistant Enterobacterales in the Irish environment, 2019–2020. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 828, 154488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimes, D.J. Ecology of estuarine bacteria capable of causing human disease: A review. Estuaries 1991, 14, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.R.; Marcelino, L.A.; Polz, M.F. Diversity, sources, and detection of human bacterial pathogens in the marine environment. In Oceans and Health: Pathogens in the Marine Environment; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 29–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, J.B.; Epstein, P.R.; Lipp, E.K.; Sherman, B.H.; Bernard, S.M.; Patz, J.A. Climate variability and change in the United States: Potential impacts on water- and foodborne diseases caused by microbiologic agents. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassard, F.; Gwyther, C.L.; Farkas, K.; Andrews, A.; Jones, V.; Cox, B.; Brett, H.; Jones, D.L.; McDonald, J.E.; Malham, S.K. Abundance and distribution of enteric bacteria and viruses in coastal and estuarine sediments-a review. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indian River Lagoon Species Inventory. Available online: https://irlspecies.org (accessed on 22 August 2023).
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Local Estuary Programs. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/nep/local-estuary-programs (accessed on 22 August 2023).
- Phlips, E.J.; Badylak, S.; Christman, M.C.; Lasi, M.A. Climatic trends and temporal patterns of phytoplankton composition, abundance, and succession in the Indian River Lagoon, Florida, USA. Estuar. Coast. 2010, 33, 498–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapointe, B.E.; Herren, L.W.; Brewton, R.A.; Alderman, P.K. Nutrient over-enrichment and light limitation of seagrass communities in the Indian River Lagoon, an urbanized subtropical estuary. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 699, 134068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, C.B.; Tilney, C.L.; Muhlbach, E.; Bouchard, J.N.; Villac, M.C.; Henschen, K.L.; Markley, L.R.; Abbe, S.K.; Shankar, S.; Shea, C.P.; et al. High-resolution spatiotemporal dynamics of harmful algae in the Indian River Lagoon (Florida)—A case study of Aureoumbra lagunensis, Pyrodinium bahamense, and Pseudo-Nitzschia. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 769877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkinson, R.W.; Seidel, V.; Henderson, C.; De Freese, D. Adaptation actions to reduce impairment of Indian River Lagoon water quality caused by climate change, Florida, USA. Coast. Manag. 2021, 49, 215–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweat, L.H.; Stephens, M.; Reed, S.A. Insights from 15 Years of benthic infaunal monitoring in a coastal lagoon system. Fla. Sci. 2021, 84, 147–161. [Google Scholar]
- Barbarite, G.M. The Occurrence of Vibrio vulnificus, V. parahaemolyticus and V. cholerae in the Indian River Lagoon, Florida, with Implications for Human Health. Ph.D. Thesis, Florida Atlantic University, Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. Available online: https://www.proquest.com/dissertations-theses/occurrence-i-vibrio-vulnificus-v-parahaemolyticus/docview/1847569447/se-2?accountid=46638 (accessed on 21 November 2023).
- Bradshaw, D.J.; Dickens, N.J.; Trefry, J.H.; McCarthy, P.J. Defining the sediment prokaryotic communities of the Indian River Lagoon, FL, USA, an Estuary of National Significance. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, T.A.; Jayakumar, J.M.; López-Pérez, M.; Almagro-Moreno, S. Vibrio floridensis sp. nov., a novel species closely related to the human pathogen Vibrio vulnificus isolated from a cyanobacterial bloom. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2023, 73, 005675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Pérez, M.; Jayakumar, J.M.; Grant, T.A.; Zaragoza-Solas, A.; Cabello-Yeves, P.J.; Almagro-Moreno, S. Ecological diversification reveals routes of pathogen emergence in endemic Vibrio vulnificus populations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2103470118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, M.X.; Miller, H.M. Response of a benthic suspension feeder (Crassostrea virginica Gmelin) to three centuries of anthropogenic eutrophication in Chesapeake Bay. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2005, 62, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grizzle, R.E.; Greene, J.K.; Coen, L.D. Seston removal by natural and constructed intertidal eastern oyster (Crassostrea virginica) reefs: A comparison with previous laboratory studies, and the value of in situ methods. Estuar. Coast. 2008, 31, 1208–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galimany, E.; Freeman, C.J.; Lunt, J.; Domingos, A.; Sacks, P.; Walters, L. Feeding competition between the native oyster Crassostrea virginica and the invasive mussel Mytella charruana. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2017, 564, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froelich, B.; Ayrapetyan, M.; Oliver, J.D. Integration of Vibrio vulnificus into marine aggregates and its subsequent uptake by Crassostrea virginica oysters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 1454–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabra, M.; Williams, L.; Watts, J.E.M.; Hale, M.S.; Couceiro, F.; Preston, J. The plastic trojan horse: Biofilms increase microplastic uptake in marine filter feeders impacting microbial transfer and organism health. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 797, 149217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galimany, E.; Lunt, J.; Freeman, C.J. Bivalve feeding on the brown tide Aureoumbra lagunensis in a shallow coastal environment. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 714816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langdon, C.; Newell, R. Utilization of detritus and bacteria as food sources by two bivalve suspension-feeders, the oyster Crassostrea virginica and the mussel Geukensia demissa. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1989, 58, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, R.I.; Jordan, S.J. Preferential ingestion of organic material by the American oyster Crassostrea virginica. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1983, 13, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.E.; Newell, R.I.E.; Thompson, R.J.; MacDonald, B.A. In vivo studies of suspension-feeding processes in the eastern oyster, Crassostrea virginica (Gmelin). Biol. Bull. 1994, 186, 221–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmichael, R.H.; Walton, W.; Clark, H. Bivalve-enhanced nitrogen removal from coastal estuaries. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2012, 69, 1131–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimaru, K.; Akagawa-Matsushita, M.; Muroga, K. Vibrio ichthyoenteri sp. nov., a pathogen of Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) larvae. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1996, 46, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, B.; Austin, D.; Sutherland, R.; Thompson, F.; Swings, J. Pathogenicity of vibrios to rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss, Walbaum) and Artemia nauplii. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 1488–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, B.; Zhang, X.H. Vibrio harveyi: A significant pathogen of marine vertebrates and invertebrates. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 43, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardan, L.; Dauga, C.; Prior, P.; Gillis, M.; Saddler, G.S. Acidovorax anthurii sp. nov., a new phytopathogenic bacterium which causes bacterial leaf-spot of Anthurium. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2000, 50, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Lin, X.; Liao, Y.; Tang, T. Characteristics and diversity of endophytic bacteria in Panax notoginseng under high temperature analysed using full-length 16S RRNA sequencing. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawabe, T.; Tanaka, R.; Iqbal, M.M.; Tajima, K.; Ezura, Y.; Ivanova, E.P.; Christen, R. Assignment of Alteromonas elyakovii KMM 162(T) and five strains isolated from spot-wounded fronds of Laminaria japonica to Pseudoalteromonas elyakovii comb. nov. and the extended description of the species. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2000, 50, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yan, Y.; Li, J.; Tang, L.; Mao, Y.; Mo, Z. Development of a PCR method for detection of Pseudoalteromonas marina associated with green spot disease in Pyropia yezoensis. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2020, 38, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Saha, M.; Zhuang, Y.; Chang, L.; Xiao, L.; Wang, G. Pseudoalteromonas piscicida X-8 causes bleaching disease in farmed Saccharina japonica. Aquaculture 2022, 546, 737354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, G.P.; Watson, M.A.; Crane, E.J.; Burt, I.G.; Bushek, D. Shewanella and Photobacterium spp. in oysters and seawater from the Delaware Bay. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 3323–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, K.E.; Hammond, R.M.; Hutchinson, R.; Blackmore, C.G.M. Vibrio illness in Florida, 1998-2007. Epidemiol. Infect. 2011, 139, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.C.; Danyluk, M.D.; Otwell, W.S. Pathogens in raw foods: What the salad bar can learn from the raw bar. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2009, 20, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indian River Oyster Company. Available online: https://irocoysters.com (accessed on 9 November 2023).
- Oysters and Clams: Recreational Regulations. Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission. Available online: https://myfwc.com/fishing/saltwater/recreational/shellfish (accessed on 13 August 2023).
- George, G.J.; Brown, K.M.; Peterson, G.W.; Thompson, B.A. Removal of black drum on Louisiana reefs to increase survival of eastern oysters Crassostrea virginica. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2008, 28, 1802–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggleston, D.B. Foraging behavior of the blue crab, Callinectes sapidus, on juvenile oysters, Crassostrea virginica: Effects of prey density and size. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1990, 46, 62–82. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, D.W.; Ellender, R.D. Relaying to decrease the concentration of oyster-associated pathogens. J. Food Prot. 1986, 49, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, A.M.; Ward, J.E.; Dobbs, F.C.; Pierce, M.L.; Drake, J.M. The contribution of marine aggregate-associated bacteria to the accumulation of pathogenic bacteria in oysters: An agent-based model. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 6, 7397–7408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeels, H.A.; Loh, A.N.; Volety, A.K. Trophic transfer and habitat use of oyster Crassostrea virginica reefs in southwest Florida, identified by stable isotope analysis. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 462, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, S.J.; Craig, C.A.; Wayles, J.; Sailor-Tynes, T.; Dark, E.; Sweat, L.H.; Fox, D.W.; Zhai, L.; Walters, L.J. Contribution of stormwater outfalls to microplastic pollution in a subtropical estuary using data collected with the assistance of citizen scientists. Environments 2023, 10, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneed, J.M.; Ritson-Williams, R.; Paul, V.J. Crustose coralline algal species host distinct bacterial assemblages on their surfaces. ISME J. 2015, 9, 2527–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, C.A.; Fox, D.W.; Zhai, L.; Walters, L.J. In-situ microplastic egestion efficiency of the eastern oyster Crassostrea virginica. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 178, 113653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apprill, A.; Mcnally, S.; Parsons, R.; Weber, L. Minor revision to V4 region SSU RRNA 806R gene primer greatly increases detection of SAR11 bacterioplankton. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 75, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parada, A.E.; Needham, D.M.; Fuhrman, J.A. Every Base matters: Assessing small subunit RRNA primers for marine microbiomes with mock communities, time series and global field samples. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 18, 1403–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajeev, M.; Sushmitha, T.J.; Toleti, S.R.; Pandian, S.K. Sediment-associated bacterial community and predictive functionalities are influenced by choice of 16S ribosomal RNA hypervariable region(s): An amplicon-based diversity study. Genomics 2020, 112, 4968–4979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galanti, L.; Shasha, D.; Gunsalus, K.C. Pheniqs 2.0: Accurate, high-performance bayesian decoding and confidence estimation for combinatorial barcode indexing. BMC Bioinform. 2021, 22, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. UNOISE2: Improved error-correction for Illumina 16S and ITS amplicon sequencing. bioRxiv 2016, 081257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UCHIME2: Improved chimera prediction for amplicon sequencing. bioRxiv 2016, 074252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mair, P.; Wilcox, R. Robust Statistical Methods Using WRS2. 2018. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/WRS2/vignettes/WRS2.pdf (accessed on 21 November 2023).
- Dixon, P. VEGAN, a package of R functions for community ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 2003, 14, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaire, J. RStudio: Integrated development environment for R. In Proceedings of the the R User Conference, useR! 2011, University of Warwick. Coventry, UK, 16–18 August 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Schrader, C.; Schielke, A.; Ellerbroek, L.; Johne, R. PCR inhibitors—Occurrence, properties and removal. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 113, 1014–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKnight, D.T.; Huerlimann, R.; Bower, D.S.; Schwarzkopf, L.; Alford, R.A.; Zenger, K.R. Methods for normalizing microbiome data: An ecological perspective. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2019, 10, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oetama, V.S.P.; Hennersdorf, P.; Abdul-Aziz, M.A.; Mrotzek, G.; Haryanti, H.; Saluz, H.P. Microbiome analysis and detection of pathogenic bacteria of Penaeus monodon from Jakarta Bay and Bali. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 110, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. Updating the 97% identity threshold for 16S ribosomal RNA OTUs. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 2371–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastroianni, A. Mycobacterium flavescens vertebral osteomyelitis in an immunocompetent host. Infez. Med. 2003, 11, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.L.; Qi, Z.; Huang, H.; Tu, J.; Song, X.J.; Qi, K.Z.; Shao, Y. Diversity and distribution of potential pathogens and antibiotic resistance genes in anthropogenic disturbances aquatic environment and their relationship with microbial indicators. Res. Sq. 2021, preprint. 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espiritu, H.M.; Mamuad, L.L.; Kim, S.H.; Jin, S.J.; Lee, S.S.; Kwon, S.W.; Cho, Y. Il Microbiome shift, diversity, and overabundance of opportunistic pathogens in bovine digital dermatitis revealed by 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing. Animals 2020, 10, 1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, C.; Davidson, J.; Wiens, G.D.; Welch, T.J.; Summerfelt, S. Flavobacterium branchiophilum and F. succinicans associated with bacterial gill disease in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum) in water recirculation aquaculture systems. J. Fish Dis. 2015, 38, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Blom, J.; Loch, T.P.; Faisal, M.; Walker, E.D. The emerging fish pathogen Flavobacterium spartansii isolated from Chinook salmon: Comparative genome analysis and molecular manipulation. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.T.; Nguyen, V.V.; Mata, W.; Kayansamruaj, P.; Senapin, S.; Nilubol, D.; Rodkhum, C. Diversity of non-Flavobacterium columnare bacteria associated with columnaris-like diseased fish. Thai J. Vet. Med. 2016, 46, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Álvarez, C.; Santos, Y. Identification and typing of fish pathogenic species of the genus Tenacibaculum. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 9973–9989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesdorpf, J.E.; Geers, A.U.; Strube, M.L.; Gram, L.; Bentzon-Tilia, M. Roseobacter group probiotics exhibit differential killing of fish pathogenic Tenacibaculum species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 88, e02418-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.; Queiroz, J.A.; Oleastro, M.; Domingues, F.C. Insights in the pathogenesis and resistance of Arcobacter: A review. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 42, 364–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, T.L.; Malnick, H.; Shah, J.; Chattaway, M.A.; Keys, C.J.; Cooke, F.J.; Shah, H.N. Characterisation of Exiguobacterium aurantiacum isolates from blood cultures of six patients. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2007, 13, 946–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Zou, W.; Cai, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, K.; Li, M.; Tan, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Zeng, L. The first report of cerebral nocardiosis caused by Nocardia terpenica together with Exiguobacterium profundum bacteremia. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2018, 11, e69604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnool, R.B.; Vithya, T.; Wadhwani, A.; Balasubramaniam, V.; Ponnusankar, S. Streptococcal infections: Race to multidrug resistance—A review. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plassart, C.; Mauvais, F.; Heurté, J.; Sautereau, J.; Legeay, C.; Bouvet, P. First case of intra-abdominal infection with Clostridium disporicum. Anaerobe 2013, 19, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, E.; Kim, T.Y.; Heo, W.Y.; Kang, O.; Yu, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Ko, J.H.; Lee, N.Y.; Huh, H.J. The first case of Clostridium saudiense bacteremia in a patient with hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann. Lab. Med. 2022, 42, 491–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanci, R.; Corti, G.; Bartoloni, A.; Tortoli, E.; Mariottini, A.; Pecile, P. Unusual Methylobacterium fujisawaense infection in a patient with acute leukaemia undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: First Case Report. Case Rep. Med. 2010, 2010, 313514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, J.W.; Martin, J.W.; Hooke, M.; Hooke, J. Methylobacterium mesophilicum infection: Case report and literature review of an unusual opportunistic pathogen. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000, 30, 936–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Tarrand, J.J.; Han, X.Y. Microbiological and clinical features of four cases of catheter-related infection by Methylobacterium radiotolerans. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 1375–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, M.; Venditti, C.; Raponi, G.; Navazio, A.S.; Alessandri, F.; Giombini, E.; Nisii, C.; Di Caro, A.; Venditti, M. A Case of persistent bacteraemia by Ralstonia mannitolilytica and Ralstonia pickettii in an Intensive care unit. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 2391–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, M.P.; Pembroke, J.T.; Adley, C.C. Ralstonia pickettii: A persistent gram-negative nosocomial infectious organism. J. Hosp. Infect. 2006, 62, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuwono, C.; Wehrhahn, M.C.; Liu, F.; Riordan, S.M.; Zhang, L. The isolation of Aeromonas species and other common enteric bacterial pathogens from patients with gastroenteritis in an Australian population. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, F.; Giraud-Morin, C.; Rossolini, G.M.; Docquier, J.D.; Fosse, T. Genetic and biochemical characterization of TRU-1, the endogenous Class C β-lactamase from Aeromonas enteropelogenes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 1547–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteve, C.; Amaro, C.; Toranzo, A.E. O-Serogrouping and surface components of Aeromonas hydrophila and Aeromonas jandaei pathogenic for eels. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1994, 117, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, J.D.; Pramanik, A.; Webster, N.S.; Llewellyn, L.E.; Gachhui, R.; Mukherjee, J. The pathogen of the Great Barrier Reef sponge Rhopaloeides odorabile is a new strain of Pseudoalteromonas agarivorans containing abundant and diverse virulence-related genes. Mar. Biotechnol. 2015, 17, 463–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Weinberger, F.; Saha, M.; Majzoub, M.E.; Egan, S. Cross-host protection of marine bacteria against macroalgal disease. Microb. Ecol. 2022, 84, 1288–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beurmann, S.; Ushijima, B.; Videau, P.; Svoboda, C.M.; Smith, A.M.; Rivers, O.S.; Aeby, G.S.; Callahan, S.M. Pseudoalteromonas piratica strain OCN003 is a coral pathogen that causes a switch from chronic to acute Montipora white syndrome in Montipora capitata. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Huang, H.; Yang, N.; Feng, H.; Li, Y.; Han, B. Isolation, identification, and biological control in vitro of tail rot pathogen strain from Hippocampus kuda. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-Ramos, C.; Rowley, A.F. Effect of extracellular products of Pseudoalteromonas atlantica on the edible crab Cancer pagurus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wu, W.; You, W.; Huang, S.; Huang, M.; Luo, X.; Lu, Y.; Ke, C.; Xie, Q. A novel screening method for the detection of Pseudoalteromonas shioyasakiensis, an emerging opportunistic pathogen that caused the mass mortality of juvenile Pacific abalone (Haliotis discus Hannai) during a record-breaking heat wave. Aquaculture 2021, 545, 737191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zheng, F.; Sun, X.; Hong, X.; Dong, S.; Wang, B.; Tang, X.; Wang, Y. Identification of the pathogens associated with skin ulceration and peristome tumescence in cultured sea cucumbers Apostichopus japonicus (Selenka). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2010, 105, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujalte, M.J.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A.; Macián, M.C.; Álvarez-Pellitero, P.; Garay, E. Occurrence and virulence of Pseudoalteromonas spp. in cultured gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.) and european sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.). Molecular and phenotypic characterisation of P. undina strain U58. Aquaculture 2007, 271, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T.; Evans, F.F.; Schleheck, D.; Mai-Prochnow, A.; Burke, C.; Penesyan, A.; Dalisay, D.S.; Stelzer-Braid, S.; Saunders, N.; Johnson, J.; et al. Analysis of the Pseudoalteromonas tunicata genome reveals properties of a surface-associated life style in the marine environment. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawabe, T.; Makino, H.; Tatsumi, M.; Nakano, K.; Tajima, K.; Iqbal, M.M.; Yumoto, I.; Ezura, Y.; Christen, R. Pseudoalteromonas bacteriolytica sp. nov., a marine bacterium that is the causative agent of red spot disease of Laminaria japonica. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1998, 48, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, M.; Chen, W.; Lin, Q.; Du, H. Isolation and pathogenicity identification of bacterial pathogens in bleached disease and their physiological effects on the red macroalga Gracilaria lemaneiformis. Aquat. Bot. 2019, 153, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saulnier, D.; de Decker, S.; Haffner, P.; Cobret, L.; Robert, M.; Garcia, C. A large-scale epidemiological study to identify bacteria pathogenic to Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas and correlation between virulence and metalloprotease-like activity. Microb. Ecol. 2010, 59, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, N.; Li, Q.; Ding, J.; Zhan, Y.; Chang, Y. Isolation and characterization of bacteria associated with a syndrome disease of sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius in North China. Aquac. Res. 2013, 44, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Qiao, G.; Li, Q.; Zhou, W.; Won, K.M.; Xu, D.H.; Park, S.I. Biological characteristics and pathogenicity of a highly pathogenic Shewanella marisflavi infecting sea cucumber, Apostichopus japonicus. J. Fish Dis. 2010, 33, 865–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabha, H.; Nataraj, K.; Rajesh, B.; Pratap Chandran, R. Isolation and molecular characterization of microbial population from the fish “Tilapia” collected from Vembanad Lake, Kerala, India. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2021, 12, 573–583. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Pérez, A.; Söderhäll, K.; Sirikharin, R.; Jiravanichpaisal, P.; Söderhäll, I. Vibrio Areninigrae as a Pathogenic Bacterium in a Crustacean. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2021, 178, 107517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Künili, İ.E.; Ertürk Gürkan, S.; Aksu, A.; Turgay, E.; Çakir, F.; Gürkan, M.; Altinağaç, U. Mass Mortality in Endangered Fan Mussels Pinna Nobilis (Linnaeus 1758) Caused by Co-Infection of Haplosporidium Pinnae and Multiple Vibrio Infection in Çanakkale Strait, Turkey. Biomarkers 2021, 26, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, A.P.B.; Duytschaever, G.; Chimetto Tonon, L.A.; Fróes, A.M.; de Oliveira, L.S.; Amado-Filho, G.M.; Francini-Filho, R.B.; De Vos, P.; Swings, J.; Thompson, C.C.; et al. Photobacterium Sanctipauli Sp. Nov. Isolated from Bleached Madracis Decactis (Scleractinia) in the St Peter & St Paul Archipelago, Mid-Atlantic Ridge, Brazil. PeerJ 2014, 2014, e427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jacobs Slifka, K.M.; Newton, A.E.; Mahon, B.E. Vibrio Alginolyticus Infections in the USA, 1988-2012. Epidemiol. Infect. 2017, 145, 1491–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, N.A.; Grim, C.J.; Lipp, E.K.; Rivera, I.N.G.; Chun, J.; Haley, B.J.; Taviani, E.; Choi, S.Y.; Hoq, M.; Munk, A.C.; et al. Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Vent Bacteria Related to Human Pathogenic Vibrio Species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E2813–E2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xie, G.; Wang, H.; Wan, X.; Li, X.; Shi, C.; Wang, Z.; Gong, M.; Li, T.; Wang, P.; et al. Characterization of a Novel Shrimp Pathogen, Vibrio Brasiliensis, Isolated from Pacific White Shrimp, Penaeus Vannamei. J. Fish Dis. 2021, 44, 1543–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Huang, H.; Huang, Z.; Chen, H.; Shao, Z. Isolation and Identification of Vibrio Campbellii as a Bacterial Pathogen for Luminous Vibriosis of Litopenaeus Vannamei. Aquac. Res. 2015, 46, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimes, N.E.; Grim, C.J.; Johnson, W.R.; Hasan, N.A.; Tall, B.D.; Kothary, M.H.; Kiss, H.; Munk, A.C.; Tapia, R.; Green, L.; et al. Temperature Regulation of Virulence Factors in the Pathogen Vibrio Coralliilyticus. ISME J. 2012, 6, 835–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, S.; Romalde, J.L.; Montes, J.; Barja, J.L. Pathogenic Bacteria Isolated from Disease Outbreaks in Shellfish Hatcheries. First Description of Vibrio Neptunius as an Oyster Pathogen. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2005, 67, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulden, E.F.; Hall, M.R.; Bourne, D.G.; Pereg, L.L.; Høj, L. Pathogenicity and Infection Cycle of Vibrio Owensii in Larviculture of the Ornate Spiny Lobster (Panulirus Ornatus). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 2841–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, S.L.; Depaola, A.; Jaykus, L.A. An Overview of Vibrio Vulnificus and Vibrio Parahaemolyticus. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2007, 6, 120–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, C.; Liu, J.; Zheng, X.; Xu, L.; Ye, H. Identification of Vibrio Ponticus as a Bacterial Pathogen of Coral Trout Plectropomus Leopardus. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.J.; Yan, B.L.; Bai, X.S.; Bi, K.R.; Gao, H.; Qin, G.M. Isolation and Characterization of Vibrio Parahaemolyticus and Vibrio Rotiferianus Associated with Mass Mortality of Chinese Shrimp (Fenneropenaeus Chinensis). J. Shellfish Res. 2014, 33, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhong, M.; Li, X.; Lu, W.; Li, J. River Bacterial Community Structure and Co-Occurrence Patterns under the Influence of Different Domestic Sewage Types. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 266, 110590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Miranda, M.; Luna-González, A.; Campa Córdova, Á.I.; Fierro-Coronado, J.A.; Partida-Arangure, B.O.; Pintado, J.; González-Ocampo, H.A. Isolation and characterization of infectious Vibrio sinaloensis strains from the Pacific shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei (Decapoda: Penaeidae). Rev. Biol. Trop. 2012, 60, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hada, H.S.; West, P.A.; Lee, J.V. Vibrio tubiashii sp. nov., a pathogen of bivalve mollusks. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1984, 34, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prayitno, S.B.; Latchford, J.W. Experimental infections of crustaceans with luminous bacteria related to Photobacterium and Vibrio. Effect of salinity and pH on infectiosity. Aquaculture 1995, 132, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yardimci, R.; Turgay, E.; Steinum, S.K. Diagnosis of Photobacterium sanguinicancri in smout-hound shark (Mustelus mustelus, Linnaeus 1758). Acta Aquat. Turc. 2019, 16, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichi, G.; Cardeti, G.; Perrucci, S.; Vanni, A.; Cersini, A.; Lenzi, C.; De Wolf, T.; Fronte, B.; Guarducci, M.; Susini, F. Skin lesion-associated pathogens from Octopus vulgaris: First detection of Photobacterium swingsii, Lactococcus garvieae and betanodavirus. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2015, 115, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamurthy, T.; Chowdhury, G.; Pazhani, G.P.; Shinoda, S. Vibrio fluvialis: An emerging human pathogen. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lux, T.M.; Lee, R.; Love, J. Genome-wide phylogenetic analysis of the pathogenic potential of Vibrio furnissii. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, A.J.; Lemos, M.L.; Osorio, C.R. Photobacterium damselae subsp. damselae, a bacterium pathogenic for marine animals and humans. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.R.; Lorenzo, L.; Alcantara, R.; Navas, J.I. Characterization of Aliivibrio fischeri strains associated with disease outbreak in brill Scophthalmus rhombus. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2017, 124, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjerde, E.; Lorentzen, M.; Holden, M.T.G.; Seeger, K.; Paulsen, S.; Bason, N.; Churcher, C.; Harris, D.; Norbertczak, H.; Quail, M.A.; et al. The genome sequence of the fish pathogen Aliivibrio salmonicida strain LFI1238 shows extensive evidence of gene decay. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjerde, E.; Karlsen, C.; Sørum, H.; Parkhill, J.; Willassen, N.P.; Thomson, N.R. Co-cultivation and transcriptome sequencing of two co-existing fish pathogens Moritella viscosa and Aliivibrio wodanis. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labreuche, Y.; Soudant, P.; Gonçalves, M.; Lambert, C.; Nicolas, J.L. Effects of extracellular products from the pathogenic Vibrio aestuarianus strain 01/32 on lethality and cellular immune responses of the oyster Crassostrea gigas. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2006, 30, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaz-Hidalgo, R.; Diéguez, A.L.; Cleenwerck, I.; Balboa, S.; Doce, A.; de Vos, P.; Romalde, J.L. Vibrio celticus sp. nov., a new Vibrio species belonging to the Splendidus clade with pathogenic potential for clams. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 33, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urtubia, R.; Miranda, C.D.; Rodríguez, S.; Dubert, J.; Barja, J.L.; Rojas, R. First report, characterization and pathogenicity of Vibrio chagasii isolated from diseased reared larvae of Chilean scallop, Argopecten purpuratus (Lamarck, 1819). Pathogens 2023, 12, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruto, M.; James, A.; Petton, B.; Labreuche, Y.; Chenivesse, S.; Alunno-Bruscia, M.; Polz, M.F.; Le Roux, F. Vibrio crassostreae, a benign oyster colonizer turned into a pathogen after plasmid acquisition. ISME J. 2017, 11, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.F.; Chen, Y.W.; Xu, J.K.; Ding, W.Y.; Shao, A.Q.; Zhu, Y.T.; Wang, C.; Liang, X.; Yang, J.L. Temperature elevation and Vibrio cyclitrophicus infection reduce the diversity of haemolymph microbiome of the mussel Mytilus coruscus. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Bai, C.; Li, C.; Li, C.; Xin, L. Isolation and characterization of Vibrio kanaloae as a major pathogen associated with mass mortalities of ark clam, Scapharca broughtonii, in cold season. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duperthuy, M.; Schmitt, P.; Garzón, E.; Caro, A.; Rosa, R.D.; Le Roux, F.; Lautrédou-Audouy, N.; Got, P.; Romestand, B.; De Lorgeril, J.; et al. Use of OmpU porins for attachment and invasion of Crassostrea gigas immune cells by the oyster pathogen Vibrio splendidus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2993–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasa, A.; Avendaño-Herrera, R.; Estrada, J.M.; Romalde, J.L. Isolation and identification of Vibrio toranzoniae associated with diseased red conger eel (Genypterus chilensis) farmed in Chile. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 179, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, B.; Paillard, C.; Auffret, M. Alterations in hemolymph and extrapallial fluid parameters in the manila clam, Ruditapes philippinarum, challenged with the pathogen Vibrio tapetis. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2000, 76, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, T.J.; Schrankel, C.S.; Vyas, H.; Rosenblatt, H.D.; Hamdoun, A. CRISPR/Cas9 mutagenesis reveals a role for ABCB1 in gut immune responses to Vibrio diazotrophicus in sea urchin larvae. J. Exp. Biol. 2021, 224, jeb232272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimaru, K.; Akagawa-Matsushita, M.; Muroga, K. Vibrio penaeicida sp. nov., a pathogen of kuruma prawns (Penaeus japonicus). Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1995, 45, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangam, A.K.; Angel, R.J.; Jangam, A.K.; Nathamuni, S.; Katneni, V.K.; Avunje, S.; Angel, R.J.; Grover, M.; Shekhar, M.S. Microbial communities associated with stunted growth syndrome in Penaeus vannamei farming. Res. Sq. 2021, preprint. 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapsinski, G.J.; Makadia, J.; Bhanot, N.; Min, Z. Pseudomonas mendocina native valve infective endocarditis: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2016, 10, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, L.; Kaur, R.; Kumar, S.; Bansal, A.; Gautam, V.; Singh, M.; Ray, P. Pseudomonas oleovorans sepsis in a child: The first reported case in India. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 68, 254–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, M.; Porcel, M.; de la Torre, J.; Molina-Henares, M.A.; Daddaoua, A.; Llamas, M.A.; Roca, A.; Carriel, V.; Garzón, I.; Ramos, J.L.; et al. Analysis of the pathogenic potential of nosocomial Pseudomonas putida strains. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwazzeh, M.J.; Alkuwaiti, F.A.; Alqasim, M.; Alwarthan, S.; El-ghoneimy, Y. Infective endocarditis caused by Pseudomonas stutzeri: A case report and literature review. Am. J. Case Rep. 2020, 12, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckers, B.; Op De Beeck, M.; Thijs, S.; Truyens, S.; Weyens, N.; Boerjan, W.; Vangronsveld, J. Performance of 16s RDNA primer pairs in the study of rhizosphere and endosphere bacterial microbiomes in metabarcoding studies. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiruy, A.M.; Mohammed, J.; Haileselassie, M.M.; Acharya, K.; Butte, G.; Haile, A.T.; Walsh, C.; Werner, D. Spatiotemporal variation in urban wastewater pollution impacts on river microbiomes and associated hazards in the Akaki Catchment, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 826, 153912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, M.; Zoch-Lesniak, B.; Karch, A.; Vital, M.; Meyer, F.; Klawonn, F.; Baillot, A.; Pieper, D.H.; Mikolajczyk, R.T. Bacterial community structure and effects of picornavirus infection on the anterior nares microbiome in early childhood. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N. PRIMER v7: User Manual/Tutorial; PRIMER_E Ltd.: Plymouth, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Grbin, D.; Geček, S.; Miljanović, A.; Pavić, D.; Hudina, S.; Žučko, J.; Rieder, J.; Pisano, S.R.R.; Adrian-Kalchhauser, I.; Bielen, A. Comparison of exoskeleton microbial communities of co-occuring native and invasive crayfish species. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2023, 201, 107996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, R.M. Best practice in statistics: Use the Welch t-test when testing the difference between two groups. Ann. Clin. Biochem. Int. J. Lab. Med. 2021, 58, 267–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, R.M.; Rappé, M.S.; Connon, S.A.; Vergin, K.L.; Siebold, W.A.; Carlson, C.A.; Giovannoni, S.J. SAR11 clade dominates ocean surface bacterioplankton communities. Nature 2002, 420, 806–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannoni, S.J. SAR11 bacteria: The most abundant plankton in the oceans. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2017, 9, 231–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberbeckmann, S.; Loeder, M.G.J.; Gerdts, G.; Osborn, M.A. Spatial and seasonal variation in diversity and structure of microbial biofilms on marine plastics in northern European waters. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 90, 478–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gignoux-Wolfsohn, S.A.; Vollmer, S.V. Identification of candidate coral pathogens on white band disease-infected staghorn coral. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, T.M.; Crews, A.; Nakano, A. Five years of surveillance for Tularemia Serovar B (Francisella tularensis holarctica) (Olsufjev) (Thiotrichales: Francisellaceae) including two human cases at an endemic site in San Mateo County, California. J. Med. Entomol. 2022, 59, 1787–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eppinger, M.; Baar, C.; Raddatz, G.; Huson, D.H.; Schuster, S.C. Comparative analysis of four Campylobacterales. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 872–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartlett, A.; Padfield, D.; Lear, L.; Bendall, R.; Vos, M. A comprehensive list of bacterial pathogens infecting humans. Microbiology 2022, 168, 001269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrotti, M.L.; de Figueiredo Lacerda, A.L.; Petit, S.; Ghiglione, J.F.; Gorsky, G. Vibrio spp. and other potential pathogenic bacteria associated to microfibers in the north-western Mediterranean Sea. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0275284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Masuda, Y.; Wang, X.; Ushijima, N.; Shiratori, Y.; Senoo, K.; Itoh, H. Genome-based taxonomic rearrangement of the order Geobacterales including the description of Geomonas azotofigens sp. nov. and Geomonas diazotrophica sp. nov. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 737531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, A.M.; DePaola, A.; Bowers, J.C.; Krantz, J.A.; Nordstrom, J.L.; Johnson, C.N.; Grimes, D.J. Variability of total and pathogenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus densities in northern Gulf of Mexico water and oysters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 7589–7596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, C.N.; Bowers, J.C.; Griffitt, K.J.; Molina, V.; Clostio, R.W.; Pei, S.; Laws, E.; Paranjpye, R.N.; Strom, M.S.; Chen, A.; et al. Ecology of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio vulnificus in the coastal and estuarine waters of Louisiana, Maryland, Mississippi, and Washington (United States). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 7249–7257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riisgård, H. Efficiency of particle retention and filtration rate in 6 species of northeast american bivalves. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1988, 45, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kach, D.J.; Ward, J.E. The role of marine aggregates in the ingestion of picoplankton-size particles by suspension-feeding molluscs. Mar. Biol. 2008, 153, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colwell, R.R. Global climate and infectious disease: The Cholera Paradigm. Science 1996, 274, 2025–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzulli, L.; Pezzati, E.; Moreno, M.; Fabiano, M.; Pane, L.; Pruzzo, C.; The VibrioSea Consortium. Benthic ecology of Vibrio spp. and pathogenic Vibrio species in a coastal Mediterranean environment (La Spezia Gulf, Italy). Microb. Ecol. 2009, 58, 808–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmström, C.; Kjelleberg, S. Marine Pseudoalteromonas species are associated with higher organisms and produce biologically active extracellular agents. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1999, 30, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iijima, S.; Washio, K.; Okahara, R.; Morikawa, M. Biofilm formation and proteolytic activities of Pseudoalteromonas bacteria that were isolated from fish farm sediments. Microb. Biotechnol. 2009, 2, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, E.T.; Franz, H.; Lacouture, R. Impact of eastern oyster Crassostrea virginica biodeposit resuspension on the seston, nutrient, phytoplankton, and zooplankton dynamics: A mesocosm experiment. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2018, 586, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, E.T.; Robins, E.; Davis, S.; Lacouture, R.; Cornwell, J.C. Effects of resuspension of eastern oyster Crassostrea virginica biodeposits on phytoplankton community structure. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2020, 640, 79–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, E.T.; Blickenstaff, S.; Cornwell, J.C.; Jackson, M.; Tolbert, S.N. Effect of tidal resuspension with oyster biodeposits on nutrient and oxygen dynamics. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2022, 686, 37–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.R.; Randa, M.A.; Marcelino, L.A.; Tomita-Mitchell, A.; Lim, E.; Polz, M.F. Diversity and dynamics of a north atlantic coastal Vibrio community. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 4103–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, J.; Crump, B.C.; Wang, K.; Chen, F. Bacterioplankton community in Chesapeake Bay: Predictable or random assemblages. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 2157–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Siboni, N.; Balaraju, V.; Carney, R.; Labbate, M.; Seymour, J.R. Spatiotemporal dynamics of Vibrio spp. within the Sydney Harbour Estuary. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, C.; Chen, F.; Kan, J. Spatial and temporal variations of bacterioplankton in the Chesapeake Bay: A re-examination with high-throughput sequencing analysis. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2020, 65, 3032–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DePaola, A.; Capers, G.M.; Alexander, D. Densities of Vibrio vulnificus in the intestines of fish from the U.S. Gulf Coast. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 984–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvell, C.D.; Mitchell, C.E.; Ward, J.R.; Altizer, S.; Dobson, A.P.; Ostfeld, R.S.; Samuel, M.D. Climate warming and disease risks for terrestrial and marine biota. Science 2002, 296, 2158–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeffer, C.S.; Hite, M.F.; Oliver, J.D. Ecology of Vibrio vulnificus in estuarine waters of eastern North Carolina. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 3526–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker-Austin, C.; Trinanes, J.A.; Taylor, N.G.H.; Hartnell, R.; Siitonen, A.; Martinez-Urtaza, J. Emerging Vibrio risk at high latitudes in response to ocean warming. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burge, C.A.; Mark Eakin, C.; Friedman, C.S.; Froelich, B.; Hershberger, P.K.; Hofmann, E.E.; Petes, L.E.; Prager, K.C.; Weil, E.; Willis, B.L.; et al. Climate change influences on marine infectious diseases: Implications for management and society. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2014, 6, 249–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterk, A.; Schets, F.M.; de Roda Husman, A.M.; de Nijs, T.; Schijven, J.F. Effect of climate change on the concentration and associated risks of Vibrio spp. in Dutch recreational waters. Risk Anal. 2015, 35, 1717–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robins, P.E.; Skov, M.W.; Lewis, M.J.; Giménez, L.; Davies, A.G.; Malham, S.K.; Neill, S.P.; McDonald, J.E.; Whitton, T.A.; Jackson, S.E.; et al. Impact of climate change on UK estuaries: A review of past trends and potential projections. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 169, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzzi, A.L.; Stat, M.; Gaston, T.F.; Siboni, N.; Williams, N.L.R.; Seymour, J.R.; Huggett, M.J. Elevated estuary water temperature drives fish gut dysbiosis and increased loads of pathogenic Vibrionaceae. Environ. Res. 2023, 219, 115144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burioli, E.A.V.; Varello, K.; Trancart, S.; Bozzetta, E.; Gorla, A.; Prearo, M.; Houssin, M. First description of a mortality event in adult Pacific oysters in Italy associated with infection by a Tenacibaculum soleae Strain. J. Fish Dis. 2018, 41, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, S.Y.; Liu, P.Y.; Lee, Y.H.; Wu, Z.Y.; Huang, C.C.; Cheng, C.C.; Tung, K.C. The pathogenicity of Shewanella algae and ability to tolerate a wide range of temperatures and salinities. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 2018, 6976897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beach, V.; Clement, J.C.; Kastner, P.D. Draft genome sequence of psychrotolerant Shewanella sp. strain VB17, isolated from marine intertidal sediment near Virginia Beach, Virginia. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2020, 9, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardade, L.; Khandeparker, L. Spatio-temporal variations in pathogenic bacteria in the surface sediments of the Zuari Estuary, Goa, India. Curr. Sci. 2017, 113, 1729–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.N.; Flowers, A.R.; Noriea, N.F.; Zimmerman, A.M.; Bowers, J.C.; DePaola, A.; Grimes, D.J. Relationships between environmental factors and pathogenic vibrios in the northern Gulf of Mexico. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 7076–7084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randa, M.A.; Polz, M.F.; Lim, E. Effects of temperature and salinity on Vibrio vulnificus population dynamics as assessed by quantitative PCR. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 5469–5476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, E. 2021 Florida Weather and Climate Summary. Available online: https://climatecenter.fsu.edu/images/docs/Fla_Annual_climate_summary_2021.pdf (accessed on 21 November 2023).
- Shiah, F.K.; Ducklow, H.W. Temperature and substrate regulation of bacterial abundance, production and specific growth rate in Chesapeake Bay, USA. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1994, 103, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julie, D.; Solen, L.; Antoine, V.; Jaufrey, C.; Annick, D.; Dominique, H.H. Ecology of pathogenic and non-pathogenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus on the French Atlantic coast. Effects of temperature, salinity, turbidity and chlorophyll a. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, G.M.; Judd, C.; Kuske, C.R.; Smith, C. Analysis of stomach and gut microbiomes of the eastern oyster (Crassostrea virginica) from coastal Louisiana, USA. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, M.L.; Evan, J. Gut microbiomes of the eastern oyster (Crassostrea virginica) and the blue mussel (Mytilus edulis): Temporal variation and the influence of marine aggregate-associated microbial communities. mSphere 2019, 4, e00730-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, Z.T.; Dufault-Thompson, K.; Russo, K.T.; Scro, A.K.; Smolowitz, R.M.; Gomez-Chiarri, M.; Zhang, Y. Microbiome analysis reveals diversity and function of Mollicutes associated with the eastern oyster, Crassostrea virginica. mSphere 2021, 6, 10–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macey, B.M.; Achilihu, I.O.; Burnett, K.G.; Burnett, L.E. Effects of hypercapnic hypoxia on inactivation and elimination of Vibrio campbellii in the eastern oyster, Crassostrea virginica. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 6077–6084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, V.M.; Chouljenko, A.; Hall, S.G. Depuration of live oysters to reduce Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio vulnificus: A review of ecology and processing parameters. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 3480–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokarskyy, O.; Marshall, D.L.; Dillon, J.; Andrews, L.S. Long-term depuration of Crassostrea virginica oysters at different salinities and temperatures changes Vibrio vulnificus counts and microbiological profile. J. Food Prot. 2019, 82, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, A.E.; Kolkmeyer, R.; Song, B.; Anderson, I.C.; Bowen, J. Bioreactivity and microbiome of biodeposits from filter-feeding bivalves. Microb. Ecol. 2019, 77, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodney, W.S.; Paynter, K.T. Comparisons of macrofaunal assemblages on restored and non-restored oyster reefs in mesohaline regions of Chesapeake Bay in Maryland. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 2006, 335, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searles, A.R.; Gipson, E.E.; Walters, L.J.; Cook, G.S. Oyster reef restoration facilitates the recovery of macroinvertebrate abundance, diversity, and composition in estuarine communities. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezek, R.J.; Lebreton, B.; Roark, E.B.; Palmer, T.A.; Pollack, J.B. How does a restored oyster reef develop? An assessment based on stable isotopes and community metrics. Mar. Biol. 2017, 164, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugnot, A.B.; Dafforn, K.A.; Coleman, R.A.; Ramsdale, M.; Gibbeson, J.T.; Erickson, K.; Vila-Concejo, A.; Figueira, W.F.; Gribben, P.E. Linking habitat interactions and biodiversity within seascapes. Ecosphere 2022, 13, e4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copertino, J.L.; Harris, K.; Chute, L.; Walters, L.J. Impact of oyster (Crassostrea virginica) reef restoration on benthic invertebrates and coastal birds in a subtropical estuary. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowski, J.H.; Hughes, A.R.; Kimbro, D.L.; Dolan, M.A. How habitat setting influences restored oyster reef communities. Ecology 2005, 86, 1926–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, M.; Izhaki, I. Fish as hosts of Vibrio cholerae. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweat, L.; Busch, S.J.; Craig, C.; Dark, E.; Sailor-Tynes, T.; Wayles, J.; Sacks, P.; Walters, L.J. Temperature and salinity data for both seasons. FigShare, National Museum of Natural History. Dataset. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweat, L.; Busch, S.J.; Craig, C.; Dark, E.; Sailor-Tynes, T.; Wayles, J.; Sacks, P.; Walters, L.J. All ESVs with consensus IDs, sequences (16S, V4 region), and relative proportions per sample. FigShare, National Museum of Natural History. Dataset. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweat, L.; Busch, S.J.; Craig, C.; Dark, E.; Sailor-Tynes, T.; Wayles, J.; Sacks, P.; Walters, L.J. PPM ESVs with consensus IDs, sequences (16S, V4 region), and relative proportions per sample. FigShare, National Museum of Natural History. Dataset. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweat, L.; Busch, S.J.; Craig, C.; Dark, E.; Sailor-Tynes, T.; Wayles, J.; Sacks, P.; Walters, L.J. Sample metadata. FigShare, National Museum of Natural History. Dataset. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweat, L.; Busch, S.J.; Craig, C.; Dark, E.; Sailor-Tynes, T.; Wayles, J.; Sacks, P.; Walters, L.J. Map of collection sites in the Indian River Lagoon. FigShare, National Museum of Natural History. Figure. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweat, L.; Busch, S.J.; Craig, C.; Dark, E.; Sailor-Tynes, T.; Wayles, J.; Sacks, P.; Walters, L.J. Assigned taxonomy (100% matches only, 16S, V4 region) for all PPM ESVs. FigShare, National Museum of Natural History. Dataset. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
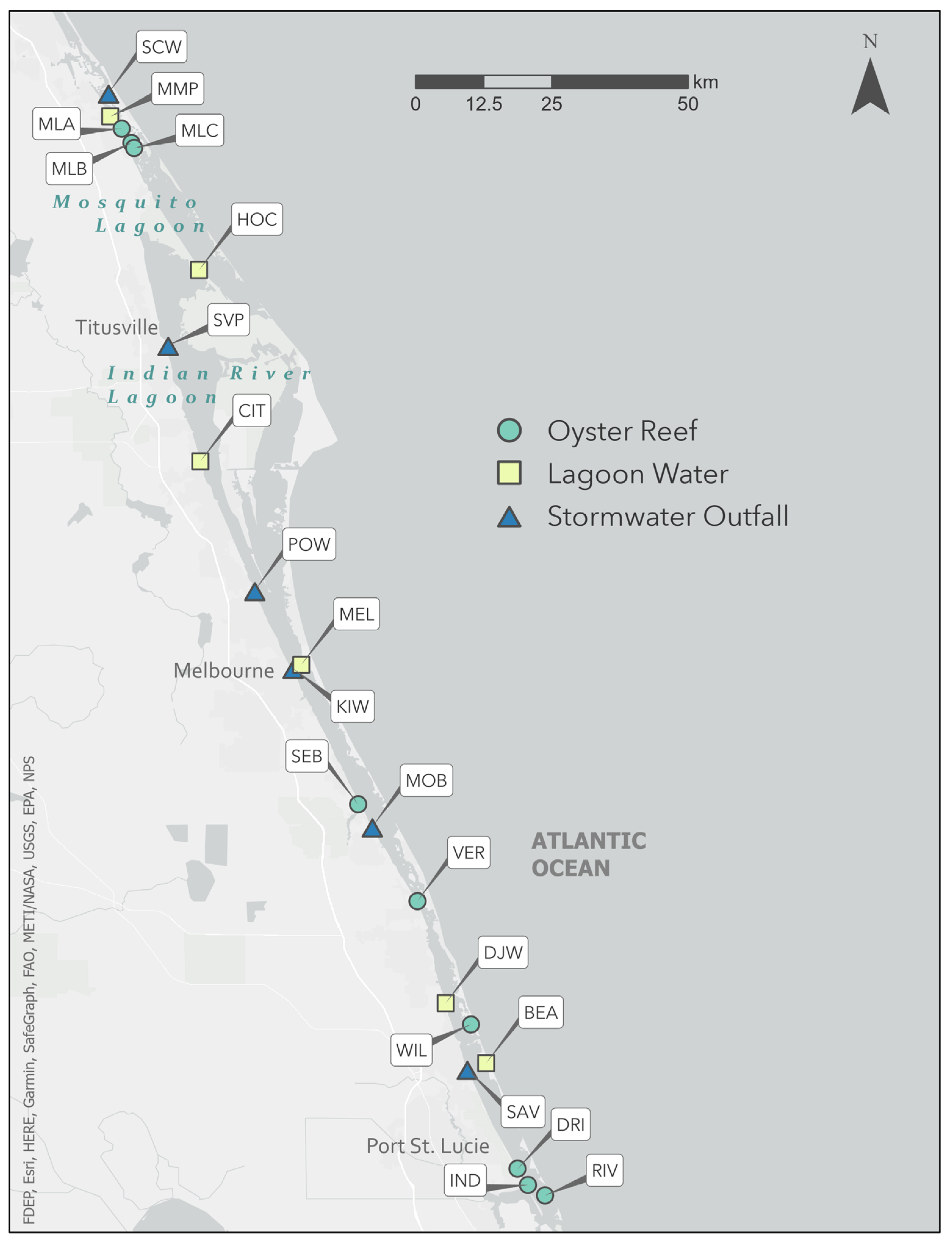



| Site | Name | City/Town | Type | Lat. | Long. | Temp. (°C) | Salinity (ppt) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jan. | Jul. | Jan. | Jul. | ||||||
| MLA | Mosquito Lagoon Reef A | Edgewater | OR | 28.9697 | −80.8820 | 14 | 28 | 37 | 32 |
| MLB | Mosquito Lagoon Reef B | Edgewater | OR | 28.9460 | −80.8660 | 13 | 29 | 37 | 29 |
| MLC | Mosquito Lagoon Reef C | Edgewater | OR | 28.9374 | −80.8615 | 13 | 28 | 34 | 30 |
| SEB | Saint Sebastian River | Sebastian | OR | 27.8553 | −80.4922 | 19 | 32 | 25 | 20 |
| VER | Vero North Relief Canal | Vero Beach | OR | 27.6967 | −80.3947 | 19 | 31 | 5 | 32 |
| WIL | Wildcat Cove | Fort Pierce | OR | 27.4933 | −80.3061 | 17 | 30 | 30 | 35 |
| DRI | Driftwood Motel | Jensen Beach | OR | 27.2551 | −80.2295 | 18 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| IND | Indian Riverside Park | Jensen Beach | OR | 27.2285 | −80.2127 | 18 | 29 | 31 | 31 |
| RIV | River Cove Park | Stuart | OR | 27.2112 | −80.1843 | 17 | 28 | 31 | 31 |
| HOC | Haulover Canal | Mims | LW | 28.7365 | −80.7547 | 21 | 29 | 14 | 19 |
| MMP | Menard-May Park | Edgewater | LW | 28.9896 | −80.9012 | 20 | 29 | 30 | 25 |
| CIT | City Point Community Church | Cocoa | LW | 28.4211 | −80.7525 | 15 | 31 | 15 | 16 |
| MEL | Melbourne Causeway | Melbourne | LW | 28.0856 | −80.5862 | 16 | 30 | 19 | 28 |
| BEA | Bear Point Sanctuary | Fort Pierce | LW | 27.4294 | −80.2813 | 15 | 30 | 33 | 35 |
| DJW | D.J. Wilcox Preserve | Fort Pierce | LW | 27.5282 | −80.3481 | 15 | 29 | 30 | 27 |
| SCW | South Causeway | New Smyrna Beach | SO | 29.0284 | −80.9039 | 21 | 30 | 28 | 21 |
| SVP | Space View Park | Titusville | SO | 28.6126 | −80.8056 | 24 | 28 | 0 | 0 |
| KIW | Claude Edge Front Street Park | Melbourne | SO | 28.0798 | −80.5997 | 14 | 29 | 17 | 26 |
| POW | POW/MIA Park | Melbourne | SO | 28.2082 | −80.6628 | 16 | 29 | 7 | 20 |
| MOB | Mo Bay Grill | Sebastian | SO | 27.8189 | −80.4690 | 23 | 30 | 0 | 17 |
| SAV | Savannah Road | Fort Pierce | SO | 27.4194 | −80.3124 | 17 | 28 | 0 | 14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sweat, L.H.; Busch, S.J.; Craig, C.A.; Dark, E.; Sailor-Tynes, T.; Wayles, J.; Sacks, P.E.; Walters, L.J. Oyster Reefs Are Reservoirs for Potential Pathogens in a Highly Disturbed Subtropical Estuary. Environments 2023, 10, 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10120205
Sweat LH, Busch SJ, Craig CA, Dark E, Sailor-Tynes T, Wayles J, Sacks PE, Walters LJ. Oyster Reefs Are Reservoirs for Potential Pathogens in a Highly Disturbed Subtropical Estuary. Environments. 2023; 10(12):205. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10120205
Chicago/Turabian StyleSweat, L. Holly, Sidney J. Busch, Casey A. Craig, Emily Dark, Tess Sailor-Tynes, Jessy Wayles, Paul E. Sacks, and Linda J. Walters. 2023. "Oyster Reefs Are Reservoirs for Potential Pathogens in a Highly Disturbed Subtropical Estuary" Environments 10, no. 12: 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10120205
APA StyleSweat, L. H., Busch, S. J., Craig, C. A., Dark, E., Sailor-Tynes, T., Wayles, J., Sacks, P. E., & Walters, L. J. (2023). Oyster Reefs Are Reservoirs for Potential Pathogens in a Highly Disturbed Subtropical Estuary. Environments, 10(12), 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10120205







