Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment of Waste to Energy Systems in the Developing World: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
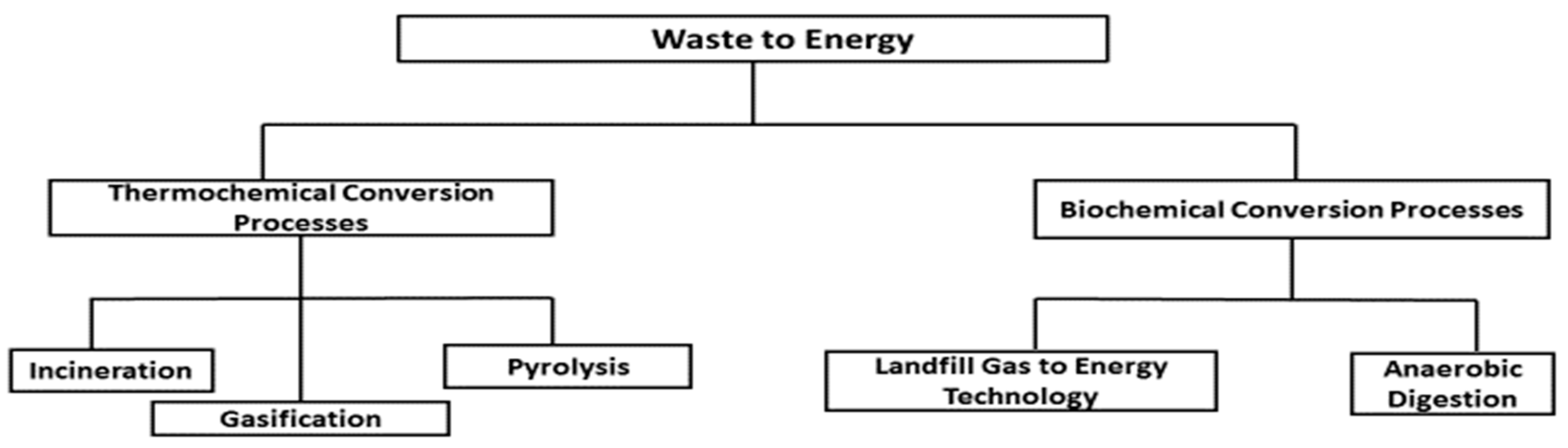
3. Overview of Waste to Energy Technologies
4. Sustainability Assessment of Waste to Energy Technologies
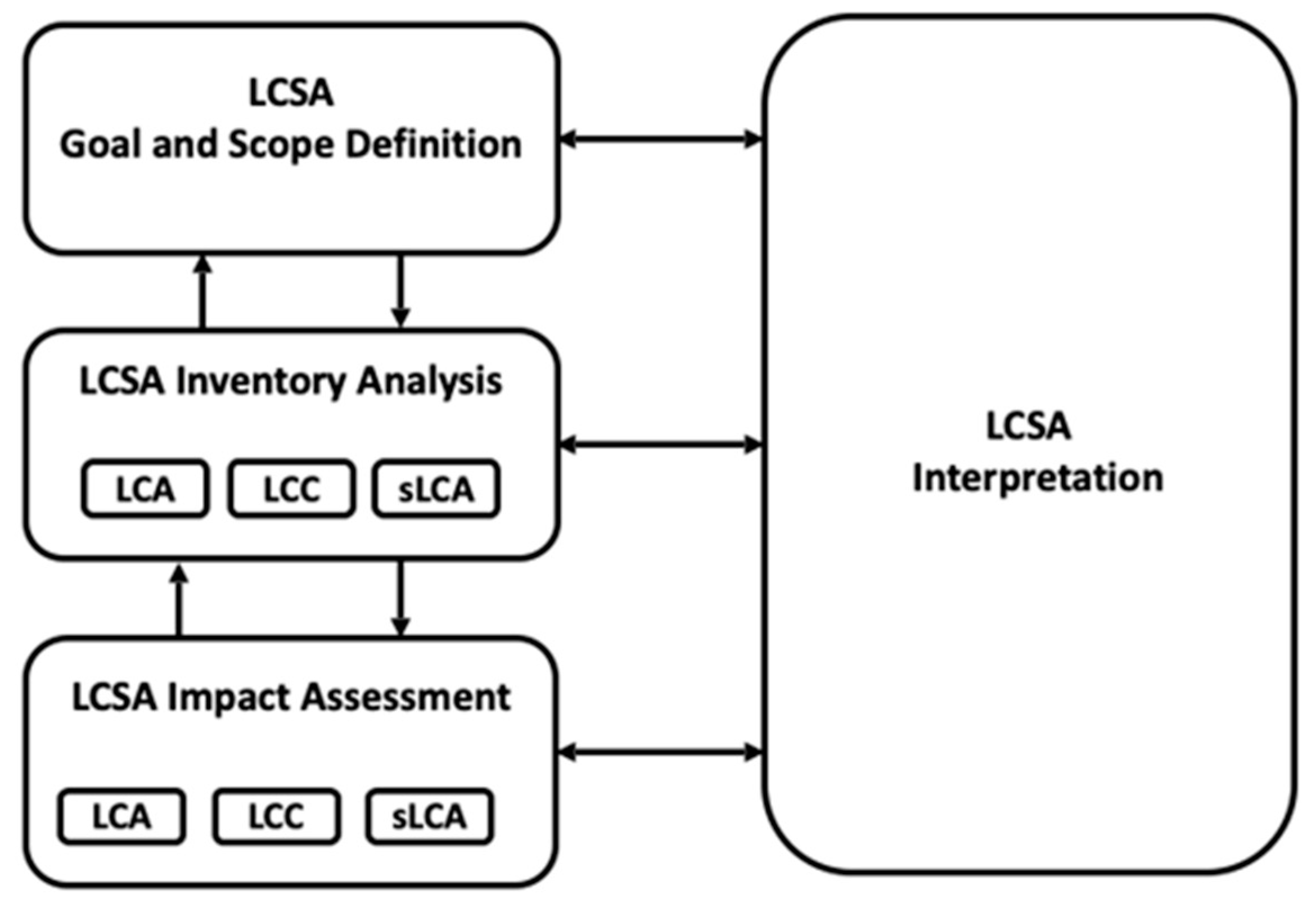
4.1. Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment for Waste to Energy Technologies
4.2. Life Cycle Assessment for Waste to Energy Technologies
4.3. Life Cycle Costing for Waste to Energy Technologies
4.4. Social Life Cycle Assessment for Waste to Energy Technologies
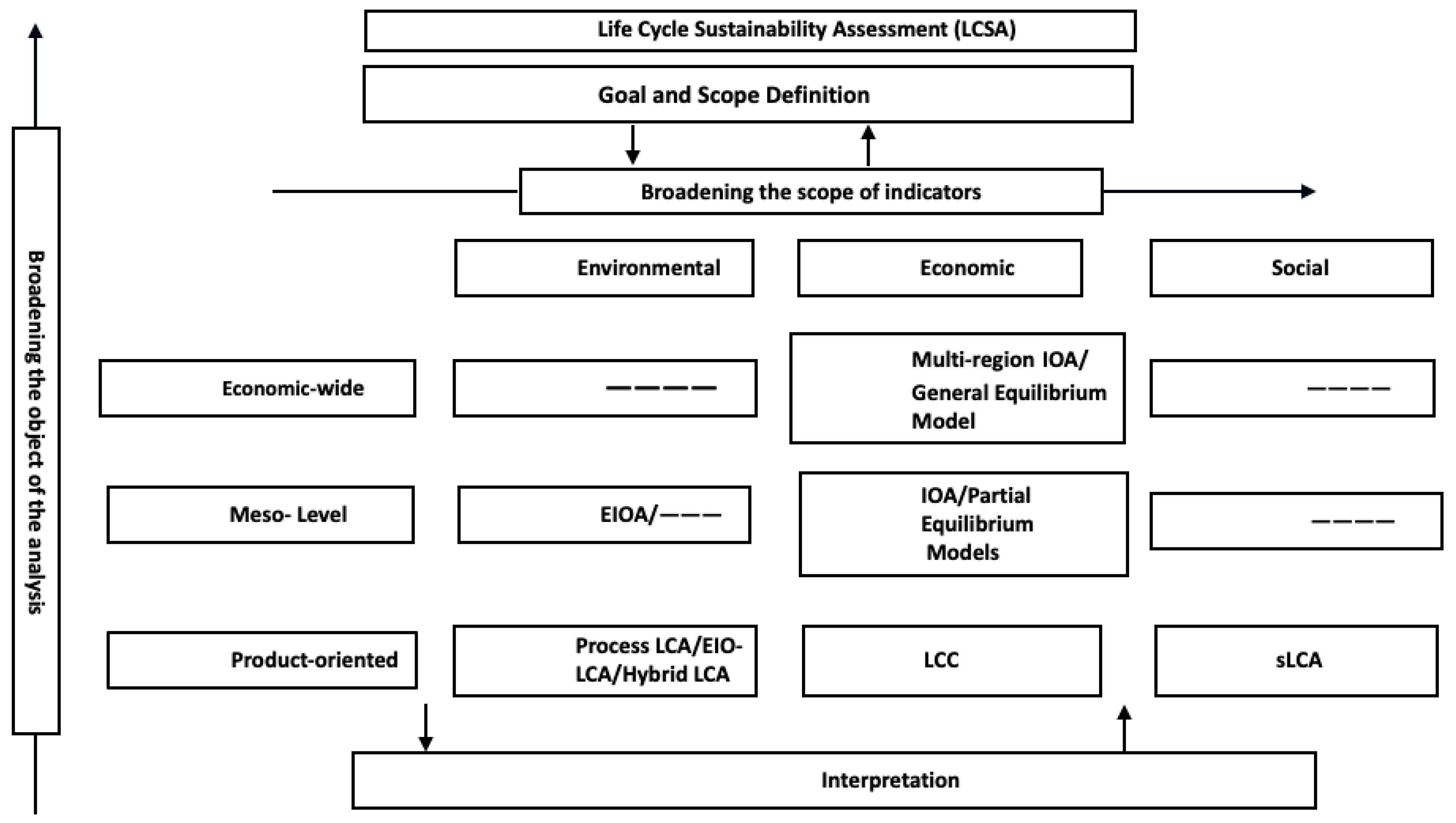
4.5. Integration of LCSA Components: LCA, LCC and sLCA
- Multi-attribute decision-making (MADM) methods, which are used to assess a finite set of options based on multiple criteria attributes;
- Multi-objective decision-making (MODM) methods, which are used to identify and evaluate Pareto optimal solutions on the efficient frontier of a mathematically constrained solution space;
- Data envelopment analysis (DEA), which is applied to analyze the efficiency of a sample of alternatives if the efficient frontier is not known [170].
5. Discussion
- Further research work on the techno-economic, environmental, and social implications of a hybrid implementation of WtE systems is required.
- More research work should be aimed towards the comprehensive study of new technologies, such as torrefaction, plasma arc gasification, fermentation (bio-ethanol production), bio-hydrogen production, use of microbial fuel cells, and esterification.
- Given the different performance of WtE technologies from a technical, economic, environmental, and social perspective based on qualitative and quantitative standards, the adoption of multi-criteria-based approaches that can simultaneously consider qualitative and quantitative criteria should be a platform for future work.
6. Conclusions and Further Research
- Continuing research and methodological development to ensure consistency, equity, and balance among the environmental, economic, and social domains of LCSA.
- Further enhancement of the data and stakeholder engagement processes to develop more regionally specific, recent, and relevant economic and social data. This should include further research on approaches to identify, prioritize, and calibrate social indicators in the sLCA component of LCSA.
- Methods to represent and calibrate the uncertainties in LCSA and its components should be further improved [68].
- Additional research on the combination and integration of LCSA results using multi-criteria decision-making frameworks and/or optimization models.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dantas, T.E.T.; Soares, S.R. Systematic literature review on the application of life cycle sustainability assessment in the energy sector. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 24, 1583–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizami, A.S.; Rehan, M.; Waqas, M.; Naqvi, M.; Ouda, O.K.; Shahzad, K.; Miandad, R.; Khan, M.Z.; Syamsiro, M.; Ismail, I.M.; et al. Waste biorefineries: Enabling circular economies in developing countries. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 241, 1101–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varjani, S.J. Microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 223, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferronato, N.; Torretta, V. Waste mismanagement in developing countries: A review of global issues. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.K.; Wu, F.; Mincheva, R.; Hakkarainen, M.; Raquez, J.M.; Mielewski, D.F.; Narayan, R.; Netravali, A.N.; Misra, M. Sustainable polymers. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2022, 2, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varjani, S.; Lee, D.J.; Zhang, Q. Valorizing agricultural biomass for sustainable development: Biological engineering aspects. Bioengineered 2020, 11, 522–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaza, S.; Yao, L. At a glance: A global picture of solid waste management. Urban Dev. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, D.; Aldás, C.; López, G.; Kaparaju, P. Municipal solid waste as a valuable renewable energy resource: A worldwide opportunity of energy recovery by using Waste-To-Energy Technologies. Energy Procedia 2017, 134, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, S.K. Importance of municipal solid waste management. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Res. Sci. 2018, 5, 361–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugwu, C.O.; Ozoegwu, C.G.; Ozor, P.A.; Agwu, N.; Mbohwa, C. Waste reduction and utilization strategies to improve municipal solid waste management on Nigerian campuses. Fuel Commun. 2021, 9, 100025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhokhikah, Y.; Trihadiningrum, Y.; Sunaryo, S. Community participation in household solid waste reduction in Surabaya, Indonesia. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 102, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azis, M.M.; Kristanto, J.; Purnomo, C.W. A Techno-Economic Evaluation of Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) Conversion to Energy in Indonesia. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piadeh, F.; Offie, I.; Behzadian, K.; Rizzuto, J.P.; Bywater, A.; Córdoba-Pachón, J.R.; Walker, M. A critical review for the impact of anaerobic digestion on the sustainable development goals. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 349, 119458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.V.; Singh, A.; Mohanty, S.S.; Srivastava, V.K.; Varjani, S. Organic solid waste: Biorefinery approach as a sustainable strategy in circular bioeconomy. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 349, 126835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varjani, S.; Shah, A.V.; Vyas, S.; Srivastava, V.K. Processes and prospects on valorizing solid waste for the production of valuable products employing bio-routes: A systematic review. Chemosphere 2021, 282, 130954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varjani, S.; Upasani, V.N. Bioaugmentation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa NCIM 5514–A novel oily waste degrader for treatment of petroleum hydrocarbons. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 319, 124240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, S.; Singh, S. Sustainable municipal solid waste management in India: A policy agenda. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2016, 35, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rene, E.R.; Ge, J.; Kumar, G.; Singh, R.P.; Varjani, S. Resource recovery from wastewater, solid waste, and waste gas: Engineering and management aspects. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 17435–17437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markande, A.R.; Patel, D.; Varjani, S. A review on Biosurfactants: Properties, Applications and Current Developments. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 330, 124963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahari, W.A.W.; Azwar, E.; Foong, S.Y.; Ahmed, A.; Peng, W.; Tabatabaei, M.; Aghbashlo, M.; Park, Y.K.; Sonne, C.; Lam, S.S. Valorization of municipal wastes using co-pyrolysis for green energy production, energy security, and environmental sustainability: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 421, 129749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.B.; Vanapalli, K.R.; Cheela, V.S.; Ranjan, V.P.; Jaglan, A.K.; Dubey, B.; Goel, S.; Bhattacharya, J. Challenges, opportunities, and innovations for effective solid waste management during and post COVID-19 pandemic. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 162, 105052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akter, H.; Howlader, H.O.R.; Nakadomari, A.; Islam, M.R.; Saber, A.Y.; Senjyu, T. A Short Assessment of Renewable Energy for Optimal Sizing of 100% Renewable Energy Based Microgrids in Remote Islands of Developing Countries: A Case Study in Bangladesh. Energies 2022, 15, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciroth, A.; Finkbeiner, M.; Traverso, M.; Hildenbrand, J.; Kloepffer, W.; Mazijn, B.; Prakash, S.; Sonnemann, G.; Valdivia, S.; Ugaya, C.M.L.; et al. Towards a Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment: Making Informed Choices on Products; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- ELSEVIER Scopus. 2020. Available online: https://www.elsevier.com/de-de/solutions/scopus (accessed on 17 May 2024).
- Asam, A.; Wangliang, L.; Sunita, V.; Siming, Y. Chapter 23—Waste-to-Energy Technologies for Sustainability: Life—Cycle Assessment and Economic Analysis; Varjani, S., Pandey, A., Bhaskar, T., Mohan, S.V., Daniel, C.W., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 599–612. ISBN 9780323898553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.G.; Jiang, G.W.; Li, A.; Wang, L. Economic analysis of waste-to-energy industry in China. Waste Manag. 2016, 48, 604–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malav, L.C.; Yadav, K.K.; Gupta, N.; Kumar, S.; Sharma, G.K.; Krishnan, S.; Rezania, S.; Kamyab, H.; Pham, Q.B.; Yadav, S.; et al. A review on municipal solid waste as a renewable source for waste-to-energy project in India: Current practices, challenges, and future opportunities. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 123227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tousle, A.; Özahi, E.; Abuşoğlu, A. Waste to energy technologies for municipal solid waste management in Gaziantep. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 54, 809–815. [Google Scholar]
- Nanda, S.; Berruti, F. A technical review of bioenergy and resource recovery from municipal solid waste. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, C.; Denney, J.; Mbonimpa, E.G.; Slagley, J.; Bhowmik, R. A review on municipal solid waste-to-energy trends in the USA. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 119, 109512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.S.; Chang, Y.; Poon, C.S.; Lee, D.J. Slow pyrolysis of municipal solid waste (MSW): A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 312, 123615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooq, A.; Haputta, P.; Silalertruksa, T.; Gheewala, S.H. A Framework for the Selection of Suitable Waste to Energy Technologies for a Sustainable Municipal Solid Waste Management System. Front. Sustain. 2021, 2, 681690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundariya, N.; Mohanty, S.S.; Varjani, S.; Ngo, H.H.; Wong, J.W.; Taherzadeh, M.J.; Chang, J.S.; Ng, H.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Bui, X.T. A review on integrated approaches for municipal solid waste for environmental and economical relevance: Monitoring tools, technologies, and strategic innovations. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 342, 125982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherzinger, M.; Kaltschmitt, M. Thermal pre-treatment options to enhance anaerobic digestibility—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 137, 110627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, K.K.; Pareek, N.; Vivekanand, V. Pre-treatment, and multi-feed anaerobic co-digestion of agro-industrial residual biomass for improved bio methanation and kinetic analysis. Front. Energy Res. 2018, 6, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Samadder, S.R. A review on technological options of waste to energy for effective management of municipal solid waste. Waste Manag. 2017, 69, 407–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naveenkumar, R.; Baskar, G.; Jeehoon, H.; Saraswathi, K.; Ananth, A.; Venugopal, K.; Sherly Priyanka, R.B. Recent advances in valorization of organic municipal waste into energy using bio refinery approach, environment and economic analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 337, 125498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzate, S.; Restrepo-Cuestas, B.; Jaramillo-Duque, Á. Municipal Solid Waste as a Source of Electric Power Generation in Colombia: A Techno-Economic Evaluation under Different Scenarios. Resources 2019, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Yan, B.; Wong, J.W.C.; Zhang, Y. Enhanced volatile fatty acids production from anaerobic fermentation of food waste: A mini review focusing on acidogenic metabolic pathways. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 248, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezhen, C.; Hesheng, Z. Preliminary study on MSWI fly ash vitrification at lower temperature. Shanghai Environ. Sci. 2002, 21, 344–349. [Google Scholar]
- Nubi, O.O. Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment of Electricity Generation from Municipal Solid Waste in Nigeria. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Surrey, Guildford, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ong, H.C.; Milano, J.; Silitonga, A.S.; Hassan, M.H.; Shamsuddin, A.H.; Wang, C.T.; Indra Mahlia, T.M.; Siswantoro, J.; Kusumo, F.; Sutrisno, J. Biodiesel production from Calophyllum inophyllum-Ceiba pentandra oil mixture: Optimization and characterization. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 219, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusti, L. A review of waste management practices and their impact on human health. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 2227–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, Z.J.; Bashir, M.J.K.; Ng, C.A.; Sethupathi, S.; Lim, J.W.; Show, P.L. Sustainable Waste-to-Energy Development in Malaysia: Appraisal of Environmental, Financial, and Public Issues Related with Energy Recovery from Municipal Solid Waste. Processes 2019, 7, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayodeji, O.; Moshood, A. Electricity generation from municipal solid waste in some selected cities of Nigeria: An assessment of feasibility, potential and technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 80, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pheakdey, D.V.; Quan, N.V.; Xuan, T.D. Economic and Environmental Benefits of Energy Recovery from Municipal Solid Waste in Phnom Penh Municipality, Cambodia. Energies 2023, 16, 3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauve, G.; Van Acker, K. The environmental impacts of municipal solid waste landfills in Europe: A life cycle assessment of proper reference cases to support decision making. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 261, 110216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landfill Methane Outreach Programme (LMOP). LFG Energy Project Development Handbook; LMOP: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Akter, S.; Mohandas, Y.; Muttaqi, K.M.; Sutanto, D.; Al-Shetwi, A.Q.; Hannan, M.A. Municipal Solid Waste Fueled Power Generation: A Case Study of Waste-to-Energy. In 2023 IEEE Industry Applications Society Annual Meeting (IAS); IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Mutz, D.; Hengevoss, D.; Hugi, C.; Gross, T. Waste-to-Energy Options in Municipal Solid Waste Management: A Guide for Decision Makers in Developing and Emerging Countries; Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH: Bonn, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Shareefdeen, Z.; Youssef, N.; Taha, A.; Masoud, C. Comments on waste to energy technologies in the United Arab Emirates (UAE). Environ. Eng. Res. 2020, 25, 129–134. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Shafy, H.I.; Mansour, M.S. Solid waste issue: Sources, composition, disposal, recycling, and valorization. Egypt. J. Pet. 2018, 27, 1275–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, N.; Aslam, M.; Yasin, M.; Hossain, S.; Shahid, M.K.; Inayat, A.; Samir, A.; Ahmad, R.; Murshed, M.N.; Khurram, M.S.; et al. Municipal solid waste treatment for bioenergy and resource production: Potential technologies, techno-economic-environmental aspects and implications of membrane-based recovery. Chemosphere 2023, 323, 138196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aderoju, O.M.; Oke, A.B.; Dias, G.A. A comparative analysis of city-based MSW for power generation. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 25, 2936–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Agamuthu, P.; Waluyo, J. Challenges for Sustainable Development of Waste to Energy in Developing Countries. Waste Manag. Res. 2020, 38, 229–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Themelis, N.J.; Ma, W. Waste to energy (WTE) in China: From latecomer to front runner. Waste Dispos. Sustain. Energy 2021, 3, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhang, L. Sustainable waste management and waste to energy: Valuation of energy potential of MSW in the Greater Bay Area of China. Energy Policy 2022, 163, 112857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouda, O.K.; Raza, M.S.A.; Nizami, A.S.; Rehan, M.; Al-Waked, R.; Korres, N.E. Waste to energy potential: A case study of Saudi Arabia, Renewable and Sustainable. Energy Rev. 2016, 61, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ABRELPE. How Much Energy Is There in Biogas; AQPER (Association Québécoise De La Production D′énergie Renouvelable): Montréal, QC, Canada, 2020; Available online: https://www.aqper.com/en/how-much-energy-is-there-in-biogas (accessed on 3 May 2024).
- MMA Ministry of the Environment. Secretariat of Environmental Quality. Consultation Publishes National Solid Waste Plan—PLANARES. 2020. Available online: http://consultaspublicas.mma.gov.br/planares/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/Plano-Nacional-de-Res%C3%ADduos-S%C3%B3lidos-Consulta-P%C3%BAblica.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2020).
- Tisi, Y.S.A.B.; Matos, F.A.; Carneiro, M.L.N. Development of waste-to-energy through integrated sustainable waste management: The case of ABREN WtERT Brazil towards changing status quo in Brazil. Waste Dispos. Sustain. Energy 2023, 5, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolmasquim, M.T. Energia Termelétrica: Gás Natural, Biomassa, Carvão, Nuclear; EPE: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dalmo, F.C.; Simão, N.M.; de Lima, H.Q.; Jimenez, A.C.M.; Nebra, S.; Martins, G.; Palacios-Bereche, R.; de Mello Sant’Ana, P. H. Energy recovery overview of municipal solid waste in São Paulo State, Brazil. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 212, 461–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Brito, R.C.; Barros, R.M.; dos Santos, I.F.S.; Tiago Filho, G.L.; da Silva, S.P.G. Municipal solid waste management and economic feasibility for electricity generation from landfill gas and anaerobic reactors in a Brazilian state. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 101453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lino, F.A.M.; Ismail, K.A.R. Evaluation of the treatment of municipal solid waste as renewable energy resource in Campinas, Brazil. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2018, 29, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauzi, R.T.; Lavoie, P.; Sorelli, L.; Heidari, M.D.; Amor, B. Exploring the current challenges and opportunities of life cycle sustainability assessment. Sustainability 2019, 11, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Y.T.; Teo, K.M.; Tang, L.C. A lifecycle-based sustainability indicator framework for waste-to-energy systems and a proposed metric of sustainability. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 56, 797–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Wang, X.; Tong, Y.W. Sustainability assessment: Focusing on different technologies recovering energy from waste. In Waste-to-Energy; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 235–264. [Google Scholar]
- Čuček, L.; Klemeš, J.J.; Varbanov, P.S.; Kravanja, Z. Life cycle assessment and multi-criteria optimization of regional biomass and bioenergy supply chains. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2011, 25, 575–800. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.K.; Murty, H.R.; Gupta, S.K.; Dikshit, A.K. An Overview of Sustainability Assessment Methodologies. Ecol. Indic. 2009, 9, 189–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milutinović, B.; Stefanović, G.; Ðekić, P.S.; Mijailović, I.; Tomić, M. Environmental assessment of waste management scenarios with energy recovery using life cycle assessment and multi-criteria analysis. Energy 2017, 137, 917–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulos, I.S.; Perkoulidis, G.; Logothetis, D.; Karkanias, C. Ranking municipal solid waste treatment alternatives considering sustainability criteria using the analytical hierarchical process tool. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2014, 86, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkbeiner, M.; Inaba, A.; Tan, R.; Christiansen, K.; Kluppel, H.-J. The new international standards for life cycle assessment: ISO 14040 and ISO 14044. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess 2006, 11, 8085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloepffer, W. Life cycle sustainability assessment of products. Int J Life Cycle Assess 2008, 13, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasia, P.T.; Zimmerman, J.B. The United Nations sustainability goals: How can sustainable chemistry contribute? Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2018, 13, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana Gerta Backes, J.G.; Traverso, M. Life cycle sustainability assessment as a metrics towards SDGs agenda 2030. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2022, 38, 100683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadhukhan, J.; Sen, S.; Gadkari, S. The Mathematics of Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 309, 127457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP/SETAC. Guidelines for Social Life Cycle Assessment of Products; United Nations Environment Programme: Paris, France, 2009; Available online: https://www.unep.org/resources/report/guidelines-social-life-cycle-assessment-products (accessed on 10 February 2024).
- SETAC. Environmental Life Cycle Costing: A Code of Practice; SETAC: Pensacola, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 14040; Environmental Management. Life Cycle Assessment Principles and Framework. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006.
- UNEP. Guidelines for Social Life Cycle Assessment of Products. Management 2020, 15, 104. [Google Scholar]
- Finkbeiner, M.; Schau, E.M.; Lehmann, A.; Traverso, M. Towards life cycle sustainability assessment. Sustainability 2010, 2, 3309–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.H.; Ng, S.T. A modeling framework to evaluate sustainability of building construction based on LCSA. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2016, 21, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinee, J.B.; Heijungs, R.; Huppes, G.; Zamagni, A.; Masoni, P.; Buonamici, R.; Ekvall, T.; Rydberg, T. Life cycle assess- ment: Past, present and future. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamagni, A.; Buttol, P.; Buonamici, R.; Masoni, P.; Guinée, J.B.; Huppes, G.; Heijungs, R.; van der Voet, E.; Ekvall, T.; Rydberg, T. Blue Paper on Life Cycle Sustainability Analysis; Deliverable 20 of the CALCAS Project. 2009. Available online: http://www.estis.net/sites/calcas (accessed on 6 February 2024).
- Guinée, J. Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment: What Is It and What Are Its Challenges? In Taking Stock of Industrial Ecology; Clift, R., Druckman, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.A.; Kuroda, K.; Otsuka, K. Inclusive impact assessment for the sustainability of vegetable oil-based biodiesel–Part I: Linkage between inclusive impact index and life cycle sustainability assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 166, 1415–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijungs, R.; Huppes, G.; Guinée, J.B. Life cycle assessment and sustainability analysis of products, materials and technologies. Toward a scientific framework for sustainability life cycle analysis. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neugebauer, S.; Martinez-Blanco, J.; Scheumann, R.; Finkbeiner, M. Enhancing the practical implementation of life cycle sustainability assessment—Proposal of a Tiered approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 102, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Roskilly, A.P.; Wang, Y. Life cycle sustainability assessment of grid-connectedphotovoltaic power generation: A case study of Northeast England. Appl. Energy 2018, 227, 465479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldız-Geyhan, E.; Yılan, G.; Altun-Çiftçioğlu, G.A.; Kadırgan, M.A.N. Environmental and social life cycle sustainability assessment of different packaging waste collection systems. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 143, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinyes, E.; Oliver-Solà, J.; Ugaya, C.; Rieradevall, J.; Gasol, C.M. Application of LCSA to used cooking oil waste management. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2013, 18, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Maier, S.D.; Horn, R.; Holländer, R.; Aschemann, R. Development of an Ex-Ante Sustainability Assessment Methodology for Municipal Solid Waste Management Innovations. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.R. A transdisciplinary review of the role of economics in life cycle sustainability assessment. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2015, 20, 1625–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucukvar, M.; Tatari, O. Towards a triple bottom-line sustainability assessment of the U.S. construction industry. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2013, 18, 958–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onat, N.C.; Kucukvar, M.; Tatari, O. Integrating triple bottom line input-output analysis into life cycle sustainability assessment framework: The case for US buildings. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2014, 19, 1488–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP. Guideliness for Social Life Cycle Impact Assessment of Products. Available online: http://www.unep.fr/shared/publications/pdf/DTIx1164xPA-guidelines_sLCA.pdf (accessed on 20 May 2024).
- Benoît, C.; Norris, G.A.; Valdivia, S.; Ciroth, A.; Moberg, A.; Bos, U.; Prakash, S.; Ugaya, C.; Beck, T. The guidelines for social life cycle assessment of products: Just in time! Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2010, 15, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastjerdi, B.; Strezov, V.; Rajaeifar, M.A.; Kumar, R.; Behnia, M. A systematic review on life cycle assessment of different waste to energy valorization technologies. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 290, 125747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsangas, M.; Gavriel, I.; Doula, M.; Xeni, F.; Zorpas, A.A. Life Cycle Analysis in the Framework of Agricultural Strategic Development Planning in the Balkan Region. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, N.P.; Matsui, Y. Assessment of potential impacts of municipal solid waste treatment alternatives by using life cycle approach: A case study in Vietnam. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 7993–8004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, A.; Bakas, I.; Clavreul, J.; Bernstad, A.; Niero, M.; Gentil, E.; Hauschild, M.Z.; Christensen, T.H. Review of LCA studies of solid waste management systems–Part I: Lessons learned and perspectives. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finnveden, G.; Hauschild, M.Z.; Ekvall, T.; Guinée, J.; Heijungs, R.; Hellweg, S.; Koehler, A.; Pennington, D.; Suh, S. Recent developments in life cycle assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 91, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banar, M.; Ozkan, A.; Kurkcuoglu, M. Characterization of the leachate in an urban landfill by physicochemical analysis and solid phase microextraction-GC/MS. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 121, 439–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yay, A.S.E. Application of life cycle assessment (LCA) for municipal solid waste management: A case study of Sakarya. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 94, 284–293. [Google Scholar]
- Khandelwal, H.; Thallaa, A.K.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, R. Life cycle assessment of municipal solid waste management options for India. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 288, 121515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinauskaite, J.; Jouhara, H.; Czajczyńska, D.; Stanchev, P.; Katsou, E.; Rostkowski, P.; Thorne, R.J.; Colon, J.; Ponsá, S.; Al-Mansour, F.; et al. Municipal solid waste management and waste-to-energy in the context of a circular economy and energy recycling in Europe. Energy 2017, 141, 2013–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabavi-Pelesaraei, A.; Kaab, A.; Hosseini-Fashami, F.; Mostashari-Rad, F.; Chau, K.W. Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) Approach to Evaluate Different Waste Management Opportunities. In Advances in Waste-to-Energy Technologies; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 195–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noya, I.; Inglezakis, V.; González-García, S.; Katsou, E.; Feijoo, G.; Moreira, M.T. Comparative environmental assessment of alternative waste management strategies in developing regions: A case study in Kazakhstan. Waste Manag. Res. 2018, 36, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, P.; Samadder, S.R. Environmental impact assessment of municipal solid waste management options using life cycle assessment: A case study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 838–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Ni, M.; Chi, Y.; Zou, D.; Fu, C. Life cycle and economic assessment of source separated MSW collection with regard to greenhouse gas emissions: A case study in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 5512–5524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorentino, G.; Ripa, M.; Protano, G.; Hornsby, C.; Ulgiati, S. Life cycle assessment of mixed municipal solid waste: Multi-input versus multi-output perspective. Waste Manag. 2015, 46, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, T.; Hirai, Y.; Asari, M.; Yano, J.; Miura, T.; Ii, R.; Sakai, S.I. Monitoring environmental burden reduction from household waste prevention. Waste Manag. 2018, 71, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkes, O.; Lettieri, P.; Bogle, I.D.L. Life cycle assessment of integrated waste management systems for alternative legacy scenarios of the London Olympic Park. Waste Manag. 2015, 40, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaman, A.U. Life cycle assessment of pyrolysis–gasification as an emerging municipal solid waste treatment technology. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 10, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nubi, O.; Morse, S.; Murphy, R.J. Electricity Generation from Municipal Solid Waste in Nigeria: A Prospective LCA Study. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeleke, O.A.; Akinlabi, S.A.; Jen, T.C.; Dunmade, I. Evaluation and Prediction of Energy Content of Municipal Solid Waste: A review. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 1107, p. 012097. [Google Scholar]
- Astrup, T.F.; Tonini, D.; Turconi, R.; Boldrin, A. Life cycle assessment of thermal Waste-to-Energy technologies: Review and recommendations. Waste Manag. 2015, 37, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, R.; Ganguly, R.; Gupta, A.K. Life-cycle assessment of municipal solid-waste management strategies in Tricity region of India. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2019, 21, 606–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulczycka, J.; Lelek, L.; Lewandowska, A.; Zarebska, J. Life cycle assessment of municipal solid waste management—Comparison of results using different LCA models. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2015, 24, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosnians, A.; Vanderreydt, I.; Geysen, D.; Helsen, L. The crucial role of Waste-to-Energy technologies in enhanced landfill mining: A technology review. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 55, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.K.; Chandel, M.K. Life cycle cost analysis of municipal solid waste management scenarios for Mumbai, India. Waste Manag. 2021, 124, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoogmartens, R.; Van Passel, S.; Van Acker, K.; Dubois, M. Bridging the gap between LCA, LCC and CBA as sustainability assessment tools. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2014, 48, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toniolo, S.; Tosato, R.C.; Gambaro, F.; Ren, J. Life cycle thinking tools: Life cycle assessment, life cycle costing and social life cycle assessment. In Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment for Decision-Making; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 39–56. [Google Scholar]
- Benoît-Norris, C.; Vickery-Niederman, G.; Valdivia, S.; Franze, J.; Traverso, M.; Ciroth, A.; Mazijn, B. Introducing the UNEP/SETAC methodological sheets for subcategories of social LCA. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2011, 16, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunkeler, D.; Lichtenvort, K.; Rebitzer, G. Environmental Life Cycle Costing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Abdeljaber, A.; Mostafa, O.; Abdallah, M. Applications of Life Cycle Costing in Waste-to-Energy Projects. In Life Cycle Costing; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 77–115. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, E.; Oliveira DS, B.L.; Oliveira LS, B.L.; Jimenez, E.; Kim, Y.; Wang, M.; Ergas, S.J.; Zhang, Q. Comparative environmental and economic life cycle assessment of high solids anaerobic co-digestion for biosolids and organic waste management. Water Res. 2020, 171, 115443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Chi, Y.; Zou, D.; Fu, C.; Huang, Q.; Ni, M. Energy–environment–economy assessment of waste management systems from a life cycle perspective: Model development and case study. Appl. Energy 2014, 114, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, F.; Zhang, D.; Ye, X. Cost management for waste to energy systems using life cycle costing approach: A case study from China. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slorach, P.C.; Jeswani, H.K.; Cuéllar-Franca, R.; Azapagic, A. Environmental and economic implications of recovering resources from food waste in a circular economy. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 693, 133516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Wahaibi, A.; Osman, A.I.; Al-Muhtaseb, A.H.; Alqaisi, O.; Baawain, M.; Fawzy, S.; Rooney, D.W. Techno-economic evaluation of biogas production from food waste via anaerobic digestion. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdeljaber, A.; Zannerni, R.; Masoud, W.; Abdallah, M.; Rocha-Meneses, L. Eco-efficiency analysis of integrated waste management strategies based on gasification and mechanical biological treatment. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadidi, L.A.; Omer, M.M. A financial feasibility model of gasification and anaerobic digestion waste-to-energy (WTE) plants in Saudi Arabia. Waste Manag. 2017, 59, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arulnathan, V.; Heidari, M.D.; Doyon, M.; Li, E.P.H.; Pelletier, N. Economic Indicators for Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment: Going beyond Life Cycle Costing. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barahmand, Z.; Eikeland, M.S. Techno-Economic and Life Cycle Cost Analysis through the Lens of Uncertainty: A Scoping Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L. Chapter 8—LCCA-Based Design Method for Asphalt Pavement. In Structural Behavior of Asphalt Pavements; Sun, L., Ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2016; pp. 549–600. ISBN 978-0-12-849908-5. [Google Scholar]
- Ayodele, T.R.; Ogunjuyigbe, A.S.O.; Alao, M.A. Economic and environmental assessment of electricity generation using biogas from organic fraction of municipal solid waste for the city of Ibadan, Nigeria. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 203, 718–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agaton, C.B.; Guno, C.S.; Villanueva, R.O.; Villanueva, R.O. Economic analysis of waste-to-energy investment in the Philippines: A real options approach. Appl. Energy 2020, 275, 115265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, I.D.; Hamam, Y.; Alayli, Y.; Jamiru, T.; Sadiku, E.R.; Kupolati, W.K.; Ndambuki, J.M.; Eze, A.A. A review on Africa energy supply through renewable energy production: Nigeria, Cameroon, Ghana and South Africa as a case study. Energy Strategy Rev. 2021, 38, 100740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhgaliyeva, D.; Mishra, R. Feed-in tariffs for financing renewable energy in Southeast Asia. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Energy Environ. 2022, 11, e425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo Llanes, J.; Kalogirou, E. Waste-to-energy conversion in Havana: Technical and economic analysis. Soc. Sci. 2019, 8, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amulen, J.; Kasedde, H.; Serugunda, J.; Lwanyaga, J.D. The potential of energy recovery from municipal solid waste in Kampala City, Uganda by incineration. Energy Convers. Manag. X 2022, 14, 100204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlas, W. What a Waste: An Updated Look into the Future of Solid Waste Management. 2018. Available online: https://www.worldbank.org/en/news/immersive-story/2018/09/20/what-a-waste-an-updated-look-into-the-future-of-solid-waste-management (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- Unaegbu, E.U.; Baker, K. Assessing the potential for energy from waste plants to tackle energy poverty and earn carbon credits for Nigeria. Int. J. Energy Policy Manag. 2019, 4, 8–16. [Google Scholar]
- Aung, T.S.; Fischer, T.B.; Azmi, A.S. Social impacts of large-scale hydropower project in Myanmar: A social life cycle assessment of Shweli hydropower dam 1. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2021, 26, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcese, G.; Benoît-Norris, C.; Berger, M.; Ekener, E.; Finkbeiner, M.; Garrido, S.R.; Lehmann, A.; Neugebauer, S.; Schaubroeck, T.; Traverso, M.; et al. Guidelines for Social Life Cycle V3 Draft (2020) (Issue February 2020); UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Vanclay, F. International principles for social impact assessment. Impact Assess Proj Apprais. 2003, 21, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, S. Social Life-Cycle Assessment: An Introduction; Abraham, M.A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 253–265. ISBN 9780128047927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Chi, Y.; Dong, J.; Tang, Y.; Ni, M. Model development of sustainability assessment from a life cycle perspective: A case study on waste management systems in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 210, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, A.; Zschieschang, E.; Traverso, M.; Finkbeiner, M.; Schebek, L. Social aspects for sustainability assessment of technologies—Challenges for social life cycle assessment (SLCA). Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2013, 18, 1581–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP. UNEP Guidelines for Social Life Cycle Assessment of Products; UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Manik, Y.; Leahy, J.; Halog, A. Social life cycle assessment of palm oil biodiesel: A case study in Jambi Province of Indonesia. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2013, 18, 1386–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umair, S.; Björklund, A.; Petersen, E.E. Social impact assessment of informal recycling of electronic ICT waste in Pakistan using UNEP SETAC guidelines. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 95, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhipi-Shrestha, G.K.; Hewage, K.; Sadiq, R. ‘Socializing’sustainability: A critical review on current development status of social life cycle impact assessment method. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2015, 17, 579–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidema, B.P. The Integration of Economic and Social Aspects in Life Cycle Impact Assessment. Int J Life Cycle Assess. 2006, 11 (Suppl. 1), 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parent, J.; Cucuzzella, C.; Revéret, J.P. Impact assessment in SLCA: Sorting the sLCIA methods according to their outcomes. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2010, 15, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macombe, C.; Leskinen, P.; Feschet, P.; Antikainen, R. Social life cycle assessment of biodiesel production at three levels: A literature review and development needs. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 52, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foolmaun, R.K.; Ramjeeawon, T. Comparative life cycle assessment and social life cycle assessment of used polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottles in Mauritius. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2013, 18, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.-T.; Lee, Y.-M.; Hong, C.-Y. Inventory Analysis and Social Life Cycle Assessment of Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Waste-to-Energy Incineration in Taiwan. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nubi, O.; Morse, S.; Murphy, R.J. A Prospective Social Life Cycle Assessment (sLCA) of Electricity Generation from Municipal Solid Waste in Nigeria. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neugebauer, S.; Emara, Y.; Hellerström, C.; Finkbeiner, M. Calculation of Fair Wage Potentials along Products’ Life Cycle—Introduction of a New Midpoint Impact Category for Social Life Cycle Assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 143, 1221–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla-Alicea, R.J.; Fu, K. Systematic Map of the Social Impact Assessment Field. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattos, F.; Calmon, J.L. Social Life Cycle Assessment in Municipal Solid Waste Management Systems with Contribution of Waste Pickers: Literature Review and Proposals for New Studies. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huertas-Valdivia, I.; Ferrari, A.M.; Settembre-Blundo, D.; García-Muiña, F.E. Social Life-Cycle Assessment: A Review by Bibliometric Analysis. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoît Norris, C. Data for social LC180A. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2014, 19, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onat, N.C.; Kucukvar, M.; Halog, A.; Cloutier, S. Systems Thinking for Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment: A Review of Recent Developments, Applications, and Future Perspectives. Sustainability 2017, 9, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannouf, M.; Assefa, G. A life cycle sustainability assessment-based decision-analysis framework. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azapagic, A.; Perdan, S. An integrated sustainability decision-support framework Part I: Problem structuring. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2005, 12, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thies, C. Operations research for sustainability assessment of products: A review. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2019, 274, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foolmaun, R.K.; Ramjeawon, T. Life cycle sustainability assessments (LCSA) of four disposal scenarios for used polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottles in Mauritius. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2013, 15, 783–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Ge, S.; Yao, X.; Li, H.; Li, X. Life cycle sustainability assessment of pumped hydro energy storage. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 44, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roinioti, A.; Koroneos, C. Integrated life cycle sustainability assessment of the Greek interconnected electricity system. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2019, 32, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabayo, J.; Marques, P.; Garcia, R.; Freire, F. Life-cycle sustainability assessment of key electricity generation systems in Portugal. Energy 2019, 176, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, S.; Unnikrishnan, S. Life cycle sustainability assessment of crude oil in India. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 283, 124654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Li, B.; Wang, L.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.V. Reusability based on life cycle sustainability assessment: Case study on WEEE. Procedia CIRP 2014, 15, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulcimen, S.; Aydogan, E.K.; Uzal, N. Life cycle sustainability assessment of a light rail transit system: Integration of environmental, economic, and social impacts. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2021, 17, 1070–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traverso, M.; Finkbeiner, M.; Jørgensen, A.; Schneider, L. Life cycle sustainability dashboard. J. Ind. Ecol. 2012, 16, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacovidou, E.; Voulvoulis, N. A multi-criteria sustainability assessment framework: Development and application in comparing two food waste management options using a UK region as a case study. Environ. Sci Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 35821–35834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltani, A.; Sadiq, R.; Hewage, K. Selecting sustainable waste-to-energy technologies for municipal solid waste treatment: A game theory approach for group decision-making. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 113, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nubi, O.; Morse, S.; Murphy, R.J. Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment of Electricity Generation from Municipal Solid Waste in Nigeria: A Prospective Study. Energies 2022, 15, 9173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Kabob, Z. Waste-to-energy generation technologies and the developing economies: A multi-criteria analysis for sustainability assessment. Renew. Energy 2020, 150, 320–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsambe, M.Z.A.; de Almeida, C.F.; Ugaya, C.M.L.; de Abreu Cybis, L.F. Application of Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment to Used Lubricant Oil Management in South Brazilian Region. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gencturk, B.; Hossain, K.; Lahourpour, S. Life cycle sustainability assessment of RC buildings in seismic regions. Eng. Struct. 2016, 110, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Manzardo, A.; Mazzi, A.; Zuliani, F.; Scipioni, A. Prioritization of bioethanol production pathways in China based on life cycle sustainability assessment and multicriteria decision-making. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2015, 20, 842–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, R.; Chevakidagarn, P.; Danteravanich, S. Life cycle sustainability assessment of community composting of agricultural and agro industrial wastes. J. Sustain. Sci. Manag. 2016, 11, 57–69. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.; Mauerhofer, V. Life cycle sustainability assessment of ground source heat pump in Shanghai, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 119, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halog, A.; Manik, Y. Advancing integrated systems modelling framework for life cycle sustainability assessment. Sustainability 2011, 3, 469–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, D.; Quinteiro, P.; Dias, A.C. A systematic review of life cycle sustainability assessment: Current state, methodological challenges, and implementation issues. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 774–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visentin, C.; da Silva Trentin, A.W.; Braun, A.B.; Thomé, A. Life cycle sustainability assessment: A systematic literature review through the application perspective, indicators, and methodologies. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 270, 122509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, G. Critique of selected peer-reviewed publications on applied social life cycle assessment: Focus on cases from developing countries. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2019, 21, 413–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulf, C.; Werker, J.; Ball, C.; Zapp, P.; Kuckshinrichs, W. Review of Sustainability Assessment Approaches Based on Life Cycles. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, H.; Rettenmaier, N.; Reinhardt, G.A. Integrated life cycle sustainability assessment–A practical approach applied to biorefineries. Appl. Energy 2015, 154, 1072–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, B.; Marzia, T. Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment—A Survey Based Potential Future Development for Implementation and Interpretation. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabalane, P.N.; Oboirien, B.O.; Sadiku, E.R.; Masukume, M. A techno-economic analysis of anaerobic digestion and gasification hybrid system: Energy recovery from municipal solid waste in South Africa. Waste Biomass Valorization 2021, 12, 1167–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alao, M.A.; Ayodele, T.R.; Ogunjuyigbe, A.S.O.; Popoola, O.M. Multi-criteria decision based waste to energy technology selection using entropy-weighted TOPSIS technique: The case study of Lagos, Nigeria. Energy 2020, 201, 117675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Impact Category | Unit | Anaerobic Digestion | Incineration | Gasification | Landfill Gas to Energy | Diesel Back Up Generators | Grid Electricity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abiotic Depletion Potential (Fossil Fuels) (ADP) | (MJ) | 0.618 | 3.17 | 6.4 | 4.59 | 14.1 | 8.69 |
| Global Warming Potential (GWP) | (kg CO2 eq) | 0.507 | 0.804 | 0.858 | 4.88 | 1.02 | 0.497 |
| Human Toxicity Potential (HTP) | (kg 1,4 DB eq) | 0.00548 | 0.0102 | 0.0195 | 0.019 | 0.0732 | 0.0117 |
| Photochemical Oxidation Potential (POCP) | (kg C2H4 eq) | 0.000106 | 0.0000396 | 0.0000464 | 0.00103 | 0.000198 | 0.0000406 |
| Acidification Potential (AP) | (kg SO2 eq) | 0.000564 | 0.000889 | 0.000974 | 0.00299 | 0.0129 | 0.000296 |
| Eutrophication Potential (EP) | (kg PO4 eq) | 0.00144 | 0.000192 | 0.000209 | 0.000717 | 0.00313 | 0.000061 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nubi, O.; Murphy, R.; Morse, S. Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment of Waste to Energy Systems in the Developing World: A Review. Environments 2024, 11, 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11060123
Nubi O, Murphy R, Morse S. Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment of Waste to Energy Systems in the Developing World: A Review. Environments. 2024; 11(6):123. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11060123
Chicago/Turabian StyleNubi, Oluwaseun, Richard Murphy, and Stephen Morse. 2024. "Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment of Waste to Energy Systems in the Developing World: A Review" Environments 11, no. 6: 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11060123
APA StyleNubi, O., Murphy, R., & Morse, S. (2024). Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment of Waste to Energy Systems in the Developing World: A Review. Environments, 11(6), 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11060123










