Ecofriendly Degradation of PET via Neutral Hydrolysis: Degradation Mechanism and Green Chemistry Metrics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Neutral Hydrolysis
2.2.2. Green Chemistry Metrics
2.3. Products Characterisation
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Temperature
3.2. Effect of Residence Time
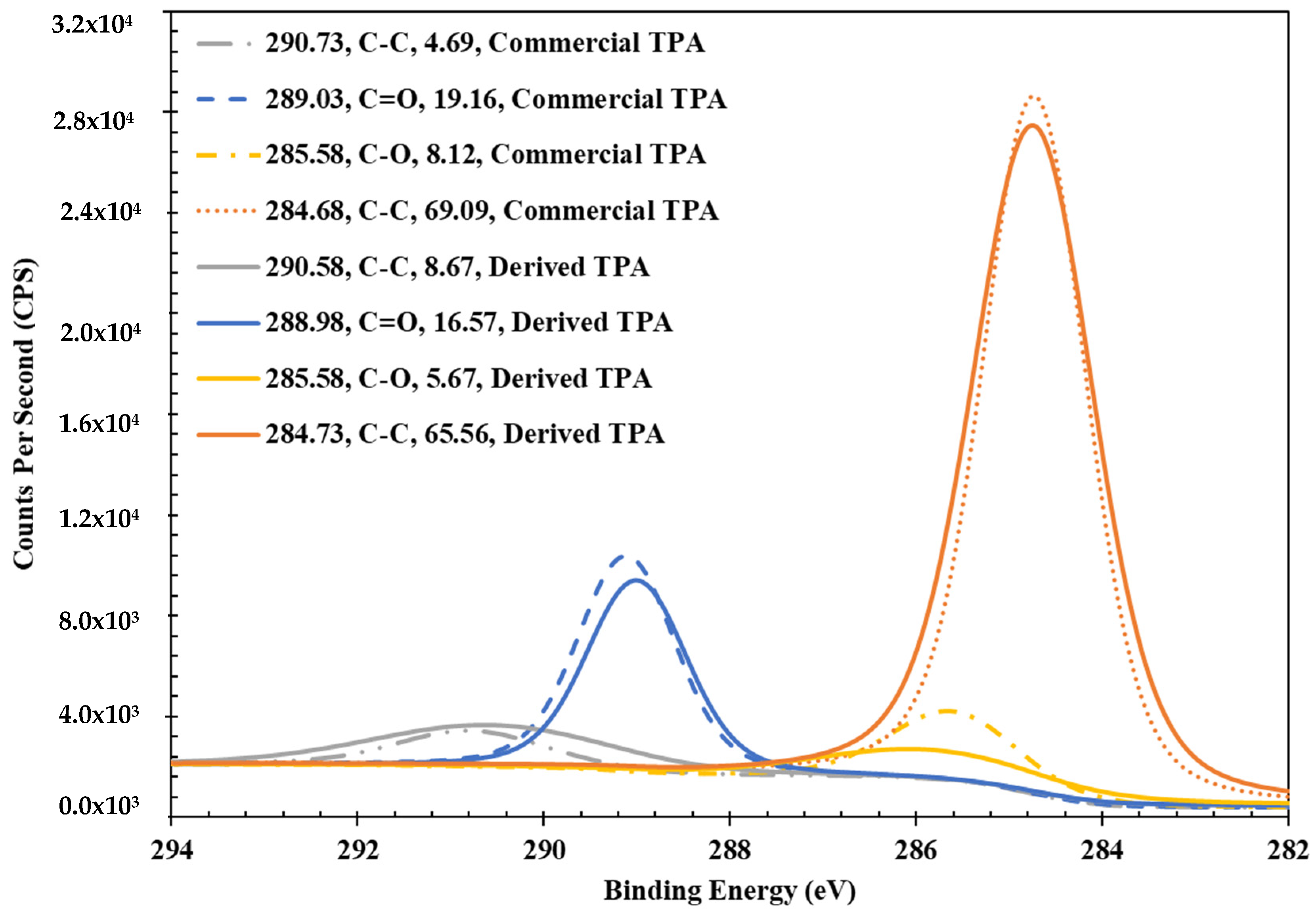
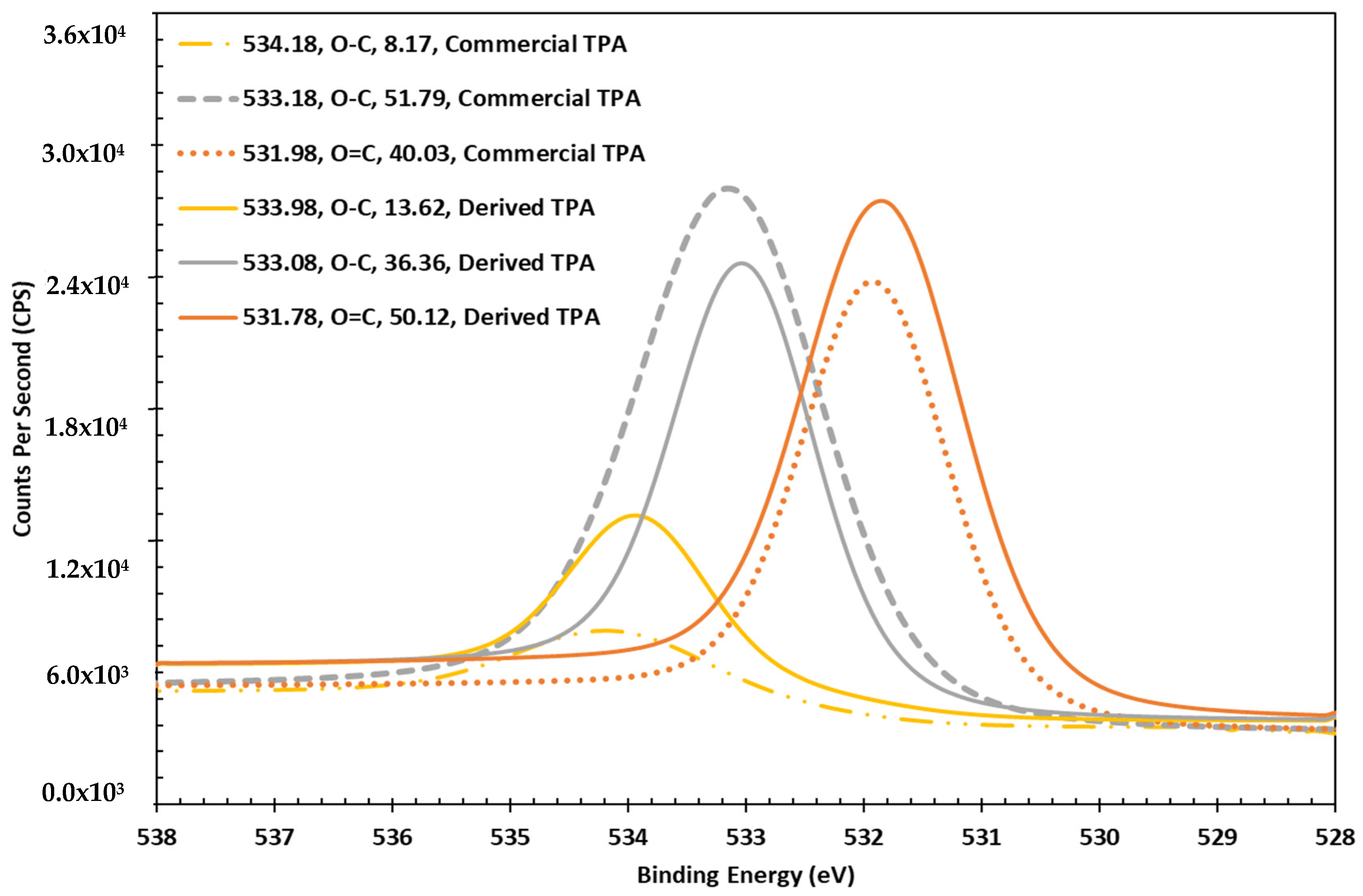
3.3. XPS Analysis of TPA Derived from PET Hydrolysis
3.3.1. Carbon Chemistry
3.3.2. Oxygen Chemistry
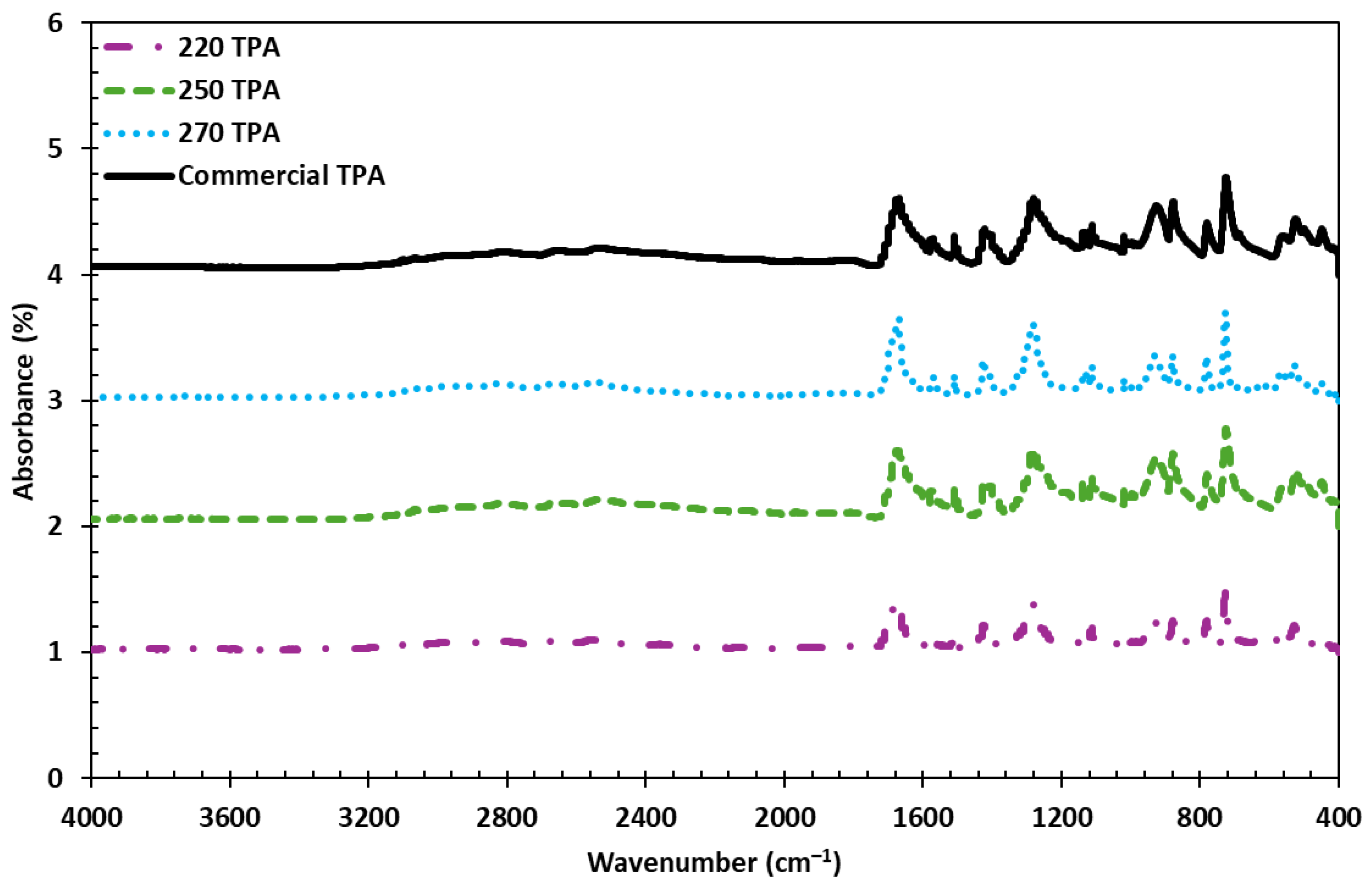
3.4. FTIR Analysis of TPA Derived from PET Hydrolysis
3.5. NMR Analysis of TPA Derived from Neutral Hydrolysis of PET
3.6. Secondary Products Derived from Neutral Hydrolysis of PET
3.6.1. Bis-Hydroxyethyl Terephthalate (BHET)
3.6.2. Isophthalic Acid (IPA)
3.6.3. Benzoic Acid (BZOH)
3.6.4. Phenol
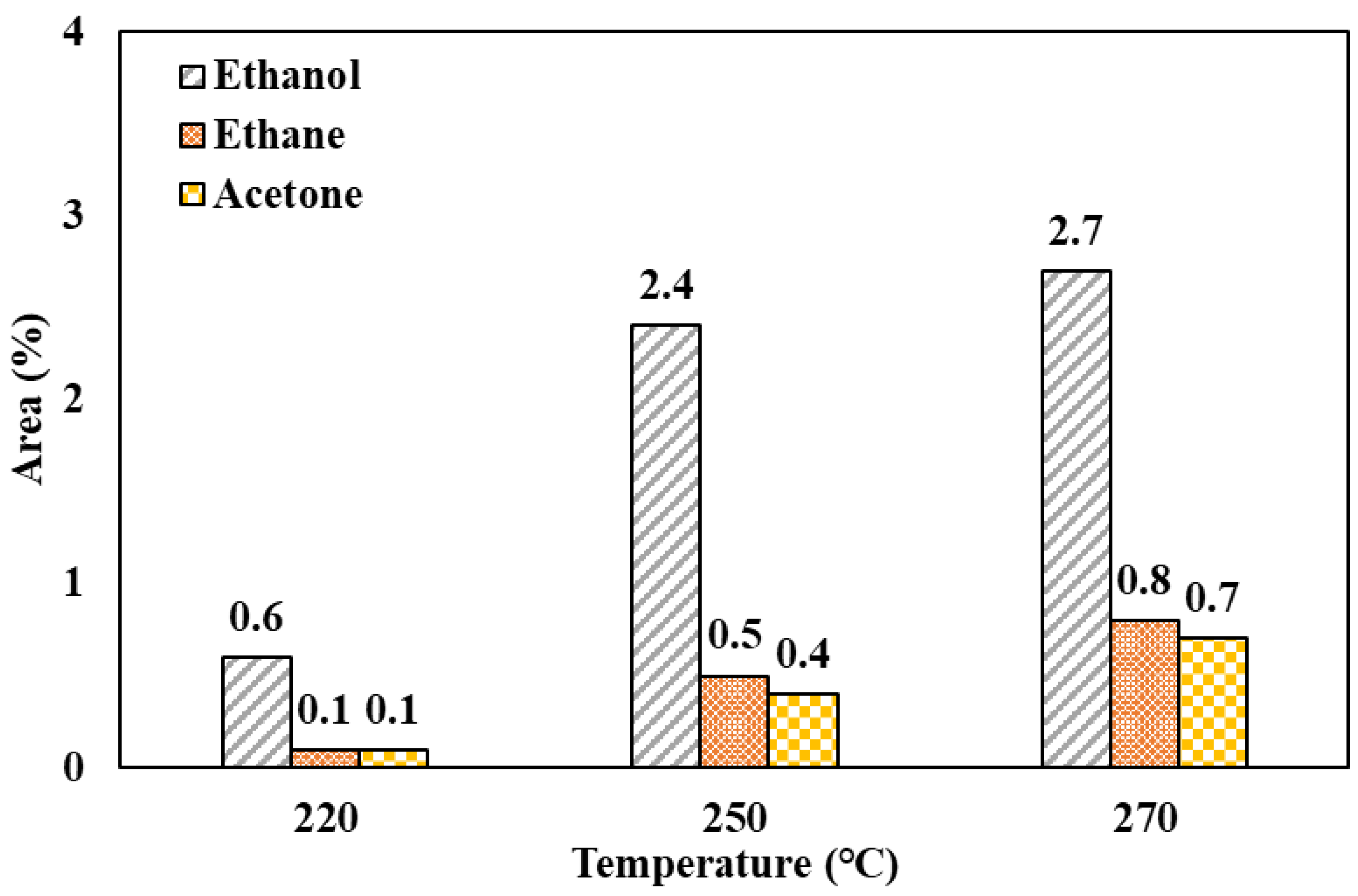
3.6.5. Ethylene Glycol and Its Derivatives
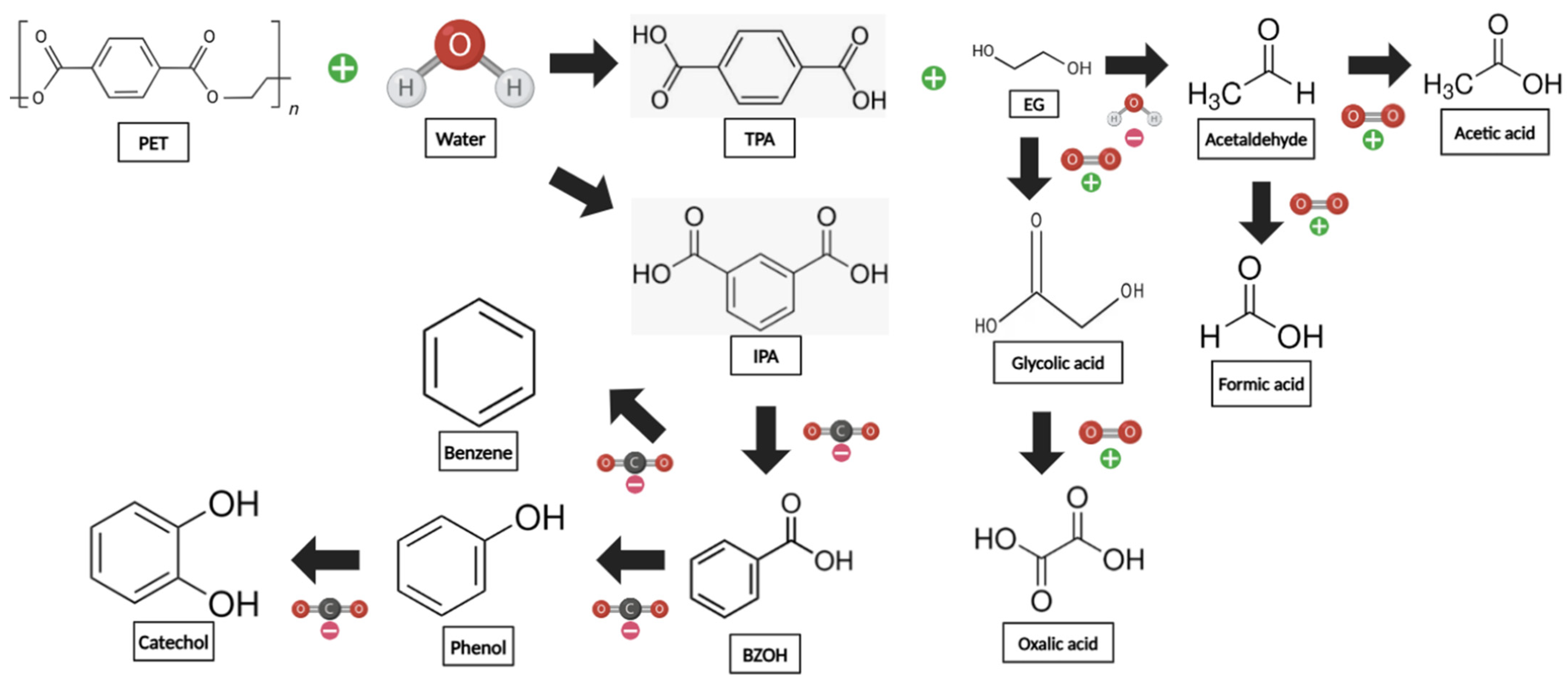
3.7. Insights into the Degradation Pathway of PET into Its Secondary Products Considering the Effect of Temperature and Residence Time
Major Secondary Products
3.8. Green Chemistry Metrics
- (1)
- The effective use of feedstocks;
- (2)
- The efficient utilisation of energy during manufacturing;
- (3)
- The valorisation of waste;
- (4)
- The elimination of the utilisation of hazardous, toxic, or corrosive solvents;
- (5)
- The minimal usage of reagents in the synthesis of chemicals [35].
4. Limitations and Recommendations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BHET | Bishydroxyethyl Terephthalate |
| BZOH | Benzoic Acid |
| 13C | Stable Isotope of Carbon |
| EEC | Economy Energy Coefficient |
| EEI | Environmental Energy Impact |
| EF | Environmental Factor |
| EG | Ethylene Glycol |
| HTT | Hydrothermal Treatment |
| FBA | Formyl Benzoic Acid |
| FTIR | Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy |
| GCMS | Gas Chromatography and Mass Spectroscopy |
| I.D. | Inner Diameter |
| IPA | Isophthalic Acid |
| L | Length |
| NMR | Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy |
| PCP | Partially Converted PET |
| PET | Polyethylene Terephthalate |
| PTSA | P-Toluene Sulphonic Acid |
| SDG-12 | Sustainable Development Goal 12—Responsible Consumption and Production |
| TH | Thickness |
| TPA | Terephthalic acid |
| XPS | X-ray Photon Spectroscopy |
| ZnI2 | Zinc Iodide |
References
- Vuppaladadiyam, S.S.V.; Vuppaladadiyam, A.K.; Sahoo, A.; Urgunde, A.; Murugavelh, S.; Šrámek, V.; Pohořelý, M.; Trakal, L.; Bhattacharya, S.; Sarmah, A.K.; et al. Waste to energy: Trending key challenges and current technologies in waste plastic management. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 913, 169436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patria, R.D.; Rehman, S.; Yuen, C.-B.; Lee, D.-J.; Vuppaladadiyam, A.K.; Leu, S.-Y. Energy-environment-economic (3E) hub for sustainable plastic management—Upgraded recycling, chemical valorisation, and bioplastics. Appl. Energy 2023, 357, 122543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard, E.; Arias, J.J.R.; Thielemans, W. Chemolytic depolymerisation of PET: A review. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 3765–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Chen, X.; Ho, D.C.W.; Wang, H. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) recycling: A review. J. Clean Prod. 2016, 112, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumartasli, S.; Avinc, O. Important Step in Sustainability: Polyethylene Terephthalate Recycling and the Recent Developments. In Sustainability in the Textile and Apparel Industries. Sustainable Textiles: Production, Processing, Manufacturing & Chemistry; Muthu, S.S., Gardetti, M.A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valh, J.V.; Vončina, B.; Lobnik, A.; Zemljič, L.F.; Škodič, L.; Vajnhandl, S. Conversion of polyethylene terephthalate to high-quality terephthalic acid by hydrothermal hydrolysis: The study of process parameters. Text. Res. J. 2019, 90, 1446–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanica-Ezeanu, D.; Matei, D. Natural depolymerisation of waste poly (ethylene terephthalate) by neutral hydrolysis in marine water. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osei, D.; Gurrala, L.; Sheldon, A.; Mayuga, J.; Lincoln, C.; Rorrer, N.A.; Rita, A. Subcritical CO2–H2O hydrolysis of polyethylene terephthalate as a sustainable chemical recycling platform. Green Chem. 2024, 26, 6436–6445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Hu, H. Solvent System with Improved Hydroxide Reactivity for Mild and High-Efficiency PET Alkaline Hydrolysis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 12925–12934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barredo, A.; Asueta, A.; Amundarain, I.; Leivar, J.; Miguel-Fernández, R.; Arnaiz, S.; Epelde, E.; Lopez-Fonseca, R.; Gutiérrez-Ortiz, J.I. Chemical recycling of monolayer PET tray waste by alkaline hydrolysis. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Islam, Z.; Hasan, R.; Islam Molla Jamal, A.S. Acidic hydrolysis of recycled polyethylene terephthalate plastic for the production of its monomer terephthalic acid. Prog. Rubber Plast. Recycl. Technol. 2022, 39, 147776062211280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Yang, J.; Deng, C.; Deng, J.; Shen, L.; Fu, Y. Acetolysis of waste polyethylene terephthalate for upcycling and life-cycle assessment study. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laldinpuii, Z.T.; Khiangte, V.; Lalhmangaihzuala, S.; Lalmuanpuia, C.; Pachuau, Z.; Lalhriatpuia, C.; Vanlaldinpuia, K. Methanolysis of PET Waste Using Heterogeneous Catalyst of Bio-waste Origin. J. Polym. Environ. 2021, 30, 1600–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Yan, D.; Xin, J.; Li, F.; Guo, M.; Zhou, Q.; Xu, J.; Hu, Y.; Lu, X. Poly (ionic liquids) as efficient and recyclable catalysts for methanolysis of PET. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2022, 199, 109905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.K.; Bhandari, S. Chemical Depolymerization of PET Bottles via Ammonolysis and Aminolysis. In Recycling of Polyethylene Terephthalate Bottles; William Andrew Publishing: Norwich, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 109–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorusso, E.; Feng, Y.; Schneider, J.; Kamps, L.; Parasothy, N.; Mayer-Gall, T.; Gutmann, J.S.; Ali, W. Investigation of aminolysis routes on PET fabrics using different amine-based materials. Nano Sel. 2021, 3, 594–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratish, Y.; Marks, T.J. Efficient Polyester Hydrogenolytic Deconstruction via Tandem Catalysis. Angew. Chem. 2021, 61, e202112576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Fan, M.; Sun, K.; Gao, G.; Li, C.; Li, D.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Hu, X. The quantitative conversion of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and Coca-Cola bottles to p-xylene over Co-based catalysts with tailored activities for deoxygenation and hydrogenation. Green Chem. 2023, 25, 10513–10529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ügdüler, S.; Van Geem, K.M.; Denolf, R.; Roosen, M.; Mys, N.; Ragaert, K.; De Meester, S. Towards closed-loop recycling of multilayer and coloured PET plastic waste by alkaline hydrolysis. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 5376–5394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tian, F.; Wu, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; He, Y. Chemical conversion of waste PET to valued-added bis(2-hydroxyethyl) terephthalamide through aminolysis. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 32, 104045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sabagh, A.M.; Yehia, F.Z.; Eshaq Gh Rabie, A.M.; ElMetwally, A.E. Greener routes for recycling of polyethylene terephthalate. Egypt. J. Pet. 2016, 25, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, M.; Jalilian, M.; Shahbaz, K. Chemical recycling of Polyethylene Terephthalate: A mini-review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argañaraz, B.Q.; Cristina, L.J.; Rodríguez, L.M.; Cossaro, A.; Verdini, A.; Floreano, L.; Fuhr, J.D.; Gayone, J.E.; Ascolani, H. Ubiquitous deprotonation of terephthalic acid in the self-assembled phases on Cu(100). Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 4329–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colnik, M.; Knez, Ž.; Škerget, M. Sub- and supercritical water for chemical recycling of polyethylene terephthalate waste. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2021, 233, 116389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colnik, M.; Pečar, D.; Knez, Ž.; Goršek, A.; Škerget, M. Kinetics Study of Hydrothermal Degradation of PET Waste into Useful Products. Processes 2022, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Jing, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yan, N. A unified view on catalytic conversion of biomass and waste plastics. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2022, 6, 635–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onwucha, C.N.; Ehi-Eromosele, C.O.; Ajayi, S.O.; Schaefer, M.; Indris, S.; Ehrenberg, H. Uncatalysed Neutral Hydrolysis of Waste PET Bottles into Pure Terephthalic Acid. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 6378–6385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M. Depolymerisation of PET Bottle via Methanolysis and Hydrolysis. In Recycling of Polyethylene Terephthalate Bottles; William Andrew Publishing: Norwich, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 85–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Liu, R.; Li, C.; Song, Y.; Hu, C. Hydrolysis of waste polyethylene terephthalate catalysed by easily recyclable terephthalic acid. Waste Manag. 2021, 135, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, P.; Savage, P.E.; Pester, C.W. Acid catalyst screening for hydrolysis of post-consumer PET waste and exploration of acidolysis. Green Chem. 2024, 26, 1964–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedsoltan, H. A focused review on recycling and hydrolysis techniques of polyethylene terephthalate. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2023, 63, 2651–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Qiao, W.-H.; Hu, Z.-Y.; Yang, B.-C.; Cao, C.-Y.; Fu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Wang, C.-X.; Cao, C.-X.; Lv, H. Hydrolysis of polyethylene terephthalate by ZSM-5 combined with supercritical carbon dioxide under neutral environment. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2024, 219, 110590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeem, M.; Fournet, M.B.; Attallah, O.A. Ultrafast 99% Polyethylene terephthalate depolymerisation into value added monomers using sequential glycolysis-hydrolysis under microwave irradiation. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 103903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, R.A. Metrics of Green Chemistry and Sustainability: Past, Present, and Future. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 6, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias JJ, R.; Thielemans, W. Instantaneous hydrolysis of PET bottles: An efficient pathway for the chemical recycling of condensation polymers. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 9945–9956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, J.J.R.; Thielemans, W. Efficient Depolymerisation of Glass Fiber Reinforced PET Composites. Polymers 2022, 14, 5171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollo, M.; Perini, M.A.G.; Sanzone, A.; Polastri, L.; Tiecco, M.; Chinillach, A.T.-; Martinelli, E.; Ciancaleoni, G. Effect of chloride salts and microwaves on polyethylene terephthalate (PET) hydrolysis by iron chloride/acetic acid Lewis/Brønsted acidic deep eutectic solvent. RSC Sustain. 2024, 2, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.S.; Jung, S.M. Direct Conversion of Waste PET to Regenerated Plastics Using Flame Retardants as Depolymerization Catalysts. Korean J. Chem. Eng. (Print) 2024, 41, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, P.; Savage, P.E.; Pester, C.W. Neutral Hydrolysis of Post-Consumer Polyethylene Terephthalate Waste in Different Phases. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 7203–7209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Bao, Y.; Cui, S. Exploring Water−Macromolecule Interactions at the Single-Molecule Level: A Comprehensive Review. Supramol. Mater. 2024, 3, 100061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Xu, W.; Du, R.; Zhou, X.; Liu, X.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y.-Z. Cosolvent-promoted selective non-aqueous hydrolysis of PET wastes and facile product separation. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 3284–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-L.; An, W.-L.; Du, R.; Tian, F.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y.-Z. Rapid hydrolysis of PET in high-concentration alcohol aqueous solution by pore formation and spontaneous separation of terephthalate. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conroy, S.; Zhang, X. Theoretical Insights into Chemical Recycling of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2024, 223, 110729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooneie, A.; Simonetti, P.; Salmeia, K.A.; Gaan, S.; Hufenus, R.; Heuberger, M.P. Enhanced PET processing with organophosphorus additive: Flame retardant products with added-value for recycling. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2019, 160, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dattilo, S.; Chiara Gugliuzzo Mirabella, E.F.; Puglisi, C.; Scamporrino, A.A.; Zampino, D.C.; Samperi, F. Characterisation of VOCs and additives in Italian PET bottles and studies on potential functional aldehydes scavengers. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2022, 248, 1407–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, R.; Welle, F. Contamination Levels in Recollected PET Bottles from Non-Food Applications and their Impact on the Safety of Recycled PET for Food Contact. Molecules 2020, 25, 4998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varaprasad, K.; Pariguana, M.; Raghavendra, G.M.; Jayaramudu, T.; Sadiku, E.R. Development of biodegradable metaloxide/polymer nanocomposite films based on poly-ε-caprolactone and terephthalic acid. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 70, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabde, S.; Yadav, G.D.; Narayan, R. Conversion of waste into wealth in chemical recycling of polymers: Hydrolytic depolymerisation of polyethylene terephthalate into terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol using phase transfer catalysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 420, 138312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Song, H.; Wang, Y.; Deng, T.; Hou, X. Zinc-catalysed ester bond cleavage: Chemical degradation of polyethylene terephthalate. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 208, 1469–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosimbescu, L.; Merkel, D.R.; Darsell, J.; Petrossian, G. Simple But Tricky: Investigations of Terephthalic Acid Purity Obtained from Mixed PET Waste. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 12792–12797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Liu, L.; Yan, D.; Zhou, Q.; Xin, J.; Lu, X.; Zhang, S. Colorless BHET obtained from PET by modified mesoporous catalyst ZnO/SBA-15. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2022, 248, 117109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.T.; Hee Ryu, M.; Jung, Y.J.; Lim, S.; Song, H.M.; Park, J.; Hwang, S.Y.; Lee, H.; Yeon, Y.J.; Sung, B.H.; et al. Chemo-Biological Upcycling of Poly (ethylene terephthalate) to Multifunctional Coating Materials. ChemSusChem 2021, 14, 4251–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Sheng, Y.; Cui, H.; Wang, M.; Wu, L.; Song, Y.; Yang, R.; Li, X.; Huang, H. Discovery and mechanism-guided engineering of BHET hydrolases for improved PET recycling and upcycling. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krisbiantoro, P.A.; Kuo, T.-J.; Chang, Y.-C.; Liao, W.; Sun, J.-P.; Yang, C.-Y.; Kamiya, Y.; Shieh, F.-K.; Chen, C.-C.; Wu, K.C.-W. PET-derived bis(2-hydroxyethyl) terephthalate as a new linker source for solvent-free and hydrothermal synthesis of BDC-based MOFs. Mater. Today Nano 2024, 25, 100459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfakhri, R.; Burley, J.C. Investigation of Potential Amorphisation and Co-Amorphisation Behaviour of the Benzene Di-Carboxylic Acids upon Cryo-Milling. Molecules 2019, 24, 3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagia, S.; Bornani, K.; Ozcan, S.; Ragauskas, A.J. Terephthalic Acid Copolyesters Containing Tetramethylcyclobutanediol for High-Performance Plastics. ChemistryOpen 2021, 10, 830–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardak, F.; Karaca, C.; Bilgili, S.; Atac, A.; Mavis, T.; Asiri, A.M.; Karabacak, M.; Kose, E. Conformational electronic spectroscopic characterization of isophthalic acid (monomer dimer structures) experimentally by, D.F.T. Spectrochim. Acta. Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2016, 165, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhtarova, M.; Golubeva, M.A.; Maximov, A.L. In situ Ni2P catalyst for the selective processing of terephthalic acid into BTX fraction. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2024, 678, 119734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Yang, Q.; Chen, D.; Yu, B.; He, J. Benzoic Acid Used as Food and Feed Additives Can Regulate Gut Functions. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 5721585, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Xu, P.; Ritter, T. Decarboxylative Hydroxylation of Benzoic Acids. Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 24214–24219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubeva, M.; Mukhtarova, M.; Sadovnikov, A.; Maximov, A. PET Waste Recycling into BTX Fraction Using In Situ Obtained Nickel Phosphide. Polymers 2023, 15, 2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Sugumaran, M.; Wakamatsu, K. Chemical Reactivities of ortho-Quinones Produced in Living Organisms: Fate of Quinonoid Products Formed by Tyrosinase and Phenoloxidase Action on Phenols and Catechols. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfieri, M.L.; Cariola, A.; Panzella, L.; Napolitano, A.; d’Ischia, M.; Valgimigli, L.; Crescenzi, O. Disentangling the Puzzling Regiochemistry of Thiol Addition to o-Quinones. J. Org. Chem. 2022, 87, 4580–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, K.A.M.; Ismail, A.F.; Karim, Z.A.; Abdullah, M.S.; Hafeez, A. A review of technologies for the phenolic compounds recovery and phenol removal from wastewater. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 151, 257–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsenzadeh, A.; Zamani, A.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Bioethylene Production from Ethanol: A Review and Techno-economical Evaluation. ChemBioEng Rev. 2017, 4, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Xiao, F.-S. Zeolite catalysts for non-oxidative ethane dehydrogenation to ethylene. EES Catal. 2024, 2, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, P.; Plessow, P.N. A computational investigation of the decomposition of acetic acid in H-SSZ-13 and its role in the initiation of the MTO process. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2023, 13, 1905–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enache, A.C.; Grecu, I.; Samoila, P. Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Recycled by Catalytic Glycolysis: A Bridge toward Circular Economy Principles. Materials 2024, 17, 2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Shen, B.; You, S.; Yin, Q.; Wang, M.; Jiang, N.; Su, R.; Qi, W. Development of a novel “4E” polyethylene terephthalate bio-recycling process with the potential for industrial application: Efficient, economical, energy-saving, and eco-friendly. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 391, 129913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomisawa, R.; Okazaki, M.; Ikaga, T.; Kim, K.; Ohkoshi, Y.; Okada, K.; Kabe, T.; Kanaya, T.; Katsuta, H.; Funatsu, Y. Fiber structure development of poly(ethylene terephthalate-co-isophthalate) copolymer. Polymer 2022, 245, 124708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-Y.; Shi, J.-X.; Cui, P.-H.; Yao, Z.-J.; Deng, W. Structural diversity and catalytic properties of five Co2(COO)4cluster-based coordination polymers modified with R-isophthalic acid (R = H, NO2, CH3, OH andtBu). CrystEngComm 2017, 19, 5038–5047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, Y.; Tsuchida, M.; Muramoto, A. The Preparation of Terephthalic Acid from Phthalic or Benzoic Acid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1957, 79, 6005–6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Z.; He, L.; Shi, Y.; Guan, Q.; Ning, P. A review of thermal homogeneous catalytic deoxygenation reactions for valuable products. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wang, J.; Jiao, L.; Song, Y.; Li, C.; Hu, C. Easily recoverable and reusable p-toluenesulfonic acid for faster hydrolysis of waste polyethylene terephthalate. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 1362–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, R.A.; Bode, M.L.; Akakios, S.G. Metrics of Green Chemistry: Waste Minimization. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2022, 33, 100569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, R.A. Biocatalysis, Solvents, and Green Metrics in Sustainable Chemistry; Elsevier EBooks: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Temperature | Time | Catalyst | EF | EEC | EEI | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| °C | min | °C−1·min−1 | °C·min | |||
| 200 | 180 | TPA | 1.486 | 2.65 × 10−5 | 5.60 × 104 | [29] |
| 200 | 120 | 4-FBA | 2.465 | 2.42 × 10−5 | 1.02 × 105 | [30] |
| 200 | 120 | ZnI2 | 1.433 | 3.58 × 10−5 | 4 × 104 | |
| 200 | 30 | None | 50.00 | 3.33 × 10−6 | 15.02 × 106 | [39] |
| 270 | 120 | 1.124 | 2.75 × 10−5 | 4.09 × 105 | ||
| 250 | 30 | 7.142 | 1.87 × 10−5 | 3.82 × 105 | ||
| 150 | 90 | PTSA | 4.347 | 7.13 × 10−5 | 6.10 × 104 | [74] |
| 250 | 90 | None | 0.017 | 3.13 × 10−3 | 5.29 × 104 | Current study |
| 220 | 60 | 0.106 | 8.23 × 10−4 | 1.29 × 106 | ||
| 220 | 90 | 0.034 | 1.68 × 10−3 | 2.08 × 105 | ||
| 250 | 30 | 0.074 | 2.08 × 10−3 | 3.57 × 105 | ||
| 250 | 60 | 0.029 | 2.62 × 10−3 | 1.12 × 105 | ||
| 270 | 30 | 0.038 | 3.83 × 10−3 | 9.73 × 104 | ||
| 270 | 60 | 0.027 | 2.62 × 10−3 | 1.04 × 105 | ||
| 270 | 90 | 0.017 | 2.34 × 10−3 | 7.44 × 104 | ||
| 300 | 30 | 0.046 | 2.77 × 10−3 | 1.67 × 105 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thulasiraman, A.V.; Vuppaladadiyam, A.K.; Hakeem, I.G.; Nahar, K.; Jena, M.K.; Shah, K. Ecofriendly Degradation of PET via Neutral Hydrolysis: Degradation Mechanism and Green Chemistry Metrics. Environments 2025, 12, 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12040127
Thulasiraman AV, Vuppaladadiyam AK, Hakeem IG, Nahar K, Jena MK, Shah K. Ecofriendly Degradation of PET via Neutral Hydrolysis: Degradation Mechanism and Green Chemistry Metrics. Environments. 2025; 12(4):127. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12040127
Chicago/Turabian StyleThulasiraman, Adhithiya Venkatachalapati, Arun Krishna Vuppaladadiyam, Ibrahim Gbolahan Hakeem, Kamrun Nahar, Manoj Kumar Jena, and Kalpit Shah. 2025. "Ecofriendly Degradation of PET via Neutral Hydrolysis: Degradation Mechanism and Green Chemistry Metrics" Environments 12, no. 4: 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12040127
APA StyleThulasiraman, A. V., Vuppaladadiyam, A. K., Hakeem, I. G., Nahar, K., Jena, M. K., & Shah, K. (2025). Ecofriendly Degradation of PET via Neutral Hydrolysis: Degradation Mechanism and Green Chemistry Metrics. Environments, 12(4), 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12040127










