A Bioremediation and Soil Fertility Study: Effects of Vermiremediation on Soil Contaminated by Chlorpyrifos
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Material
2.1.1. Soil Description
2.1.2. Earthworms
2.1.3. Vermicompost
2.1.4. Chlorpyrifos
2.2. Research Methods and Experimental Scheme
2.2.1. Experimental Design
2.2.2. Chlorpyrifos Extraction and Analysis
2.2.3. Microbial Biomass Carbon
2.2.4. Enzymatic Activity Analysis
2.2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Chlorpyrifos Trend and Reduction Percentages
3.2. Microbial Biomass Carbon
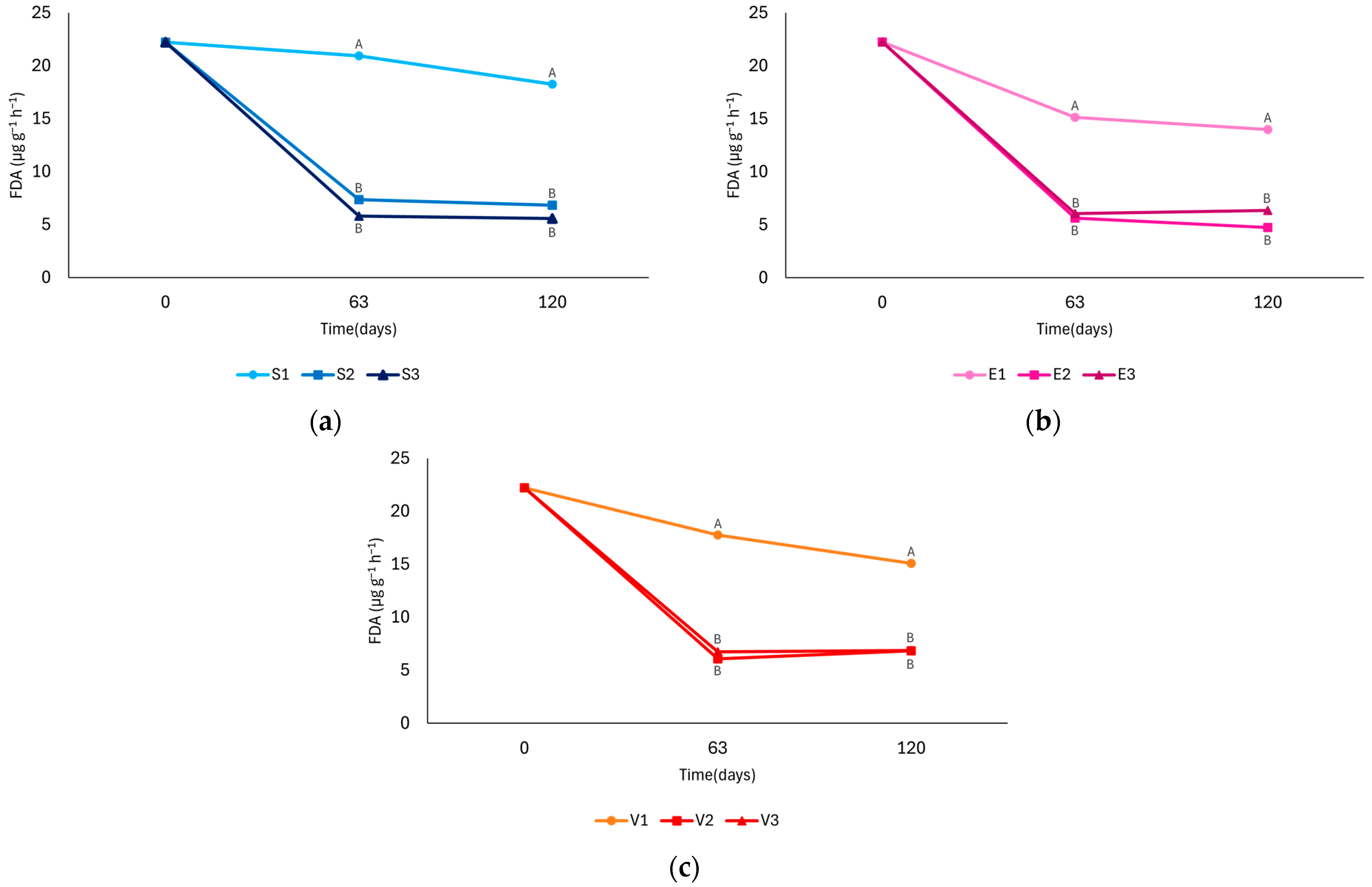
3.3. FDA
3.4. Alkaline Phosphatase
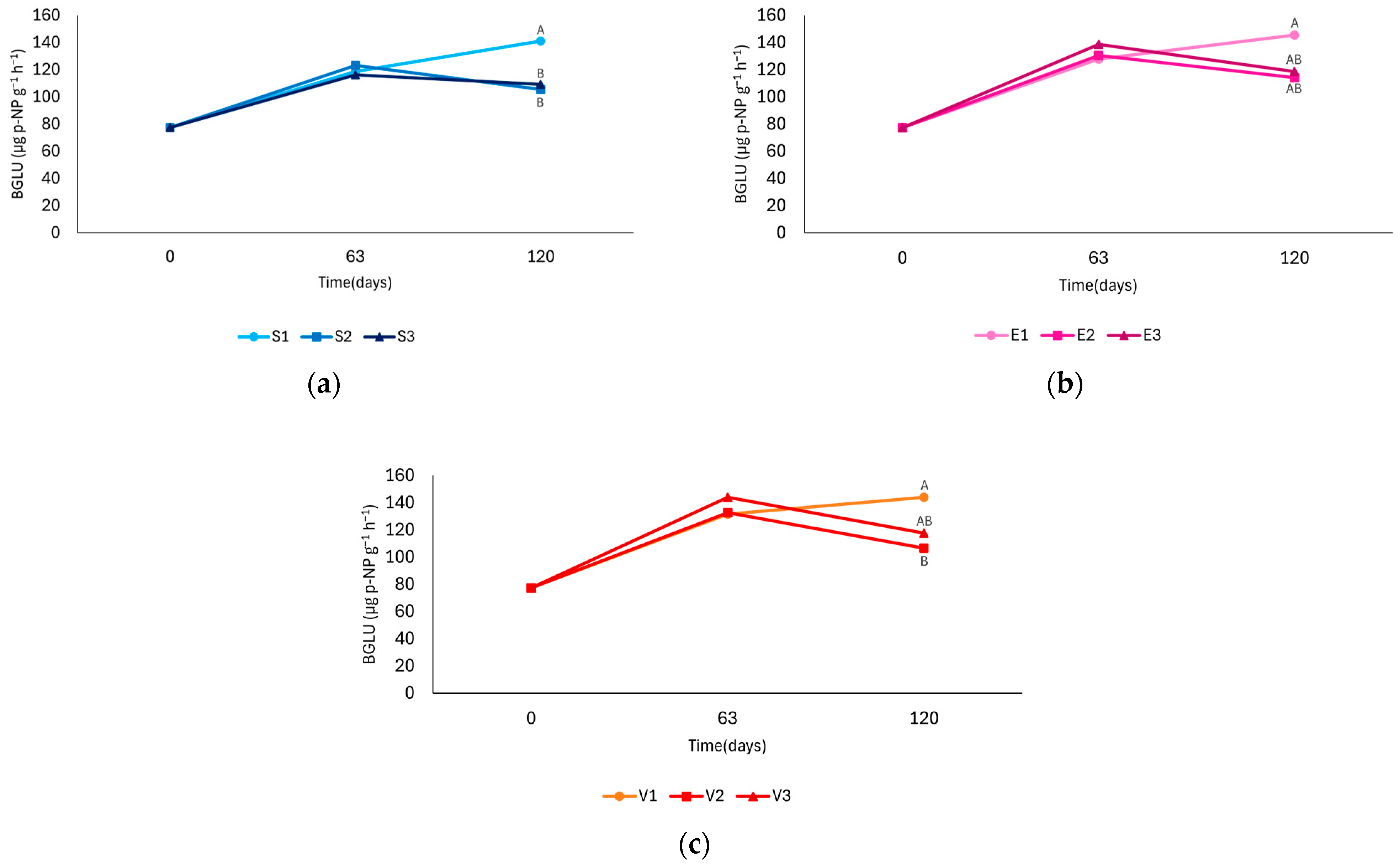
3.5. β-Glucosidase
3.6. NAG
4. Discussion
4.1. Chlorpyrifos Trend and Reduction Percentages
4.2. Microbial Biomass Carbon
4.3. FDA
4.4. Alkaline Phosphatase
4.5. β-Glucosidase
4.6. NAG
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liang, L.; Liu, W.; Sun, Y.; Huo, X.; Li, S.; Zhou, Q. Phytoremediation of Heavy Metal-Contaminated Saline Soils Using Halophytes: Current Progress and Future Perspectives. Environ. Rev. 2017, 25, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, A.; Li, S.; Wu, J.; Lian, J.; Liu, W.; Sun, Y. Insights into the Mechanisms Underlying the Remediation Potential of Earthworms in Contaminated Soil: A Critical Review of Research Progress and Prospects. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 740, 140145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, J. Environmental Pollution. In Pollution: Causes, Effects and Control; The Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 1997; pp. 276–277. [Google Scholar]
- Coban, O.; de Deyn, G.B.; van der Ploeg, M. Soil Microbiota as Game-Changers in Restoration of Degraded Lands. Science 1979, 2022, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, A.K.; Singh, J.; Soni, R.; Tripathi, P.; Kamle, M.; Tripathi, V.; Kumar, P. The Role of Microorganisms in Bioremediation for Sustainableenvironment Management. In Bioremediation of Pollutants; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 227–249. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan Al-Taai, S.H. Soil Pollution—Causes and Effects. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing Ltd.: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 790. [Google Scholar]
- Tagliabue, F.; Marini, E.; De Bernardi, A.; Vischetti, C.; Casucci, C. A Systematic Review on Earthworms in Soil Bioremediation. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). Pesticides Use, Pesticides Trade and Pesticides Indicators 1990–2019. In FAOSTAT 29; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cara, I.G.; Țopa, D.; Puiu, I.; Jităreanu, G. Biochar a Promising Strategy for Pesticide-Contaminated Soils. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kole, R.K.; Banerjee, H.; Bhattacharyya, A. Monitoring of Market Fish Samples for Endosulfan and Hexachlorocyclohexane Residues in and Around Calcutta. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2001, 67, 0554–0559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakootian, M.; Shahesmaeili, A.; Faraji, M.; Amiri, H.; Martinez, S.S. Advanced Oxidation Processes for The Removal of Organophosphorus Pesticides in Aqueous Matrices: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 134, 292–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, B.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Lu, T.; Sun, L.; Peijnenburg, W.; Qian, H. Effect of Chlorpyrifos on Freshwater Microbial Community and Metabolic Capacity of Zebrafish. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 262, 115230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, L.-K.; Wong, M.-H.; Hansen, H.C.B. Degradation of Chlorpyrifos in Humid Tropical Soils. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 125, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Pang, S.; Chen, J.; Bhatt, P.; Mishra, S.; Chen, S. Insights into the Microbial Degradation and Catalytic Mechanisms of Chlorpyrifos. Environ. Res. 2021, 194, 110660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Liu, W.; Hou, K.; Zhang, J.; Du, Z.; Li, B.; Zhu, L. Ecological Safety Evaluation of Chlorpyrifos on Agricultural Soil: Effects on Soil Microbes. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 189, 104954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Iqbal, S.; Anwar, S.; Afzal, M.; Islam, E.; Mustafa, T.; Khan, Q.M. Enhanced Remediation of Chlorpyrifos from Soil Using Ryegrass (Lollium multiflorum) and Chlorpyrifos-Degrading Bacterium Bacillus pumilus C2A1. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 237–238, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echeverri-Jaramillo, G.; Jaramillo-Colorado, B.; Sabater-Marco, C.; Castillo-López, M. Cytotoxic and Estrogenic Activity of Chlorpyrifos and Its Metabolite 3,5,6-Trichloro-2-Pyridinol. Study of Marine Yeasts as Potential Toxicity Indicators. Ecotoxicology 2021, 30, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Racke, K.D.; Coats, J.R.; Titus, K.R. Degradation of Chlorpyrifos and Its Hydrolysis Product, 3, 5, 6-Trichloro-2-Pyrinidol, in Soil. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 1988, 23, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briceño, G.; Fuentes, M.; Palma, G.; Jorquera, M.; Amoroso, M.; Diez, M. Chlorpyrifos Biodegradation and 3,5,6-Trichloro-2-Pyridinol Production by Actinobacteria Isolated from Soil. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2012, 73, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foong, S.Y.; Ma, N.L.; Lam, S.S.; Peng, W.; Low, F.; Lee, B.H.; Alstrup, A.K.; Sonne, C. A Recent Global Review of Hazardous Chlorpyrifos Pesticide in Fruit and Vegetables: Prevalence, Remediation and Actions Needed. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhende, R.S.; Jhariya, U.; Srivastava, S.; Bombaywala, S.; Das, S.; Dafale, N.A. Environmental Distribution, Metabolic Fate, and Degradation Mechanism of Chlorpyrifos: Recent and Future Perspectives. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 194, 2301–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racke, K.D.; Fontaine, D.D.; Yoder, R.N.; Miller, J.R. Chlorpyrifos Degradation in Soil at Termiticidal Application Rates. Pestic. Sci. 1994, 42, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, E.M.; Shaike, J.M. Chlorpyrifos: Pollution and Remediation. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2015, 13, 269–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getzin, L.W. Degradation of Chlorpyrifos in Soil: Influence of Autoclaving, Soil Misture, and Temperature. J. Econ. Entomol. 1981, 74, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.-X.; Jiang, W.W.; Wang, J.-L.; Jian, Q.; Shen, Y.; Liu, X.-J.; Yu, X.-Y. Persistence and Dissipation of Chlorpyrifos in Brassica Chinensis, Lettuce, Celery, Asparagus Lettuce, Eggplant, and Pepper in a Greenhouse. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baskaran, S.; Kookana, R.S.; Naidu, R. Degradation of Bifenthrin, Chlorpyrifos and Imidacloprid in Soil and Bedding Materials at Termiticidal Application Rates. Pestic. Sci. 1999, 55, 1222–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supreeth, M.; Raju, N. Biotransformation of Chlorpyrifos and Endosulfan by Bacteria and Fungi. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 5961–5971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, S.; Bara, J.K.; Soni, R.; Shrivastava, K. Bioremediation of Chlorpyrifos Contaminated Soil by Microorganism. Int. J. Environ. Agric. Biotechnol. 2017, 2, 1624–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, L.; Castillo, M.D.P.; Monaci, E.; Vischetti, C. Adaptation of the Biobed Composition for Chlorpyrifos Degradation to Southern Europe Conditions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Ruan, H. Comparative Study on the Biodegradation of Chlorpyrifos-Methyl by Bacillus megaterium CM-Z19 and Pseudomonas syringae CM-Z6. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2019, 91, e20180694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chishti, Z.; Hussain, S.; Arshad, K.R.; Khalid, A.; Arshad, M. Microbial Degradation of Chlorpyrifos in Liquid Media and Soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 114, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komárek, M.; Čadková, E.; Chrastný, V.; Bordas, F.; Bollinger, J.-C. Contamination of Vineyard Soils with Fungicides: A Review of Environmental and Toxicological Aspects. Environ. Int. 2010, 36, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaci, E.; Coppola, L.; Casucci, C.; Vischetti, C. Evaluation of Pesticide Losses and Drift During Treatments in Vineyard. 2011. Available online: https://core.ac.uk/download/297890141.pdf (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- Das, S.; Adhya, T.K. Degradation of Chlorpyrifos in Tropical Rice Soils. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 152, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vischetti, C.; Cardinali, A.; Monaci, E.; Nicelli, M.; Ferrari, F.; Trevisan, M.; Capri, E. Measures to Reduce Pesticide Spray Drift in a Small Aquatic Ecosystem in Vineyard Estate. Sci. Total. Environ. 2008, 389, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggio, S.A.; Janney, P.K.; Jenkins, J.J. Neurotoxicity of Chlorpyrifos and Chlorpyrifos-Oxon to Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 2021, 276, 130120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, D.L.; Daroff, R.B.; Autrup, H.; Bridges, J.; Buffler, P.; Costa, L.G.; Coyle, J.; McKhann, G.; Mobley, W.C.; Nadel, L.; et al. Review of the Toxicology of Chlorpyrifos with an Emphasis on Human Exposure and Neurodevelopment. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2008, 38, 1–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, Q.; Xia, Z.; Chen, S.; Gao, P.; Zhang, Z.; Gu, L.; Guo, S. Palladium Single Atoms on TiO2 as a Photocatalytic Sensing Platform for Analyzing the Organophosphorus Pesticide Chlorpyrifos. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2019, 59, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.G.; Jiang, X.; Mao, Y.M.; Zhao, Z.H.; Bian, Y.R. Organophosphorus Pesticide Extraction and Cleanup from Soils and Measurement Using GC-NPD. Pedosphere 2005, 15, 386–394. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzales-Condori, E.G.; Choquenaira-Quispe, C.; Ramírez-Revilla, S.A. Study of the Degradation of Chlorpyrifos in Contaminated Soils in the Presence of the Red California Earthworm Eisenia foetida. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient. 2020, 36, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, K.; Cheng, C.; Shi, B.; Liu, W.; Du, Z.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhu, L. New Insights into the Effects of Chlorpyrifos on Soil Microbes: Carbon and Nitrogen Cycle Related Microbes in Wheat/Maize Rotation Agricultural Field. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 318, 120908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bernardi, A.; Marini, E.; Casucci, C.; Tiano, L.; Marcheggiani, F.; Ciani, M.; Comitini, F.; Taskin, E.; Puglisi, E.; Vischetti, C. Ecotoxicological Effects of a Synthetic and a Natural Insecticide on Earthworms and Soil Bacterial Community. Environ. Adv. 2022, 8, 100225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curieses, S.P.; Sáenz, M.E.; Alberdi, J.L.; Martinez, R.S.; Larramendy, M.L.; Di Marzio, W.D. Genotoxic Evidences of Glyphosate and Chlorpyriphos on Eisenia Fetida Coelomocytes. Adv. Environ. Stud. 2018, 2, 211258139. [Google Scholar]
- Avila, V.C.; Valenzuela, C.M.; Noya, Y.E.N.; Bastidas, P.J.B. Inoculation with Azotobacter vinelandii Enhanced Chlorpyrifos Degradation and Reduced Cytotoxic and Genotoxic Effects in Soil. Span. J. Soil Sci. 2025, 15, 14033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, P.M.C.; Pathiratne, A.; van Gestel, C.A. Toxicity of Chlorpyrifos, Carbofuran, Mancozeb and Their Formulations to the Tropical Earthworm Perionyx excavatus. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2010, 44, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Shen, D.; Yu, K.; Zhong, J.; Li, Z.; Ye, Q.; Jiang, J.; Wang, W. Reducing the Environmental Risk of Chlorpyrifos Application through Appropriate Agricultural Management: Evidence from Carbon-14 Tracking. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 7324–7333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarfeen, N.; Nisa, K.U.; Hamid, B.; Bashir, Z.; Yatoo, A.M.; Dar, M.A.; Mohiddin, F.A.; Amin, Z.; Ahmad, R.A.; Sayyed, R.Z. Microbial Remediation: A Promising Tool for Reclamation of Contaminated Sites with Special Emphasis on Heavy Metal and Pesticide Pollution: A Review. Processes 2022, 10, 1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.J.; Zia, M.S.; Qasim, M. Use of Pesticides and Their Role in Environmental Pollution. World Acad. Sci Eng. Technol. 2010, 4, 122–128. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.; Kumar, V.; Shahzad, B.; Tanveer, M.; Sidhu, G.P.S.; Handa, N.; Kohli, S.K.; Yadav, P.; Bali, A.S.; Parihar, R.D.; et al. Worldwide Pesticide Usage and Its Impacts on Ecosystem. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.K.; Herat, S.; Valani, D.; Chauhan, K. Earthworms—the Environmental Engineers: Review of Vermiculture Technologies for Environmental Management and Resource Development. Int. J. Glob. Environ. Issues 2010, 10, 265–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Ali, A.; Xu, Y.; Abdelrahman, H.; Li, R.; Lin, Y.; Bolan, N.; Shaheen, S.M.; Rinklebe, J.; Zhang, Z. Earthworms as Candidates for Remediation of Potentially Toxic Elements Contaminated Soils and Mitigating the Environmental and Human Health Risks: A Review. Environ. Int. 2022, 158, 106924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dada, E.O.; Akinola, M.O.; Owa, S.O.; Dedeke, G.A.; Aladesida, A.A.; Owagboriaye, F.O.; Oludipe, E.O. Efficacy of Vermiremediation to Remove Contaminants from Soil. J. Health Pollut. 2021, 11, 210302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Campos, J.; Dendooven, L.; Alvarez-Bernal, D.; Contreras-Ramos, S.M. Potential of Earthworms to Accelerate Removal of Organic Contaminants from Soil: A Review. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2014, 79, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaswamy, V.G.; Jaffar, M.F.; Sridharan, R.; Ganesh, S.; Kalidas, S.; Palanisamy, V.; Mani, K. Effect of Chlorpyrifos on the Earthworm Eudrilus Euginae and Their Gut Microbiome by Toxicological and Metagenomic Analysis. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 37, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatoo, A.M.; Ali, N.; Zaheen, Z.; Baba, Z.A.; Ali, S.; Rasool, S.; Sheikh, T.A.; Sillanpää, M.; Gupta, P.K.; Hamid, B.; et al. Assessment of Pesticide Toxicity on Earthworms Using Multiple Biomarkers: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 2573–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelosi, C.; Barot, S.; Capowiez, Y.; Hedde, M.; Vandenbulcke, F. Pesticides and Earthworms. A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 34, 199–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, M.F.; Poch, R.M.; Olarieta, J.R.; Wiedner, K. Charcoal and Biological Activity in Formiguer Soils of Catalonia (Spain): Application of a Micromorphological Approach. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 234, 105810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, M. Assessing 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene (TNT)-Contaminated Soil Using Three Different Earthworm Test Methods. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2004, 57, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svobodová, M.; Šmídová, K.; Hvězdová, M.; Hofman, J. Uptake Kinetics of Pesticides Chlorpyrifos and Tebuconazole in the Earthworm Eisenia Andrei in Two Different Soils. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Ji, D.; Wang, C. Interaction Between Earthworms and Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi on the Degradation of Oxytetracycline in Soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 90, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, J. Earthworms and Vermicomposting. In Eartworms: The Ecological Engineers of Soil; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; pp. 63–77. [Google Scholar]
- Plytycz, B.; Bigaj, J.; Osikowski, A.; Hofman, S.; Falniowski, A.; Panz, T.; Grzmil, P.; Vandenbulcke, F. The Existence of Fertile Hybrids of Closely Related Model Earthworm Species, Eisenia andrei and E. fetida. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD). Guideline for Testing of Chemicals “Earthworm, Acute Toxicity Test” 207; Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development: Paris, France, 1984.
- Nobili, S.; Masin, C.E.; Zalazar, C.S.; Lescano, M.R. Bioremediation of Hydrocarbon Contaminated Soil Using Local Organic Materials and Earthworms. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 314, 120169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, A.; Wrights, J.; Jaikishun, S. Earthworms in Bioremediation of Soils Contaminated with Petroleum Hydrocarbons. In Vermicomposting for Sustainable Food Systems in Africa; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2023; pp. 349–368. [Google Scholar]
- Chachina, S.; Voronkova, N.; Baklanova, O. Biological Remediation of the Petroleum and Diesel Contaminated Soil with Earthworms Eisenia fetida. Procedia Eng. 2016, 152, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.-J.; Huang, J.-C.; Chachar, A.; Zhou, C.; He, S. Bioremediation of Selenium-Contaminated Soil Using Earthworm Eisenia Fetida: Effects of Gut Bacteria in Feces on the Soil Microbiome. Chemosphere 2022, 300, 134544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, X.; Huang, J.-C.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, C.; He, S.; Zhou, W. Remediation of Selenium-Contaminated Soil Through Combined Use of Earthworm Eisenia fetida and Organic Materials. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 124212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Goswami, L.; Pegu, R.; Chatterjee, S.K.; Bhattacharya, S.S. Epigenetic Regulations Enhance Adaptability and Valorization Efficiency in Eisenia fetida and Eudrilus eugeniae During Vermicomposting of Textile Sludge: Insights on Repair Mechanisms of Metal-Induced Genetic Damage and Oxidative Stress. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 345, 126493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, S.; Choudhury, M.; Deb, U.; Pegu, R.; Das, S.; Bhattacharya, S.S. Assessing the Ecological Impacts of Ageing on Hazard Potential of Solid Waste Landfills: A Green Approach Through Vermitechnology. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 236, 117643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xiao, R.; Li, R.; Amjad, A.; Zhang, Z. Bioremediation of Cd-Contaminated Soil by Earthworms (Eisenia fetida): Enhancement with EDTA and Bean Dregs. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Liu, X.; Ali, A.; Chen, A.; Zhang, M.; Li, R.; Chang, H.; Zhang, Z. Bioremediation of Cd-Spiked Soil Using Earthworms (Eisenia fetida): Enhancement with Biochar and Bacillus megatherium Application. Chemosphere 2021, 264, 128517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Sun, Y.; Li, X.; Weng, L.; Xu, H.; Li, Y. Enhancement Effect of Earthworm (Eisenia fetida) on Acetochlor Biodegradation in Soil and Possible Mechanisms. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 728–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Zhen, Z.; Wu, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhong, L.; Hu, H.; Luo, C.; Bai, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, D. The Impact on the Soil Microbial Community and Enzyme Activity of Two Earthworm Species During the Bioremediation of Pentachlorophenol-Contaminated Soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 301, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Zhao, L.; Li, X.; Hao, Y.; Xu, H.; Weng, L.; Li, Y. Stimulation of Earthworms (Eisenia fetida) on Soil Microbial Communities to Promote Metolachlor Degradation. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Moreno, L.; Nogales, R.; Romero, E. Vermiremediation of Biomixtures from Biobed Systems Contaminated with Pesticides. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Zhen, Z.; Liang, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Zhong, L.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; Luo, C.; Ren, L.; et al. Changes in Atrazine Speciation and the Degradation Pathway in Red Soil During the Vermiremediation Process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 364, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.L.; Lee, L.H.; Wu, T.Y. Sustainability of Using Composting and Vermicomposting Technologies for Organic Solid Waste Biotransformation: Recent Overview, Greenhouse Gases Emissions and Economic Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 111, 262–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olle, M. Review: Vermicompost, Its Importance and Benefit in Agriculture. Agraarteadus 2019, 30, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, S.; Ren, L.; Wu, W.; Chen, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, W.; Wei, T.; Liang, Y.-Q.; Zhang, D.; Wang, X.; et al. Impacts of Earthworm Casts on Atrazine Catabolism and Bacterial Community Structure in Laterite Soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 425, 127778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi-Moghadam, F.; Khodadadi, R.; Sedehi, M.; Arbabi, M. Bioremediation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Contaminated Soils Using Vermicompost. Int. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 2022, 5294170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Proctor, G.; Larson, S.L.; Ballard, J.H.; Zan, S.; Yang, R.; Wang, X.; Han, F.X. Earthworm Enhanced Phytoremediation of U in Army Test Range Soil with Indian Mustard and Sunflower. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2022, 6, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseer, A.; Andleeb, S.; Basit, A.; Ali, S.; Ud-Din, M.S.; Ali, N.M.; Liaqat, I.; Nazir, A. Efficacy of Cow and Buffalo Dung on Vermiremediation and Phytoremediation of Heavy Metals via Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy and Comet Assay. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 37912–37928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Gautam, K.; Seth, M.; Anbumani, S.; Manickam, N. Bioremediation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Crude Oil by Bacterial Consortium in Soil Amended with Eisenia fetida and Rhamnolipid. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 82517–82531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, A.; Jury, W.; Luepromchai, E.; Yahng, C.-S.; Crowley, D. Contribution of Earthworms to PCB Bioremediation. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2001, 33, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, M.; Hu, H.-W.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Wang, J.-T.; Hayden, H.; Tang, Y.-Q.; He, J.-Z. Aerobic Composting Reduces Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Cattle Manure and the Resistome Dissemination in Agricultural Soils. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 612, 1300–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vischetti, C.; Monaci, E.; Cardinali, A.; Casucci, C.; Perucci, P. The Effect of Initial Concentration, Co-Application and Repeated Applications on Pesticide Degradation in a Biobed Mixture. Chemosphere 2008, 72, 1739–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, M.F.; Haq, M.A.; Yasmin, N.; Khan, M.F.U. Degradation Analysis of Some Synthetic and Bio-Insecticides Sprayed on Okra Crop Using HPLC. J. Chem. Soc. Pak. 2012, 34, 306–311. [Google Scholar]
- Munch, J.-C. Ratios Between Estimates of Microbial Biomass Content and Microbial Activity in Soils; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1998; Volume 27. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, L.; Zeng, G.; Fan, C.; Lu, L.; Chen, X.; Chen, M.; Wu, H.; He, X.; He, Y. Response of Rhizosphere Microbial Community Structure and Diversity to Heavy Metal Co-Pollution in Arable Soil. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 8259–8269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Li, S.; Chen, S.; Meng, N.; Li, X.; Zheng, H.; Zhao, C.; Wang, D. Manipulation of the Rhizosphere Bacterial Community by Biofertilizers Is Associated with Mitigation of Cadmium Phytotoxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Q.; Fu, W.; Chen, B.; Zhang, X.; Xing, S.; Ji, C.; Zhang, X. Community Response of Soil Microorganisms to Combined Contamination of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Potentially Toxic Elements in a Typical Coking Plant. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1143742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, E.D.; Brookes, P.C.; Jenkinson, D.S. An Extraction Method for Measuring Soil Microbial Biomass C. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1987, 19, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, V.S.; Stott, D.E.; Diack, M. Assay for Fluorescein Diacetate Hydrolytic Activity: Optimization for Soil Samples. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnürer, J.; Rosswall, T. Fluorescein Diacetate Hydrolysis as a Measure of Total Microbial Activity in Soil and Litter. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1982, 43, 1256–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabai, M.A. Soil Enzymes. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2 Microbiological and Biochemical Properties; Access Publishers Ltd.: Nairobi, Kenya, 1994; pp. 775–833. [Google Scholar]
- Nannipieri, P.; Giagnoni, L.; Landi, L.; Renella, G. Role of Phosphatase Enzymes in Soil. In Phosphorus in Action: Biological Processes in Soil Phosphorus Cycling; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; Volume 26, pp. 215–243. [Google Scholar]
- Eivazi, F.; Tabatabai, M.A. Phosphatases in Soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1977, 9, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz-Almeida, R.; Pinheiro Da Mota, R.; Ferraz De Almeida, R.; Rezende Naves, E. Soil Quality: Enzymatic Activity of Soil β-Glucosidase. Glob. J. Agric. Res. Rev. 2015, 3, 146–150. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.; Meng, H.; Gu, J.-D. Microbial Extracellular Enzymes in Biogeochemical Cycling of Ecosystems. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 197, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eivazi, F.; Tabatabai, M. Glucosidases and Galactosidases in Soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1988, 20, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekenler, M.; Tabatabai, M.A. β-Glucosaminidase Activity of Soils: Effect of Cropping Systems and Its Relationship to Nitrogen Mineralization. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2002, 36, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parham, J.A.; Deng, S.P. Detection, Quantification and Characterization of β-Glucosaminidase Activity in Soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 1183–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Foundation for Statistical Computing. 2022. Available online: https://posit.co/download/rstudio-desktop/ (accessed on 5 January 2022).
- Federle, T.W.; Dobbins, D.C.; Thornton-Manning, J.R.; Jones, D.D. Microbial biomass, activity, and community structure in subsurface soils. Groundwater 1986, 24, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Lal, S.; Soni, S.K.; Maurya, S.K.; Shukla, P.K.; Chaudhary, P.; Bhattacherjee, A.K.; Garg, N. Mechanism and kinetics of chlorpyrifos co-metabolism by using environment restoring microbes isolated from rhizosphere of horticultural crops under subtropics. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 891870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardar, D.; Kole, R.K. Metabolism of Chlorpyrifos in Relation to Its Effect on the Availability of Some Plant Nutrients in Soil. Chemosphere 2005, 61, 1273–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racke, K.D.; Steele, K.P.; Yoder, R.N.; Dick, W.A.; Avidov, E. Factors Affecting the Hydrolytic Degradation of Chlorpyrifos in Soil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 1582–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, C.P.; Nochetto, C.B.; Zara, P. Volatilization of Trifluralin, Atrazine, Metolachlor, Chlorpyrifos, α-Endosulfan, and β-Endosulfan from Freshly Tilled Soil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 4009–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.K.; Walker, A.; Morgan, J.A.W.; Wright, D.J. Effects of Soil PH on the Biodegradation of Chlorpyrifos and Isolation of a Chlorpyrifos-Degrading Bacterium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 5198–5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremariam, S.Y.; Beutel, M.W.; Yonge, D.R.; Flury, M.; Harsh, J.B. Adsorption and Desorption of Chlorpyrifos to Soils and Sediments. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 215, 123–175. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Hernandez, J.C.; del Pino, J.N.; Capowiez, Y.; Mazzia, C.; Rault, M. Soil Enzyme Dynamics in Chlorpyrifos-Treated Soils Under the Influence of Earthworms. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 612, 1407–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheu, S.; Schlitt, N.; Tiunov, A.V.; Newington, J.E.; Jones, H.T. Effects of the Presence and Community Composition of Earthworms on Microbial Community Functioning. Oecologia 2002, 133, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Maliki, S.; Al-Taey, D.K.; Al-Mammori, H.Z. Earthworms and Eco-Consequences: Considerations to Soil Biological Indicators and Plant Function: A Review. Ecol. Front. 2021, 41, 512–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, J.; Aira, M.; Gómez-Brandón, M. Vermicomposting: Earthworms Enhance the Work of Microbes. In Microbes at Work: From Wastes to Resources; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; pp. 93–114. [Google Scholar]
- Drake, H.L.; Horn, M.A. As the Worm Turns: The Earthworm Gut as a Transient Habitat for Soil Microbial Biomes. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 61, 169–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskar, P.; Sachan, K.; Singh, B.V.; Saikanth, D.R.K.; Kumar, R.K.M.H.; Gautam, R.; Singh, O. Earthworm Castings in Ecosystem Health through Their Elemental Composition. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 2023, 35, 2076–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheu, S. Effects of Earthworms on Plant Growth: Patterns and Perspectives. Pedobiologia 2003, 47, 846–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Shi, L.; Wen, D.; Wang, R. Consistent Effects of a Non-Native Earthworm on Soil Microbial Communities in Three Subtropical Forests. Pedobiologia 2020, 79, 150613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scullion, J.; Malik, A. Earthworm Activity Affecting Organic Matter, Aggregation and Microbial Activity in Soils Restored After Opencast Mining for Coal. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, X.; Song, N. Biochar and Vermicompost Improve the Soil Properties and the Yield and Quality of Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) Grown in Plastic Shed Soil Continuously Cropped for Different Years. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 315, 107425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Chang, T.; Wang, Q.; Shaghaleh, H.; Hamoud, Y.A. Effects of Biochar and Vermicompost on Microorganisms and Enzymatic Activities in Greenhouse Soil. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 10, 1060277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, B.; Dai, J.; Zhang, C. Microbial Activity Was Greater in Soils Added with Herb Residue Vermicompost than Chemical Fertilizer. Soil Ecol. Lett. 2020, 2, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkowski, P.G.; Fenchel, T.; Delong, E.F. The Microbial Engines That Drive Earth’s Biogeochemical Cycles. Science 2008, 320, 1034–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehan, C.; Kirwan, L.; Connolly, J.; Bolger, T. The Effects of Earthworm Functional Diversity on Microbial Biomass and the Microbial Community Level Physiological Profile of Soils. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2008, 44, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, E.B.; Knelman, J.E.; Schindlbacher, A.; Siciliano, S.; Breulmann, M.; Yannarell, A.; Beman, J.M.; Abell, G.; Philippot, L.; Prosser, J.; et al. Microbes as Engines of Ecosystem Function: When Does Community Structure Enhance Predictions of Ecosystem Processes? Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, M.; Sardar, D.; Pal, R.; Kole, R.K. Effect of Chlorpyrifos on Microbial Biomass and Activities in Tropical Clay Loam Soil. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 160, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vischetti, C.; Coppola, L.; Monaci, E.; Cardinali, A.; Castillo, M.D.P. Microbial Impact of the Pesticide Chlorpyrifos on Swedish and Italian Biobeds. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2007, 27, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fang, H.; Yu, Y.; Chu, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Yu, J. Degradation of Chlorpyrifos in Laboratory Soil and Its Impact on Soil Microbial Functional Diversity. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tejada, M.; Rodríguez-Morgado, B.; Gómez, I.; Parrado, J. Degradation of Chlorpyrifos Using Different Biostimulants/Biofertilizers: Effects on Soil Biochemical Properties and Microbial Community. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2014, 84, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathma, J.; Sakthivel, N. Microbial Diversity of Vermicompost Bacteria That Exhibit Useful Agricultural Traits and Waste Management Potential. SpringerPlus 2012, 1, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przemieniecki, S.W.; Zapałowska, A.; Skwiercz, A.; Damszel, M.; Telesiński, A.; Sierota, Z.; Gorczyca, A. An Evaluation of Selected Chemical, Biochemical, and Biological Parameters of Soil Enriched with Vermicompost. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 8117–8127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceves-Diez, A.E.; Estrada-Castañeda, K.J.; Castañeda-Sandoval, L.M. Use of Bacillus Thuringiensis Supernatant from a Fermentation Process to Improve Bioremediation of Chlorpyrifos in Contaminated Soils. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 157, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H. Application of Acclimated Sewage Sludge as a Bio-Augmentation/Bio-Stimulation Strategy for Remediating Chlorpyrifos Contamination in Soil with/without Cadmium. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 579, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Racke, K.D.; Laskowski, D.A.; Schultz, M.R. Resistance of Chlorpyrifos to Enhanced Biodegradation in Soil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1990, 38, 1430–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, S.; Liaquat, F.; Khan, Q.M.; Khalid, Z.M.; Iqbal, S. Biodegradation of Chlorpyrifos and Its Hydrolysis Product 3,5,6-Trichloro-2-Pyridinol by Bacillus pumilus Strain C2A1. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liu, J.; Shen, W.; Zhao, X.; Hou, Y.; Cao, H.; Cui, Z. Isolation and Characterization of 3,5,6-Trichloro-2-Pyridinol-Degrading Ralstonia sp. Strain T6. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 7479–7483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jastrzebska, A. The Effect of Chlorpyrifos and Teflubenzuron on the Enzymatic Activity of Soil. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2011, 20, 903–910. [Google Scholar]
- Orts, A.; Cabrera, S.; Gómez, I.; Parrado, J.; Rodriguez-Morgado, B.; Tejada, M. Use of Okara in the Bioremediation of Chlorpyrifos in Soil: Effects on Soil Biochemical Properties. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 121, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Hernandez, J.C.; Sandoval, M.; Pierart, A. Short-Term Response of Soil Enzyme Activities in a Chlorpyrifos-Treated Mesocosm: Use of Enzyme-Based Indexes. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 73, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadian, N.; Malik, A.; Satya, S.; Dureja, P. Effect of Organic Amendments on Microbial Activity in Chlorpyrifos Contaminated Soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 95, S199–S202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riah, W.; Laval, K.; Laroche-Ajzenberg, E.; Mougin, C.; Latour, X.; Trinsoutrot-Gattin, I. Effects of Pesticides on Soil Enzymes: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2014, 12, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Liu, Q.; Chen, S.; Liu, K.; Chen, Y.; Motelica-Heino, M.; Zhong, H.; Zhang, M.; Tibihenda, C.; Lavelle, P.; et al. Individual and Combined Effects of Earthworms and Sphingobacterium sp. on Soil Organic C, N Forms and Enzyme Activities in Non-Contaminated and Cd-Contaminated Soil. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2024, 120, 103576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescano, M.R.; Masin, C.E.; Rodríguez, A.R.; Godoy, J.L.; Zalazar, C.S. Earthworms to Improve Glyphosate Degradation in Biobeds. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 27023–27031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Xie, T.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, J.; Li, C.; Xiong, W.; Xu, L.; Wu, Y.; He, Z.; Li, X. Alkaline Phosphatase Activity Mediates Soil Organic Phosphorus Mineralization in a Subalpine Forest Ecosystem. Geoderma 2021, 404, 115376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.M.; Wang, C.; Li, W.X.; Guo, L.; Cai, Z.J.; Wang, B.R.; Chen, J.; Shen, R.F. Changes of Acid and Alkaline Phosphatase Activities in Long-Term Chemical Fertilization Are Driven by the Similar Soil Properties and Associated Microbial Community Composition in Acidic Soil. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2021, 104, 103312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supreeth, M.; Chandrashekar, M.A.; Sachin, N.; Raju, N.S. Effect of Chlorpyrifos on Soil Microbial Diversity and Its Biotransformation by Streptomyces sp. HP-11. 3 Biotech 2016, 6, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Garg, V. Comparative Analysis of Vermicompost Quality Produced from Rice Straw and Paper Waste Employing Earthworm Eisenia fetida (Sav.). Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 250, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pramanik, P.; Ghosh, G.; Ghosal, P.; Banik, P. Changes in Organic—C, N, P and K and Enzyme Activities in Vermicompost of Biodegradable Organic Wastes Under Liming and Microbial Inoculants. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 2485–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarnam, T.; Velmurugan, A.; Pandey, S.K.; Roy, S.D. Enhancing Nutrient Recovery and Compost Maturity of Coconut Husk by Vermicomposting Technology. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 207, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, B.L.; Hopkins, D.W.; Haygarth, P.M.; Ostle, N. Glucosidase Activity in Pasture Soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2002, 20, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Fang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Li, Y.; Ge, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Yu, B.; Song, X.; Chen, J.; et al. Linking Soil Carbon Availability, Microbial Community Composition and Enzyme Activities to Organic Carbon Mineralization of a Bamboo Forest Soil Amended with Pyrogenic and Fresh Organic Matter. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 801, 149717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Griffiths, B.; Zhang, S.; Chen, X.; Liu, M.; Hu, F.; Li, H. Effects of Earthworms on Soil Enzyme Activity in an Organic Residue Amended Rice–Wheat Rotation Agro-Ecosystem. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2009, 42, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aira, M.; Monroy, F.; Domínguez, J. Effects of Two Species of Earthworms (Allolobophora spp.) on Soil Systems: A Microfaunal and Biochemical Analysis. Pedobiologia 2003, 47, 877–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aira, M.; Monroy, F.; Domínguez, J. Eisenia fetida (Oligochaeta, Lumbricidae) Activates Fungal Growth, Triggering Cellulose Decomposition During Vermicomposting. Microb. Ecol. 2006, 52, 738–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco-Andreu, L.; Gómez, I.; Parrado, J.; García, C.; Hernández, T.; Tejada, M. Behavior of Two Pesticides in a Soil Subjected to Severe Drought. Effects on Soil Biology. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 105, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, S.K.; Mariyam, A.; Gowda, N.K.; Singh, A.; Nair, V. Mechanistic Understanding of Biochar-Bacteria System for Enhanced Chlorpyrifos Bioremediation in Water and Soil Medium. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 483, 149119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Pandey, V.; Yadav, S.K.; Khare, P. Comparative Evaluation of Biodegradation of Chlorpyrifos by Various Bacterial Strains: Kinetics and Pathway Elucidation. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2024, 203, 105989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhao, Y.-H.; Zhang, B.-X.; Yang, C.-H.; Zhang, X. Isolation and Characterization of a Chlorpyrifos and 3,5,6-Trichloro-2-Pyridinol Degrading Bacterium. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 251, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olander, L.P.; Vitousek, P.M. Regulation of Soil Phosphatase and Chitinase Activity by N and P Availability. Biogeochemistry 2000, 49, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Don, A.; Steinberg, B.; Schöning, I.; Pritsch, K.; Joschko, M.; Gleixner, G.; Schulze, E.-D. Organic Carbon Sequestration in Earthworm Burrows. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 1803–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karas, P.; Baguelin, C.; Pertile, G.; Papadopoulou, E.; Nikolaki, S.; Storck, V.; Ferrari, F.; Trevisan, M.; Ferrarini, A.; Fornasier, F.; et al. Assessment of the Impact of Three Pesticides on Microbial Dynamics and Functions in a Lab-to-Field Experimental Approach. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 637–638, 636–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Gupta, R.; Kumari, M.; Sharma, S. Nontarget Effects of Chemical Pesticides and Biological Pesticide on Rhizospheric Microbial Community Structure and Function in Vigna radiata. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 11290–11300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeomans, J.; Bremner, J. Denitrification in Soil: Effects of Insecticides and Fungicides. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1985, 17, 453–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, D.T.; Razavi, B.S.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Blagodatskaya, E. Earthworm Burrows: Kinetics and Spatial Distribution of Enzymes of C-, N- and P- Cycles. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 99, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Ni, J.; Zou, X.; Chen, H.Y.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Li, Y.; Ren, T.; Shi, K.; Ruan, H. Earthworms Regulate Soil Microbial and Plant Residues Through Decomposition. Geoderma 2024, 450, 117040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubbers, I.M.; Brussaard, L.; Otten, W.; Van Groenigen, J.W. Earthworm-Induced N Mineralization in Fertilized Grassland Increases both N2O Emission and Crop-N Uptake. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2011, 62, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlian, O.; Thakur, M.P.; González, A.C.; Emeterio, L.M.S.; Marr, S.; Rocha, B.d.S.; Eisenhauer, N. Soil Chemistry Turned Upside Down: A Meta-Analysis of Invasive Earthworm Effects on Soil Chemical Properties. Ecology 2020, 101, e02936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Li, X.; Liu, T.; Yang, X.; Cao, J.; Tao, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Yao, Q.; Li, Y.; et al. Earthworms Negate the Adverse Effect of Arbuscular Mycorrhizae on Living Bacterial Biomass and Bacterial Necromass Accumulation in a Subtropical Soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 151, 108052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flach, J.; Pilet, P.-E.; Jolles, P. What’s New in Chitinase Research? Experientia 1992, 48, 701–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Italian Official Gazette Ministry. Italian Official Gazette Ministerial Decree: Approval of the Official Methods of Soil Chemical Analysis; Italian Official Gazette Ministry: Rome, Italy, 1999; Volume 248.
- PPDB Database. Available online: http://sitem.herts.ac.uk/aeru/ppdb/ (accessed on 27 February 2025).




| CP Concentrations | Treatments | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Soil | Soil + Earthworms | Soil + Vermicompost | |
| 0 ppm | S1 | E1 | V1 |
| 25 ppm | S2 | E2 | V2 |
| 50 ppm | S3 | E3 | V3 |
| Sampling Time | Treatment | MBC (mg kg−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (0 ppm) | 2 (25 ppm) | 3 (50 ppm) | ||
| 0 days | S | 147.66 ± 15.25 a | 147.66 ± 15.25 ab | 147.66 ± 15.25 ab |
| 63 days | S | 253.67 ± 27.72 ab | 213.56 ± 14.45 ab | 147.29 ± 16.27 ab |
| E | 304.56 ± 36.34 ab | 402.26 ± 23.87 a | 612.99 ± 70.29 a | |
| V | 318.91 ± 20.55 b | 221.07 ± 27.06 ab | 130.87 ± 15.70 b | |
| 120 days | S | 169.12 ± 18.27 ab | 130.60 ± 1.03 b | 134.21 ± 11.03 b |
| E | 264.86 ± 32.09 ab | 288.43 ± 33.66 a | 393.94 ± 41.93 ab | |
| V | 229.00 ± 24.52 ab | 183.15 ± 16.95 ab | 219.96 ± 5.49 ab | |
| Sampling Time | Treatment | FDA (µg g−1 h−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (0 ppm) | 2 (25 ppm) | 3 (50 ppm) | ||
| 0 days | S | 22.23 ± 0.98 a | 22.23 ± 0.98 a | 22.23 ± 0.98 a |
| 63 days | S | 20.94 ± 1.76 a | 7.36 ± 0.90 b | 5.81 ± 0.70 b |
| E | 15.14 ± 1.84 ab | 5.62 ± 0.54 b | 6.07 ± 0.74 b | |
| V | 17.75 ± 2.10 ab | 6.07 ± 0.69 b | 6.71 ± 0.79 b | |
| 120 days | S | 18.24 ± 1.73 ab | 6.84 ± 0.81 b | 5.58 ± 0.67 b |
| E | 14.00 ± 1.67 ab | 4.74 ± 0.57 b | 6.36 ± 0.68 b | |
| V | 15.08 ± 1.13 ab | 6.81 ± 0.83 b | 6.87 ± 0.69 b | |
| Sampling Time | Treatment | ALKP (µg g−1 h−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (0 ppm) | 2 (25 ppm) | 3 (50 ppm) | ||
| 0 days | S | 28.71 ± 0.93 a | 28.71 ± 0.93 a | 28.71 ± 0.93 a |
| 63 days | S | 50.10 ± 5.39 ab | 34.40 ± 3.83 ab | 28.50 ± 3.35 a |
| E | 50.42 ± 5.92 ab | 35.57 ± 4.40 ab | 42.07 ± 4.91 ab | |
| V | 49.50 ± 5.99 ab | 47.59 ± 5.78 b | 55.59 ± 6.54 b | |
| 120 days | S | 39.37 ± 4.55 ab | 28.41 ± 3.37 ab | 27.97 ± 3.21 ab |
| E | 46.54 ± 5.60 ab | 33.96 ± 2.38 ab | 31.88 ± 3.41 ab | |
| V | 61.18 ± 7.39 b | 49.80 ± 6.15 b | 51.76 ± 6.35 b | |
| Sampling Time | Treatment | BGLU (µg g−1 h−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (0 ppm) | 2 (25 ppm) | 3 (50 ppm) | ||
| 0 days | S | 77.22 ± 8.66 a | 77.22 ± 8.66 a | 77.22 ± 8.66 a |
| 63 days | S | 118.73 ± 14.37 ab | 123.00 ± 15.50 ab | 116.22 ± 13.94 ab |
| E | 127.82 ± 13.61 ab | 130.56 ± 13.86 b | 138.60 ± 16.08 b | |
| V | 131.66 ± 16.28 ab | 132.74 ± 11.68 b | 143.93 ± 7.01 b | |
| 120 days | S | 140.97 ± 9.69 b | 105.44 ± 13.05 ab | 109.14 ± 12.00 ab |
| E | 145.48 ± 18.54 b | 114.06 ± 14.19 ab | 118.63 ± 14.58 ab | |
| V | 143.99 ± 17.29 b | 106.67 ± 5.16 ab | 117.51 ± 12.41 ab | |
| Sampling Time | Treatment | NAG (µg g−1 h−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (0 ppm) | 2 (25 ppm) | 3 (50 ppm) | ||
| 0 days | S | 17.78 ± 2.18 a | 17.78 ± 2.18 a | 17.78 ± 2.18 a |
| 63 days | S | 22.99 ± 2.31 ab | 20.05 ± 1.56 ab | 21.36 ± 2.35 ab |
| E | 37.56 ± 3.70 b | 41.71 ± 4.44 b | 88.16 ± 10.61 c | |
| V | 25.42 ± 2.99 ab | 23.07 ± 2.49 ab | 24.43 ± 2.98 ab | |
| 120 days | S | 23.25 ± 2.70 ab | 19.26 ± 2.09 ab | 23.09 ± 2.66 ab |
| E | 35.99 ± 4.08 b | 37.51 ± 4.61 b | 31.67 ± 3.82 b | |
| V | 23.74 ± 2.84 ab | 23.81 ± 2.68 ab | 26.74 ± 3.30 ab | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tagliabue, F.; Marini, E.; De Bernardi, A.; Vischetti, C.; Brunetti, G.; Casucci, C. A Bioremediation and Soil Fertility Study: Effects of Vermiremediation on Soil Contaminated by Chlorpyrifos. Environments 2025, 12, 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12050136
Tagliabue F, Marini E, De Bernardi A, Vischetti C, Brunetti G, Casucci C. A Bioremediation and Soil Fertility Study: Effects of Vermiremediation on Soil Contaminated by Chlorpyrifos. Environments. 2025; 12(5):136. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12050136
Chicago/Turabian StyleTagliabue, Francesca, Enrica Marini, Arianna De Bernardi, Costantino Vischetti, Gianluca Brunetti, and Cristiano Casucci. 2025. "A Bioremediation and Soil Fertility Study: Effects of Vermiremediation on Soil Contaminated by Chlorpyrifos" Environments 12, no. 5: 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12050136
APA StyleTagliabue, F., Marini, E., De Bernardi, A., Vischetti, C., Brunetti, G., & Casucci, C. (2025). A Bioremediation and Soil Fertility Study: Effects of Vermiremediation on Soil Contaminated by Chlorpyrifos. Environments, 12(5), 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12050136








