Analytical and Experimental Studies on the Application of a Series of Treatment Chambers for Escherichia coli Inactivation by Pulsed Electric Fields
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
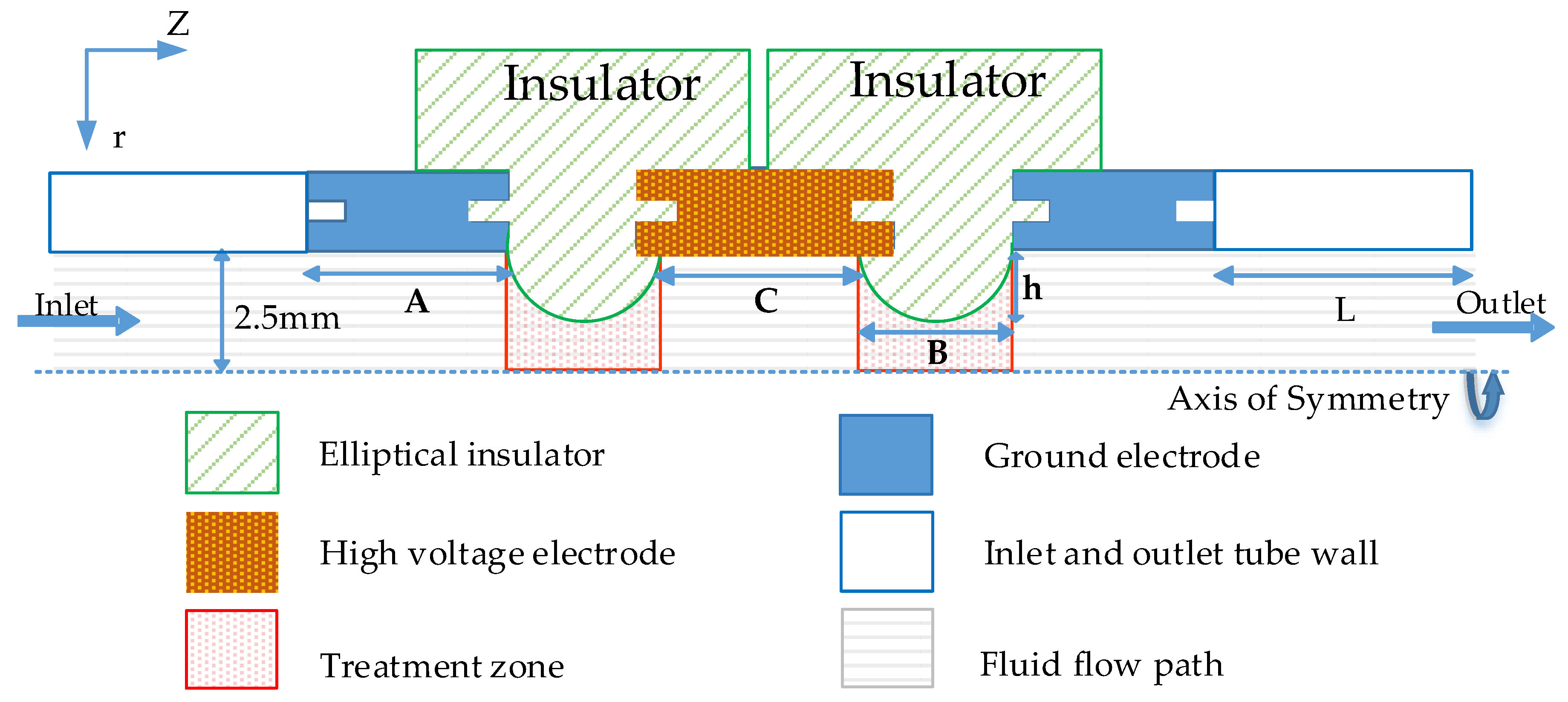
2.1. Co-Field Treatment Chamber Configuration
2.2. E. coli and Treated Liquid Medium Preparations
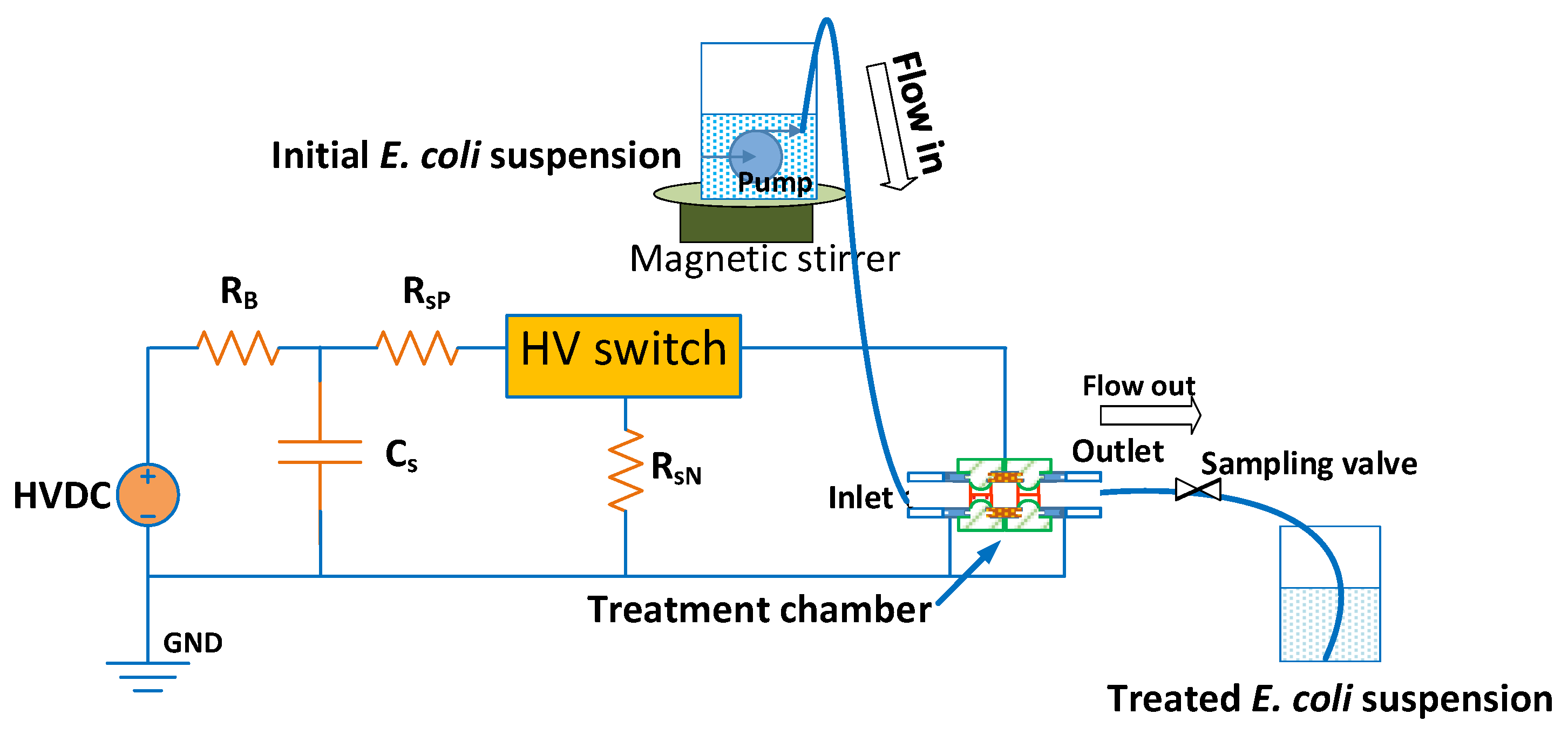
2.3. Implementation of the PEF Treatment for Microorganism Inactivation
3. Experimental Results and Discussion
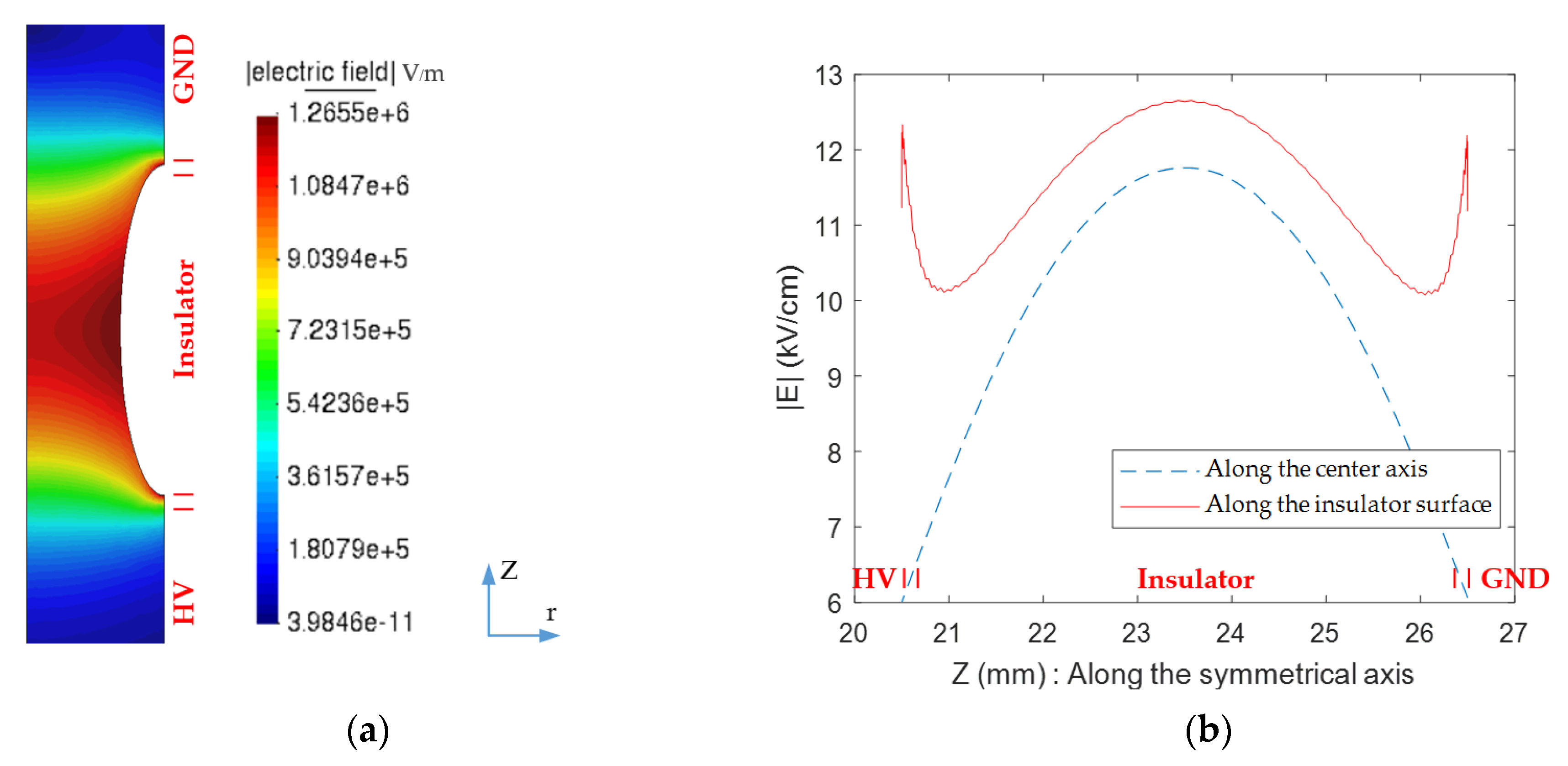
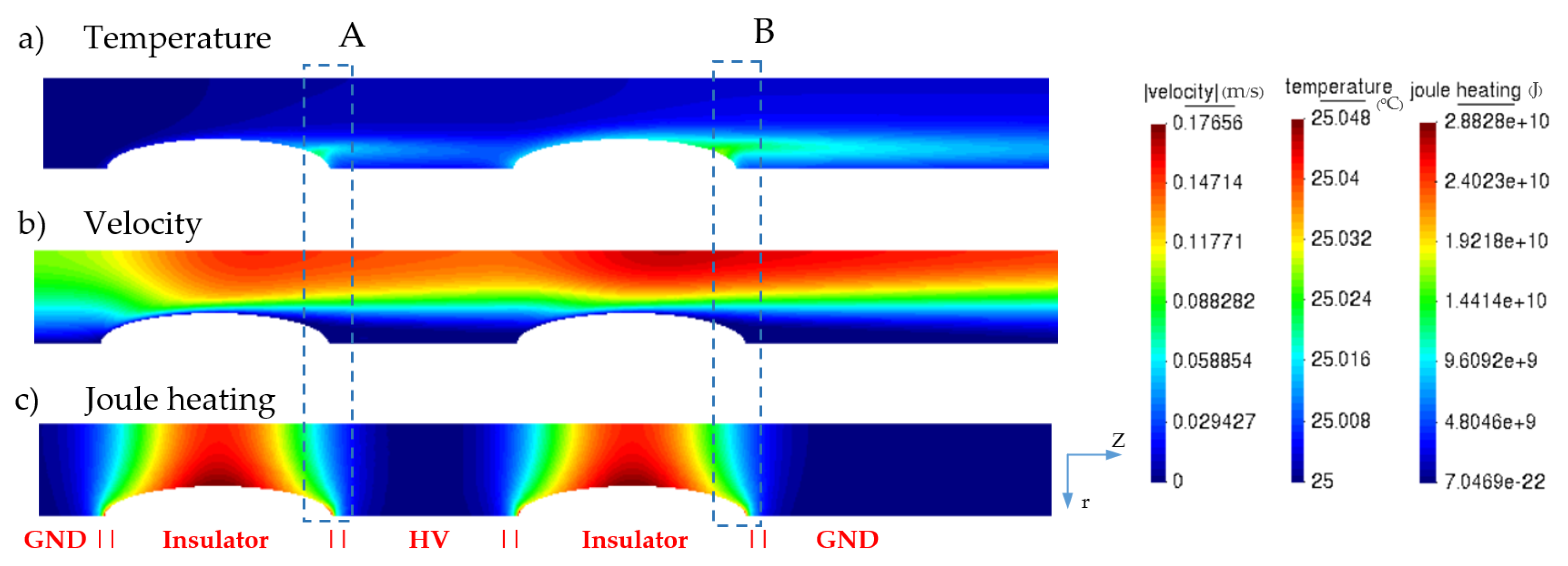
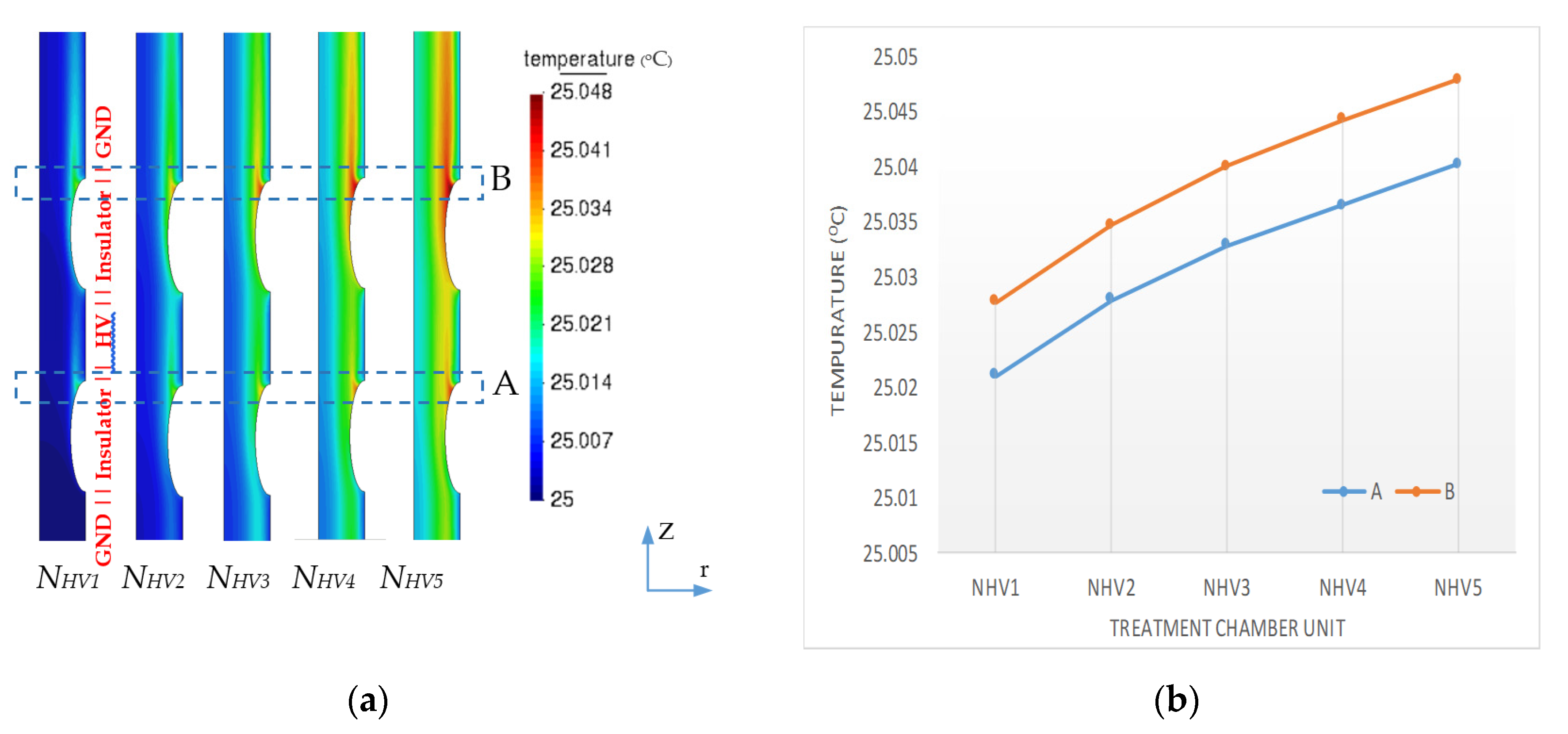
3.1. Electric Field and Temperature Field
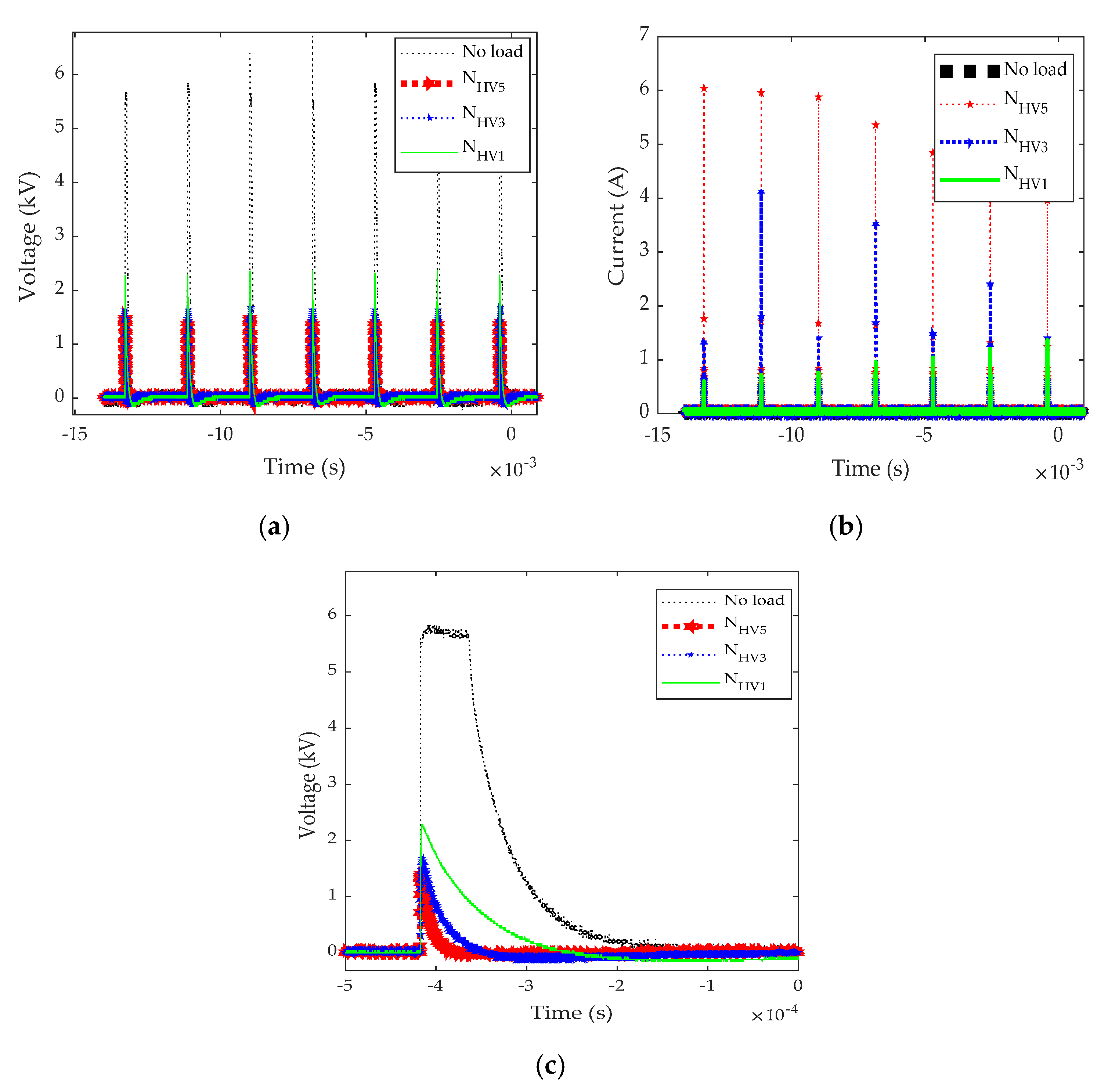
3.2. Electrical Characteristics of PEF During the Treatment Process
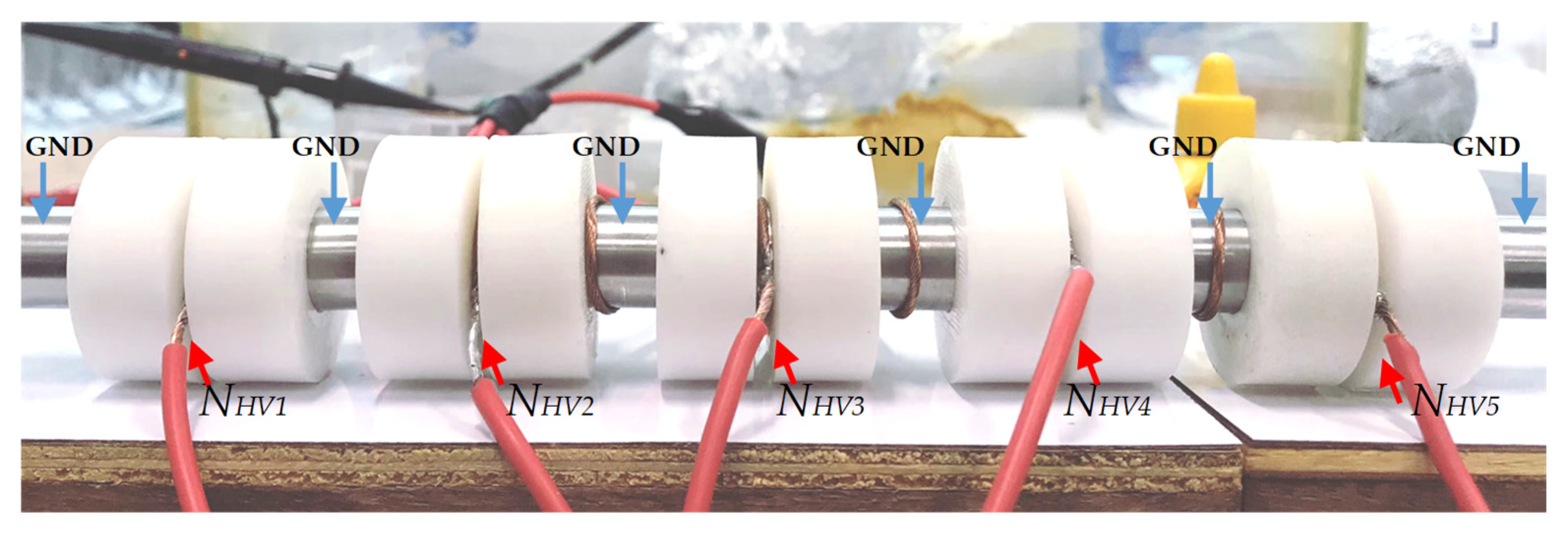
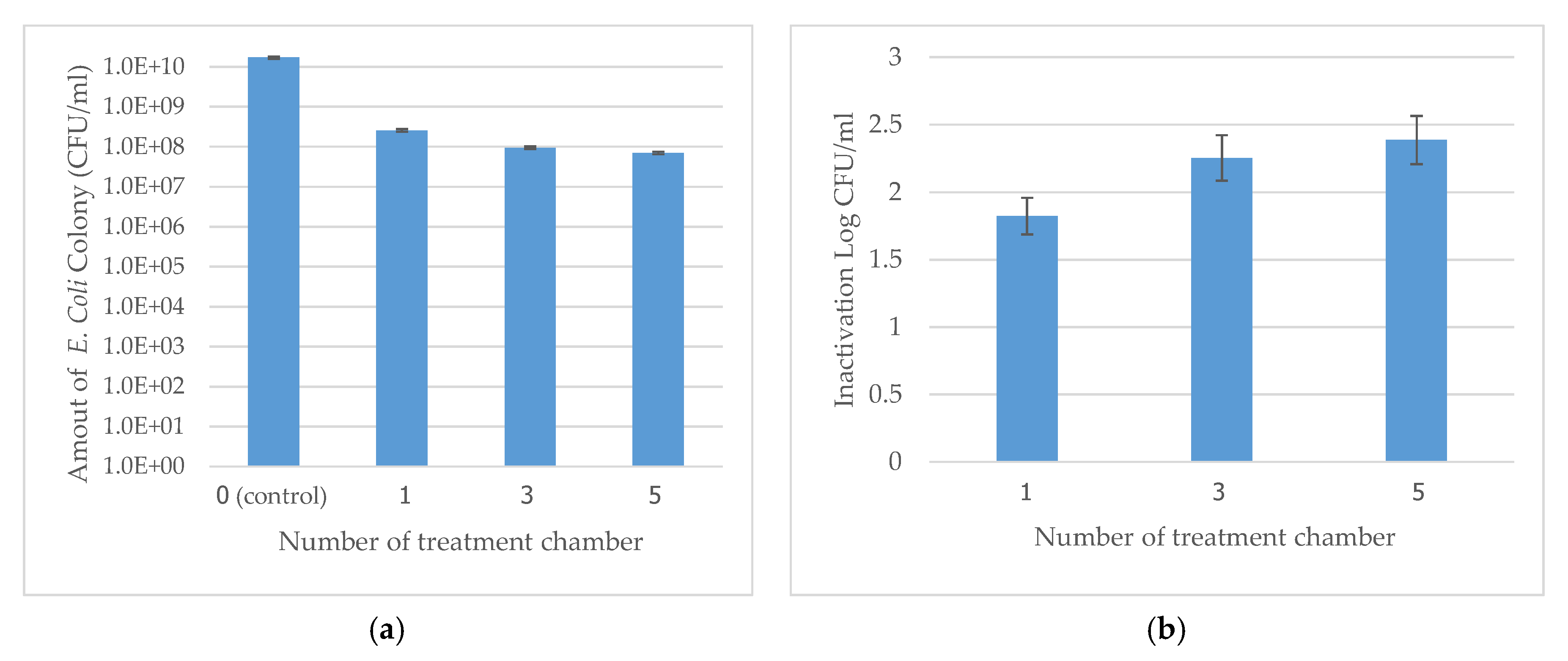
3.3. Effect of the Number of Treatment Chambers on E. coli Inactivation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pakhomov, A.G.; Miklavcic, D.; Markov, M.S. Advanced Electroporation Techniques in Biology and Medicine; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Marcela Gongora-Nieto, M.; Swanson, B.; Barbosa-Canovas, G.; Vega-Mercado, H. Pulsed Electric Fields in Food Preservation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 783–813. [Google Scholar]
- Timmermans, R.A.H.; Mastwijk, H.C.; Berendsen, L.B.J.M.; Nederhoff, A.L.; Matser, A.M.; Van Boekel, M.A.J.S.; Nierop Groot, M.N. Moderate intensity Pulsed Electric Fields (PEF) as alternative mild preservation technology for fruit juice. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 298, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziadek, K.; Kopeć, A.; Dróżdż, T.; Kiełbasa, P.; Ostafin, M.; Bulski, K.; Oziembłowski, M. Effect of pulsed electric field treatment on shelf life and nutritional value of apple juice. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 1184–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palaniappan, S.; Sastry, S.K. Electrical conductivity of selected juices: Influences of temperature, solids content, applied voltage, and particle size. J. Food Process Eng. 1991, 14, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Oey, I.; Bremer, P.; Everett, D.W. Microbiological and enzymatic activity of bovine whole milk treated by pulsed electric fields. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2018, 71, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba, F.J.; Parniakov, O.; Pereira, S.A.; Wiktor, A.; Grimi, N.; Boussetta, N.; Saraiva, J.A.; Raso, J.; Martin-Belloso, O.; Witrowa-Rajchert, D.; et al. Current applications and new opportunities for the use of pulsed electric fields in food science and industry. Food Res. Int. 2015, 77, 773–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobiev, E.; Lebovka, N. Applications of Pulsed Electric Energy for Biomass Pretreatment in Biorefinery; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 151–168. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann, U.; Pilwat, G.; Riemann, F. Dielectric Breakdown of Cell Membranes. In Membrane Transport in Plants; Ulrich, Z., Jack, D., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1974; pp. 146–153. [Google Scholar]
- Mussatto, S.I. Biomass Fractionation Technologies for a Lignocellulosic Feedstock Based Biorefinery; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 18 February 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Benz, R.; Zimmermann, U. Pulse-length dependence of the electrical breakdown in lipid bilayer membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 1980, 597, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Muramoto, Y.; Shimizu, N. Influence of ion concentration in aqueous solution on sterilization of E. coli by high electric field pulse. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomena (CEIDP), Des Moines, IA, USA, 19–22 October 2014; pp. 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneses, N.; Jaeger, H.; Moritz, J.; Knorr, D. Impact of insulator shape, flow rate and electrical parameters on inactivation of E. coli using a continuous co-linear PEF system. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2011, 12, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salengke, S.; Sastry, S.K.; Zhang, H.Q. Pulsed electric field technology: Modeling of electric field and temperature distributions within continuous flow PEF treatment chamber. Int. Food Res. J. 2012, 19, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar]
- Fiala, A.; Wouters, P.C.; Van den Bosch, E.; Creyghton, Y.L.M. Coupled electrical-fluid model of pulsed electric field treatment in a model food system. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba, F.J.; Koubaa, M.; do Prado-Silva, L.; Orlien, V.; Sant’Ana, A.D.S. Mild processing applied to the inactivation of the main foodborne bacterial pathogens: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 66, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemat, F.; Rombaut, N.; Meullemiestre, A.; Turk, M.; Perino, S.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.S.; Abert-Vian, M. Review of Green Food Processing techniques. Preservation, transformation, and extraction. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 41, 357–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.E.; Amer Eiss, A.H. Pulsed Electric Fields for Food Processing Technology. In Structure and Function of Food Engineering; Eiss, A.A., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012; Volume 11, pp. 275–306. [Google Scholar]
- Raso, J.; Frey, W.; Ferrari, G.; Pataro, G.; Knorr, D.; Teissie, J.; Miklavčič, D. Recommendations guidelines on the key information to be reported in studies of application of PEF technology in food and biotechnological processes. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2016, 37, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masood, H.; Diao, Y.; Cullen, P.J.; Lee, N.A.; Trujillo, F.J. A comparative study on the performance of three treatment chamber designs for radio frequency electric field processing. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2018, 108, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandušer, M.; Belič, A.; Čorović, S.; Škrjanc, I. Modular Serial Flow Through device for pulsed electric field treatment of the liquid samples. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kriengkriwut, T.; Techaumnat, B. Simulation of Electric Field in Co-Field Treatment Chamber Using FEM. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2015, 781, 612–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, A.; Sood, M.; Sofi, S.A.; Norzom, T. Non-thermal processing in food applications: A review. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 2, 171–180. [Google Scholar]
- Pyatkovskyy, T.I.; Shynkaryk, M.V.; Mohamed, H.M.; Yousef, A.E.; Sastry, S.K. Effects of combined high pressure (HPP), pulsed electric field (PEF) and sonication treatments on inactivation of Listeria innocua. J. Food Eng. 2018, 233, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Wang, L.H.; Zeng, X.A.; Han, Z.; Brennan, C.S. Non-thermal technologies and its current and future application in the food industry: A review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Puértolas, E.; Luengo, E.; Álvarez, I.; Raso, J. Improving Mass Transfer to Soften Tissues by Pulsed Electric Fields: Fundamentals and Applications. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 3, 263–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, A.; Parpinello, G.P.; Versari, A. Recent Advances and Applications of Pulsed Electric Fields (PEF) to Improve Polyphenol Extraction and Color Release during Red Winemaking. Beverages 2018, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kriengkriwut, T. Numerical Study of the Geometrical and Electrical Parameters for the Pulsed Electric Field (PEF) Treatment. Master’s Thesis, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, Y.H.; Culbertson, J.D.; Duncan, S.E.; Legarreta, I.G.; Li-Chan, E.C.Y.; Ma, C.Y.; Manley, C.; McMeekin, T.; Nip, W.K.; Nollet, L.M.L.; et al. Handbook of Food Science, Technology, and Engineering; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder, S.; Buckow, R.; Knoerzer, K. Numerical simulation of pulsed electric fields (PEF) processing for chamber design and optimisation. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on CFD in the Minerads and Process Industries CSIRO, Melbourne, Australia, 9–11 December 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Knoerzer, K.; Baumann, P.; Buckow, R. An iterative modelling approach for improving the performance of a pulsed electric field (PEF) treatment chamber. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2012, 37, 48–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchmann, L.; Böcker, L.; Frey, W.; Haberkorn, I.; Nyffeler, M.; Mathys, A. Energy input assessment for nanosecond pulsed electric field processing and its application in a case study with Chlorella vulgaris. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2018, 47, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, K.; Annus, I.; Vassiljev, A.; Kändler, N. Determination of Pressure Drop and Flow Velocity in Old Rough Pipes. Proceedings 2018, 2, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wouters, P.C.; Dutreux, N.; Smelt, J.P.P.M.; Lelieveld, H.L.M. Effects of pulsed electric fields on inactivation kinetics of Listeria innocua. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 5364–5371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raso, J.; Barbosa-Cánovas, G.V. Nonthermal Preservation of Foods Using Combined Processing Techniques. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2003, 43, 265–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boziaris, I.S. Novel Food Preservation and Microbial Assessment Techniques; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matra, K.; Buppan, P.; Techaumnat, B. Analytical and Experimental Studies on the Application of a Series of Treatment Chambers for Escherichia coli Inactivation by Pulsed Electric Fields. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4071. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10124071
Matra K, Buppan P, Techaumnat B. Analytical and Experimental Studies on the Application of a Series of Treatment Chambers for Escherichia coli Inactivation by Pulsed Electric Fields. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(12):4071. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10124071
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatra, Khanit, Pattakorn Buppan, and Boonchai Techaumnat. 2020. "Analytical and Experimental Studies on the Application of a Series of Treatment Chambers for Escherichia coli Inactivation by Pulsed Electric Fields" Applied Sciences 10, no. 12: 4071. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10124071
APA StyleMatra, K., Buppan, P., & Techaumnat, B. (2020). Analytical and Experimental Studies on the Application of a Series of Treatment Chambers for Escherichia coli Inactivation by Pulsed Electric Fields. Applied Sciences, 10(12), 4071. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10124071




