Soil Nitrogen Fractions, Nitrogen Use Efficiency and Yield of Zea mays L. Grown on a Tropical Acid Soil Treated with Composts and Clinoptilolite Zeolite
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinoptilolite Zeolite, Rice Straw, and Paddy Husk Composts Characterization
2.2. Study Area Characterization
2.3. Experimental Design and Treatments
- T0:
- No fertilizer application (Control);
- T1:
- 100% recommended chemical fertilizers (0.13 t ha−1 urea + 0.10 t ha−1 triple superphosphate (TSP) + 0.07 t ha−1 muriate of potash (MOP));
- T2:
- 100% recommended chemical fertilization amended with CZ (0.13 t ha−1 urea + 0.10 t ha−1 TSP + 0.07 t ha−1 MOP + 5 t ha−1 CZ);
- T3:
- 25% reduction of recommended chemical fertilization and amendment with rice straw compost and CZ (0.09 t ha−1 kg urea + 0.07 t ha−1 TSP + 0.05 t ha−1 MOP + 10 t ha−1 compost + 5 t ha−1 CZ);
- T4:
- 50% reduction of recommended chemical fertilization and amendment with rice straw compost and CZ (0.04 t ha−1 urea + 0.03 t ha−1 TSP + 0.02 t ha−1 MOP + 15 t ha−1 compost + 5 t ha−1 CZ);
- T5:
- 25% reduction of recommended chemical fertilization and amendment with paddy husk compost and CZ (0.09 t ha−1 kg urea + 0.07 t ha−1 TSP + 0.05 t ha−1 MOP + 10 t ha−1 compost + 5 t ha−1 CZ);
- T6:
- 50% reduction of recommended chemical fertilization and amendment with paddy husk compost and CZ (0.04 t ha−1 urea + 0.03 t ha−1 TSP + 0.02 t ha−1 MOP + 15 t ha−1 compost + 5 t ha−1 CZ).
2.4. Soil Sampling and Analysis
2.5. Plant Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency
- (i)
- AEN = Agronomic efficiency of applied N = (YN−Y0)/FN (kg yield increase/kg N applied)
- (ii)
- REN Crop recovery efficiency of applied N = (UN−U0)/FN (kg increase in N uptake/kg N applied)
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
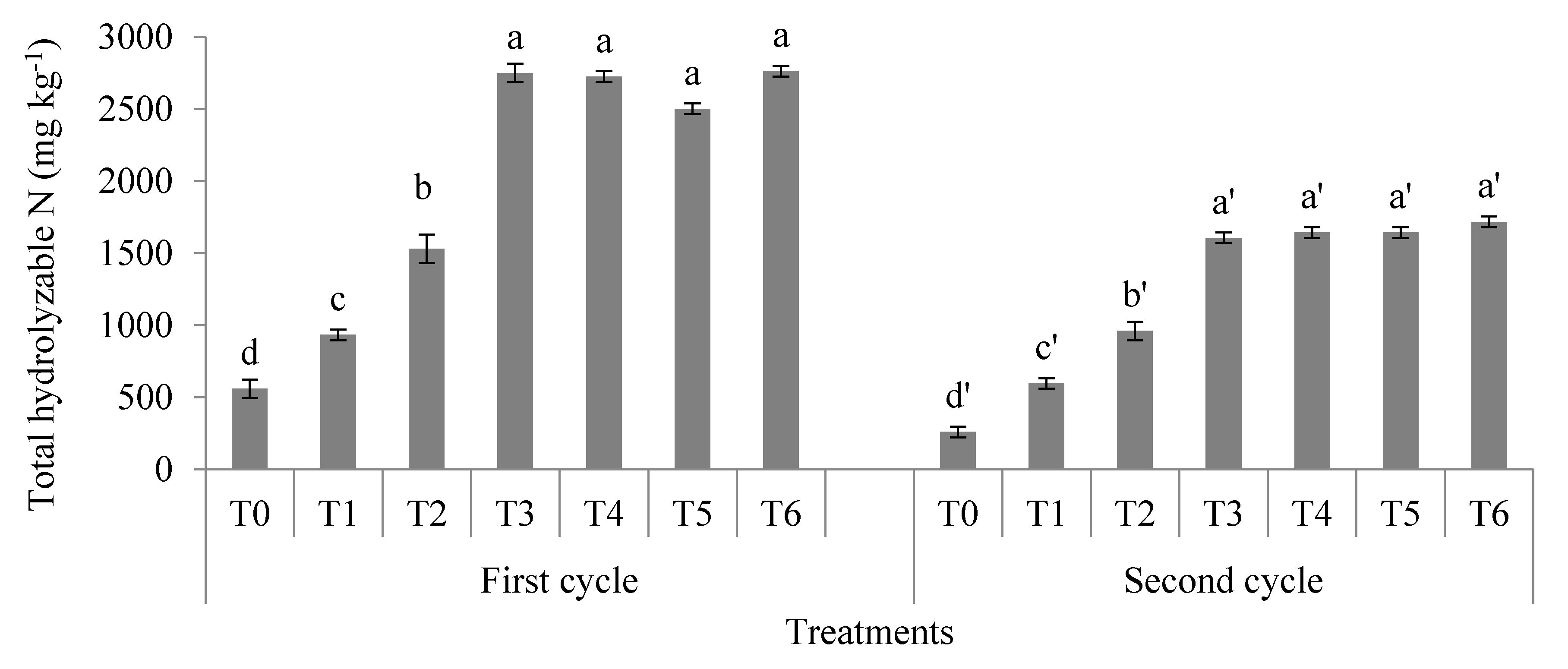
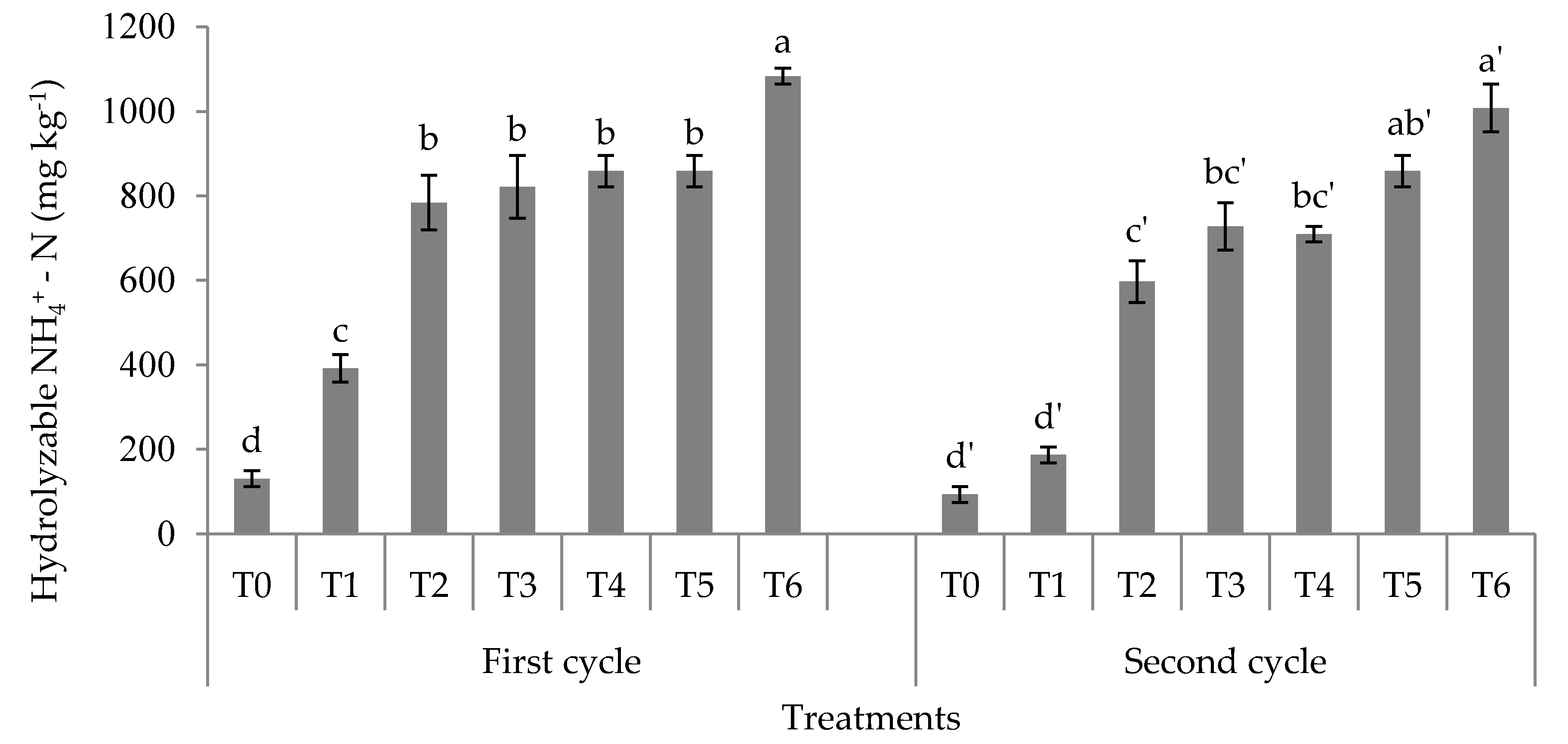
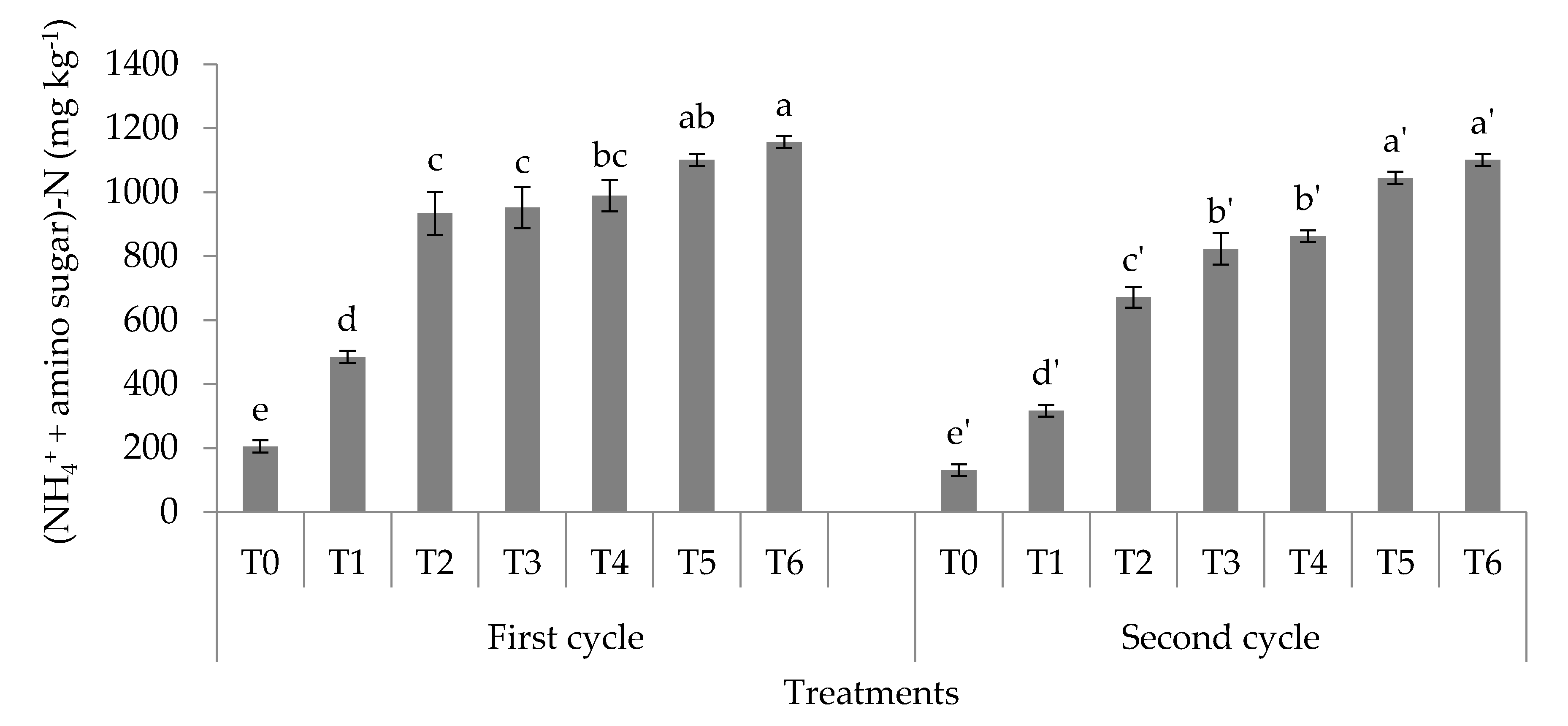
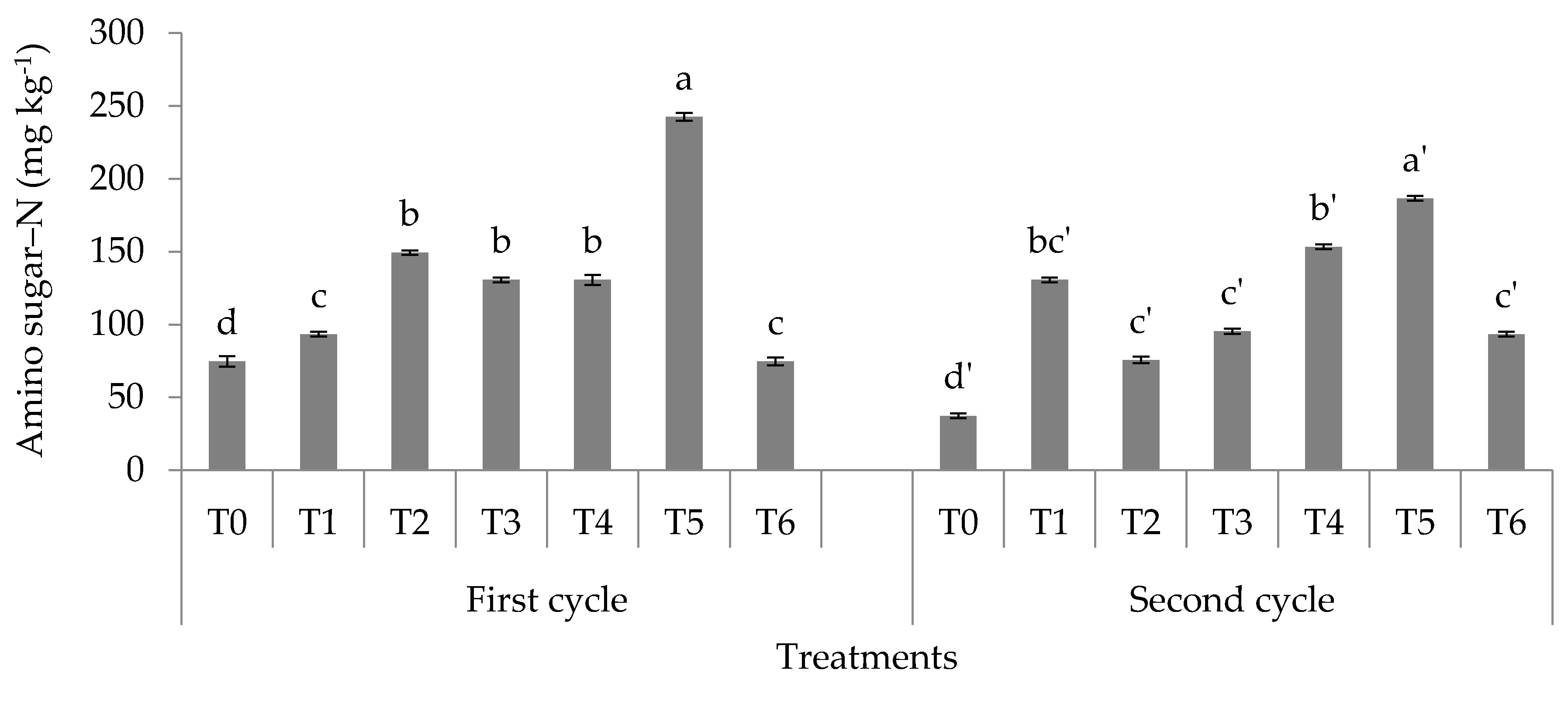
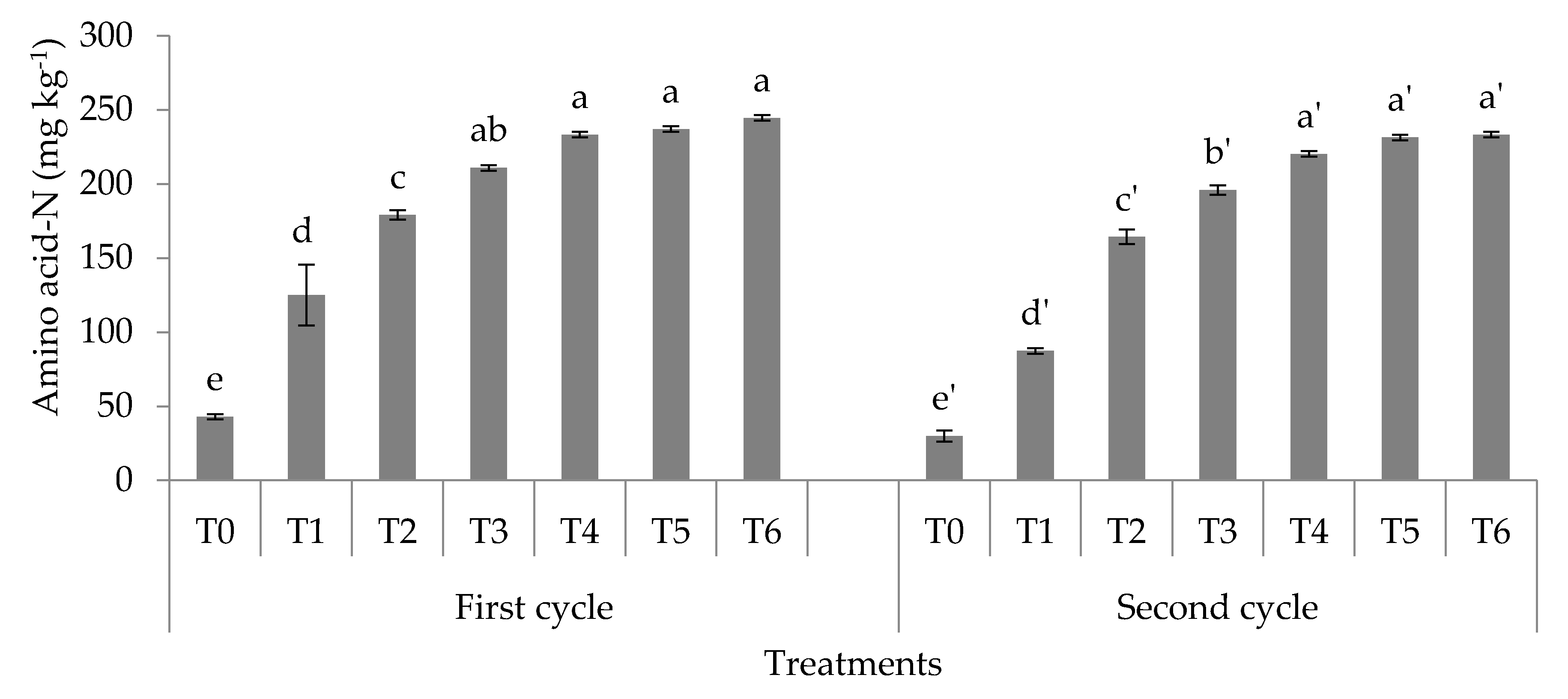
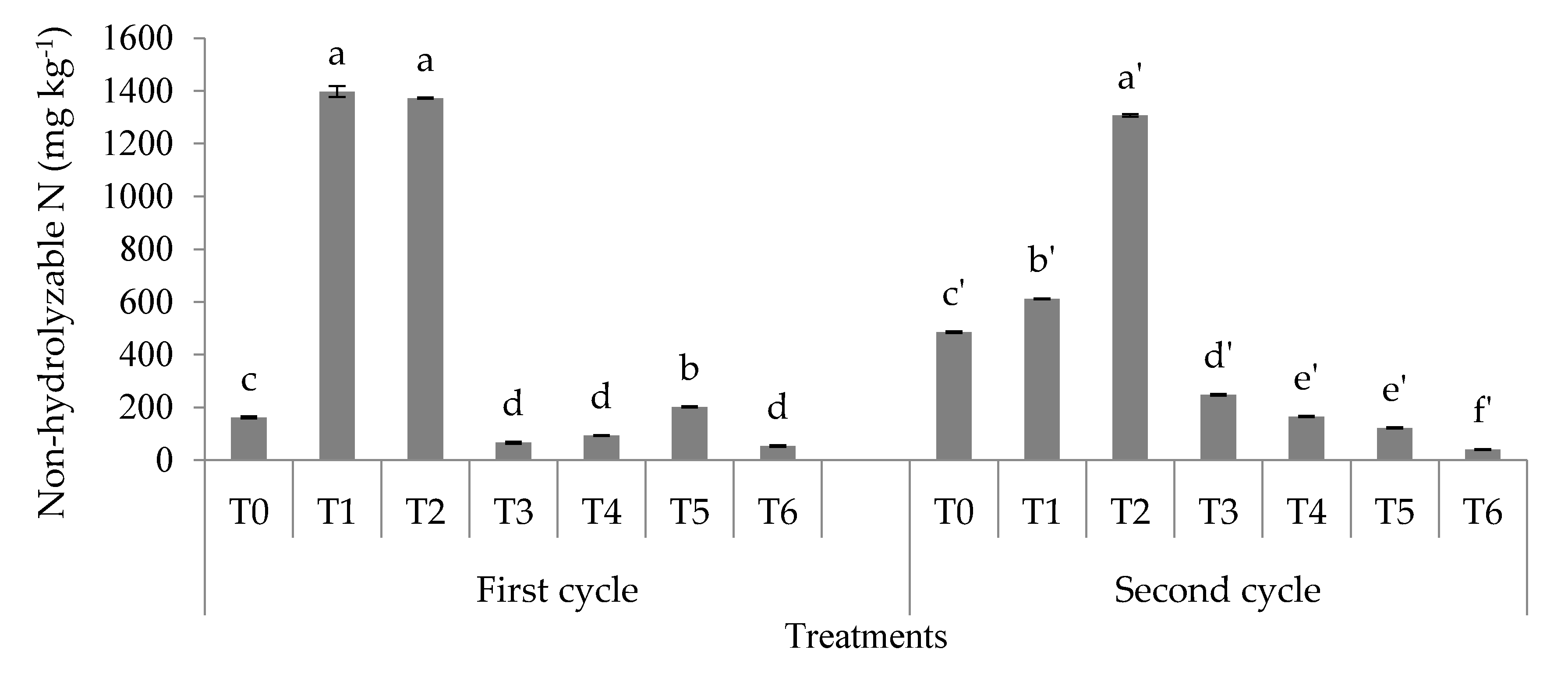
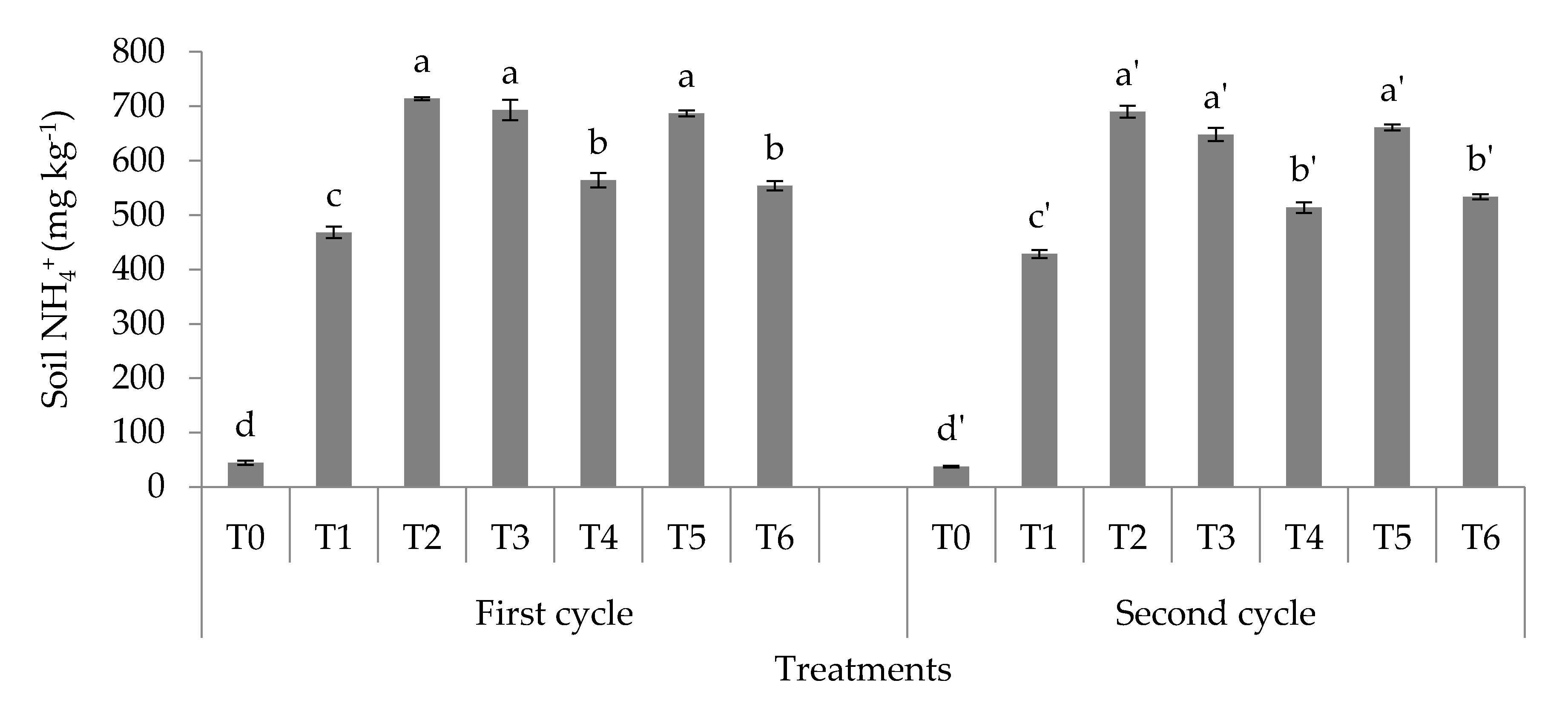
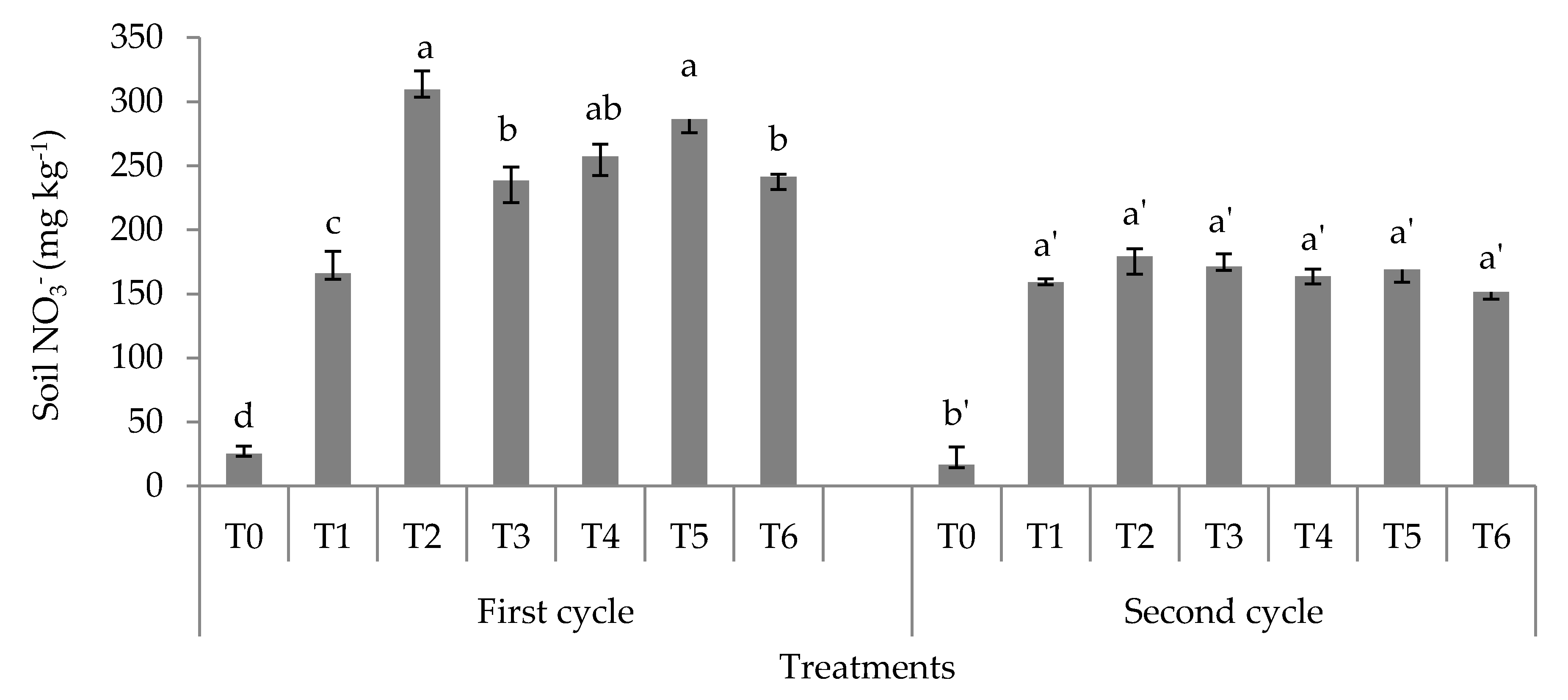
3.1. Soil Total, Organic, and Inorganic Nitrogen Fractions
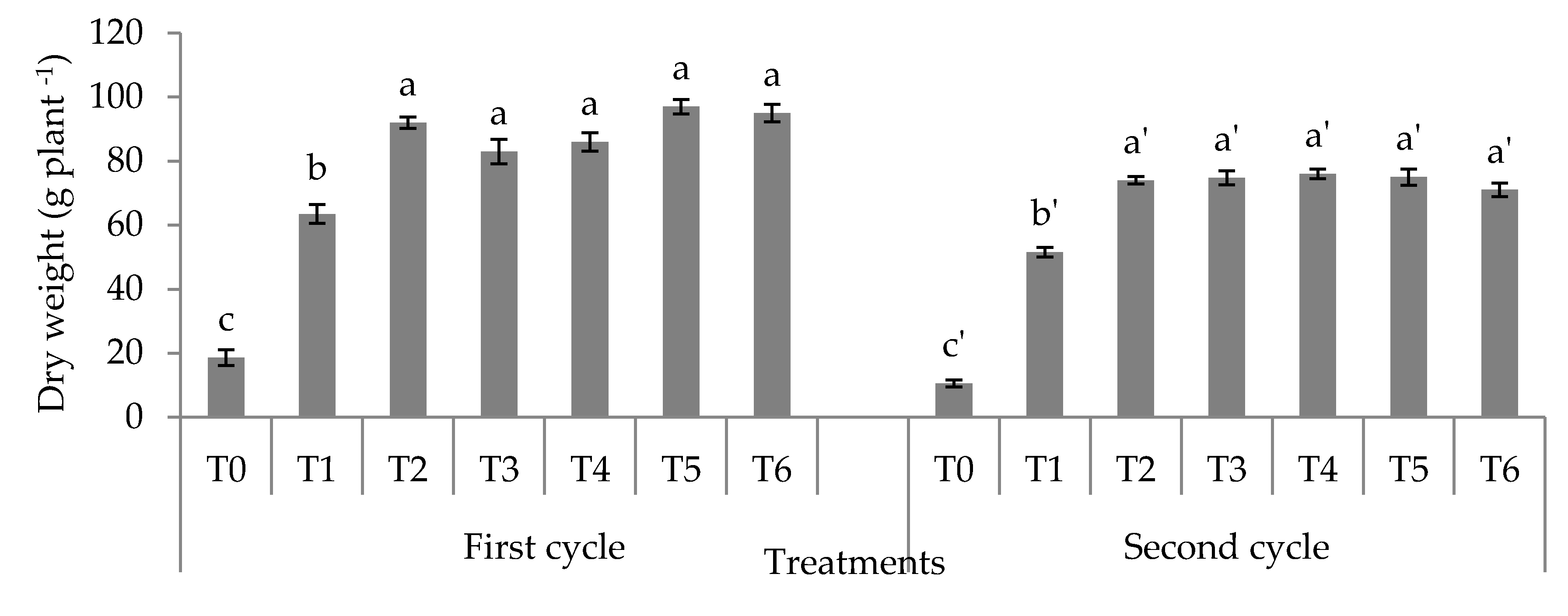
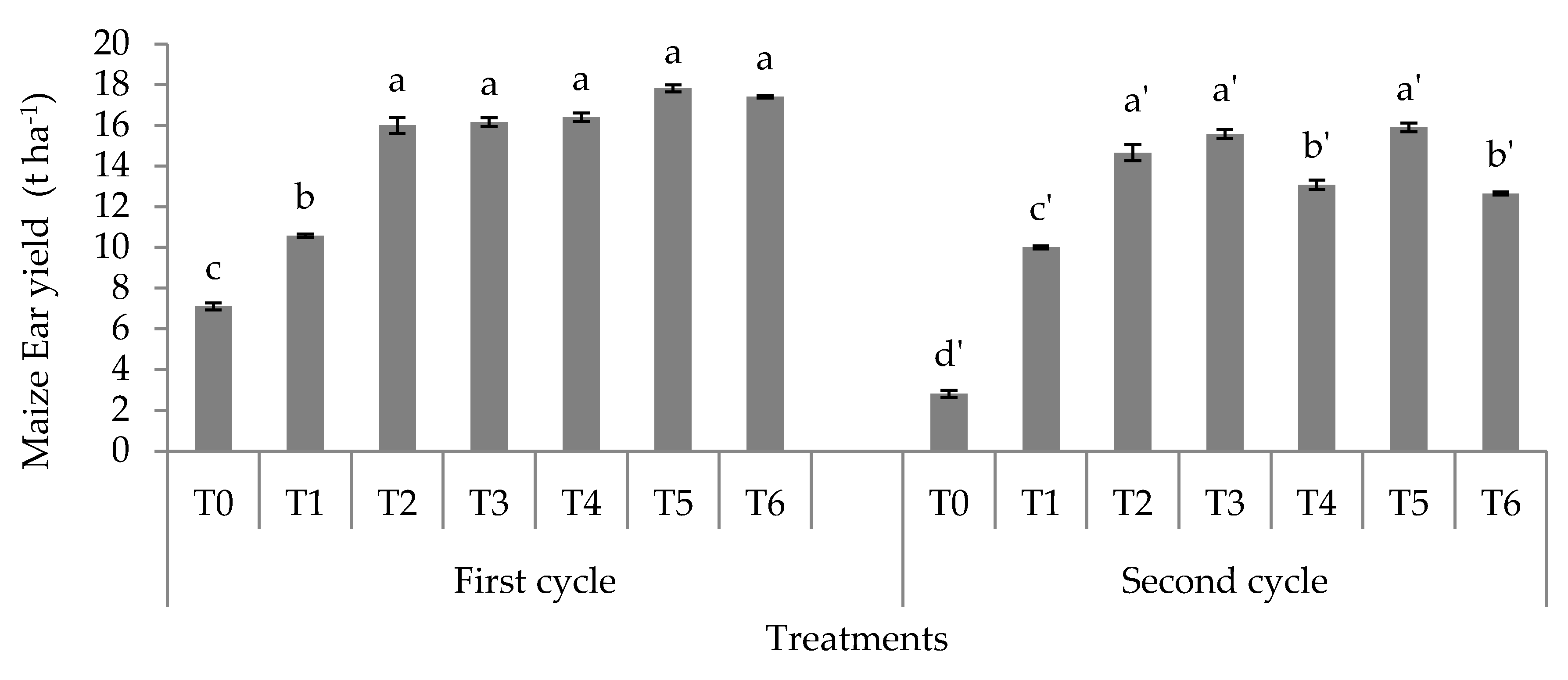
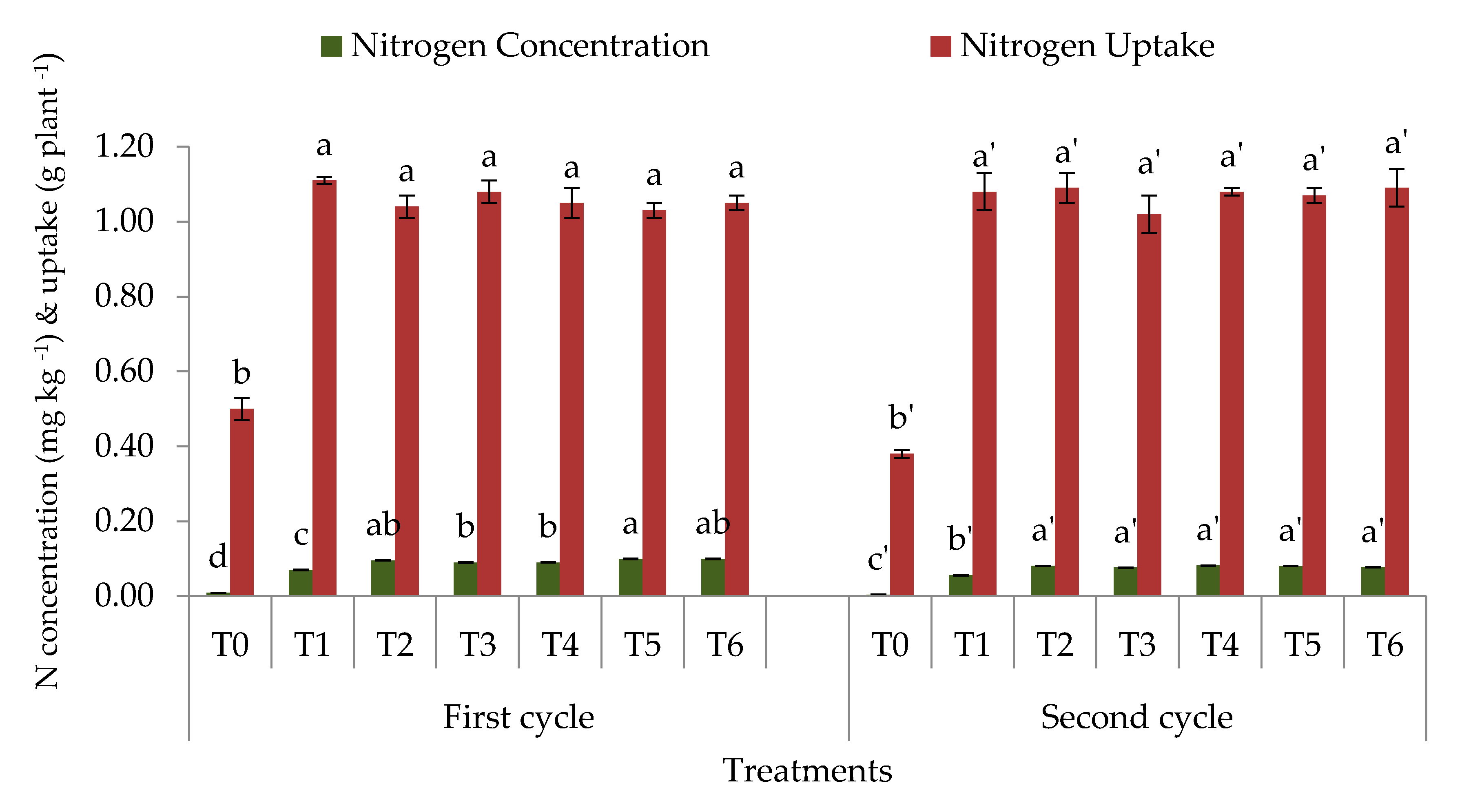
3.2. Dry Weight, Ear Weight, and Nitrogen Use Efficiency
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Total Nitrogen, Hydrolyzable Organic Nitrogen Fractions, and Mineral Nitrogen
4.2. Dry Weight, Fresh Cob Weight, and Nitrogen Use Efficiency
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, S.A.; Mulvaney, R.L.; Hoeft, R.G. A simple soil test for detecting sites that are nonresponsive to nitrogen fertilization. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2001, 65, 1751–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.P.; Verma, T.S. Dynamics of nitrogen fractions with long-term addition of Lantana camara biomass in rice-wheat cropping sequence. J. Ind. Soc. Soil Sci. 2001, 49, 407–412. [Google Scholar]
- Wander, M.M. Soil organic matter fractions and their relevance to soil function. In Soil Organic Matter in Sustainable Agriculture; Magdoff, F.R., Weil, R.R., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; pp. 67–102. [Google Scholar]
- Sainju, U.M.; Senwo, Z.N.; Nyakatama, E.Z.; Tazisong, L.A.; Reddy, R.C. Tillage, cropping system, and nitrogen fertilizer sources effects on soil and carbon sequestration. J. Environ. Qual. 2008, 37, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, J.M.; Rubio, G.; Häner, L.L.; Jorge, A.; Carlos, D.A.; Lucho-Constantino, A.; Islas-Valdez, S.; Pellet, D. Emerging and established technologies to increase nitrogen use efficiency of cereals. Agronomy 2016, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alvarez, R.; Grigera, S. Analysis of soil fertility and management effects on yields of wheat and corn in the rolling Pampa of Argentina. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2005, 191, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, R.L. N Loss Mechanisms and Nitrogen Use Efficiency. 2006 Purdue Nitrogen Management Workshops. Available online: http://www.agry.purdue.edu/ext/pubs/2006NLossMechanisms.pdf (accessed on 21 March 2020).
- Dobermann, A. Nitrogen use efficiency: State of the art. In Proceedings of the IFA International Workshop on Enhanced-Efficiency Fertilizers, Frankfurt, Germany, 28–30 June 2005; International Fertilizer Industry Association: Paris, France, 2005; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Cassman, K.G.; Dobermann, A.; Walters, D.T. Agroecosystems, nitrogen-use efficiency, and nitrogen management. Ambio 2002, 31, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latifah, O.; Ahmed, O.H.; Majid, N.M.A. Short term enhancement of nutrient availability in Zea mays L. cultivation on an acid soil using compost and clinoptilolite zeolite. Compost Sci. Util. 2017, 25, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latifah, O.; Ahmed, O.H.; Majid, N.M.A. Improving ammonium and nitrate release from urea using clinoptilolite zeolite and compost. Sci. World J. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latifah, O.; Ahmed, O.H.; Majid, N.M.A. Effect of organic amendment derived from co-composting of chicken slurry and rice straw on reducing nitrogen loss from urea. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2016, 47, 639–656. [Google Scholar]
- Latifah, O.; Ahmed, O.H.; Majid, N.M.A. Amending chemical fertilizers with rice straw compost and clinoptilolite zeolite and their effects on nitrogen use efficiency and fresh cob yield of Zea mays L. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2018, 49, 1795–1813. [Google Scholar]
- Bremner, J.M. Total nitrogen. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2; Black, C.A., Evans, D.D., Ensminger, L.E., White, J.L., Clark, F.F., Dinauer, R.C., Eds.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1965; pp. 1149–1178. [Google Scholar]
- Keeney, D.R.; Nelson, D.W. Nitrogen-inorganic forms. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2, 2nd ed.; Page, A.G., Keeney, D.R., Baker, D.E., Miller, R.H., Rhoades, J.D., Eds.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1982; pp. 643–698. [Google Scholar]
- Ming, D.W.; Dixon, J.B. Clinoptilolite in South Texas soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1986, 50, 1618–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingenfelder, U.; Nowack, B.; Furrer, G.; Schulin, R. Adsorption of Pb and Cd by amine-modified zeolite. Water Res. 2005, 39, 3287–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, T.C.; Weatherley, L.R. Continuous ion-exchange removal of ammonium ion onto clinoptilolite in the presence of contaminants. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2008, 3, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torma, S.; Vilcek, J.; Adamisin, P.; Hronec, E. Influence of natural zeolite on nitrogen dynamics in soil. Turk. J. Agric. For. 2014, 38, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.H. Soil Sampling, Preparation, and Analysis, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; p. 672. [Google Scholar]
- Paramananthan, S. Soils of Malaysia: Their Characteristics and Identification; Academy of Sciences Malaysia & Param Agricultural Soil Surveys: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2000; Volume 1, pp. 121–125. [Google Scholar]
- Malaysia Agriculture Research and Development Institute (MARDI). Jagung Manis Baru (New Sweet Corn): Masmadu; Malaysia Agriculture Research and Development Institute: Serdanag, Malaysia, 2010; pp. 3–5.
- Mulvaney, R.L.; Khan, S.A. Diffusion methods to determine different forms of nitrogen in soil hydrolysates. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2001, 65, 1284–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, O.H.; Husni, A.; Ahmad, H.M.N.; Jalloh, M.B.; Rahim, A.A.; Majid, N.M.A. Enhancing the urea-N use efficiency in maize (Zea mays) cultivation on acid soils using urea amended with zeolite and TSP. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2009, 6, 829–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Junrungreang, S.; Limtong, P.; Wattanaprapat, K.; Patsarayeangyong, T. Effect of zeolite and chemical fertilizer on the change of physical and chemical properties on Lat Ya soil series for sugar cane. In Proceedings of the 17th WCSS Symposium, Bangkok, Thailand, 14–21 August 2002; Paper No. 1987-1–1987-7. WCSS: Vienna, Austria, 2002. Available online: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/aed7/110630d1c16897a4dd82f9556dd38be636bd.pdf (accessed on 19 March 2020).
- Ferguson, G.A.; Pepper, I.L. Ammonium retention in soils amended with clinoptilolite. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1987, 51, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.L.; Alva, A.K.; Calvert, D.V.; Banks, D.J. Ammonia volatilization from different nitrogen fertilizers and effects of temperature and soil pH. Soil Sci. 1999, 164, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ros, M.; Klammer, S.; Knapp, B.; Aichberger, K.; Insam, H. Long term effects of compost amendment of soil on functional and structural diversity and microbial activity. Soil Use Manag. 2006, 22, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejada, M.; Garcia-Martinez, A.M.; Parrado, J. Effects of a vermicompost composted with beet vinasse on soil properties, soil losses and soil restoration. Catena 2009, 77, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulvaney, R.L.; Khan, S.A.; Hoeft, R.G.; Brown, H.M. A soil organic nitrogen fraction that reduces the need for nitrogen fertilization. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2001, 65, 1164–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, J.W. Chemistry and distribution of amino sugars. In Soil Biochemistry; Paul, E.A., Ladd, J.N., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1981; pp. 197–227. [Google Scholar]
- Guggenberger, G.; Frey, S.D.; Six, J.; Paustian, K.; Elliot, E.T. Bacterial and fungal cell wall residues in conventional and no-tillage agroecosystems. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1999, 63, 1188–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, T.R.; Cotta, M.A. Isolation and identification of hyper-ammonia producing bacteria from swine manure storage pits. Curr. Microbiol. 2004, 48, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadej, W.; Przekwas, K. Fluctuations of nitrogen levels in soil profile under conditions of a long term fertilization experiment. Plant Soil Environ. 2008, 54, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leinweber, P.; Schulten, H.R. Non-hydrolyzable forms of soil organic nitrogen: Extractability and composition. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2000, 163, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, F.J. Release of nitrogen from plant and animal residues and consequent plant uptake efficiency. In Humus Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Stockdale, E.A., Rees, R.M., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 229–245. [Google Scholar]
- Praveen-Kumar, K.; Tripathi, P.; Aggarwal, R.K. Influence of crops, crop residues and manure on amino acid and amino sugar fractions of organic nitrogen in soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2002, 35, 210–213. [Google Scholar]
- Ramesh, K.; Biswas, A.K.; Somasundaram, J.; Subba Rao, A. Nanoporous zeolites in farming: Current status and issues ahead. Curr. Sci. 2010, 99, 760–765. [Google Scholar]
- Polat, E.; Karaca, M.; Demir, A.; Naci-Onus, A. Use of natural zeolite (clinoptilolite) in agriculture. J. Fruit Ornam. Plant Res. 2004, 12, 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Petrovic, A.M. The potential of natural zeolite as a soil amendment. Golf Course Manag. 1990, 58, 92–94. [Google Scholar]
- Amanuallah, M.Z.; Khalil, A.K. Timing and rate of phosphorus application influence maize phenology, yield and profitability in Northwest Pakistan. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2010, 4, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, T.S.; Boettinger, J.L.; Drost, D.T.; Norton, J.M. Decreasing nitrogen leaching from sandy soil with ammonium-loaded clinoptilolite. J. Environ. Qual. 1998, 27, 656–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kithome, M.; Paul, J.W.; Lavkulich, L.M.; Bomke, A.A. Kinetics of ammonium adsorption and desorption by the natural zeolite clinoptilolite. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1998, 62, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montemurro, F. Different nitrogen fertilization sources, soil tillage, and crop rotations in winter wheat: Effect on yield, quality, and nitrogen utilization. J. Plant Nutr. 2009, 32, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habteselassie, M.Y.; Miller, B.E.; Thacker, S.G.; Stark, J.M.; Norton, J.M. Soil nitrogen and nutrient dynamics after repeated application of treated dairy-waste. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2006, 70, 1328–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Singh, R.; Prasad, J.; Kumar, B. Effect of green manuring, FYM and bio- fertilizer in relation to fertilizer nitrogen on yield and major nutrient uptake by upland rice. J. Ind. Soc. Soil Sci. 2002, 50, 313–314. [Google Scholar]
- Uher, A.; Balogh, Z. Use of zeolites for re-cultivation of sandy soils in horticulture. Acta Hortic. 2004, 7, 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Palm, C.A.; Myers, R.J.K.; Nandwa, S.M. Combined use of organic and inorganic nutrient sources for soil fertility maintenance and replenishment. In Replenishing Soil Fertility in Africa; Buresh, R., Sanchez, P.A., Calhoun, F., Eds.; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1997; pp. 193–217. [Google Scholar]

| Parameters | Values Obtained | Product Information † |
|---|---|---|
| pHwater | 6.80 (±0.03) †† | 8.0–9.0 |
| Cation exchange capacity (cmol(+) kg−1) | 100.33 (±0.35) | 160.0 |
| Total nitrogen (%) | 1.8 (±0.04) | 1.36 |
| Calcium (mg kg−1) | 18400 (±19.09) | 25600.0 |
| Magnesium (mg kg−1) | 11200 (±4.48) | 15000.0 |
| Potassium (mg kg−1) | 14850 (±10.17) | 22600.0 |
| Ammonium (mg kg−1) | 12.60 (±0.43) | Not determined |
| Nitrate (mg kg−1) | 11.58 (±0.18) | Not determined |
| Parameters | Rice Straw Compost | Paddy Husk Compost |
|---|---|---|
| Cation exchange capacity (cmol(+) kg−1) | 86 (±0.07) | 176 (±3.17) |
| pHwater | 7.6 (±0.07) †† | 7.9 (±0.03) |
| Phenolic (OH, cmol(+) kg−1) | 300 (±6.42) | 350 (±7.90) |
| Carboxylic acid (cmol(+) kg−1) | 450 (±10.39) | 400 (±11.35) |
| Total acidity (cmol(+) kg−1) | 750 (±8.08) | 750 (±6.90) |
| E4/E6 ratio † | 7.73 (±0.07) | 7.78 (±0.02) |
| Humic Acid (%) | 15.2 (±0.32) | 5.7 (±0.03) |
| Electrical Conductivity (ds m−1) | 1.1 (±0.02) | 1.2 (±0.02) |
| Carbon (%) | 27.3 (±0.42) | 28.2 (±0.52) |
| Organic Matter (%) | 47.1 (±0.73) | 48.6 (±0.55) |
| Nitrogen (%) | 1.8 (±0.06) | 1.6 (±0.03) |
| C/N Ratio | 15 | 17 |
| Ammonium (mg kg−1) | 294 (±2.84) | 362 (±2.92) |
| Nitrate (mg kg−1) | 161 (±5.23) | 172 (±1.85) |
| Phosphorus (mg kg−1) | 458.2 (±5.50) | 1097 (±0.88) |
| Calcium (mg kg−1) | 14,080 (±6.91) | 15,080 (±0.88) |
| Magnesium (mg kg−1) | 15,350 (±3.92) | 15,189 (±1.45) |
| Potassium (mg kg−1) | 27,720 (±2.72) | 27,150 (±0.88) |
| Sodium (mg kg−1) | 13,326 (±1.03) | 14,001 (±0.14) |
| Copper (mg kg−1) | 12.4 (±0.21) | 2.4 (±0.11) |
| Iron (mg kg−1) | 13.1 (±0.42) | 3.6 (±0.14) |
| Manganese (mg kg−1) | 2.1 (± 0.05) | 1.1 (±0.12) |
| Zinc (mg kg−1) | 11.8 (±0.15) | 11.2 (±0.17) |
| Ash (%) | 6.4 (±0.33) | 7.9 (±0.29) |
| Moisture Content (%) | 43 (±0.10) | 44 (±0.71) |
| Parameters | Mean Value (±Standard Error) | Standard Data Range †† |
|---|---|---|
| CEC (cmol(+) kg−1) | 9.32 (±0.03) | 5.89 |
| pHwater | 4.25 (±0.05) | 4.7–5 |
| Exchangeable calcium (cmol(+) kg−1) | 0.82 (±0.008) | 0.05 |
| Exchangeable magnesium (cmol(+) kg−1) | 0.53 (±0.05) | <0.01 |
| Exchangeable potassium (cmol(+) kg−1) | 0.36 (±0.02) | <0.09 |
| Total nitrogen (%) | 0.15 (±0.01) | 0.06 |
| Organic matter (%) | 5.51 (±0.06) | Not determined |
| Total organic carbon (%) | 3.20 (±0.09) | 1.30 |
| Total phosphorus (mg kg−1) | 0.005 (±0.001) | Not determined |
| Available phosphorus (mg kg−1) | 2.16 (±0.05) | Not determined |
| Exchangeable ammonium (mg kg−1) | 12.35 (±0.05) | Not determined |
| Available nitrate (mg kg−1) | 2.12 (±0.01) | Not determined |
| Crop Recovery of Applied N (kg kg−1) | Agronomic Efficiency of Applied N (kg grain kg−1) | |
|---|---|---|
| (Mean ± Standard Error) kg ha−1 | ||
| First Crop | ||
| T1 | 34 c (±4.40) | 12 c (±0.88) |
| T2 | 58 a (±1.52) | 29 a (±1.52) |
| T3 | 54 a (±0.88) | 27 a (±0.88) |
| T4 | 45 b (±1.73) | 19 b (±0.57) |
| T5 | 58 a (±0.57) | 27 a (±0.52) |
| T6 | 48 a (±0.88) | 23 b (±0.57) |
| Second Crop | ||
| T1 | 32 b (±0.88) | 9 c (±0.88) |
| T2 | 52 a (±0.88) | 21 ab (±2.40) |
| T3 | 48 a (±1.45) | 24 a (±0.88) |
| T4 | 33 b (±0.88) | 16 b (±1.45) |
| T5 | 45 a (±1.45) | 24 a (±0.57) |
| T6 | 39 b (±0.88) | 20 b (±1.15) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Omar, L.; Ahmed, O.H.; Jalloh, M.B.; Nik Muhamad, A.M. Soil Nitrogen Fractions, Nitrogen Use Efficiency and Yield of Zea mays L. Grown on a Tropical Acid Soil Treated with Composts and Clinoptilolite Zeolite. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4139. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10124139
Omar L, Ahmed OH, Jalloh MB, Nik Muhamad AM. Soil Nitrogen Fractions, Nitrogen Use Efficiency and Yield of Zea mays L. Grown on a Tropical Acid Soil Treated with Composts and Clinoptilolite Zeolite. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(12):4139. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10124139
Chicago/Turabian StyleOmar, Latifah, Osumanu Haruna Ahmed, Mohamadu Boyie Jalloh, and Abdul Majid Nik Muhamad. 2020. "Soil Nitrogen Fractions, Nitrogen Use Efficiency and Yield of Zea mays L. Grown on a Tropical Acid Soil Treated with Composts and Clinoptilolite Zeolite" Applied Sciences 10, no. 12: 4139. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10124139
APA StyleOmar, L., Ahmed, O. H., Jalloh, M. B., & Nik Muhamad, A. M. (2020). Soil Nitrogen Fractions, Nitrogen Use Efficiency and Yield of Zea mays L. Grown on a Tropical Acid Soil Treated with Composts and Clinoptilolite Zeolite. Applied Sciences, 10(12), 4139. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10124139






