Abstract
In addition to adverse health outcomes, neurological disorders have serious societal and economic impacts on patients, their family and society as a whole. There is no definite treatment for these disorders, and current available drugs only slow down the progression of the disease. In recent years, application of stem cells has been widely advanced due to their potential of self-renewal and differentiation to different cell types which make them suitable candidates for cell therapy. In particular, this approach offers great opportunities for the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders. However, some major issues related to stem-cell therapy, including their tumorigenicity, viability, safety, metastases, uncontrolled differentiation and possible immune response have limited their application in clinical scales. To address these challenges, a combination of stem-cell therapy with nanotechnology can be a solution. Nanotechnology has the potential of improvement of stem-cell therapy by providing ideal substrates for large scale proliferation of stem cells. Application of nanomaterial in stem-cell culture will be also beneficial to modulation of stem-cell differentiation using nanomedicines. Nanodelivery of functional compounds can enhance the efficiency of neuron therapy by stem cells and development of nanobased techniques for real-time, accurate and long-lasting imaging of stem-cell cycle processes. However, these novel techniques need to be investigated to optimize their efficiency in treatment of neurologic diseases.
1. Introduction
Neurodegenerative disorders (ND) are characterized by the progressive loss of structure or function of neurons, resulting from degeneration of selected neurons in the central nervous system (CNS). Neurological diseases have serious economic and societal impacts on patients, their family and society as a whole. There are no treatments for neurodegenerative diseases and the currently used medicines can only reduce the symptoms or slow down the progress of disease [1]. Successful design of therapies for a patient population needs careful consideration involving collaboration between clinicians, neuroscientists and bioengineers to cover both the disease aspects and clinical requirements [2].
The perception of neurogenesis have been developed during the recent cascades and the traditional concept of a static brain has been drastically altered with discovery of the presence of adult-born neurons and observation of the dynamic proliferation of progenitor cells and generation of new neurons [3]. Stem cells—which can be derived from many sources—have the potential to self-renew and differentiate to different cell types and are suitable candidates for cell therapy purposes [4]. The main purpose of cell-based regenerative therapy in the CNS is to improve neuroprotection, compensate for loss of cell function and enhance the ability to repair tissue. Cell therapy for CNS consists of cell injection into an injured brain tissue to retrieve a loss of neuron function [5]. In recent years, the application of stem cells in cell therapy for neurodegenerative diseases has attracted great interest in scientific societies [6]. Stem cells have great potential in inducing neuroprotection in a variety of neural diseases or brain injuries [7]. There are several reports of the beneficial effects of stem-cell transplantation on improvement of sensory motor and cognitive functions in stroke, Parkinson’s disease (PD), Huntington’s disease, Alzheimer’s diseases (AD), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and spinal muscular atrophy [8]. The quality of life has recently improved due to the development of science technologies and the discovery of novel methods such as cell therapy to treat degenerative disorders [1]. Despite promising results in preclinical trials, currently there is no stem-cell-based therapy. Furthermore, the application of stem cells on a clinical scale are limited due to their safety and ethical issues. Some of these concerns include tumorigenesis, stem-cell metastasis, unwanted differentiation, vital organ sequestration, irreversibility of treatment and long-term survival of transplanted cells [9,10,11,12]. For addressing some of these challenges, combination of stem-cell therapy with other technologies can be a leading solution. Nanotechnology has the potential to collaborate with stem-cell therapy and improve the efficiency of cell-based therapy thanks to the unique characteristics of nanomaterials [13]. Moreover, the marriage of these technologies can form a novel interdisciplinary field with an area of intense research [12,14]. Nanoparticles (NPs) and nanomaterials (NMs) can interact with proneurogenic factors within the stem-cell niche and thus, promote self-renewal, proliferation and differentiation of endogenous and exogenous neural stem cells (NSCs) [15]. Moreover, super-paramagnetic NPs labeled with functional peptides can be intravenously injected into injured area and significantly detected by MRI techniques [16]. The internalized modified-NPs would efficiently enhance neurogenesis and appears to be a promising approach for therapeutic purposes and drug delivery in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. In this review, we will provide an assessment of the recent advances in stem-cell therapy and the applications of nanotechnology in cell-based methods to boost the efficiency in the treatment of neurological diseases. Despite many efforts in application of nanotechnology to enhance the efficiency of stem-cell therapy for preventing neuroregeneration, the interaction between stem cells and nanoparticles remains obscure and hence, needs more investigation. We have attempted to provide an overview of nanoparticle applications across various aspects of stem-cell therapy. In particular, we have focused on the nanodelivery of stem cells for neurotherapeutic approaches and, the induction and monitoring of the differentiation process of stem cells using nanotechnology; with the overarching aim being the need to alert researchers in this field to both existing and new prospects.
2. Stem Cells and their Therapeutic Significance
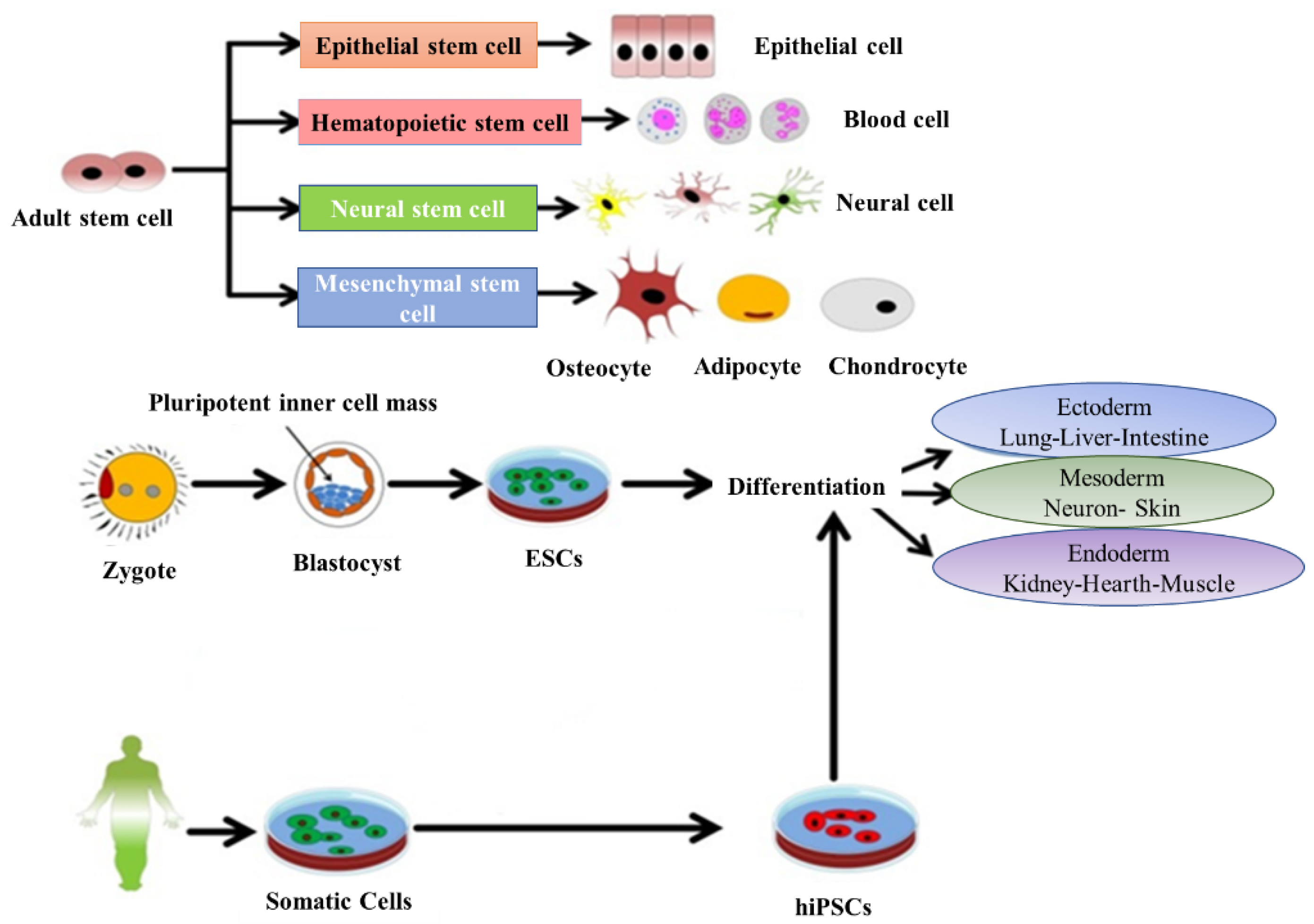
Stem cells have the potential to cure and diagnose diseases and can be also used to study the therapeutic effects of drugs. Stem cells have two origins: embryonic and adult tissues. Furthermore, based on the potential for differentiation, they are categorized into three types: (1) totipotent stem cells (with the ability to differentiated into all cell types of a living body and are able to make both fetus and placenta), (2) pluripotent stem cells (with the ability to differentiate into all kind of cells and are able to generate only the fetus and not the placenta) and (3) multipotent stem cells (can be differentiated into some limited kinds of cell) [17]. The origin of the embryonic stem cells (ESC) is within the inner mass of the blastocyst and are considered pluripotent, while the adult tissues contain mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), which are able to differentiate toward the mesodermal lineage (i.e., osteoblasts, adipocytes and chondrocytes) (Figure 1). Despite their greater proliferative and differentiative potential, the use of ESC for clinical applications due to medical ethics and possible immune rejection is limited. By contrast, the number of researchers who have turned to MSCs and NSCs are increasing rapidly. The transplanted MSCs due to ability of migration to the damaged or inflamed tissues have regenerative potential and they can improve tissue hemostasis by increasing the nutrient supply to endogenous cells [18]. MSCs are capable of inhibiting apoptosis and fibrosis, while enhancing angiogenesis, stimulating mitosis and/or differentiation of tissue-resident progenitor cells and modulating the function of immune system [19]. There is evidence for the potential of MSCs to support tissue protection and repair due to secretion of paracrine factors. They have been proven to be effective in stimulating the structural and functional regeneration of many tissues such as cardinal, renal, tendon and spinal cord [13,19,20]. Therefore, they can be considered as a powerful tool for therapeutic applications. Cell therapy is a promising approach to treat various diseases where common drugs administration could not be fully effective. Moreover, many conventional drugs show limitations in the aspect of their dosage or time window. Nowadays, tailored medicines have attracted greater attention and the engineered drugs derived from cellular and molecular approaches have become more developed [21]. Most research efforts in this field focus on producing tailored medicines with the capacity to regenerate the structure and function of defective organs. The regenerative therapeutic medicines directly target patient cells, e.g., cell cycle components or cell metabolites. Therefore, they exert considerable influence on the regenerative process by recovering cell division and cellular transformation [21].
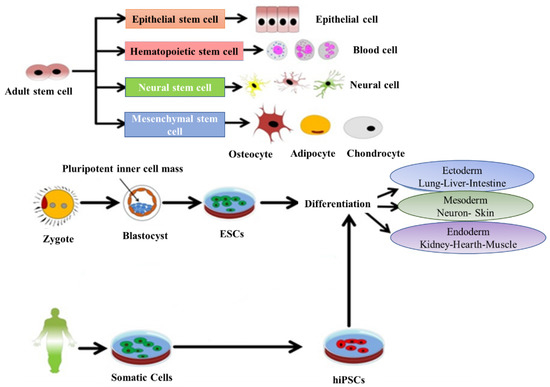
Figure 1.
Representative diagram depicting the main types and sources of stem cells and their potential to differentiate into various lineages. Adapted with permission from [22], Abdal Dayem et al., 2018.
2.1. Cell Therapy of Neural System Using Stem Cells
The complex structure of the brain and central neural system make them more restricted to access and understand the mechanism of diseases related to these regions. Their successful treatment is not yet feasible and thus prevention and neuroprotection become more important than cure. Telomerase enzyme inside the cells have a protective function against neurons damage. Stem-cell therapy techniques have been recently developed; and similar to telomerase enzyme activity, have the ability of protection and maintenance of neuron function. [17].
For many years, it was believed that CNS tissue does not have the ability of renewal, but recent studies have challenged this dogma. Numerous experiments have been successfully carried out on the application of neural stem cells (NSC) or neural precursor cells (NPC) for transplantation therapy for CNS diseases.
Throughout human life, like most other mammalian species, generation of new neurons through a process known as neurogenesis are carried out by NSCs. Generation of new neurons will occur in the subventricular zone (SVZ) of the lateral ventricles and they reach the olfactory bulb through the rostral migratory system. Simultaneously, movement of the new hippocampal granule neurons to granule cell layer leads to formation of a chain network of migrating neuroblasts which eventually differentiate into various neural cells [16,23].
In most known neurodegenerative diseases, neural cell structures are affected and eventually lose function. Therefore, successful regenerative therapy can be achieved by replacement of damaged neurons with the new ones or by restoration of neural tissue/organs [2]. The progress of cell therapy techniques in transplantation of stem cells has improved the shortage of neuron function in both acute and chronic neurodegenerative disorders. During the last few years, the advance in transplantation techniques of human or animal stem cells has expended much effort in preclinical brain research. This method also has the advantage of increasing the restorative response to CNS injury, which can be directly triggered by the stimulation of activated astrocytes. This response is believed to be mediated by different trophic and growth factors, such as nerve growth factor, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, vascular endothelial growth factor, fibroblast growth factor and erythropoietin. These factors can play neurotrophic roles for neural stem cells in vitro and can also retain neurogenesis in the adult CNS. Cell therapies have been developed to aid in CNS injuries, but to succeed in therapeutic approaches of stem cells therapy it is necessary to fully understand the physiological mechanism related to neurological diseases. Since current knowledge in neural development is incomplete, it is unclear whether these findings obtained in vitro can be operational for in vivo experiments or not.
However, implantation of stem-cell scaffolds may induce a host tissue response. Encapsulation of stem cells can be a promising approach to minimize immune response and facilitate safety issues. Encapsulation can also promote the application of stem-cell therapies in clinical trials. Some preclinical reports demonstrated the feasibility and efficacy of microencapsulation methods for coating individual cells in AD models. For example, encapsulation of human mesenchymal stem cells with glycan-like peptide and their transplantation in an AD mouse model decreased amyloid deposition or suppression of glial and microglial responses [24]. Furthermore, other studies demonstrated the improvement of stem-cell survival and the cognitive abilities in AD mouse models using the encapsulation of neural stem cells (NSCs) within different types of hydrogels (e.g., dextran dialdehyde cross-linked with gelatin) [25,26]. Biodegradable collagen scaffolds can be placed on brain slices without any toxic response on dopamine neurons and thus, using these scaffolds, potentially provide a novel and promising approach to enhance dopaminergic cell survival and controlled release of neurotrophic factor in the brains of PD models [27]. Lastly, it has been demonstrated that the pretreatment of neuroblastoma cells with controlled release of MSCs from biodegradable hydrogels produced neuroprotective factors in a PD-relevant experimental context [28].
These are promising findings which provide strong proof of ability of the destroyed brain tissue to be recovered similar to the other tissues and organs in body. Therefore, stem-cell therapy provides solutions to overcome the clinical challenges in neurologic fields [29].
2.2. Stem-Cell Types in Regenerative Therapy
Various cells can be considered in tissue engineering, stem or modified cells to replace lost neurons and somatic cells due to their neuroprotective potential. In order to develop safe and effective cell therapy methods that can be translated to clinical applications, it is important to understand the inherent characteristics of these potent cells; for instance, their engraftment, distribution pattern, differentiation and survival rate.
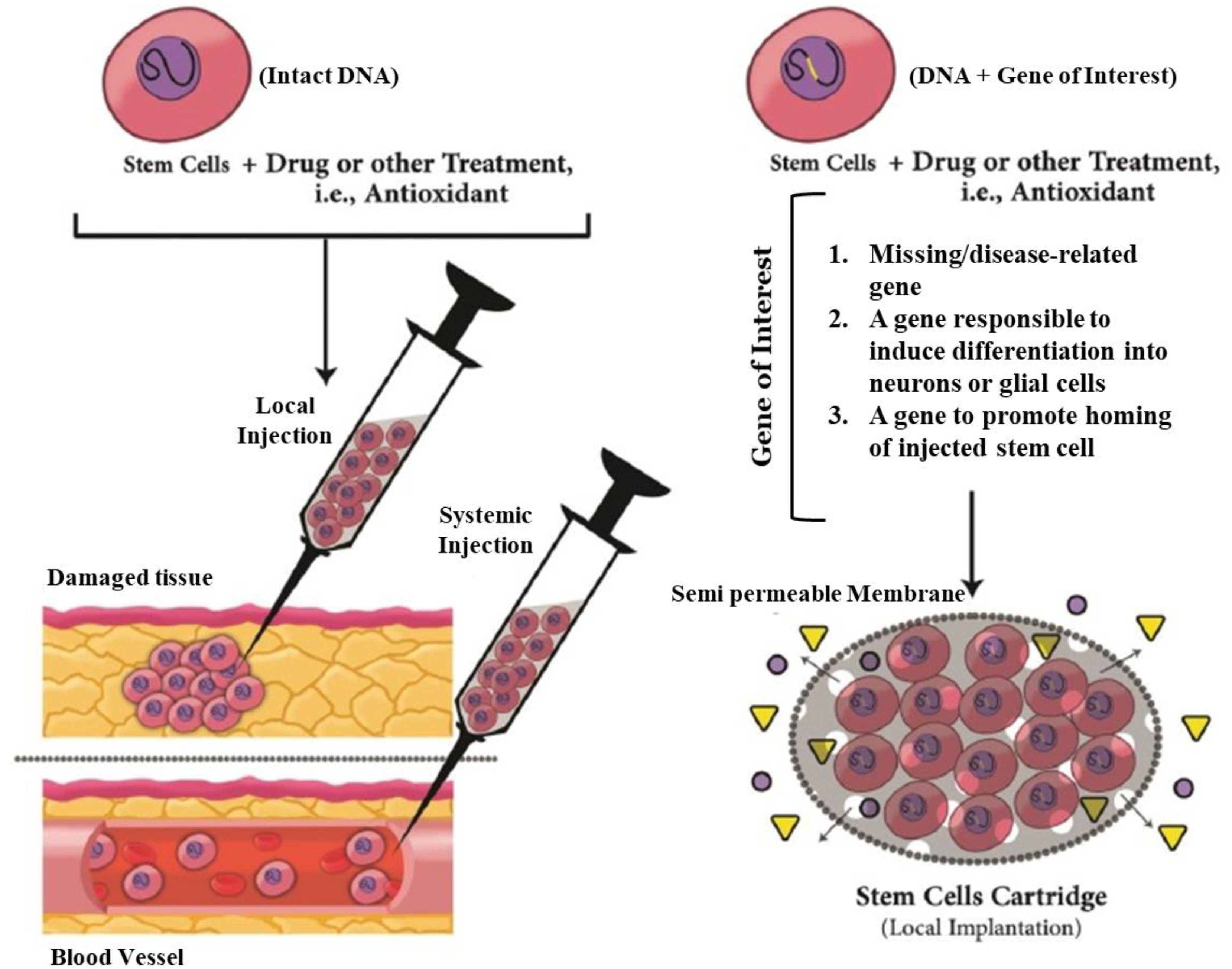
Moreover, recognition of the differentiation process of stem cells is critical to enhance the treatment success of neurological diseases such as AD and PD. Finding the stem-cell “niche”, the specific microenvironment of stem-cell generation, is an important factor in order to utilize the regenerative potential of these cells for treatment of neurodegenerative diseases [30]. The recognition of the NSC and their potential for neurogenesis has attracted researchers to assess the feasibility of their application in treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. NSCs have the ability to self-renew and generate multiple neural lineages, e.g., axonal regrowth or cell replacement [31]. They are able to differentiate into the three main cell types present in the central nervous system: neurons, astrocytes and oligodendrocytes [30]. Recently, numerus studies have been focused on stem-cell based therapies as promising solutions for treatment of CNS-related diseases and disorders [32]. Currently, for neurological repair therapy the main used stem cells are comprised of NSCs, neuroprecursor stem cells, induced pluripotent stem cell (iPS cells), mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) and embryonic stem cells (ESC). The efficacy of differentiation of stem cells can be also improved genetically for transfer of new genes to induce better differentiation into neural lineages or to secrete defined therapeutic compounds (Figure 2) [32].
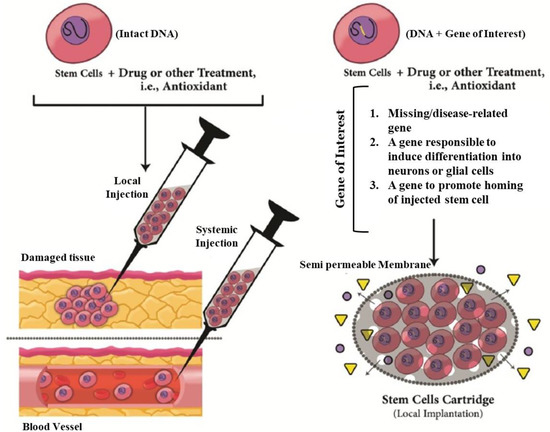
Figure 2.
Strategies and innovations to get better outcomes in treatment of neurodegenerative disease by stem-cell therapy. In addition to other drug or treatment, approaches could be used innate trophic actions of stem cells. Furthermore, stem cells could be genetically engineered to secret a specific therapeutic factor into site of neural damage by a novel carrier system like a cartridge. The engineered cells could deliver new therapeutic genes, differentiation induction genes or migration-induced gene or a missing/disease-relevant gene product. Adapted with permission from [33], Mirahmadi et al., 2016.
Some researchers have selected the iPSs as the most promising autologous source of stem cells which can be generated by genetic reprogramming of transcription factors of autologous somatic cells (e.g., fibroblasts). Novel gene editing techniques have been used for generating genetically corrected lines from patient derived iPSCs and/or for induction of mutations in control cell lines. They have attracted the attention of researchers for their apparent similarity to ESCs; while iPSCs grafts avoid the ethical issues intrinsic to human ESC work. The iPSCs are derived from individual patients, so they can be used for modeling diseases on a patient-by-patient basis. This makes the opportunity of screening the genomic variations among individuals that may aid in early diagnosis and preventing the progression of disease and also can be effective in finding the most appropriate pharmacological compounds for each individual. The striatal neuros derived from iPSCs obtained from Huntington’s disease (HD) patients, provided an in vitro disease model of HD [34].
The unilateral transplantation of syngeneic somatic NSCs within the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNps) of aged PD mice revealed a considerable ability of grafted NSCs to fix nigrostriatal functionality [35]. In another study, to investigate the effectiveness of NSC transplantation, the NSCs were isolated from postnatal day 14 mice and transplanted to the hippocampus in the mouse AD model. Results revealed the enhance of survival, differentiation and improvement of brain memory in transplanted mouse [36]. In another effort to examine the potential of transplanted NSCs for improved AD symptoms, they were modified to express metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9), a protease with ability of degradation of aggregated Aβ peptides. The injected engineered MMP-9 NSCs were able to survive in the AD mouse brain but were mainly distributed in the white matter tract and were unable to migrate to amyloid plaques. It can be concluded that in spite of significant achievements in NSCs transplantation, to enhance their therapeutic efficiency, their delivery procedure needs to be improved [37,38].
There is also research proving safety and competence of MSCs in treatment of neurodegenerative diseases such as stroke, trauma and HD [39]. MSCs can be easily restored and do not need the intake of immunosuppressants. The unilateral transplantation of autologous bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs) were performed into the sublateral ventricular zone of PD patients, by stereotaxic surgery. Following up the patients for a period of 10 to 36 months indicated a subjective improvement in symptoms like facial expression, gait, freezing episodes and significant reduction in the dosage of PD medicine. The results also represented the safety of the protocol and no considerable adverse events were observed after stem-cell transplantation [40]. The safety of intraarterial (IA) delivery of MSCs for acute ischemic stroke was evaluated in a rat model of reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion (rMCAo). The findings suggested the IA delivery of MSCs in rodent model of stroke can be carried out safely and delivered efficiently at the maximum tolerated dose at 24 h [41]. BM-MSCs can play a stimulatory role in neurogenesis and angiogenesis process in stroke therapy. They can act as small biologic pumps that secrete cytokines and growth factors with autocrine effects on themselves and paracrine effects on their neighbor resident cells. Their activity can lead to reduction of apoptosis in the affected area. There is also evidence of migration of implanted BM-MSCs and their combination with local cells or differentiation into other cells types, including glia or neurons. Therefore, they can be considered as promising candidates for neurodegenerative related stem-cell therapy purposes [42,43].
3. Application of Nanotechnology in Stem-Cell Therapy
Stem cells are a source of donor cells in regenerative medicine. In particular, induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) provide a unique opportunity for self-therapies in a personalized approach [21]. In addition, the efficiency of NSC-mediated treatment of neurological disorders has been proven by numerous studies and it can be a promising approach to treat various neuron disfunction problems.
Although, a growing number of researchers have discovered therapeutic advantages of NSCs in neurological disease therapy, there are serious obstacles in their clinical application. The main limitations including screening the migration of NSCs to the injured tissues, their directional differentiation and real-time imaging-guided therapy in vivo [44,45]. These challenges are due to the interactions of NSCs with a variety of internal or external factors, mainly extracellular matrix (ECM), surrounding cells, growth factors and inflammation at the damaged site. Therefore, to achieve success in the application of NSC-mediated therapy and to overcome the obstacles of using stem cells in clinical scale, these issues must be resolved. The unique properties of nanomaterials such as high surface-to-volume ratio (S/V), high surface energy, distinctive mechanical, thermal, electrical, magnetic, and optical behaviors make them appropriate to address barriers in neural stem-cell therapy [32,46]. Improvement of the efficiency of stem-cell culture system through nanomaterials can be carried out by various methods such as direct addition of NMs to the culture media, coating of culture container and also conjugation of NMs with specific scaffold for 3D culture systems. Nanomaterials will exhibit various aspects of interaction with membrane or intracellular constituents of stem cells which consequently the internalized NPs will modify the cellular signaling pathways [22,47,48,49]. Here we will discuss about how the marriage of stem-cell therapy with nanotechnology approaches, e.g., application of nanoparticles (NPs) or nanoengineered compounds, can help in overcoming these obstacles to allow clinical application of NSCs therapy. By recently developed synthetic and modification methodologies, engineered NPs can be designed to desired sizes, shapes, compositions and properties. Moreover, the combination of bioorganic/bioinorganic techniques with chemistry facilitated fabrication of multiple functionalized NPs as nanoengineered compounds [46].
3.1. Nanosubstrates for Large Scale Production of Stem Cells
One of the major advantages of nanotechnology in stem-cell research is the preparing of the substrate for producing stem cells in large scales. Much effort has been focused mainly on the amplification of neural cells, which has significant impact on the development of the therapies for treatment of neurodegenerative diseases [21]. Having a mass culture of cells which can efficiently remain undifferentiated during mass production process, is one of the most essential prerequisites for cell transplantation procedures [50].
Metallic nanoparticle (NPs) have a unique potential in terms of their application over a wide range of biomedicine, due to their specific physicochemical characteristics such as locating high energy atoms on their surface area. For example, in the transformation process of gold nanorods by using laser photofragmentation method, if the rate of photothermal heating increases, the internal energy of the lattice elevates and high-energy channels above that of melting open up. In this technique, using a nanosecond laser with longer pulse helps in opening up these channels, result in more photon absorption during the longer pulse, and as a consequence, would increase the lattice internal energy. There are various studies indicating the considerable influence of metallic nanoparticles (NPs) on proliferation and differentiation of different types of cells including stem cells. Intriguingly, there are various mechanisms which are involved in the proliferation and differentiation of stem cells via metallic NP-induced procedures, such as modulation of signaling pathways, generation of reactive oxygen species and adjustment of different transcription factors. Metallic NPs and their possible potential of toxicity, in vivo and in vitro have significant effects on stem-cell differentiation and proliferation [22]. Superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO) NPs are a type of IONPs (iron oxide NPs) that possess superparamagnetism properties which enable them to migrate to the injured site, so they can be a promising tool for regenerative disease therapy [51]. SPIO- (Ferucarbotran)NPs are able to promote the proliferation of human MSCs (hMSCs) via counteracting intracellular H2O2 and improve the progression of the cell cycle through upregulation of the proteins related to cell cycle, such as cyclin D1, cyclin B and cyclin-dependent kinase 4. Therefore, SPIO-NPs can be used as a safe nanomaterial resource to enhance proliferation of stem cells [52].
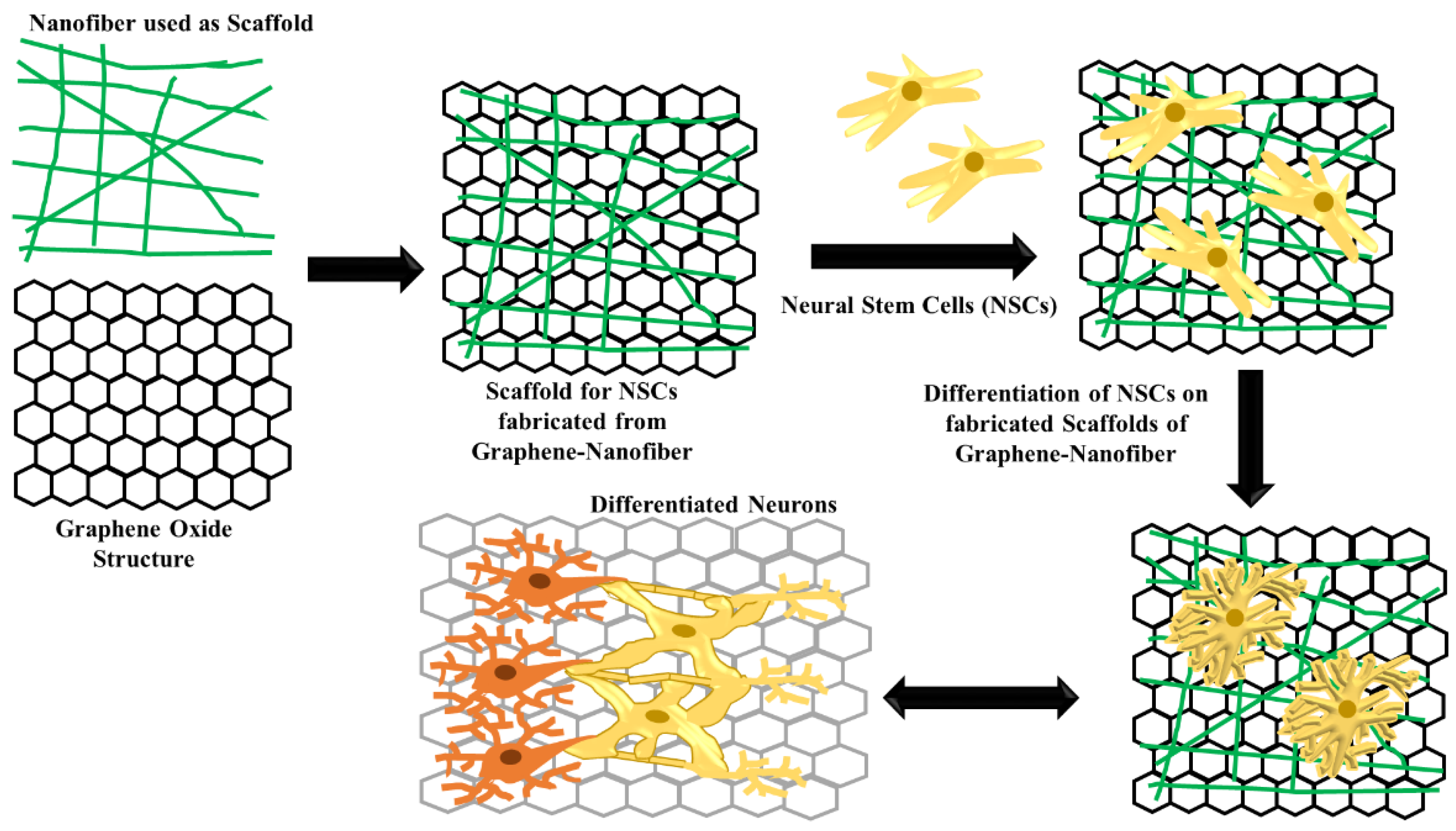
To maintain the pluripotency, iPSCs generally need to be cultured on the feeder layer cells. Due to the high biocompatibility at low concentration and 2D structure with ultralarge surface area, graphene (G) and graphene oxide (GO) have recently been developed as cell culture substrates. The culture of mouse iPSCs can be supported by G and GO which allow spontaneous differentiation of stem cells. These graphene structures induce discrete cell proliferation and differentiation properties (Figure 3). iPSCs culture on the G surface represent similar rate of cell adhesion and proliferation compare to glass surface, while GO surface exhibit faster rate of adherence and proliferation. Moreover, G have another advantage of maintaining the iPSCs in the undifferentiated stage while GO accelerates the differentiation [53].
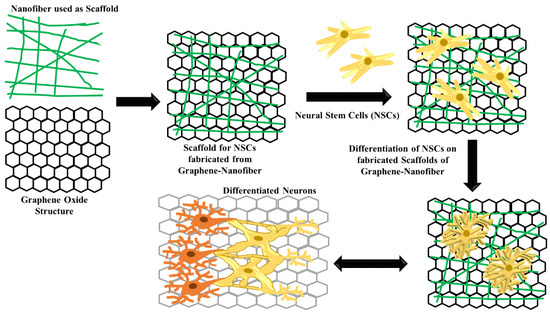
Figure 3.
Schematic representative of scaffold structure fabricated from graphene–nanofiber for differentiation of neural stem cells.
3.2. Nanomedicine for Modulation of Neural Stem-Cell Differentiation
The application of biomaterials, including nanoparticles will be a benefit to the regenerative medicine over the use of existing media that facilitates cell growth and differentiation into specific lineages. Based on size-dependent cellular uptake rates, NPs in size range of 20–70 nm have shown the best efficiency for stem-cell differentiation [46,54]. Using tissue engineering technology, stem cells have the potential to produce patient-specific tissues or cells without concern of immune rejection. The culture of stem cells along with the nanoparticle-including biomaterials aids in effectively differentiation of stem cells into a specific lineage of mature cells or tissues. They can also remain undifferentiated and maintain their self-renewal activity [55]. Development and design of self-assembling, biodegradable nanoparticles of poly (β-amino esters) for embedding plasmid DNA within the nanoparticles results in successful, high-efficiency transfection of hESCs (Human Embryonic Stem Cells). It has been demonstrated that hESCs transfected with this procedure maintain their viability, undifferentiated state, and pluripotency following transfection with nanoparticles [56].
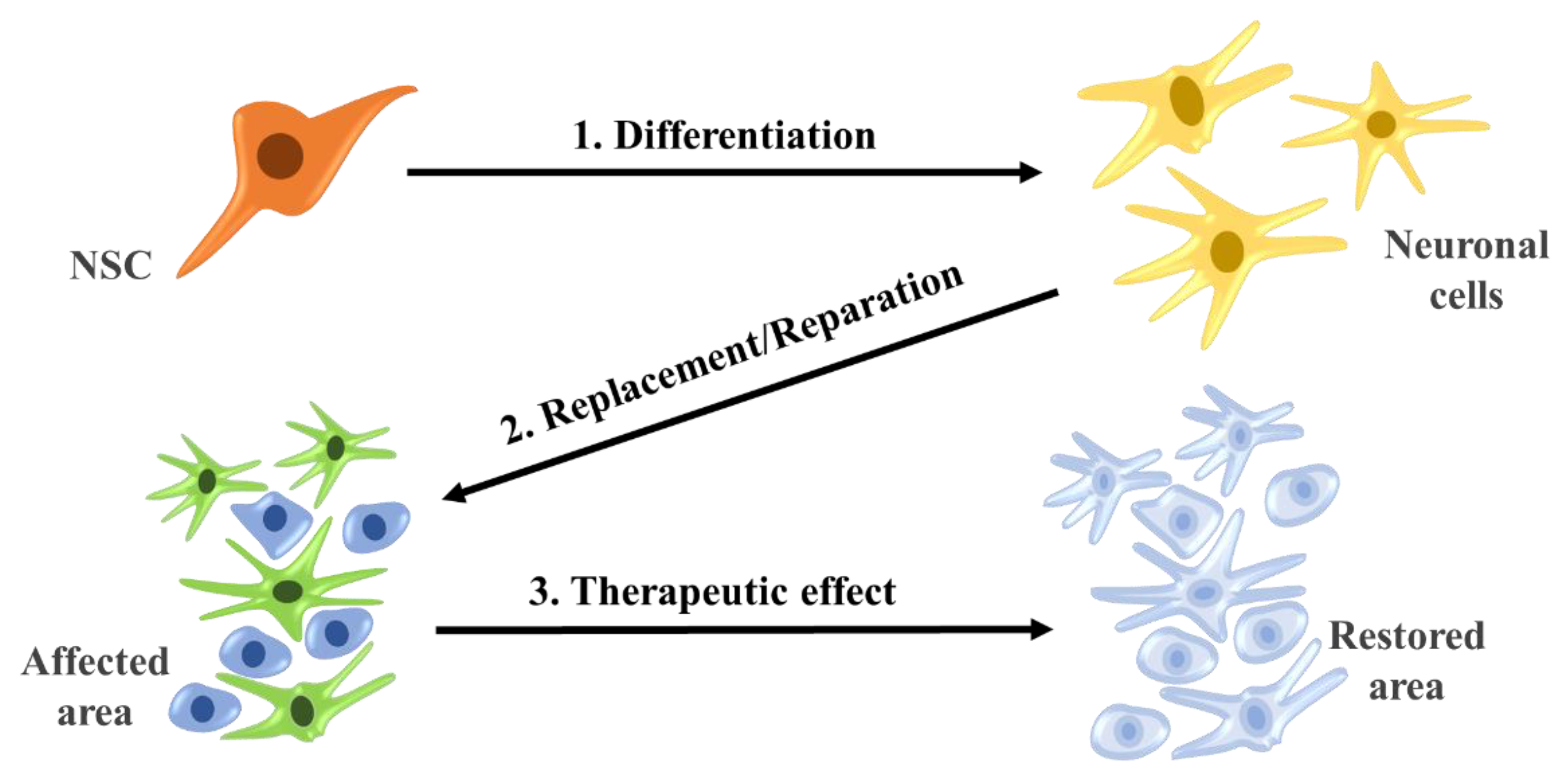
Linking tissue engineering technology and stem cell-based strategy can aid in producing regenerative medicine and facilitate therapeutic replacement of injured or damaged tissues. Some tissue-specific stem cells have the ability of mutual dedifferentiate, redifferentiate or also transdifferentiate of certain cell types in response to particular chemical or physical stimuli (Figure 4) [57].
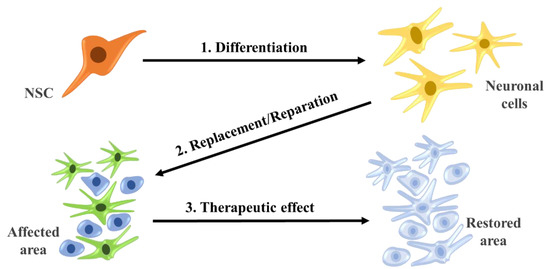
Figure 4.
Differentiate and reparation of neural stem cells with therapeutic effects.
In order to be successful in the therapeutic replacement of tissue, it is necessary to enhance the interaction of the cells and tissues by combination of a beneficial physical microenvironment and cellular biochemical signals.
Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs), including the iron oxide core and magnetic coating, have specific properties such as high saturation magnetic moment, relatively stable chemical features and minimized potential toxicity [58]. Conjunction of nanomaterial compounds with SPIO co-covered with photonic ZnO can facilitate noncovalent binding of nanostructure and functional proteins which leads to enhancement in the catalytic function of key proteins in the stem-cell cycle and effectively improves the differentiation of stem cells. Modified core-shelled nanoparticles including an SPIOs have been developed for modulation of stem-cell expansion and transdifferentiation, in vitro and in vivo. Therefore, stem cells along with nanomaterials have a good potential for developing the regenerative medicine and controlled neurogenesis [55]. Loading of polymeric nanoparticles (dextran sulfate and polyethylenimine) with retinoic acid (NP–RA) is another safe and efficient method to restore the ischemic brain by preparing a proangiogenic environment which improves neurogenesis and neural recovery. This complex compound increased proliferation of endothelial cell and formation of tubule network and also provided a protective property against ischemia-related death. In an effort to examine the efficiency of NP–RA on improving neural stem-cell differentiation and survival, endothelial cell-conditioned media (EC-CM) were examined and the findings revealed that NP–RA can protect these cells from ischemic death. NP–RA compound also stimulated the release of proliferation-related factors and induced differentiation signals for neural stem cells. It has been determined that NP–RA have efficiently increased the hEPC proliferation 83-fold more than RA-alone. Therefore, the various complexes of NP–RA can be considered as powerful neurogenic agents for vascular diseases or neurodegenerative disorders incorporated with vasculature [59].
3.3. Nanodelivery of Stem-Cell for Neuron Recovery
Neurogenesis occurs via neural stem cells which are located in special points called niches, such as subventricular zone, subgranular zone in the brain and central canal (CC) in the spinal cord [60,61]. NSC-based therapeutic approach have the potential of neuron repair or replacement by NSC transplantation at the injured point. However, the most important limitation in this method is the high rate of implanted cell mortality, availability and metastases. Thus, inducing endogenous NSC in situ to stimulate their differentiation to neural cells is a probable solution for this problem [62,63]. While this method may address the issues related to NSC transplantation, selective NSC targeting is the more difficult restriction for development of transplantation approach. Carradori et al. have provided lipid nanocapsules (LNC) to encapsulate the NFL, a synthetic peptide involved in differentiation of SVZ–NSC. The most significant advantage of NFL compared to other cell penetrating peptides is the stronger interaction of NFL with LNC via energy-independent mechanism. They demonstrated that NFL–LNC complexes have preferably been taken up by neural brain stem cell, while they did not interact with spinal cord stem cells. In vivo results confirmed in vitro findings, indicating NFL–LNC has a good potential for delivering bioactive molecules to brain targeting neural stem cells [64]. Metal oxide NPs such as iron oxide (Fe3O4), cerium oxide (CeO), and zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles have all been developed to be used in imaging techniques and also as therapies to minimize oxidative stress in the brain [65]. Applying an external magnetic field prior to systemic injection of Fe3O4 NPs can improve passing the NPs through the blood brain barrier (BBB) and reaching the brain parenchyma.
The heterogeneity and uniformity of stem-cell differentiation is a critical issue to avoid tumorigenesis. The activation of immune response due to inhospitable host environment is another obstacle for successful transplantation of stem cells for regenerative purposes. Development of intracellular delivery of functional molecules, such as drugs, DNA, RNAi, peptides and proteins is a practical solution to control the stem-cell differentiation [66,67]. The dynamic external magnetic of SPIO gold NPs coated with nerve growth factor (NGF) enable them to induce neuron growth and differentiation. Moreover, immobilization of short hairpin RNA (shRNA) onto the Fe3O4 NPs can reduce neural apoptosis in a model of Parkinson’s disease [65]. Among several biomolecules capable to differentiate stem-cell progeny to desired lineage-specific precursors [68], retinoic acid (RA) is an ideal candidate to activate gene transcription related to cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis. Manipulation of endogenous stem cells from their neurogenic niche, can trigger neurogenesis and enhances regenerative potential of brain. In a study by Maia et al. the ability of polyelectrolyte NPs to intracellularly release of RA and consequently to induce differentiate the SVZ cells into neurons was investigated. They demonstrated that these NPs in concentrations below 100-µg/mL have no harmful cytotoxic effects and do not interfere with cell morphology and proliferation. They showed RA–NP internalization improved neurogenesis and also revealed the importance of their influence in stem-cell differentiation; and thus, they can be considered as an excellent choice for drug delivery into the brain and cells. These modified NPs offers an opportunity for delivery of neurogenic-inducing factors such as key proteins, peptides, DNA and RNAi which ultimately can aid in neurodegenerative disease treatment [69]. Thus, the nanoparticles with covalently conjugated drugs can transport bioactive compounds and functional factors due to their surface characteristics, size and charge (Figure 5).
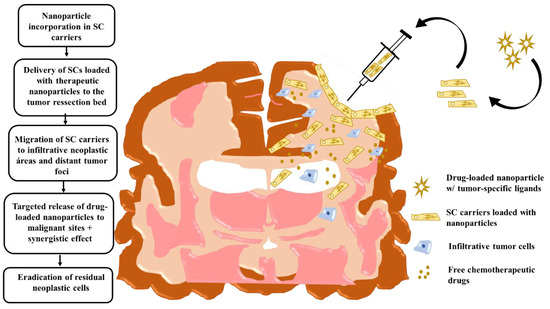
Figure 5.
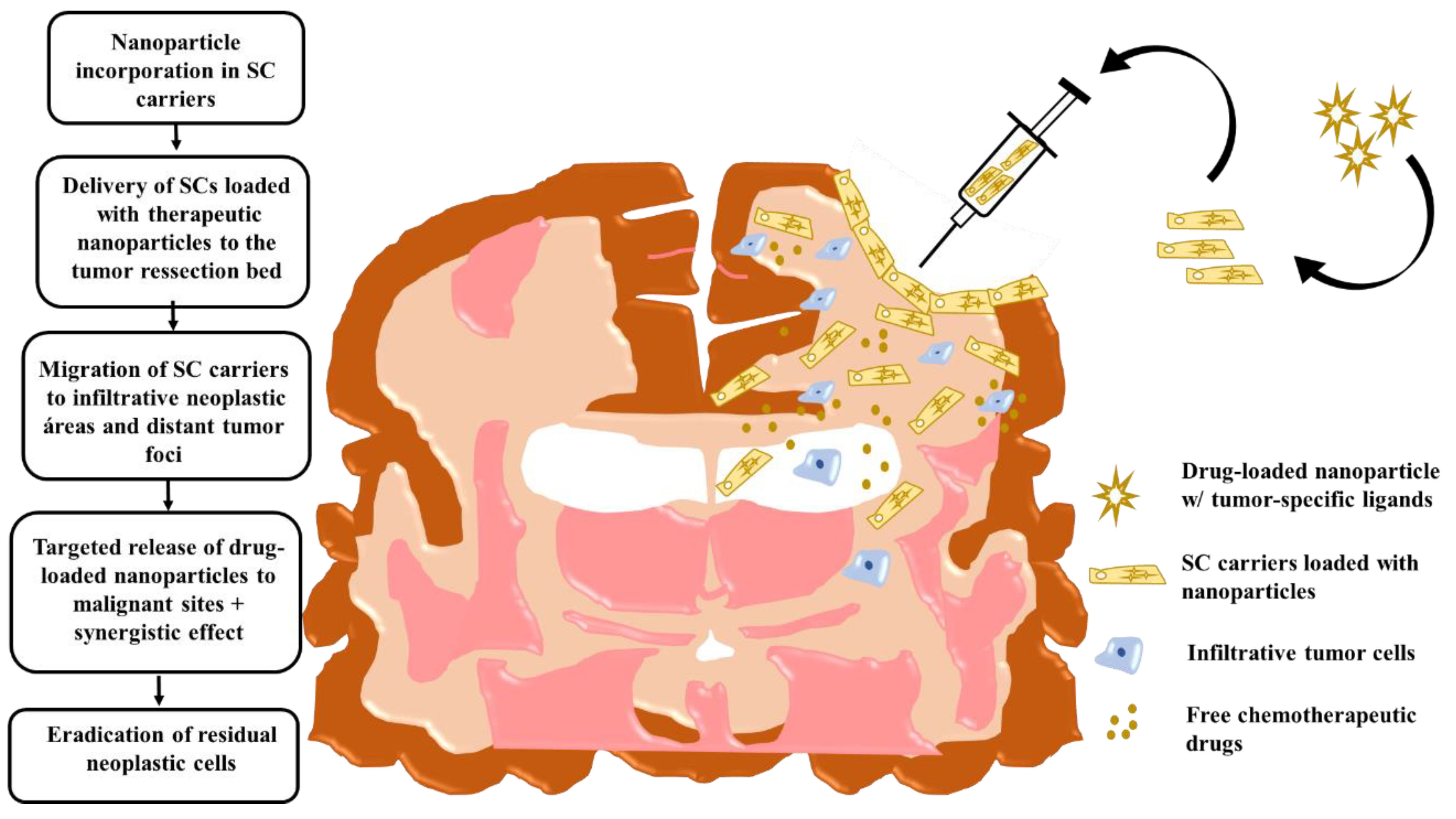
Intraoperative transplantation of stem cells carrying drug-loaded nanoparticles into the human brain post-tumor resection. Chronological order of the events that take place post-surgical transplantation. Here, stem-cell carrier tumor-tropic migration results in a targeted drug release in infiltrative tumor zones. Modified cell carriers contribute to the local toxic effects caused by the drug-loaded system in neoplastic areas. Stem-cell immunosuppressive properties hide loaded nanocarriers from the host-immune system and facilitate targeted anti-glioma therapy. Adapted with some modification from [70], Auffinger et al., 2013.
3.4. Nanotechnology Application for Monitoring Stem-Cell Therapy Progress
The effective treatments for AD rely on the early diagnosis by detection and quantitation of AD biomarkers. With its relatively large size and being located intercellularly, amyloid β (Aβ) can be considered as a suitable imaging biomarker. Therefore, tracking the deposition of Aβ is one of the primary histopathologic methods to control AD progress [71]. By MRI technique, accumulated amyloid β plaques and inflammatory responses of neurons can be detected via anti-amyloid targeted superparamagnetic IONPs. The SPIONs have beneficial for improve the MRI sensitivity acting as in vivo or in vitro contrast agents (CAs) and thus have unique potential for biomedical applications, namely as MRI CAs (Figure 6) [72]. Moreover, gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) due to their gold core have several specific optical features, namely plasmonic properties, which make them ideal candidates for imaging applications. In particular, surface plasmon resonance (SPR) of gold particles is the resonation of surface conduction electrons induced by the oscillating electromagnetic wave generated by light striking the particles. By these optic features, AuNPs through X-ray and micro-CT scanning can absorb and reduce X-rays more efficiently than traditional CT contrast agents.
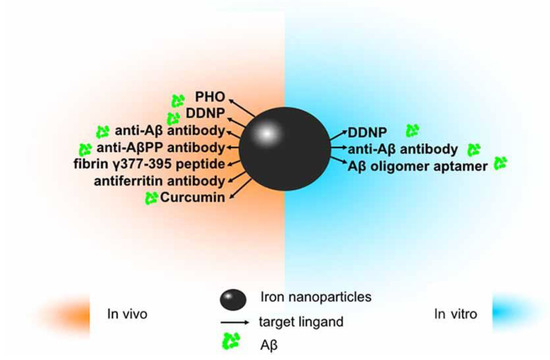
Figure 6.
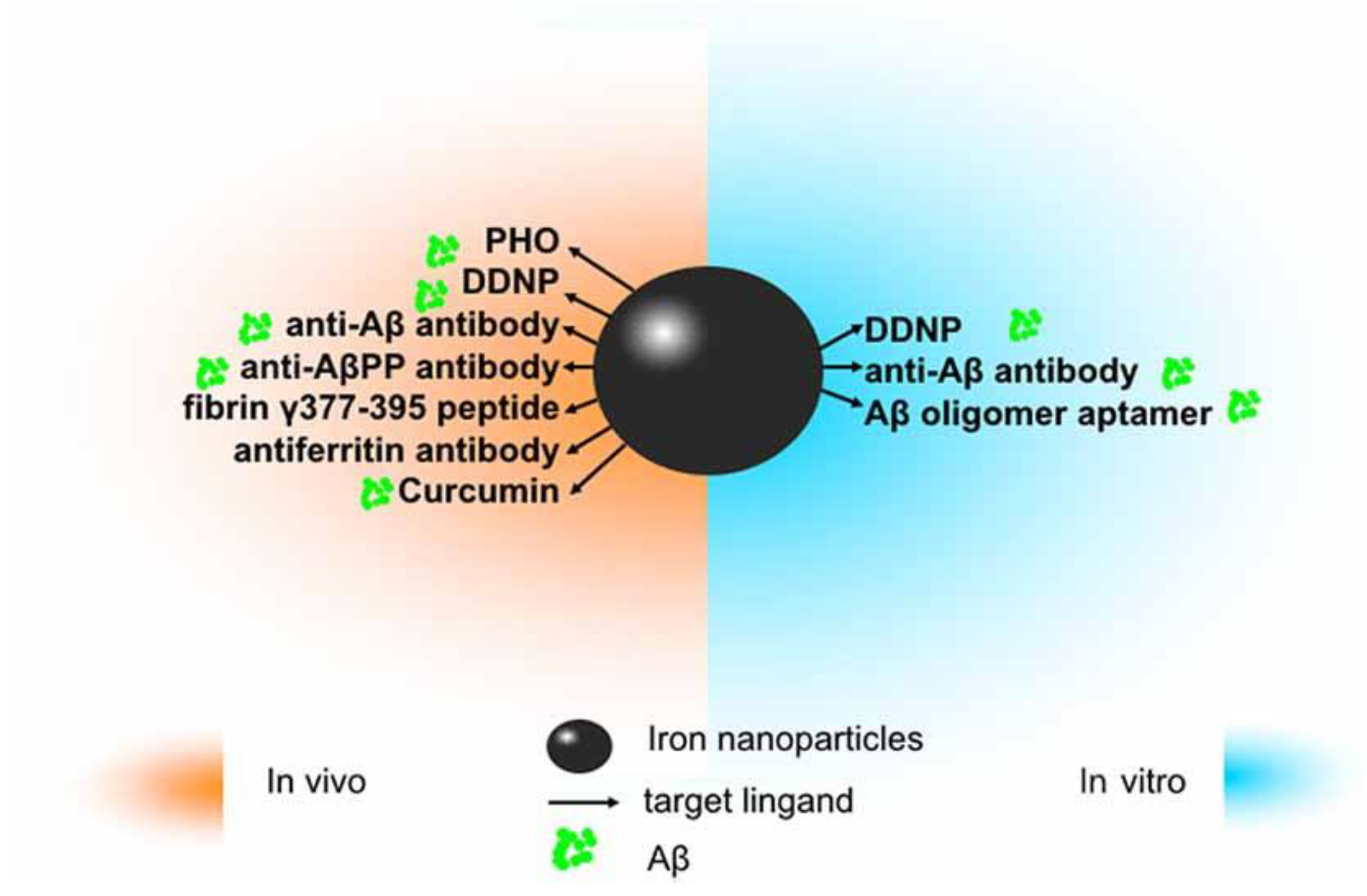
The application of iron oxide nanoparticles (IONPs) in diagnosis and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Since amyloid β (Aβ) has been identified as an ideal imaging biomarker of AD at present, with the help of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), IONPs can be used for the detection of Aβ to assist in diagnosis and treatment of AD. In vitro, magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) labeled with antibodies against Aβ-40 and Aβ-42 is applicable to detect Aβ in the blood. Conjugated with the Aβ oligomer aptamer and the complementary oligonucleotide of the Aβ oligomer aptamer, IONPs can be developed as a method to measure the Aβ oligomer in the artificial cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). DDNP-superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) with high affinities to Aβ aggregates can be detected by fluorophotometry. In vivo, ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide (USPIO)-PHO could mark amyloid plaques in the NMRI mice brain; anti-Aβ protein precursor (AβPP) antibody-conjugated SPIONs can visualize the number of plaques in AβPP/PS1 transgenic mice. DDNP–SPIONs nanoparticles significantly decrease the signal intensity (SI) in the hippocampal area in the rat AD model. Curcumin-conjugated superparamagnetic iron oxides (SPIOs) can detect amyloid plaques in Tg2576 mice brains. Fibrin γ377–395 peptide-conjugatedγ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles could specifically inhibit the microglial cells in rTg4510 tau-mutant mice and thus provide a possible therapeutic strategy towards neurodegenerative tauopathies. In addition, magnetic IONPs bound to an anti-ferritin antibody were developed to detect ferritin protein in areas with a high amount of amyloid plaques in the brain of a transgenic AD mouse model. BBB, blood–brain barrier. Adapted with some modification from [72], Luo et al., 2020.
Development of NSC transplantation approach has led to considerable progress in reducing central nervous system damage or restitute the brain function [73]. A better understanding of the position of transplanted NSCs has improved the efficiency of this approach. Cell tracking methods have revealed the potential of optimizing transplantation therapy via providing accurate picture of the fate and area effect of implanted cells. The main obstacle in application of stem-cell therapies at the clinical-scale is the evaluation of the precise location of implanted cells and the status of graft host cells in vivo [74]. Until recent years, mapping the in vivo control over specific differentiation, dynamic behavior and dispensation of implanted cells were major issues of this technique. In vivo imaging of transplanted cells is based on tagging these cells and following their differentiation from host tissue, like the brain (Figure 7) [75].
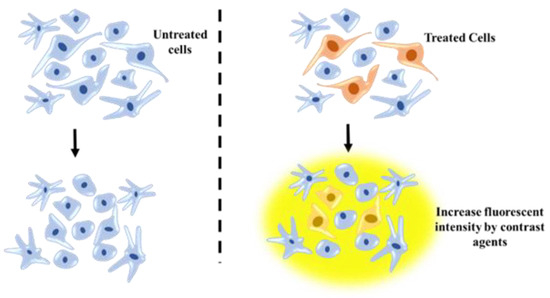
Figure 7.
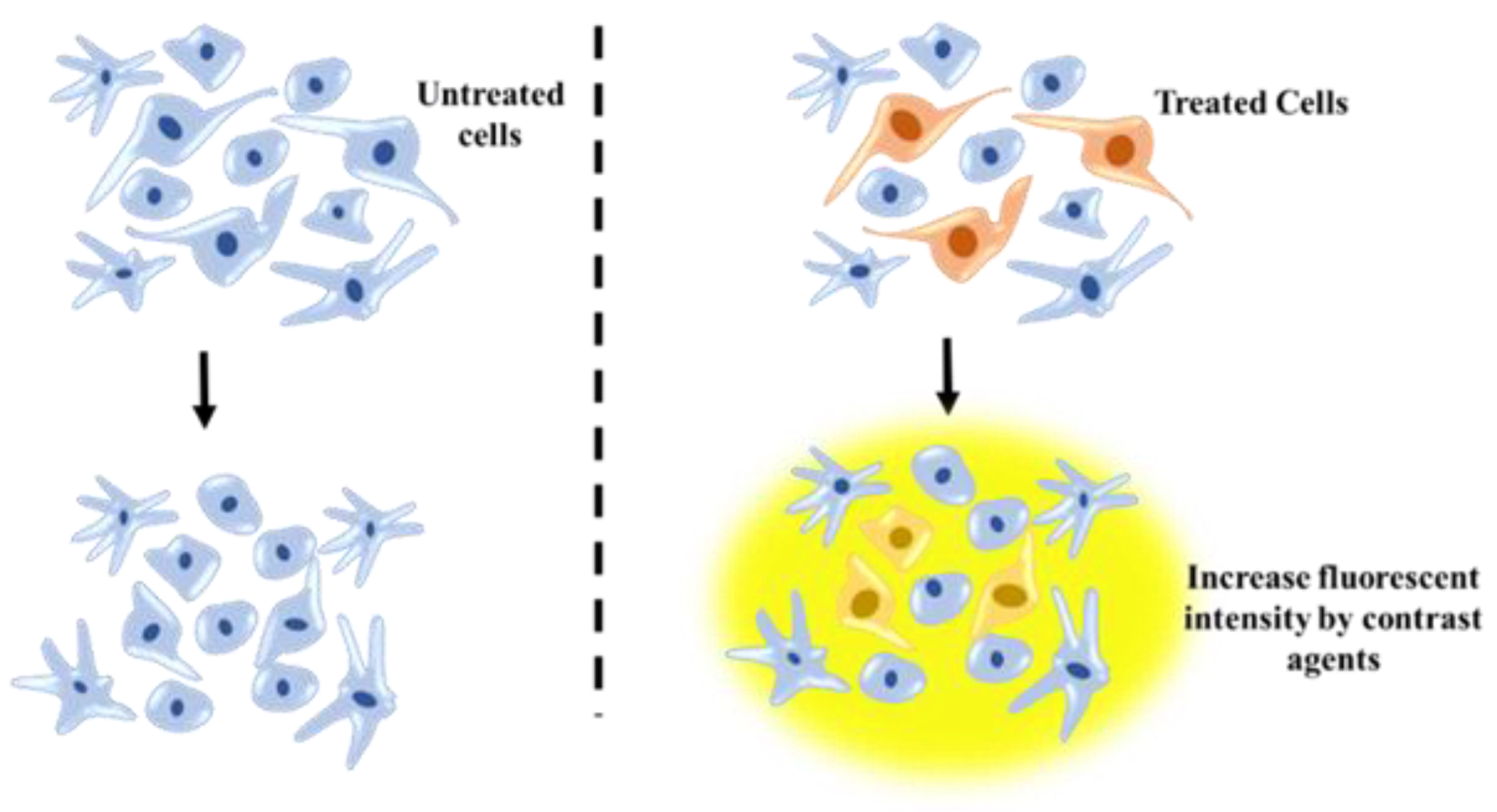
MRI technique for tracking posttransplanted neural stem cells (NSCs) using contrast agents and understanding NSC differentiation process.
Currently, developing techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT), positron emission tomography (PET), and near-infrared (NIR) fluorophores offer noninvasive models for tracking transplanted stem cells. Among these techniques, MRI by high spatial resolution is an ideal tool to gain high quality cellular and molecular images and is used in tracking engrafted stem cells in treatment of brain diseases. Treating the implanted cell with an intracellular contrast agent provides visualization of MSCs using MRI. Combination of PET with MRI can render useful information regarding cell tracking, optimal cell dose and graft volume. SPECT is a nuclear tomographic imaging technique equipped with a gamma ray camera. In a cell-transplanted brain of a PD model, activity of dopaminergic compounds was measured by SPECT-[123I] altropane. Near-infrared light (NIR) is another noninvasive imaging tool with ability of penetrating deep into tissues. To define the precise location of implanted hMSCs, NIR scanner was used to provide 3D images contain the contour, reconstruction and coronal section at cell-engrafted site of hMSCs [76].
Nanotechnology has beneficial for improve efficiency of these techniques in localization of transplanted stem cells. The magnetic properties of metallic NPs make them useful for magnetic resonance imaging. Loading stem cells with AuNPs can facilitate tracking of transplanted cells in stem-cell therapy procedures. Complexation of 40-nm AuNPs with two ligands, poly L-lysine (PLL) and rhodamine B isothiocyanate (RITC) improved NPs uptake by human mesenchymal stem cells, without inhibition of cell proliferation or differentiation [77]. Carbon quantum dots (CQDs) are also ideal tools for tracking transplanted cells. Covering mesenchymal stem cells with CQDs prior to implantation into the sciatic nerves allowed their tracking for at least 35 days, in vivo [78]. Some specifically developed lipid–base NPs like liposomes are able to treat neurodegenerative diseases and can be promising candidates for integrated treatment with stem-cell therapies. Conjugation of liposomes with apolipoprotein E (ApoE) increased delivery of siRNA or plasmid DNA to the brain, result in improving target liposomes to neural stem and progenitor cells [79].
Paramagnetic compounds such as SPIO-NPs are commonly used contrast agents. Recently, research has been carried out to evaluate the effects of SPIO-uptake on the in vitro activity of hMSCs and as a consequence, the effect of SPIO concentration on MRI sensitivity. Outputs of these studies revealed that during generation of high contrast MRI signals, SPIO-uptake would not have negative effects on the proliferation or differentiation processes. Implantation of SPIO-tagged MSCs in experimental models lead to high resolution MRI, supporting the beneficial behavior of SPIO labeling for stable MRI tracing [80]. Modification of SPIOs and their addition to human neural stem cells (hNSCs) allowed tracking of implanted NSCs by MRI for up to three months, without any significant impairment in cell viability or proliferation [81] (Table 1).

Table 1.
Summary of different types of stem cells and application of nanoparticles in stem-cell therapy.
The ability of cell proliferation and differentiation on labeled human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neural precursors (iPSC-NPs) was investigated using the MRI technique. Comparison between two iron-based nanoparticles contrast agents, silica-coated cobalt zinc ferrite nanoparticles (CZF) and poly-l-lysine-coated iron oxide superparamagnetic nanoparticles (PLL-coated γ-Fe2O3) revealed that PLL-coated γ-Fe2O3 would not affect cell proliferation, while CZF would slow down this process. However, no significant differences in neural differentiation were observed between unlabeled cells or cells labeled with both magnetic nanoparticles [82]. Thus, MRI-based stem-cell tracking may offer a novel practical method to follow transplanted stem-cell therapy for neurological disorders.
4. Conclusions
Recent progress in cell-based therapy and discovery of stem-cell capacity of neurogenesis in adults have emerged as novel prospects in terms of neurologic therapeutic approaches. Differentiation of NSCs to specific neurons have efficiently improved repair of damaged neurons and injured sections of the brain. There are various methods to induce NSC differentiation, including the transplantation of stem cells in their specific niche. However, viability, heterogeneity, uniformity, controlled differentiation of stem cell, tumorigenicity rate of implanted cells—as well as real-time tracking of the fate of transplanted cells are major concerns for this therapeutic approach. Introducing nanotechnology to this field has brought excellent opportunities to overcome these challenges. In recent years, nanobased approaches have been widely developed and represent beneficial impacts in the medical fields—particularly, as potential tools for the diagnosis and treatment of various neurodegenerative diseases. Integration of nanomaterial and stem-cell cultures provides a vital tool for enhancing NSC proliferation, accurate delivery of functional molecules to targeting areas to induce NSC differentiation and also for permitting real-time, noninvasive, durable monitoring of the implanted cell migration. However, as with any novel emerging technology, all aspects in the application of nanomaterials need to be considered in terms of any side-effect or toxicity of these compounds on a clinical scale. Moreover, to optimize the efficiency of these methods and to address their current challenges, a combination of nanotechnology, molecular biology and stem-cell therapy can be a leading solution. The more specific the differentiation, the more accurate delivery of bioactive compounds—and the more reliable tracking of injected cells are possible through molecular engineering of nanomaterials and thus, improve the efficacy of the conventional NSC-based therapy of neurodegenerative diseases.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.M.A.; methodology, G.G.B.; software, M.N.; validation, S.M.A. and M.N.; formal analysis, J.A.; investigation, S.M.A., J.A. and G.G.B.; resources, M.N.; data curation, S.M.A. and M.N.; writing—original draft preparation, S.M.A.; J.A.; G.G.B.; and M.N. writing—review and editing, S.M.A. and M.N.; visualization, S.M.A. and G.G.B.; supervision, M.N.; project administration, S.M.A., J.A.; G.G.B. and M.N.; funding acquisition, M.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Institutes of Health (NIH), grant number 1SC3 GM111200 01A1.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Nguyen, H.; Zarriello, S.; Coats, A.; Nelson, C.; Kingsbury, C.; Gorsky, A.; Rajani, M.; Neal, E.G.; Borlongan, C.V. Stem cell therapy for neurological disorders: A focus on aging. Neurobiol. Dis. 2019, 126, 85–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemeth, C.; Fine, A.; Fatemi, A. Translational challenges in advancing regenerative therapy for treating neurological disorders using nanotechnology. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 148, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carradori, D.; Eyer, J.; Saulnier, P.; Préat, V.; des Rieux, A. The therapeutic contribution of nanomedicine to treat neurodegenerative diseases via neural stem cell differentiation. Biomaterials 2017, 123, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindvall, O. Developing dopaminergic cell therapy for Parkinson’s disease—Give up or move forward? Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunnett, S.B.; Rosser, A.E. Clinical translation of cell transplantation in the brain. Curr. Opin. Organ Transplant. 2011, 16, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoveizi, E.; Ebrahimi-Barough, S.; Tavakol, S.; Sanamiri, K. In vitro differentiation of human iPS cells into neural like cells on a biomimetic polyurea. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunsberger, J.G.; Rao, M.; Kurtzberg, J.; Bulte, J.W.; Atala, A.; LaFerla, F.M.; Greely, H.T.; Sawa, A.; Gandy, S.; Schneider, L.S. Accelerating stem cell trials for Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.; Muresanu, D.; Lafuente, J.; Patnaik, R.; Tian, Z. Need to explore nanodelivery of stem cells with multimodal drug like cerebrolysin for effective strategies for enhanced neuroprotection and neurorecovery in neurodegenerative disorders. Int. J. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. Nanomed. 2016, 3492, 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Nori, S.; Okada, Y.; Nishimura, S.; Sasaki, T.; Itakura, G.; Kobayashi, Y.; Renault-Mihara, F.; Shimizu, A.; Koya, I.; Yoshida, R. Long-term safety issues of iPSC-based cell therapy in a spinal cord injury model: Oncogenic transformation with epithelial-Mesenchymal transition. Stem. Cell Rep. 2015, 4, 360–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, L. US stem cell clinics, patient safety, and the FDA. Trends Mol. Med. 2015, 21, 271–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Lin, T.; Xu, Y. Stem cell therapy and immunological rejection in animal models. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2016, 9, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farzamfar, S.; Nazeri, N.; Salehi, M.; Valizadeh, A.; Marashi, S.M.; Kouzehkonan, G.S.; Ghanbari, H. Will nanotechnology bring new hope for stem cell therapy? Cells Tissues Organs 2018, 206, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corradetti, B.; Ferrari, M. Nanotechnology for mesenchymal stem cell therapies. J. Control. Release 2016, 240, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalingam, M.; Haj, A.E.; Webster, T.J.; Ramakrishna, S. A special section on the role of nanotechnology in stem cell research. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 16, 8859–8861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, T.; Maia, J.; Agasse, F.; Xapelli, S.; Ferreira, L.; Bernardino, L. Nanomedicine boosts neurogenesis: New strategies for brain repair. Integr. Biol. 2012, 4, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Khan, A.A.; Wu, H.; Chen, L.; Gu, Y.; Gu, N. The application of nanomaterials in stem cell therapy for some neurological diseases. Curr. Drug Targets 2018, 19, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omrani, M.M.; Ansari, M.; Kiaie, N. Therapeutic effect of stem cells and nano-biomaterials on Alzheimer’s disease. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2016, 6, 1814–1820. [Google Scholar]
- Anthony, D.F.; Shiels, P.G. Exploiting paracrine mechanisms of tissue regeneration to repair damaged organs. Transplant. Res. 2013, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, H.; Soto-Gutierrez, A.; Parekkadan, B.; Kitagawa, Y.; Tompkins, R.G.; Kobayashi, N.; Yarmush, M.L. Mesenchymal stem cells: Mechanisms of immunomodulation and homing. Cell Transplant. 2010, 19, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quertainmont, R.; Cantinieaux, D.; Botman, O.; Sid, S.; Schoenen, J.; Franzen, R. Mesenchymal stem cell graft improves recovery after spinal cord injury in adult rats through neurotrophic and pro-angiogenic actions. PLoS ONE 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodiroga-Vukobrat, N.; Rukavina, D.; Pavelić, K.; Sander, G.G. Personalized Medicine in Healthcare Systems: Legal, Medical and Economic Implications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Abdal Dayem, A.; Lee, S.B.; Cho, S.-G. The impact of metallic nanoparticles on stem cell proliferation and differentiation. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martino, G.; Pluchino, S.; Bonfanti, L.; Schwartz, M. Brain regeneration in physiology and pathology: The immune signature driving therapeutic plasticity of neural stem cells. Physiol. Rev. 2011, 91, 1281–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinge, P.M.; Harmening, K.; Miller, M.C.; Heile, A.; Wallrapp, C.; Geigle, P.; Brinker, T. Encapsulated native and glucagon-like peptide-1 transfected human mesenchymal stem cells in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 497, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordoni, M.; Scarian, E.; Rey, F.; Gagliardi, S.; Carelli, S.; Pansarasa, O.; Cereda, C. Biomaterials in neurodegenerative disorders: A promising therapeutic approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senthilkumar, K.S.; Saravanan, K.S.; Chandra, G.; Sindhu, K.M.; Jayakrishnan, A.; Mohanakumar, K.P. Unilateral implantation of dopamine-loaded biodegradable hydrogel in the striatum attenuates motor abnormalities in the 6-hydroxydopamine model of hemi-parkinsonism. Behav. Brain Res. 2007, 184, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ucar, B.; Humpel, C. Therapeutic efficacy of glial cell-Derived neurotrophic factor loaded collagen scaffolds in ex vivo organotypic brain slice Parkinson’s disease models. Brain Res. Bull. 2019, 149, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chierchia, A.; Chirico, N.; Boeri, L.; Raimondi, I.; Riva, G.A.; Raimondi, M.T.; Tunesi, M.; Giordano, C.; Forloni, G.; Albani, D. Secretome released from hydrogel-Embedded adipose mesenchymal stem cells protects against the Parkinson’s disease related toxin 6-hydroxydopamine. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 121, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandu, N.; Momen-Heravi, F.; Sadr-Eshkevari, P.; Schaller, B. Molecular imaging for stem cell transplantation in neuroregenerative medicine. Neurodegener. Dis. 2012, 9, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, A.C.; González, C.H.; Miller, B.S.; Edgington, R.J.; Ferretti, P.; Jackman, R.B. Surface functionalisation of nanodiamonds for human neural stem cell adhesion and proliferation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.K.; Agarwal, S.; Seth, B.; Yadav, A.; Nair, S.; Bhatnagar, P.; Karmakar, M.; Kumari, M.; Chauhan, L.K.S.; Patel, D.K. Curcumin-loaded nanoparticles potently induce adult neurogenesis and reverse cognitive deficits in Alzheimer’s disease model via canonical Wnt/β-catenin pathway. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 76–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Yan, W.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, W.; Le, W.; Chen, B.; Zhu, R.; Cheng, L. Nanomaterials in neural-stem-cell-mediated regenerative medicine: Imaging and treatment of neurological diseases. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirahmadi, M.; Rezanejadbardaji, H.; Irfan-Maqsood, M.; Mokhtari, M.J.; Naderi-Meshkin, H. Stem cell therapy for neurodegenerative diseases: Strategies for regeneration against degeneration. Cell Ther. Regen. Med. 2016, 1, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, E.M.; Passirani, C.; Seijo, B.; Sanchez, A.; Montero-Menei, C.N. Nano and microcarriers to improve stem cell behaviour for neuroregenerative medicine strategies: Application to Huntington’s disease. Biomaterials 2016, 83, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- L’episcopo, F.; Tirolo, C.; Peruzzotti-Jametti, L.; Serapide, M.F.; Testa, N.; Caniglia, S.; Balzarotti, B.; Pluchino, S.; Marchetti, B. Neural stem cell grafts promote astroglia-Driven neurorestoration in the aged parkinsonian brain via Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Stem. Cells 2018, 36, 1179–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasaki, T.R.; Blurton-Jones, M.; Morrissette, D.A.; Kitazawa, M.; Oddo, S.; LaFerla, F.M. Neural stem cells improve memory in an inducible mouse model of neuronal loss. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 11925–11933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantorovich, S.; Astary, G.W.; Green, C.; Zheng, T.; Semple-Rowland, S.L.; Steindler, D.A.; Sarntinoranont, M.; Streit, W.J.; Borchelt, D.R. A preclinical assessment of neural stem cells as delivery vehicles for anti-amyloid therapeutics. PLoS ONE 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Wang, W.; Chen, C. Research progress in animal models and stem cell therapy for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurorestoratology 2015, 3, 11–22. [Google Scholar]
- Ghanekar, S.; Corey, S.; Stonesifer, C.; Lippert, T.; Diamandis, Z.; Sokol, J.; Borlongan, C.V. Current challenges in regenerative medicine for central nervous system disorders. Brain Circ. 2016, 2, 105–107. [Google Scholar]
- Venkataramana, N.K.; Kumar, S.K.; Balaraju, S.; Radhakrishnan, R.C.; Bansal, A.; Dixit, A.; Rao, D.K.; Das, M.; Jan, M.; Gupta, P.K. Open-Labeled study of unilateral autologous bone-Marrow-Derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in Parkinson’s disease. Transl. Res. 2010, 155, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavagal, D.R.; Lin, B.; Raval, A.P.; Garza, P.S.; Dong, C.; Zhao, W.; Rangel, E.B.; McNiece, I.; Rundek, T.; Sacco, R.L. Efficacy and dose-Dependent safety of intra-arterial delivery of mesenchymal stem cells in a rodent stroke model. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez-Monteagudo, C.; Hernandez-Ramirez, P.; Álvarez-González, L.; Garcia-Maeso, I.; de la Cuetara-Bernal, K.; Castillo-Diaz, L.; Bringas-Vega, M.L.; Martínez-Aching, G.; Morales-Chacón, L.M.; Baez-Martin, M.M. Autologous bone marrow stem cell neurotransplantation in stroke patients. An open study. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2009, 27, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daviaud, N.; Garbayo, E.; Schiller, P.C.; Perez-Pinzon, M.; Montero-Menei, C.N. Organotypic cultures as tools for optimizing central nervous system cell therapies. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 248, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aswendt, M.; Henn, N.; Michalk, S.; Schneider, G.; Steiner, M.-S.; Bissa, U.; Dose, C.; Hoehn, M. Novel bimodal iron oxide particles for efficient tracking of human neural stem cells in vivo. Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 2499–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, C.; Israel, L.L.; Ostrovsky, S.; Taylor, A.; Poptani, H.; Lellouche, J.P.; Chari, D. Development of multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles for genetic engineering and tracking of neural stem cells. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yuan, L.; Wu, C.; Luo, G.; Deng, J.; Mao, Z. Recent review of the effect of nanomaterials on stem cells. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 17656–17676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilie, I.; Ilie, R.; Mocan, T.; Bartos, D.; Mocan, L. Influence of nanomaterials on stem cell differentiation: Designing an appropriate nanobiointerface. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 2211–2225. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chang, X.; Chen, C.; Zhao, Y. Cellular uptake, intracellular trafficking, and cytotoxicity of nanomaterials. Small 2011, 7, 1322–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bannunah, A.M.; Vllasaliu, D.; Lord, J.; Stolnik, S. Mechanisms of nanoparticle internalization and transport across an intestinal epithelial cell model: Effect of size and surface charge. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 4363–4373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingham, E.; Oreffo, R.O. Embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells: Understanding, creating, and exploiting the nano-niche for regenerative medicine. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 1867–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, T.-H.; Hsu, S.-C.; Wu, S.-H.; Hsiao, J.-K.; Lin, C.-P.; Yao, M.; Huang, D.-M. Dextran-coated iron oxide nanoparticle-improved therapeutic effects of human mesenchymal stem cells in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 2998–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.-M.; Hsiao, J.-K.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chien, L.-Y.; Yao, M.; Chen, Y.-K.; Ko, B.-S.; Hsu, S.-C.; Tai, L.-A.; Cheng, H.-Y. The promotion of human mesenchymal stem cell proliferation by superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 3645–3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.-Y.; Pang, D.-P.; Hwang, S.-M.; Tuan, H.-Y.; Hu, Y.-C. A graphene-based platform for induced pluripotent stem cells culture and differentiation. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Kawazoe, N.; Chen, G. Gold nanoparticle size and shape influence on osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 7992–8007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.I.; Cho, H.T.; Jee, M.K.; Kang, S.K. Core-shell nanoparticle controlled hATSCs neurogenesis for neuropathic pain therapy. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 4956–4970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, J.J.; Zhou, B.Y.; Mitalipova, M.M.; Beard, C.; Langer, R.; Jaenisch, R.; Anderson, D.G. Nanoparticles for gene transfer to human embryonic stem cell colonies. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 3126–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, H. How is pluripotency determined and maintained? Development 2007, 134, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dulińska-Litewka, J.; Łazarczyk, A.; Hałubiec, P.; Szafrański, O.; Karnas, K.; Karewicz, A. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles—Current and prospective medical applications. Materials 2019, 12, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, R.; Fonseca, M.; Santos, T.; Sargento-Freitas, J.; Tjeng, R.; Paiva, F.; Castelo-Branco, M.; Ferreira, L.; Bernardino, L. Retinoic acid-Loaded polymeric nanoparticles enhance vascular regulation of neural stem cell survival and differentiation after ischaemia. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 8126–8137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabelström, H.; Stenudd, M.; Frisén, J. Neural stem cells in the adult spinal cord. Exp. Neurol. 2014, 260, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, A.M.; Ming, G.-l.; Song, H. Adult mammalian neural stem cells and neurogenesis: Five decades later. Cell Stem. Cell 2015, 17, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, L.S.; Nobrega, C.; Hirai, H.; Kaspar, B.K.; Pereira de Almeida, L. Transplantation of cerebellar neural stem cells improves motor coordination and neuropathology in Machado-Joseph disease mice. Brain 2015, 138, 320–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwai, H.; Shimada, H.; Nishimura, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Itakura, G.; Hori, K.; Hikishima, K.; Ebise, H.; Negishi, N.; Shibata, S. Allogeneic neural stem/progenitor cells derived from embryonic stem cells promote functional recovery after transplantation into injured spinal cord of nonhuman primates. Stem. Cells Transl. Med. 2015, 4, 708–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carradori, D.; Saulnier, P.; Préat, V.; Des Rieux, A.; Eyer, J. NFL-Lipid nanocapsules for brain neural stem cell targeting in vitro and in vivo. J. Control. Release 2016, 238, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sintov, A.; Velasco-Aguirre, C.; Gallardo-Toledo, E.; Araya, E.; Kogan, M. Metal nanoparticles as targeted carriers circumventing the blood–brain barrier. In International Review of Neurobiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 130, pp. 199–227. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, K.; Tu, C.; Zoldan, J.; Suggs, L.J. Gene transfection for stem cell therapy. Curr. Stem. Cell Rep. 2016, 2, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, X.; Shi, D.; Wen, X. Particle systems for stem cell applications. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2015, 11, 1107–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, L.; Karp, J.M.; Nobre, L.; Langer, R. New opportunities: The use of nanotechnologies to manipulate and track stem cells. Cell Stem. Cell 2008, 3, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maia, J.; Santos, T.; Aday, S.; Agasse, F.; Cortes, L.; Malva, J.O.; Bernardino, L.; Ferreira, L. Controlling the neuronal differentiation of stem cells by the intracellular delivery of retinoic acid-Loaded nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auffinger, B.; Morshed, R.; Tobias, A.; Cheng, Y.; Ahmed, A.U.; Lesniak, M.S. Drug-loaded nanoparticle systems and adult stem cells: A potential marriage for the treatment of malignant glioma? Oncotarget 2013, 4, 378–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Atluri, V.; Kaushik, A.; Yndart, A.; Nair, M. Alzheimer’s disease: Pathogenesis, diagnostics, and therapeutics. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 5541–5554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Ma, C.; Zhu, M.-Q.; Ju, W.-N.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X. Application of iron oxide nanoparticles in the diagnosis and treatment of neurodegenerative diseases with emphasis on Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Gutkind, J.S.; Srivatsan, A.; Zhang, G.; Liao, H.-S.; Fu, X.; Jin, A. Polymeric nanovehicle regulated spatiotemporal real-time imaging of the differentiation dynamics of transplanted neural stem cells after traumatic brain injury. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 6683–6695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, T.; Valenzuela, A.; Petit, F.; Chow, S.; Leung, K.; Gorin, F.; Louie, A.Y.; Dhenain, M. In vivo MRI of functionalized iron oxide nanoparticles for brain inflammation. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2018, 2018, 3476476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, F.J.; Rotz, M.W.; Ghuman, H.; MacRenaris, K.W.; Meade, T.J.; Modo, M. DNA–Gadolinium–Gold nanoparticles for in vivo T1 MR imaging of transplanted human neural stem cells. Biomaterials 2016, 77, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, B.-W. In vivo assessment of stem cells for treating neurodegenerative disease: Current approaches and future prospects. Stem. Cells Int. 2017, 2017, 9751583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.; Lee, N.; Arifin, D.R.; Shats, I.; Janowski, M.; Walczak, P.; Hyeon, T.; Bulte, J.W. In vivo micro-CT imaging of human mesenchymal stem cells labeled with gold-poly-l-lysine nanocomplexes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1604213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, D.N.R.; Bertanha, M.; Fernandes, T.D.; de Lima Resende, L.A.; Deffune, E.; Amorim, R.M. Effects of canine and murine mesenchymal stromal cell transplantation on peripheral nerve regeneration. Int. J. Stem. Cells 2017, 10, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaru, M.; Akita, H.; Nakatani, T.; Kajimoto, K.; Sato, Y.; Hatakeyama, H.; Harashima, H. Application of apolipoprotein E-modified liposomal nanoparticles as a carrier for delivering DNA and nucleic acid in the brain. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 4267–4276. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg, J.T.; Yuan, X.; Grant, S.; Ma, T. Tracking mesenchymal stem cells using magnetic resonance imaging. Brain Circ. 2016, 2, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goodfellow, F.T.; Simchick, G.A.; Mortensen, L.J.; Stice, S.L.; Zhao, Q. Tracking and quantification of magnetically labeled stem cells using magnetic resonance imaging. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 3899–3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiráková, K.; Šeneklová, M.; Jirak, D.; Turnovcova, K.; Vosmanska, M.; Babič, M.; Horak, D.; Veverka, P.; Jendelova, P. The effect of magnetic nanoparticles on neuronal differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cell-Derived neural precursors. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 6267–6281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).