Wind-Energy-Powered Electric Vehicle Charging Stations: Resource Availability Data Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Wind Data and Preprocessing
3. Methodology
3.1. Wind Turbine Selection
3.2. Wind Energy Calculation
| Algorithm 1: EV wind power supply | ||
| Inputs: | , | The instantaneous wind power; |
| , | EV battery time to charge; | |
| , | Overlap time of intervals; | |
| EV charger power; | ||
| Output: | Constant supplied energy; | |
| , | Number of EVs | |
| /* Calculate the number of overlap intervals */ | ||
| 1: | ||
| 2: for to step do | ||
| 3: | ||
| 4: | ||
| /* Check the stability of wind power*/ | ||
| 5: if std 0.1 or std0.1 then | ||
| 6: Continue | ||
| 7: end if | ||
| /* Find non-overlap intervals*/ | ||
| 8: if then | ||
| 9: | ||
| 10: end if | ||
| 11: end for | ||
| /* Calculate the total energy*/ | ||
| 12: | ||
| /* Calculate number of EVs*/ | ||
| 13: | ||
3.3. Charging Station Capacity
4. Results
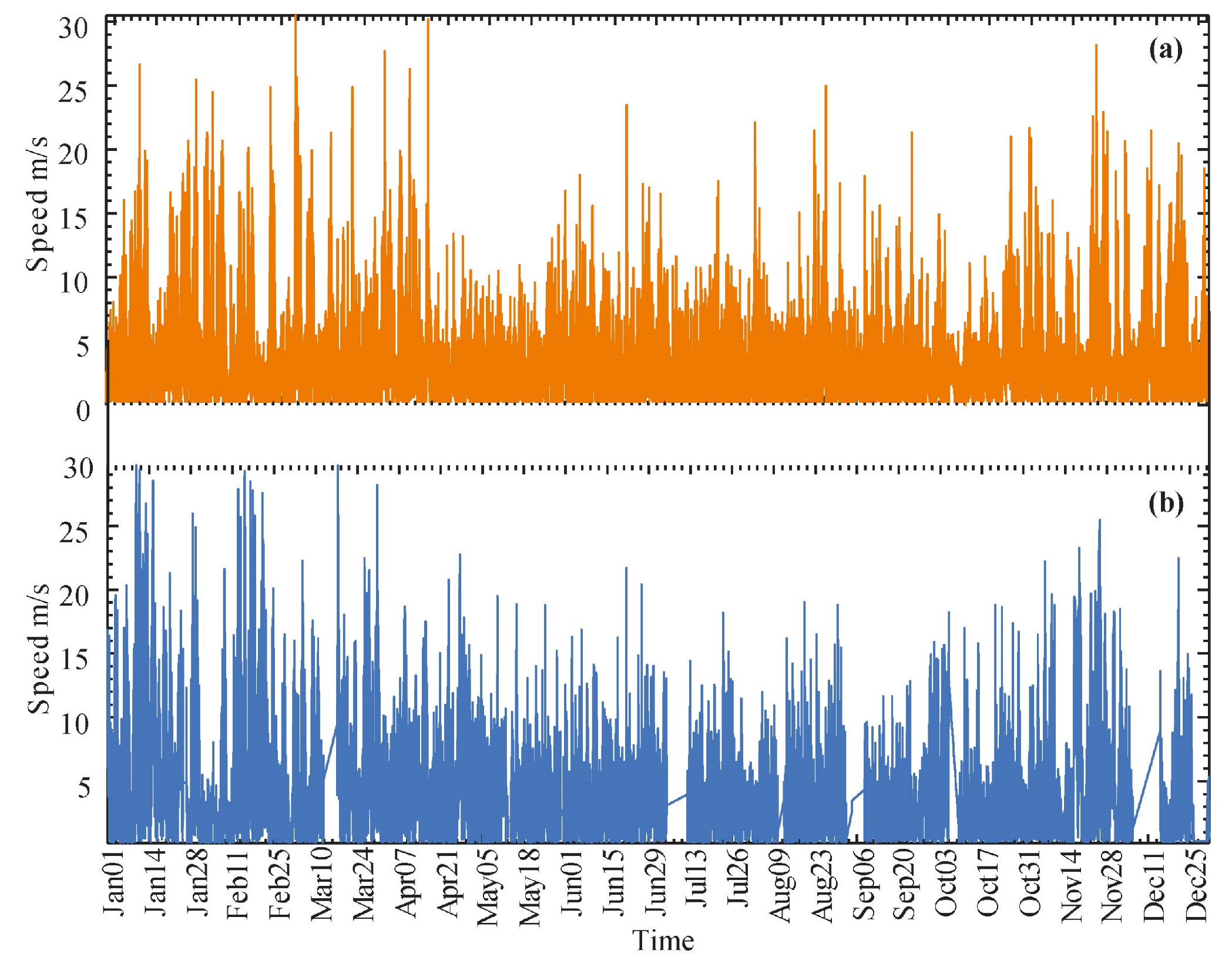
4.1. Wind Speed Data Averaging
4.2. Wind Turbine Selection
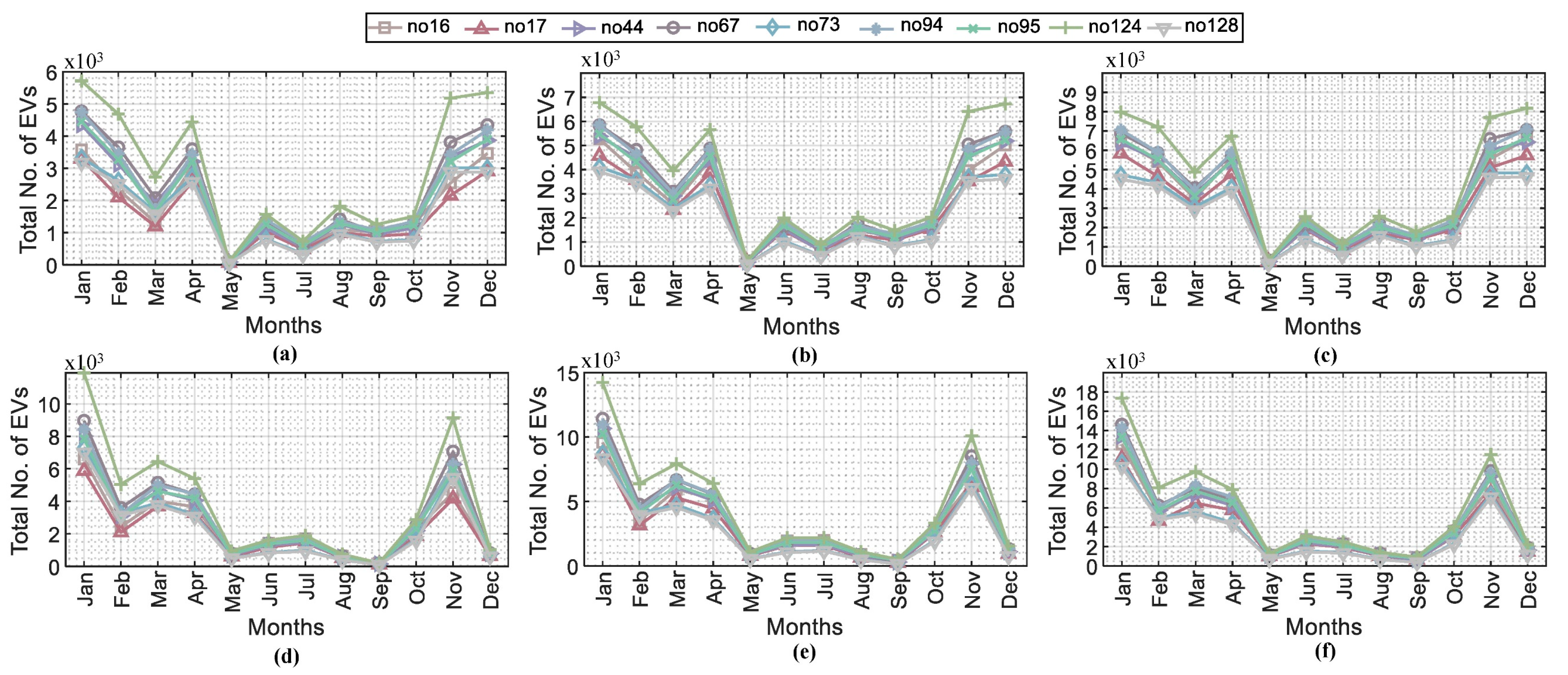
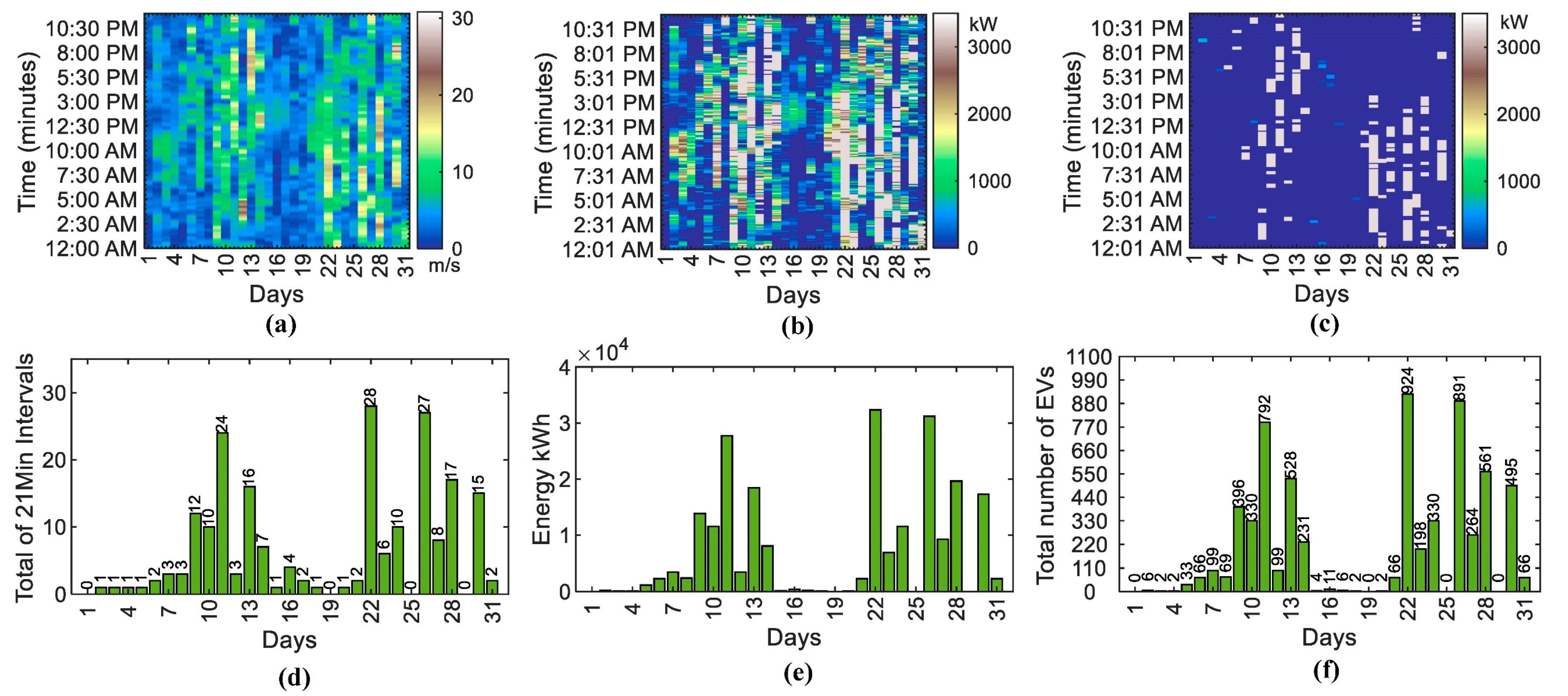
4.3. Charging Station Capacity
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cerna, F.V.; Pourakbari-Kasmaei, M.; Contreras, J.; Gallego, L.A. Optimal selection of navigation modes of HEVs considering CO2 emissions reduction. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 2196–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, C. Technology development of electric vehicles: A review. Energies 2020, 13, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, H.; Rahman, M.; Li, S.; Tan, C. Electric vehicles standards, charging infrastructure, and impact on grid integration: A technological review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 120, 109618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, M.R.; Alam, M.S.; Sarwar, A.; Asghar, M.J. A comprehensive review on electric vehicles charging infrastructures and their impacts on power-quality of the utility grid. ETransportation 2019, 1, 100006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathabadi, H. Utilizing solar and wind energy in plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 156, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Niyato, D.; Wang, P.; Han, Z. The PHEV charging scheduling and power supply optimization for charging stations. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2015, 65, 566–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Gu, W.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, S. Joint planning of distributed generation and electric vehicle charging stations considering real-time charging navigation. Appl. Energy 2019, 242, 1274–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashique, R.H.; Salam, Z.; Aziz, M.J.B.A.; Bhatti, A.R. Integrated photovoltaic-grid dc fast charging system for electric vehicle: A review of the architecture and control. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 69, 1243–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathabadi, H. Novel wind powered electric vehicle charging station with vehicle-to-grid (V2G) connection capability. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 136, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goli, P.; Shireen, W. Wind powered smart charging facility for PHEVs. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE). IEEE, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 14–18 September 2014; pp. 1986–1991. [Google Scholar]
- Ahadi, A.; Sarma, S.; Moon, J.S.; Kang, S.; Lee, J.H. A robust optimization for designing a charging station based on solar and wind energy for electric vehicles of a smart home in small villages. Energies 2018, 11, 1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Falahi, M.D.; Jayasinghe, S.; Enshaei, H. A review on recent size optimization methodologies for stand-alone solar and wind hybrid renewable energy system. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 143, 252–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Navarro, J.; Dufo-López, R.; Yusta-Loyo, J.; Artal-Sevil, J.; Bernal-Agustín, J. Design of an electric vehicle fast-charging station with integration of renewable energy and storage systems. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2019, 105, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Niu, S.; Shang, Y.; Shao, Z.; Jian, L. Integrating plug-in electric vehicles into power grids: A comprehensive review on power interaction mode, scheduling methodology and mathematical foundation. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 112, 424–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardman, S.; Jenn, A.; Tal, G.; Axsen, J.; Beard, G.; Daina, N.; Figenbaum, E.; Jakobsson, N.; Jochem, P.; Kinnear, N.; et al. A review of consumer preferences of and interactions with electric vehicle charging infrastructure. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2018, 62, 508–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Sáinz, H.; García-Vázquez, C.A.; Llorens Iborra, F.; Fernández-Ramírez, L.M. Methodology for the optimal design of a hybrid charging station of electric and fuel cell vehicles supplied by renewable energies and an energy storage system. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, A.; Marzband, M.; Mohamadi-Ivatloo, B.; Contreras, J.; Pourakbari-Kasmaei, M.; Lehtonen, M.; Godina, R. Uncertainty-Based models for optimal management of energy hubs considering demand response. Energies 2019, 12, 1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teleke, S.; Baran, M.E.; Huang, A.Q.; Bhattacharya, S.; Anderson, L. Control strategies for battery energy storage for wind farm dispatching. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2009, 24, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yan, Z.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, X.P. Wind power smoothing by controlling the inertial energy of turbines with optimized energy yield. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 23374–23382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Shang, Y.; Ouyang, Q.; Widanage, W. A data-driven approach with uncertainty quantification for predicting future capacities and remaining useful life of lithium-ion battery. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Hu, X.; Wei, Z.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Y. Modified Gaussian process regression models for cyclic capacity prediction of lithium-ion batteries. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2019, 5, 1225–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zou, C.; Li, K.; Wik, T. Charging pattern optimization for lithium-ion batteries with an electrothermal-aging model. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 14, 5463–5474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Hu, X.; Yang, Z.; Xie, Y.; Feng, S. Lithium-Ion battery charging management considering economic costs of electrical energy loss and battery degradation. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 195, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Liu, K.; Xu, G.; Li, Y. Optimal charging control for lithium-ion battery packs: A distributed average tracking approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 16, 3430–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathabadi, H. Novel stand-alone, completely autonomous and renewable energy based charging station for charging plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs). Appl. Energy 2020, 260, 114194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton, A. 135-M Meteorological Masts at the National Wind Technology Center: Instrumentation, Data Acquisition, and Processing. Technical Report; July 2014. Available online: https://wind.nrel.gov (accessed on 30 January 2020).
- Harper, B.; Kepert, J.; Ginger, J. Guidelines for Converting between Various Wind Averaging Periods in Tropical Cyclone Conditions; WMO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Malte, P.; Christian, H.; Jonas, H.; Ludee. Wind Turbine Library. 2019. Available online: https://openenergy-platform.org/ (accessed on 3 February 2020).
- International Electrotechnical Commission. Wind Energy Generation Systems—Part 12-1: Power Performance Measurements of Electricity Producing Wind Turbines; IEC 61400-12-1:2017; International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Astolfi, D.; Castellani, F.; Terzi, L. Wind turbine power curve upgrades. Energies 2018, 11, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.; Mekhilef, S.; Afifi, F.; Halabi, L.M.; Olatomiwa, L.; Seyedmahmoudian, M.; Horan, B.; Stojcevski, A. Application of the hybrid ANFIS models for long term wind power density prediction with extrapolation capability. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolude, A.T.; Zhou, W. Assessment and performance evaluation of a wind turbine power output. Energies 2018, 11, 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Parameter | Description or Value |
|---|---|
| Battery pack capacity () | 50 kW |
| Driving range | Between 225–465 km |
| Fast charging range | From 10–80% |
| Charging point | Supercharger v3 (250 kW DC) |
| Charging point max power | 170 kW |
| Charging point avg power () | 100 kW |
| DC charging time () | 21 min |
| Real energy consumption | 10.2–21.1 kWh/100 km |
| ID * | Height (m/s) | Cut-In (m/s) | Rated (m/s) | Cut-Out (m/s) | Power | M4 Tower Data (%) | M2 Tower Data (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (kW) | 1 Min | 2 Min | 3 Min | 1 Min | 2 Min | 3 Min | |||||
| no16 | 134 | 3 | 10 | 20 | 3300 | 9.41 | 14.34 | 18.35 | 5.22 | 8.28 | 9.78 |
| no17 | 114 | 3 | 10 | 20 | 3000 | 9.22 | 14.44 | 17.74 | 5.22 | 7.74 | 9.64 |
| no44 | 119 | 3 | 10 | 22 | 3000 | 12.61 | 17.69 | 21.26 | 6.82 | 9.12 | 10.49 |
| no67 | 129 | 3 | 10 | 23 | 3150 | 13.41 | 17.94 | 22.20 | 7.20 | 9.41 | 10.87 |
| no73 | 99.5 | 3 | 10 | 25 | 2300 | 14.96 | 18.73 | 22.20 | 6.92 | 8.97 | 10.21 |
| no94 | 139 | 3 | 10 | 22 | 3200 | 12.42 | 17.05 | 21.45 | 7.10 | 9.41 | 11.01 |
| no95 | 136 | 3 | 10 | 22 | 3000 | 12.33 | 17.00 | 21.31 | 7.10 | 9.46 | 10.91 |
| no124 | 137 | 3 | 10 | 25 | 3500 | 16.04 | 20.21 | 23.76 | 7.86 | 9.96 | 11.34 |
| no128 | 99 | 3 | 10 | 25 | 2200 | 14.96 | 18.73 | 22.20 | 6.86 | 8.97 | 10.21 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Noman, F.; Alkahtani, A.A.; Agelidis, V.; Tiong, K.S.; Alkawsi, G.; Ekanayake, J. Wind-Energy-Powered Electric Vehicle Charging Stations: Resource Availability Data Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5654. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10165654
Noman F, Alkahtani AA, Agelidis V, Tiong KS, Alkawsi G, Ekanayake J. Wind-Energy-Powered Electric Vehicle Charging Stations: Resource Availability Data Analysis. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(16):5654. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10165654
Chicago/Turabian StyleNoman, Fuad, Ammar Ahmed Alkahtani, Vassilios Agelidis, Kiong Sieh Tiong, Gamal Alkawsi, and Janaka Ekanayake. 2020. "Wind-Energy-Powered Electric Vehicle Charging Stations: Resource Availability Data Analysis" Applied Sciences 10, no. 16: 5654. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10165654
APA StyleNoman, F., Alkahtani, A. A., Agelidis, V., Tiong, K. S., Alkawsi, G., & Ekanayake, J. (2020). Wind-Energy-Powered Electric Vehicle Charging Stations: Resource Availability Data Analysis. Applied Sciences, 10(16), 5654. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10165654







