Suitability of Active Noise Barriers for Construction Sites
Abstract
1. Introduction
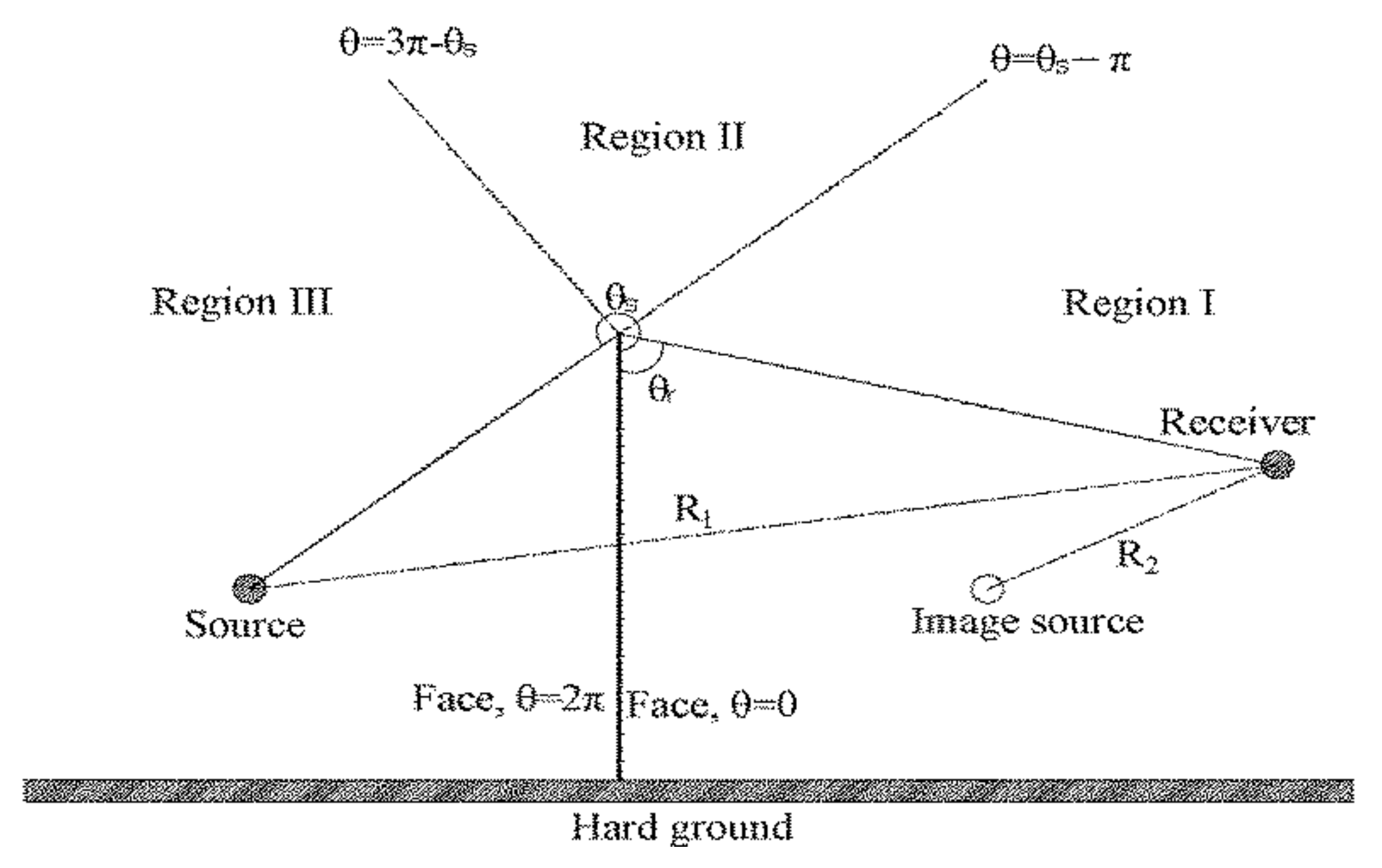
2. Theory
2.1. Diffraction Model
2.2. Active Noise Barriers
Minimization of Squared Pressure
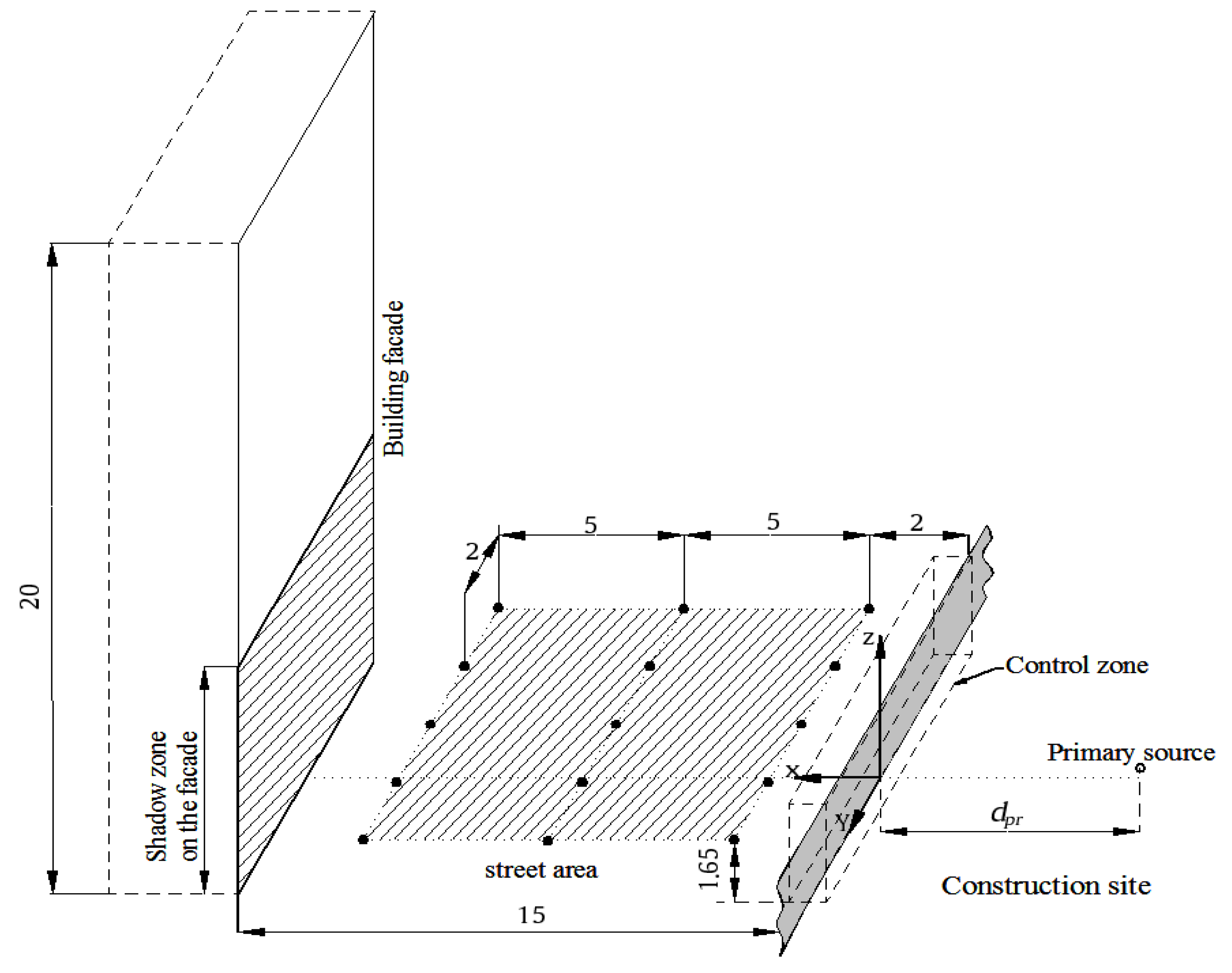
3. Method
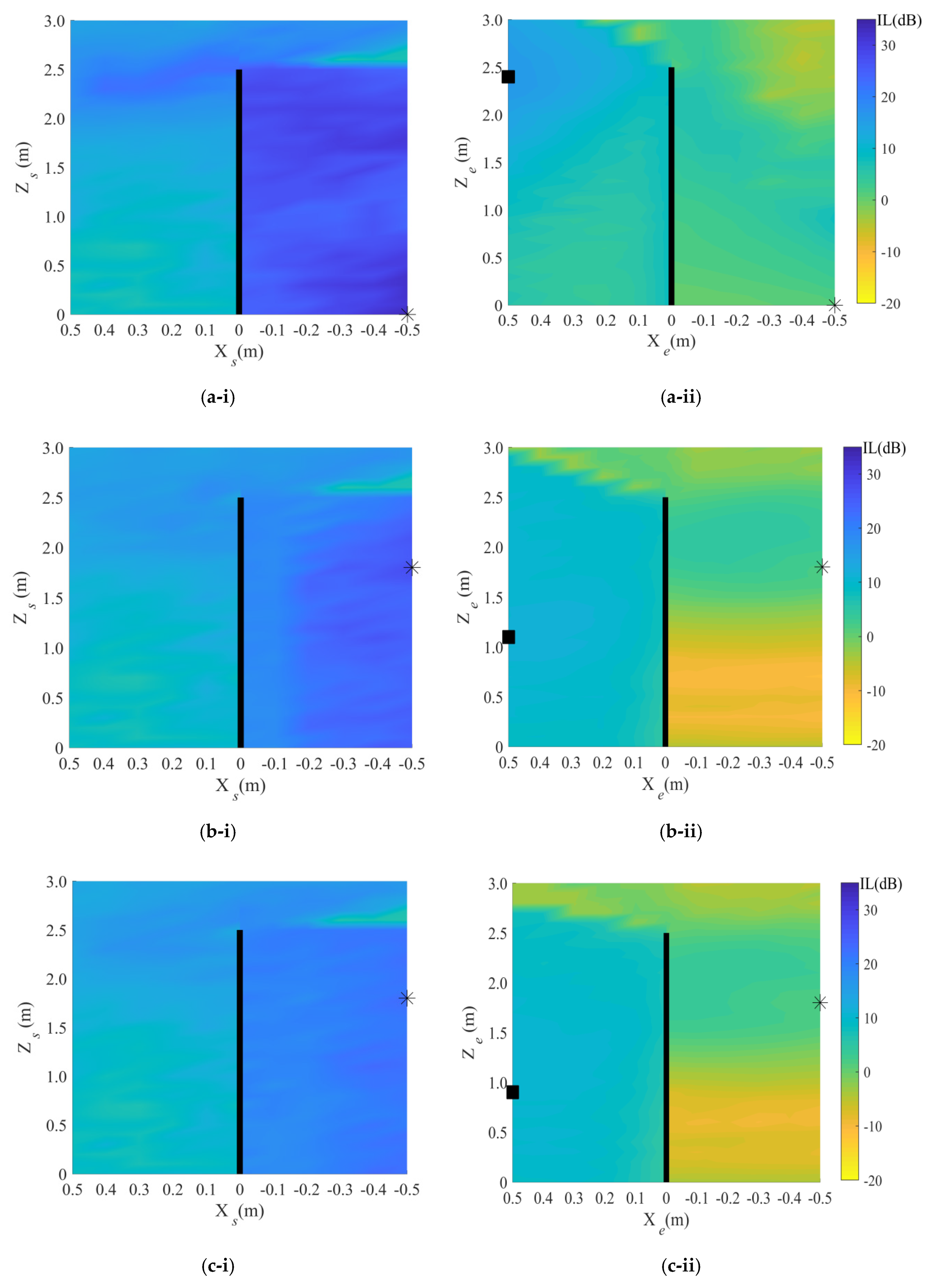
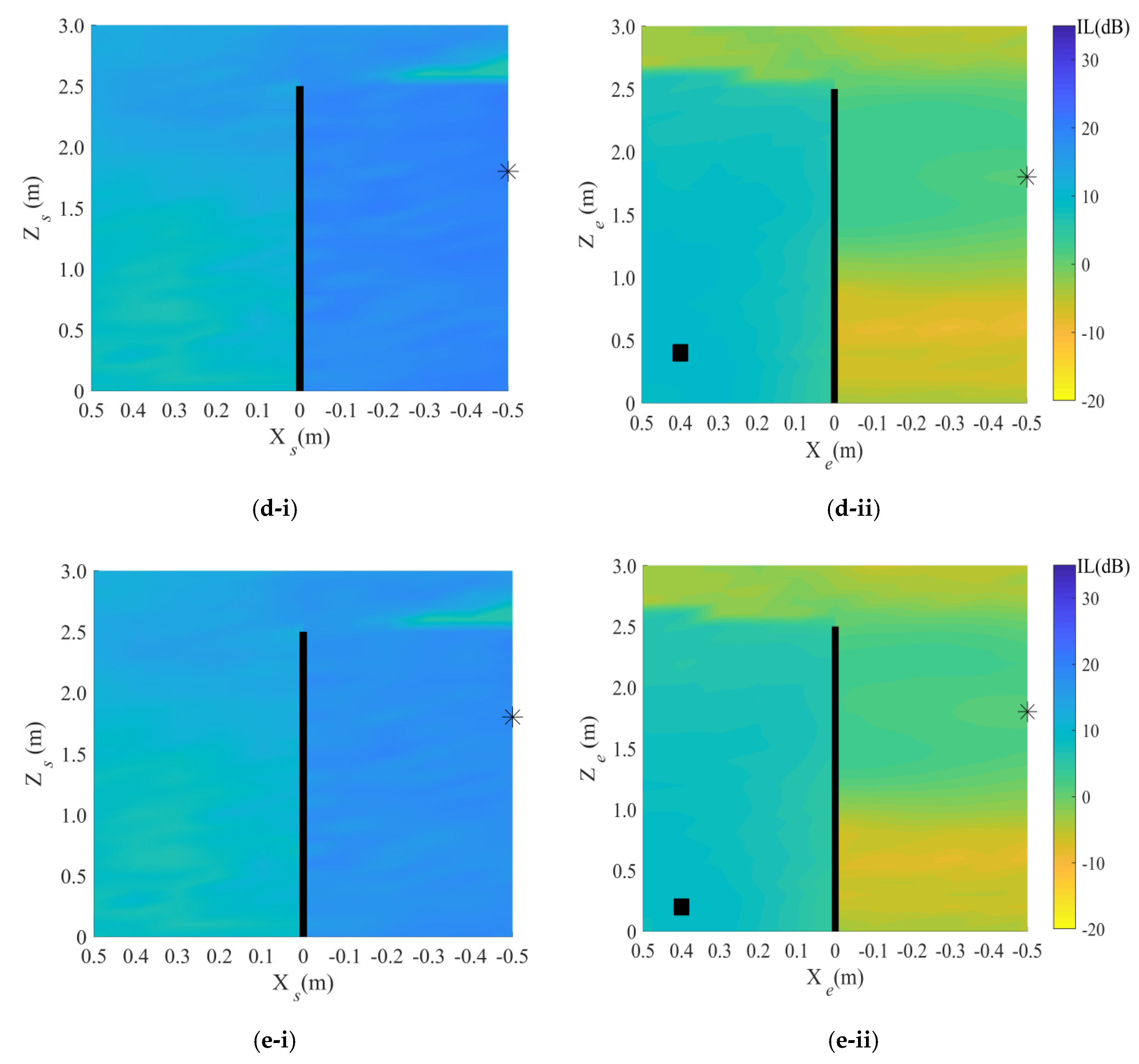
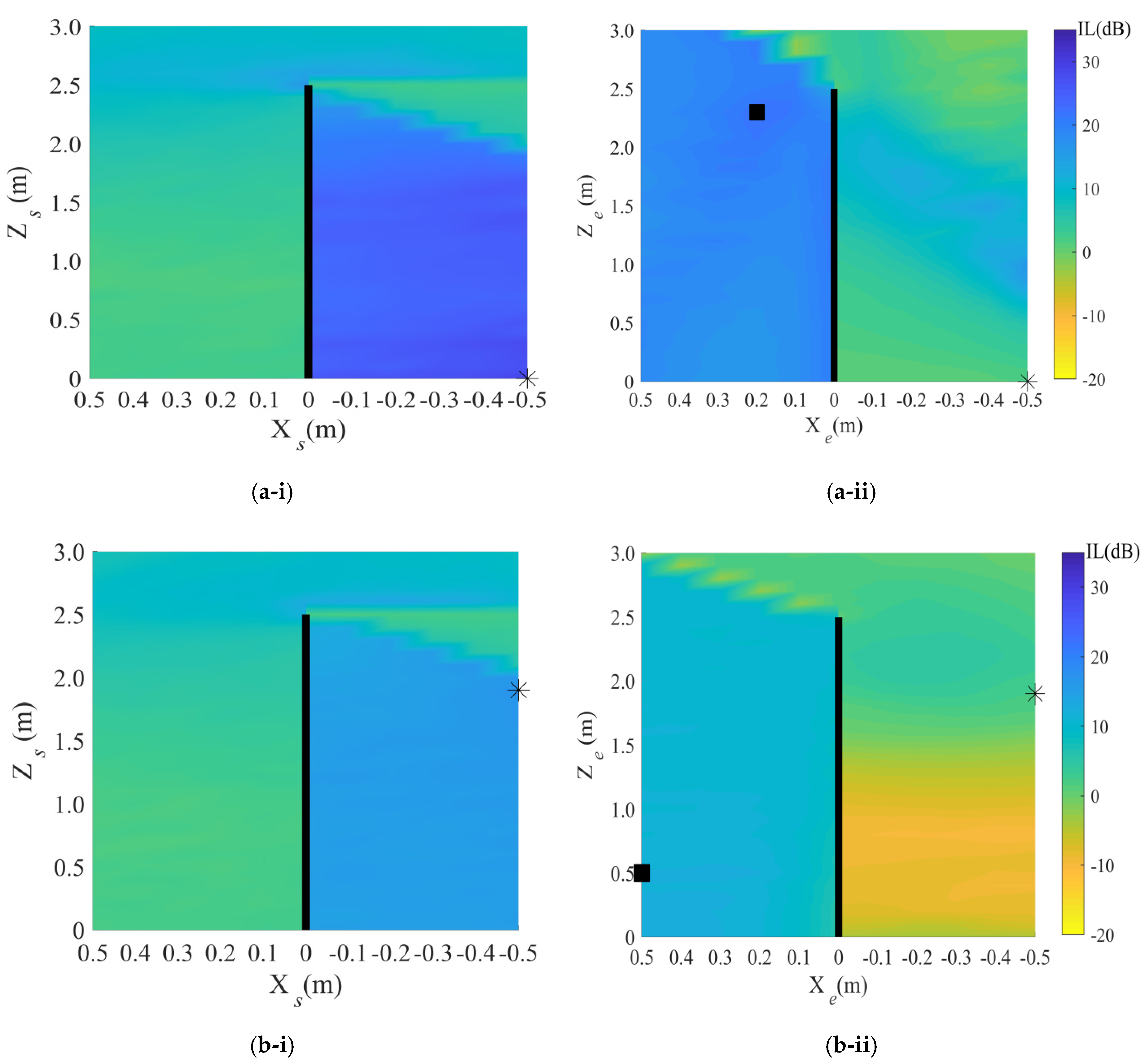
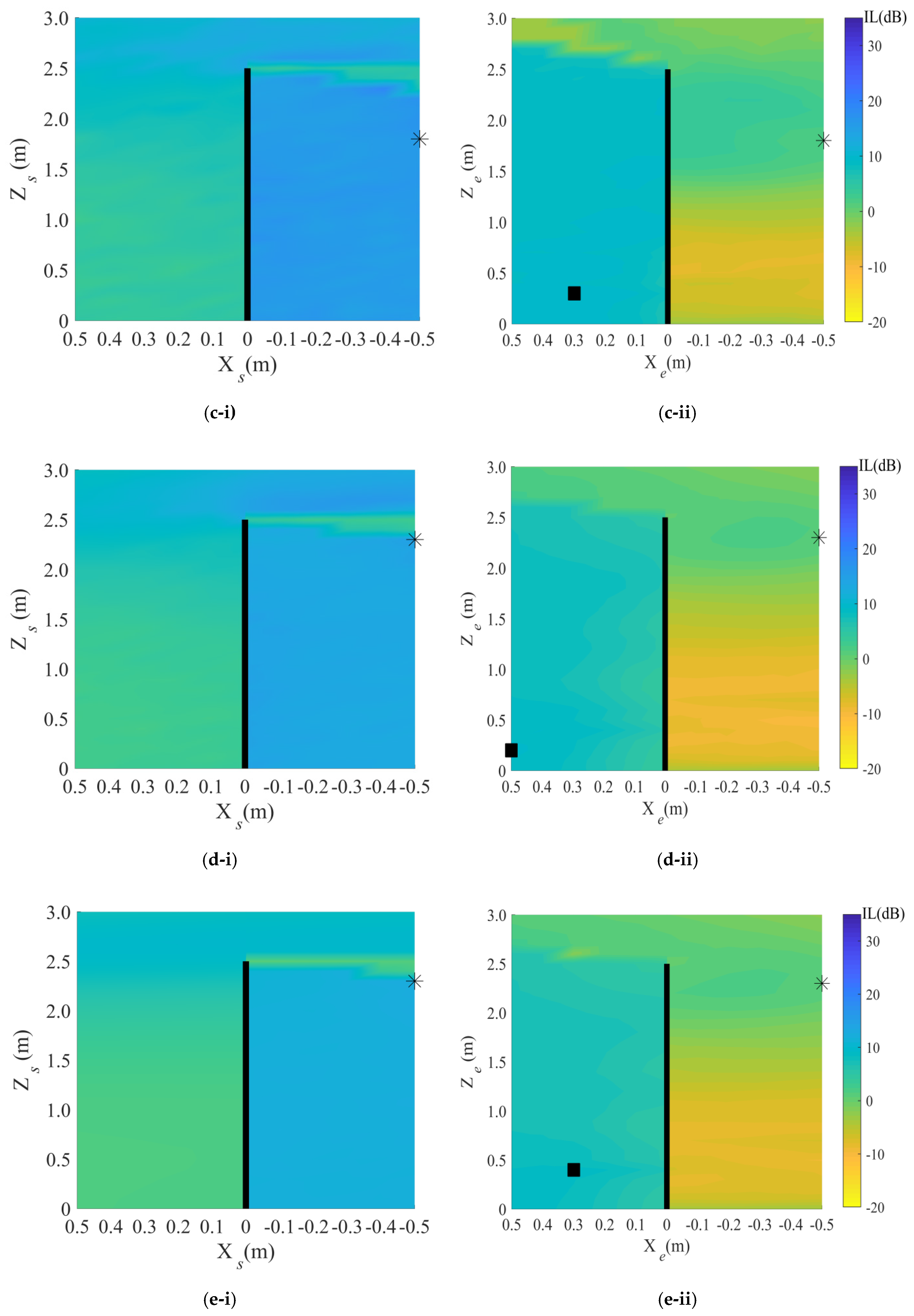
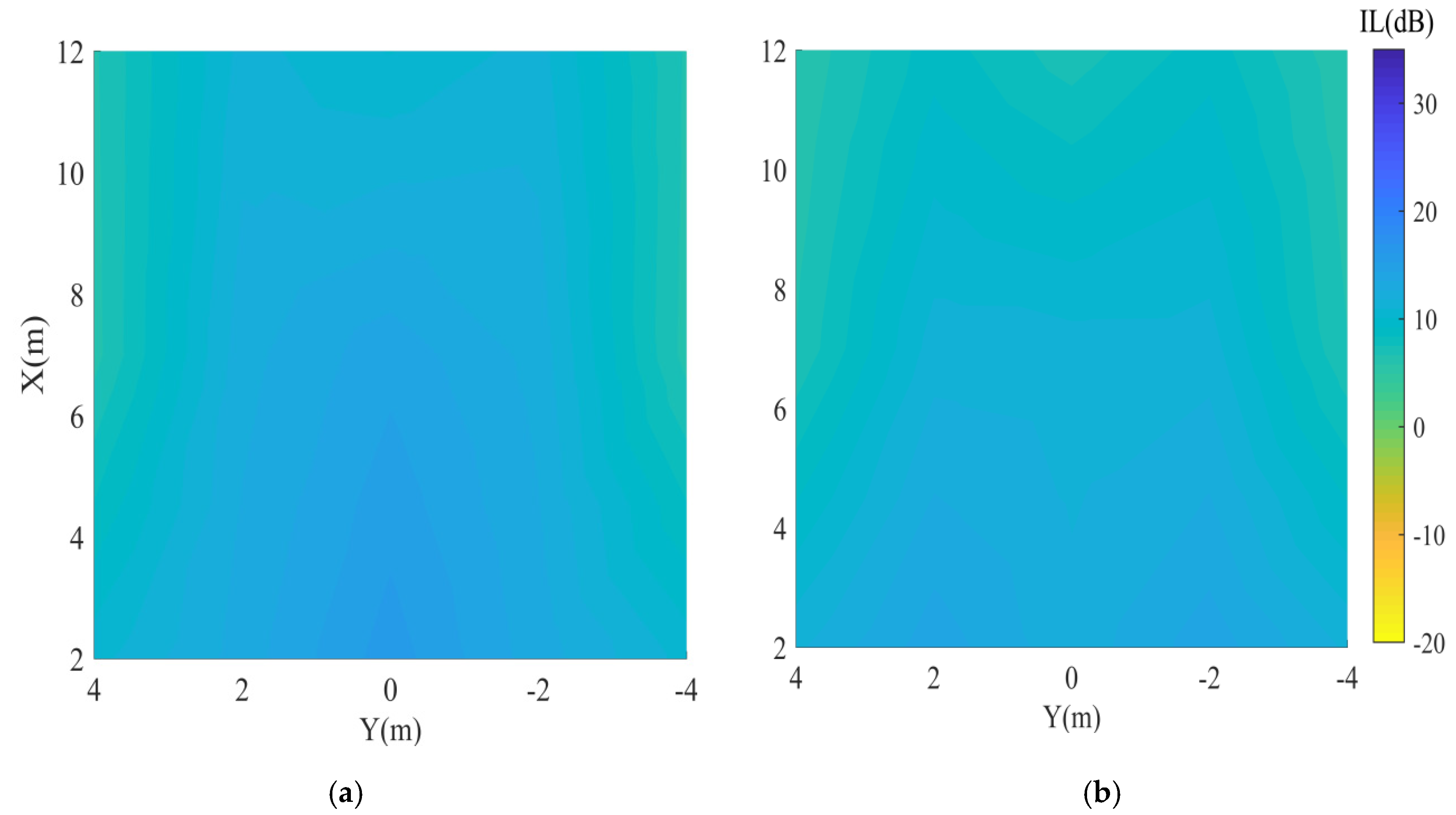
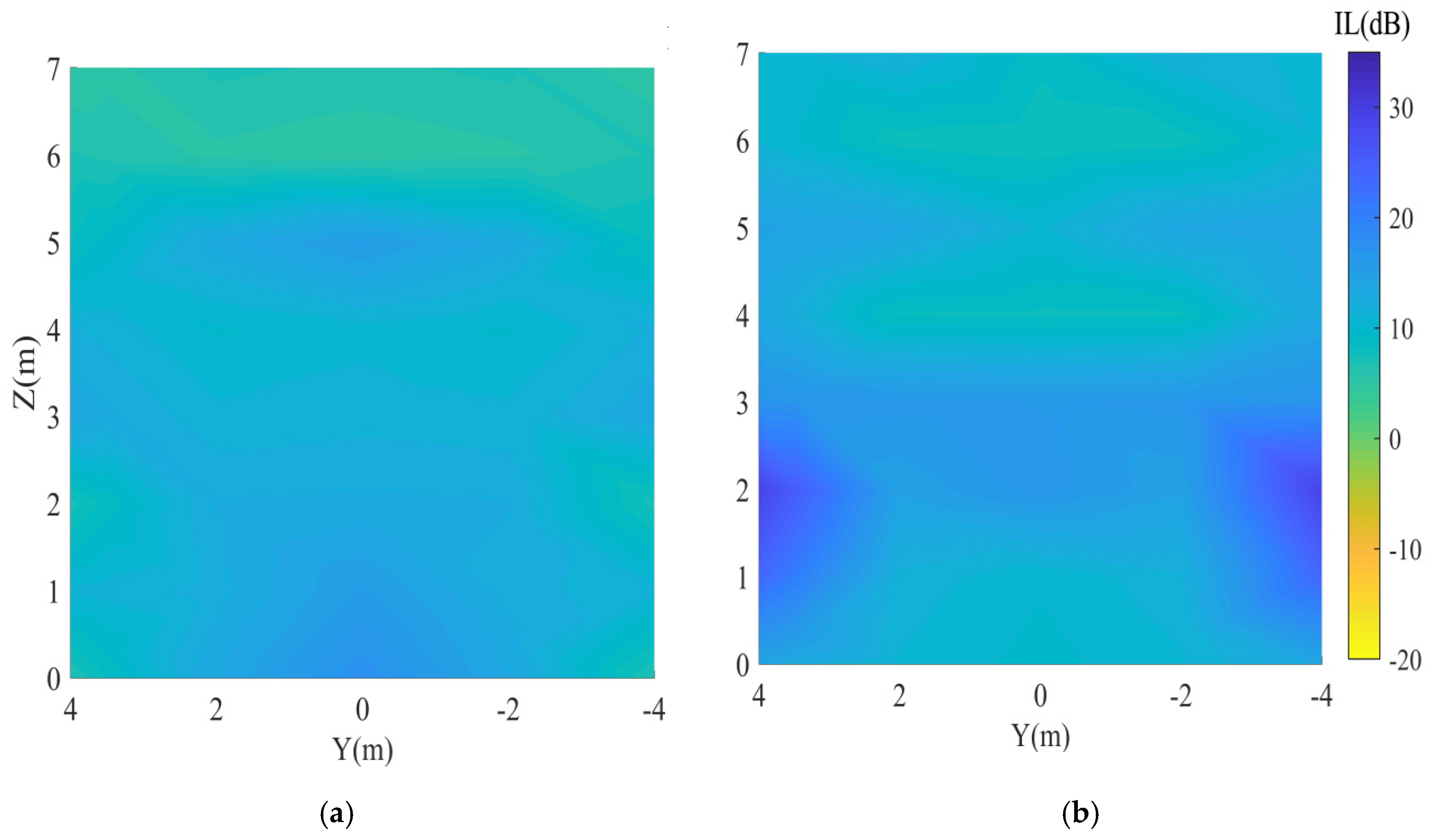
4. Results
4.1. Target Area: Street Area
4.2. Target Area: Shadow Zone of the Façade
5. Discussion
5.1. Target Area: Street Area
5.2. Target Area: Shadow Zone of the Façade
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, S.C.; Kim, J.H.; Hong, J.Y. Characterizing perceived aspects of adverse impact of noise on construction managers on construction sites. Build. Environ. 2019, 152, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Song, Z.; Wang, T.; Zheng, Y.; Ning, X. Health impacts of construction noise on workers: A quantitative assessment model based on exposure measurement. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 135, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C.; Hong, J.Y.; Jeon, J.Y. Effects of acoustic characteristics of combined construction noise on annoyance. Build. Environ. 2015, 92, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xia, B.; Cui, C.; Skitmore, M. Community response to construction noise in three central cities of Zhejiang province, China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, N.; Song, K.; Lee, H.-S.; Kim, J.; Park, M. Construction Noise Risk Assessment Model Focusing on Construction Equipment. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2018, 144, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.F. Effects of building construction noise on residents: A quasi-experiment. J. Environ. Psychol. 2000, 20, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, M.J.; Fernandez, M.D.; Quintana, S.; Ballesteros, J.A.; González, I. Noise emission evolution on construction sites. Measurement for controlling and assessing its impact on the people and on the environment. Build. Environ. 2010, 45, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.W.; Law, C.W.; Wong, C.L. Quiet construction: State-of-the-art methods and mitigation measures. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2014—43rd International Congress on Noise Control Engineering, Melbourne, Australian, 16–19 November 2014; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, N.; Park, M.; Lee, H.-S.; Ahn, J.; Shin, M. Construction Noise Management Using Active Noise Control Techniques. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2016, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilchrist, A.; Allouche, E.N.; Cowan, D. Prediction and mitigation of construction noise in an urban environment. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2003, 30, 659–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thalheimer, E. Construction noise control program and mitigation strategy at the Central Artery/Tunnel Project. Noise Control. Eng. J. 2000, 48, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhaomeng, W.; Meng, L.K.; Priyadarshinee, P.; Pueh, L.H. Applications of noise barriers with a slanted flat-tip jagged cantilever for noise attenuation on a construction site. J. Vib. Control. 2017, 24, 5225–5232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ireland, T.I.; Centre, P.B.; Street, P. Noise management during the construction of a light rail scheme through Dublin city centre. In Proceedings of the INTER-NOISE 2019, Madrid, Spain, 16–19 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, P.M. Innovations that make infrastructure and construction noise control more effective. In Proceedings of the INTER-NOISE 2016—45th International Congress and Exposition on Noise Control Engineering, Hamburg, Germany, 21–24 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.P.; Tan, L.B.; Lim, K.M. Assessment of the performance of sonic crystal noise barriers for the mitigation of construction noise. In Proceedings of the INTER-NOISE 2016—45th International Congress and Exposition on Noise Control Engineering, Hamburg, Germany, 21–24 August 2016; pp. 4220–4226. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.M.; Wang, Z.; Lim, K.M.; Lee, H.P. A Review of Active Noise Control Applications on Noise Barrier in Three-Dimensional/Open Space: Myths and Challenges. Fluct. Noise Lett. 2019, 18, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanazawa, L.; Mizutani, K. Reduction of construction machinery noise in multiple dominant frequencies using feedforward type active control. In Proceedings of the INTER-NOISE 2018—47th International Congress and Exposition on Noise Control Engineering, Chicago, IL, USA, 26–29 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Min, H.; Qiu, X. Noise reduction mechanisms of active noise barriers. Noise Control Eng. J. 2013, 61, 120–126. [Google Scholar]
- Han, N.; Qiu, X. A study of sound intensity control for active noise barriers. Phys. Appl. Acoust. 2007, 68, 1297–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Pan, J. Increasing the insertion loss of noise barriers using an active-control system. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1998, 104, 3408–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omoto, A. Active suppression of sound diffracted by a barrier: An outdoor experiment. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1997, 102, 1671–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, C.; Castiñeira-Ibañez, S.; Uris, A.; Belmar, F.; Candelas, P. Numerical simulation and laboratory measurements on an open tunable acoustic barrier. Appl. Acoust. 2018, 141, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, P.; Wehr, R.; Ziegelwanger, H. Simulation and measurement of noise barrier sound-reflection properties. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 123, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omoto, A. A study of an actively controlled noise barrier. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1993, 94, 2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, F.; Zou, H.; Qiu, X.; Wu, M. Error sensor location optimization for active soft edge noise barrier. J. Sound Vib. 2007, 299, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.C.; Niu, F. Study on the analogy feedback active soft edge noise barrier. Appl. Acoust. 2008, 69, 728–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, C.R.; Lau, S.-K. Active noise control with linear control source and sensor arrays for a noise barrier. J. Sound Vib. 2012, 331, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Rao, W.; Min, H.; Qiu, X. An active noise barrier with unidirectional secondary sources. Appl. Acoust. 2011, 72, 969–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duhamel, D.; Sergent, P.; Hua, C.; Cintra, D. Measurement of active control efficiency around noise barriers. Appl. Acoust. 1998, 55, 217–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wong, H. A review of commonly used analytical and empirical formulae for predicting sound diffracted by a thin screen. Appl. Acoust. 2005, 66, 45–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnishi, K.; Saito, T.; Teranishi, S.; Namikawa, Y.; Mori, T.; Kimura, K.; Uesaka, K. Development of the product-type active soft edge noise barrier. In Proceedings of the 18th International Congress on Acoustics, Kyoto, Japan, 4–9 April 2004; pp. 1041–1044. [Google Scholar]
- Berkhoff, A.P. Control strategies for active noise barriers using near-field error sensing. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2005, 118, 1469–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Pan, J. Application of active noise control to noise barriers. Acoust. Aust. 1997, 25, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, S.-K.; Tang, S.K. Sound fields in a rectangular enclosure under active sound transmission control. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2001, 110, 925–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, J.I.; Romeu, J.; Balastegui, A. Two Step Optimization of Transducer Locations in Single Input Single Output Tonal Global Active Noise Control in Enclosures. J. Vib. Acoust. 2010, 132, 061011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monson, B.B.; Sommerfeldt, S.D.; Gee, K.L. Improving compactness for active noise control of a small axial cooling fan. Noise Control. Eng. J. 2007, 55, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, V.; Gronier, C. Sensor configuration efficiency and robustness against spatial error in the primary field for active sound control. J. Sound Vib. 2001, 246, 679–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeu, J.; Palacios, J.I.; Balastegui, A.; Pàmies, T. Optimization of the Active Control of Turboprop Cabin Noise. J. Aircr. 2015, 52, 1386–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjösten, P.; Johansson, S.; Persson, P.; Claesson, I. Considerations on Large Applications of Active Noise Control. Part II: Experimental Results. Acta Acust. 2003, 89, 834–843. [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald, H.M. A Class of Diffraction Problems. Proc. Lond. Math. Soc. 1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, S.; Nelson, P. The active control of sound. Electron. Commun. Eng. J. 1990, 2, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, T.; Takagi, K.; Hiramatsu, K.; Yamamoto, T. Outdoor sound propagation from a source having dimensions. J. Acoust. Soc. Jpn. 1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Sha, J.-Z.; Zhang, Z.-L. The method of the minimum sum of squared acoustic pressures in an actively controlled noise barrier. J. Sound Vib. 1997, 204, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Su, Z.; Cheng, L. Modeling, analysis, and validation of an active T-shaped noise barrier. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 134, 1990–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ise, S.; Yano, H.; Tachibana, H. Basic study on active noise barrier. J. Acoust. Soc. Jpn. 1991, 12, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| ANB | PNB | ANB | PNB | ANB | PNB | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (−0.5, 0) | (0.5,2.4) | 16.4 | 14.9 | 17.9 | 10.8 | 17.9 | 10.8 |
| 2.5 | (−0.5,1.8) | (0.5,1.1) | 11.9 | 13.2 | 10.8 | 9.6 | 0.9 | 8.7 |
| 4 | (−0.5, 1.8) | (0.5,0.9) | 10.9 | 12.3 | 8.4 | 9.5 | −0.3 | 8.3 |
| 5.5 | (−0.5, 1.8) | (0.4,0.4) | 9.9 | 11.8 | 8.1 | 9.2 | −0.4 | 8.3 |
| 7 | (−0.5, 1.8) | (0.4,0.2) | 9.3 | 11.4 | 7.9 | 9.1 | −0.1 | 8.3 |
| ANB | PNB | ANB | PNB | ANB | PNB | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (−0.5, 0) | (0.2, 2.3) | 11.8 | 14.9 | 22.0 | 10.8 | 22.0 | 10.8 |
| 2.5 | (−0.5,1.9) | (0.5, 0.5) | 11.4 | 13.2 | 12.1 | 9.6 | 0.6 | 8.7 |
| 4 | (−0.5,1.8) | (0.3, 0.3) | 10.3 | 12.3 | 9.7 | 9.5 | −0.5 | 8.3 |
| 5.5 | (−0.5,2.3) | (0.5, 0.2) | 10.7 | 11.8 | 9.4 | 9.2 | 1.1 | 8.3 |
| 7 | (−0.5,2.3) | (0.3,0.4) | 8.3 | 11.4 | 8.9 | 9.1 | 0.1 | 8.3 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sohrabi, S.; Pàmies Gómez, T.; Romeu Garbí, J. Suitability of Active Noise Barriers for Construction Sites. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6160. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10186160
Sohrabi S, Pàmies Gómez T, Romeu Garbí J. Suitability of Active Noise Barriers for Construction Sites. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(18):6160. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10186160
Chicago/Turabian StyleSohrabi, Shahin, Teresa Pàmies Gómez, and Jordi Romeu Garbí. 2020. "Suitability of Active Noise Barriers for Construction Sites" Applied Sciences 10, no. 18: 6160. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10186160
APA StyleSohrabi, S., Pàmies Gómez, T., & Romeu Garbí, J. (2020). Suitability of Active Noise Barriers for Construction Sites. Applied Sciences, 10(18), 6160. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10186160





