Experimental Investigation of the Multi-Physical Properties of an Energy Efficient Translucent Concrete Panel for a Building Envelope
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. TCP Specimen
2.1. Volumetric Ratio (VR)
2.2. Compressive Strength
3. Test Methodology
3.1. Thermal Property Test
3.2. Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC, G-Value) Test
3.3. Visible Light Transmittance (VLT) Test
4. Test Result
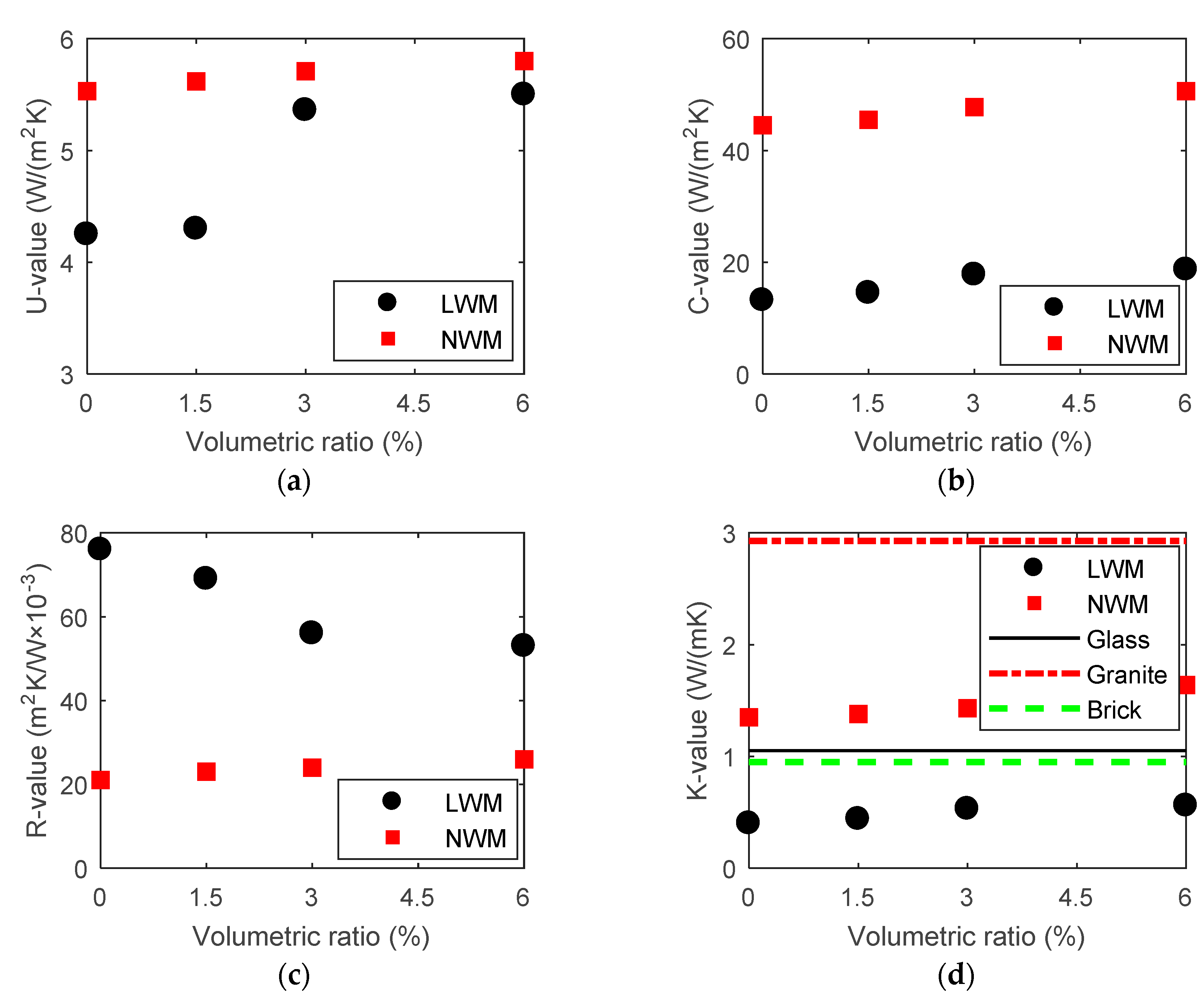
4.1. Thermal Properties
4.2. SHGCs
4.3. VLT
5. Conclusions and Future Research
5.1. Conclusions
- (1)
- The mechanical properties of the NWM and LWM mortars determine the load-bearing capacity of the two materials. As a result of the proper mixing ratio of the materials, the compressive strength of the LWM was higher than that of the NWM, while the LWM was more brittle than the NWM.
- (2)
- The U-values of the plain panel were 4.25 and 5.45 W/(m2 K) for TCPs with LWM and NWM, respectively. The existence of the OFs improved the thermal insulation property. The K-values of the LWM TCP were smaller than that of the common façade, which proved its excellent energy efficient performance. This potentiality of replacement of the traditional glass curtain wall system was predictable in the locations where the lighting requirement was not particularly high (Huang, 2020) [48].
- (3)
- The SHGCs (G-values) of the two tested TCP types—LWM and NWM—were 0.198 and 0.242, respectively.
- (4)
- The VLT tests showed that the light transmitted by the TCP was proportional to the density of the OFs in a matrix of concrete. The experimental light acceptance angle of the OF was measured to be 35 °C, which was close to the computational value shown by Equations (6) and (7).
5.2. Future Research
- (1)
- The effect of the optical fibers on the mechanical strength of the TCP will be determined in future study.
- (2)
- (3)
- The multi-physical analysis of the TCPs should be conducted considering thermal, light transmission and mechanical actions. Furthermore, numerical analysis and physical testing approaches should be developed to comprehensively evaluate the overall performance of the building façade.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Edwards, L.; Torcellini, P. A Literature Review of the Effects of Natural Light on Building Occupants; NREL/TP-550-30769; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Litracon. Available online: http://www.litracon.hu/ (accessed on 11 July 2012).
- Bates, D. Mortar This than Meets the Eye: The ‘Transparent’ Cement that Lets Daylight Flood into a Room. 2010. Available online: http://www.dailymail.co.uk/sciencetech/article-1344383/Transparent-light-cement-lets-light-flood-room.html (accessed on 6 September 2020).
- Hipstomp. Transparent Concrete and Cement at World Expo. 2010. Available online: http://www.core77.com/blog/materials/transparent_concrete_and_cement_at_world_expo_16562.asp (accessed on 6 September 2020).
- Lucem. Available online: http://www.lucem.de/fileadmin/templates/Downloads/Planungsordner/LUCEMplanningfolderenglisch_email.pdf (accessed on 6 September 2020).
- Klemenc, S.E. Wave of the Future: 21st Century Concrete on Display. 2011. Available online: http://www.concretedecor.net/Articles/CD404/CD404_transparent_concrete.cfm (accessed on 6 September 2020).
- He, J.; Zhou, Z.; Ou, J. Study on smart transparent concrete product and its performances. In Proceedings of the 6th International Workshop on Advanced Smart Materials and Smart Structures Technology (ANCRiSST2011), Dalian, China, 25 July 2011; p. 107. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.; Mosalam, K. Construction and Testing of the Energy Efficient Translucent Concrete Panels; Structural Engineering Mechanics and Materials (SEMM) Report No. UCB/SEMM-[2015/04]; University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ahuja, A.; Mosalam, K.M.; Zohdi, T.I. Computational modeling of translucent concrete panels. J. Arch. Eng. 2015, 21, 4014008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, A.; Mosalam, K.M. Evaluating energy consumption saving from translucent concrete building envelope. Energy Build. 2017, 153, 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacy, E. Fiber Optics; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Matsui, T.; Nakajima, K.; Toge, K.; Kurashima, T.; Tsubokawa, M. Fiber identification technique based on mechanically-induced long-period grating for bending-loss insensitive fibers. J. Light. Technol. 2010, 28, 3556–3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.C. Textbook on Optical Fiber Communication and Its Applications; Prentice Hall of India: Delhi, India, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Farrell, G.; Freir, T. Theoretical and experimental investigations of macro-bend losses for standard single mode fibers. Opt. Express 2005, 13, 4476–4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangnon, G.L.; Hsu, H.P.; Jones, V.; Pikulshi, J. Bend loss measurements for small mode field diameter fibers. Electron. Lett. 1989, 25, 142–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renner, H. Bending losses of coated single-mode fibers: A simple approach. J. Light. Technol. 1992, 10, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Industrial Fiber Optics. Available online: http://i-fiberoptics.com/fiber-detail.php?id=114 (accessed on 24 April 2018).
- ASTM International. ASTM C39/C39M-19: Standard Test Method for Compressive Strength of Cylindrical Concrete Specimens; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM International. C617/C617M-15: Standard Practice for Capping Cylindrical Concrete Specimens; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Wittkopf, S.K. Summer condition thermal transmittance measurement of fenestration systems using calorimetric hot box. Energy Build. 2012, 53, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM International. ASTM C1363-11: Standard Test Method for Thermal Performance of Building Materials and Envelope Assembly by Means of a Hot Box Apparatus; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Building and Construction Authority (BCA). Code on Envelope Thermal Performance for Buildings; Building and Construction Authority: Singapore, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Baenas, T.; Machado, M. On the analytical calculation of the solar heat gain coefficient of a BIPV module. Energy Build. 2017, 151, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlos, J.S.; Corvacho, H. Evaluation of the performance indices of a ventilated double window through experimental and analytical procedures: SHGC-values. Energy Build. 2015, 86, 886–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinoski, D.L.; Güths, S.; Pereira, F.O.R.; Lamberts, R. Improvement of a measurement system for solar heat gain through fenestrations. Energy Build. 2007, 39, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 9050 (International Standard), Determination of Light Transmittance, Solar Direct Transmittance, Total Solar Energy Transmittance, Ultraviolet Transmittance and Related Glazing Factors; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003.
- EN 410 (European Standard), Glass in Buildings, Determination of Luminous and Solar Characteristics of Glazing; British Standards Institution: London, UK, 2011.
- ISO 15099 (International Standard), Thermal Performance of Windows, Doors and Shading Devices Detailed Calculations; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003.
- EN 13363-2 (European Standard), Solar Protection Devices Combined with Glazing—Calculation of Total Solar Energy Transmittance and Light Transmittance—Part 2: Detailed Calculation Method; British Standards Institution: London, UK, 2005.
- Carlos, J.S.; Corvacho, H.; Silva, P.D.; Castro-Gomes, J.P. Modelling and simulation of a double ventilated window. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2011, 31, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, C.; Kuhn, T.E. Variable g value of transparent façade collectors. Energy Build. 2012, 51, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Wittkopf, S.K.; Ng, P.K.; Du, H. Solar heat gain coefficient measurement of semi-transparent photovoltaic modules with indoor calorimetric hot box and solar simulator. Energy Build. 2012, 53, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM International. ASTM C1199-09: Standard Test Method for Measuring the Steady-State Thermal Transmittance of Fenestration Systems Using Hot Box Methods; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- National Fenestration Rating Council. NFRC 200-2010, Procedure for Determining Fenestration Product Solar Heat Gain Coefficient and Visible Transmittance at Normal Incidence; National Fenestration Rating Council: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- National Fenestration Rating Council. NFRC 300-2010, Test Method for Determining the Solar Optical Properties of Glazing Materials and Systems; National Fenestration Rating Council: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Rund, R.C. International Organization for Standardization (ISO). J. AOAC Int. 1992, 75, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM International. ASTM G173-03: Standard Tables for Reference Solar Spectral Irradiances: Direct Normal and Hemispherical on 37° Tilted Surface; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, R.; O’Sullivan, M. Fiber Optic Measurement Techniques; Elsevier Academic Press: Burlington, VT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- International Commission on Illumination (CIE). Radiometric and Photometric Characteristics of Materials and Their Measurement, CIE 38 (TC-2.3); CIE Central Bureau: Vienna, Austria, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- International Commission on Illumination (CIE). Practical Methods for the Measurement of Reflectance and Transmittance, CIE 130; CIE Central Bureau: Vienna, Austria, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- National Fenestration Rating Council, Inc. NFRC 200-2014: Procedure for Determining Fenestration Product Solar Heat Gain Coefficient and Visible Transmittance at Normal Incidence; National Fenestration Rating Council: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- McCormick, E.; Jakubiec, J.A.; Budig, M. Analysis of architectural façade elements in tropical climates for daylight, Thermal Comfort and Passive Climatization. In Proceedings of the 15th IBPSA Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 7–9 August 2017; pp. 2540–2548. [Google Scholar]
- Koo, B.; Lee, K.; An, Y.-S.; Lee, K.D. Solar heat gain reduction of ventilated double skin windows without a shading device. Sustainability 2017, 10, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzali, U.; Ruggeri, P.; Zinzi, M.; Peron, F.; Romagnoni, P.; Dáneo, A. Set-up and calibration by experimental data of a numerical model for the estimation of solar factor and UG-value of building integrated photovoltaic systems. Energy Procedia 2015, 78, 2202–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, P.K.; Mithraratne, N. Lifetime performance of semi-transparent building-integrated photovoltaic (BIPV) glazing systems in the tropics. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 31, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, L.; Frontini, F.; Polo-López, C.; Pahud, D.; Caamano-Martin, E. G-value indoor characterization of semi-transparent photovoltaic elements for building integration: New equipment and methodology. Energy Build. 2015, 101, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, T.E. Calorimetric determination of the solar heat gain coefficient g with steady-state laboratory measurements. Energy Build. 2014, 84, 388–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B. Light transmission performance of translucent concrete building envelope. Cogent Eng. 2020, 7, 1756145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston, R.; Miñano, J.C.; Benitez, P. Nonimaging Optics, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Academic Press: London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]






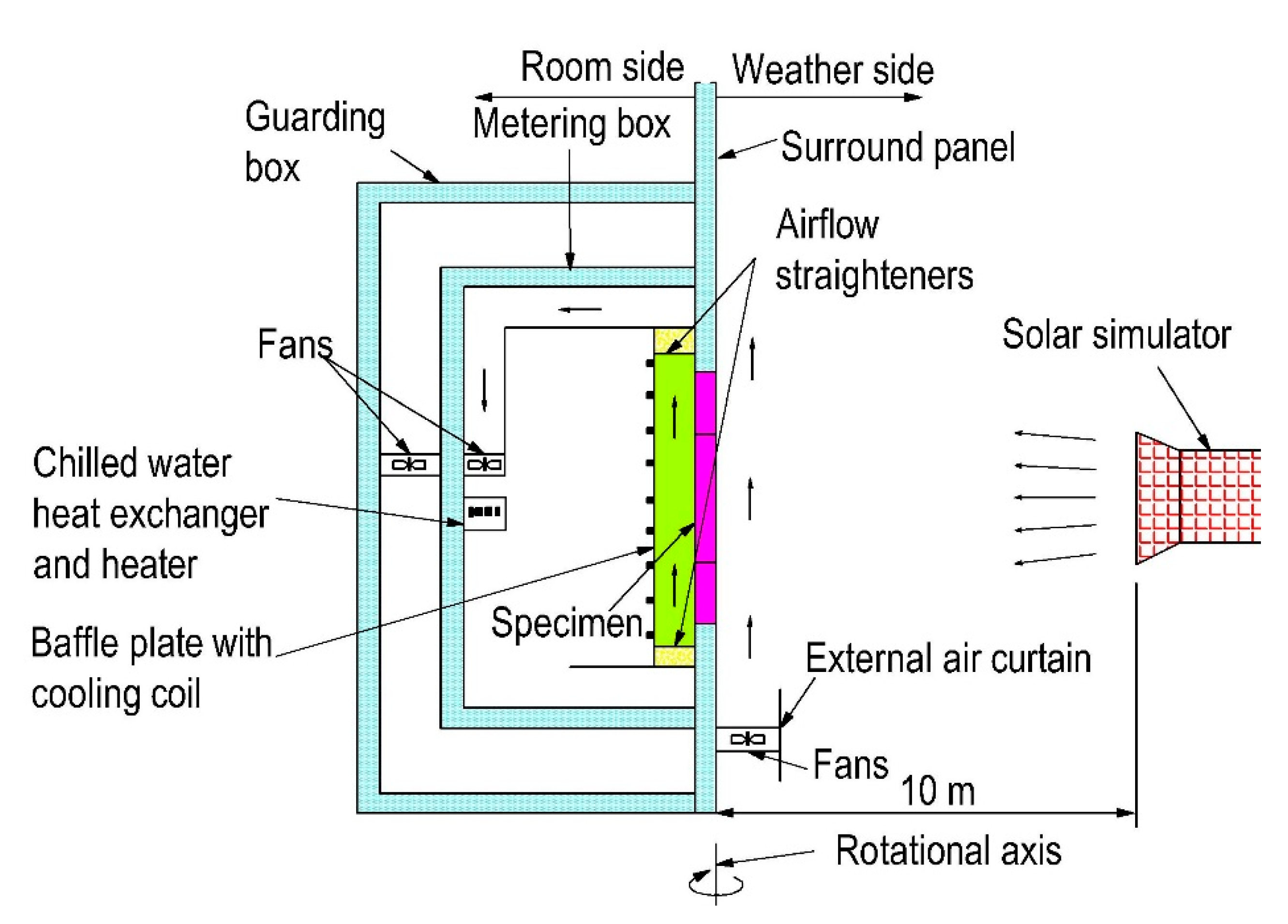








| Type | W/C | Water (kg/m3) | Cement (kg/m3) | Fly ash (kg/m3) | Silica Fume (kg/m3) | Fine Aggregate (kg/m3) | SRA (kg/m3) | SP (kg/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NWM | 0.50 | 253.0 | 405.0 | 101.0 | 0.0 | 1391.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| LWM | 0.35 | 258.0 | 742.0 | 0.0 | 65.0 | 335.0 | 20.0 | 4.5 |
| Property | Specification |
|---|---|
| Core material | Polymethyl-methacrylate (PMMA) resin |
| Cladding material | Fluorinated polymer |
| Core refractive index | 1.49 |
| Refractive index profile | Step-index |
| Numerical aperture | 0.50 |
| Core diameter (µm) | 2765–3125 |
| Cladding diameter (µm) | 2820–3180 |
| Approximate weight (g/m) | 8.6 |
| Tensile strength (N) | 550.0 |
| Environmental Properties | Temperature/Air Flow |
|---|---|
| Indoor side air temperature | 40 °C |
| Outdoor side air temperature | 20 °C |
| Indoor side airflow velocity and direction | 0.3 m/s, vertically upwards |
| Outdoor side airflow velocity and direction | 3.5 m/s, vertically upwards |
| Item | LWM | NWM |
|---|---|---|
| Average metering air temperature (°C) | 24.0 | 24.0 |
| Average external air curtain temperature (°C) | 26.9 | 27.0 |
| Metering airflow velocity (m/s) | 0.26 | 0.26 |
| External air curtain velocity (m/s) | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| Specimen heat flow rate (W) | 9.0 | 11.1 |
| Solar irradiance (W/m2) | 510.0 | 508.0 |
| SHGC | 0.198 ± 0.033 | 0.242 ± 0.034 |
| TCP Type | NWM | LWM | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VR | 1.5 | 3.0 | 6.0 | 1.5 | 3.0 | 6.0 |
| Test 1 | 1.1 | 2.3 | 6.9 | 1.1 | 2.1 | 6.9 |
| 2 | 1.2 | 2.3 | 7.0 | 1.0 | 2.1 | 6.9 |
| 3 | 1.0 | 2.3 | 7.0 | 1.1 | 1.9 | 6.9 |
| 4 | 1.1 | 2.3 | 6.9 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 6.9 |
| 5 | 1.1 | 2.3 | 6.9 | 1.1 | 1.9 | 6.9 |
| Average | 1.1 | 2.3 | 6.9 | 1.1 | 2.0 | 6.9 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, B.; Lu, W. Experimental Investigation of the Multi-Physical Properties of an Energy Efficient Translucent Concrete Panel for a Building Envelope. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6863. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10196863
Huang B, Lu W. Experimental Investigation of the Multi-Physical Properties of an Energy Efficient Translucent Concrete Panel for a Building Envelope. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(19):6863. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10196863
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Baofeng, and Wensheng Lu. 2020. "Experimental Investigation of the Multi-Physical Properties of an Energy Efficient Translucent Concrete Panel for a Building Envelope" Applied Sciences 10, no. 19: 6863. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10196863
APA StyleHuang, B., & Lu, W. (2020). Experimental Investigation of the Multi-Physical Properties of an Energy Efficient Translucent Concrete Panel for a Building Envelope. Applied Sciences, 10(19), 6863. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10196863






