Abstract
This work is to study the relationship between the exposure conditions and the quality of cell imaging with soft X-ray contact microscopy (SXCM). It is a crucial step in the efficient visualization of cell structures. Three different human cell lines: DU145 prostate carcinoma cells, HCC38 breast cancer cells, and Poietics mesenchymal stem cells were used to establish the optimal exposure conditions in SXCM. The image quality depended on the soft X-ray (SXR) absorbed energy and photoresist development conditions. At lower SXR energy (200 or 400 SXR pulses), sharp cell edges, membrane projections, and cell–cell connections were visible. In contrast, higher energy (600 or 800 SXR pulses) allowed observation of the cytoskeleton and the nucleus in a cell type-dependent manner (the influence of cell thickness and internal complexity was noted).
1. Introduction
Soft X-ray contact microscopy (SXCM) is a potent technique enabling imaging with a nanometric resolution of specific features in cells [1,2]. Most structures of mammalian cells have already been visualized by electron and fluorescent microscopy, commonly used in biological research [3,4]. However, these methods were biased by protocols for consecutive sample preparation and had insufficient resolution to analyse the structures inside the cell [5,6]. The great advantage of SXCM is the possibility to observe the cell structure without the necessity to use invasive preparative procedures such as dehydration (for scanning electron microscopy) or immunofluorescent labeling (for fluorescent microscopy) of the samples [7,8]. The contrast required for cell imaging under SXCM stems from the strong absorption of carbon atoms. SXCM works within the energy range between the carbon and oxygen K-absorption edges known as the “water window” (2.3–4.4 nm wavelength; 284–540 eV photon energy) [9]. In this spectral region, water-containing intracellular compartments absorb much less than carbon-rich structures (e.g., plasma membranes and organelles), which absorb photons efficiently, leading to high contrast images. As previously reported, in the “water window”, intact biological specimens up to 10 µm thick can be observed [10,11].
The desk-top SXCM used in this study is based on a laser-plasma source of soft X-rays. It was specially developed to acquire images of biological objects in and out of the vacuum environment. The system was first developed for dried samples [12,13], showing its applicability potential and the need to optimise soft X-ray (SXR) conditions to visualize the internal cell structures in the thickness and morphological complexity-dependent manner. Currently, the system can imagine living cells in the He-filled environmental chamber using an additional silicon nitride (Si3N4) membrane, allowing moisture underneath the membrane during the entire exposure. Exposure of the samples is much easier to perform, without the necessity to encapsulate or sandwich the samples between two Si3N4 membranes, as it is done typically using transmission-based electron microscopy (TEM [14,15,16]), synchrotron-based [17], and plasma-based [18] SXR microscopes, or in some kind of encapsulated vacuum-tight holder [7].
In our case, the evacuation of the sample chamber is not necessary; thus, we save time and avoid potential problems with sample degassing if the capsule is not properly sealed. Finally, the SXCM system is based on the source with a gas puff target; thus, it is debris-free and easy for operation and maintenance. It does not produce ablation products associated with laser interactions with solid targets [19], nor does it require any surface polishing before the operation [20].
The polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) photoresist is the most often applied detector in SXCM [21,22]. The exposure of PMMA to ionizing radiation causes breakage of bonds along the polymer chain. The photoresist’s subsequent chemical development in a solvent mixture leads to a change in its surface topography. This change depends on the X-ray energy deposited in the photoresist [23]. The cells adherent to the PMMA sheathe its surface from the radiation. Depending on the cell thickness, the 3D visualization of internal structures within eukaryotic cells becomes possible [24,25].
Despite the technological progress of the source design and improvement of its parameters, the SXCM analysis of biological specimens still requires optimization due to different cell morphologies. Three morphologically different cell lines were chosen for this study: DU145 prostate carcinoma cell line, HCC38 breast cancer cell line, and Poietics mesenchymal stem cells. The SXR absorbed energy in the photoresist, determined by the number of soft X-ray pulses, and the photoresist development procedure was optimized to obtain images of internal structures of a cell with a resolution of a few tens of nanometer. The novelty of our work lies in demonstrating that each cell line requires different technological approaches to be observed in detail under SXCM.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characterization of Soft X-ray Contact Microscope (SXCM) System
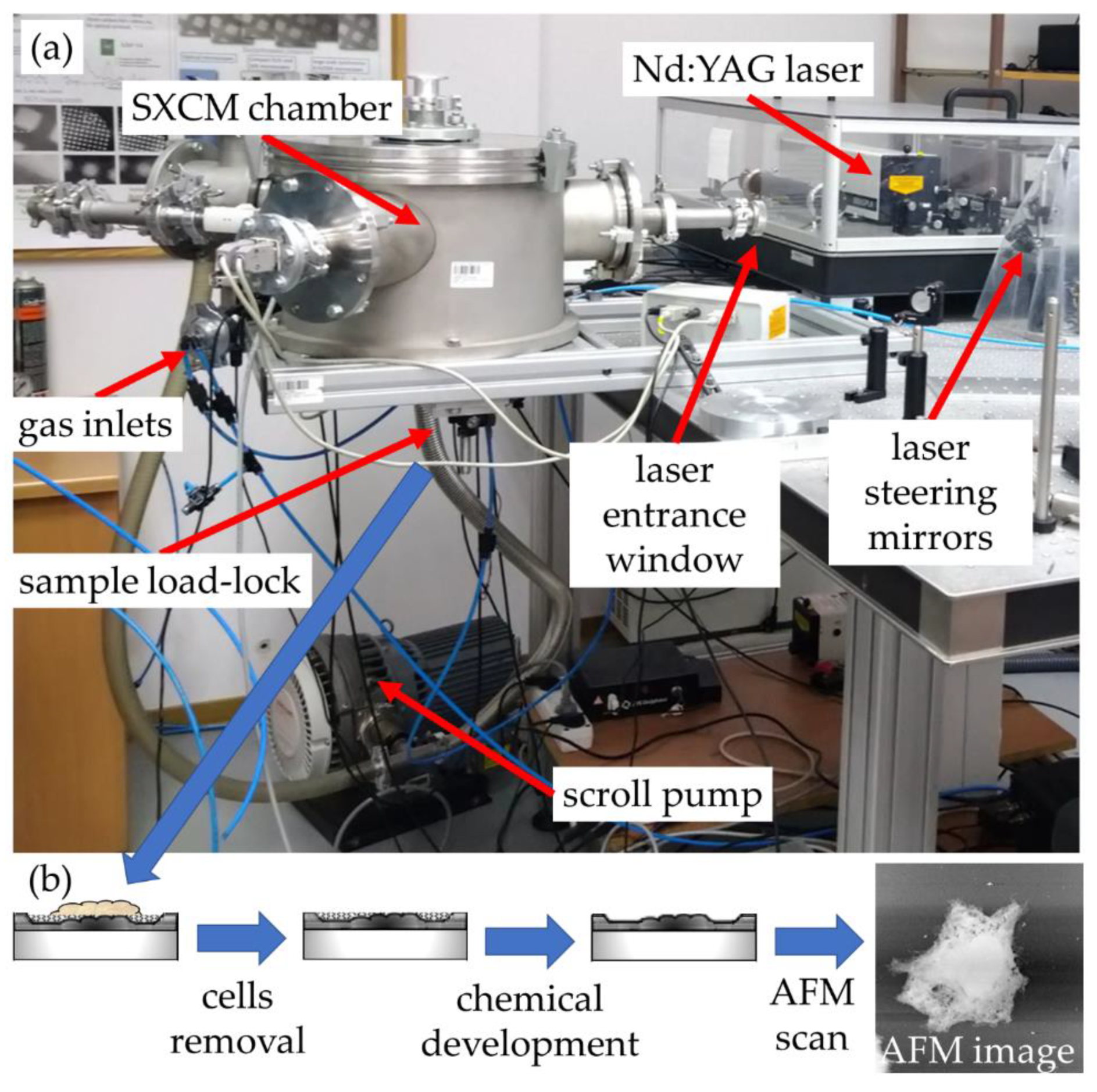
The system is based on a laser-plasma soft X-ray source with an argon/helium gas puff target, and it is shown in Figure 1. A small cylindrical chamber was used to house a double stream valve with two colinear nozzles, injecting argon through the central round (0.4 mm in diameter) nozzle and helium through the outer, ring-shaped nozzle (diameter of 0.7–1.5 mm). A commercial compact 10 Hz, 740 mJ, 4 ns, 1064 nm Nd:YAG laser (NL 303HT, from EKSPLA, Lithuania) was focused using a 25 mm focal length lens (CVI, Norfolk, VA, USA), to a spot ~100 microns in diameter, reaching the power density of ~2 × 1012 W/cm2.
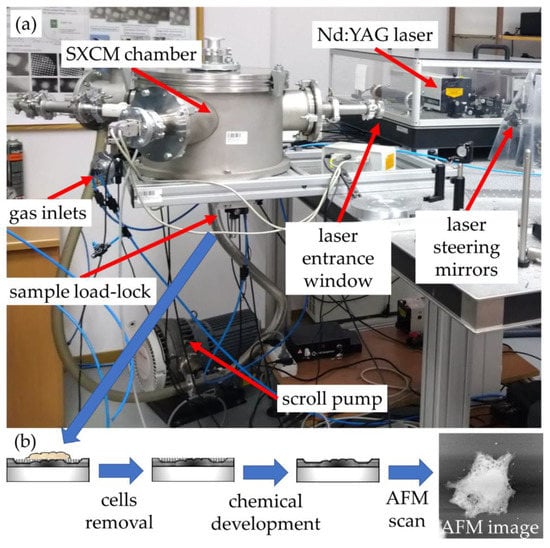
Figure 1.
(a) Soft X-ray contact microscopy (SXCM) system and (b) the flowchart of the SXCM sample-processing procedure.
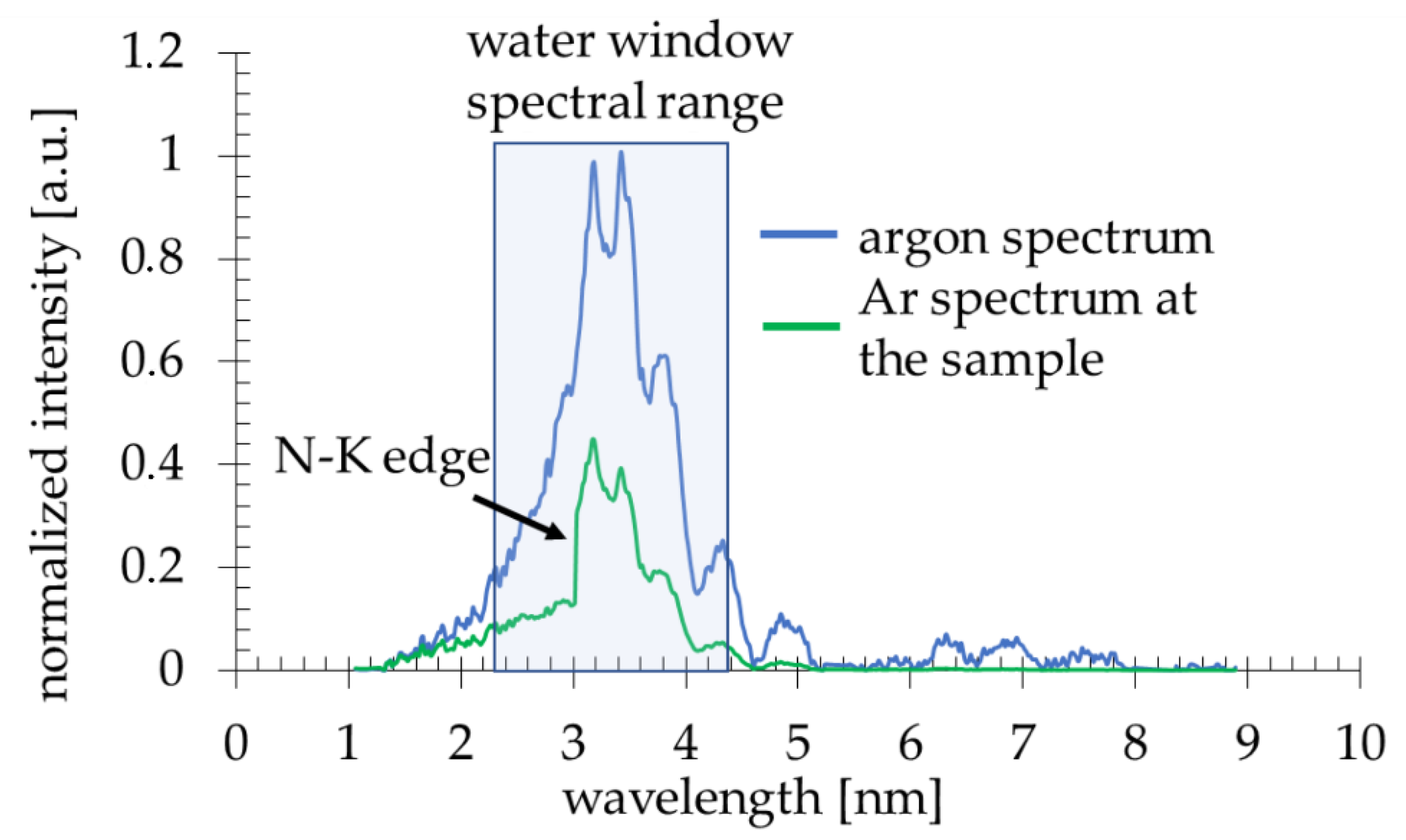
Due to a laser-matter interaction, argon plasma is produced with a sufficient ionization degree to emit radiation in the 2.3–4.4 nm spectral band (Figure 2, blue line). The plasma emission spectrum was obtained using a transmission grating spectrometer equipped with a 30 µm-wide entrance slit and 5000 lines per mm gold free-standing transmission grating. The resolving power of the spectrometer was estimated to be λ/Δλ~50. The 200 nm-thick Si3N4 membrane 0.5 × 0.5 mm2 in size was placed ~16 mm from the plasma. This membrane separates the source chamber’s vacuum environment from the He environment inside a cylindrical-shaped smaller sample chamber. A specially designed sample holder allowed loading the PMMA-coated Si wafers and locating them ~21 mm from the plasma, so only a few mm gap filled with He gas at slightly higher than 1 bar pressure was between the sample and the separating membrane. The use of He gas allowed the removal of the air from the sample chamber, which efficiently attenuates the SXR radiation. A 5 mm gap filled with He at 770 Torr gas pressure had, on average, ~85% transmission in the wavelength range from 3–5 nm, while air at 760 Torr pressure ~12–15%. This allowed obtaining ~8 × 103 ph/µm2/pulse at the surface of the PMMA in the wavelength band from 3 nm to 4 nm, narrowed by the nitrogen N-K edge of the Si3N4 membrane (Figure 2, green line), taking into account the attenuation of He gas and Si3N4 separating membrane.
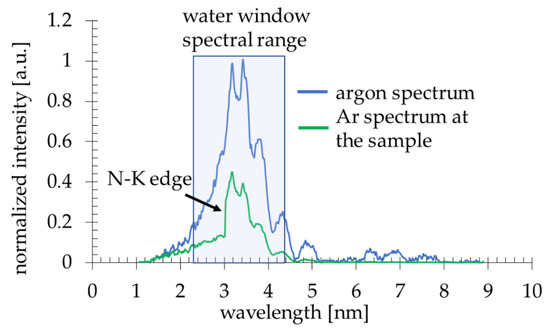
Figure 2.
The Ar spectrum (the normalized intensity plotted versus wavelength) directly from the plasma ( ) and at the sample plane (
) and at the sample plane ( ).
).
 ) and at the sample plane (
) and at the sample plane ( ).
).
The photon yield was measured using AXUV 100 (Opto Diode Corporation, Camarillo, CA, USA) photodiode. More details about the source and the system were reported in [12].
2.2. Cell Culture
Three different types of human cell were used: prostate DU145 carcinoma cells (ATCC® HTB-81), breast HCC38 cancer cells (ATCC® CRL-2314TM), and human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hMSC, PoieticsTM, PT-2501, Lonza, Walkersville, MD, USA). DU145 cells were cultured in Minimum Essential Medium (MEM) with GlutaMAX™ (Life Technologies, Grand Island, NY, USA), 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, Life Technologies, USA), and 1% solution of antibiotic-antimycotic (Life Technologies, USA). HCC38 cells were grown in Roswell Park Memorial Institute (RPMI 1640) medium with L-glutamine (Life Technologies, USA) with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, Life Technologies, Grand Island, NY, USA) and 1% solution of Antibiotic-Antimycotic (Life Technologies, USA). Poietics hMSCs were maintained in the Mesenchymal Stem Cell Growth Medium (MSCGM) Bullet kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Lonza, USA).
The media were changed three times in a week. The cells were incubated at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere of 95% air and 5% CO2. After a few passages, the cells were transferred to the 24-well plates and cultured on the PMMA photoresist’s surface for 24 h. Afterward, the cells were fixed with 3.7% paraformaldehyde solution in PBS (phosphate-buffered saline, pH 7.4, Sigma-Aldrich, Poznań, Poland), and washed with PBS and deionized water. Such protocol allowed drying of the cells without any signs of salt crystallization on the PMMA surface. The cell morphology was observed under an optical microscope (Primo Vert, Zeiss, Jena, Germany) with a 20× objective.
2.3. Optimization of the Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) Exposure to Soft X-ray Radiation
PMMA photoresists had a thickness of ~500 nm, obtained by a spin-coating technique (ITME, Warsaw, Poland). It was exposed to 200, 400, 600, 800, 1000, 1200, and 1400 pulses of SXR radiation to change the SXR absorbed energy, and further it was chemically developed. The imprints’ surface was scanned with an atomic force microscope (AFM, di CP-II, Veeco, Santa Barbara, CA, USA) in a tapping mode with the RTESPA MPP11123-10 cantilevers. The PMMA thickness was scanned as a cross-section of the area exposed and not exposed to soft X-ray radiation. The amount of dissolved PMMA (removed after the radiation exposure and development) was calculated as a difference in the height between these two areas, averaged over 10 scan lines for each sample. The AFM images were analyzed with the Gwyddion 2.53 software (available at http://gwyddion.net/, Czech Metrology Institute, Brno, Czech Republic, accessed on 28 August 2020).
2.4. Cell Imaging
The ~500 nm thick PMMA photoresist was spin-coated on top of a Si wafer (~670 µm thick). The cells adherent on its surface were exposed to soft X-ray radiation from 3 to 4 nm wavelength (see the green plot in Figure 2). The SXCM images of DU145, HCC38, and hMSC cells were acquired using 400–800 SXR pulses. Following exposure to the soft X-rays, the photoresist was cleaned using a 5% sodium hypochlorite (NaClO, Achem, Wiązowna, Poland) for 5 min to eliminate the biological specimen’s residues. The material was developed in a mixture of methyl isobutyl ketone (MIBK, Chempur, Piekary Śląskie, Poland) and isopropyl alcohol (IPA, POCH, Gliwice, Poland) (MIBK: IPA, 1:2 v/v) for 4 min at 20° C. The samples were finally washed in pure isopropyl alcohol. This process resulted in a high-resolution relief map on the PMMA surface. The cell imprints on the photoresist’s surface were visualized using AFMs working in contact (Xe120, Park Systems, Suwon, South Korea, using OTR4 cantilevers) and tapping (di CP-II, Veeco, using MPP11123-10 cantilevers) modes. The images of surface topography were processed as described above.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of SXCM Technique for Cell Imaging
The optimization aimed to select the appropriate absorbed energy of SXR radiation and conditions for developing the photoresist after the SXR exposure. PMMA is a standard, often-used photoresist in SXCM because its particular optical properties provide high resolution. PMMA is also a suitable material for the cell culturing [26,27,28]. The photoresist development required the optimized content of the developer mixture (the optimal ratio of MIBK and isopropanol). The thickness of the dissolved photoresist depends on the SXR absorbed energy and the developer concentration. It translates into the height of the cell imprint and, thus, the contrast obtained. To our best knowledge, there is no literature data on the effect of the soft X-ray exposure on the quality of the internal structure imaging of cells of different origin and morphology. Therefore, we adjusted the basic parameters of SXCM imaging to visualize subtle internal structures of adherent DU145, HCC38, and MSC cells.
3.1.1. Optimization of the PMMA Development
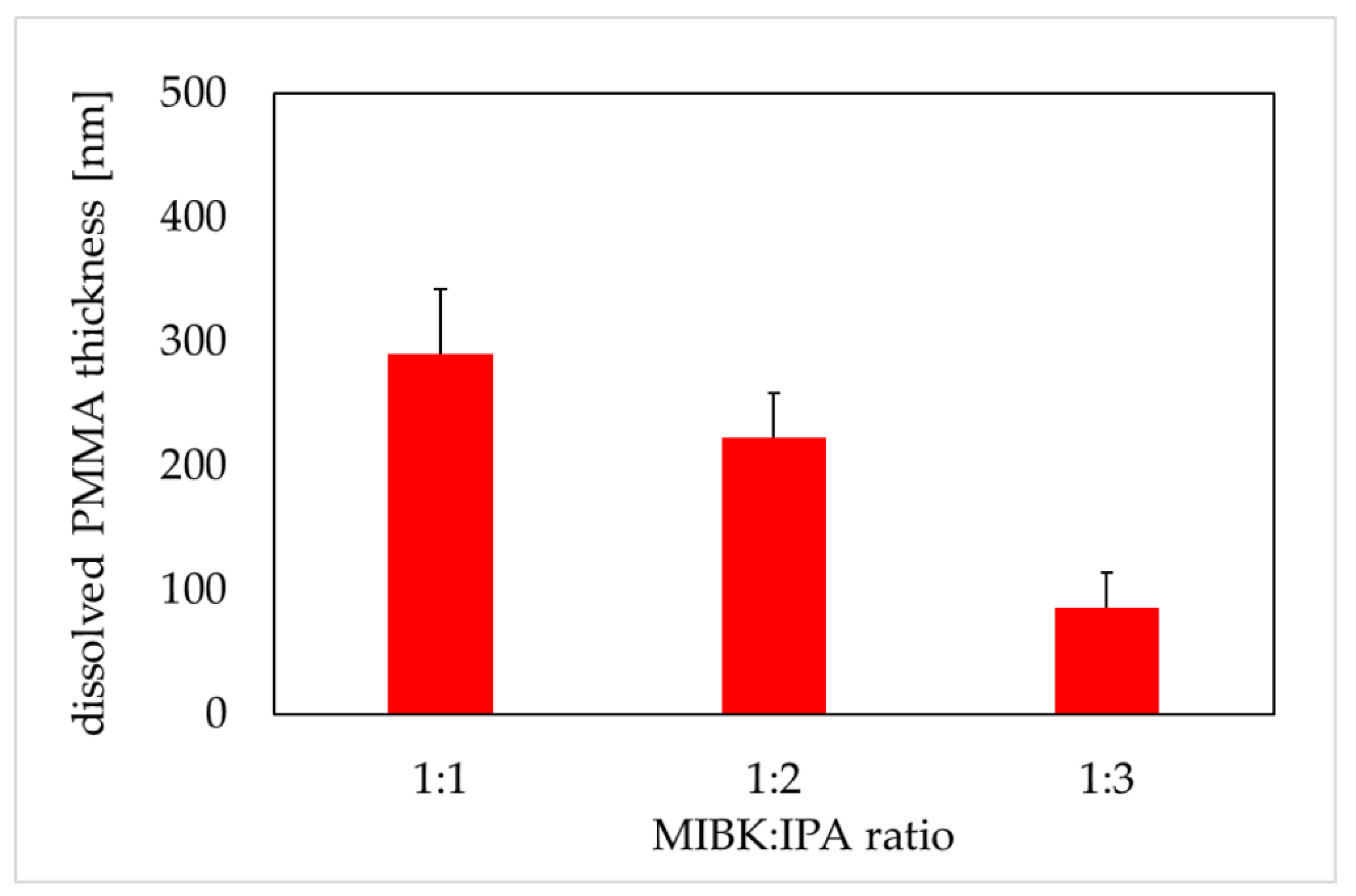
The development of light-sensitive materials is a critical step in their usage for SXCM because it can affect the contrast of the image, the image resolution, and the shape and threshold parameters of the photoresist’s response curve (Figure 3).
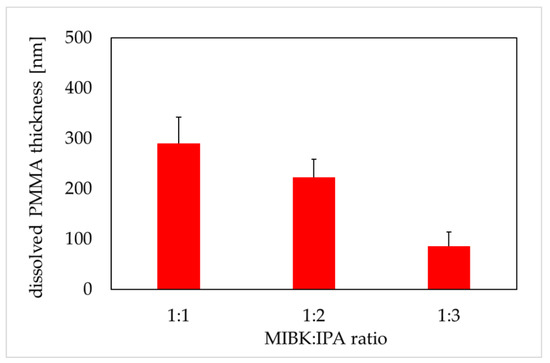
Figure 3.
Dissolved polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) thickness versus MIBK:IPA ratio (600 soft X-ray (SXR) pulses, the development time of 4 min). PMMA thickness was obtained from atomic force microscopy images (AFM, di CPII Veeco) as described in Material and Methods. Data are expressed as a mean ± standard deviation from 10 images.
The PMMA is a positive photoresist (a fraction of the photoresist exposed to radiation is soluble in the photoresist developer) with high spatial resolution. MIBK is a strong solvent for PMMA, that is why MIBK is usually diluted with IPA. IPA is a very weak solvent for PMMA and cannot be used efficiently to dissolve PMMA [29]. In our study, the samples of PMMA were irradiated with 600 SXR pulses, and then chemically developed in different MIBK to IPA ratios for four minutes. This duration of the development phase was confirmed in the independent experiments (data not shown). The thickness of degraded PMMA was 290 ± 52, 223 ± 35, and 86 ± 25 nm for the MIBK:IPA ratio 1:1, 1:2, and 1:3, respectively (Figure 3). The results showed a proportional decrease in the thickness of the dissolved PMMA in relation to the increased concentration of IPA in the mixture.
It has already been shown that sensitivity, contrast, roughness, and resolution depend on the photoresist and its development conditions [30,31]. Thus, it is necessary to select the photoresist development conditions required to obtain a high spatial resolution while preserving the cellular structures. The developer concentration must be finely tuned to dissolve the degraded PMMA and leave unaffected the regions unexposed to soft X-ray radiation [32,33]. Yasin and coworkers [31] investigated the influence of an unconventional developer comprising of IPA and water on the photoresist characteristics. Three developers, i.e., water/IPA, MIBK/IPA, and water/MIBK were studied. The water/MIBK mixture was rejected due to the low contrast of the final images. Improvements in sensitivity (~40%), contrast (~20%), and roughness (nearly an order of magnitude) were observed when the 3:7 water/IPA ratio was used when compared to the 1:3 MIBK/IPA developer. In our study, cell imprints were visualized after the development with three different ratios of MIBK to IPA, i.e., 1:1, 1:2, and 1:3 (Figure 4).
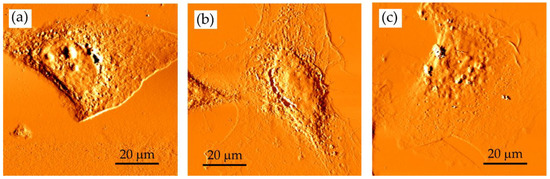
Figure 4.
The developer concentration influences SXCM imaging. MIBK:IPA ratio: (a) 1:1; (b) 1:2 and (c) 1:3 (the development time was 4 min). AFM deflection images of fixed HCC38 cells recorded using Xe120 AFM (Park Systems) with OTR4 cantilevers (0.02 N/m, Bruker, Camarillo, CA, USA). Scan size of 80 × 80 µm2; 600 SXR pulses.
The MIBK of high concentration in a mixture (pure MIBK or MIBK:IPA—1:1) seems to be too aggressive as the edges of the cells appeared to be smoothed by the developer; also, no cellular protrusions were observed (Figure 4a). In the case of the 1:2 developer, the spreading of cells was preserved (Figure 4b). The central part of the cells is smooth, but the cell nucleus could be identified. The use of MIBK solution that was too diluted (MIBK:IPA 1:3) failed to reveal small and thick details of the imaged sample (Figure 4c). Here, no cell details were observed in the images indicating that such development conditions did not enable to obtain the images with high contrast. Ultrasonically assisted development has been used to improve the resolution and line-edge roughness [31]. However, in our case, PMMA deposited on a silicon wafer was damaged due to the ultrasonic agitation. Therefore, in further steps, the adequate concentration of MIBK was chosen to be 1:2 MIBK:IPA. It can be concluded that in this particular condition where the photoresist of specific molecular weight, thickness, this biological sample, and exposure wavelength were used in the experiments, the optimal concentration of MIBK/IPA for sensitivity, linear response region, and developing time was 1:2. However, one has to keep in mind that the optimal ratio of MIBK to IPA must be established experimentally, according to exposure conditions, photoresist, and sample characteristics and will vary for different applications.
3.1.2. Soft X-ray (SXR) Pulses Number Optimization
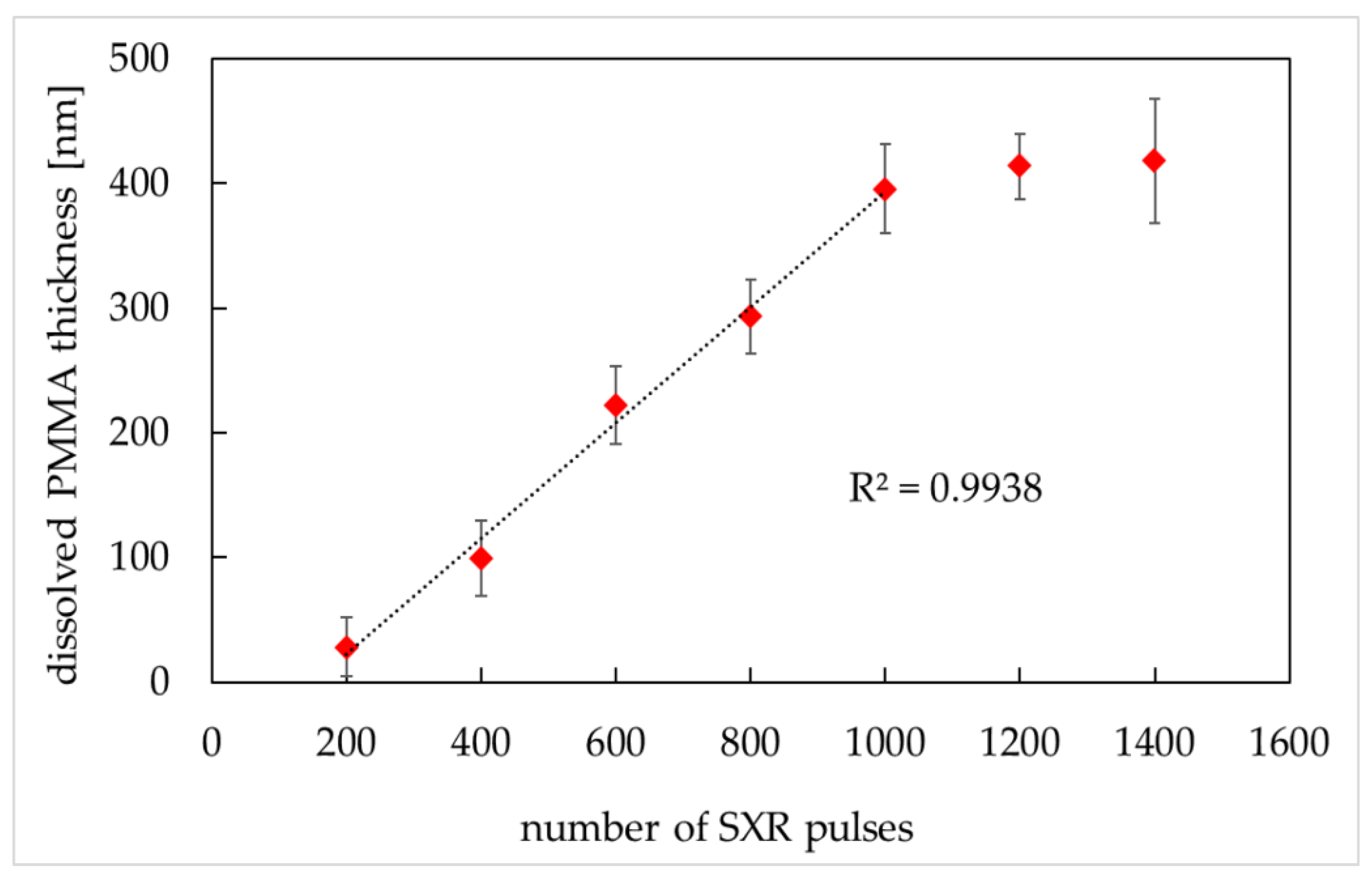
In addition to using an appropriate developer, PMMA degradation depends on the SXR absorbed energy. Therefore, we examined the correlation between the applied number of SXR pulses and PMMA degradation (Figure 5).
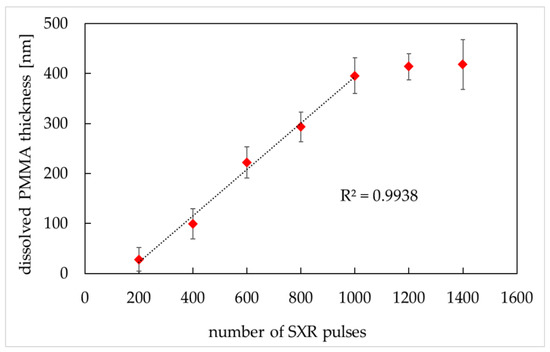
Figure 5.
Dissolved PMMA thickness versus the number of SXR pulses (MIBK:IPA 1:2 ratio (v/v), development time: 4 min). PMMA thickness was obtained from AFM images (AFM, di CPII, Veeco) as described in Material and Methods. Data are expressed as a mean ± standard deviation from 10 images.
The PMMA degradation increased in direct proportion to the number of SXR pulses in the range from 200 to 1000 (linear exposure region) with a regression correlation coefficient R2 equal to 0.9938. The PMMA exposure to pulses above 1000 did not cause higher PMMA degradation (the saturation region). To ensure the full linear region between the dissolved PMMA thickness and SXR absorbed energy, 400–800 SXR pulses were chosen for further experiments. To verify which number of pulses gives better resolution of cellular imprints, the SXCM images of HCC38 cells were prepared for exposures of 400, 600, and 800 pulses (Figure 6).
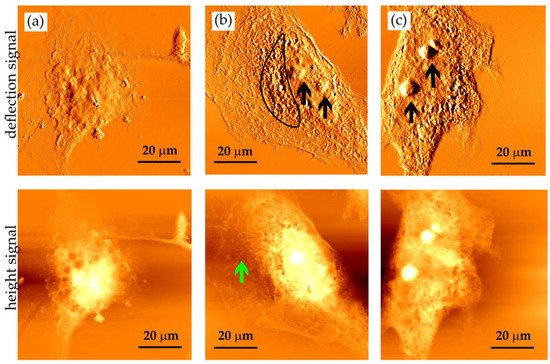
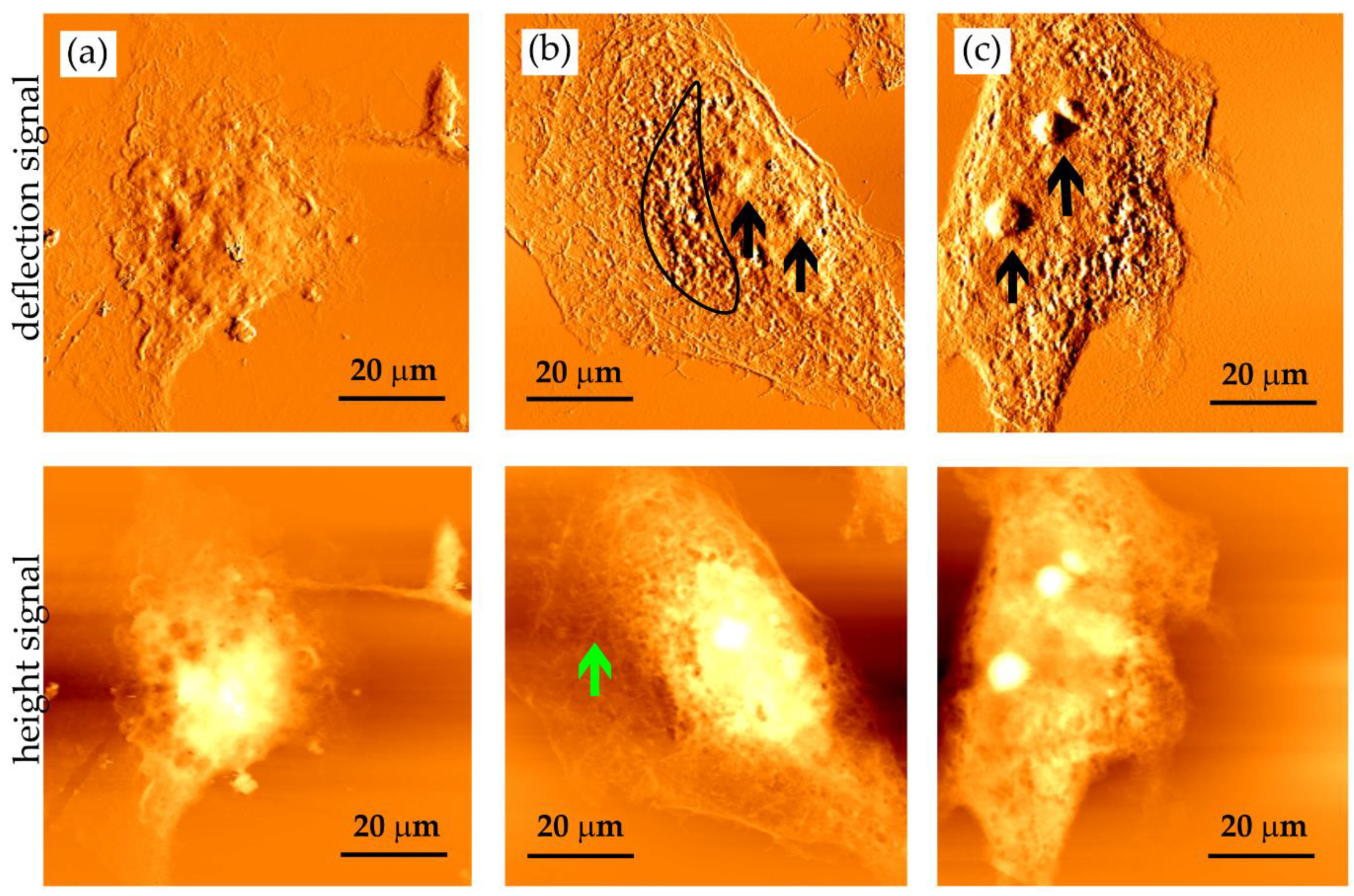
Figure 6.
AFM images of cellular imprints of fixed HCC38 breast cancer cells saved in PMMA photoresists by soft X-ray contact microscopy. Images were obtained with SXR exposure of (a) 400, (b) 600, and (c) 800 pulses. Imprints were recorded by AFM working in contact mode (Xe120, Park Systems) with OTR4 cantilevers (0.02 N/m, Bruker). Scan size of 80 × 80 µm2. Two types of signal are presented: deflection (top panel) and height (bottom panel).
The imprints obtained were visualized using AFM working in a contact mode (Figure 6). After the exposure to 400 SXR pulses, the cell outlines can be observed; however, such large organelles as nuclei are barely visible (Figure 6a). After the exposure to 600 SXR pulses, the cell nucleus is clearly visible (Figure 6b). Inside the cell nucleus, two nucleoli are located (indicated by the black arrows), while the outside region is rich in the rounded structures, which were presumed to comprise endoplasmic reticulum, vacuoles, and mitochondria (outlined with a frame). Within the cell’s peripheral region, filamentous structures could be identified (indicated by the green arrow) as the bundles of cytoskeletal filaments. In some cells, the protrusions were also observed (images not shown). Increasing the absorbed energy up to 800 SXR pulses enhanced the image of the cell nucleus in HCC38 cells (Figure 6c). These cells usually contain more than one nucleolus in their nuclei (indicated by the black arrows). They are poorly visible when lower numbers of SXR pulses were applied. These results showed that depending on the cellular structure studied, the adjustment of the number of pulses should always be conducted.
3.2. SXCM Imaging of Various Cell Lines
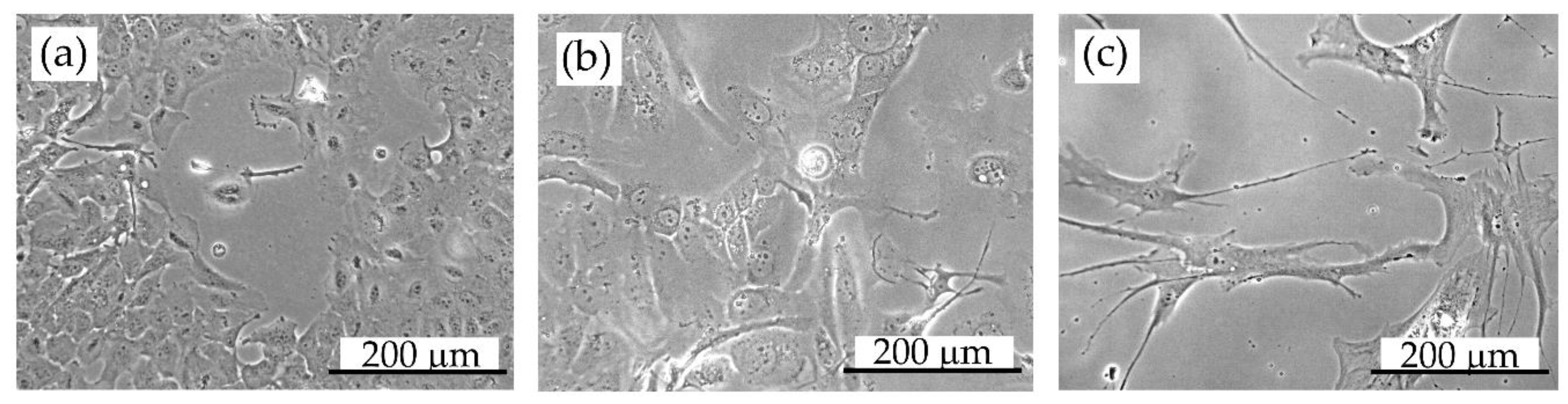
Cell morphology is essential for cell imaging with SXCM because differences in cell thicknesses and internal complexity influence X-rays’ adsorption through the sample. Therefore, in our studies, three human cell lines with significantly different morphology were chosen to show the effect of the soft X-ray radiation absorbed energy on the SXCM based imprint preparation. HCC38 breast cancer cells and hMSC present various shapes and sizes compared to DU145 prostate carcinoma cells under the inverted optical microscope (Figure 7). HCC38 and hMSC cells are of elongated shape with several thin and long protrusions. hMSCs are much bigger, extending up to 400 µm in length. DU145 prostate carcinoma cells, instead, are smaller and of a rhombic shape. The thickness of the attached DU145 cells is approximately 6 µm [34], which is even three times more than the thickness of hMSC cells, which is 2.5–3.5 µm (depending on the number of passages [35]).
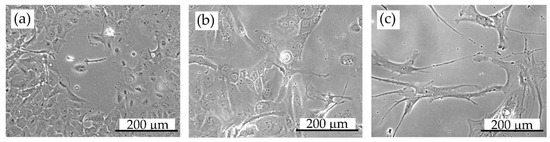
Figure 7.
Cell morphology: (a) DU145 prostate cancer cells, (b) HCC38 breast cancer cells, (c) hMSC (human mesenchymal stem cells). Images were taken using an inverse optical microscope (Primo Vert, Zeiss) with a 20× objective. The scale bar is 200 µm.
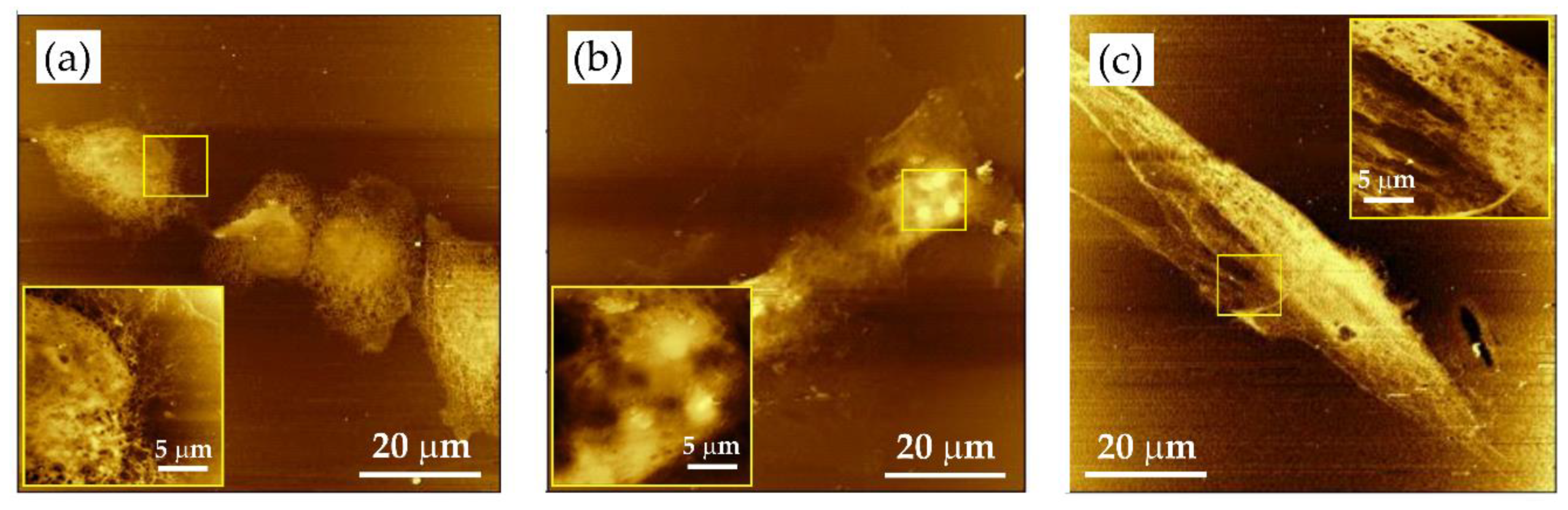
The images of morphologically different DU145, hMSC, and HCC38 cells obtained by AFM after using SXCM are presented in Figure 8. Each cell line was prepared; PMMA imprinted, and visualized using the same protocol. PMMA photoresist was irradiated with 800 SXR pulses and developed with the optimized MIBK:IPA ratio of 1:2.
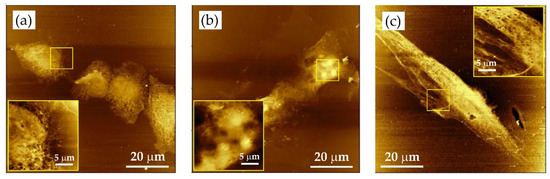
Figure 8.
Soft X-ray contact microscopy images of various cell lines: (a) DU145, (b) HCC38, and (c) hMSC. Images obtained with SXR exposure of 800 pulses. Cells fixed with 3.7% paraformaldehyde in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Results were collected using AFM (di CPII, Veeco) working in tapping mode. Scan size: 80 × 80 μm2. Insets: fragments of cells showing detailed cellular structures (image size 20 × 20 μm2).
Depending on the cell type, different details were preserved by the SXCM, as revealed by images recorded by AFM working in tapping mode. It turned out that in small and rhombic DU145 cells, the intracellular organelles were densely packed, and it was difficult to visualize their internal structures (Figure 8a). The HCC38 cells are larger and more flattened with clearly visible cell nuclei accompanied by nucleoli (Figure 8b). hMSCs were the largest adherent cells among the cell lines studied. In these cells, the nucleus was less visible. However, it was quite easy to visualize the cytoskeleton elements inside the cell, the sharp edges of the cell membrane, and its projections (Figure 8c). The cell–cell interactions could also be observed (Figure S1).
In conclusion, our results demonstrate that it is impossible to use the same SXR absorbed energy (expressed as the number of photons or pulses) for imaging the different types of cell. The experimental condition for imprint preparation must be optimized for each cell line separately. However, one can conclude that high SXR absorbed energy can be essential for visualization of the intracellular structures like the nucleus. At low exposures, on the other hand, the membrane protrusions could be visible.
4. Conclusions
Soft X-ray contact microscopy may provide a powerful tool for studying cell structures. What distinguishes SXCM from other techniques used to visualize a biological sample (electron microscopy, super-resolution fluorescence microscopy) is the possibility of high-resolution imaging of internal cell structures without the need for the expensive and lengthy procedures of sample preparation. Optimizing the SXR exposure energy and PMMA development conditions affects the resolution and visibility of subcellular structures. In this work, good-quality images of biological cells were obtained using an easy to operate desk-top contact SXR microscopy system based on a double stream gas puff target. However, the energy used must be adapted directly to the cell line. We have demonstrated that more pulses are required to visualize internal structures in the DU-145 prostate carcinoma cells than for HCC38 breast cancer cells. The imaging conditions (the number of pulses, development conditions) should be adjusted adequately to the cell type and internal structure, which are to be observed. Therefore, if adjusted correctly and properly optimized, the contact soft X-ray microscopy can efficiently provide various information concerning cells’ biology, complementing the other existing microscopy techniques. For further research, we plan to assemble a small compact device with an implemented fluorescence microscope. Such a device will identify individual cell structures imaged by SXCM with immunofluorescence methods with accurate specificity.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/10/19/6895/s1, Figure S1: AFM images of DU145 cells saved on the PMMA photoresists by soft X-ray contact microscopy. Images were obtained after the exposure to 400 SXR pulses. Imprints were recorded by AFM (di CPII, Veeco) working in tapping mode. Scan size of 25 × 25 µm2. Insets: fragments of the cell showing detailed structures (image size 5 × 5 μm2).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.N.O., P.W. and A.N.-S.; methodology, P.N.O., P.W. and A.N.-S.; validation, A.B. and J.C.; investigation, P.N.O., P.W. and A.N.-S.; writing—original draft preparation, P.N.O., A.N.-S. and P.W.; writing—review and editing, E.A.T., M.L.; visualization, M.L., K.G., P.N.O. and A.N.-S.; supervision, E.A.T. and H.F.; funding acquisition, H.F. and P.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Science Centre, Poland under the Beethoven Programme, grant number 2016/23/G/ST2/04319 and the European Union under the Horizon 2020 Programme Laserlab-Europe Project, grant number 871124.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest
References
- Kado, M.; Kishimoto, M.; Tamotsu, S.; Yasuda, K.; Aoyama, M.; Tone, S.; Shinohara, K. Correlative imaging of live biological cells with a soft x-ray microscope and a fluorescence microscope. Aip Conf. Proc. 2016, 1696, 020019. [Google Scholar]
- Reale, L.; Bonfigli, F.; Lai, A.; Flora, F.; Albertano, P.; ML, D.I.G.; Mezi, L.; Montereali, R.M.; Faenov, A.; Pikuz, T.; et al. Contact X-ray microscopy of living cells by using LiF crystal as imaging detector. J. Microsc. 2015, 258, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen Hyams, T.; Mam, K.; Killingsworth, M.C. Scanning electron microscopy as a new tool for diagnostic pathology and cell biology. Micron 2020, 130, 102797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorn, K. A quick guide to light microscopy in cell biology. Mol. Biol. Cell 2016, 27, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Shinohara, K. Application of X-ray microscopy in analysis of living hydrated cells. Anat. Rec. 2002, 269, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poletti, G.; Orsini, F.; Batani, D. Study of Multicellular Living Organisms by SXCM (Soft X-Ray Contact Microscopy). Solid State Phenom. 2005, 107, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kado, M.; Kishimoto, M.; Tamotsu, S.; Yasuda, K.; Shinohara, K. In situ observation of cellular organelles with a contact x-ray microscope. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2013, 463, 012056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakdinawat, A.; Attwood, D. Nanoscale X-ray imaging. Nat. Photonics 2010, 4, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirz, J.; Sayre, D. Soft X-Ray Microscopy of Biological Specimens. In Synchrotron Radiation Research; Winick, H., Doniach, S., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1980; pp. 277–322. [Google Scholar]
- Gowa, T.; Takahashi, T.; Oshima, A.; Tagawa, S.; Washio, M. Study on resist sensitivities for nano-scale imaging using water window X-ray microscopy. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2011, 80, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirz, J.; Jacobsen, C.; Howells, M. Soft X-ray microscopes and their biological applications. Q. Rev. Biophys. 1995, 28, 33–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayele, M.G.; Wachulak, P.W.; Czwartos, J.; Adjei, D.; Bartnik, A.; Wegrzynski, Ł.; Szczurek, M.; Pina, L.; Fiedorowicz, H. Development and characterization of a laser-plasma soft X-ray source for contact microscopy. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2017, 411, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachulak, P.; Torrisi, A.; Ayele, M.; Czwartos, J.; Bartnik, A.; Wegrzynski, L.; Fok, T.; Parkman, T.; Salacova, S.; Turňová, J.; et al. Bioimaging Using Full Field and Contact EUV and SXR Microscopes with Nanometer Spatial Resolution. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, S.; Gong, C.; Robertson, A. Liquid cell transmission electron microscopy and its applications. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2020, 7, 191204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayre, D.; Kirz, J.; Feder, R.; Kim, D.; Spiller, E. Transmission microscopy of unmodified biological materials. Comparative radiation dosages with electrons and ultrasoft X-ray photons. Ultramicroscopy 1977, 2, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, A.A.; Leapman, R.D. Development and application of STEM for the biological sciences. Ultramicroscopy 2012, 123, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, C.; Kirz, J. X-ray microscopy with synchrotron radiation. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1998, 5, 650–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takman, P.A.C.; Stollberg, H.; Johansson, G.A.; Holmberg, A.; Lindblom, M.; Hertz, H.M. High-resolution compact X-ray microscopy. J. Microsc. 2007, 226, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, H.; Tomie, T. Optimization of a laser-plasma x-ray source for contact x-ray microscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 1994, 75, 3798–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhareshwar, L.; Chaurasia, S. Laser plasma interaction in solid metal, mixed metal alloy and metal nano-particle coated targets. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2008, 112, 032050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.J.; Kim, D.S.; Jeon, S.C.; Park, J.; Lee, K.H.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, K.N.; Yoo, J.J.; Nam, C.H. Soft x-ray microscope constructed with a PMMA phase-reversal zone plate. Opt. Lett. 2009, 34, 235–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletti, G.; Orsini, F.; Batani, D.; Bernardinello, A.; Desai, T.; Ullschmied, J.; Skala, J.; Kralikova, B.; Krousky, E.; Juha, L.; et al. Soft X-ray contact microscopy of nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Eur. Phys. J. D At. Mol. Opt. Plasma Phys. 2004, 30, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinozaki, D.M. High Resolution Image Storage in Polymers, X-Ray Microscopy II; Sayre, D., Kirz, J., Howells, M., Rarback, H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1988; pp. 118–123. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen, C. Future challenges for x-ray microscopy. Aip Conf. Proc. 2016, 1696, 020035. [Google Scholar]
- Weinhardt, V.; Chen, J.; Ekman, A.A.; McDermott, G.; Gros, M.A.L.; Larabell, C.A. Imaging cell morphology and physiology using X-rays. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2019, 472, 489–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broers, A.N. Resolution limits for electron-beam lithography. IBM J. Res. Dev. 1988, 32, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Thakar, R.G.; Wong, J.; McLeod, S.D.; Li, S. Control of cell adhesion on poly(methyl methacrylate). Biomaterials 2006, 27, 2890–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghmaie, F.; Fleck, J.; Gusman, A.; Prohaska, R. Improvement of PMMA electron-beam lithography performance in metal liftoff through a poly-imide bi-layer system. Microelectron. Eng. 2010, 87, 2629–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooks, M.J.; Kratschmer, E.; Viswanathan, R.; Katine, J.R.E.F., Jr.; MacDonald, S.A. Low stress development of poly(methylmethacrylate) for high aspect ratio structures. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B Microelectron. Nanometer Struct. Process. Meas. Phenom. 2002, 20, 2937–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleunitz, A.; Schift, H. Fabrication of 3D nanoimprint stamps with continuous reliefs using dose-modulated electron beam lithography and thermal reflow. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2010, 20, 095002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasin, S.; Hasko, D.; Ahmed, H. Comparison of MIBK/IPA and water/IPA as PMMA developers for electron beam nanolithography. Microelectron. Eng. 2002, 61, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, M.A.; Dew, S.K.; Westra, K.; Li, P.; Aktary, M.; Lauw, Y.; Kovalenko, A.; Stepanova, M. Nanoscale resist morphologies of dense gratings using electron-beam lithography. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B Microelectron. Nanometer Struct. Process. Meas. Phenom. 2007, 25, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Choi, S.; Subramanian, K.R.V.; Adesida, I. The effects of molecular weight on the exposure characteristics of poly(methylmethacrylate) developed at low temperatures. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B Microelectron. Nanometer Struct. Process. Meas. Phenom. 2008, 26, 2306–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilloteaux, J.; Jamison, J.M.; Neal, D.; Arnold, D.; Taper, H.S.; Summers, J.L. Human prostate DU145 carcinoma cells implanted in nude mice remove the peritoneal mesothelium to invade and grow as carcinomas. Anat. Rec. 2013, 296, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsube, Y.; Hirose, M.; Nakamura, C.; Ohgushi, H. Correlation between proliferative activity and cellular thickness of human mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 368, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).