Effects of Owinema Bio-Preparation on Vermicomposting in Earthworm Ecological Boxes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
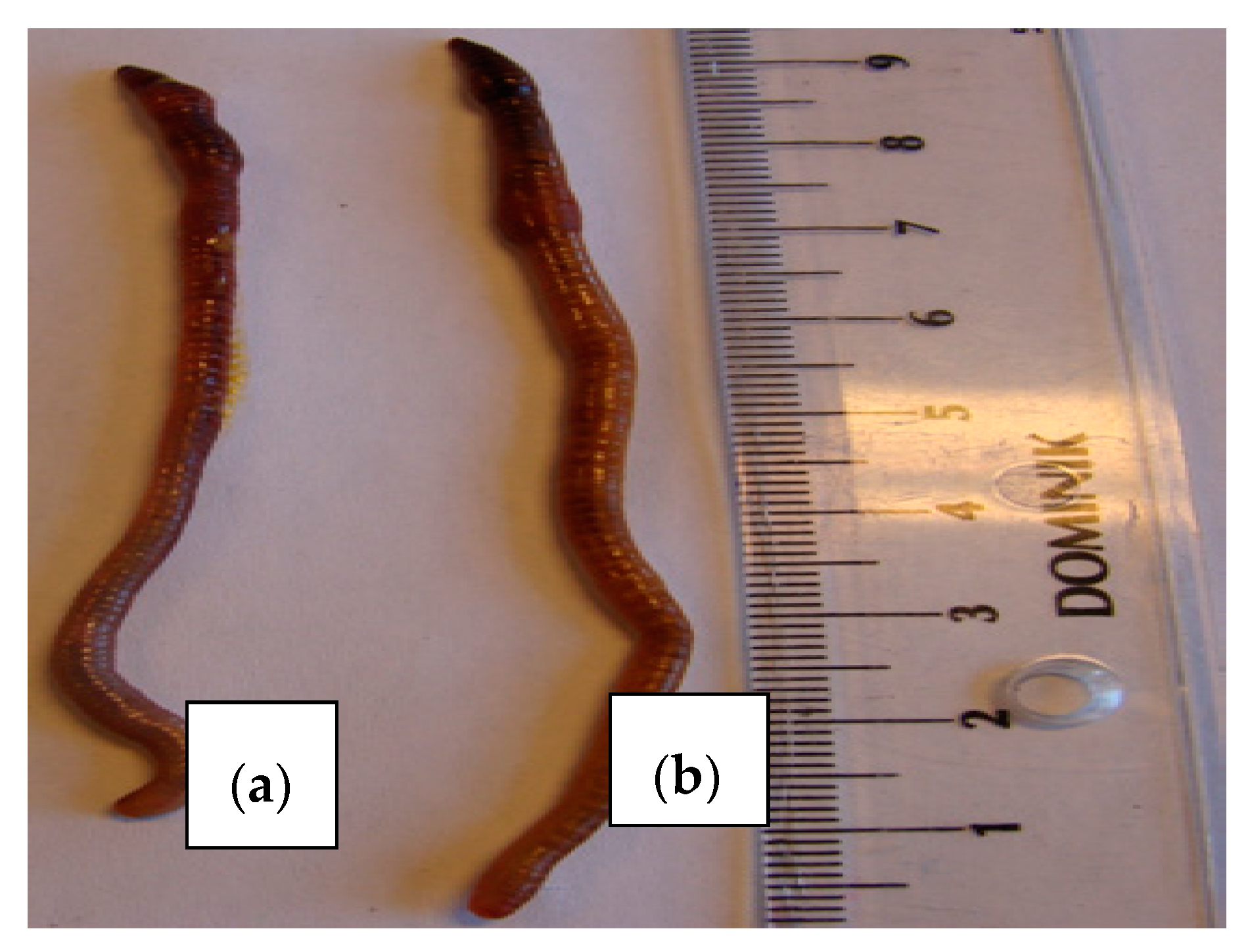
2.1. Earthworms and the Influence of an Owinema Bio-Preparation on Population Dynamics
2.2. Kitchen Wastes and the Rate of Vermicomposting
2.3. The Influence of Owinema Bio-Preparation on Sciaridae Larvae
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Influence of Owinema Preparation on Earthworms
3.1.1. Number of Earthworms
3.1.2. Body Mass
3.2. Kitchen Wastes and the Rate of Vermicomposting
3.3. The Influence of Owinema Bio-Preparation on Sciaridae Larvae
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kostecka, J.; Garczyńska, M.; Pączka, G.; Mroczek, J. Modelling the Processes of Vermicomposting in an Ecological Box-Recognized Critical Points. In Contemporary Problems of Management and Environmental Protection; Skibniewska, K.A., Ed.; Some Aspects of Environmental Impact of Waste Dumps: Olsztyn, Poland, 2011; pp. 143–156. [Google Scholar]
- Suthar, S. Pilot-scale vermireactors for sewage sludge stabilization and metal remediation process: Comparison with small-scale vermireactors. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostecka, J.; Pączka, G.; Garczyńska, M.; Podolak-Machowska, A.; Dunin-Mugler, C.; Szura, R. Some remarks on utilization of kitchen organic waste. Inżynieria I Ochrona Środowiska 2014, 17, 21–30. [Google Scholar]
- Selden, P.; DuPonte, M.; Sipes, B.; Dinges, K.; Vasudevan, P. Small-scale vermicomposting. Cooperative Extension Service. Home Gard. 2005, 45, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Kostecka, J.; Garczyńska, M.; Pączka, G.; Podolak, A.; Mazur-Pączka, A. Education for circular economy—Earthworm ecological boxes. Environ. Educ. Res. 2020. in review. [Google Scholar]
- Garczyńska, M.; Kostecka, J. Dynamika muchówek ziemiórkowatych (Sciaridae) na odpadach organicznych w skrzynce ekologicznej w laboratorium. Zesz. Nauk. Poł.-Wsch. Oddziału PTIE I PTG W Rzeszowie 2014, 17, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Garczyńska, M.; Kostecka, J. Influence of nomolt 150sc insecticide, used against diptera in ecological boxes, on characteristics of Eisenia fetida (sav.) earthworms. Inżynieria Ekol. 2011, 27, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Garczyńska, M.; Kostecka, J. Influence of Dimilin 25 WP on characteristics of earthworm Eisenia fetida Sav, vermicomposting organic waste. Ecol. Chem. Eng. A 2011, 18, 1557–1563. [Google Scholar]
- Garczyńska, M.; Kostecka, J. Reducing dipterian larvae Turing vermicomposting of household organic waste in ecological boxes. Soil Sci. Annu. 2012, LXIII, 18–21. Available online: http://versitaopen.com/ssa (accessed on 14 December 2019).
- Monroy, F.; Aira, M.; Dominguez, J.; Velando, A. Seasonal population dynamics of Eisenia fetida (Savigny, 1826) (Oligochaeta, Lumbricidae) in the field. Popul. Biol. 2006, 329, 912–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aira, M.; Dominguez, J.; Monroy, F.; Velando, A. Stress promotes changes in resource allocation to growth and reproduction in a simultaneous hermaphrodite with indeterminate growth. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2007, 91, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katagi, T.; Ose, K. Toxicity, bioaccumulation and metabolism of pesticides in the earthworm. J. Pestic. Sci. 2015, 40, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pino, M.R.; Val, J.; Mainar, A.M.; Zuriaga, E.; Espanol, C.; Langa, E. Acute toxicological effects on the earthworm Eisenia fetida of 18 common pharmaceuticals in artificial soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 518, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velki, M.; Ecimović, S. Changes in exposure temperature lead to changes: A preliminary study. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 40, 774–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumbos, I.C.H.; Athanassiou, C.G. The use of entomopathogenic nematodes in the control of stored-product insects. J. Pest Sci. 2017, 90, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruselman, E.; Beck, B.; Pollet, S.; Temmerman, F.; Spanoghe, P.; Moens, M.; Nuyttens, D. Effect of the spray application technique on the deposition of entomopathogeic nematodes in vegatables. Pest Manag. Sci. 2011, 68, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahenswaran, R.; Ignacimuthu, S. Bioefficiacy of essential oil from Polygonum hydropiper L. against mosquitoes, Anopheles stephensi and Culex quinquefasciatus. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 97, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponskar, A.; Vasantha-Srinivasan, P.; Senthil-Nathan, S.; Thanigaivel, A.; Edwin, E.-S.; Selin-Rani, S.; Kalaivani, K.; Hunter, W.B.; Alessandro, R.T.; Abdel-Megeed, A.; et al. Target and non-target toxicity of botanical insecticide derived from Couroupita guianensis L. flower against generalist herbivore, Spodoptera litura Fab. And an earthworm, Eisenia foetida Savigny. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 133, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selin-Rani, S.; Senthil-Nathan, S.; Thanigaivel, A.; Vasantha-Srinivasan, P.; Edwin, E.-S.; Ponskar, A.; Lija-Escaline, J.; Kalaivani, K.; Abdel-Megeed, A.; Hunter, W.B.; et al. Toxicity and physiological effect of quercetin on generalist herbivore, Spodoptera litura Fab. and a non-target earthworm Eisenia fetida Savigny. Chemosphere 2016, 165, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwa, A.A. Entomopathogenic nematodes as pesticides. In Basic and Applied Aspects of Biopesticides; Sahay, K., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, K.G.; Gouge, D.H. Identification of the entomopathogenic nematode bacterial symbiont Xenorhabdus species. Nematologica 1998, 44, 478. [Google Scholar]
- Kucharska, K.; Kucharski, D.; Zajdel, B. Bacteria Xenorhabdus and Photorhabdus, entomopathogenic nematodes and insects—Their role in the complex symbiont-parasite-host relationship. Postępy Mikrobiologii 2015, 54, 154–164. Available online: http://www.pm.microbiology.pl (accessed on 11 December 2019).
- Karkas, M. The effect of earthworm on vertical dispersal of entomopathogenic nematode, Steinernema feltiae (Rhabditida: Steinernematidae). DUFED 2015, 4, 83–86. [Google Scholar]
- Campos-Herrera, R.; Trigo, D.; Gutierrez, C. Phoresy of the entomopathogenic nematode Steinernema feltiae by the earthworm Eisenia fetida. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2006, 92, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro-Ilan, D.I.; Brown, I. Earthworm as phoretic hosts for Steinernema carpocapsae and Beauveria bassiana: Implications for enhaced biological control. Biol. Control 2013, 66, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostecka, J. Investigation into vermicomposting of organic wastes. Sci. Pap. Agr. Univ. Crac. 2000, 268, 1–88. [Google Scholar]
- Owiplant. Available online: https://owinska.cylex.pl/firmy/owiplant--sp--z-o-o--10348244.html (accessed on 14 December 2019).
- Pelosi, C.; Bertrand, M.; Capowiez, Y.; Boizard, H.; Roger-Estrade, J. Earthworm collection from agricultural fields: Comparisons of selected expellants in presence/absence of hand-sorting. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2009, 45, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didden, W.; Born, H.; Domm, H.; Graefe, U.; Heck, M.; Kǖhle, J.; Mellin, A.; Römbke, J. The relative efficiency of wet funnel techniques for the extraction of Enchytraeidae. Pedobiologia 1995, 39, 52–57. [Google Scholar]
- ISO Soil Quality. Effects of Pollutants on Earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Part. 1: Determination of Acute Toxicity Using Artificial Soil Substrate; No 11268-1; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- ISO Soil Quality. Effect of Pollutants on Earthworms (Eisenia Fetida). Part. 2: Determination of Effects on Reproduction; No 11268-2; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- MAFF. The Analysis of Agricultural Materials, 2nd ed.; A manual of the analytical methods used by the agricultural Development and Advisory Service (ADAS); HMSO: London, UK, 1981.
- Stanisz, A. Przystępny Kurs Statystyki Z Zastosowaniem Statistica Pl Na Przykładach Z Medycyny; StatSoft Polska Sp. Z o. o.: Kraków, Poland, 2006; p. 532. [Google Scholar]
- Meissner, W. Metody Statystyczne W Biologii; Wydawnictwo Uniwersytetu Gdańskiego: Gdańsk, Poland, 2014; p. 158. [Google Scholar]
- Dominguez, J.; Parmelee, R.W.; Edwards, C.A. Interactions between Eisenia andrei (Oligochaeta) and nematode populations during vermicomposting. Pedobiologia 2003, 47, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Timper, P.; Davies, K.G. Biotic interactions. In Nematode Behaviour; Gaugler, R., Bilgrami, A.L., Eds.; CAPI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2004; pp. 277–307. [Google Scholar]










| Container | Medium | Earthworm Eisenia fetida | Feeding |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1–5 A Control | 2 dm3 of garden soil * | by 50 individuals of known biomass by 50 individuals of known biomass | 5 times, after 600 mL of designed mixture of organic waste and cellulose (2:1) |
| 6–10 B | 2 dm3 of garden soil * + preparation ** |
| Time | Start of the Experiment | 1st Month | 2nd Month | 3rd Month | 4th Month | 5th Month |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 50.0 ± 0.0 a | 239.8 ± 24.8 a | 303.6 ± 25.6 a | 461.0 ± 59.0 a | 421.8 ± 45.7 a | 123.2 ± 55.8 a |
| Owinema | 50.0 ± 0.0 a | 302.4 ± 19.5 a | 372.0 ± 51.6 b | 552.4 ± 113.1 b | 732.0 ± 34.6 b | 640.6 ± 59.2 b |
| Time | Start of the Experiment | 1st Month | 2nd Month | 3rd Month | 4th Month | 5th Month |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 20.14 ± 0.19 a | 25.47 ± 3.58 a | 26.73 ± 7.96 a | 20.31 ± 2.74 a | 36.62 ± 4.08 a | 14.75 ± 6.75 a |
| Owinema | 20.09 ± 0.10 a | 31.74 ± 5.73 b | 24.66 ± 1.52 a | 44.64 ± 6.62 b | 82.57 ± 5.26 b | 37.75 ± 5.35 b |
| Time | Start of the Experiment | 1st Month | 2nd Month | 3rd Month | 4th Month | 5th Month | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 0.0 ± 0.0 a | 2.9 ± 0.4 a | 4.2 ± 1.0 a | 2.8 ± 3.2 a | 3.6 ± 2.6 a | 2.5 ±.1 9 a | 2.7 ± 1.5 a |
| Owinema | 0.0 ± 0.0 a | 3.9 ± 0.4 a | 5.0 ± 1.0 a | 1.7 ± 0.5 a | 1.8 ±.0.2 a | 2.3 ± 1.2 a | 2.4 ± 1.8 a |
| Characteristics | pH in H2O | Salinity NaCl [g dm−3] | Components (mg.dm−3 of Fresh Mass) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N-NO3 | P | K | Ca | Mg | |||
| Control | 6.06 ± 0.21 a | 5.39 ± 1.01 a | 880 ± 89 a | 345 ± 66 a | 1415 ± 198 a | 2124 ± 351 a | 279 ± 67 a |
| Vermicomposting with Owinema | 6.13 ± 0.44 a | 4.80 ± 1.36 a | 879 ± 131 a | 324 ± 60 a | 1394 ± 283 a | 1951 ± 286 a | 284 ± 62 a |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garczyńska, M.; Pączka, G.; Podolak, A.; Mazur-Pączka, A.; Szura, R.; Butt, K.R.; Kostecka, J. Effects of Owinema Bio-Preparation on Vermicomposting in Earthworm Ecological Boxes. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10020456
Garczyńska M, Pączka G, Podolak A, Mazur-Pączka A, Szura R, Butt KR, Kostecka J. Effects of Owinema Bio-Preparation on Vermicomposting in Earthworm Ecological Boxes. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(2):456. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10020456
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarczyńska, Mariola, Grzegorz Pączka, Agnieszka Podolak, Anna Mazur-Pączka, Renata Szura, Kevin R. Butt, and Joanna Kostecka. 2020. "Effects of Owinema Bio-Preparation on Vermicomposting in Earthworm Ecological Boxes" Applied Sciences 10, no. 2: 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10020456
APA StyleGarczyńska, M., Pączka, G., Podolak, A., Mazur-Pączka, A., Szura, R., Butt, K. R., & Kostecka, J. (2020). Effects of Owinema Bio-Preparation on Vermicomposting in Earthworm Ecological Boxes. Applied Sciences, 10(2), 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10020456





