A Novel Spectral–Spatial Classification Method for Hyperspectral Image at Superpixel Level
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The SLIC algorithm is improved so that it can be directly used to divide any dimensional HSI into superpixels without using PCA and parameters.
- The superpixel-to-superpixel similarity is defined properly, which is unrelated to the shape of superpixel.
- A novel spectral–spatial HSI classification method at superpixel level is proposed.
2. The Proposed HSI Classification Method at Superpixel Level
2.1. SLIC Algorithm and Its Improvement
2.2. Superpixel-To-Superpixel Similarity
- (1)
- Compute the similarity between pixel and each pixel by Equation (4). Sort in an ascending order according to the corresponding similarities, represented as .
- (2)
- Calculate local mean vector of the first m nearest pixels of pixel ,are their corresponding similarities obtained by Equation (4).
- (3)
- Calculate the similarity between pixel and superpixel ,
- (4)
- Arrange in an ascending order according to their values, represented as . The similarity s between two superpixels can be calculated
2.3. Superpixel-To-Superpixel Similarity-Based Label Assignment
2.4. Complexity
3. Experimental Results
3.1. Hyperspectral Datasets
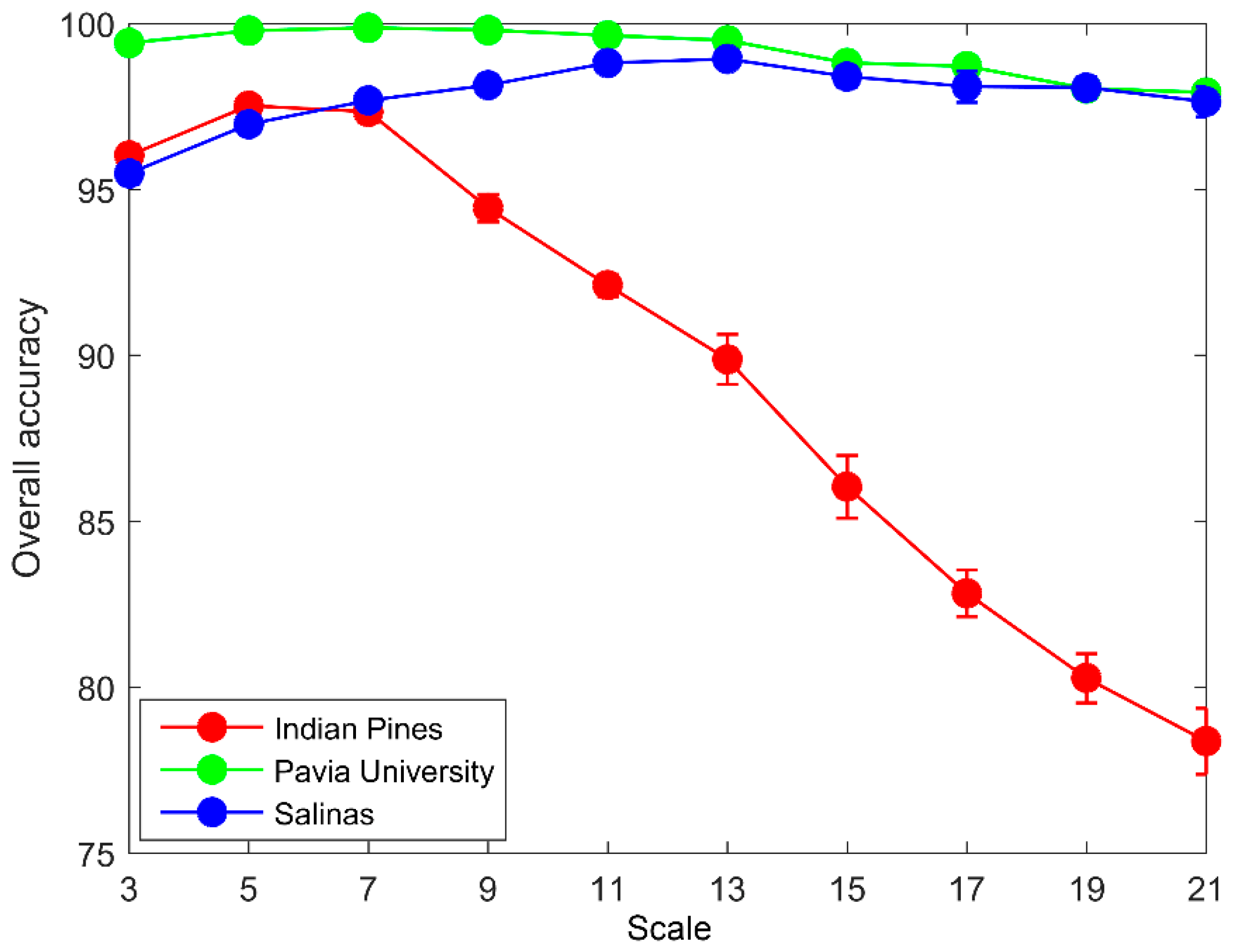
3.2. Impact of Segmentation Scale
3.3. Classification Results
3.4. Effect of Different Numbers of Training Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, M.; Huang, Y.; Yao, H.; Thomson, S. Determining the effects of storage on cotton and soybean leaf samples for hyperspectral analysis. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 2562–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanning, M.; Siegmann, B.; Jarmer, T. Regionalization of uncovered agricultural soils based on organic carbon and soil texture estimations. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clark, M.L.; Roberts, D.A. Species-level differences in hyperspectral metrics among tropical rainforest trees as determined by a tree-based classifier. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 1820–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryan, J.; Davis, C.; Tufillaro, N.; Kudela, R.; Gao, B. Application of the hyperspectral imager for the coastal ocean to phytoplankton ecology studies in Monterey Bay CA, USA. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1007–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muller-Karger, F.; Roffer, M.; Walker, N.; Oliver, M. Satellite remote sensing in support of an integrated ocean observing system. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2013, 1, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, G.; Gu, Y. Tensor matched subspace detector for hyperspectral target detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 1967–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Du, B.; Zhang, L.; Liu, T. Joint sparse representation and multitask learning for hyperspectral target detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 894–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melgani, F.; Bruzzone, L. Classification of hyperspectral remote sensing images with support vector machines. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 1778–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camps-Valls, G.; Bruzzone, L. Kernel-based methods for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Bioucas-Dias, J.; Plaza, A. Semi-supervised hyperspectral image segmentation using multinomial logistic regression with active learning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 4085–4098. [Google Scholar]
- Ratle, F.; Camps-Valls, G.; Weston, J. Semi-supervised neural networks for efficient hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 2271–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, S.; Ghosh, J.; Crawford, M. An active learning approach to hyperspectral data classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 1231–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Ghamisi, P.; Yokoya, N.; Iwasaki, A. Random forest ensembles and extended multi-extinction profiles for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 1, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, T.; Li, S.; Fang, L.; Jia, X.; Benediktsson, J. From Subpixel to Superpixel: A Novel Fusion Framework for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 4398–4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Xu, Z.; Meng, D. Spectral-Spatial Hyperspectral Image Classification via Robust Low-Rank Feature Extraction and Markov Random Field. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, C.; Naghedolfeizi, M.; Aberra, D.; Zeng, X. Spectral–Spatial Discriminant Feature Learning for Hyperspectral Image Classification. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghamisi, P.; Mura, M.D.; Benediktsson, J. A survey on spectral-spatial classification techniques based on attribute profiles. IEEE Trans. Geos. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 2335–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xi, B.; Du, Q.; Song, R.; Li, Y.; Ren, G. Deep Kernel Extreme-Learning Machine for the Spectral-Spatial Classification of Hyperspectral Imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, L.; Cao, X.; Zhang, X.; Jiao, L.; Yu, T. CNN-Based Multilayer Spatial-Spectral Feature Fusion and Sample Augmentation with Local and Nonlocal Constraints for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 1299–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Yu, H.; Wang, L.; Cao, X.; Zhang, X.; Jiao, L. Classification of Hyperspectral Images Based on Multiclass Spatial-Spectral Generative Adversarial Networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 5329–5343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shan, C.; Gao, Q.; Gao, X.; Han, J.; Cui, R. Hyperspectral image denoising via minimizing the partial sum of singular values and superpixel segmentation. Neurocomputing 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, S.; Deng, B.; Zhu, J.; Jia, X.; Li, Q. Superpixel-Based Multitask Learning Framework for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 2575–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Khodadadzadeh, M.; Plaza, A.; Jia, X.; Bioucas-Dias, J.M. A discontinuity preserving relaxation scheme for spectral–spatial hyperspectral image classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dundar, T.; Ince, T. Sparse Representation-Based Hyperspectral Image Classification Using Multiscale Superpixels and Guided Filter. IEEE Trans. Geos. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Li, S.; Duan, W.; Ren, J.; Benediktsson, J.A. Classification of hyperspectral images by exploiting spectral–spatial information of superpixel via multiple kernels. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 6663–6674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, T.; Gu, Y.; Chanussot, J.; Dalla Mura, M. Multimorphological Superpixel Model for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 6950–6963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Su, H.; Shen, J. Hyperspectral Dimensionality Reduction Based on Multiscale Superpixelwise Kernel Principal Component Analysis. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, F.; Lei, C.; Yang, J.; Jin, C. An Effective Classification Scheme for Hyperspectral Image Based on Superpixel and Discontinuity Preserving Relaxation. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xue, Z.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, P. Active Learning Improved by Neighborhoods and Superpixels for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 99, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, J.; He, L. Superpixel-Based Semisupervised Active Learning for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Prasad, S.; Fowler, J.E. Hyperspectral image classification using gaussian mixture models and markov random fields. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sen Lett. 2013, 11, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Plaza, A. Spectral-spatial hyperspectral image segmentation using subspace multinomial logistic regression and Markov random fields. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 809–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Deng, B.; Zhu, J.; Jia, X.; Li, Q. Local Binary Pattern-Based Hyperspectral Image Classification with Superpixel Guidance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Ren, J.; Zhao, H.; Yan, Y.; Zabalza, J.; Marshall, S. Superpixel based Feature Specific Sparse Representation for Spectral-Spatial Classification of Hyperspectral Images. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, J.; Ma, J.; Chen, C.; Wang, Z.; Cai, Z.; Wang, L. SuperPCA: A Superpixelwise PCA Approach for Unsupervised Feature Extraction of Hyperspectral Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 4581–4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Li, S.; Fu, W.; Fang, L. Multiscale Superpixel-Based Sparse Representation for Hyperspectral Image Classification. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tarabalka, Y.; Benediktsson, J.; Chanussot, J.; Tilton, J. Multiple Spectral–Spatial Classification Approach for Hyperspectral Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.; Li, E.; Du, Q.; Du, P. An efficient semi-supervised classification approach for hyperspectral imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 97, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, B.; Xia, K.; Li, T.; He, Z.; Li, Y.; Hou, J.; Du, W. SLIC Superpixel-Based l2,1-Norm Robust Principal Component Analysis for Hyperspectral Image Classification. Sensors 2019, 19, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, T.; Li, S.; Fang, L.; Bruzzone, L.; Benediktsson, J.A. Set-to-Set Distance-Based Spectral–Spatial Classification of Hyperspectral Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellars, P.; Aviles-Rivero, A.; Schönlieb, C. Superpixel Contracted Graph-Based Learning for Hyperspectral Image Classification. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1903.06548v3. [Google Scholar]
- Achanta, R.; Shaji, A.; Smith, K.; Lucchi, A.; Fua, P.; Süsstrunk, S. SLIC superpixels compared to state-of- the-art superpixel methods. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 2274–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, T.; Wang, J.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, J.; Ma, J.; Wang, Z. Rectangular-Normalized Superpixel Entropy Index for Image Quality Assessment. Entropy 2018, 20, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vincent, L.; Soille, P. Watersheds in digital spaces: An efficient algorithm based on immersion simulations. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1991, 13, 583–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Comaniciu, D.; Meer, P. Mean shift: A robust approach toward feature space analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2002, 24, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levinshtein, A.; Stere, A.; Kutulakos, K.N.; Fleet, D.J.; Dickinson, S.J.; Siddiqi, K. Turbopixels: Fast superpixels using geometric flows. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2009, 31, 2290–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tu, B.; Wang, J.; Kang, X.; Zhang, G.; Ou, X.; Guo, L. KNN-Based Representation of Superpixels for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 4032–4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, J.; Zhan, Y.; Rao, Y.; Shen, X.; Wang, X.; He, W. Improved pseudo nearest neighbor classification. Knowl. Based Syst. 2014, 70, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cover, T.; Hart, P. Nearest neighbor pattern classification. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 1967, 13, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitani, Y.; Hamamoto, Y. A local mean-based nonparametric classifier. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2006, 27, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, L. Pseudo nearest neighbor rule for pattern classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 3587–3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Li, S.; Benediktsson, J.A. Spectral–Spatial Hyperspectral Image Classification with Edge Preserving Filtering. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 2666–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Li, S.; Benediktsson, J.A. Feature Extraction of Hyperspectral Images with Image Fusion and Recursive Filtering. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 3742–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
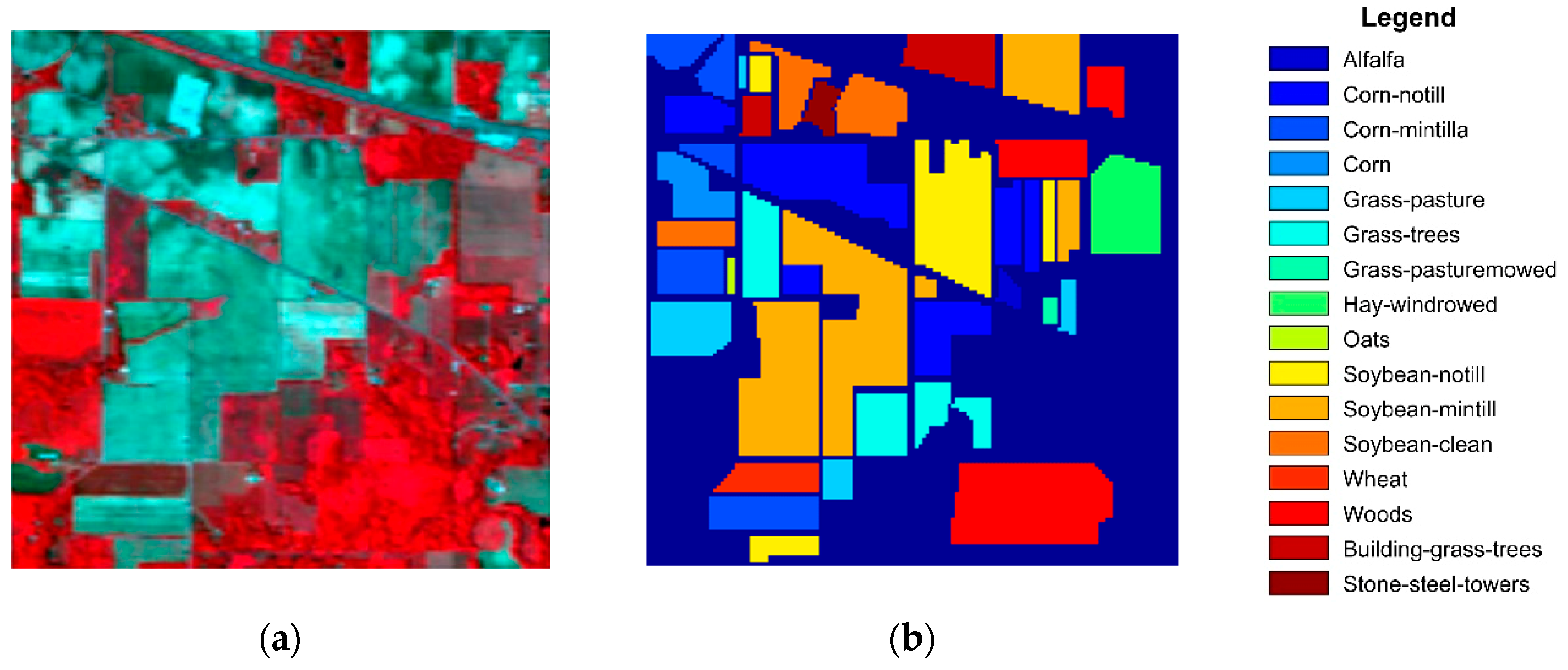
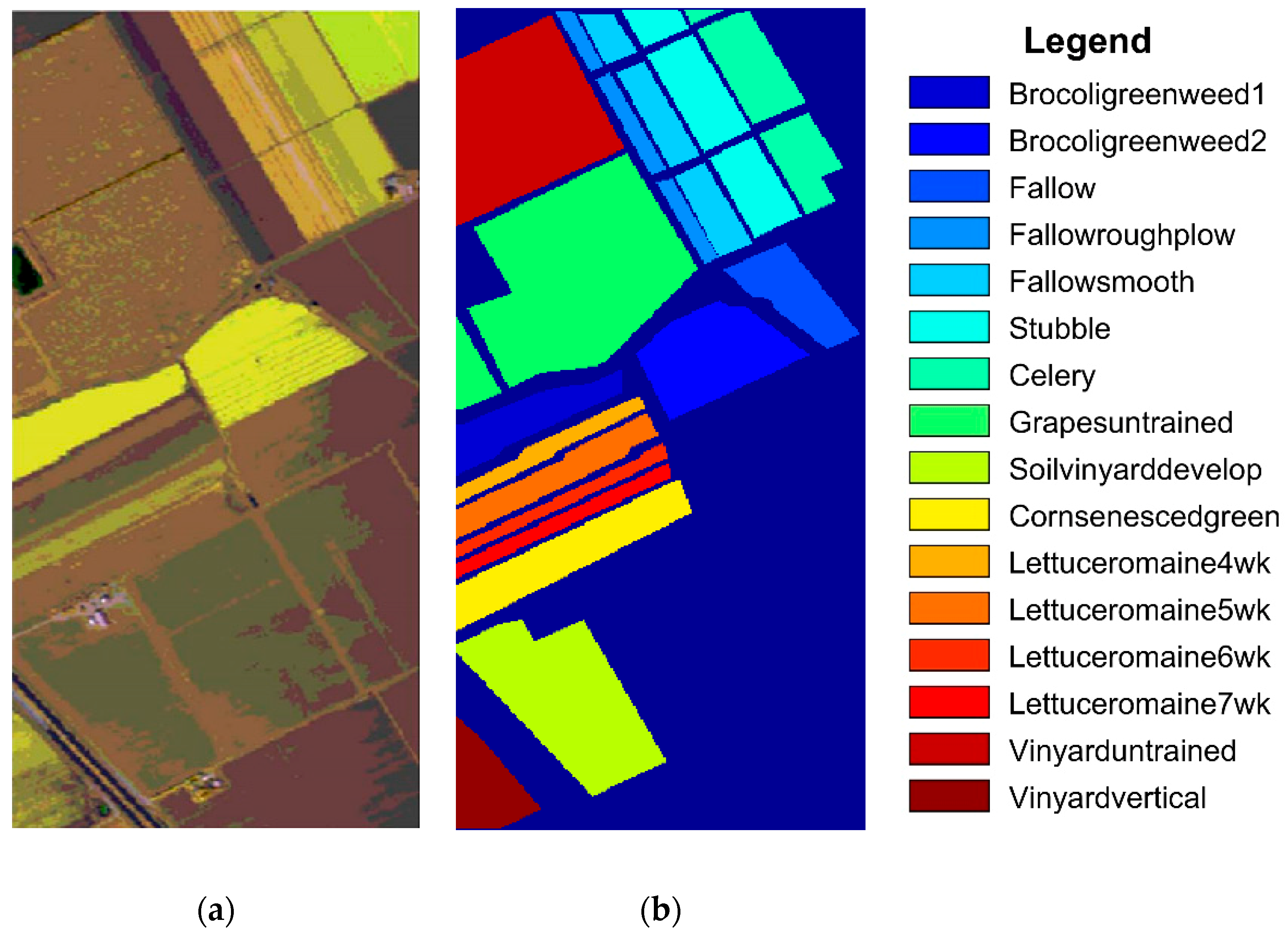

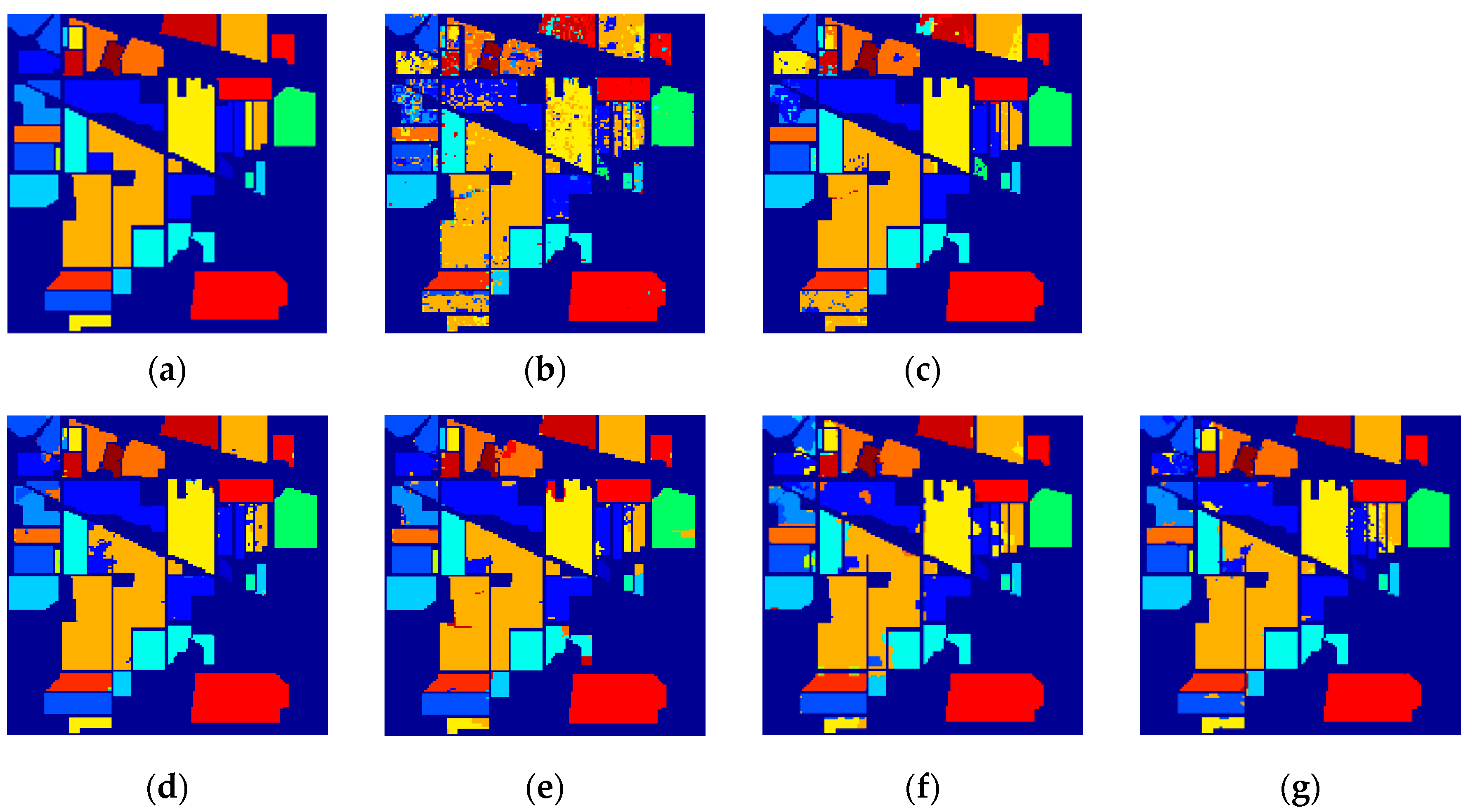
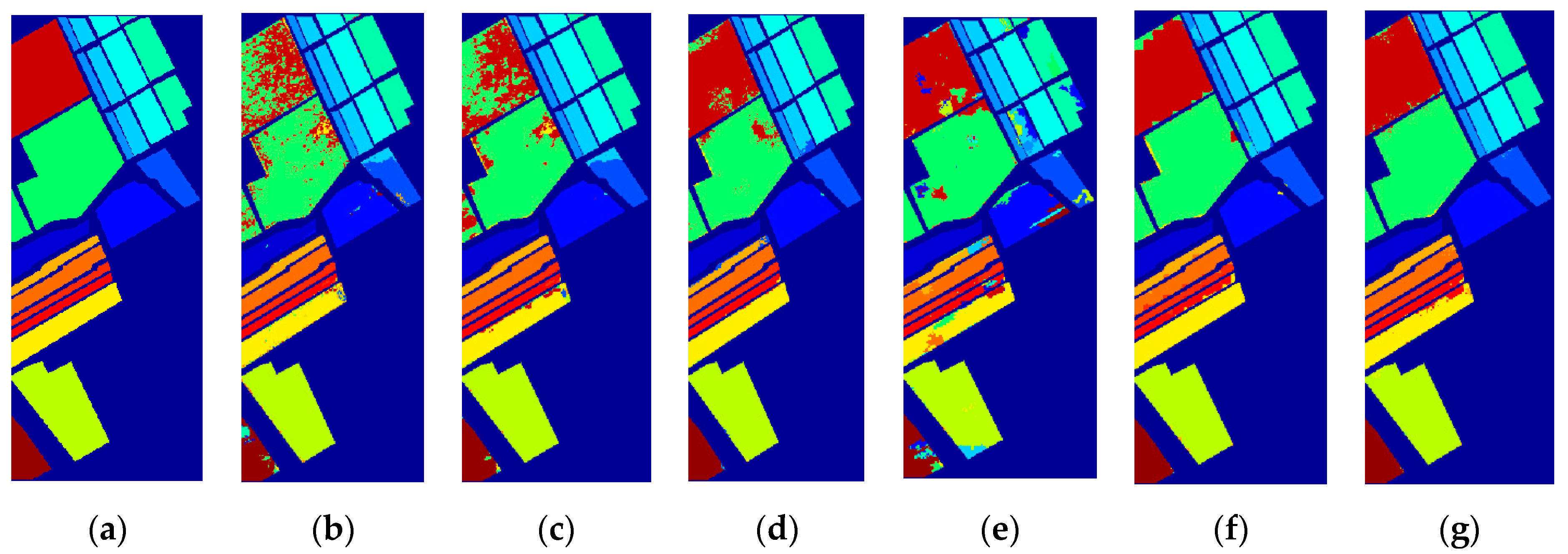
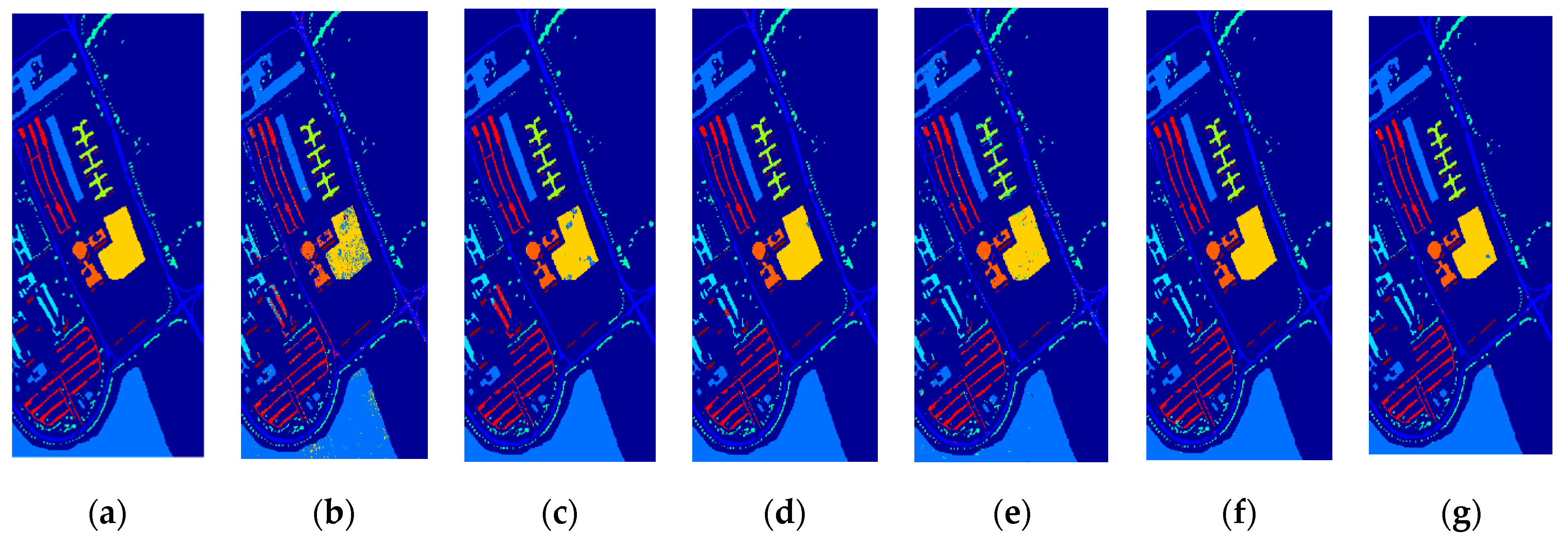
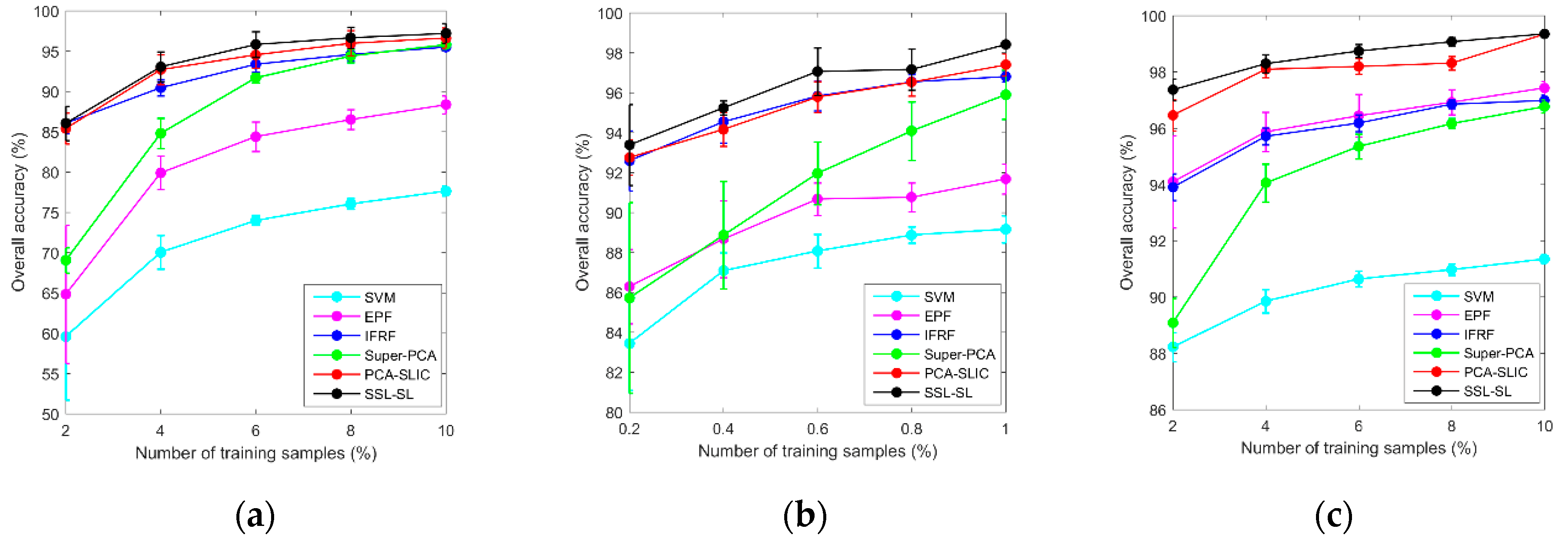
| Class | Train/Test | SVM | EPF | IFRF | SuperPCA | PCA-SLIC | SSC-SL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alfalfa | 5/41 | 49.76 ± 16.71 | 51.22 ± 40.17 | 94.63 ± 6.97 | 95.61 ± 1.54 | 100 ± 0 | 100.00 ± 0.00 |
| Corn-notill | 143/1285 | 67.87 ± 2.73 | 81.5 ± 4.22 | 91.27 ± 0.67 | 93.6 ± 2.34 | 95.86 ± 2.4 | 96.91 ± 2.53 |
| Corn-mintilla | 83/747 | 54.11 ± 2.2 | 60.48 ± 3.49 | 94 ± 2.84 | 95.57 ± 3.65 | 95.66 ± 3.4 | 96.13 ± 4.17 |
| Corn | 24/213 | 38.87 ± 7.74 | 66.95 ± 25.57 | 87.51 ± 6.59 | 87.23 ± 6.73 | 93.01 ± 7.57 | 93.21 ± 6.58 |
| Grass-pasture | 49/434 | 88.48 ± 2.99 | 94.45 ± 1.25 | 96.08 ± 1.73 | 95.83 ± 2.45 | 95.85 ± 3.19 | 96.17 ± 2.83 |
| Grass-trees | 73/657 | 96.41 ± 1.37 | 99.85 ± 0.16 | 99.09 ± 0.72 | 96.74 ± 2.76 | 97.42 ± 1.87 | 98.85 ± 0.35 |
| Grass-pasturemowed | 3/25 | 79.6 ± 7.65 | 96.8 ± 1.69 | 87.6 ± 14.78 | 96.4 ± 1.26 | 90.71 ± 6.9 | 93.57 ± 2.26 |
| Hay-windrowed | 48/430 | 97.37 ± 1.43 | 100 ± 0 | 100 ± 0 | 99.02 ± 1.79 | 99.79 ± 0.04 | 100.00 ± 0.00 |
| Oats | 2/18 | 26.67 ± 9.37 | 2.22 ± 7.03 | 15 ± 21.12 | 80 ± 25.82 | 100 ± 0 | 100.00 ± 0.00 |
| Soybean-notill | 98/874 | 65.94 ± 3.09 | 77.25 ± 2.74 | 89.99 ± 2.64 | 92.95 ± 2.66 | 93.37 ± 1 | 93.27 ± 2.71 |
| Soybean-mintill | 246/2209 | 84.83 ± 0.95 | 96.57 ± 0.83 | 98.47 ± 0.55 | 98.33 ± 1.35 | 97.76 ± 1.16 | 98.21 ± 1.06 |
| Soybean-clean | 60/533 | 64.43 ± 5.12 | 93.73 ± 8.21 | 90.51 ± 4.62 | 92.35 ± 2.56 | 94.2 ± 2.36 | 94.35 ± 2.82 |
| Wheat | 21/184 | 97.34 ± 2.15 | 99.3 ± 0.27 | 99.41 ± 0.17 | 97.39 ± 1.08 | 98.02 ± 1.87 | 98.69 ± 0.46 |
| Woods | 127/1138 | 96.57 ± 0.64 | 99.48 ± 0.43 | 99.68 ± 0.31 | 99.13 ± 0.88 | 98.62 ± 0.98 | 99.49 ± 0.38 |
| Building-grass-trees | 39/347 | 49.31 ± 7 | 73.31 ± 10.92 | 96.89 ± 1.94 | 91.96 ± 5.5 | 95.9 ± 3.01 | 96.61 ± 3.68 |
| Stone-steel-towers | 10/83 | 88.07 ± 4.66 | 99.28 ± 1.9 | 98.68 ± 1.33 | 83.73 ± 16.25 | 97.69 ± 5.19 | 97.74 ± 0.79 |
| OA | -- | 77.63 ± 0.6 | 88.34 ± 1.1 | 95.49 ± 0.26 | 95.79 ± 0.51 | 96.61 ± 1.23 | 97.18 ± 1.26 |
| AA | -- | 71.6 ± 4.74 | 80.77 ± 6.81 | 89.93 ± 4.19 | 93.49 ± 4.91 | 96.49 ± 2.28 | 97.07 ± 2.45 |
| κ | -- | 0.7424 ± 0.69 | 0.8657 ± 1.28 | 0.9485 ± 0.3 | 0.9518 ± 0.59 | 0.960 ± 1.32 | 0.9649 ± 1.37 |
| Class | Train/Test | SVM | EPF | IFRF | Super-PCA | PCA-SLIC | SSL-SL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brocoligreenweed1 | 21/1988 | 97.64 ± 1.32 | 99.43 ± 0.63 | 100 ± 0 | 98.61 ± 4.39 | 100 ± 0 | 99.95 ± 0.01 |
| Brocoligreenweed2 | 38/3688 | 98.81 ± 0.19 | 99.86 ± 0.08 | 99.34 ± 0.47 | 98 ± 2.86 | 99.7 ± 0 | 99.59 ± 0.32 |
| Fallow | 20/1956 | 84.92 ± 4.77 | 83.64 ± 5.08 | 99.95 ± 0.15 | 98.99 ± 0.2 | 99.59 ± 0.7 | 99.86 ± 0.13 |
| Fallowroughplow | 14/1380 | 98.96 ± 0.4 | 99.37 ± 0.34 | 96.63 ± 1.84 | 94.51 ± 4.95 | 89.45 ± 9.3 | 90.17 ± 8.6 |
| Fallowsmooth | 27/2651 | 97.26 ± 1.15 | 99.55 ± 0.28 | 99.27 ± 0.27 | 95.95 ± 5.8 | 97.26 ± 1.08 | 98.74 ± 0.26 |
| Stubble | 40/3919 | 99.56 ± 0.11 | 99.97 ± 0.02 | 99.92 ± 0.03 | 96 ± 5.1 | 99.92 ± 0 | 99.9 ± 0.01 |
| Celery | 36/3543 | 99.33 ± 0.25 | 99.74 ± 0.02 | 99.66 ± 0.2 | 96.64 ± 2.27 | 99.92 ± 0.02 | 99.92 ± 0.02 |
| Grapesuntrained | 113/11158 | 88.53 ± 2.05 | 91.35 ± 1.9 | 92.83 ± 0.81 | 97.74 ± 1.59 | 97.83 ± 1.18 | 99.1 ± 0.23 |
| Soilvinyarddevelop | 63/6140 | 98.54 ± 0.8 | 99.5 ± 0.32 | 99.98 ± 0 | 97.91 ± 3.54 | 99.89 ± 0.18 | 99.68 ± 0.29 |
| Cornsenescedgreen | 33/3245 | 87.34 ± 4.17 | 92.07 ± 3.35 | 99.67 ± 0.22 | 95.88 ± 2.2 | 95.33 ± 3.9 | 97.51 ± 0.62 |
| Lettuceromaine 4wk | 11/1057 | 90.67 ± 1.85 | 97.02 ± 1.38 | 90.59 ± 4.39 | 73.8 ± 22.74 | 94.4 ± 3.98 | 96.69 ± 4.25 |
| Lettuceromaine 5wk | 20/1907 | 99.76 ± 0.31 | 100 ± 0 | 100 ± 0.02 | 89.24 ± 8.71 | 95.11 ± 0.91 | 98.58 ± 1.06 |
| Lettuceromaine 6wk | 10/906 | 97.64 ± 0.61 | 97.79 ± 0.22 | 81.45 ± 2.9 | 92.41 ± 9.23 | 89.67 ± 6.89 | 97.39 ± 0.06 |
| Lettuceromaine 7wk | 11/1059 | 90.93 ± 4.02 | 94.24 ± 0.86 | 92.6 ± 1.32 | 83.9 ± 10.31 | 88.59 ± 6.91 | 95.75 ± 0.11 |
| Vinyarduntrained | 73/7195 | 55.39 ± 4.96 | 62.68 ± 5.37 | 93.97 ± 1.84 | 96.66 ± 3.92 | 94.98 ± 2.41 | 95.5 ± 1.8 |
| Vinyardvertical | 19/1788 | 95.35 ± 3.74 | 97.71 ± 1.87 | 98.98 ± 0.86 | 92.25 ± 4.77 | 98.66 ± 2.4 | 99.78 ± 0.01 |
| OA | -- | 89.16 ± 0.68 | 91.68 ± 0.75 | 96.8 ± 0.27 | 95.90 ± 0.62 | 97.39 ± 0.56 | 98.41 ± 0.13 |
| AA | -- | 92.54 ± 1.92 | 94.62 ± 1.36 | 96.55 ± 0.96 | 93.66 ± 5.8 | 96.27 ± 2.49 | 98.01 ± 1.1 |
| κ | -- | 0.879 ± 0.76 | 0.9071 ± 0.85 | 0.9644 ± 0.3 | 0.9543 ± 0.69 | 0.9710 ± 0.63 | 0.9823 ± 0.15 |
| Class | Train/Test | SVM | EPF | IFRF | Super-PCA | PCA-SLIC | SSB-SL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Broccoligreenweed1 | 664/5967 | 91.68 ± 0.55 | 99.67 ± 0.21 | 98.42 ± 0.21 | 95.55 ± 0.46 | 99.6 ± 0.23 | 99.62 ± 0.2 |
| Broccoligreenweed2 | 1865/16784 | 97.4 ± 0.3 | 99.94 ± 0.02 | 99.93 ± 0.05 | 99.3 ± 0.07 | 99.64 ± 0.22 | 99.77 ± 0.13 |
| Fallow | 210/1889 | 70.05 ± 2.22 | 72.32 ± 5.26 | 91.08 ± 4.18 | 95.74 ± 0.85 | 99.02 ± 0.53 | 97.98 ± 0.58 |
| Fallowroughplough | 307/2757 | 93.82 ± 0.95 | 98.23 ± 0.66 | 94.85 ± 0.86 | 83.71 ± 1.63 | 97.29 ± 0.75 | 97.36 ± 0.58 |
| Fallowsmooth | 135/1210 | 99.45 ± 0.18 | 99.93 ± 0.03 | 99.63 ± 0.18 | 91.23 ± 1.25 | 96.68 ± 2.17 | 99.78 ± 0.04 |
| Stubble | 503/4526 | 76.69 ± 1.25 | 94.21 ± 1.71 | 99.8 ± 0.07 | 98.21 ± 0.37 | 99.97 ± 0.04 | 99.8 ± 0.12 |
| Celery | 133/1197 | 82.87 ± 0.96 | 94.05 ± 1.2 | 98.52 ± 0.56 | 98.47 ± 0.42 | 99.92 ± 0 | 98.55 ± 0.93 |
| Grapesuntrained | 369/3313 | 88.37 ± 1.32 | 98.86 ± 0.3 | 89.36 ± 1.74 | 97.21 ± 0.36 | 99.23 ± 0.35 | 98.66 ± 0.38 |
| Soilvineyarddevelop | 95/852 | 98.88 ± 0.38 | 98.09 ± 0.63 | 57.56 ± 4.6 | 95.82 ± 0.79 | 99.25 ± 0.71 | 99.65 ± 0.11 |
| OA | -- | 91.35 ± 0.18 | 97.43 ± 0.24 | 96.98 ± 0.19 | 95.03 ± 0.69 | 99.31 ± 0.09 | 99.35 ± 0.09 |
| AA | -- | 88.8 ± 0.9 | 95.03 ± 1.11 | 92.13 ± 1.38 | 96.77 ± 0.17 | 98.96 ± 0.56 | 99.02 ± 0.34 |
| κ | -- | 0.8844 ± 0.23 | 0.9658 ± 0.32 | 0.96 ± 0.26 | 0.957 ± 0.23 | 0.9913 ± 0.12 | 0.9915 ± 0.12 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, F.; Lei, C.; Jin, C.; An, N. A Novel Spectral–Spatial Classification Method for Hyperspectral Image at Superpixel Level. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 463. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10020463
Xie F, Lei C, Jin C, An N. A Novel Spectral–Spatial Classification Method for Hyperspectral Image at Superpixel Level. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(2):463. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10020463
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Fuding, Cunkuan Lei, Cui Jin, and Na An. 2020. "A Novel Spectral–Spatial Classification Method for Hyperspectral Image at Superpixel Level" Applied Sciences 10, no. 2: 463. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10020463
APA StyleXie, F., Lei, C., Jin, C., & An, N. (2020). A Novel Spectral–Spatial Classification Method for Hyperspectral Image at Superpixel Level. Applied Sciences, 10(2), 463. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10020463





