Tooth Segmentation of 3D Scan Data Using Generative Adversarial Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.1.1. Digital Orthodontics
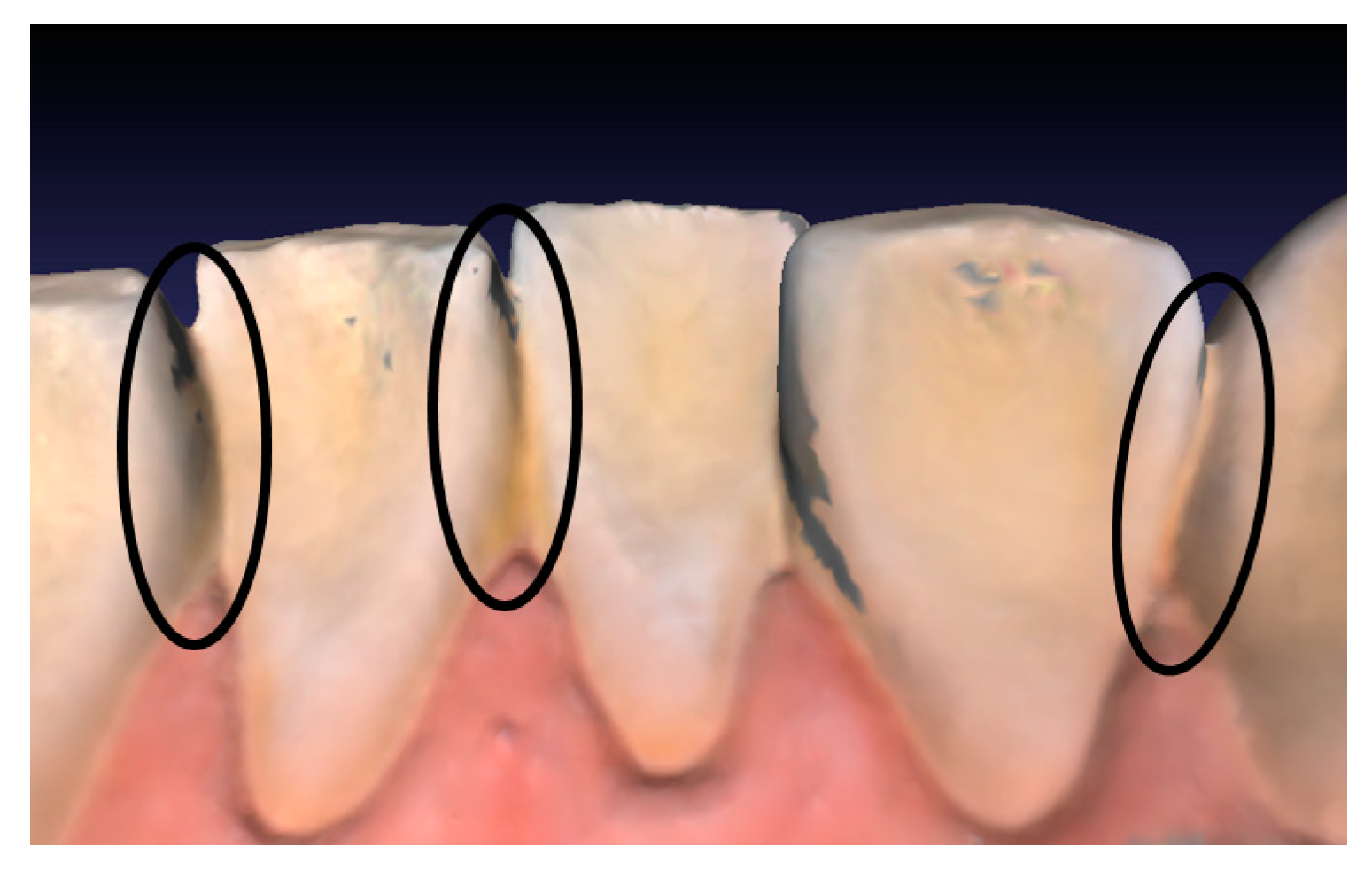
1.1.2. Tooth Segmentation
1.2. Related Studies
1.3. Motivation and Contributions of This Paper
1.3.1. Generative Adversarial Network (GAN)
1.3.2. Image Completion
1.3.3. Goals
2. Proposed Method
2.1. Overview
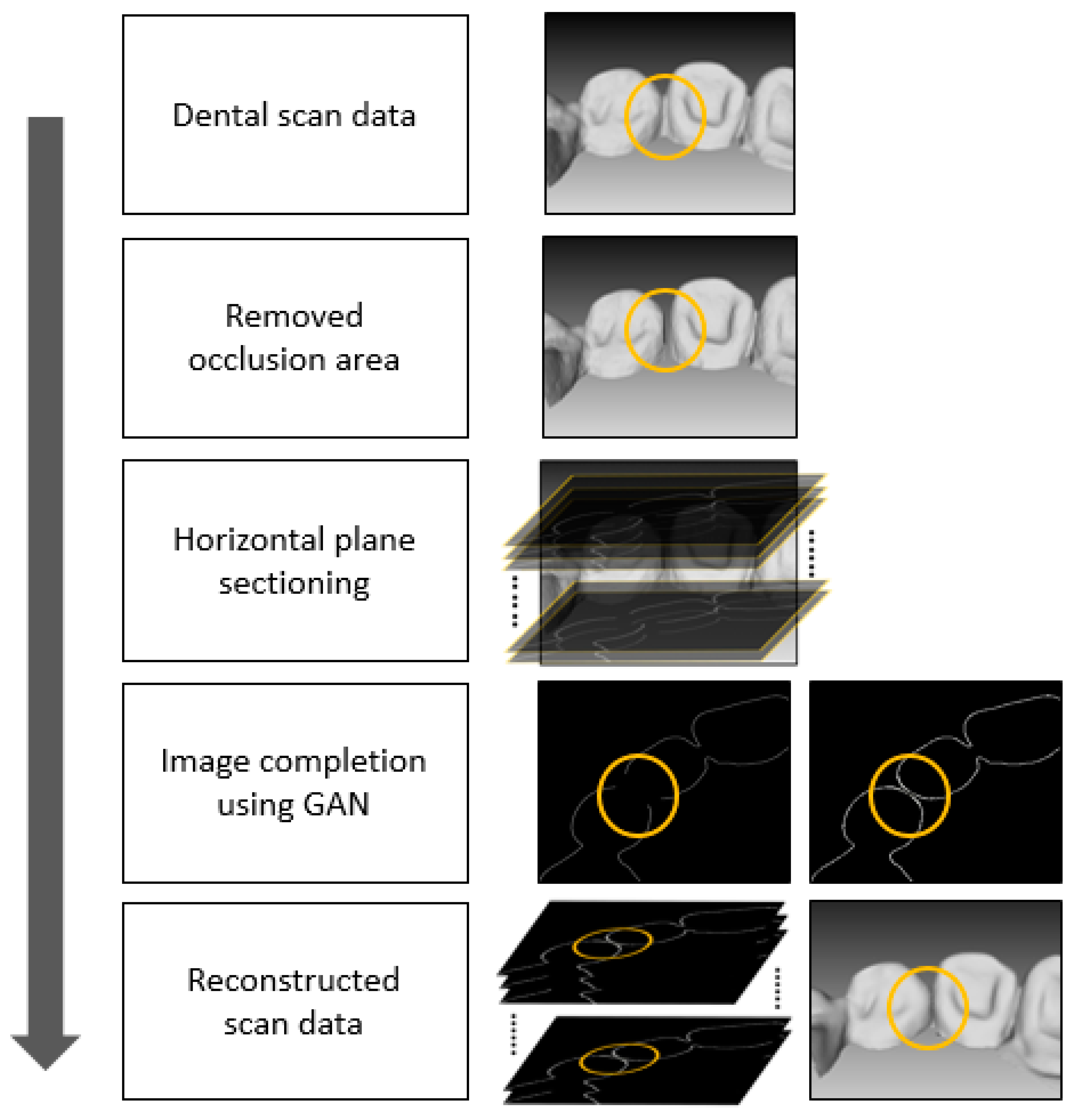
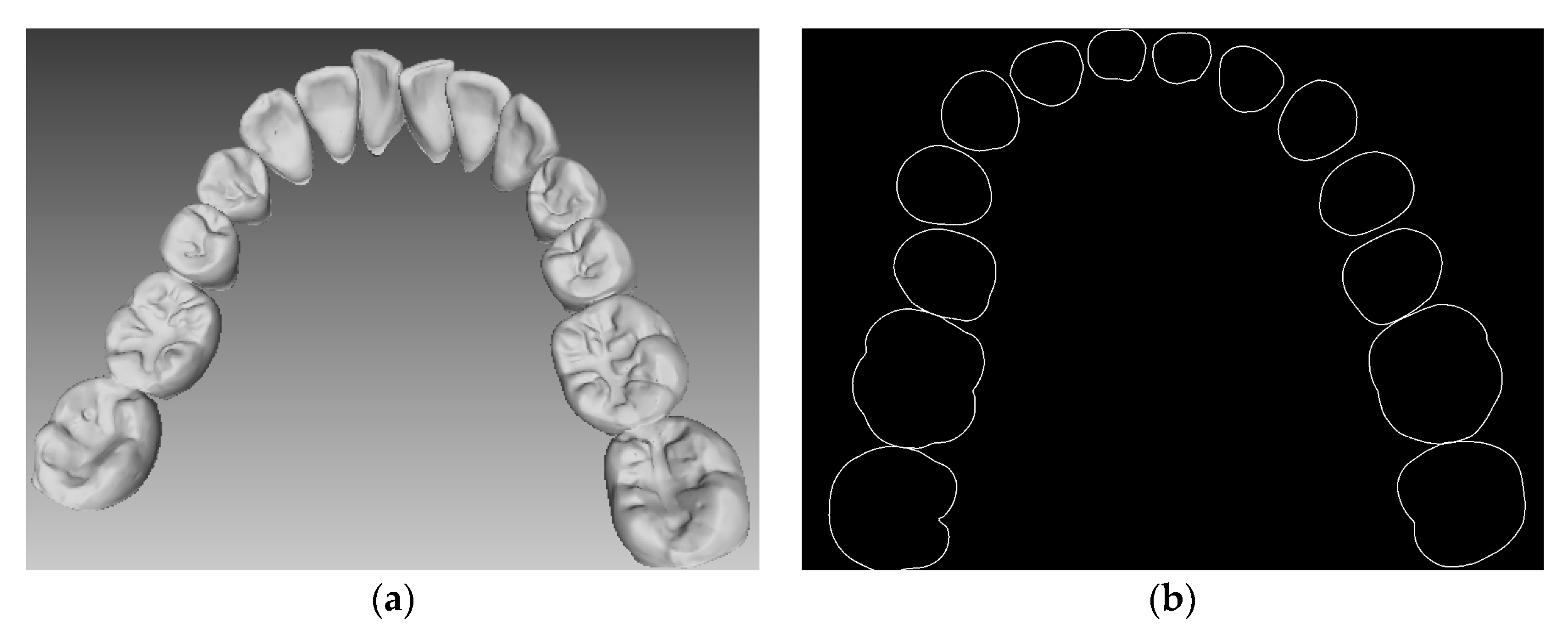
2.2. Reconstruction of Dental Scan Data
2.3. Training GAN
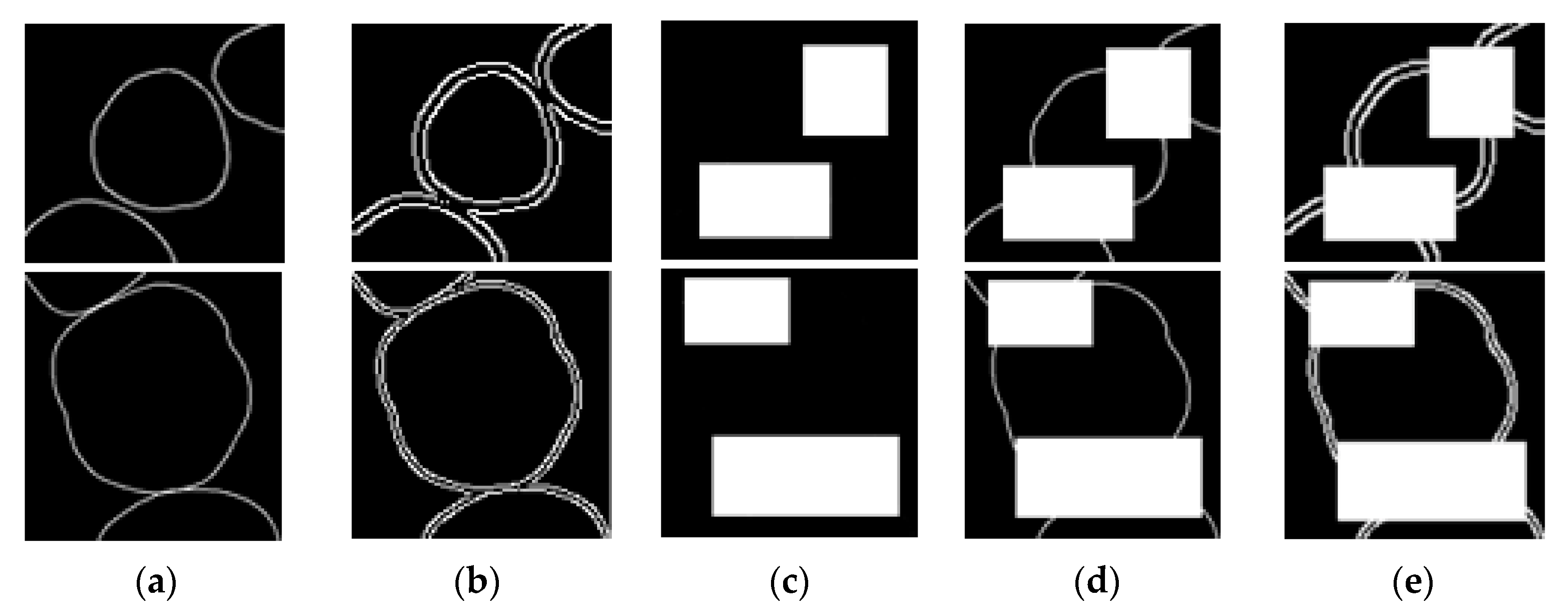
2.3.1. Data Preparation
2.3.2. Training Steps
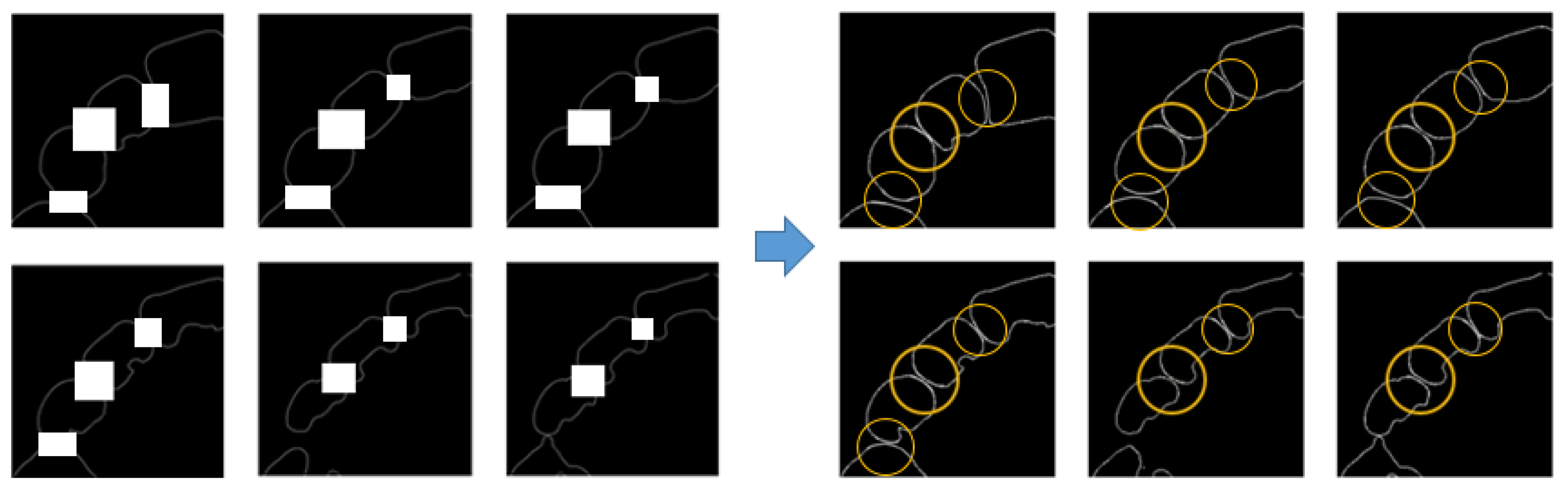
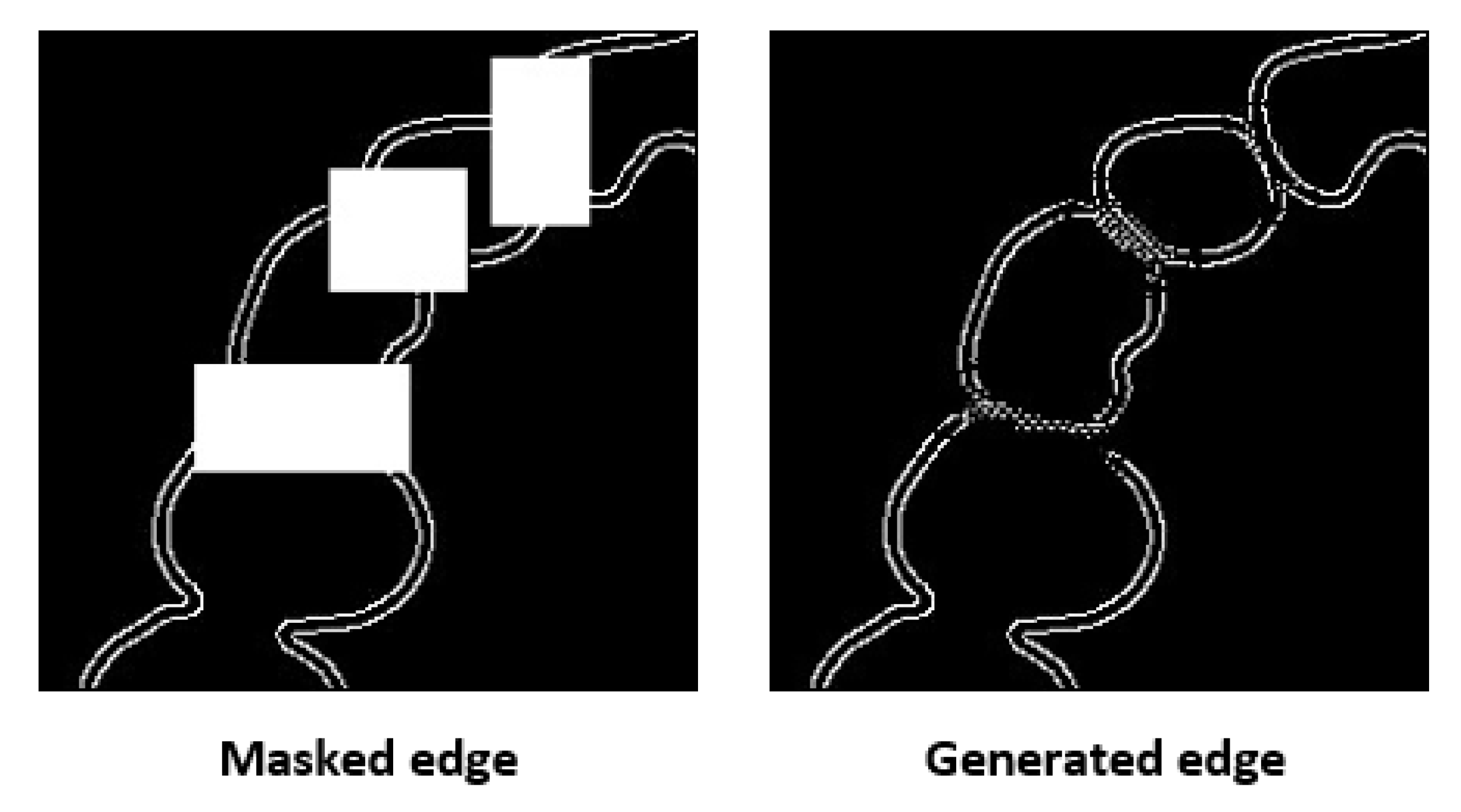
3. Results and Discussion
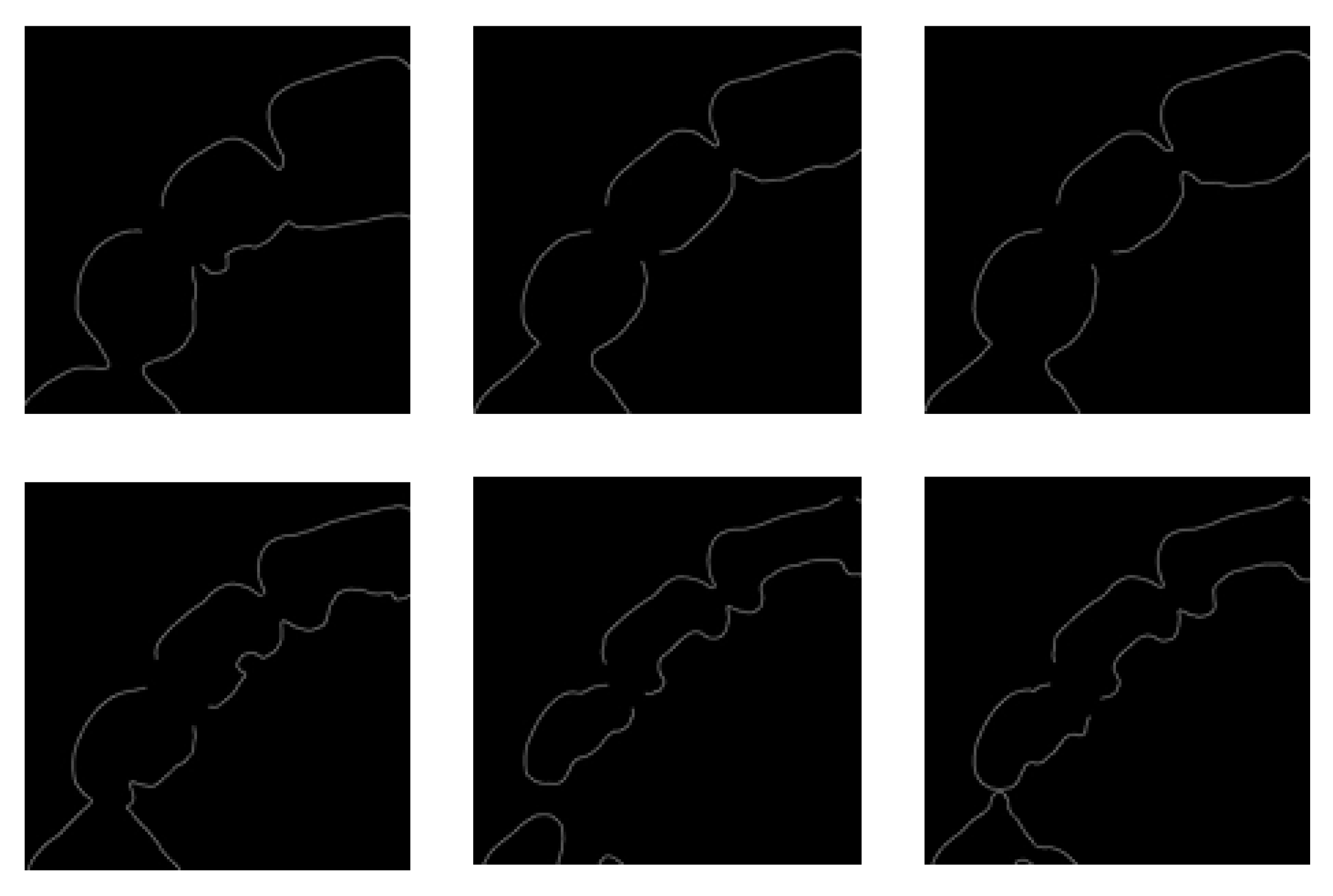
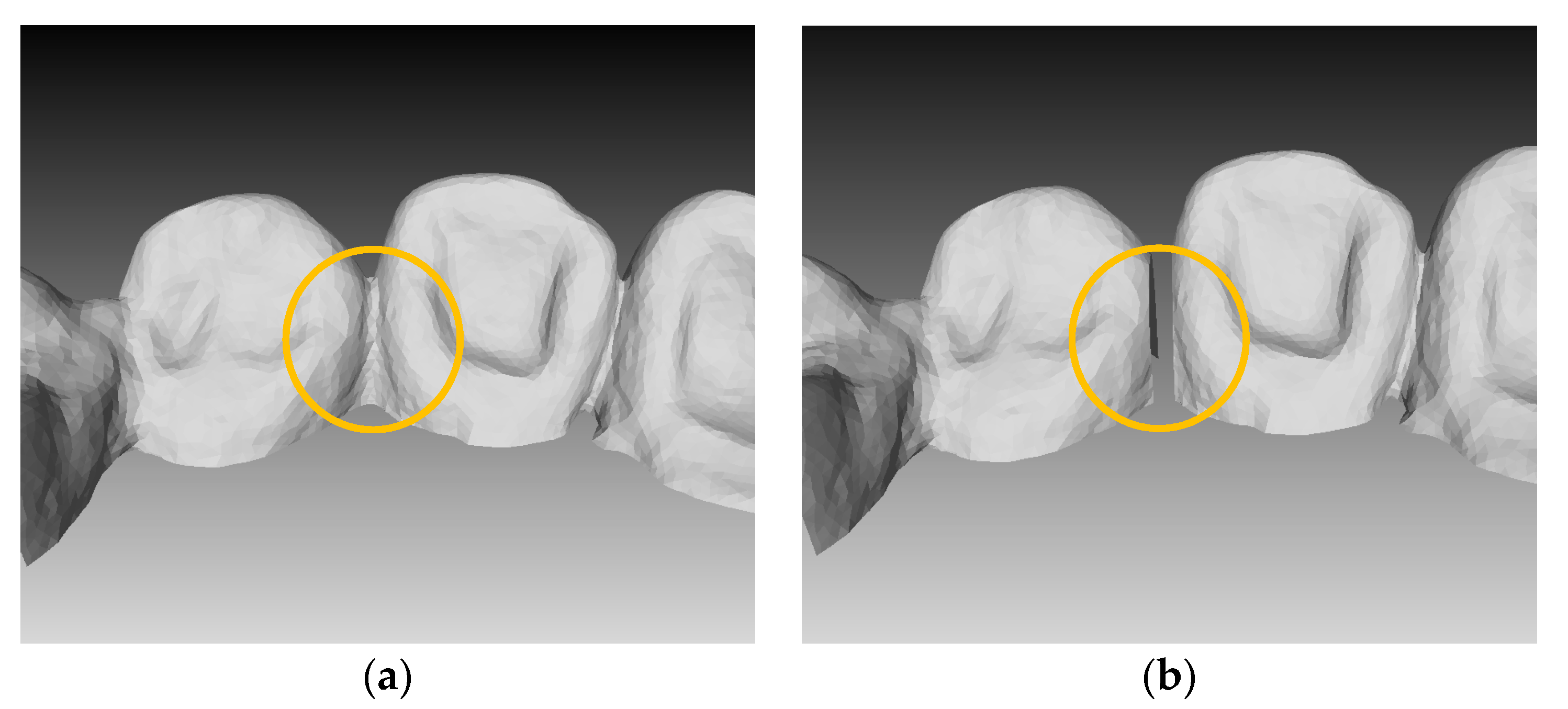
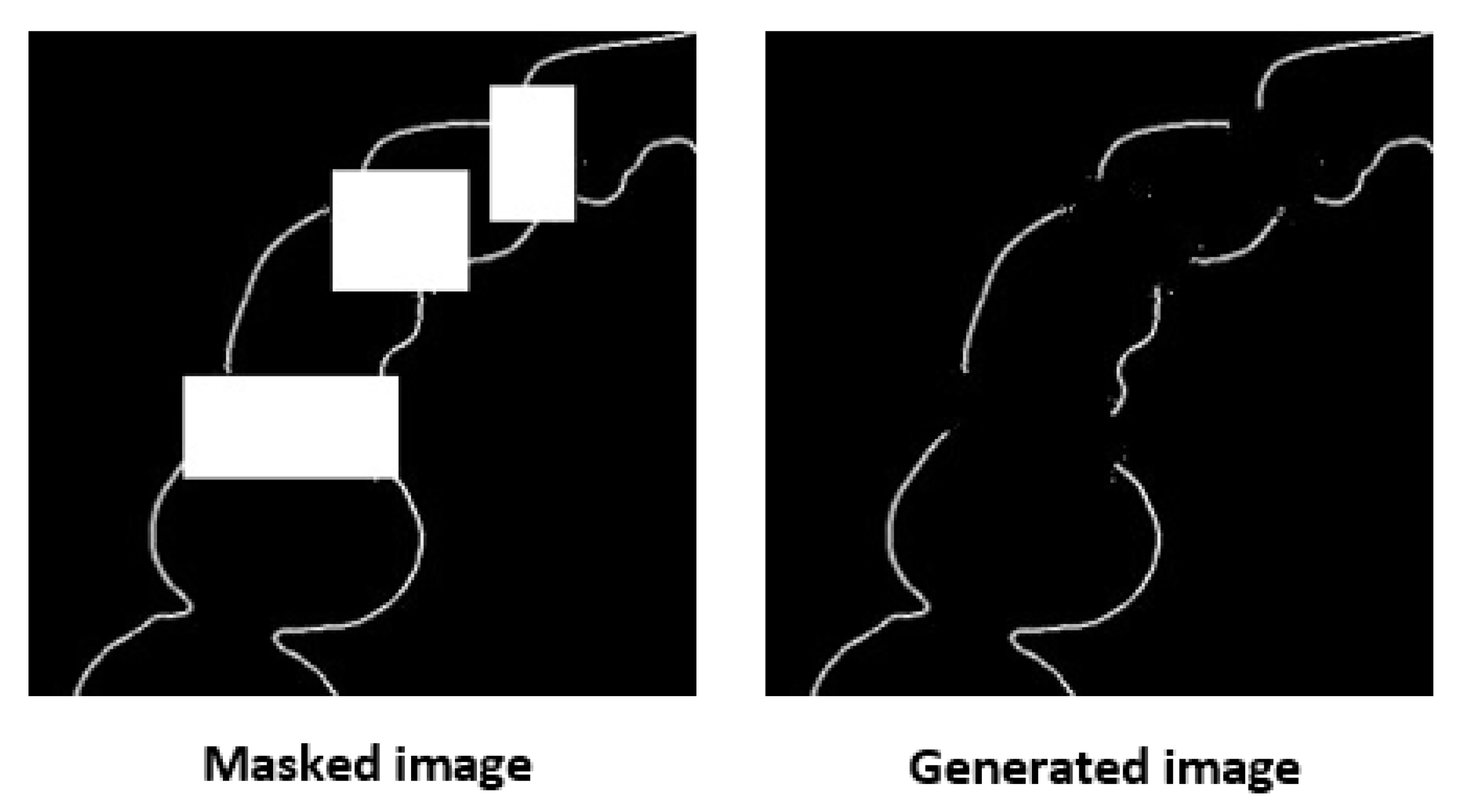
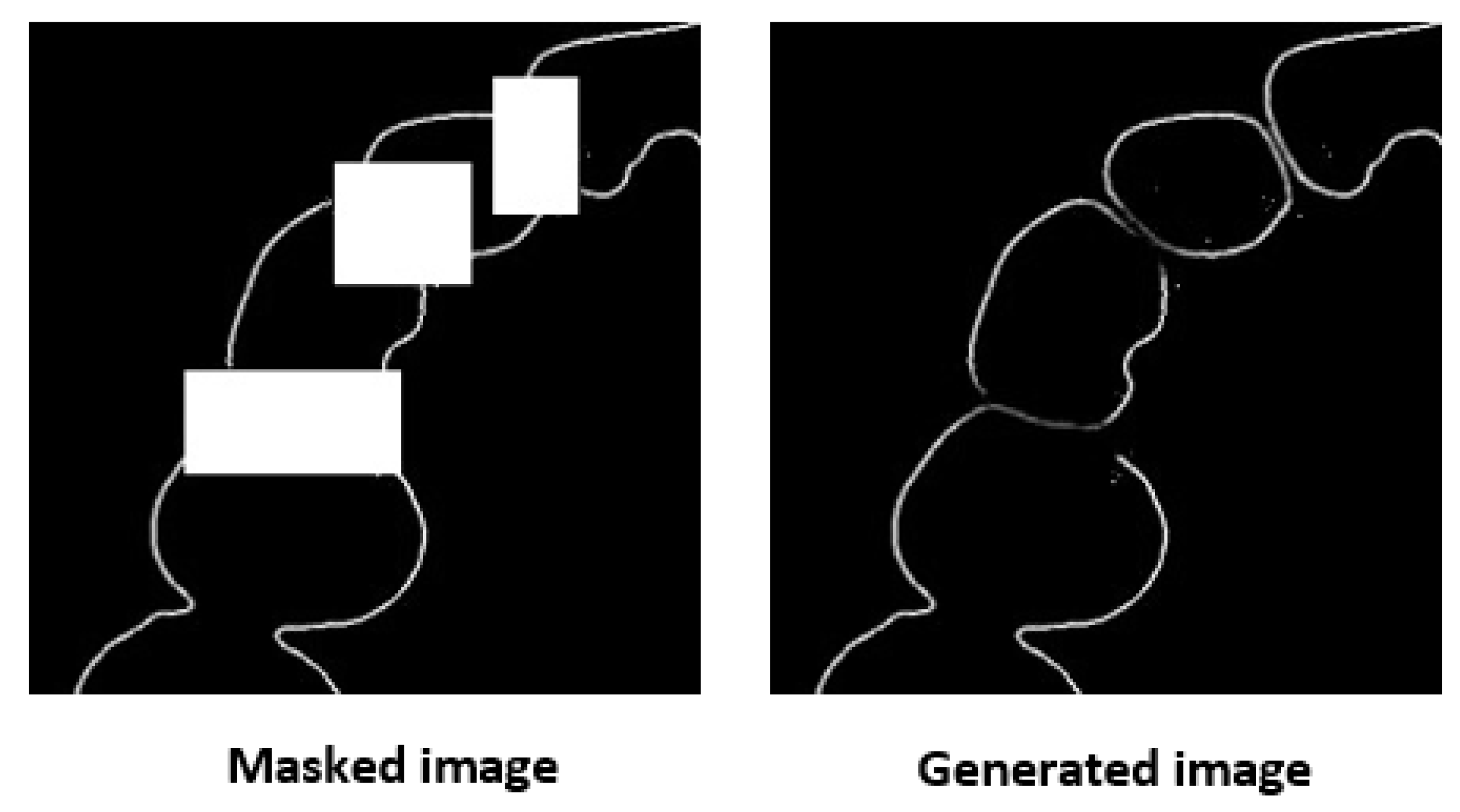
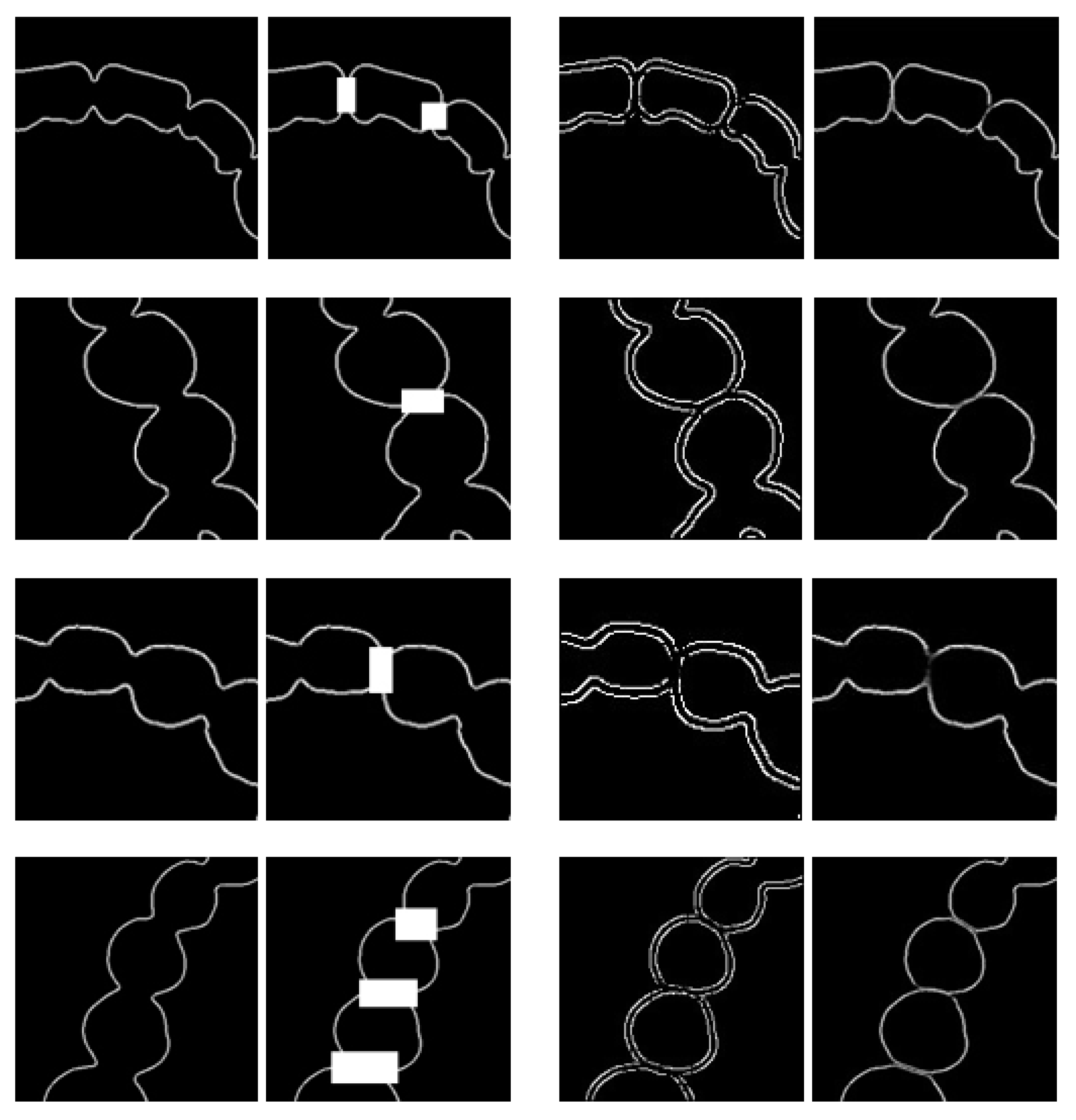
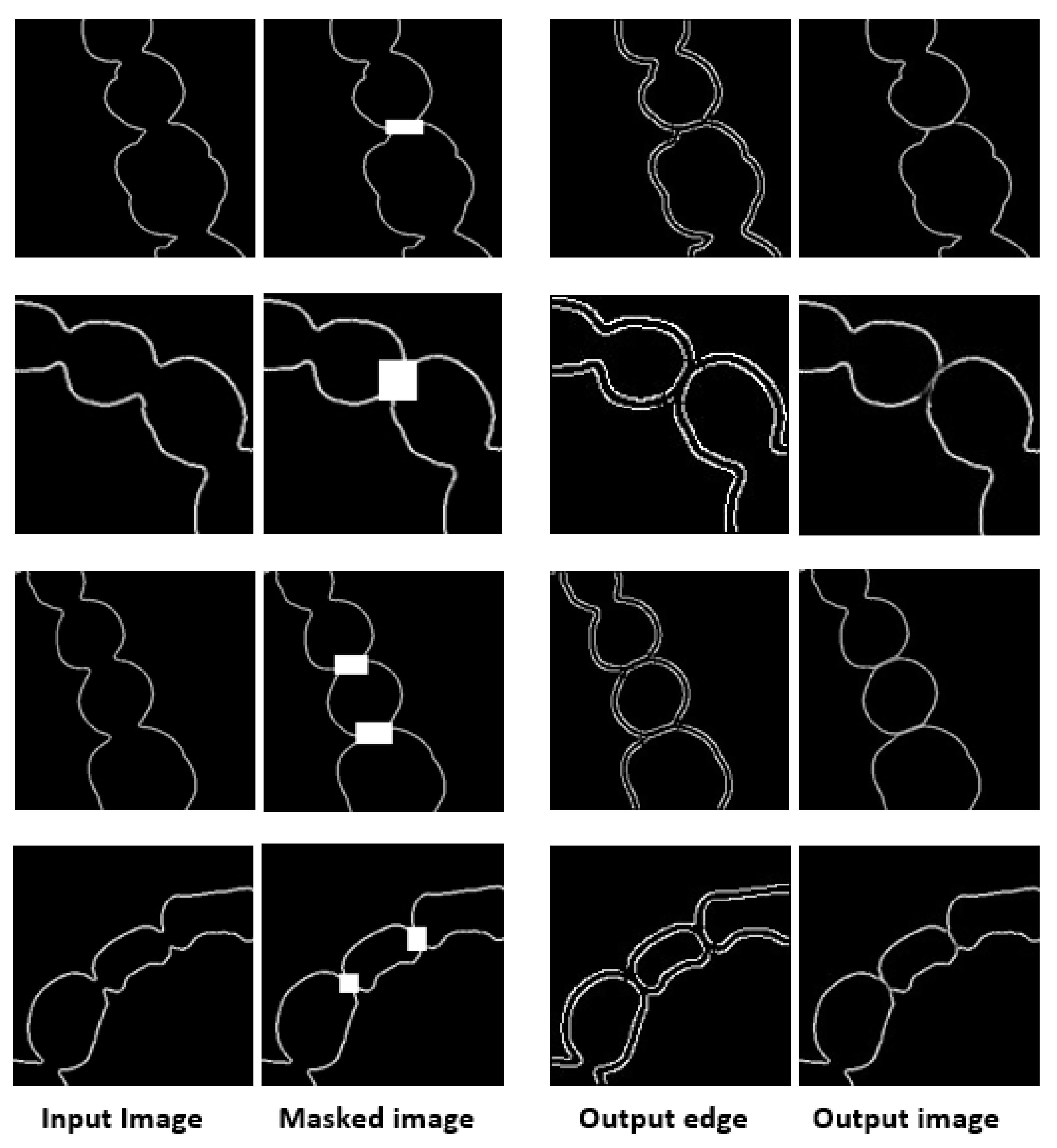
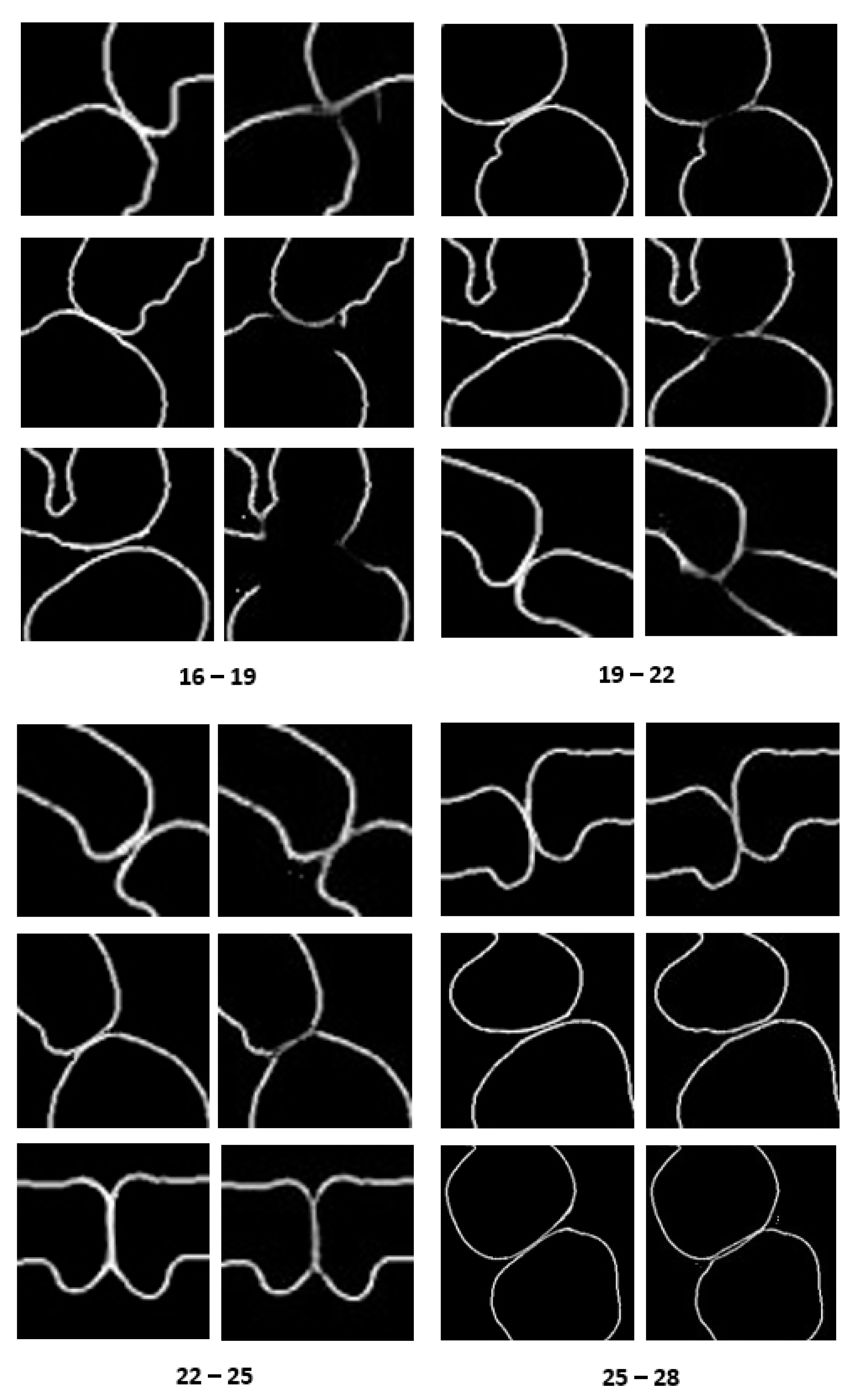
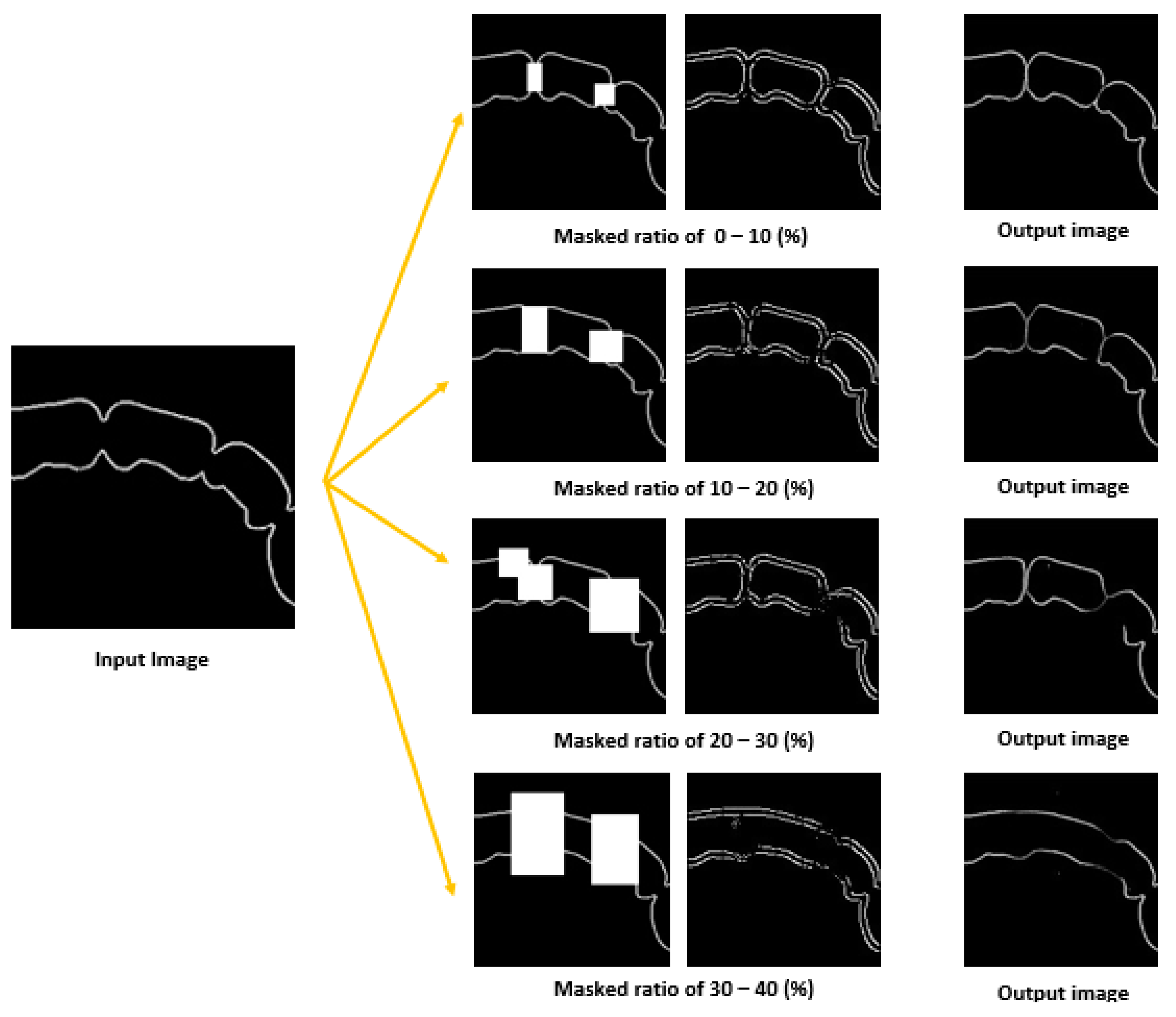
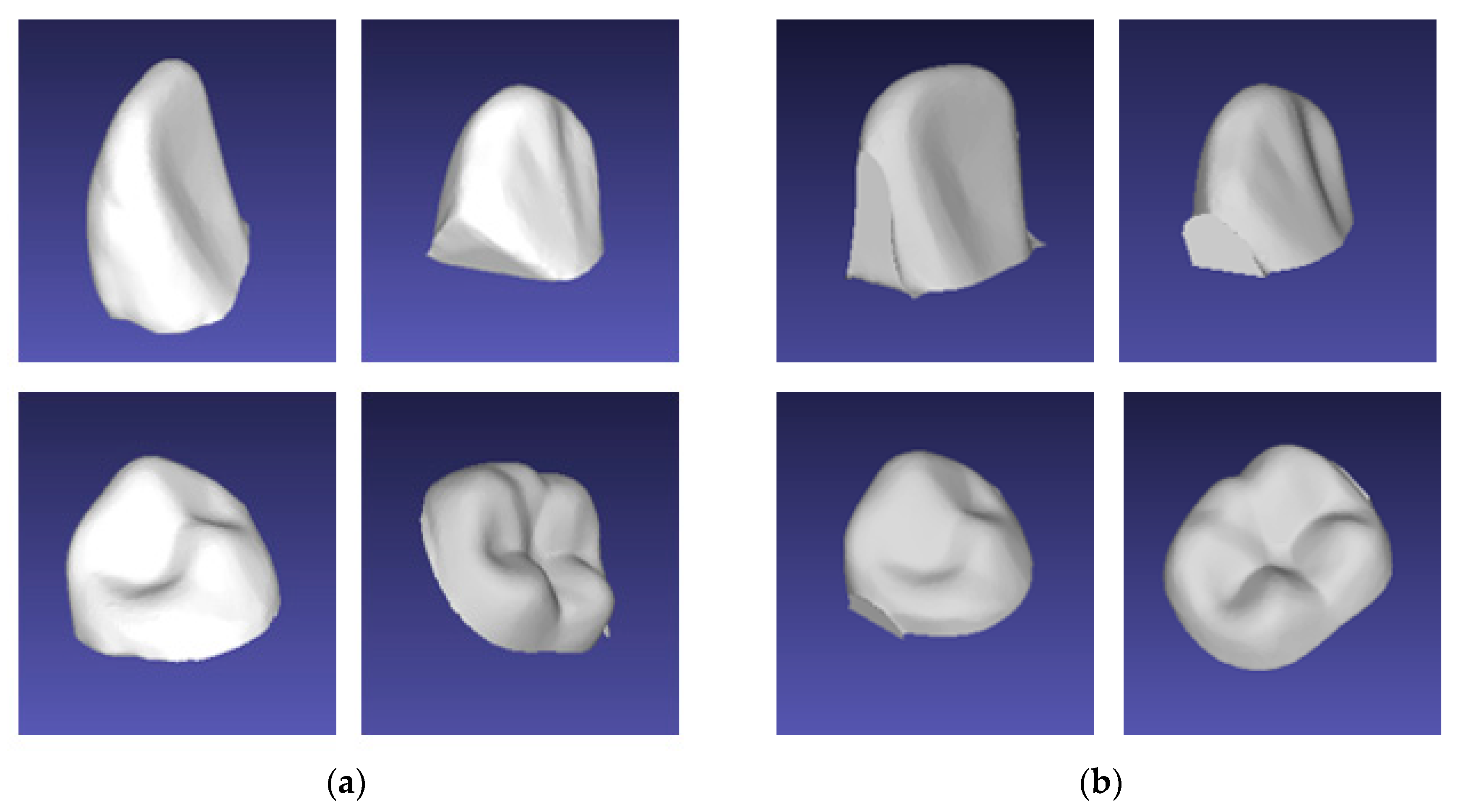
3.1. Result of Image Completion
3.2. Results of Tooth Segmentation
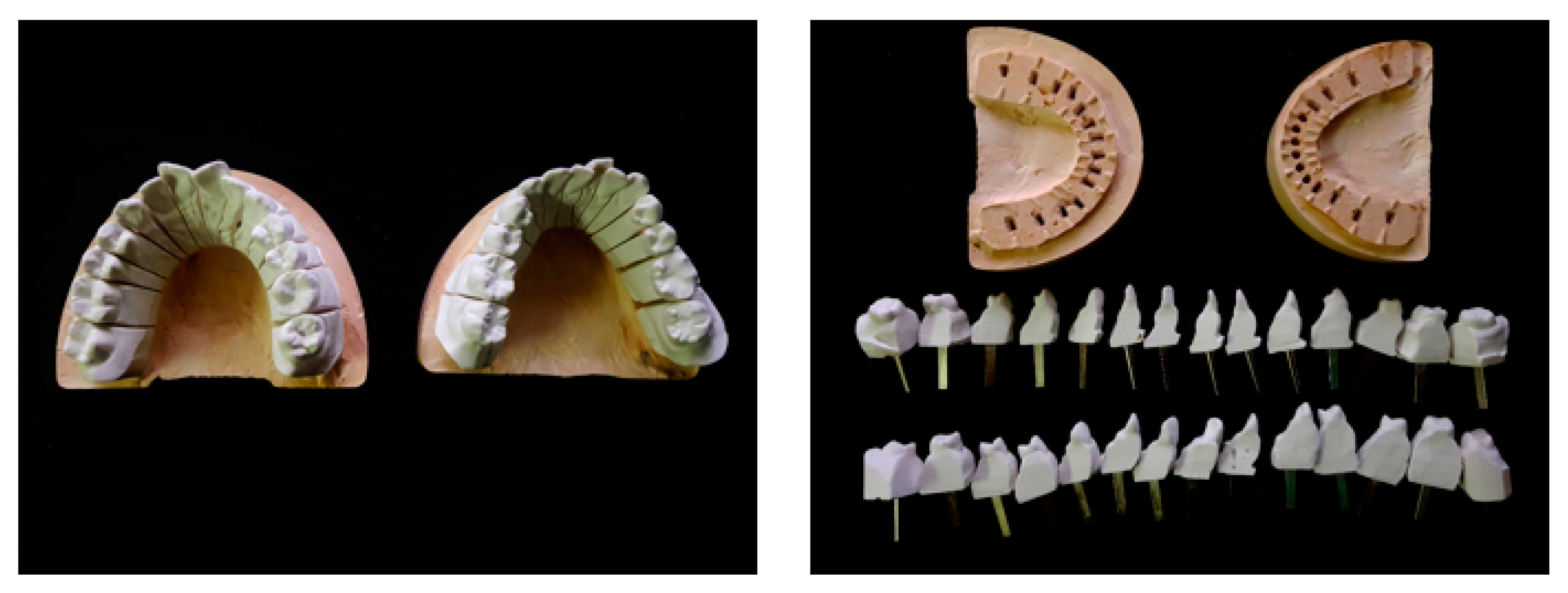
3.2.1. Tooth Model
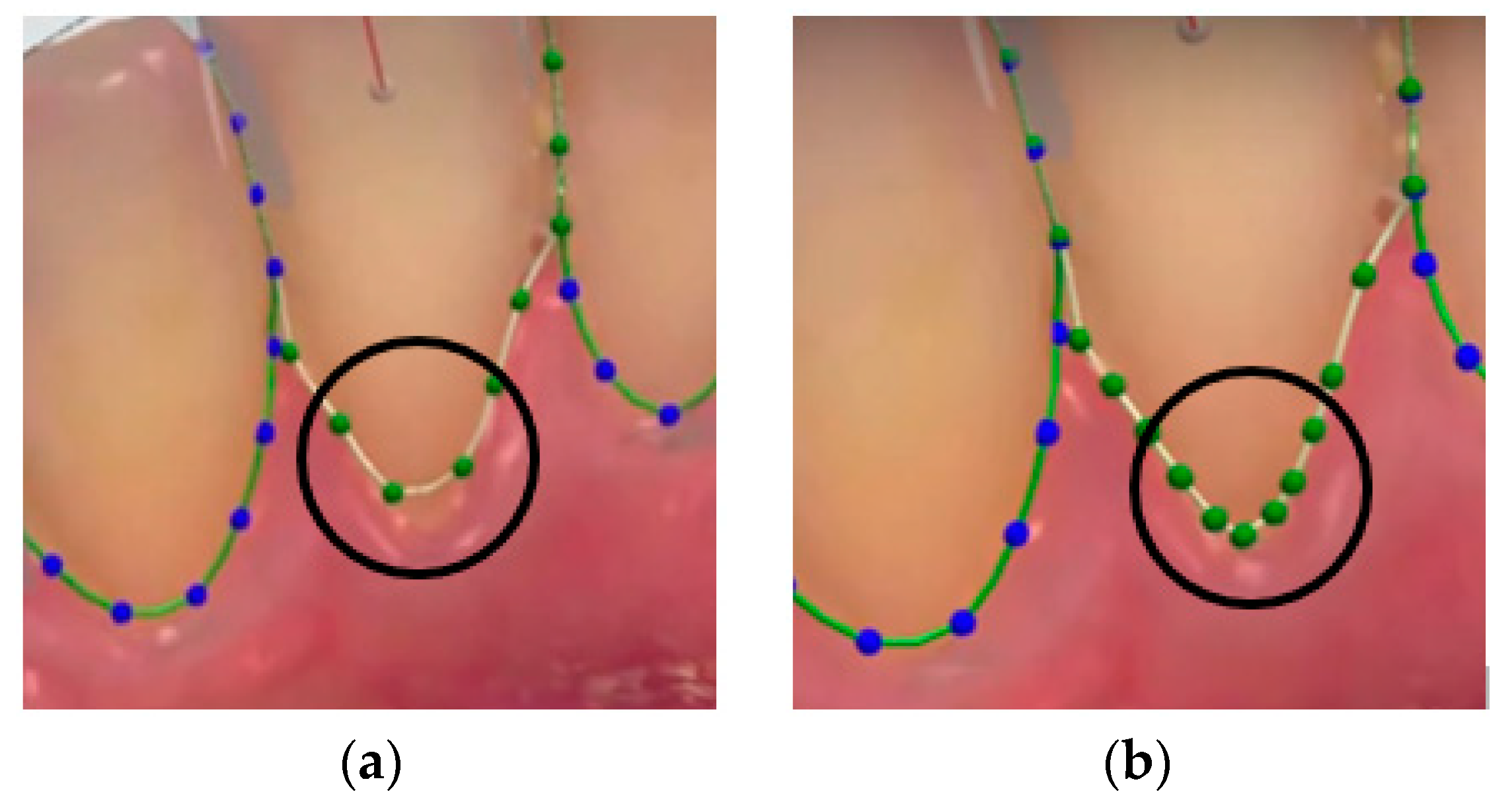
3.2.2. Accuracy Measurement Process
3.2.3. Measurement Accuracy Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kesling, H. The diagnostic setup with consideration of the third dimension. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1956, 42, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, M.S.; Faber, J.; Vogel, C.J.; Araujo, T.M. Reliability of digital orthodontic setups. Angle Orthod. 2016, 86, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Im, J.; Cha, J.Y.; Lee, K.J.; Yu, H.S.; Hwang, C.J. Comparison of virtual and manual tooth setups with digital and plaster models in extraction cases. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2014, 145, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.T.; Lou, W.S.; Chen, C.C.; Lin, H.C. A 3D scanning system based on low-occlusion approach. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on 3-D Digital Imaging and Modeling (Cat. No. PR00062), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 8 October 1999; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1999; pp. 506–515. [Google Scholar]
- Shlafman, S.; Tal, A.; Katz, S. Metamorphosis of polyhedral surfaces using decomposition. In Computer Graphics Forum; Blackwell Publishing, Inc.: Oxford, UK, 2002; pp. 219–228. [Google Scholar]
- Mangan, A.P.; Whitaker, R.T. Partitioning 3D surface meshes using watershed segmentation. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 1999, 5, 308–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, S.; Shamir, A.; Cohen-Or, D.; Seidel, H.P. Mesh scissoring with minima rule and part salience. Comput. Aided Geom. Des. 2005, 22, 444–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanjani, F.G.; Moin, D.A.; Claessen, F.; Cherici, T.; Parinussa, S.; Pourtaherian, A.; Zinger, S. Mask-MCNet: Instance segmentation in 3D point cloud of intra-oral scans. In International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 128–136. [Google Scholar]
- Podolak, J.; Shilane, P.; Golovinskiy, A.; Rusinkiewicz, S.; Funkhouser, T. A planar-reflective symmetry transform for 3D shapes. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2006, 25, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.K.; Hu, S.M.; Martin, R.R.; Rosin, P.L. Fast mesh segmentation using random walks. In Proceedings of the 2008 ACM Symposium on Solid and Physical Modeling, New York, NY, USA, 2–4 June 2008; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 183–191. [Google Scholar]
- Kronfeld, T.; Brunner, D.; Brunnett, G. Snake-based segmentation of teeth from virtual dental casts. Comput. Aided Des. Appl. 2010, 7, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barnes, C.; Shechtman, E.; Goldman, D.B.; Finkelstein, A. The generalized patchmatch correspondence algorithm. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 29–43. [Google Scholar]
- Darabi, S.; Shechtman, E.; Barnes, C.; Goldman, D.B.; Sen, P. Image melding: Combining inconsistent images using patch-based synthesis. ACM Trans. Graph. 2012, 31, 82-1–82-10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.B.; Kang, S.B.; Ahuja, N.; Kopf, J. Image completion using planar structure guidance. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2014, 33, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simakov, D.; Caspi, Y.; Shechtman, E.; Irani, M. Summarizing visual data using bidirectional similarity. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, AK, USA, 23–28 June 2008; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Köhler, R.; Schuler, C.; Schölkopf, B.; Harmeling, S. Mask-specific inpainting with deep neural networks. In German Conference on Pattern Recognition; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 523–534. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.S.; Xu, L.; Yan, Q.; Sun, W. Shepard convolutional neural networks. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 901–909. [Google Scholar]
- Iizuka, S.; Simo-serra, E.; Ishikawa, H. Globally and locally consistent image completion. ACM Trans Graph. (ToG) 2017, 36, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazeri, K.; Ng, E.; Joseph, T.; Qureshi, F.; Ebrahimi, M. Edgeconnect: Generative image inpainting with adversarial edge learning. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.00212. [Google Scholar]
- Besl, P.J.; Mckay, N.D. Method for registration of 3-D shapes. In Sensor Fusion IV: Control Paradigms and Data Structures; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1992; pp. 586–606. [Google Scholar]
- Sajjadi, M.S.; Scholkopf, B.; Hirsch, M. Enhancenet: Single image super-resolution through automated texture synthesis. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 4491–4500. [Google Scholar]
- Waleed Gondal, M.; Scholkopf, B.; Hirsch, M. The unreasonable effectiveness of texture transfer for single image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A.A. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1125–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2223–2232. [Google Scholar]
- Canny, J. A computational approach to edge detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1986, 6, 679–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Boer, J.F.; Cense, B.; Park, B.H.; Pierce, M.C.; Tearney, G.J.; Bouma, B.E. Improved signal-to-noise ratio in spectral-domain compared with time-domain optical coherence tomography. Opt. Lett. 2003, 28, 2067–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.; Song, S.; Chang, M.; Park, S. Range image registration based on 2D synthetic images. Comput. Aided Des. 2018, 94, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





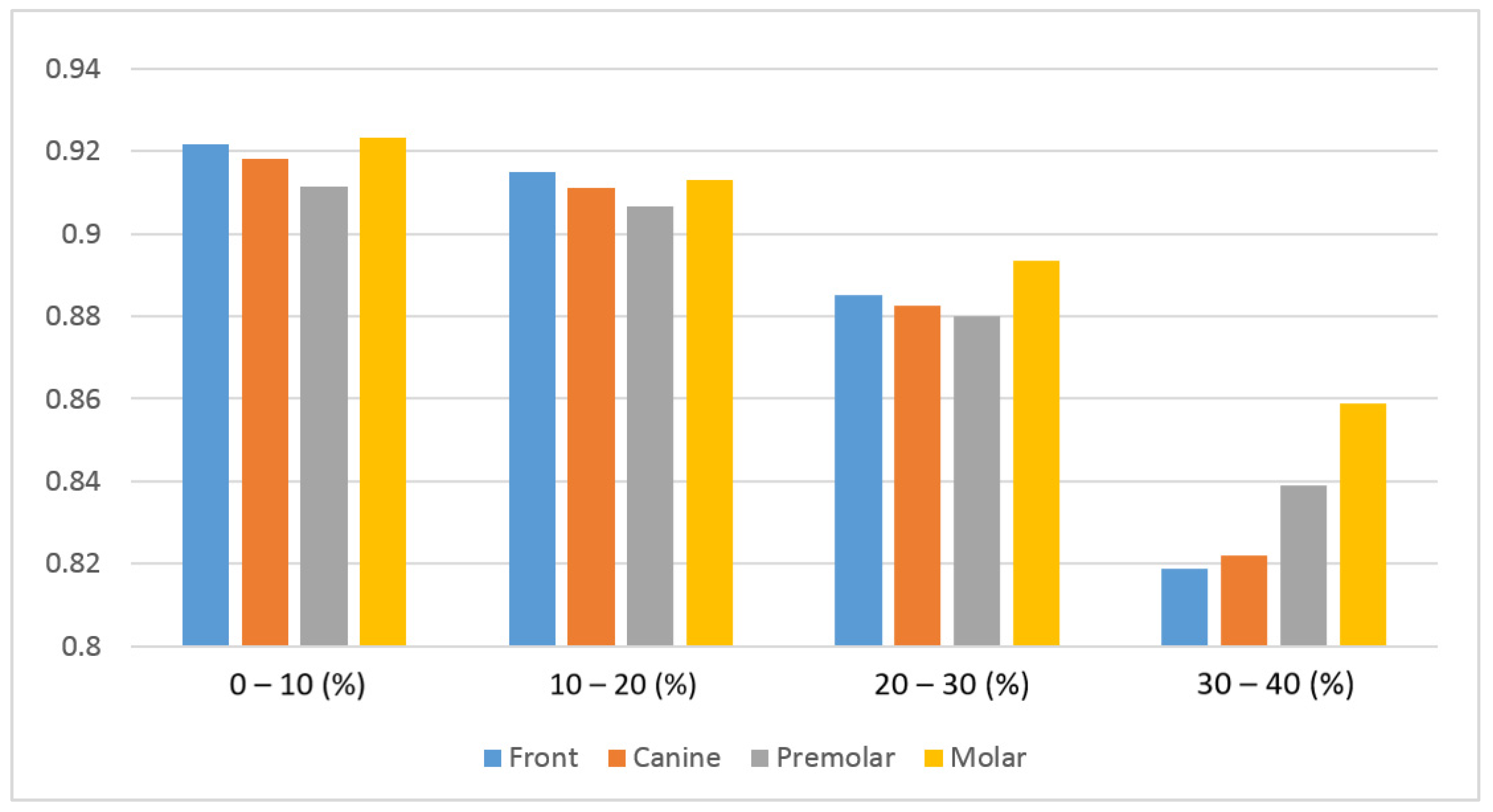
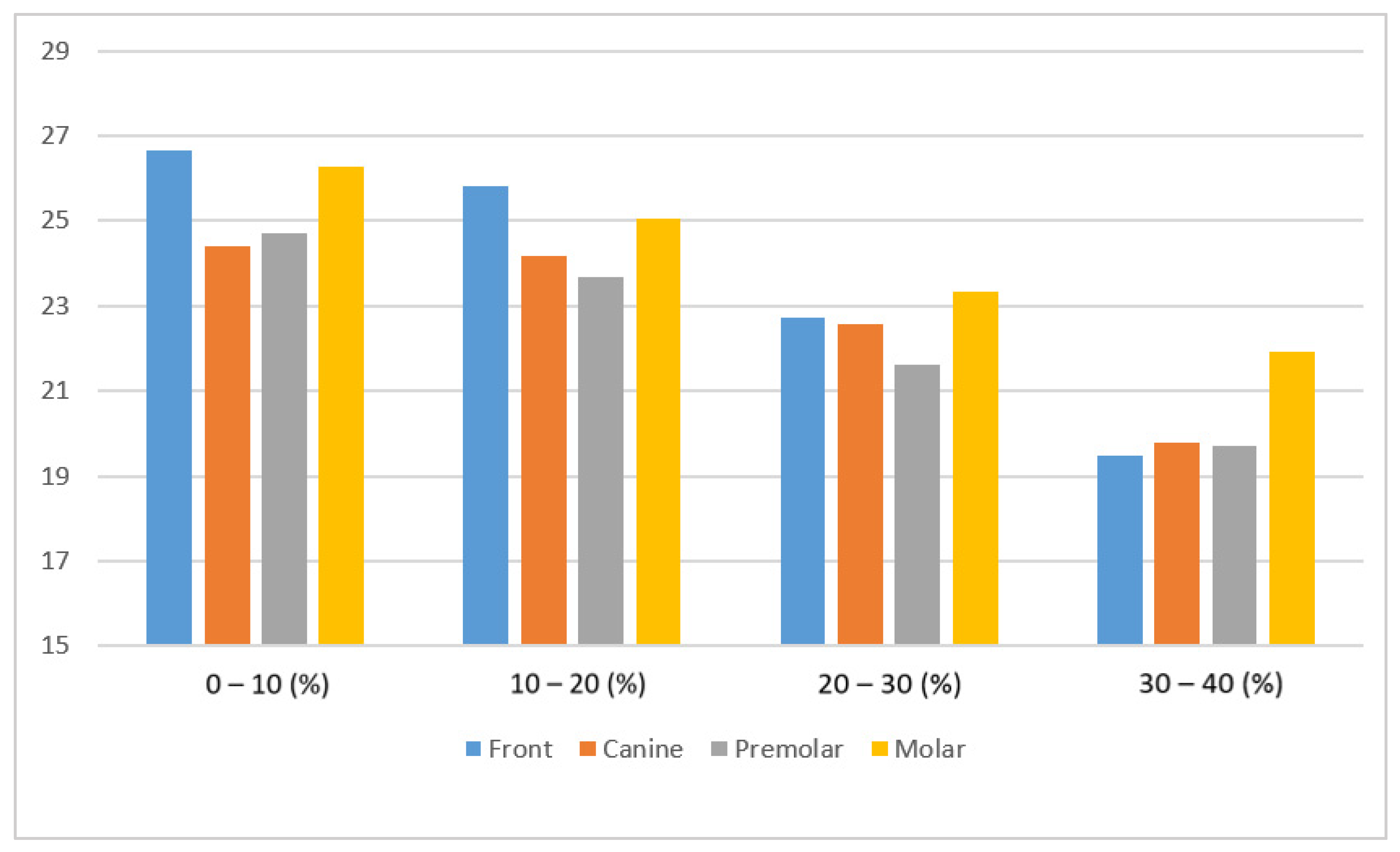
| Mask | Incisor | Canine | Premolar | Molar |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–10% | 0.921 | 0.918 | 0.911 | 0.923 |
| 10–20% | 0.915 | 0.911 | 0.906 | 0.913 |
| 20–30% | 0.885 | 0.883 | 0.879 | 0.894 |
| 30–40% | 0.819 | 0.822 | 0.839 | 0.859 |
| Mask | Incisor | Canine | Premolar | Molar |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–10% | 26.68 | 24.42 | 24.71 | 26.27 |
| 10–20% | 25.82 | 24.19 | 23.69 | 25.07 |
| 20–30% | 22.72 | 22.57 | 21.62 | 23.33 |
| 30–40% | 19.49 | 19.78 | 19.71 | 21.93 |
| Method | Mean Distance (mm) | p |
|---|---|---|
| Conventional | 0.031 ± 0.008 | 0.033 |
| Proposed | 0.027 ± 0.007 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, T.; Cho, Y.; Kim, D.; Chang, M.; Kim, Y.-J. Tooth Segmentation of 3D Scan Data Using Generative Adversarial Networks. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10020490
Kim T, Cho Y, Kim D, Chang M, Kim Y-J. Tooth Segmentation of 3D Scan Data Using Generative Adversarial Networks. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(2):490. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10020490
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Taeksoo, Youngmok Cho, Doojun Kim, Minho Chang, and Yoon-Ji Kim. 2020. "Tooth Segmentation of 3D Scan Data Using Generative Adversarial Networks" Applied Sciences 10, no. 2: 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10020490
APA StyleKim, T., Cho, Y., Kim, D., Chang, M., & Kim, Y.-J. (2020). Tooth Segmentation of 3D Scan Data Using Generative Adversarial Networks. Applied Sciences, 10(2), 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10020490






