Prediction of Solvatochromic Polarity Parameters for Aqueous Mixed-Solvent Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
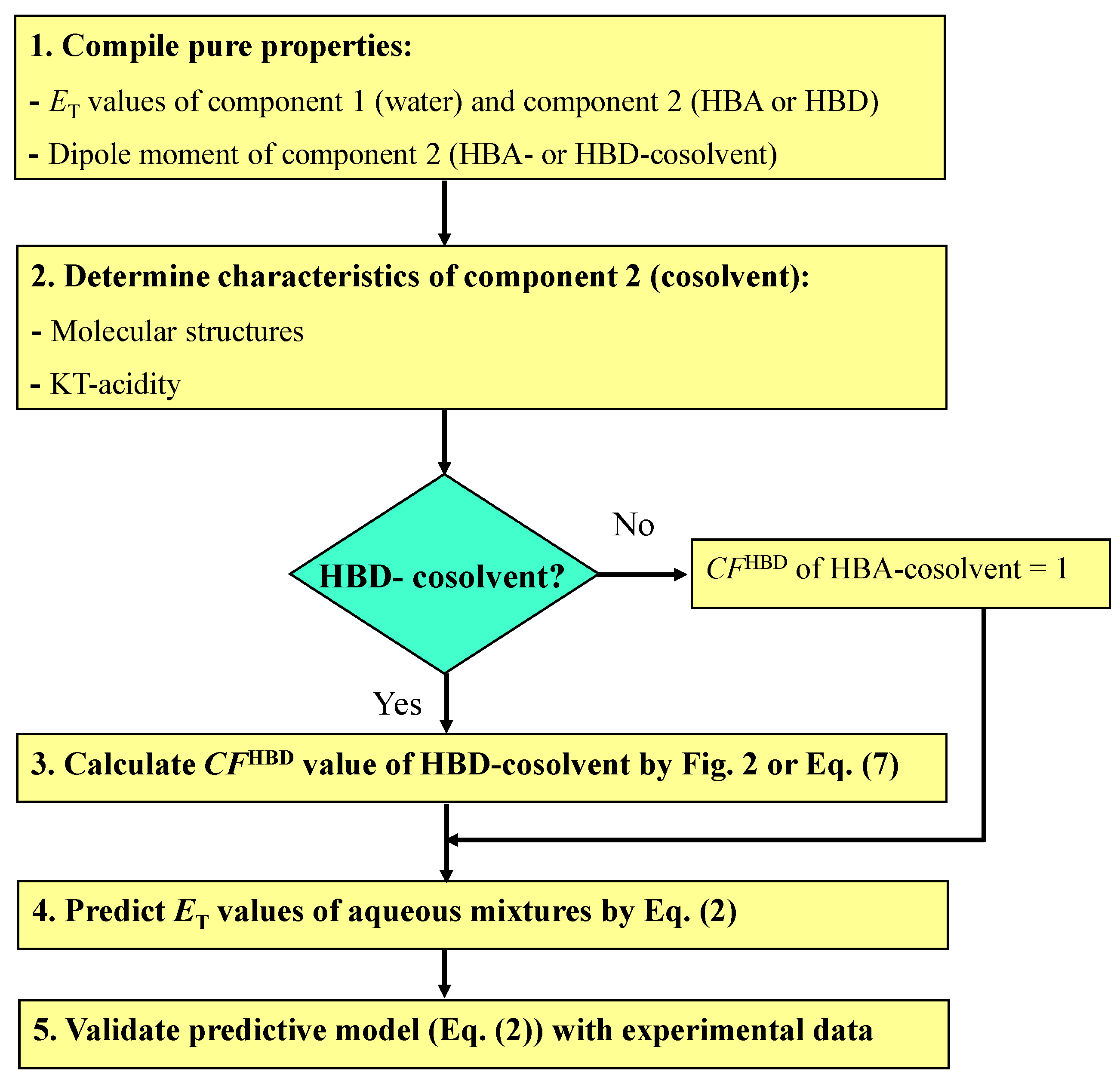
2. Models and Methods
2.1. Ideal Model
2.2. Predictive Model
2.3. Evaluation of the Frameworks
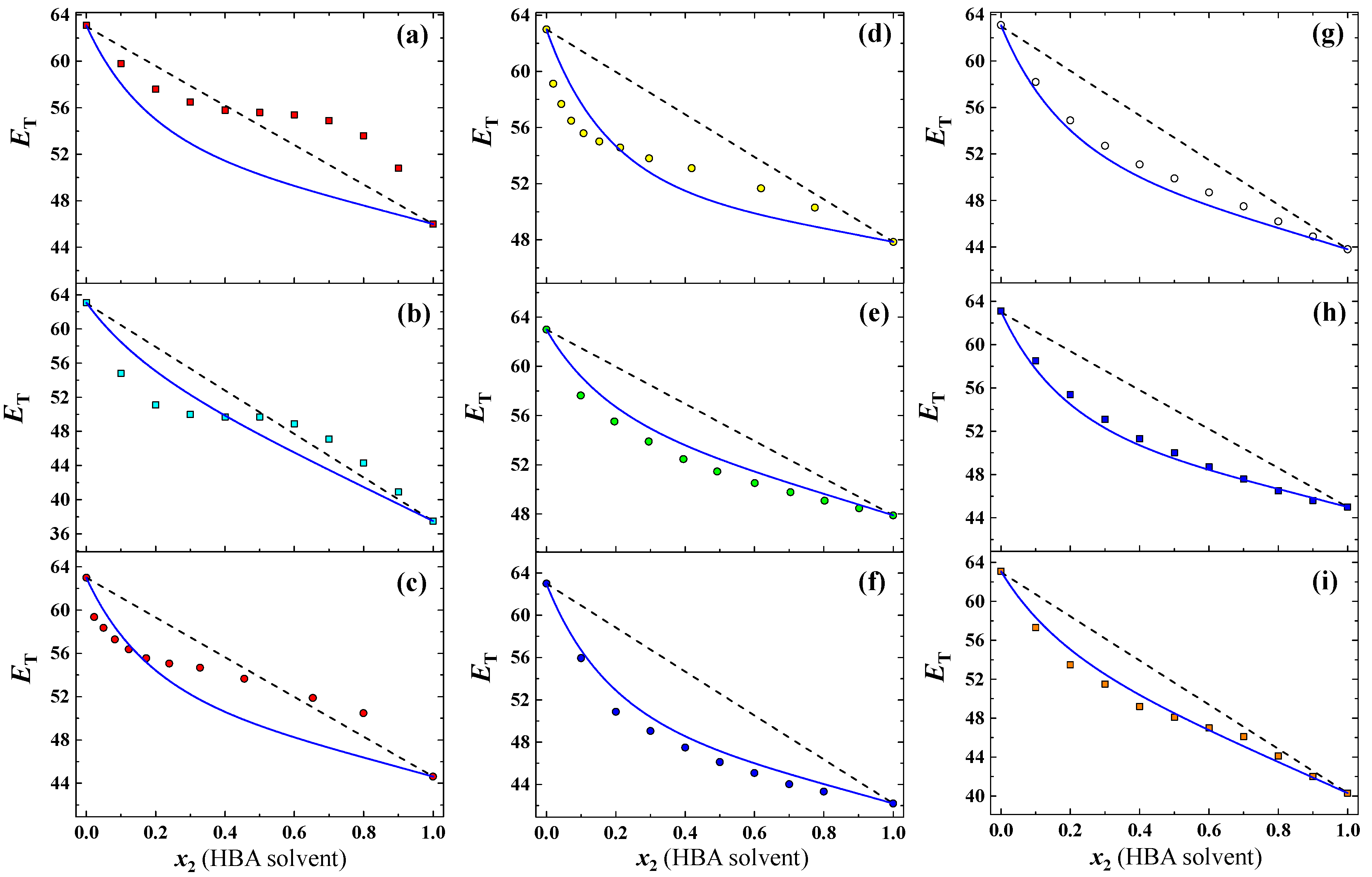
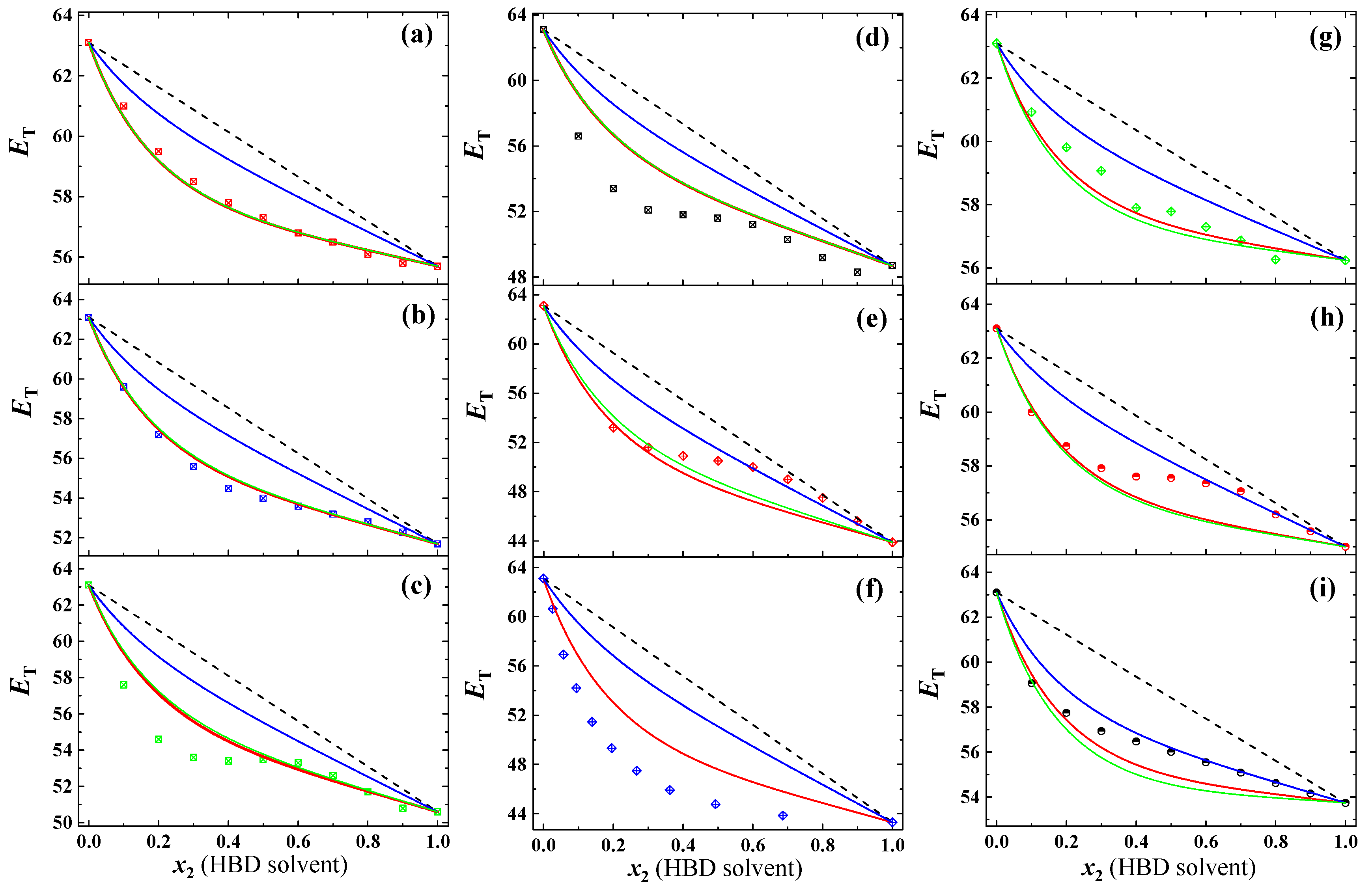
3. Results and Discussion
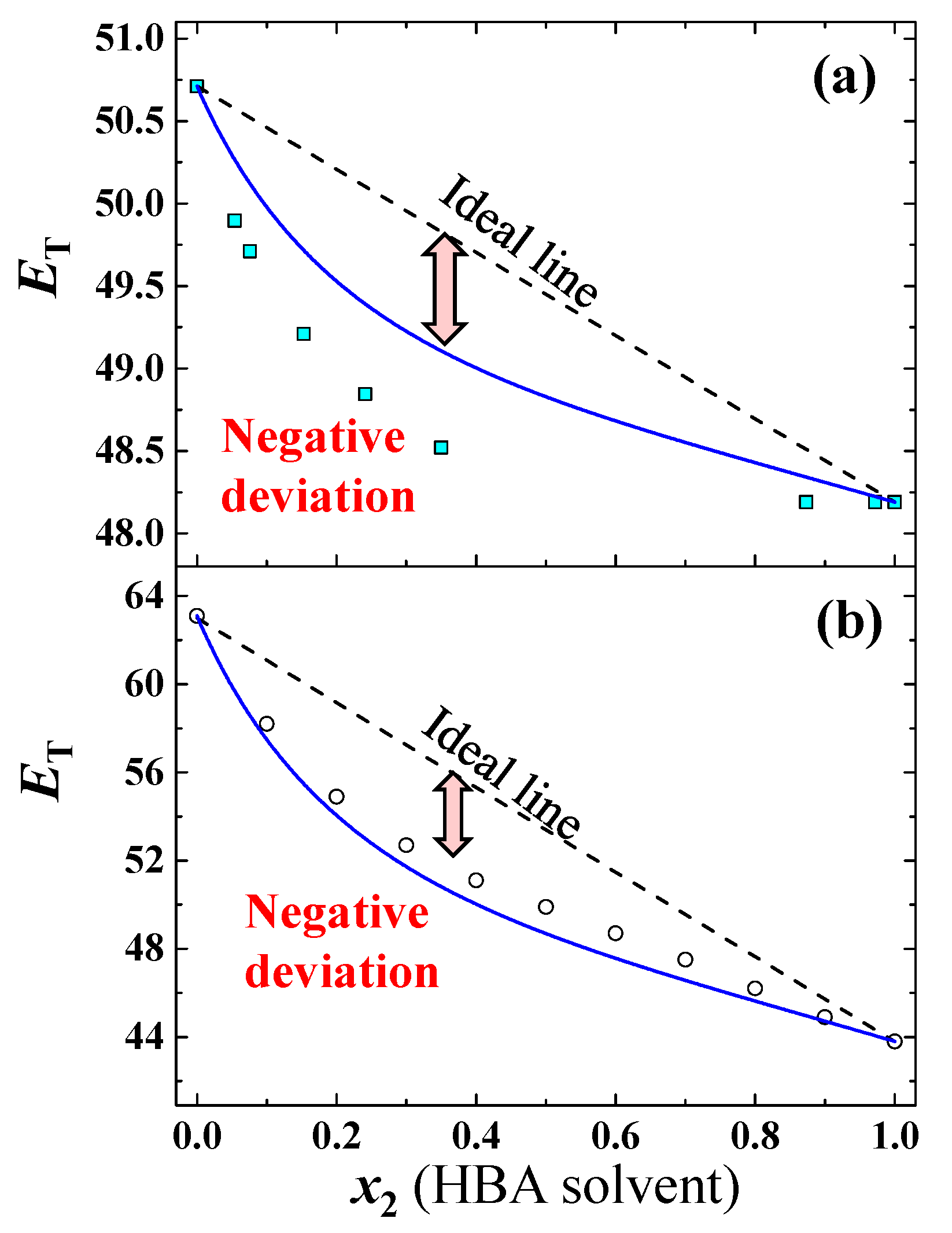
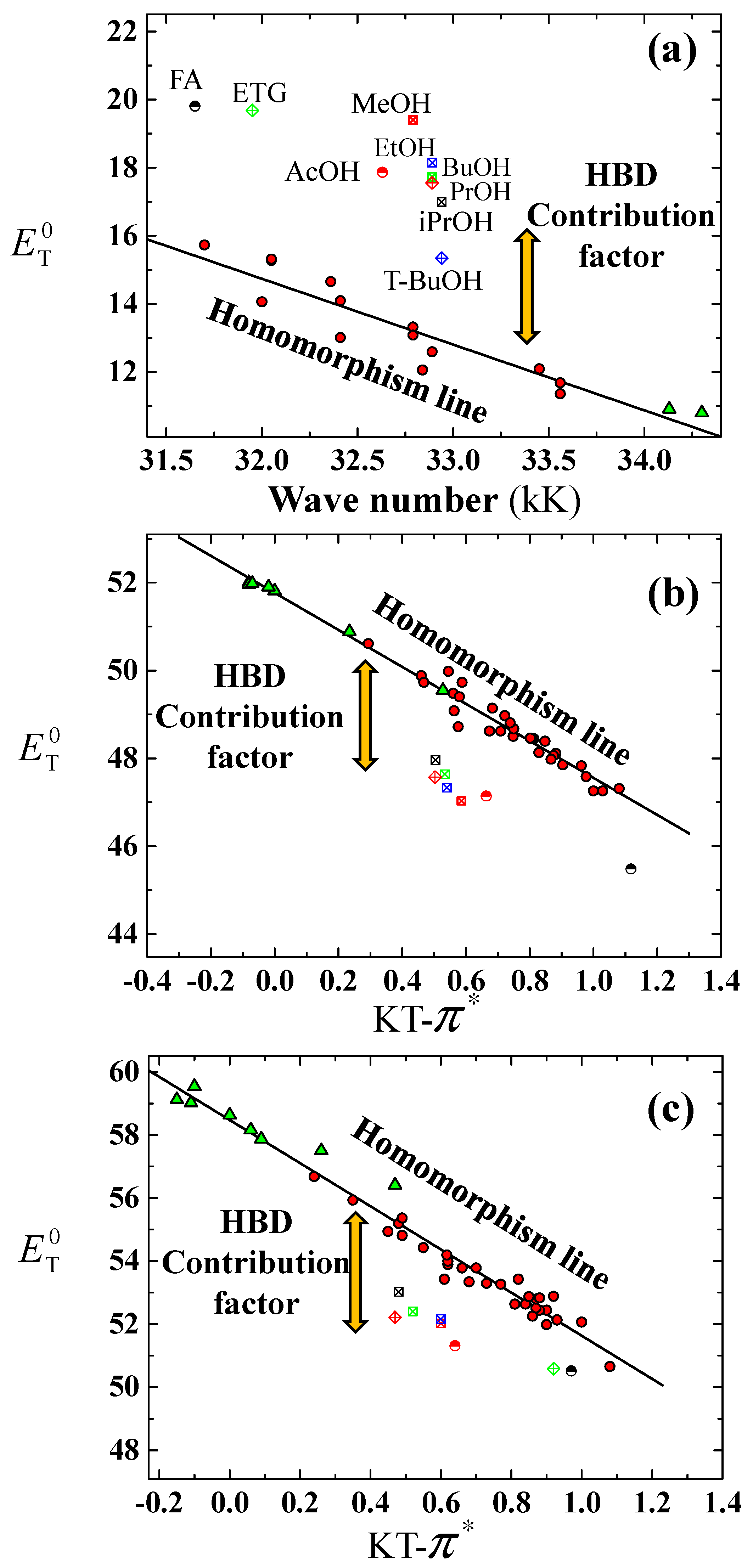
3.1. Prediction for Aqueous Mixtures of HBA Cosolvents
3.2. Prediction for Aqueous Mixtures of HBD Cosolvents
3.3. Evaluation of CFHBD Methods for Predictions
3.4. Limitation of the Predictive Model
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AcOH | acetic acid |
| ACN | acetonitrile |
| ARD | average relative deviation, according to Equation (8) |
| BuOH | 1-butanol |
| DMF | dimethylformamide |
| DMSO | dimethyl sulfoxide |
| ETG | ethylene glycol |
| EtOH | ethanol |
| FA | formamide |
| GBL | gamma butyrolactone |
| GVL | gamma valerolactone |
| HBA | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| HBD | hydrogen bond donor |
| iPrOH | 2-propanol |
| Ind | indicator |
| KT | Kamlet–Taft solvatochromic parameter |
| MeOH | methanol |
| Nile red | 9-diethylamino-5-benzo(a) phenoxazinone indicator |
| NMP | N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone |
| Phenol blue | N, N-dimethylindoaniline indicator |
| PrOH | 1-propanol |
| PYR | 2-pyrrolidinone |
| Reichardt | 2,6-diphenyl-4-(2,4,6-triphenyl-1-pyridinio) phenolate indicator |
| T-BuOH | tert-butyl alcohol |
| THF | tetrahydrofuran |
| Latin symbols | |
| CFHBD | HBD contribution factor, according to Equation (6) |
| x | mole fraction of solvent i |
| Greek symbols | |
| βH | Hunter basicity |
| α | Kamlet–Taft acidity |
| ET | electronic transition of solvent polarity |
| non-HBD bonding electronic transition, according to Equation (6) | |
| relative normalized electronic transition energy, according to Equation (3) | |
| normalized electronic transition energy, according to Equation (4) | |
| ET (ideal) | ideal electronic transition energy, according to Equation (1) |
| calculated electronic transition energy, according to Equation (8) | |
| µ | gas-phase dipole moments |
| π* | Kamlet–Taft dipolarity/polarizability |
| Superscript | |
| 0 | pure property |
| N | normalized property |
| Subscript | |
| 1 | water, solvent type 1 |
| 2 | HBA or HBD, solvent type 2 |
| mix | mixture property |
References
- Guo, H.; Duereh, A.; Su, Y.; Hensen, E.J.M.; Qi, X.; Smith, R.L. Mechanistic role of protonated polar additives in ethanol for selective transformation of biomass-related compounds. Appl. Catal. B 2020, 264, 118509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghatta, A.A.; Wilton-Ely, J.D.E.T.; Hallett, J.P. Rapid, High-Yield Fructose Dehydration to 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural in Mixtures of Water and the Noncoordinating Ionic Liquid [bmim][OTf]. ChemSusChem 2019, 12, 4452–4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingali, S.V.; Smith, M.D.; Liu, S.H.; Rawal, T.B.; Pu, Y.; Shah, R.; Evans, B.R.; Urban, V.S.; Davison, B.H.; Cai, C.M.; et al. Deconstruction of biomass enabled by local demixing of cosolvents at cellulose and lignin surfaces. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 107, 16776–16781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farajtabar, A.; Zhao, H. Equilibrium solubility of 7-amino-4-methylcoumarin in several aqueous co-solvent mixtures revisited: Transfer property, solute-solvent and solvent-solvent interactions and preferential solvation. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 320, 114407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Farajtabar, A.; Zhao, H. Solubility of 4-amino-2,6-dimethoxypyrimidine in aqueous co-solvent mixtures revisited: Solvent effect, transfer property and preferential solvation analysis. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 288, 111033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Farajtabar, A.; Wu, J.; Zhao, H. 5,7-Dibromo-8-hydroxyquinoline dissolved in binary aqueous co-solvent mixtures of isopropanol, N,N-dimethylformamide, 1,4-dioxane and N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone: Solubility modeling, solvent effect and preferential solvation. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2020, 148, 106138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccione, P.M.; Baumeister, J.; Salvesen, T.; Grosjean, C.; Flores, Y.; Groelly, E.; Murudi, V.; Shyadligeri, A.; Lobanova, O.; Lothschütz, C. Solvent Selection Methods and Tool. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2019, 23, 998–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, F.P.; Forier, B.; Bossaert, G.; Hoebers, C.; Farmer, T.J.; Hunt, A.J. A methodical selection process for the development of ketones and esters as bio-based replacements for traditional hydrocarbon solvents. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 4003–4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, S.; Byrne, F.; McElroy, C.R.; Sherwood, J.; Clark, J.H.; Hunt, A.J. Challenges in the development of bio-based solvents: A case study on methyl(2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl)methyl carbonate as an alternative aprotic solvent. Faraday Discuss. 2017, 202, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duereh, A.; Sato, Y.; Smith, R.L.; Inomata, H. Methodology for Replacing Dipolar Aprotic Solvents Used in API Processing with Safe Hydrogen-Bond Donor and Acceptor Solvent-Pair Mixtures. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2017, 21, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, B.; Yu, Y.; Wu, H. Solvent effect of gamma-valerolactone (GVL) on cellulose and biomass hydrolysis in hot-compressed GVL/water mixtures. Fuel 2018, 232, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katritzky, A.R.; Fara, D.C.; Yang, H.; Tämm, K.; Tamm, T.; Karelson, M. Quantitative Measures of Solvent Polarity. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 175–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, P.A.R.; El Seoud, O.A.; Machado, V.G.; de Jesus, J.C.; de Melo, C.E.A.; Buske, J.L.O.; Cardozo, A.P. Understanding Solvation: Comparison of Reichardt’s Solvatochromic Probe and Related Molecular “Core” Structures. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2019, 64, 2213–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichardt, C. Solvatochromic Dyes as Solvent Polarity Indicators. Chem. Rev. 1994, 94, 2319–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, Y. The use of chemical probes for the characterization of solvent mixtures. Part 2. Aqueous mixtures. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1994, 2, 1751–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roses, M.; Buhvestov, U.; Rafols, C.; Rived, F.; Bosch, E. Solute-solvent and solvent-solvent interactions in binary solvent mixtures. Part 6. A quantitative measurement of the enhancement of the water structure in 2-methylpropan-2-ol-water and propan-2-ol-water mixtures by solvatochromic indicators. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1997, 2, 1341–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duereh, A.; Sato, Y.; Smith, R.L.; Inomata, H. Correspondence between spectral-derived and viscosity-derived local composition in binary liquid mixtures having specific interactions with preferential solvation theory. JPC B 2018, 122, 10894–10906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duereh, A.; Guo, H.; Honma, T.; Hiraga, Y.; Sato, Y.; Lee Smith, R.; Inomata, H. Solvent polarity of cyclic ketone (cyclopentanone, cyclohexanone): Alcohol (methanol, ethanol) renewable mixed-solvent systems for applications in pharmaceutical and chemical processing. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 7331–7344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouyban, A.A.G.; Khoub Nasab Jafari, M.; Eugen Acree, W., Jr. Modeling the solvatochromic parameter (e) of mixed solvents with respect to solvent composition and temperature using the jouyban-acree model. Daru J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 14, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Duereh, A.; Inomata, H. Prediction of solvatochromic parameters of electronic transition energy for characterizing dipolarity/polarizability and hydrogen bonding donor interactions in binary solvent systems of liquid nonpolar-polar mixtures, CO2-expanded liquids and supercritical carbon dioxide with cosolvent. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 320, 114394. [Google Scholar]
- Duereh, A.; Sugimoto, Y.; Ota, M.; Sato, Y.; Inomata, H. Kamlet–Taft dipolarity/polarizability of binary mixtures of supercritical carbon dioxide with cosolvents: Measurement, prediction, and applications in separation processes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 12319–12330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duereh, A.; Guo, H.; Sato, Y.; Smith, R.L.; Inomata, H. Predictive framework for estimating dipolarity/polarizability of binary nonpolar–polar mixtures with relative normalized absorption wavelength and gas-phase dipole moment. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 18986–18996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duereh, A.; Sato, Y.; Smith, R.L.; Inomata, H. Analysis of the Cybotactic Region of Two Renewable Lactone–Water Mixed-Solvent Systems that Exhibit Synergistic Kamlet–Taft Basicity. JPC B 2016, 120, 4467–4481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, B.; Aparicio, S.; Alcalde, R.; Ruiz, R.; Dávila, M.J.; Leal, J.M. Characterization of Lactam-Containing Binary Solvents by Solvatochromic Indicators. JPC B 2004, 108, 3024–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindreu, R.; Moyá, M.; Sánchez Burgos, F.; González, A.G. Kamlet-Taft solvatochromic parameters of aqueous binary mixtures oftert-butyl alcohol and ethyleneglycol. J. Solut. Chem. 1996, 25, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellein, B.R.; Aki, S.N.V.K.; Ladewski, R.L.; Brennecke, J.F. Solvatochromic studies of ionic liquid/organic mixtures. JPC B 2007, 111, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taft, R.W.; Kamlet, M.J. The solvatochromic comparison method. 2. The alpha-scale of solvent hydrogen-bond donor (HBD) acidities. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1976, 98, 2886–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamlet, M.J.; Abboud, J.L.M.; Abraham, M.H.; Taft, R.W. Linear solvation energy relationships. 23. A comprehensive collection of the solvatochromic parameters, .pi.*, .alpha., and .beta., and some methods for simplifying the generalized solvatochromic equation. J. Org. Chem. 1983, 48, 2877–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaws, C. Chemical Properties Handbook: Physical, Thermodynamics, Environmental Transport, Safety and Health Related Properties for Organic and Inorganic Chemicals; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, C.A. Quantifying intermolecular interactions: Guidelines for the molecular recognition toolbox. Angew. Chem. 2004, 43, 5310–5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duereh, A.; Smith, R.L. Strategies for using hydrogen-bond donor/acceptor solvent pairs in developing green chemical processes with supercritical fluids. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2018, 141, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Liu, M.; Huang, K.; Walker, T.W.; Maravelias, C.T.; Dumesic, J.A.; Huber, G.W. Production of levoglucosenone and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural from cellulose in polar aprotic solvent-water mixtures. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 3642–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migron, Y.; Marcus, Y. Polarity and hydrogen-bonding ability of some binary aqueous-organic mixtures. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1991, 87, 1339–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, Y.; Migron, Y. Polarity, hydrogen bonding, and structure of mixtures of water and cyanomethane. JPC 1991, 95, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duereh, A.; Sato, Y.; Smith, R.L.; Inomata, H.; Pichierri, F. Does Synergism in Microscopic Polarity Correlate with Extrema in Macroscopic Properties for Aqueous Mixtures of Dipolar Aprotic Solvents? JPC B 2017, 121, 6033–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
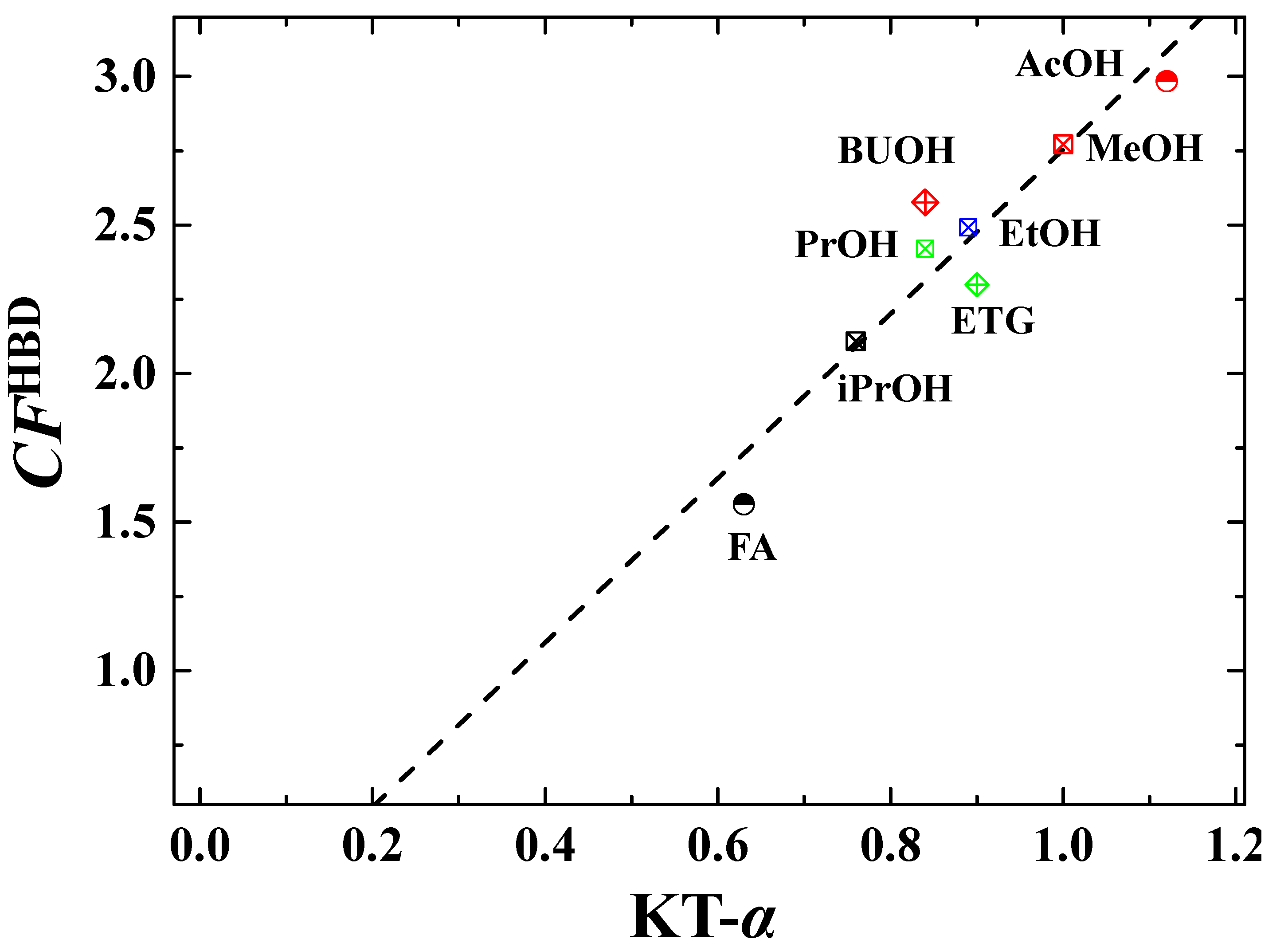

| Entry | HBD Solvents | KT-α | Actual CFHBD (-) b | Calculated CFHBD (-) c | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Symbol) | (Abbreviation) | (-) | Ind. 1 | Ind. 2 | Ind. 3 | Avg | (Equation (7)) |
1 (  ) ) | Methanol (MeOH) | 1.00 | 3.65 | 2.32 | 2.34 | 2.77 | 2.75 |
2 (  ) ) | Ethanol (EtOH) | 0.89 | 3.05 | 2.21 | 2.21 | 2.49 | 2.45 |
3 (  ) ) | 1-Propanol (PrOH) | 0.84 | 2.79 | 1.96 | 2.51 | 2.42 | 2.31 |
4 (  ) ) | 2-Propanol (iPrOH) | 0.76 | 2.44 | 1.72 | 2.17 | 2.11 | 2.09 |
5 (  ) ) | 1-Butanol (BuOH) | 0.84 | 2.65 | 2.04 | 3.04 | 2.58 | 2.31 |
6 (  ) ) | Tert-Butanol (T-BuOH) | - | 2.65 | - | - | 2.65 | - |
7 (  ) ) | Ethylene glycol (ETG) | 0.90 | 3.01 | - | 1.59 | 2.30 | 2.48 |
8 (  ) ) | Acetic acid (AcOH) | 1.12 | 4.34 | 1.83 | 2.78 | 2.98 | 3.09 |
9 (  ) ) | Formamide (FA) | 0.63 | 2.09 | 1.27 | 1.32 | 1.56 | 1.73 |
| Entry | Component 2 | µ2 | CFHBD | βH | ARD (%) | N | Ref. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Symbol) | D | (-) | (-) | (1) | (2) | Predict | Ideal | |||
| Water (1)—HBA cosolvent (2) | ||||||||||
| 1 (■) | ACN | 3.92 | 1.00 | 4.7 | 63.10 | 46.00 | 6.64 | 3.36 | 11 | [15] |
| 2 (■) | THF | 1.63 | 1.00 | 5.3 | 63.10 | 37.50 | 4.36 | 4.97 | 11 | [15] |
| 3 (●) | GBL | 3.82 | 1.00 | 5.3 | 63.00 | 44.62 | 3.45 | 4.42 | 12 | [23] |
| 4 (●) | GVL | 5.30 | 1.00 | 5.3 | 63.00 | 47.85 | 2.61 | 6.27 | 12 | [23] |
| 5 (●) | PYR | 3.10 | 1.00 | 8.3 | 63.00 | 47.90 | 1.49 | 5.24 | 11 | [24] |
| 6 (●) | NMP | 4.09 | 1.00 | 8.3 | 63.00 | 42.20 | 1.85 | 9.85 | 10 | [24] |
| 7 (●) | DMF | 3.86 | 1.00 | 8.3 | 63.10 | 43.80 | 1.37 | 4.77 | 11 | [15] |
| 8 (■) | DMSO | 3.96 | 1.00 | 8.9 | 63.10 | 45.00 | 0.75 | 5.29 | 11 | [15] |
| 9 (■) | Pyridine | 2.19 | 1.00 | 7.0 | 63.10 | 40.30 | 1.29 | 4.77 | 11 | [15] |
| Overall (aqueous HBA mixtures) | 2.65 | 5.44 | ||||||||
| Water (1)—HBD cosolvent (2) | ||||||||||
10 (  ) ) | MeOH | 1.70 | 2.77 | 5.8 | 63.10 | 55.70 | 0.23 | 2.40 | 11 | [15] |
| 2.75 | 0.23 | |||||||||
11 (  ) ) | EtOH | 1.69 | 2.49 | 5.8 | 63.10 | 51.70 | 0.34 | 3.92 | 11 | [15] |
| 2.45 | 0.38 | |||||||||
12 (  ) ) | PrOH | 1.66 | 2.42 | 5.8 | 63.10 | 50.60 | 1.42 | 5.14 | 11 | [15] |
| 2.31 | 1.53 | |||||||||
13 (  ) ) | iPrOH | 1.66 | 2.11 | 5.8 | 63.10 | 48.70 | 2.64 | 6.73 | 11 | [15] |
| 2.09 | 2.67 | |||||||||
14 (  ) ) | BuOH | 1.66 | 2.58 | 5.8 | 63.10 | 43.90 | 2.58 | 4.28 | 10 | [15] |
| 2.31 | 2.19 | |||||||||
15 (  ) ) | T-BuOH | 1.67 | 2.65 | 5.8 | 63.10 | 43.30 | 4.67 | 12.54 | 11 | [25] |
16 (  ) ) | ETG | 2.31 | 2.30 | - | 63.10 | 56.24 | 0.50 | 2.44 | 10 | [15] |
| 2.48 | 0.69 | |||||||||
17 (  ) ) | AcOH | 1.74 | 2.98 | 5.3 | 63.10 | 55.00 | 1.03 | 2.10 | 11 | [15] |
| 3.09 | 1.12 | |||||||||
18 (  ) ) | FA | 3.73 | 1.56 | 5.8 | 63.10 | 53.74 | 0.97 | 3.22 | 11 | [15] |
| 1.73 | 1.32 | |||||||||
| Overall (aqueous HBD mixtures) | 1.60 | 4.75 | ||||||||
| Overall (both HBA and HBD mixtures) | 2.12 | 5.10 | 197 | |||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duereh, A.; Anantpinijwatna, A.; Latcharote, P. Prediction of Solvatochromic Polarity Parameters for Aqueous Mixed-Solvent Systems. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8480. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10238480
Duereh A, Anantpinijwatna A, Latcharote P. Prediction of Solvatochromic Polarity Parameters for Aqueous Mixed-Solvent Systems. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(23):8480. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10238480
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuereh, Alif, Amata Anantpinijwatna, and Panon Latcharote. 2020. "Prediction of Solvatochromic Polarity Parameters for Aqueous Mixed-Solvent Systems" Applied Sciences 10, no. 23: 8480. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10238480
APA StyleDuereh, A., Anantpinijwatna, A., & Latcharote, P. (2020). Prediction of Solvatochromic Polarity Parameters for Aqueous Mixed-Solvent Systems. Applied Sciences, 10(23), 8480. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10238480





