Development of an NT-ProBNP Assay Reagent Based on High Specific Activity Alkaline Phosphatase CmAP and an Improved Coupling Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. CmAP Cloning, Expression and Purification
2.4. Enzyme Activity Characterisation
2.5. ALP Labelling of the NT-proBNP Detection Antibody
2.6. Immunomagnetic Particles Labelling of the NT-proBNP Capture Antibody
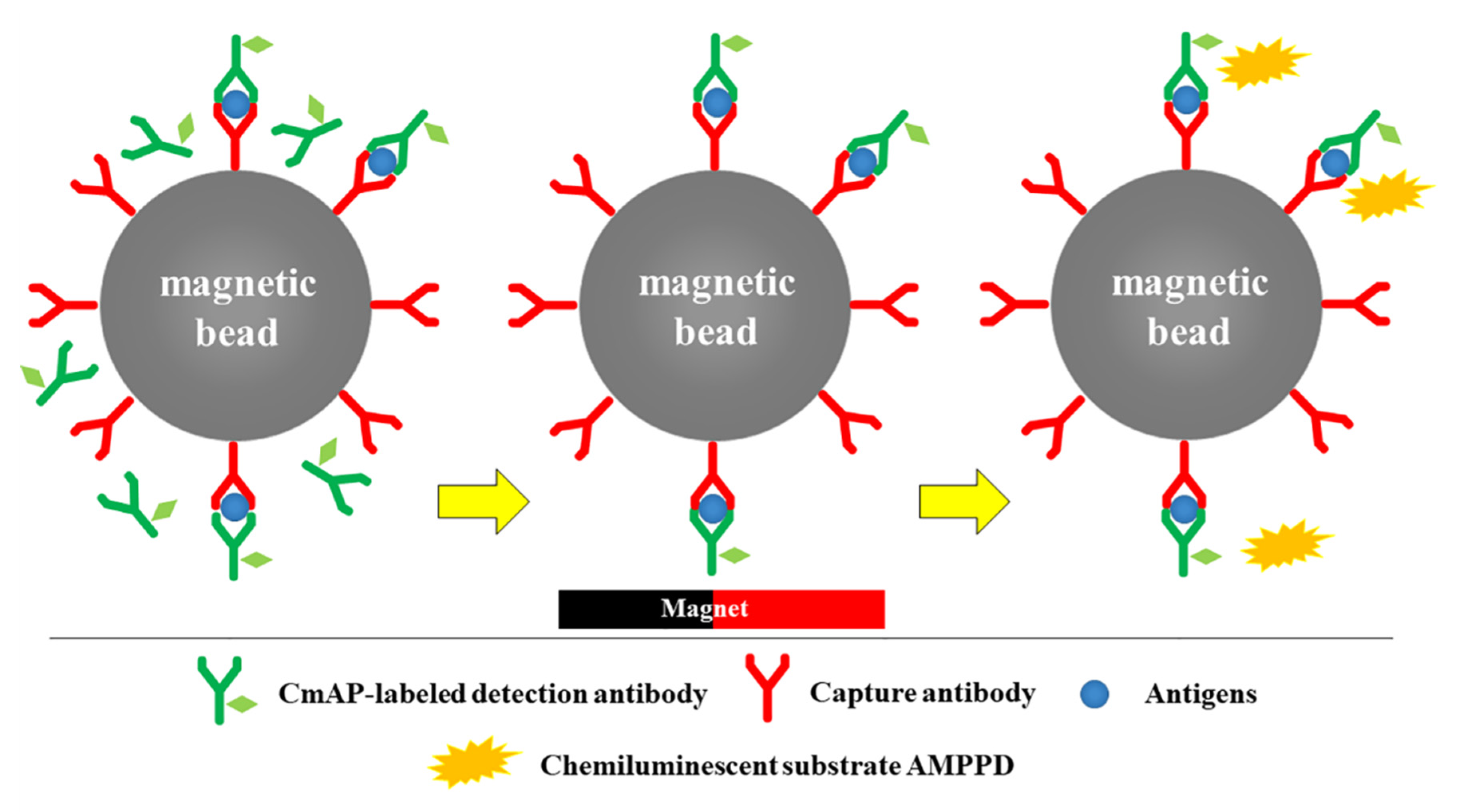
2.7. CLEIA Method
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Purified Recombinant CmAP
3.2. Influence of Immunoreagents
3.3. Standard Curve and Sensitivity
3.4. Recovery and Precision
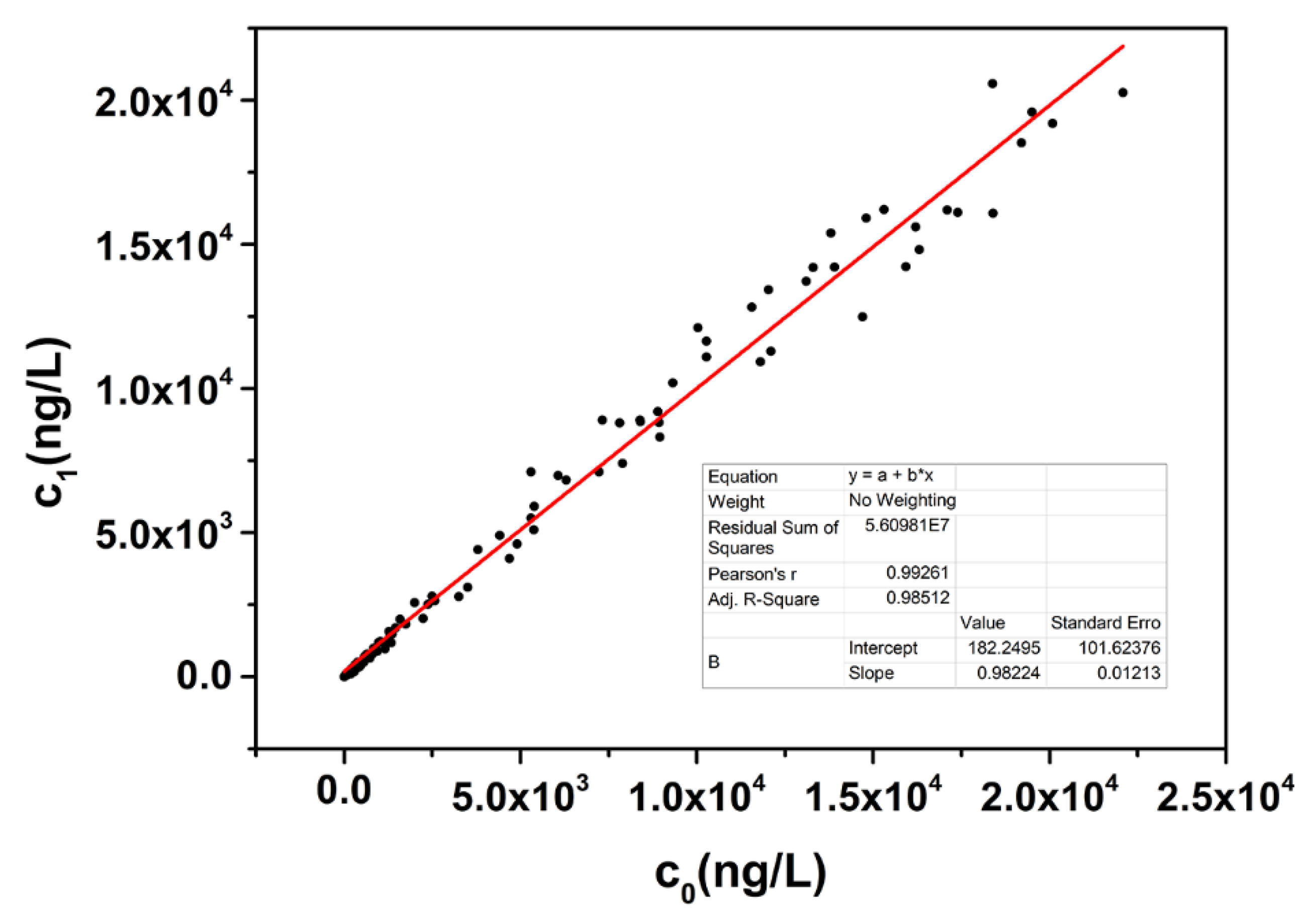
3.5. Linearity-Dilution Effect
3.6. Specificity and Interferences
3.7. Comparison with the Roche NT-proBNP Diagnostic System
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, R.; Wang, C.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Yue, Z.; Liu, G. Magnetic-particle-based, ultrasensitive chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay for free prostate-specific antigen. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 801, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Lin, J.-M.; Wang, X.; Xin, T.-B.; Liang, S.-X.; Li, Z.-J.; Hu, G.-M. Magnetic particle-based chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay for free thyroxine in human serum. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2009, 50, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.-L.; Ren, H.-L.; Li, Y.-S.; Hu, P.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Z.-S.; Yan, D.-M.; Hui, Q.; Liu, D.; Lin, C.; et al. A magnetic particles-based chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay for rapid detection of ovalbumin. Anal. Biochem. 2014, 459, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hai, Z.; Li, J.; Wu, J.; Xu, J.; Liang, G. Alkaline Phosphatase-Triggered Simultaneous Hydrogelation and Chemiluminescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 1041–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azam, G.; Shibata, T.; Kabashima, T.; El-Mahdy, A.F.M. Alkaline phosphatase-labeled macromolecular probe for sensitive chemiluminescence detection of proteins on a solid-phase membrane. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 401, 1211–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Wu, Y.; Yu, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Qu, L.; Harrington, P.D.B. A competitive chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay for rapid and sensitive determination of enrofloxacin. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2012, 93, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Yang, M.; Yu, D.; Yu, C. Pyrophosphate as substrate for alkaline phosphatase activity: A convenient flow-injection chemiluminescence assay. Lumin 2017, 32, 1150–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plisova, E.Y.; Balabanova, L.A.; Ivanova, E.P.; Kozhemyako, V.B.; Mikhailov, V.V.; Agafonova, E.V.; Rasskazov, V.A. A Highly Active Alkaline Phosphatase from the Marine Bacterium Cobetia. Mar. Biotechnol. 2005, 7, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasu, E.; Ichiyanagi, A.; Gomi, K. Cloning and expression of a highly active recombinant alkaline phosphatase from psychrotrophic Cobetia marina. Biotechnol. Lett. 2011, 34, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, H.-H.; Yeh, C.-W.; Hsu, C.F.; Hsu, L.; Chi, S. Multiscale Entropy Analysis with Low-Dimensional Exhaustive Search for Detecting Heart Failure. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hill, S.A.; Booth, R.A.; Santaguida, P.L.; Don-Wauchope, A.; Brown, J.A.; Oremus, M.; Ali, U.; Bustamam, A.; Sohel, N.; Mckelvie, R.; et al. Use of BNP and NT-proBNP for the diagnosis of heart failure in the emergency department: A systematic review of the evidence. Heart Fail. Rev. 2014, 19, 421–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streng, K.W.; Ter Maaten, J.M.; Cleland, J.G.; O’Connor, C.M.; Davison, B.A.; Metra, M.; Givertz, M.M.; Teerlink, J.R.; Ponikowski, P.; Bloomfield, D.M.; et al. Associations of Body Mass Index with Laboratory and Biomarkers in Patients with Acute Heart Failure. Circ. Hear. Fail. 2017, 10, e003350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mueller, T.; Gegenhuber, A.; Poelz, W.; Haltmayer, M. Comparison of the Biomedica NT-proBNP Enzyme Immunoassay and the Roche NT-proBNP Chemiluminescence Immunoassay: Implications for the Prediction of Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Structural Heart Disease. Clin. Chem. 2003, 49, 976–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mueller, T.; Gegenhuber, A.; Poelz, W.; Haltmayer, M. Diagnostic accuracy of B type natriuretic peptide and amino terminal proBNP in the emergency diagnosis of heart failure. Heart 2005, 91, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gogia, S.; Ho, J. Biomarkers: Heart Failure. Encycl. Cardiovasc. Res. Med. 2018, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnsworth, C.W.; Bailey, A.L.; Jaffe, A.S.; Scott, M.G. Diagnostic concordance between NT-proBNP and BNP for suspected heart failure. Clin. Biochem. 2018, 59, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, T.I.; Chen, H.H.; Kao, J.T. Comparison of Abbott AxSYM and Roche Elecsys 2010 for measurement of BNP and NT-proBNP. Clin. Chim. Acta 2006, 369, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A.; Gurbuz, Y.; Niazi, J.H. Biosensors for cardiac biomarkers detection: A review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 171–172, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, X.; Meng, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xi, R. Chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay using magnetic nanoparticles for detection of neuron specific enolase in human serum. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 722, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.T.; Wang, H.J.; Xiong, C.Y.; Chai, Y.Q.; Yuan, R. An ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescence immunosensor for NT-proBNP based on self-catalyzed luminescence emitter coupled with PdCu@carbon nanohorn hybrid. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, M.; Bieniarz, C. Fc Site-Specific Labeling of Immunoglobulins with Calf Intestinal Alkaline Phosphatase. Bioconjugate Chem. 1994, 5, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wan, X.; Lu, S.; Zhang, L.; Yu, S.; Lu, X. Evaluation of a magnetic particles-based chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay for Golgi protein 73 in human serum. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 445, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Lin, J.-M.; Ying, X. Evaluation of carbohydrate antigen 50 in human serum using magnetic particle-based chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 598, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Q.-Y.; Li, Z.-J.; Ying, X.-T.; Lin, J.-M. Development of high-performance magnetic chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay for α-fetoprotein (AFP) in human serum. Clin. Chim. Acta 2008, 393, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Li, H.; Hu, G.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Lin, J.-M. Development of a rapid and sensitive magnetic chemiluminescent enzyme immunoassay for detection of luteinizing hormone in human serum. Clin. Biochem. 2009, 42, 1461–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Zhao, G.; Li, X.; Miao, J.; Fang, J.; Wei, Q.; Cao, W. Electrochemiluminescence immunoassay for the N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide based on resonance energy transfer between a self-enhanced luminophore composed of silver nanocubes on gold nanoparticles and a metal-organic framework of type MIL-125. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Method | Total Activity (U) | Total Protein (mg) | Specific Activity (U/mg) | Yield (%) | Purification (fold) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude extract | 61,300 | 472 | 130 | 100 | 1 |
| High Q | 44,180 | 49 | 902 | 72 | 7 |
| Phenyl HP | 33,800 | 5.2 | 6500 | 55 | 50 |
| SephacrylTM S-300 | 31,520 | 2.4 | 13,133 | 51 | 101 |
| Antigens | Tested Concentration (ng/mL) | NT-proBNP Concentration Determined (ng/L) | CR (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| cTn complex | 100 | NA | 0 |
| CK-MB | 100 | NA | 0 |
| Myoglobin | 500 | NA | 0 |
| BNP | 100 | 8.8 | 0.0088 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.-C.; He, X.; Qiao, S.-P.; Liu, Z.-N.; Gao, Y.-Z. Development of an NT-ProBNP Assay Reagent Based on High Specific Activity Alkaline Phosphatase CmAP and an Improved Coupling Method. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8682. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10238682
Li H-C, He X, Qiao S-P, Liu Z-N, Gao Y-Z. Development of an NT-ProBNP Assay Reagent Based on High Specific Activity Alkaline Phosphatase CmAP and an Improved Coupling Method. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(23):8682. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10238682
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hai-Chao, Xin He, Shan-Peng Qiao, Zhen-Ni Liu, and Yu-Zhou Gao. 2020. "Development of an NT-ProBNP Assay Reagent Based on High Specific Activity Alkaline Phosphatase CmAP and an Improved Coupling Method" Applied Sciences 10, no. 23: 8682. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10238682
APA StyleLi, H.-C., He, X., Qiao, S.-P., Liu, Z.-N., & Gao, Y.-Z. (2020). Development of an NT-ProBNP Assay Reagent Based on High Specific Activity Alkaline Phosphatase CmAP and an Improved Coupling Method. Applied Sciences, 10(23), 8682. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10238682




