Abstract
The introduction of new ceramic materials for dental restorations is currently a reality; however, little information is available on their surface treatment for the bonding process. Furthermore, surface treatment with plasma on ceramic materials has been recently introduced, although not many studies are available. The aim of this study was to evaluate the surface properties of a leucite-reinforced feldspar ceramic (LIC) and resin matrix ceramic (RMC) after low-pressure plasma treatment. From each material, 48 discs were prepared and subject to surface treatment. The LIC group was treated by hydrofluoric acid (HF) (LIC-HF), plasma with oxygen (LIC-O2), and plasma with argon (LIC-Ar). The RMC group was treated by sandblasting with alumina (RMC-SB), plasma with oxygen (RMC-O2), and plasma with argon (RMC-Ar). The groups whose surfaces were not subjected to treatment were considered as the control group. Surface wettability and roughness was analyzed. The results showed significant differences among the treatments for both ceramics regarding wettability and roughness. Plasma treatments increased the wettability and had a very low effect on the roughness. Plasma treatments achieved similar values for both surface properties in each ceramic group with no differences between both treatments. Plasma treatment seems to be a promising alternative for ceramic surface treatments since it increased the surface energy of the ceramics analyzed and hardly affects the roughness. Further studies are necessary to evaluate the effect of plasma treatment on the bond strength of ceramics.
1. Introduction
Ceramic materials have been in continuous development throughout the 20th century and continue today, being the mainstay of esthetic dentistry [1]. Since ceramic restorations were introduced in dentistry, many changes in their composition have been made to improve their properties, and in recent years there are many products available [1,2]. Currently, the most common ceramic materials for clinical use are lithium disilicate due to its outstanding esthetics, and zirconia because of its excellent mechanical properties [3,4]. New products are being introduced, such as resin-matrix materials, in an attempt to obtain a material that simulates the modulus of elasticity of dentin and that would be easy to repair [1]. Their composition consists of an organic matrix highly filled with ceramic particles [1]. These materials have ceramic-like properties and combine the advantages of glass-ceramics and composite resin [5].
In addition, with the continuous research in new ceramic materials, the introduction of computer-aided design–computer-aided manufacturing (CAD-CAM) technology offers new insights into conventional technology, facilitating the fabrication of the restorations [6], and it has become a part of daily practice in dentistry [7]. In recent years, several developments have improved the CAD-CAM technology, especially concerning the precision in their marginal adaptation and shortening the manufacturing time [3,5,8,9]. Furthermore, with the use of CAD-CAM technology, there has been an increase in the materials to be used to fabricate the restorations, including glass-ceramic, zirconia ceramic, and resin matrix ceramic (RMC), among others [5,10,11].
Cementation is an important process for clinical success of ceramic restorations [12]. There is consensus regarding glass-ceramic restorations, which should be cemented with adhesive cements for reinforcement and support [13,14]. However, for polycrystalline ceramics, clinical studies reveal comparable survival rates with conventional or adhesive cementation [14,15], and for RMC, due to their recent introduction, there are few studies and there is a need of clinical protocols [1,5,11,16,17]. Resin bonding cementation requires the pretreatment of the surfaces to be adhered, both the tooth and the restoration, increasing the complexity compared to conventional cementation [14]. The surface of the ceramic material needs to be sufficiently rough during the bonding process to obtain the appropriate retention [5]. Several surface treatments have been proposed to improve the bonding of resin cements to ceramic, and the composition of the ceramic to be adhered is an important factor that must be taken into account [1,11,14]. The most frequent pretreatments methods used are acid etching, air abrasion, or a combination of them [10]. It is very important to select the type of pretreatment, concentration, exposure time, and cleaning method. Over exposure of the material, or improper use of the type of treatment, can cause microcracks in the material, which would cause a decrease in flexural strength [18]. Feldspathic ceramics and their derivatives, such as ceramics reinforced with synthetic crystals or ceramics infiltrated with resin, are materials suitable to be etched. The most commonly used method is hydrofluoric acid (HF) in concentrations of around 5–10%, and with exposure times of 20–60 s [19]. The HF acid interacts with the glassy parts of the ceramic, creating a porous surface and increasing the surface roughness. It provides microretention and increases the bond strength [4,7,14,20,21]. On the other hand, the pretreatment for polycrystalline ceramics, composites, and nanoceramic resins include sandblasting. They are usually sandblasted with aluminum oxide of 50 µm, between 1.5 bar if it has an organic matrix like composite, and 2 bar if it is a polycrystalline ceramic. Regarding the exposure time, the size and the distance to which the particles are applied in sandblasting, and their influence on the material, controversy exists [22,23]. RMC have been recently introduced, and little information exists on the surface treatment for bonding cementation [9]. Furthermore, their composition varies substantially [1], which makes the problem even more difficult. In addition, few manufacturers provide information on whether RMC should be etched or not [1].
Recently, plasma has been introduced in dentistry for surface treatment. It has been used as an alternative or additional procedure for adhesion enhancement [24,25]. Several materials have been investigated, including polymers, alloys, or ceramics, especially zirconia, to which bonding is more difficult to achieve [26,27,28]. Plasma enhances adhesion by producing carboxyl groups and the surface becomes hydrophilic with an improvement of wettability [26,28,29,30,31]. The interaction of plasma with surfaces is greatly affected by the type of gas used, the exposure time, and the type of material on which it is applied [26,31]. Depending on these factors, four effects can be described that can be created on the surfaces of the materials: cleaning, activation, etching, and coating [32].
Studies on surface treatment in new ceramic materials are scarce. Likewise, studies on the effect of plasma on the surface of restorative materials are also scarce. Therefore, the objective of the present study was to evaluate and compare the effect of two surface treatment by low-pressure plasma on the roughness and wettability of leucite-reinforced feldspar and resin matrix ceramics. The null hypothesis tested was that the surface treatment by plasma would not affect the surface of the materials tested.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
Two different CAD-CAM restorative materials, namely, leucite-reinforced feldspar ceramic (Initial LRF BLOCK; GC Corp. Tokyo, Japan) (LIC) and resin matrix ceramic (Cerasmart; GC Corp. Tokyo, Japan) (RMC), were tested in the present study. The brands, manufacturers, and chemical composition are displayed in Table 1. The CAD-CAM blocks (18 mm × 14 mm × 12 mm) were sectioned and forty-eight discs of each material were obtained (10 mm diameter x 1 mm height). The blocks were cut with a 0.4 mm diamond disc in a cutting machine (IsoMet Low Speed Saw; Buehler, Uzwil, Switzerland) and finished with a low-speed handpiece. Subsequently, the discs were polished using 600-grit silicon carbide paper (CarbiMet PSA 600; Buehler), ultrasonically cleaned in distilled water for 5 min, and stored in plastic boxes. The boxes were cleaned with isopropyl alcohol and introduced in 100% oxygen plasma in a 1-min cleaning cycle (to avoid the contamination of the surfaces to be treated).

Table 1.
Ceramic materials used in the study.
2.2. Specimens Treatments
The 48 specimens of each material were randomly divided into 4 groups (n = 12) according to the surface treatment performed. Each ceramic group was subjected to four surface treatments: control (no treatment); sandblasting for the LIC and etching with HF acid for the RMC group, as the manufacturers recommend; plasma activation by oxygen; and plasma etching by argon. Details of the groups and the surface treatments are described in Table 2. The materials and instrument used for the surface treatment are displayed in Table 3 and Figure 1. Prior to the surface treatment, specimens from all the groups were cleaned with distilled water in an ultrasonic device for 5 min.

Table 2.
Surface treatments groups.

Table 3.
Instrument and materials used for surface treatment.

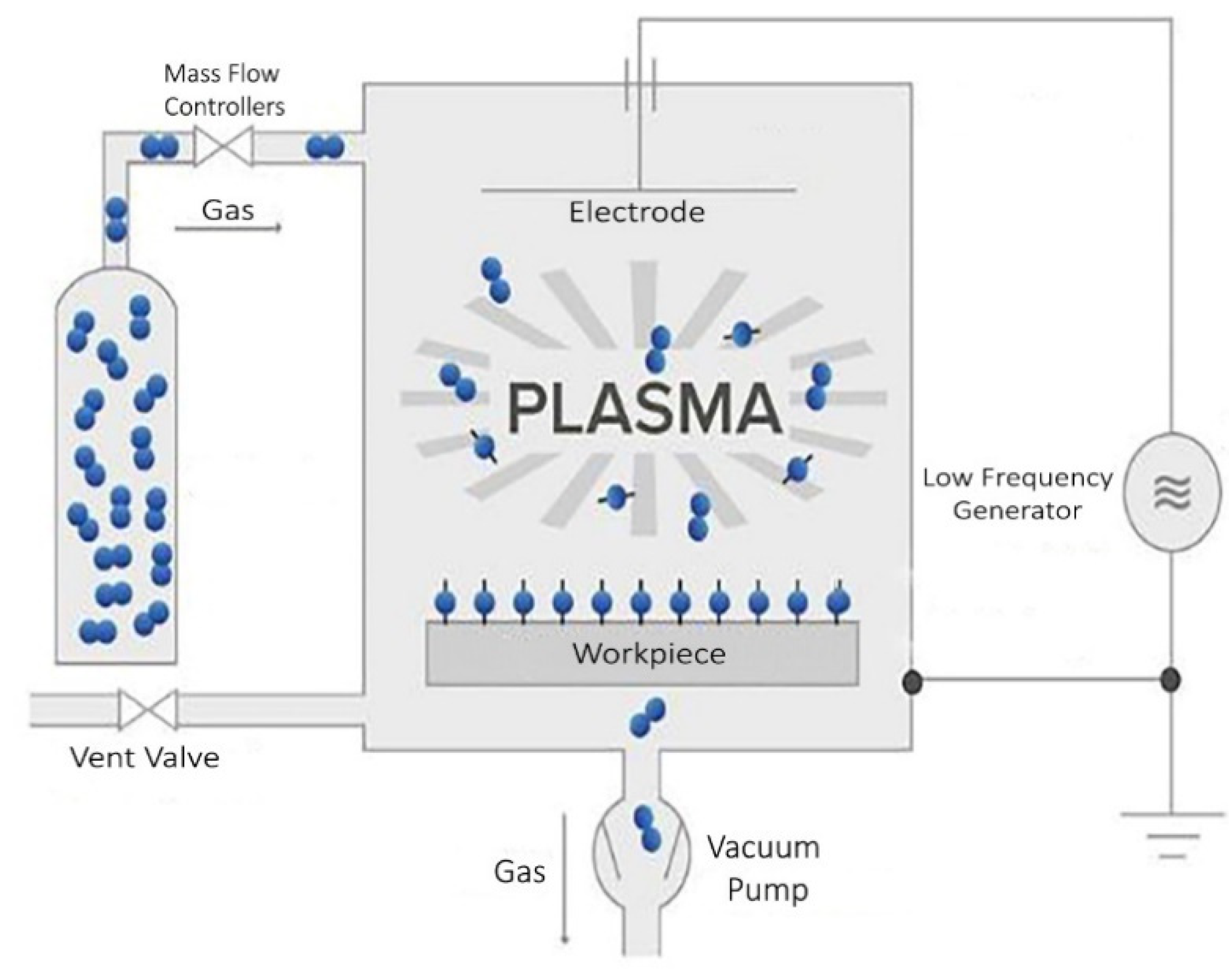
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the plasma system (PICO).
2.3. Surface Wettability
The water contact angle was measured by the sessile drop method [31,33,34,35,36,37], using the FTA 1000 B Class (First Ten Angstroms Inc., Portsmouth, VA, USA) machine connected to a video camera. A video with a drop of water (3 µL) was recorded, after 20 s of the drop deposition, at 3 different locations of the disc on each specimen. The video was later decomposed into 55 images analyzed using drop shade analysis FTA 32 2.0 software (First Ten Angstroms Inc.), and the average contact angle that formed the drop over the ceramic surface was obtained. The measurements were performed at a constant temperature (22 °C) and relative humidity (30 ± 10%).
2.4. Surface Roughness
The arithmetical median roughness (Ra) was measured by an atomic force microscope (Multimode AFM Nanoscope III; Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA), with a TESP-SS tip with a 2 nm radius of curvature. Measurements were performed in the center of the specimen, in the perimeter, and at a point between the center and perimeter, with an area of 25 µm2 (5 µm in length) on each disc. Thereafter, the images obtained were analyzed using Nanoscope Analysis 1.5 software (Bruker).
2.5. Data Processing
The mean values and standard deviations (SD) per group were calculated. The Kolmogorov–Smirnoff test was used to test the normality of data distribution. Since the normality of the variables was not confirmed, data were analyzed using non-parametric tests. The Kruskal–Wallis test, post hoc test for multiple comparisons, and Mann–Whitney U test were used for comparisons among the surface treatments. The statistical analysis was performed with SPSS 22.0 (SPSS Inc, Chicago, IL, USA) software at the Center for Data Processing of the Computing Service for Research Support of the Complutense University of Madrid. The level of significance was set at α = 0.05.
3. Results
In the LIC group in terms of wettability, the highest values were obtained by the LIC-HF group (15.51°). On the other hand, the control group showed the lowest roughness (104.68 nm). The Kruskal–Wallis test showed significant differences (p = 0.001) regarding wettability and roughness among the different surface treatments. The differences were observed among the different surface treatments, except for the LIC-C and LIC-O2 groups for wettability, and the LIC-Ar and LIC-O2 groups for roughness. The results are shown in Table 4, and Figure 2 and Figure 3.

Table 4.
Mean and standard deviation (SD) values of wettability (degree) and roughness (Ra, nm) in the leucite-reinforced feldspar ceramic (LIC) group (C: control; HF: hydrofluoric acid; O2: oxygen; Ar: argon).
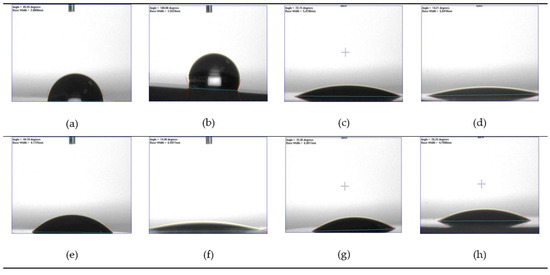
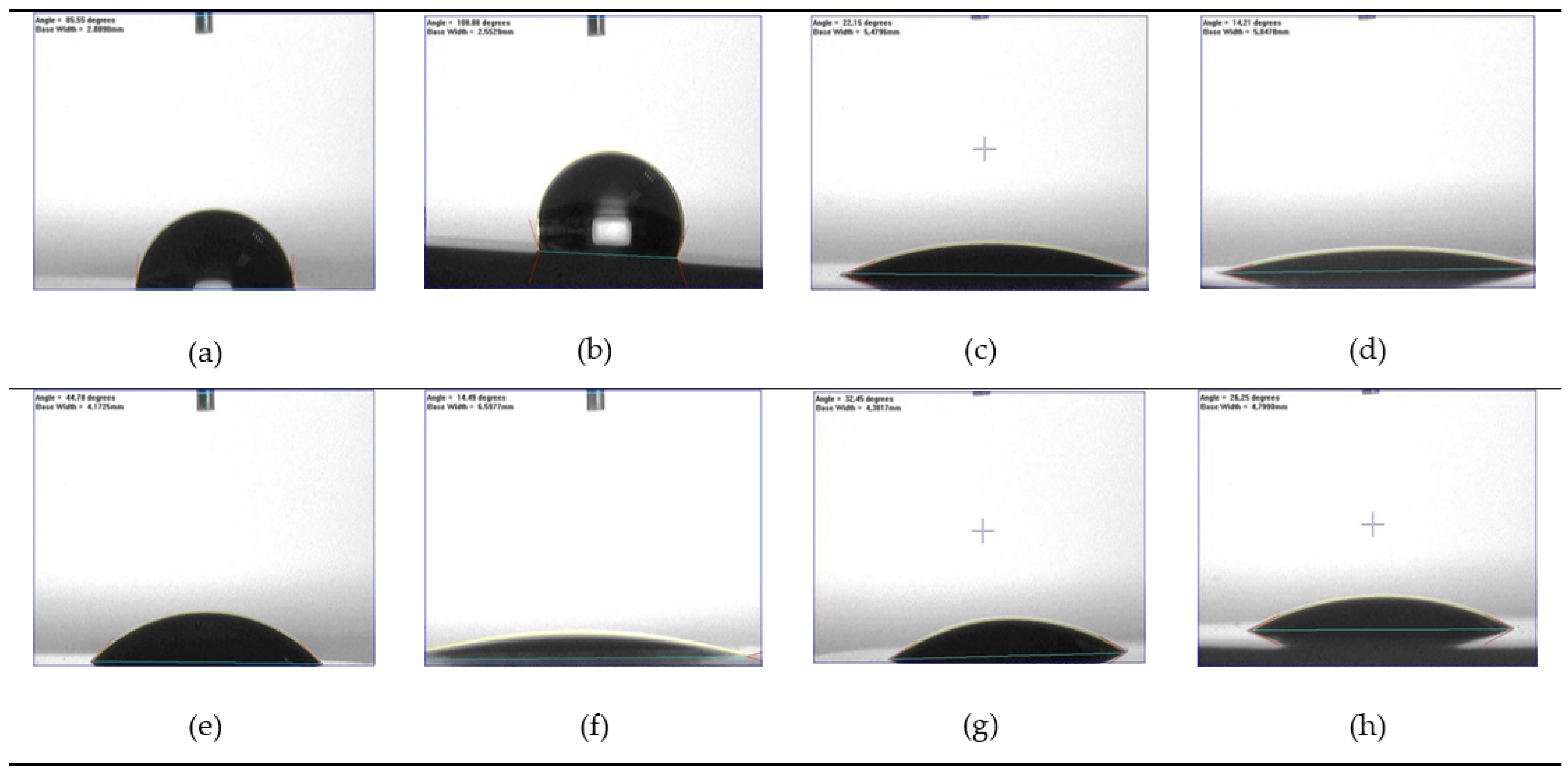
Figure 2.
Water drop images on the surface of the representative specimens of each group: (a) RMC-C; (b) RMC-SB; (c) RMC-O2; (d) RMC-Ar; (e) LIC-C; (f) LIC-HF; (g) LIC-O2; (h) LIC-Ar. RMC: resin matrix ceramic; SB; sandblasting.
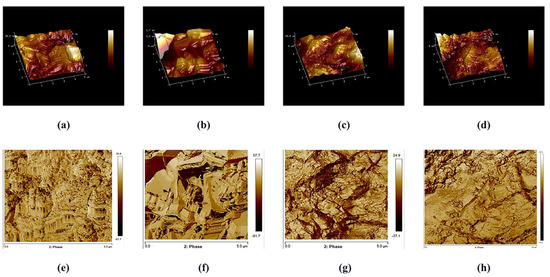
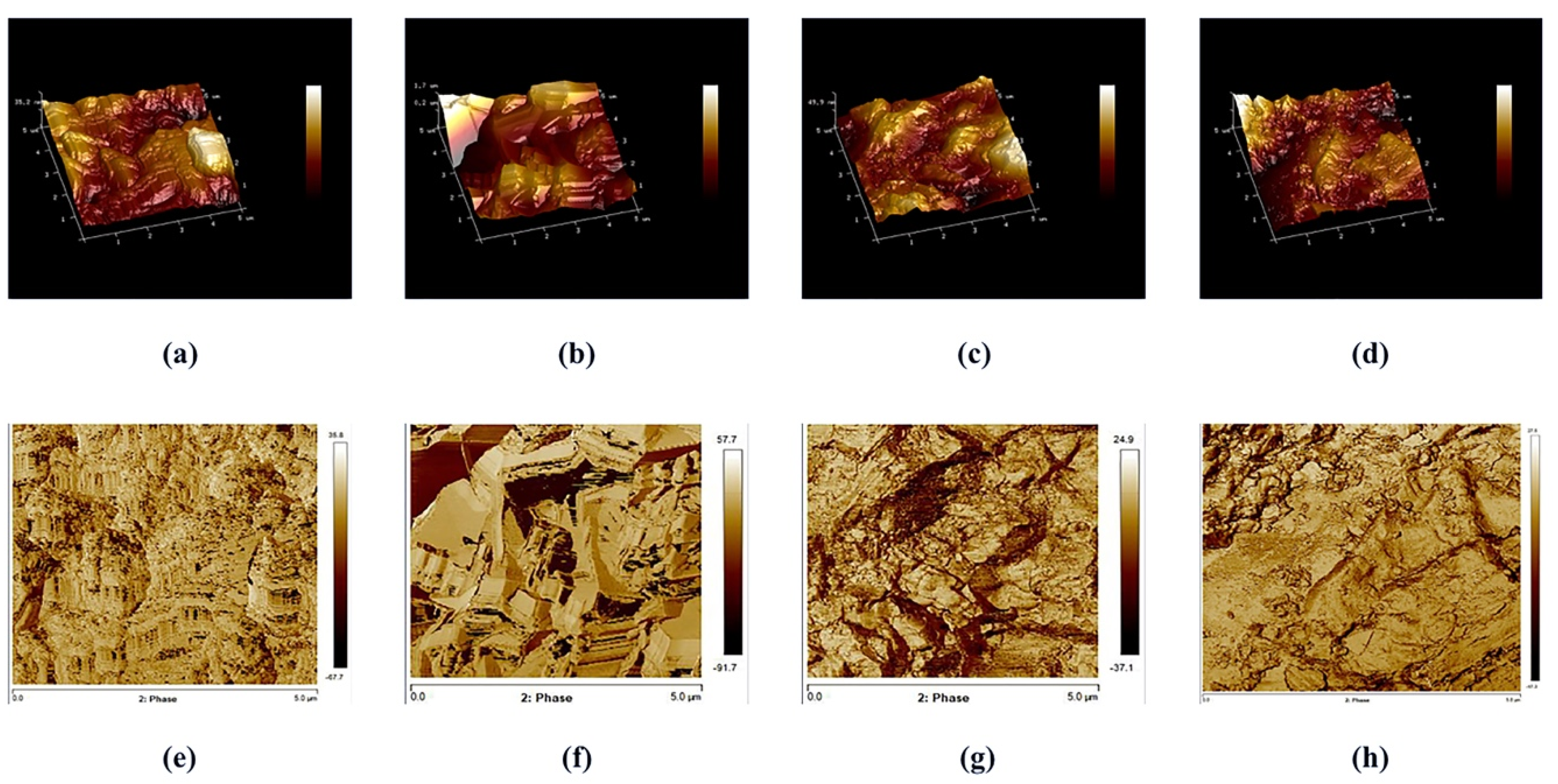
Figure 3.
AFM 3D and 2D images of the surface roughness in representative specimens of the LIC: (a,e) control group; (b,f) etching; (c,g) plasma O2; (d,h) plasma argon.
In the RMC, the highest values in wettability were obtained by the RMC-AR group (12.82°). Regarding roughness, the control group obtained the lowest values (62.25 nm). Differences were also observed (p = 0.001) among all the surface treatments regarding wettability. Regarding roughness, the RMC-SB group demonstrated differences with the other groups; however, no differences were shown between the RMC-O2 and RMC-Ar groups. The results are shown in Table 5 and Figure 2 and Figure 4.

Table 5.
Mean and standard deviation (SD) values of wettability (degree) and roughness (Ra, nm) in the RMC group.
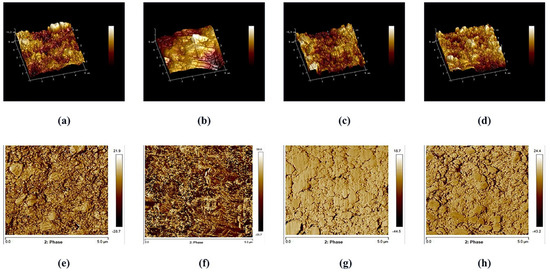
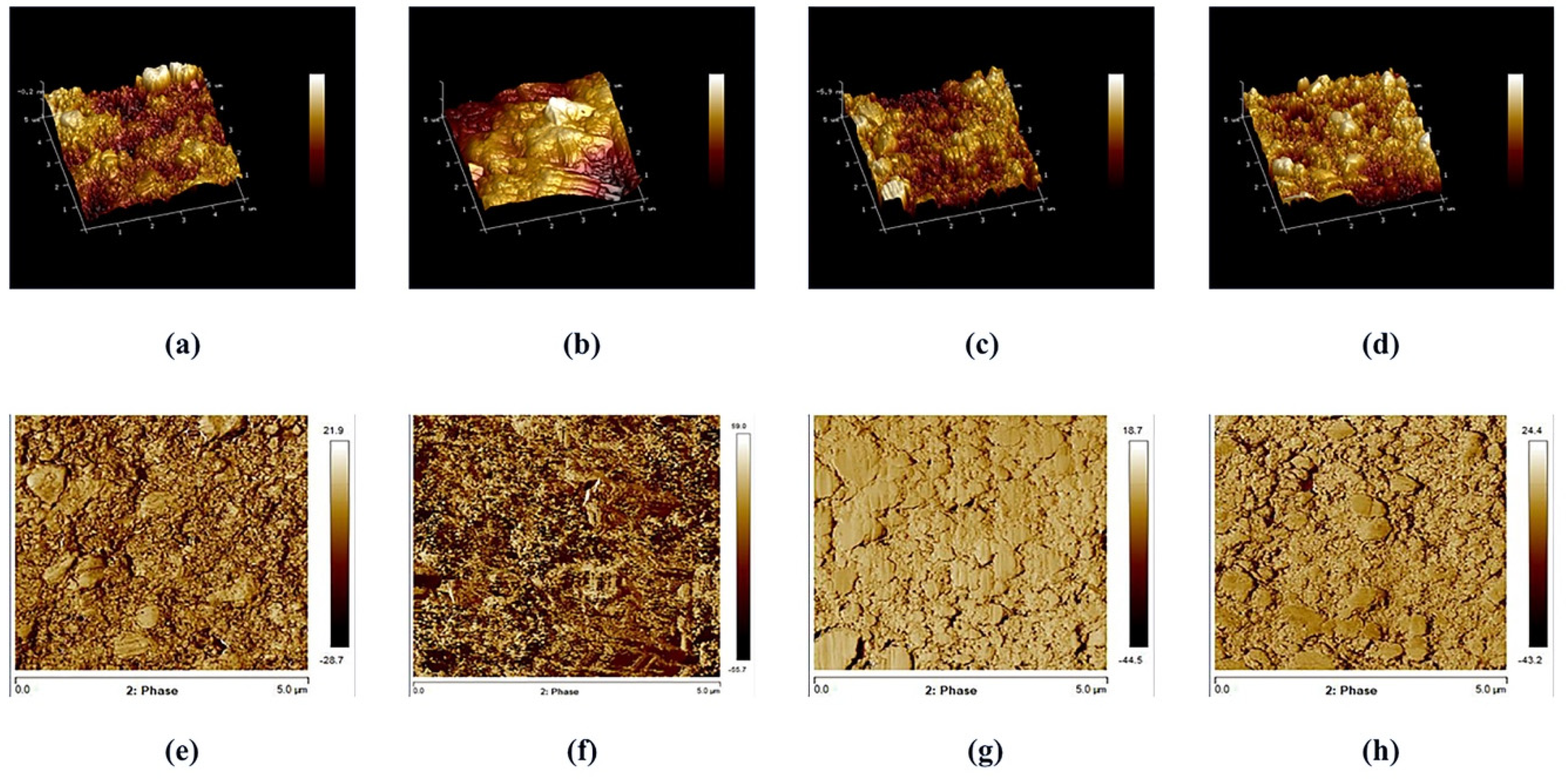
Figure 4.
AFM 3D and 2D images of the surface roughness in representative specimens of RMC: (a,e) control group; (b,f) sandblasting; (c,g) plasma O2; (d,h) plasma argon.
Significant differences were observed for wettability and roughness between both materials for plasma activation. The values for the LIC were significantly lower for wettability and higher for roughness than those for RMC (Table 6).

Table 6.
Intergroup inferential analysis for the wettability and roughness parameters, depending on the type of material, with plasma activation surface treatment.
Significant differences were also observed for wettability and roughness between both materials for plasma etching. Likewise, the values for LIC were significantly lower for wettability and higher for roughness than those for RMC (Table 7).

Table 7.
Intergroup inferential analysis for the wettability and roughness parameters, depending on the type of material, with plasma etching surface treatment.
4. Discussion
This study evaluated the effect of surface treatments by plasma on the wettability and roughness of two different CAD-CAM ceramics. The results of the present research demonstrated significant differences among the surface treatments in both materials analyzed, for wettability and roughness. Likewise, differences in wettability and roughness were observed between the two ceramic materials evaluated, with both surface treatments by plasma analyzed. Therefore, the null hypothesis must be rejected.
Resin bonding requires pretreatment steps to prepare the bonding surfaces [14]. The strategies involve micromechanical and chemical pretreatments, implying that the restoration surface requires surface roughening for mechanical bonding and surface activation for chemical adhesion [38]. Roughness increases the surface area available for bonding, promoting micromechanical interlocking with the resin cement [39,40]. On the other hand, wettability of the surface is an important actor for the bonding of ceramics, regardless of the bonding mechanism used [33,41,42]. Surface free energy influences the wetting of a solid by a liquid and can be determined by the contact angle [33,41,42]. Increasing the surface free energy improves the wettability of the surface for resin bonding [33,43]. Furthermore, the surface roughness also affects wettability of the ceramic surface since an increase in surface area induces an increase in wettability [39,44].
During the past decades the properties of glass-ceramics have been improved by varying their composition [4]. LIC is a glass-ceramic whose surface must be treated prior to bonding cementation to increase its adhesion to the cement [20]. Previous studies demonstrated that etching with HF acid is the preferred surface treatment. However, there is no consensus regarding the different HF acid concentration and etching times [21], even previous studies stated that the HF acid concentration had no influence on the bond strength [20,45]. In the present study, for the LIC group an HF acid treatment was included, as recommended by the manufacturer. The results obtained suggest that conventional treatment with HF acid results in the best wettability values, and up to four times more roughness than in the rest of the groups. A previous study also demonstrated an increase in the roughness of LIC with 10% HF acid for 60 s [20]. HF etching acts on the microstructure of the lithium disilicate and LIC by dissolving their glassy phase, creating a porous microstructure that increased the surface area and wettability [41]. Previous studies on glass-ceramics demonstrated that the HF etching induces an increase in wettability, which is associated with a lower contact angle, higher surface energy, and greater bonding potential [20,39,41,43,44]. The exposure time to HF also has been analyzed and the studies concluded that longer exposures resulted in wider and irregular grooves, increasing the surface roughness [20,33]. Furthermore, Ramakrishnaiah et al. [33] reported that an increase in the etching time resulted in increased wettability and demonstrated a strong association between the surface roughness and wettability. In the plasma groups, there have been significant differences in roughness comparing to the HF acid group, although with much lower values and close to the control group. However, the contact angle has been reduced to 20° with etching plasma. It would be necessary to consider whether the surface energy obtained with plasma treatments is enough to obtain acceptable adhesion values. Studies that evaluated the effect of wettability on the bonding cementation strength are sparse and showed that greater wettability enhanced the bonding strength of ceramic restorations [34,46,47,48]. The results obtained are interesting because with decreased roughness can reduce the possible defects or cracks that may compromise the restorations. Regarding the effect of both plasma treatments on the LIC group, it was observed that although the exposure times are very different, 5 min with oxygen and 60 min with argon, the roughness’s obtained were very similar, although slightly higher in the case of plasma oxygen. This may be due to the inorganic origin of the matrix in the LIC group, which makes the effect of the argon on its surface difficult to achieve. One of the possible solutions is to increase the exposure time of the argon, or even mixing it with oxygen. Furthermore, it should be noted that oxygen is a reactive gas as it was observed during the preliminary tests, and it can affect the color of the restoration when using it in periods longer than 5 min.
Regarding the RMC, different surface treatments were used, such as chemical etching with HF acid, airborne particle abrasion with aluminum oxide particles, tribochemical silica coating, or laser treatment. Nevertheless, there is still no consensus about which method is suitable and effective for the bonding process of RMC [9]. HF treatment provides a higher bond strength when the ceramic content increases in the material composition, whereas air-borne particle abrasion showed higher bond strength values when the composite content increases [7]. Previous studies found that HF acid is not an appropriate method for surface treatment on a similar RMC to the present study and that could alter the surface and reduce their bond strength [10,49]. Therefore, in the study, HF acid was not used in the RMC group, but sandblasting was performed with 50 μm alumina particles for 20 s at 1.5 bar pressure and 10 mm away from the surface, following the manufacturer’s recommendations. In general, airborne-abrasion surface treatment will increase the surface roughness [5]. Park et al. [10] reported in resin nanoceramics that an increasing surface roughness through mechanical surface treatment is more effective than chemical bonding with HF acid. In the study, an increase in the roughness almost three times more with respect to the control group was observed for the sandblasting group, as previously reported [5]. However, an increase in the contact angle by 20° was observed, therefore its surface energy decreased, making the material more hydrophobic. In contrast, both plasma treatments used in the study on RMC increased the roughness slightly (about 20 nm both) and decreased the contact angle by 60° with plasma oxygen, and by 70° with plasma argon, compared to the control group. Therefore, low-pressure plasma treatments showed excellent results in terms of wettability and only a slight increase in roughness. The best results were those obtained by plasma argon, which are comparable to those obtained by the acid etching with HF in the LIC group, although with a completely different roughness.
Nowadays, the use of RMC is increasing in dentistry; however, there are not many studies regarding the procedure of surface treatment before adhesive cementation [5]. The success of the surface treatments can vary depending on the material type and depends more on the RMC’s chemical composition than the surface treatment itself [5,7,50]. Furthermore, few studies focused on plasma treatment of ceramic surfaces, and to the authors’ knowledge there are no studies on plasma surface treatment on LIC and RMC. The few studies that have focused on plasma surface treatment investigated its effect especially on zirconia surfaces [30,31,34,35,36,47,48,51,52,53,54,55], and it is thus not possible to make comparisons of their results with those obtained in this study; therefore, comparisons will be made with other materials.
Vechiato Filho et al. [56] studied the effect of atmospheric plasma treatment on lithium disilicate ceramics. The gas used was a combination of an 85% hexamethydisiloxane (HMDSO) monomer and 15% argon for 30 min. The roughness obtained on the lithium disilicate was lower than those obtained in the LIC group. The authors observed a higher surface energy in the plasma treatment than in traditional HF acid etching, with the monomer being the key of the results obtained. These data were also found by Dos Santos et al. [57], in a similar study with the same combination of HMDSO and argon gas, but instead of using atmospheric plasma they used low-pressure plasma. The data could not be compared because of the differences in the materials and methodologies employed.
Zirconia is a high-strength ceramic introduced as an alternative to metal-ceramic restorations [6]. Its popularity has increased considerably; however, resin-bonding protocols for zirconia are still controversial [14,34]. Zirconia is a polycrystalline ceramic with no glass phase, and it is more difficult to obtain a proper bonding. Surface treatment by HF acid cannot be used for zirconia ceramics, because it fails to achieve adequate surface roughness [58]. Airborne alumina particle abrasion has been recommended to improve the surface roughness on the zirconia surface [59,60,61]. It also improves the surface energy and wettability [61]. However, it has been reported that particle abrasion by alumina can create mechanical damage on the surface of the ceramic [51]. To avoid this problem, alternative surface treatments have been proposed and, recently, surface treatment by plasma has been introduced [25,47,51]. The few studies found concluded that plasma treatment of zirconia surface decreased the contact angle, and therefore improve the surface energy [30,31,34,35,36,47,48,53,54,55]. However, the surface roughness was not affected [35,37,52,53,55]. The results were consistent to those obtained in the present study, although the ceramic materials analyzed were different.
Although the most commonly used gases are argon and oxygen, to date it is not clear which of the two to use, or whether to mix both, and how long the exposure to gas should be. Tabari et al. [34] tested different plasma treatments on zirconia: atmospheric air, 100% oxygen, 100% argon, 10% argon, a 90% oxygen combination, a 20% argon, and an 80% oxygen combination. The lower contact angles values were those achieved by the group with 20% argon and the 80% oxygen combination. Therefore, there is no standardization regarding which gas is the most appropriate, the exposure times, the type of plasma, or the way in which to apply it.
The use of laser technology for surface treatment has been also introduced. Fornaini et al. [38] reported that a 1070 nm fiber laser can be considered as a good device to increase the adhesion of lithium disilicate ceramics. Several studies investigated the effect of laser on zirconia surface treatment and the results are inconclusive. Kasrei et al. [62] reported that surface treatment with a CO2 laser increased the shear bond strength between the resin cement and the zirconia ceramic. Popa et al. [63] found that Nd:YAG laser irradiation produced significantly higher alterations in the surface roughness of zirconia than Er:YAG. Recently, it has been reported that repeating CO2 laser treatment methods could be considered reliable approaches for zirconia surface treatment [61]. Thus, further studies are necessary to evaluate the ceramic surface treatment by laser.
The results of the study indicate that low-pressure plasma is an alternative to traditional surface treatments that are based on obtaining surface energy by increasing the roughness. However, similar or better values can be obtained with plasma, without the need to create such roughness. Furthermore, based on the roughness values obtained in the study, no plasma etching could be demonstrated with plasma argon at 60 min. Regarding which material is the most effective plasma treatment, according to the results obtained in the study, materials with an organic matrix, such as RMC, are the most favorable to obtain high surface energy values. Concerning the clinical application of plasma surface treatment on ceramic materials, its effect is long enough to last until bonding cementation, but the surface should not be manipulated until the ceramic primer application.
There are some limitations in the study. Only two ceramic materials were analyzed and no shear bond strength test of the resin cements was performed, since the objective was to analyze only the surface properties. Another limitation is the specimen design and that testing was performed under controlled conditions that may not reflect the clinical situation.
More research is needed to analyze whether plasma modifies the surface of other restorative materials, if it creates more or less imperfections/fissures in the materials, and to standardize the appropriate gases and exposure time for each material. It is also important to create clinical protocols for the surface treatment of the different ceramic materials.
5. Conclusions
Considering the limitations of this in vitro study, the following conclusions can be drawn:
- Plasma treatment increases the wettability of the LIC group (22–38%) and RMC group (72–85%).
- Plasma treatments had little influence on surface roughness in both ceramic materials.
- When comparing the effectiveness of the plasma treatments between the two materials, the LIC group, in both plasma etching and plasma activation, obtained the lowest values of wettability and the highest values of roughness.
- Further studies are needed to evaluate the surface treatment of ceramic materials.
Author Contributions
All the authors contributed to the study, writing, review, and editing of the manuscript. Conceptualization and methodology: P.S., C.L.-S., J.P., C.T., V.R.-A. and M.J.S.; supervision: M.J.S.; data curation: P.S. and J.P.; writing—reviewing and editing: P.S., C.L.-S., J.P., C.T., V.R.-A. and M.J.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research did not receive any external funding.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Company GC Corporation for the contribution of the ceramic materials; the Company ANAME for its help during the plasma treatments; and Carmen Bravo, Centre of Data Processing, Computing Service for Research Support, University Complutense of Madrid, for her assistance with the statistical analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare
References
- Gracis, S.; Thompson, V.P.; Ferencz, J.L.; Silva, N.R.F.A.; Bonfante, E.A. A new classification system for all-ceramic and ceramic-like restorative materials. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2015, 28, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelaez, J.; G Cogolludo, P.; Serrano, B.; L Lozano, J.F.; Suarez, M.J. A four-year prospective clinical evaluation of zirconia and metal- ceramic posterior fixed dental prostheses. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2012, 25, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Freire, Y.; Gonzalo, E.; López Suárez, C.; Suárez, M.J. The marginal fit of CAD/CAM monolithic ceramic and metal-ceramic crowns. J. Prosthodont. 2019, 28, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Engqvist, H.; Xia, W. Glass-ceramics in dentistry: A review. Materials 2020, 13, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.E.; Kim, J.H.; Shim, J.S.; Roh, B.D.; Shin, Y. Effect of air-particle pressures on the surface topography and bond strengths of resin cement to the hybrid ceramics. Dent. Mater. J. 2017, 36, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelaez, J.; Cogolludo, P.G.; Serrano, B.; L Lozano, J.F.; Suarez, M.J. A prospective evaluation of zirconia posterior fixed dental prostheses: Three-year clinical results. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2012, 107, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şişmanoğlu, S.; Gürcan, A.T.; Yıldırım-Bilmez, Z.; Turunç-Oğuzman, R.; Gümüştaş, B. Effect of surface treatments and universal adhesive application on the microshear bond strength of CAD/CAM materials. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2020, 12, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruse, N.D.; Sadoun, M.J. Resin-composite blocks for dental CAD/CAM applications. J. Dent. Res. 2014, 93, 1232–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, E.; Sahin, S.C.; Dede, D.Ö. Shear bond strength of nanohybrid composite to the resin matrix ceramics after different surface treatments. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2018, 36, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Choi, Y.S. Microtensile bond strength and micromorphologic analysis of surface-treated resin nanoceramics. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2016, 8, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cekic-Nagas, I.; Ergun, G.; Egilmez, F.; Vallittu, P.K.; Lassila, L.V. Micro-shear bond strength of different resin cements to ceramic/glass-polymer CAD-CAM block materials. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2016, 60, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, F.J.; Fleming, G.J.; Nathanson, D.; Marquis, P.M. Are adhesive technologies needed to support ceramics? An assessment of the current evidence. J. Adhes. Dent. 2002, 4, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stawarczyk, B.; Beuer, F.; Ender, A.; Roos, M.; Edelhoff, D.; Wimmer, T. Influence of cementation and cement type on the fracture load testing methodology of anterior crowns made of different materials. Dent. Mater. J. 2013, 32, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blatz, M.B.; Vonderheide, M.; Bonejo, J. The effect of resin bonding on long-term success of high-strength ceramics. J. Dent. Res. 2018, 97, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maroulakos, G.; Thompson, G.A.; Kontogiorgos, E.D. Effect of cement type on the clinical performance and complications of zirconia and lithium disilicate tooth-supported crowns: A systematic review. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019, 121, 754–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emsermann, I.; Eggmann, F.; Krastl, G.; Weiger, R.; Amato, J. Influence of pretreatment methods on the adhesion of composite and polymer infiltrated ceramic CAD-CAM blocks. J. Adhes. Dent. 2019, 21, 433–443. [Google Scholar]
- Ustun, S.; Ayaz, E.A. Effect of different cement systems and aging on the bond strength of chairside CAD-CAM ceramics. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2020, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zogheib, L.V.; Bona, A.D.; Kimpara, E.T.; McCabe, J.F. Effect of hydrofluoric acid etching duration on the roughness and flexural strength of a lithium disilicate-based glass ceramic. Braz. Dent. J. 2011, 22, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaoping, L.; Dongfeng, R.; Silikas, N. Effect of etching time and resin bond on the flexural strength of IPS e.max Press glass ceramic. Dent. Mater. 2014, 30, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veríssimo, A.H.; Moura, D.M.D.; Tribst, J.P.M.; Araújo, A.M.M.; Leite, F.P.P.; Souza, R.O.A.E. Effect of hydrofluoric acid concentration and etching time on resin-bond strength to different glass ceramics. Braz. Oral Res. 2019, 33, e041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, D.M.D.; Araújo, A.M.M.; Souza, K.B.; Veríssimo, A.H.; Tribst, J.P.M.; Souza, R.O.A.E. Hydrofluoric acid concentration, time and use of phosphoric acid on the bond strength of feldspathic ceramics. Braz. Oral Res. 2020, 34, e018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poitevin, A.; De Munck, J.; Van Ende, A.; Suyama, Y.; Mine, A.; Peumans, M. Bonding effectiveness of self-adhesive composites to dentin and enamel. Dent. Mater. 2013, 29, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özcan, M.; Bernasconi, M. Adhesion to zirconia used for dental restorations: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Adhes. Dent. 2015, 17, 7–26. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cho, B.H.; Han, G.J.; Oh, K.H.; Chung, S.N.; Chun, B.H. The effect of plasma polymer coating using atmospheric-pressure glow discharge on the shear bond strength of composite resin to ceramic. J. Mater. Sci. 2011, 46, 2755–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, S.; Park, Y.S. Plasma in dentistry. Clin. Plasma Med. 2014, 2, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seker, E.; Kilicarslan, M.A.; Deniz, S.T.; Mumcu, E.; Ozkan, P. Effect of atmospheric plasma versus conventional surface treatments on the adhesion capability between self-adhesive resin cement and titanium surface. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2015, 7, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koodaryan, R.; Hafezeqoran, A. Surface modification of dental polymers by plasma treatment: A review. Biomed. Pharmacol. J. 2016, 9, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seker, E.; Kilicarslan, M.A.; Polat, S.; Ozkir, E.; Pat, S. Non-thermal atmospheric plasma: Can it be taken as a common solution for the surface treatment of dental materials? Plasma Sci. Technol. 2016, 18, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.J.; Chung, S.N.; Chun, B.H.; Kim, C.K.; Oh, K.H.; Cho, B.H. Effect of the applied power of atmospheric pressure plasma on the adhesion of composite resin to dental ceramic. J. Adhes. Dent. 2012, 14, 461–469. [Google Scholar]
- Canullo, L.; Micarelli, C.; Bettazzoni, L.; Koci, B.; Baldissara, P. Zirconia composite bonding after plasma of argon treatment. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2014, 27, 267–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Hong, L.; Hottel, T.; Dong, X.; Yu, Q.; Chen, M. Non-thermal plasma enhanced bonding of resin cement to zirconia ceramic. Clin. Plasma Med. 2016, 4, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonitz, M.; Lopez, J.; Becker, K.H.; Thomsen, H. Complex Plasmas: Scientific Challenges and Technological Opportunities; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 455–485. [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishnaiah, R.; Alkheraif, A.A.; Divakar, D.D.; Matinlinna, J.P.; Vallittu, P.K. The effect of hydrofluoric acid etching duration on the surface micromorphology, roughness, and wettability of dental ceramics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabari, K.; Hosseinpour, S.; Mohammad-Rahimi, H. The impact of plasma treatment of Cercon® zirconia ceramics on adhesion to resin composite cements and surface properties. J. Lasers Med. Sci. 2017, 8, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.S.; Ahn, J.J.; Bae, E.B.; Kim, G.C.; Jeong, C.M.; Huh, J.B.; Lee, S.H. Influence of non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma treatment on shear bond strength between Y-TZP and self-adhesive resin cement. Materials 2019, 12, 3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lümkemann, N.; Eichberger, M.; Stawarczyk, B. Different surface modifications combined with universal adhesives: The impact on the bonding properties of zirconia to composite resin cement. Clin. Oral Investig. 2019, 23, 3941–3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.J.; Kim, D.S.; Bae, E.B.; Kim, G.C.; Jeong, C.M.; Huh, J.B.; Lee, S.H. Effect of non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma (NTP) and zirconia primer treatment on shear bond strength between Y-TZP and resin cement. Materials 2020, 13, 3934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornaini, C.; Poli, F.; Merigo, E.; Brulat-Bouchard, N.; El Gamal, A.; Rocca, J.P.; Selleri, S.; Cucinotta, A. Disilicate dental ceramic surface preparation by 1070 nm fiber laser: Thermal and ultrastructural analysis. Bioengineering 2018, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prochnow, C.; Venturini, A.B.; Grasel, R.; Gundel, A.; Bottino, M.C.; Valandro, L.F. Adhesion to a lithium disilicate glass ceramic etched with hydrofluoric acid at distinct concentrations. Braz. Dent. J. 2018, 29, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, D.C.S.; Gonçalves, L.M.; Walter, R.; Chung, Y.; Blatz, M.B. Bond strengths of various resin cements to different ceramics. Braz. Oral Res. 2019, 33, e095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, F.; Tsujimoto, A.; Ishii, R.; Nojiri, K.; Takamizawa, T.; Miyazaki, M.; Latta, M.A. Influence of surface treatment of contaminated lithium disilicate and leucite glass ceramics on surface free energy and bond strength of universal adhesives. Dent. Mater. J. 2015, 34, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, R.; Tsujimoto, A.; Takamizawa, T.; Tsubota, K.; Suzuki, T.; Shimamura, Y.; Miyazaki, M. Influence of surface treatment of contaminated zirconia on surface free energy and resin cement bonding. Dent. Mater. J. 2015, 34, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lise, D.P.; Perdigão, J.; Van Ende, A.; Zidan, O.; Lopes, G.C. Microshear bond strength of resin cements to lithium disilicate substrates as a function of surface preparation. Oper. Dent. 2015, 40, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Bona, A.; Borba, M.; Benetti, P.; Pecho, O.E.; Alessandretti, R.; Mosele, J.C.; Mores, R.T. Adhesion to dental ceramics. Curr. Oral Health Rep. 2014, 1, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottino, M.A.; Snellaert, A.; Bergoli, C.D.; Özcan, M.; Bottino, M.C.; Valandro, L.F. Effect of ceramic etching protocols on resin bond strength to a feldspar ceramic. Oper. Dent. 2015, 40, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pashley, D.H.; Carvalho, R.M.; Sano, H.; Nakajima, M.; Yoshiyama, M.; Shono, Y.; Fernandes, C.A.; Tay, F. The microtensile bond test: A review. J Adhes Dent. 1999, 1, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Valverde, G.B.; Coelho, P.G.; Janal, M.N.; Lorenzoni, F.C.; Carvalho, R.M.; Thompson, V.P.; Weltemann, K.D.; Silva, N.R. Surface characterisation and bonding of Y-TZP following non-thermal plasma treatment. J. Dent. 2013, 41, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, A.B.; Simao, R.A.; Prado, M.; Cesar, P.F.; Botelho Dos Santos, G.; Moreira da Silva, E. Effect of different times of nonthermal argon plasma treatment on the microtensile bond strength of self-adhesive resin cement to yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal ceramic. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019, 121, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duzyol, M.; Sagsoz, O.; Polat Sagsoz, N.; Akgul, N.; Yildiz, M. The effect of surface treatments on the bond strength between CAD/CAM blocks and composite resin. J. Prosthodont. 2016, 25, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasser, T.; Preis, V.; Behr, M.; Rosentritt, M. Roughness, surface energy, and superficial damages of CAD/CAM materials after surface treatment. Clin. Oral Investig. 2018, 22, 2787–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallmann, L.; Ulmer, P.; Wille, S.; Polonskyi, O.; Köbel, S.; Trottenberg, T.; Bornholdt, S.; Haase, F.; Kersten, H.; Kern, M. Effect of surface treatments on the properties and morphological change of dental zirconia. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2016, 115, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitencourt, S.B.; Dos Santos, D.M.; da Silva, E.V.F.; Barão, V.A.R.; Rangel, E.C.; da Cruz, N.C.; de Souza, G.M.; Goiato, M.C.; Pesqueira, A.A. Characterization of a new plasma-enhanced film to improve shear bond strength between zirconia and veneering ceramic. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 92, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.C.; Hsieh, J.P.; Chen, Y.C.; Kang, L.L.; Hwang, C.S.; Chuang, S.F. Promoting porcelain-zirconia bonding using different atmospheric pressure gas plasmas. Dent. Mater. 2018, 34, 1188–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pott, P.C.; Syvari, T.S.; Stiesch, M.; Eisenburger, M. Influence of nonthermal argon plasma on the shearbond strength between zirconia and different adhesives and luting composites after artificial aging. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2018, 10, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.; Yoo, S.H.; Park, S.W.; Yun, K.D.; Ji, M.K.; Shin, J.H.; Lim, H.P. The effect of plasma on shear bond strength between resin cement and colored zirconia. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2017, 9, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vechiato Filho, A.J.; dos Santos, D.M.; Goiato, M.C.; de Medeiros, R.A.; Moreno, A.; da Bonatto L, R. Surface characterization of lithium disilicate ceramic after nonthermal plasma treatment. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2014, 112, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, D.M.; da Silva, E.V.F.; Vechiato-Filho, A.J.; Cesar, P.F.; Rangel, E.C.; da Cruz, N.C. Aging effect of atmospheric air on lithium disilicate ceramic after nonthermal plasma treatment. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2016, 115, 780–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kern, M. Resin bonding to oxide ceramics for dental restorations. J Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2009, 23, 1097–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, N.; Yue, L.; Liao, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Shen, J. The effect of various sandblasting conditions on surface changes of dental zirconia and shear bond strength between zirconia core and indirect composite resin. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2015, 7, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okutan, Y.; Yucel, M.T.; Gezer, T.; Donmez, M.B. Effect of airborne particle abrasion and sintering order on the surface roughness and shear bond strength between Y-TZP ceramic and resin cement. Dent. Mater. J. 2019, 38, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śmielak, B.; Klimek, L.; Wojciechowski, R.; Bąkała, M. Effect of zirconia surface treatment on its wettability by liquid ceramics. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019, 122, 410.e1–410.e6. [Google Scholar]
- Kasraei, S.; Atefat, M.; Beheshti, M.; Safavi, N.; Mojtahedi, M.; Rezaei-Soufi, L. Effect of surface treatment with CO2 laser on bond strength between cement resin and zirconia. J. Lasers Med. Sci. 2014, 5, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Popa, D.; Bordea, I.-R.; Burde, A.V.; Crişan, B.; Câmpian, R.S.; Constantiniuc, M. Surface modification of zirconia after laser irradiation. Optoelectron. Adv. Mat. 2016, 10, 785–788. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).