A Systematic Review of Virtual Reality Interfaces for Controlling and Interacting with Robots
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
- IEEE Xplore
- ACM Digital Library
- SAGE Publications
- Springer Link
- MDPI
| (“virtual reality” OR “vr”) AND robot |
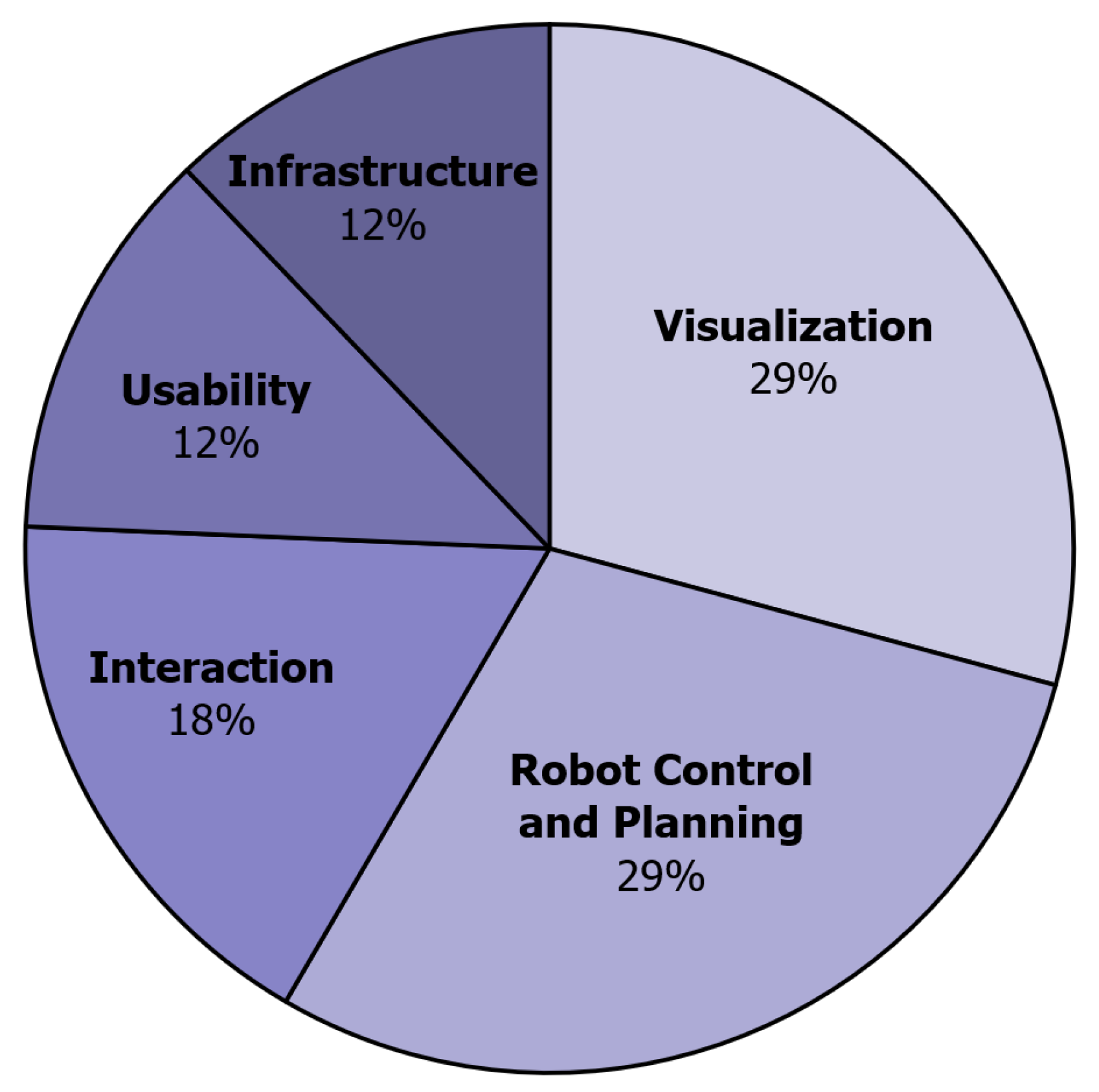
3. Results and Discussion
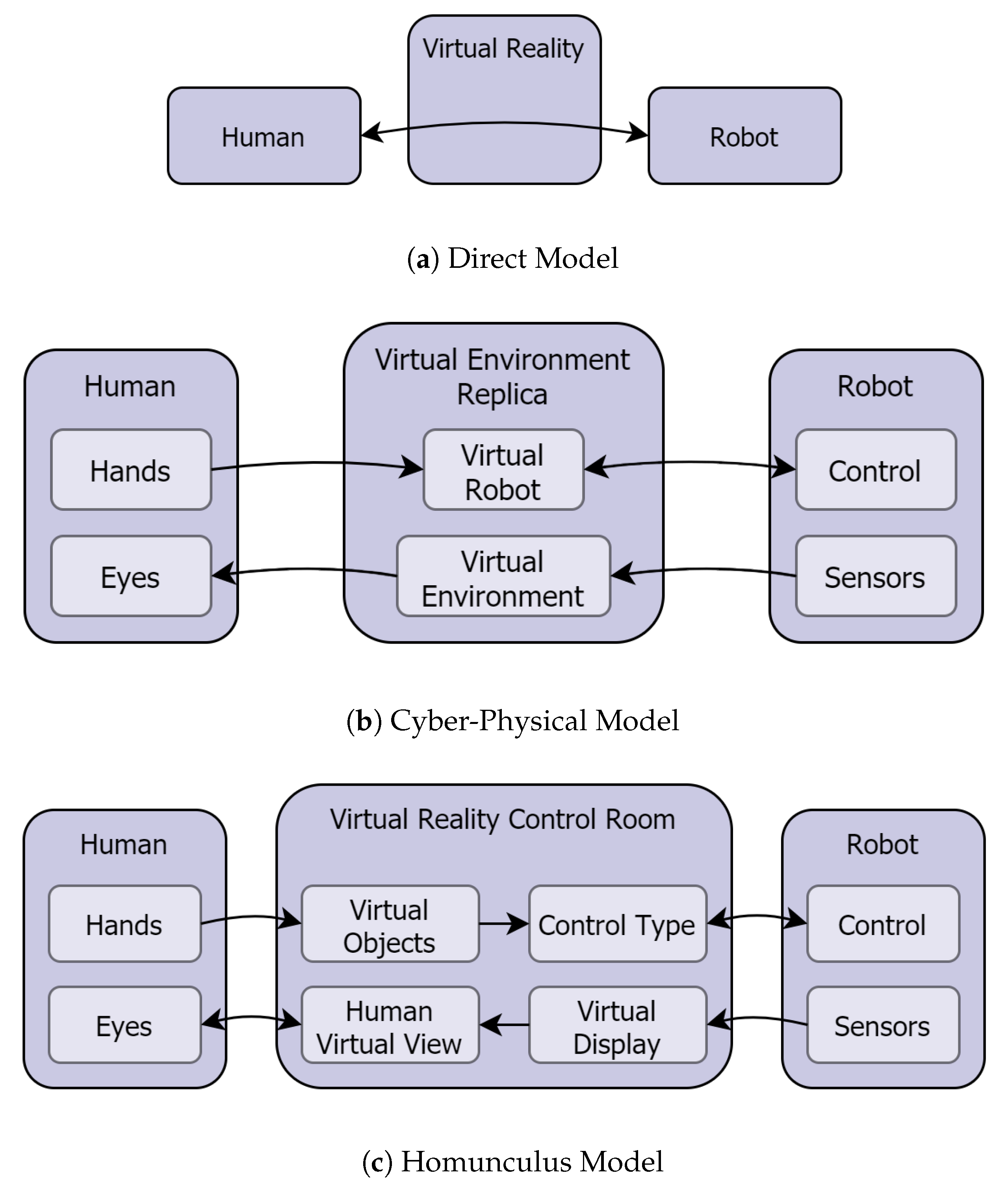
3.1. Visualization
3.2. Robot Control and Planning
3.3. Interaction
3.4. Usability
3.5. Infrastructure
4. Takeaways
5. Future Directions
5.1. Visualization
5.2. Robot Control and Motion Planning
5.3. Interaction
5.4. Usability
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Ref | Year | Category | Robot Type | Contribution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [54] | 2016 | Usability | (Virtual) Mobile | Identifies user preferences between using a traditional computer interface over an immersive VR interface for teleoperation |
| [47] | 2016 | Interaction | Mobile | Develops a collaborative human-robot system to accomplish real-time mapping in VR |
| [45] | 2016 | Interaction | Mobile | Develops a visual programming system to define navigation tasks |
| [29] | 2016 | Visualization | Humanoid | Develops a method to use stereo panoramic reconstruction to reduce perceived visual latency during teleoperation |
| [25] | 2016 | Visualization | Manipulator | Evaluates the affects of different viewpoints on success when teleoperating a construction robot |
| [46] | 2017 | Interaction | (Virtual) Mobile & Aerial | Investigates the utility of predictive capabilities in VR interfaces for multi-robot teams using a traditional interface as a baseline |
| [51] | 2017 | Usability | Manipulator | Compares a developed VR programming interface with a direct manipulation interface and a keyboard, mouse, and monitor interface |
| [56] | 2017 | Infrastructure | N/A | Develops an open-source cloud-based software architecture to interface ROS with Unity |
| [23] | 2018 | Visualization | Dual-Arm Manipulator | Evaluates using virtual features to display task-related information to improve operator performance in completing teleoperation pick-and-place tasks |
| [40] | 2018 | Robot Control and Planning | Manipulator | Compares different VR interaction techniques for teleoperation |
| [22] | 2018 | Visualization | Manipulator | Develops a method to efficiently process and visualize point-clouds in VR |
| [30] | 2018 | Visualization | Mobile with Manipulator | Evaluates the best way to visualize stereo cameras inside a VR headset to minimize motion sickness |
| [32] | 2018 | Robot Control and Planning | Dual-Arm Manipulator | Develops a teleoperation framework that can quickly map user input to robot movement and vice-versa |
| [27] | 2018 | Visualization | (Virtual) Aerial | Evaluates the effects of visual and control latency in drones when using VR |
| [59] | 2018 | Infrastructure | N/A | Develops a framework to interface ROS with Unity |
| [57] | 2018 | Infrastructure | N/A | Develops an open-source framework to interface ROS with Unity |
| [28] | 2019 | Visualization | (Virtual) Mobile | Develops an image projection method that remove discrepancies between robot and user head pose |
| [50] | 2019 | Interaction | Dual-Arm Manipulator | Evaluates using different controllers in teleoperation |
| [44] | 2019 | Interaction | Dual-Arm Manipulator | Develops a telemanipulation framework that incorporates a set of grasp affordances to simplify operation |
| [49] | 2019 | Interaction | Humanoid (Bipedal) | Summarizes data visualization and interaction techniques of VR video games for adoption to VR robot interfaces |
| [33] | 2019 | Robot Control and Planning | Humanoid (Mobile Base) | Develops teleoperation system that imitates user’s upper body pose data in real-time |
| [53] | 2019 | Usability | Mobile with Manipulator & Aerial | Compares a traditional interface to a VR interface for multi-robot missions |
| [24] | 2019 | Visualization | Mobile with Manipulator | Compares an immersive VR visualization to a monitor video-based visualization for robot navigation |
| [21] | 2019 | Visualization | Manipulator | Compares a representative model visualization of the full environment to a real-time point cloud visualization of the real environment for teleoperation |
| [37] | 2019 | Robot Control and Planning | Manipulator | Develops a framework that allows robot teleoperation through uses of a digital twin |
| [20] | 2019 | Visualization | Manipulator | Investigates the influence of displaying different levels of environmental information has on task performance and operator situation awareness in VR robot interfaces |
| [42] | 2019 | Robot Control and Planning | Aerial | Develops an optimization based planner to control a painting drone in VR |
| [43] | 2019 | Robot Control and Planning | Aerial with Manipulator | Develops a teleoperation system for aerial manipulation that includes tactile feedback |
| [34] | 2019 | Robot Control and Planning | Dual-Arm Manipulator | Develops a deep correspondence model that maps user input to robot motion for teleoperation |
| [36] | 2019 | Robot Control and Planning | Dual-Arm Manipulator | Develops a predict-then-blend framework to increase efficiency and reduce user workload |
| [60] | 2019 | Infrastructure | N/A | Develops an open-source solution that help calibrate VR equipment (HTC Vive) inside a robot cell (hardware-agnostic, only requires ROS-Industrial and MoveIt plugin) |
| [55] | 2019 | Infrastructure | N/A | Defines a system architecture to work with multi-robot systems using ROS and Unity |
| [31] | 2020 | Visualization | Mobile | Develops and evaluates a human perception-optimized planner to reduce motion sickness |
| [13] | 2020 | Robot Control and Planning | Humanoid (Bipedal) | Develops a control architecture that utilizes a VR setup with an omni-directional treadmill to create a fully immersive teleoperation interface |
| [48] | 2020 | Interaction | Dual-Arm Manipulator | Compares two different VR control interactions, position control and trajectory control, for robot operation |
| [52] | 2020 | Usability | Mobile with Manipulator | Compares displaying camera streams on a monitor and displaying stereo cameras streams inside a VR headset for teleoperation |
| [38] | 2020 | Robot Control and Planning | Manipulator | Develops two robot controllers to decouple an operator from the robot’s control loop for teleoperation |
| [41] | 2020 | Robot Control and Planning | Manipulator | Develops a method that estimates human intent in VR to control a welding robot |
| [26] | 2020 | Visualization | Aerial | Develops a controller that synchronizes a drone’s movement with the user’s head movement to reduce motion sickness |
| [39] | 2020 | Usability | Dual-Arm Manipulator | Compares a VR interface to traditional interfaces for teleoperation |
| [35] | 2020 | Robot Control and Planning | Manipulator | Develops a motion planner using deep reinforcement learning to map the human workspace to the robot workspace for teleoperation |
References
- Mazuryk, T.; Gervautz, M. Virtual Reality-History, Applications, Technology and Future; Vienna University of Technology: Vienna, Austria, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Bric, J.D.; Lumbard, D.C.; Frelich, M.J.; Gould, J.C. Current state of virtual reality simulation in robotic surgery training: A review. Surg. Endosc. 2016, 30, 2169–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moglia, A.; Ferrari, V.; Morelli, L.; Ferrari, M.; Mosca, F.; Cuschieri, A. A systematic review of virtual reality simulators for robot-assisted surgery. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 1065–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Meijden, O.A.; Schijven, M.P. The value of haptic feedback in conventional and robot-assisted minimal invasive surgery and virtual reality training: A current review. Surg. Endosc. 2009, 23, 1180–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adamovich, S.V.; Fluet, G.G.; Tunik, E.; Merians, A.S. Sensorimotor training in virtual reality: A review. Neuro Rehabil. 2009, 25, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baur, K.; Schättin, A.; de Bruin, E.D.; Riener, R.; Duarte, J.E.; Wolf, P. Trends in robot-assisted and virtual reality-assisted neuromuscular therapy: A systematic review of health-related multiplayer games. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2018, 15, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, M.C. A meta-analysis and systematic literature review of virtual reality rehabilitation programs. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2017, 70, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdea, G.C. Invited review: The synergy between virtual reality and robotics. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1999, 15, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Sada, M.; Jiang, K.; Ranade, S.; Kalkattawi, M.; Nakajima, T. HapticSnakes: Multi-haptic feedback wearable robots for immersive virtual reality. Virtual Real. 2020, 24, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vonach, E.; Gatterer, C.; Kaufmann, H. VRRobot: Robot actuated props in an infinite virtual environment. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Virtual Reality (VR), Los Angeles, CA, USA, 18–22 March 2017; pp. 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Kim, L.H.; Wang, Y.; Le Goc, M.; Follmer, S. Robotic Assembly of Haptic Proxy Objects for Tangible Interaction and Virtual Reality. In Proceedings of the Interactive Surfaces and Spaces on ZZZ—ISS ’17, Brighton, UK, 17–20 October 2017; pp. 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, R.; Hedayati, H.; Zheng, C.; Bohn, J.L.; Szafir, D.; Do, E.Y.L.; Gross, M.D.; Leithinger, D. RoomShift: Room-Scale Dynamic Haptics for VR with Furniture-Moving Swarm Robots. In Proceedings of the 2020 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, CHI ’20, Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 April 2020; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elobaid, M.; Hu, Y.; Romualdi, G.; Dafarra, S.; Babic, J.; Pucci, D. Telexistence and Teleoperation for Walking Humanoid Robots. In Intelligent Systems and Applications; Bi, Y., Bhatia, R., Kapoor, S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1106–1121. [Google Scholar]
- Bolano, G.; Roennau, A.; Dillmann, R.; Groz, A. Virtual Reality for Offline Programming of Robotic Applications with Online Teaching Methods. In Proceedings of the 2020 17th International Conference on Ubiquitous Robots (UR), Kyoto, Japan, 22–26 June 2020; pp. 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, O.; Rakita, D.; Mutlu, B.; Gleicher, M. Understanding human-robot interaction in virtual reality. In Proceedings of the 2017 26th IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN), Lisbon, Portugal, 28 August–1 September 2017; pp. 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villani, V.; Capelli, B.; Sabattini, L. Use of Virtual Reality for the Evaluation of Human-Robot Interaction Systems in Complex Scenarios. In Proceedings of the 2018 27th IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN), Nanjing, China, 27–31 August 2018; pp. 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijnen, L.; Lemaignan, S.; Bremner, P. Towards using Virtual Reality for Replicating HRI Studies. In Proceedings of the Companion of the 2020 ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human-Robot Interaction, HRI ’20, Cambridge, UK, 23–26 March 2020; pp. 514–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsas, E.; Vosniakos, G.C. Design of a virtual reality training system for human–robot collaboration in manufacturing tasks. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. (IJIDeM) 2017, 11, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; Prisma Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van de Merwe, D.B.; Van Maanen, L.; Ter Haar, F.B.; Van Dijk, R.J.E.; Hoeba, N.; der Stap, N. Human-Robot Interaction During Virtual Reality Mediated Teleoperation: How Environment Information Affects Spatial Task Performance and Operator Situation Awareness. In Virtual, Augmented and Mixed Reality, Applications and Case Studies; Chen, J.Y.C., Fragomeni, G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 163–177. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.H.; Xu, Y.Q.; Cheng, S.L.; Ko, C.H.; Young, K.Y. Development of an Effective 3D VR-Based Manipulation System for Industrial Robot Manipulators. In Proceedings of the 2019 12th Asian Control Conference (ASCC), Kitakyushu-shi, Japan, 9–12 June 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kohn, S.; Blank, A.; Puljiz, D.; Zenkel, L.; Bieber, O.; Hein, B.; Franke, J. Towards a Real-Time Environment Reconstruction for VR-Based Teleoperation Through Model Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 1–5 October 2018; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brizzi, F.; Peppoloni, L.; Graziano, A.; Stefano, E.D.; Avizzano, C.A.; Ruffaldi, E. Effects of Augmented Reality on the Performance of Teleoperated Industrial Assembly Tasks in a Robotic Embodiment. IEEE Trans. Hum. Mach. Syst. 2018, 48, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stotko, P.; Krumpen, S.; Schwarz, M.; Lenz, C.; Behnke, S.; Klein, R.; Weinmann, M. A VR System for Immersive Teleoperation and Live Exploration with a Mobile Robot. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Macau, China, 3–8 November 2019; pp. 3630–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xinxing, T.; Pengfei, Z.; Hironao, Y. VR-based construction tele-robot system displayed by HMD with active viewpoint movement mode. In Proceedings of the 2016 Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC), Yinchuan, China, 28–30 May 2016; pp. 6844–6850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Takahashi, M. Head-synced Drone Control for Reducing Virtual Reality Sickness. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2020, 97, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Allison, R.S.; Vinnikov, M.; Jennings, S. The Effects of Visual and Control Latency on Piloting a Quadcopter Using a Head-Mounted Display. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Miyazaki, Japan, 7–10 October 2018; pp. 2972–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cash, H.; Prescott, T.J. Improving the Visual Comfort of Virtual Reality Telepresence for Robotics. In Social Robotics; Salichs, M.A., Ge, S.S., Barakova, E.I., Cabibihan, J.J., Wagner, A.R., Castro-González, Á., He, H., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 697–706. [Google Scholar]
- Theofilis, K.; Orlosky, J.; Nagai, Y.; Kiyokawa, K. Panoramic view reconstruction for stereoscopic teleoperation of a humanoid robot. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE-RAS 16th International Conference on Humanoid Robots (Humanoids), Cancun, Mexico, 15–17 November 2016; pp. 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kot, T.; Novák, P. Application of virtual reality in teleoperation of the military mobile robotic system TAROS. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2018, 15, 1729881417751545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Becerra, I.; Suomalainen, M.; Lozano, E.; Mimnaugh, K.J.; Murrieta-Cid, R.; LaValle, S.M. Human Perception-Optimized Planning for Comfortable VR-Based Telepresence. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 6489–6496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipton, J.I.; Fay, A.J.; Rus, D. Baxter’s Homunculus: Virtual Reality Spaces for Teleoperation in Manufacturing. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirschmanner, M.; Tsiourti, C.; Patten, T.; Vincze, M. Virtual Reality Teleoperation of a Humanoid Robot Using Markerless Human Upper Body Pose Imitation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE-RAS 19th International Conference on Humanoid Robots (Humanoids), Toronto, ON, Canada, 15–17 October 2019; pp. 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaurav, S.; Al-Qurashi, Z.; Barapatre, A.; Maratos, G.; Sarma, T.; Ziebart, B.D. Deep Correspondence Learning for Effective Robotic Teleoperation Using Virtual Reality. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE-RAS 19th International Conference on Humanoid Robots (Humanoids), Toronto, ON, Canada, 15–17 October 2019; pp. 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamali, K.; Bonev, I.A.; Desrosiers, C. Real-time Motion Planning for Robotic Teleoperation Using Dynamic-goal Deep Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 17th Conference on Computer and Robot Vision (CRV), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 13–15 May 2020; pp. 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, B.; Wang, S.; Ye, X.; Cai, Y.; Lu, T.; Wang, R. A robotic shared control teleoperation method based on learning from demonstrations. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2019, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsokalo, I.A.; Kuss, D.; Kharabet, I.; Fitzek, F.H.P.; Reisslein, M. Remote Robot Control with Human-in-the-Loop over Long Distances Using Digital Twins. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 9–13 December 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Kiselev, A.; Liao, Q.; Stoyanov, T.; Loutfi, A. A New Mixed-Reality-Based Teleoperation System for Telepresence and Maneuverability Enhancement. IEEE Trans. Hum. Mach. Syst. 2020, 50, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whitney, D.; Rosen, E.; Phillips, E.; Konidaris, G.; Tellex, S. Comparing Robot Grasping Teleoperation Across Desktop and Virtual Reality with ROS Reality. In Robotics Research; Amato, N.M., Hager, G., Thomas, S., Torres-Torriti, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 335–350. [Google Scholar]
- Just, C.; Ortmaier, T.; Kahrs, L.A. A user study on robot path planning inside a Virtual Reality environment. In Proceedings of the ISR 2018 50th International Symposium on Robotics, Munich, Germany, 20–21 June 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Jiao, W.; Yu, R.; Johnson, M.T.; Zhang, Y. Virtual Reality Robot-Assisted Welding Based on Human Intention Recognition. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2020, 17, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vempati, A.S.; Khurana, H.; Kabelka, V.; Flueckiger, S.; Siegwart, R.; Beardsley, P. A Virtual Reality Interface for an Autonomous Spray Painting UAV. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 2870–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashin, G.A.; Trinitatova, D.; Agishev, R.T.; Ibrahimov, R.; Tsetserukou, D. AeroVr: Virtual Reality-based Teleoperation with Tactile Feedback for Aerial Manipulation. In Proceedings of the 2019 19th International Conference on Advanced Robotics (ICAR), Belo Horizonte, Brazil, 2–6 December 2019; pp. 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gorjup, G.; Dwivedi, A.; Elangovan, N.; Liarokapis, M. An Intuitive, Affordances Oriented Telemanipulation Framework for a Dual Robot Arm Hand System: On the Execution of Bimanual Tasks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Macau, China, 3–8 November 2019; pp. 3611–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Song, D. Visual programming for mobile robot navigation using high-level landmarks. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Daejeon, Korea, 9–14 October 2016; pp. 2901–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldán, J.; Peña-Tapia, E.; Martín-Barrio, A.; Olivares-Méndez, M.; Del Cerro, J.; Barrientos, A. Multi-Robot Interfaces and Operator Situational Awareness: Study of the Impact of Immersion and Prediction. Sensors 2017, 17, 1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, J.; Sheng, W.; Liu, M. Human-guided robot 3D mapping using virtual reality technology. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Daejeon, Korea, 9–14 October 2016; pp. 4624–4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetrick, R.; Amerson, N.; Kim, B.; Rosen, E.; de Visser, E.J.; Phillips, E. Comparing Virtual Reality Interfaces for the Teleoperation of Robots. In Proceedings of the 2020 Systems and Information Engineering Design Symposium (SIEDS), Charlottesville, VA, USA, 24 April 2020; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allspaw, J.; Heinold, L.; Yanco, H.A. Design of Virtual Reality for Humanoid Robots with Inspiration from Video Games. In Virtual, Augmented and Mixed Reality, Applications and Case Studies; Chen, J.Y.C., Fragomeni, G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 3–18. [Google Scholar]
- Franzluebbers, A.; Johnson, K. Remote Robotic Arm Teleoperation through Virtual Reality. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Spatial User Interaction, SUI ’19, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–20 October 2019; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theofanidis, M.; Sayed, S.I.; Lioulemes, A.; Makedon, F. VARM. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on PErvasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments, PETRA ’17, Island of Rhodes, Greece, 21–23 June 2017; pp. 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciaś, M.; Da̧browski, A.; Fraś, J.; Karczewski Michałand Puchalski, S.; Tabaka, S.; Jaroszek, P. Measuring Performance in Robotic Teleoperation Tasks with Virtual Reality Headgear. In Automation 2019; Szewczyk, R., Zieliński, C., Kaliczyńska, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 408–417. [Google Scholar]
- Roldan, J.J.; Pena-Tapia, E.; Garcia-Aunon, P.; Del Cerro, J.; Barrientos, A. Bringing Adaptive and Immersive Interfaces to Real-World Multi-Robot Scenarios: Application to Surveillance and Intervention in Infrastructures. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 86319–86335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conn, M.A.; Sharma, S. Immersive Telerobotics Using the Oculus Rift and the 5DT Ultra Data Glove. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Collaboration Technologies and Systems (CTS), Orlando, FL, USA, 31 October–4 November 2016; pp. 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldán, J.J.; Peña-Tapia, E.; Garzón-Ramos, D.; de León, J.; Garzón, M.; del Cerro, J.; Barrientos, A. Multi-robot Systems, Virtual Reality and ROS: Developing a New Generation of Operator Interfaces. In Robot Operating System (ROS): The Complete Reference (Volume 3); Koubaa, A., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 29–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuchi, Y.; Inamura, T. Cloud-based multimodal human-robot interaction simulator utilizing ROS and unity frameworks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII), Taipei, Taiwan, 11–14 December 2017; pp. 948–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, D.; Rosen, E.; Ullman, D.; Phillips, E.; Tellex, S. ROS Reality: A Virtual Reality Framework Using Consumer-Grade Hardware for ROS-Enabled Robots. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 1–5 October 2018; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, M. ROS#. 2019. Available online: https://github.com/siemens/ros-sharp (accessed on 17 December 2020).
- Babaians, E.; Tamiz, M.; Sarfi, Y.; Mogoei, A.; Mehrabi, E. ROS2Unity3D; High-Performance Plugin to Interface ROS with Unity3d engine. In Proceedings of the 2018 9th Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Robotics and 2nd Asia-Pacific International Symposium, Kish Island, Iran, 10 December 2018; pp. 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astad, M.A.; Hauan Arbo, M.; Grotli, E.I.; Tommy Gravdahl, J. Vive for Robotics: Rapid Robot Cell Calibration. In Proceedings of the 2019 7th International Conference on Control, Mechatronics and Automation (ICCMA), Delft, The Netherlands, 6–8 November 2019; pp. 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wonsick, M.; Padir, T. A Systematic Review of Virtual Reality Interfaces for Controlling and Interacting with Robots. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 9051. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10249051
Wonsick M, Padir T. A Systematic Review of Virtual Reality Interfaces for Controlling and Interacting with Robots. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(24):9051. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10249051
Chicago/Turabian StyleWonsick, Murphy, and Taskin Padir. 2020. "A Systematic Review of Virtual Reality Interfaces for Controlling and Interacting with Robots" Applied Sciences 10, no. 24: 9051. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10249051
APA StyleWonsick, M., & Padir, T. (2020). A Systematic Review of Virtual Reality Interfaces for Controlling and Interacting with Robots. Applied Sciences, 10(24), 9051. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10249051





