High-Intensity Ultrasound Pulses Effect on Physicochemical and Antioxidant Properties of Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Skin Gelatin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials and Reagents
2.2. Gelatin Extraction
2.3. High-Intensity Ultrasound Pulses Treatments
2.4. Protein Solubility
2.5. Molecular Weight Distribution
2.6. Surface Hydrophobicity
2.7. Circular Dichroism
2.8. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectra
2.9. ABTS Radical Cation Scavenger
2.10. Ferric Reducing Antioxidant Power
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Ultrasound Pulses
3.2. Protein Solubility
3.3. Surface Hydrophobicity
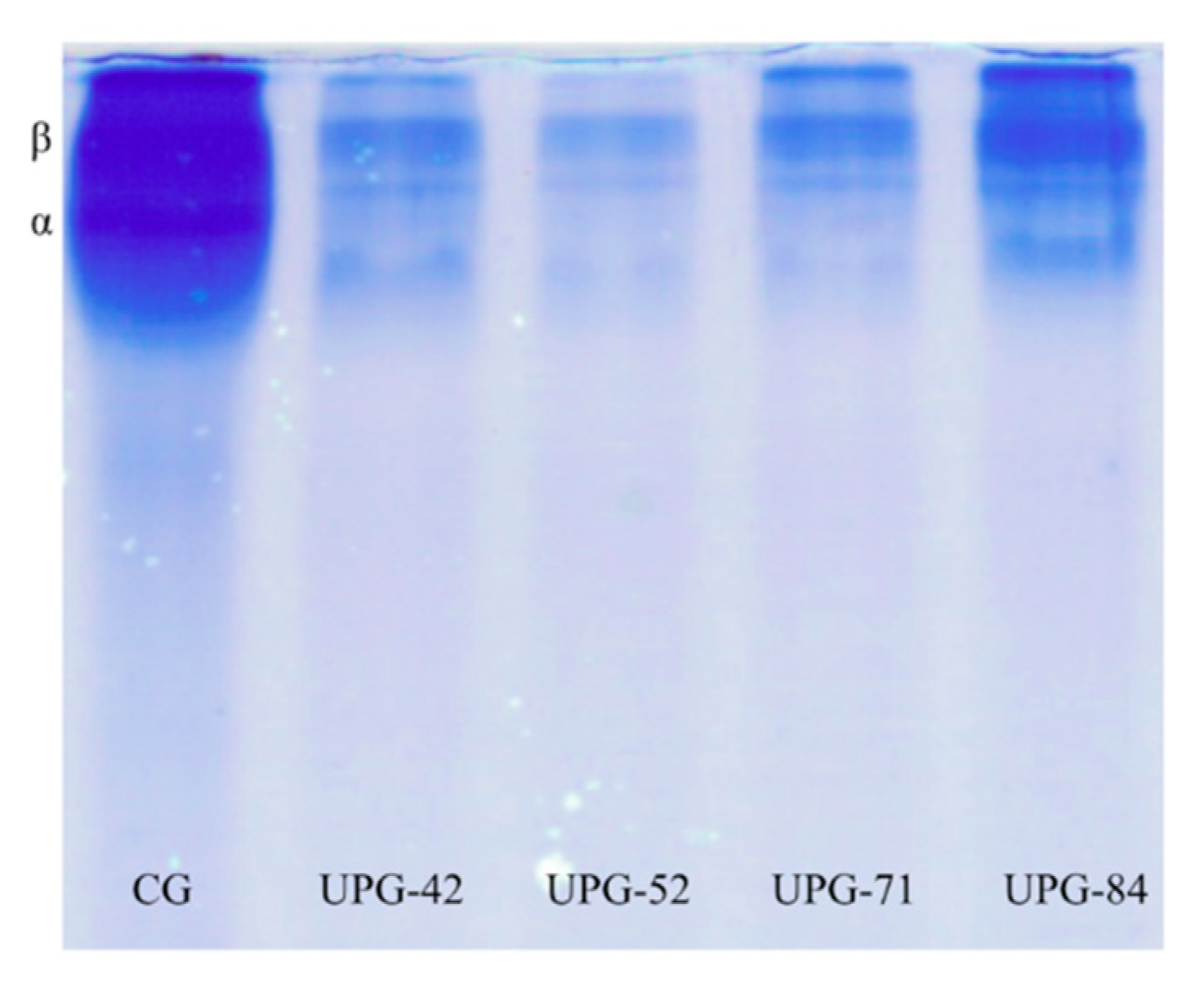
3.4. Molecular Weight Distribution
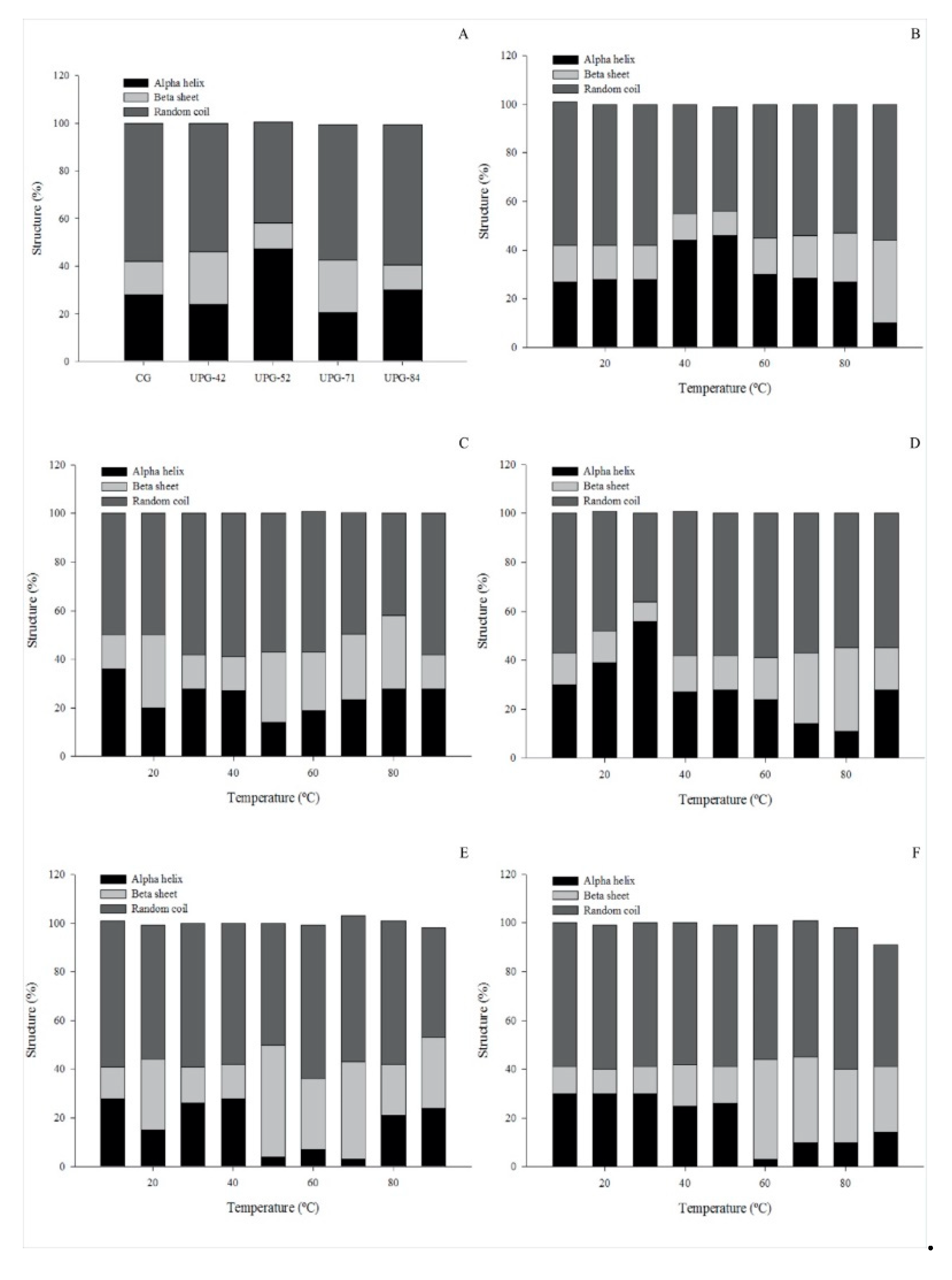
3.5. Circular Dichroism
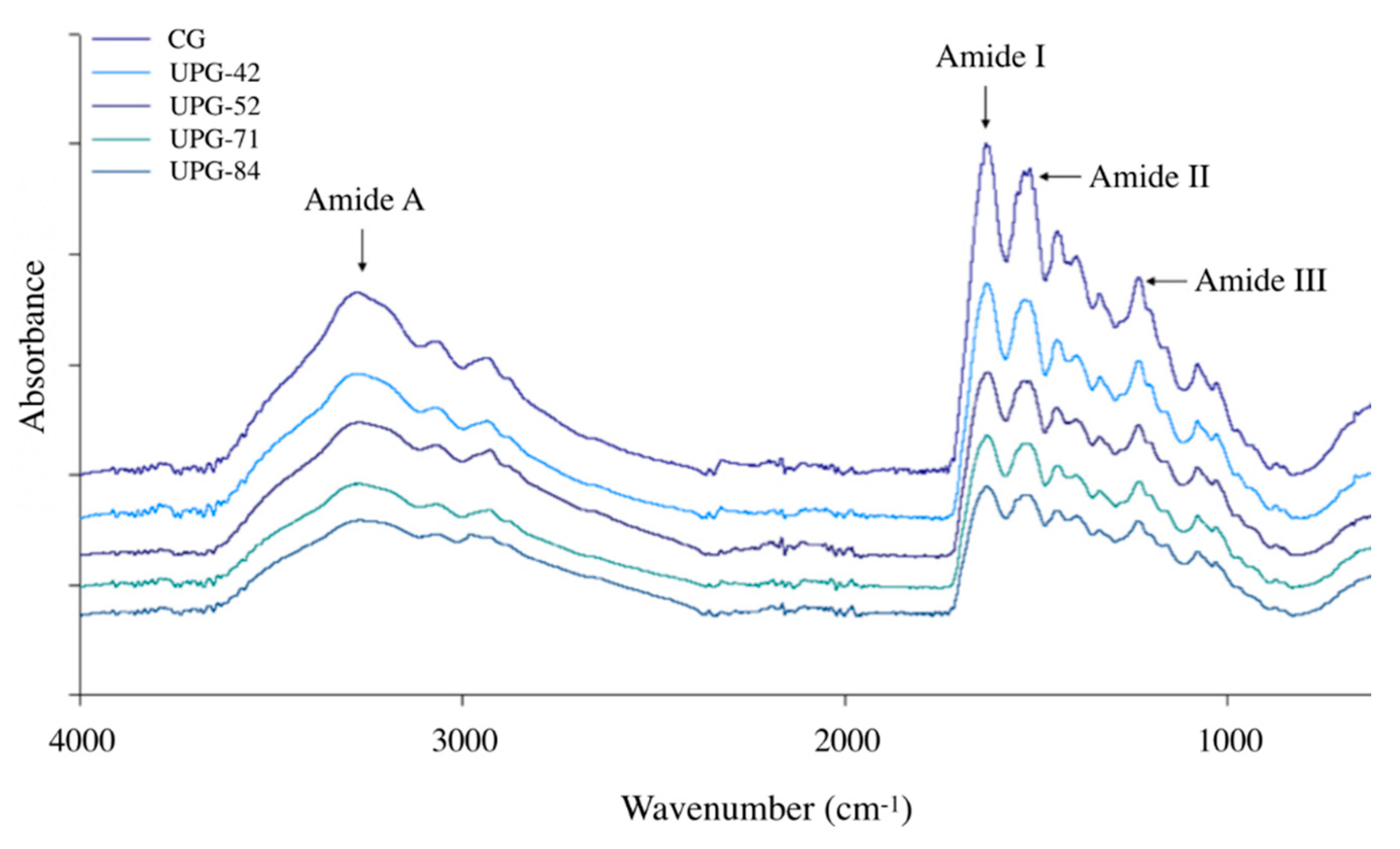
3.6. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectra
3.7. ABTS Radical Cation Scavenger
3.8. Ferric Reducing Antioxidant Power
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arzeni, C.; Martínez, K.; Zema, P.; Arias, A.; Pérez, O.E.; Pilosof, A.M.R. Comparative study of high intensity ultrasound effects on food proteins functionality. J. Food Eng. 2012, 108, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.M.; Jung, S.K.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, Y.E.; Lee, N.H. Development of industrial ultrasound system for mass production of collagen and biochemical characteristics of extracted collagen. Food Bioprod. Process. 2018, 110, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuera-Barraza, O.A.; Del Toro-Sanchez, C.L.; Ruiz-Cruz, S.; Márquez-Ríos, E. Effects of high-energy ultrasound on the functional properties of proteins. Ultrason. Sonochem 2016, 31, 558–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jambrak, A.R.; Mason, T.J.; Lelas, V.; Herceg, Z.; Herceg, I.L. Effect of ultrasound treatment on solubility and foaming properties of whey protein suspensions. J. Food Eng. 2008, 86, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Yang, Y.L.; Tang, X.Z.; Ni, W.X.; Zhou, L. Effects of pulsed ultrasound on rheological and structural properties of chicken myofibrillar protein. Ultrason. Sonochem 2017, 38, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, J.; Murray, B.; Flynn, C.; Norton, I. The effect of ultrasound treatment on the structural, physical and emulsifying properties of animal and vegetable proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 53, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuera-Barraza, O.A.; Torres-Arreola, W.; Ezquerra-Brauer, J.M.; Cinco-Moroyoqui, F.J.; Figueroa, J.R.; Marquez-Ríos, E. Effect of pulsed ultrasound on the physicochemical characteristics and emulsifying properties of squid (Dosidicus gigas) mantle proteins. Ultrason. Sonochem 2017, 38, 829–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Wu, J.; Li-Chan, E.C.Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, F.; Xu, X.; Fan, G.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Pan, S. Effects of ultrasound on structural and physical properties of soy protein isolate (SPI) dispersions. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 30, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Wu, C.; Ma, W.; Wang, Z.; Yu, C.; Du, M. Effects of ultrasound treatment on the physicochemical and emulsifying properties of proteins from scallops (Chlamys farreri). Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 89, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, A.; Valenzuela, M.A.; Yazdani-Pedram, M.; Tapia, C.; Abugoch, L. Conformational and physicochemical properties of quinoa proteins affected by different conditions of high-intensity ultrasound treatments. Ultrason. Sonochem 2019, 51, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chotphruethipong, L.; Aluko, R.E.; Benjakul, S. Hydrolyzed collagen from porcine lipase-defatted seabass skin: Antioxidant, fibroblast cell proliferation, and collagen production activities. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Jia, J.; Kuang, C.; Yang, H. Effect of ultrasonic pretreatment on whey protein hydrolysis by alcalase: Thermodynamic parameters, physicochemical properties and bioactivities. Process Biochem. 2018, 67, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketnawa, S.; Martínez-Alvarez, O.; Benjakul, S.; Rawdkuen, S. Gelatin hydrolysates from farmed Giant catfish skin using alkaline proteases and its antioxidative function of simulated gastro-intestinal digestion. Food Chem. 2016, 192, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikoo, M.; Benjakul, S.; Yasemi, M.; Gavlighi, H.A.; Xu, X. Hydrolysates from rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) processing by-product with different pretreatments: Antioxidant activity and their effect on lipid and protein oxidation of raw fish emulsion. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 108, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Yurrita, P.J. La Acuacultura en México: II. Época actual y perspectivas. Biol. Inf. 2000, 32, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Arpi, N.; Hardianti, E. Preparation and characterization of biodegradable film based on skin and bone fish gelatin. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 207, 012050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. Rapid and sensitive method for quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, S.; Nakai, S. Relationships of hydrophobicity and net charge to the solubility of milk and soy proteins. J. Food Sci. 1985, 50, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzie, I.F.; Strain, J.J. The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “antioxidant power”: The FRAP assay. Anal. Biochem 1996, 239, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Shao, S.; Guo, M. Ultrasound-induced changes in physical and functional properties of whey proteins. Int. J. Food Sci. Tech. 2017, 52, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potaros, T.; Raksakulthai, N.; Runglerdkreangkrai, J.; Worawattanamateekul, W. Characteristics of collagen from nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) skin isolated by two different methods. Nat. Sci. 2009, 43, 584–593. [Google Scholar]
- Kittiphattanabawon, P.; Sriket, C.; Kishimura, H.; Benjakul, S. Characteristics of acid and pepsin solubilized collagens from Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) scale. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2019, 31, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrapala, J.; Zisu, B.; Palmer, M.; Kentish, S.; Ashokkumar, M. Effects of ultrasound on the thermal and structural characteristics of proteins in reconstituted whey protein concentrate. Ultrason. Sonochem 2011, 18, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muyonga, J.H.; Cole, C.G.B.; Duodu, K.G. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopic study of acid soluble collagen and gelatin from skins and bones of young and adult Nile perch (Lates niloticus). Food Chem. 2004, 86, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittiphattanabawon, P.; Benjakul, S.; Sinthusamran, S.; Kishimura, H. Gelatin from clown featherback skin: Extraction conditions. LWT-Food Sci. Tech. 2016, 66, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, B.; Ananthanarayan, L.; Jamdar, S.N. Effect of enzymatic hydrolysis on the functional, antioxidant, and angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory properties of whole horse gram flour. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 28, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozuna, C.; Paniagua-Martínez, I.; Castaño-Tostado, E.; Ozimek, L.; Amaya-Llano, S.L. Innovative applications of high-intensity ultrasound in the development of functional food ingredients: Production of protein hydrolysates and bioactive peptides. Food Res. Int. 2015, 77, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Treatment | pH | Soluble Protein (%) | Surface Hydrophobicity | ABTS (μM TE/mg gelatin) | FRAP (μM TE/mg gelatin) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 7.00 ± 2.0 a | 27.6 ± 8.3 b | 62.1 ± 7.7 c | 539 ± 73 c | 112 ± 32 c |
| UPG-42 | 6.40 ± 0.2 b | 43.6 ± 1.2 a | 71.7 ± 6.5 b | 301 ± 88 d | 244 ± 50 b |
| UPG-52 | 6.30 ± 0.2 b | 27.4 ± 3.9 b | 75.2 ± 4.9 ab | 209 ± 28 d | 293 ± 15 b |
| UPG-71 | 6.08 ± 0.3 b | 43.7 ± 1.6 a | 66.5 ± 4.0 b | 698 ± 65 b | 385 ± 143 b |
| UPG-84 | 6.10 ± 0.2 b | 42.0 ± 2.9 a | 81.4 ± 6.3 a | 1001 ± 38 a | 732 ± 91 a |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cuevas-Acuña, D.A.; Arias-Moscoso, J.L.; Torres-Arreola, W.; Cadena-Cadena, F.; Valdez-Melchor, R.G.; Chaparro-Hernandez, S.; Santacruz-Ortega, H.d.C.; Ruiz-Cruz, S. High-Intensity Ultrasound Pulses Effect on Physicochemical and Antioxidant Properties of Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Skin Gelatin. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10031004
Cuevas-Acuña DA, Arias-Moscoso JL, Torres-Arreola W, Cadena-Cadena F, Valdez-Melchor RG, Chaparro-Hernandez S, Santacruz-Ortega HdC, Ruiz-Cruz S. High-Intensity Ultrasound Pulses Effect on Physicochemical and Antioxidant Properties of Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Skin Gelatin. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(3):1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10031004
Chicago/Turabian StyleCuevas-Acuña, Dulce Alondra, Joe Luis Arias-Moscoso, Wilfrido Torres-Arreola, Francisco Cadena-Cadena, Ramón Gertrudis Valdez-Melchor, Sarai Chaparro-Hernandez, Hisila del Carmen Santacruz-Ortega, and Saúl Ruiz-Cruz. 2020. "High-Intensity Ultrasound Pulses Effect on Physicochemical and Antioxidant Properties of Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Skin Gelatin" Applied Sciences 10, no. 3: 1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10031004
APA StyleCuevas-Acuña, D. A., Arias-Moscoso, J. L., Torres-Arreola, W., Cadena-Cadena, F., Valdez-Melchor, R. G., Chaparro-Hernandez, S., Santacruz-Ortega, H. d. C., & Ruiz-Cruz, S. (2020). High-Intensity Ultrasound Pulses Effect on Physicochemical and Antioxidant Properties of Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Skin Gelatin. Applied Sciences, 10(3), 1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10031004