Range Localization of a Moving Source Based on Synthetic Aperture Beamforming Using a Single Hydrophone in Shallow Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
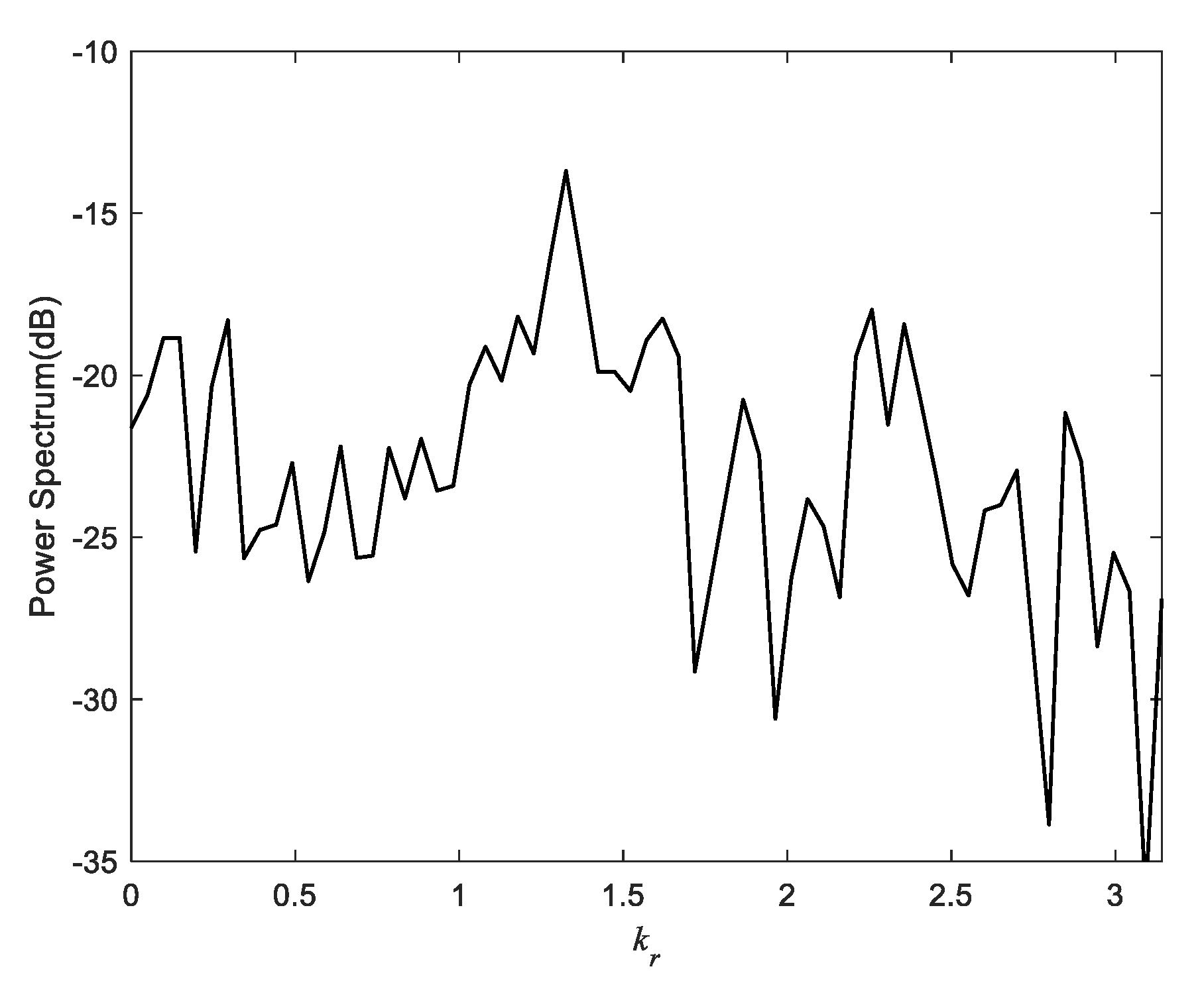
2. The Range Localization Method
3. Simulation and Results
4. SWellEx-96 Experimental Data Analysis
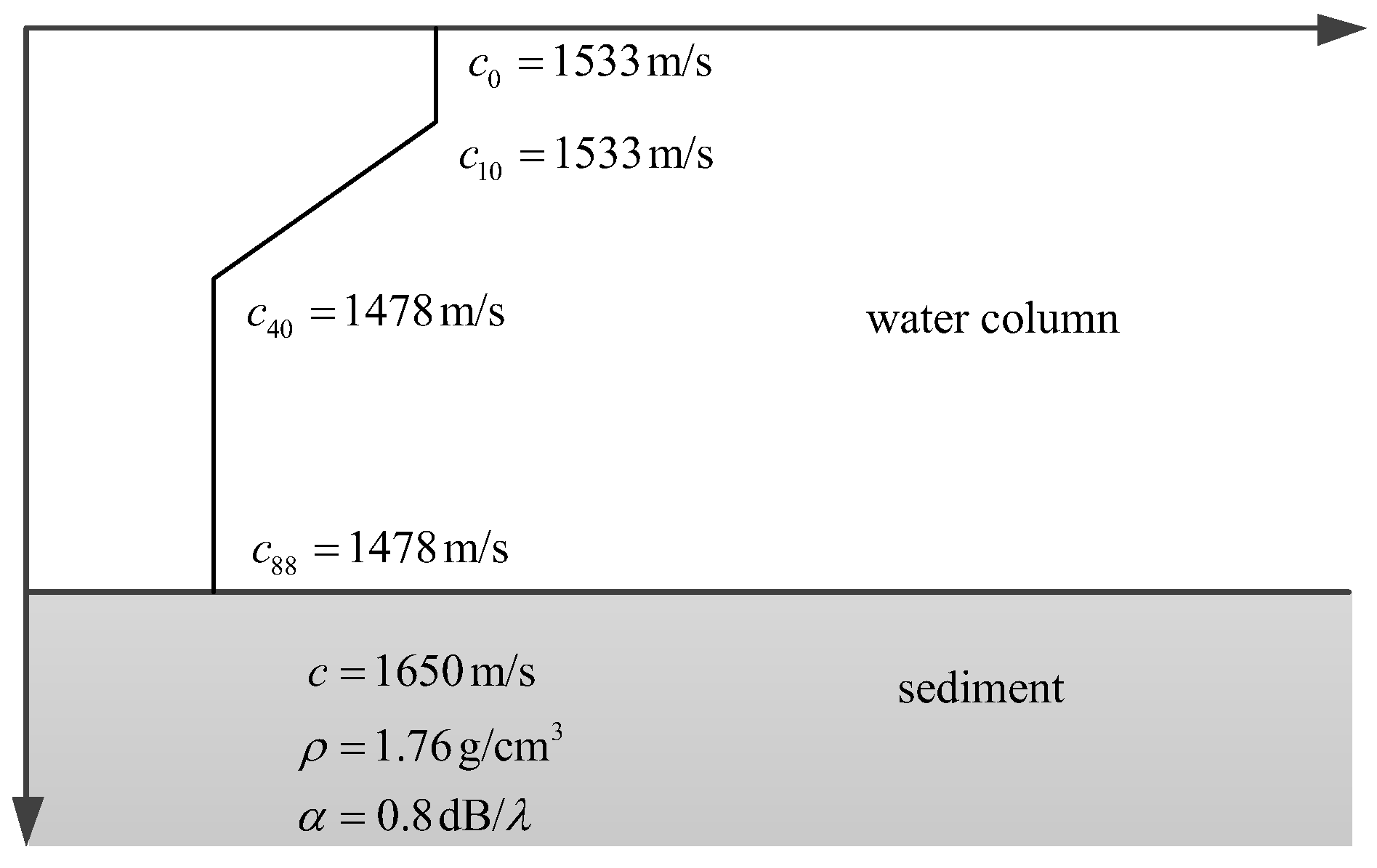
4.1. Experiment Description
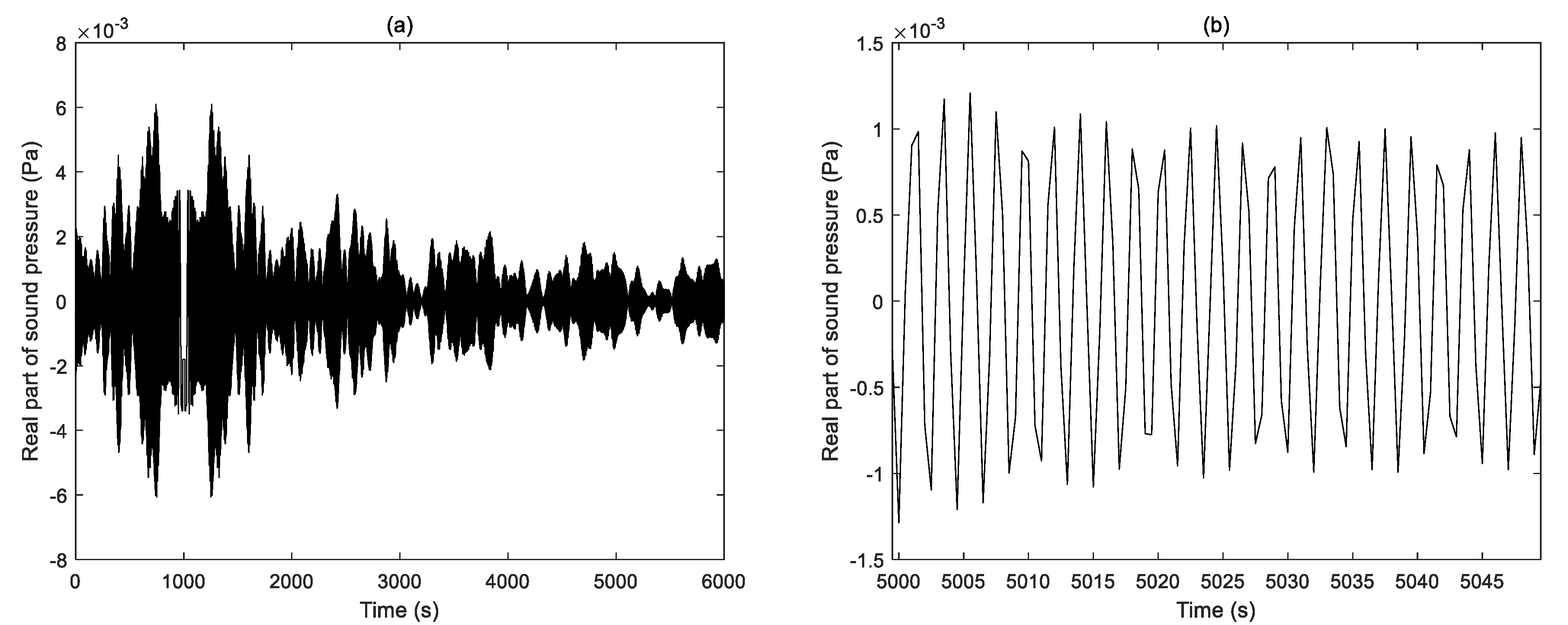
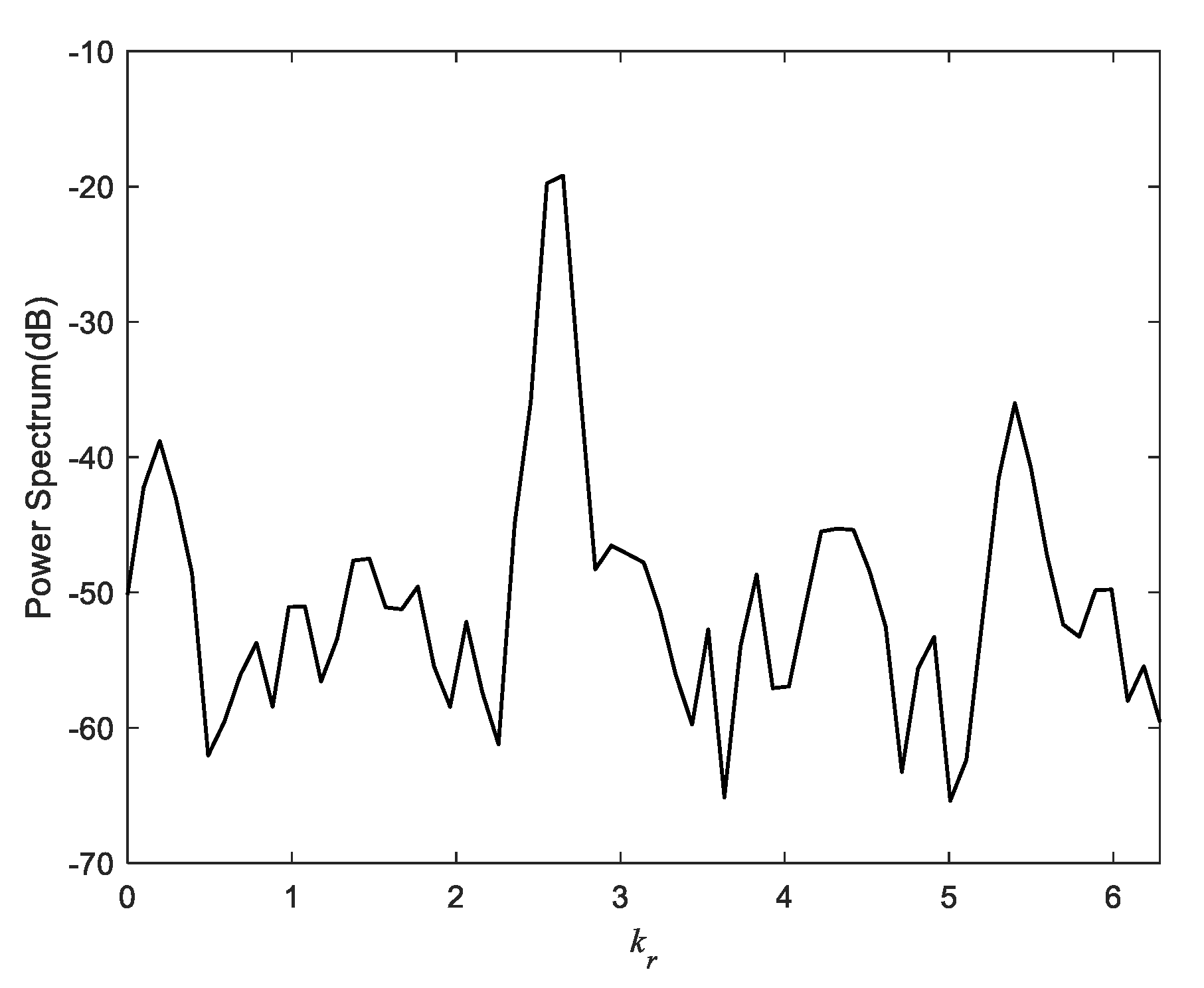
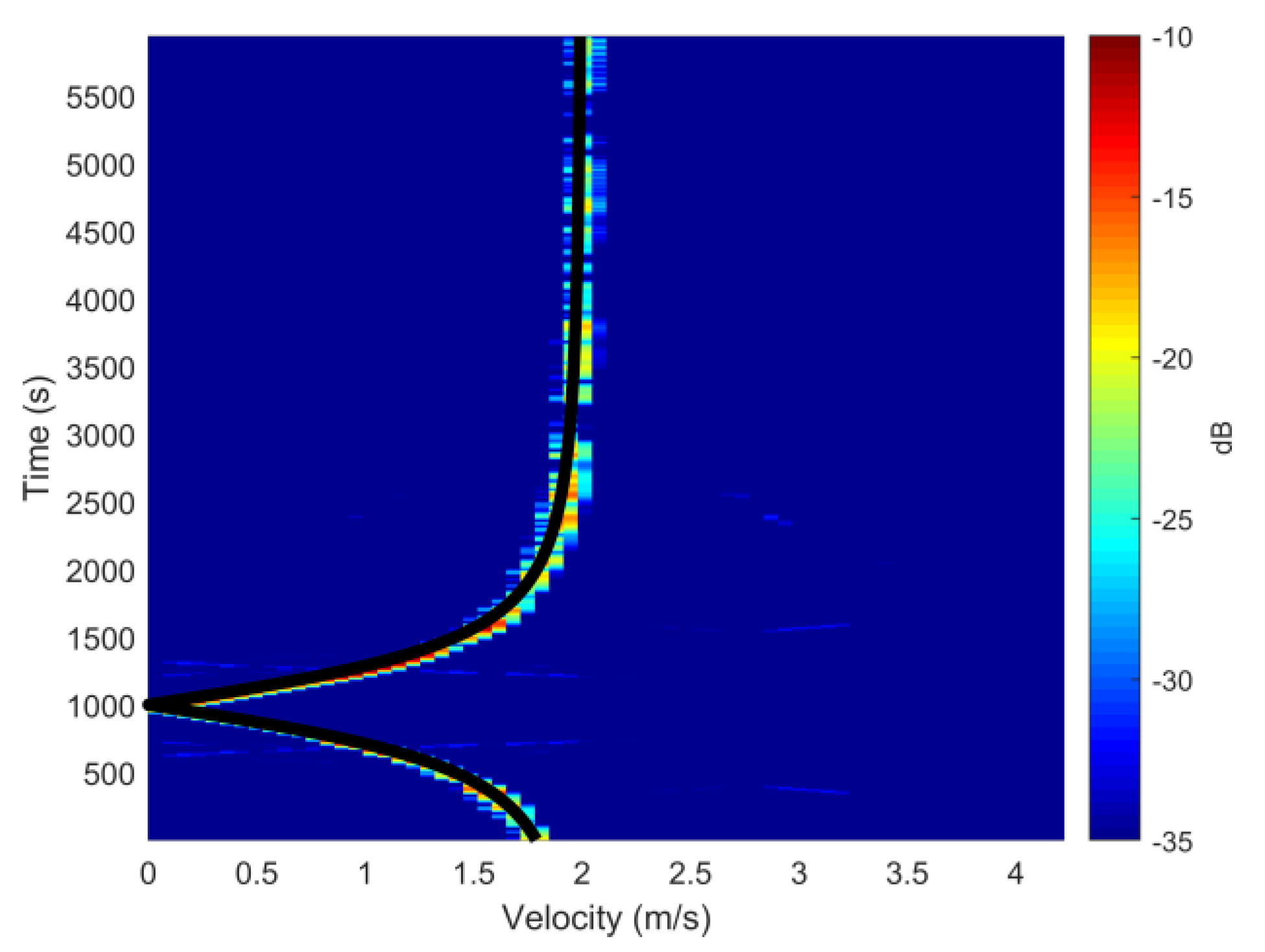
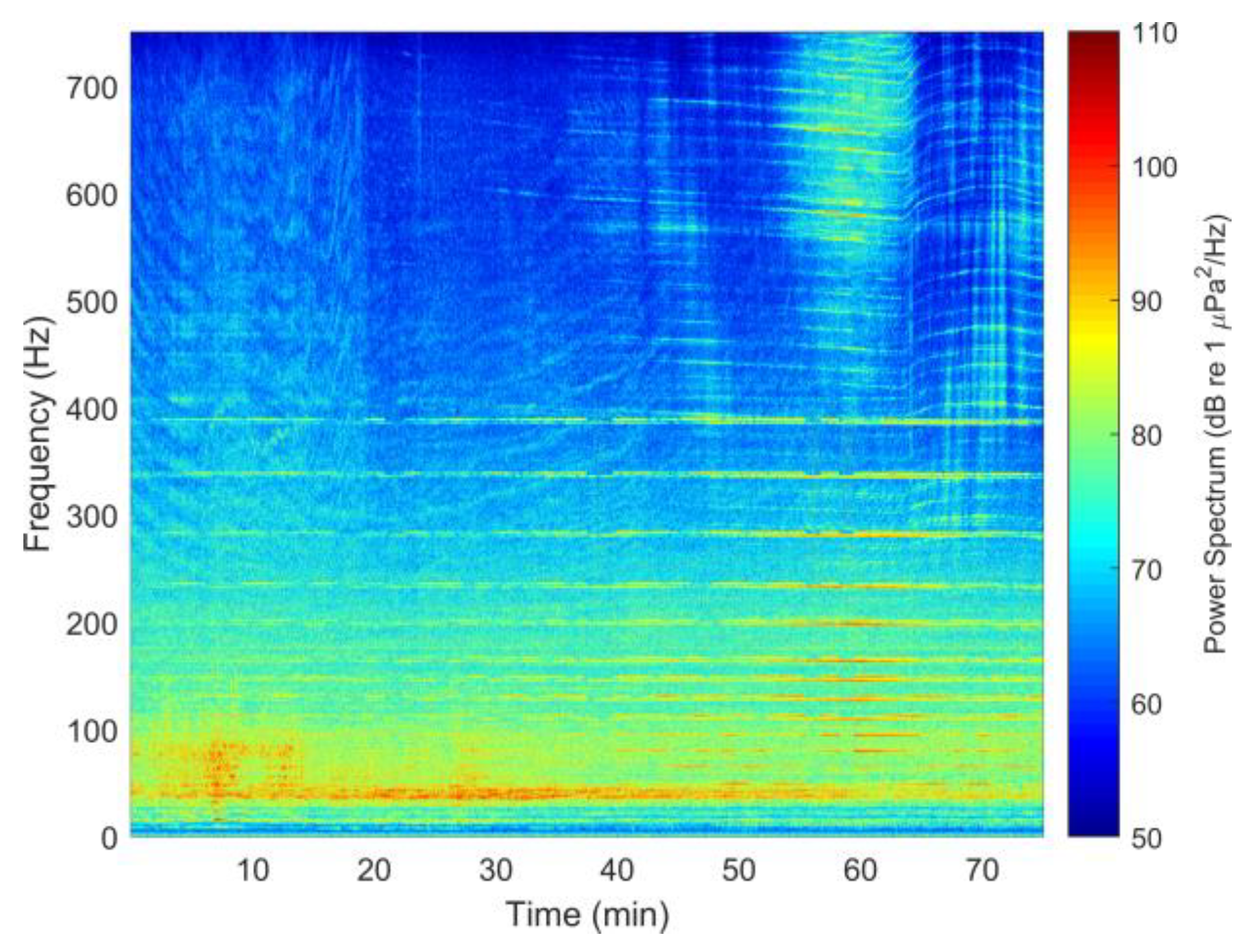
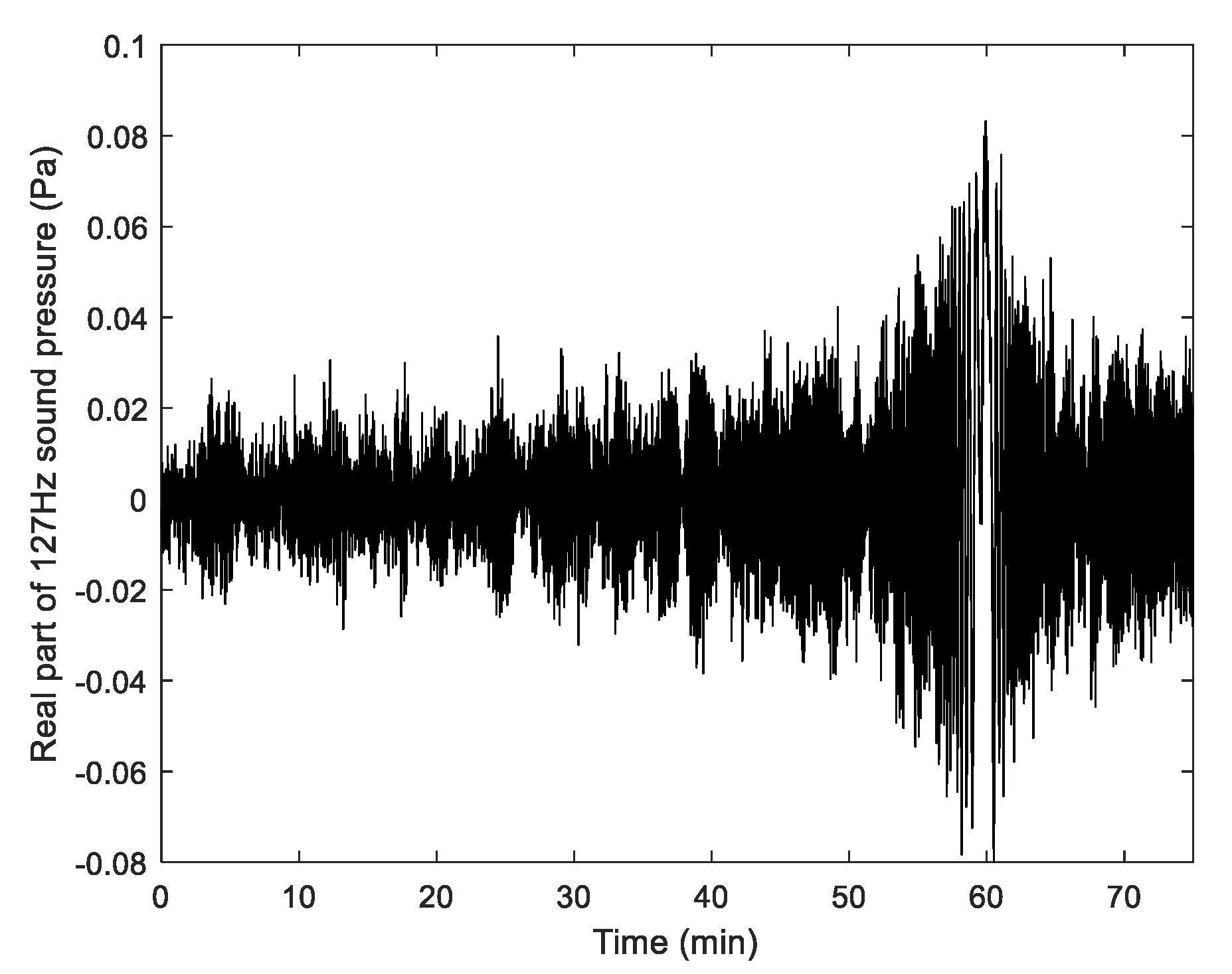
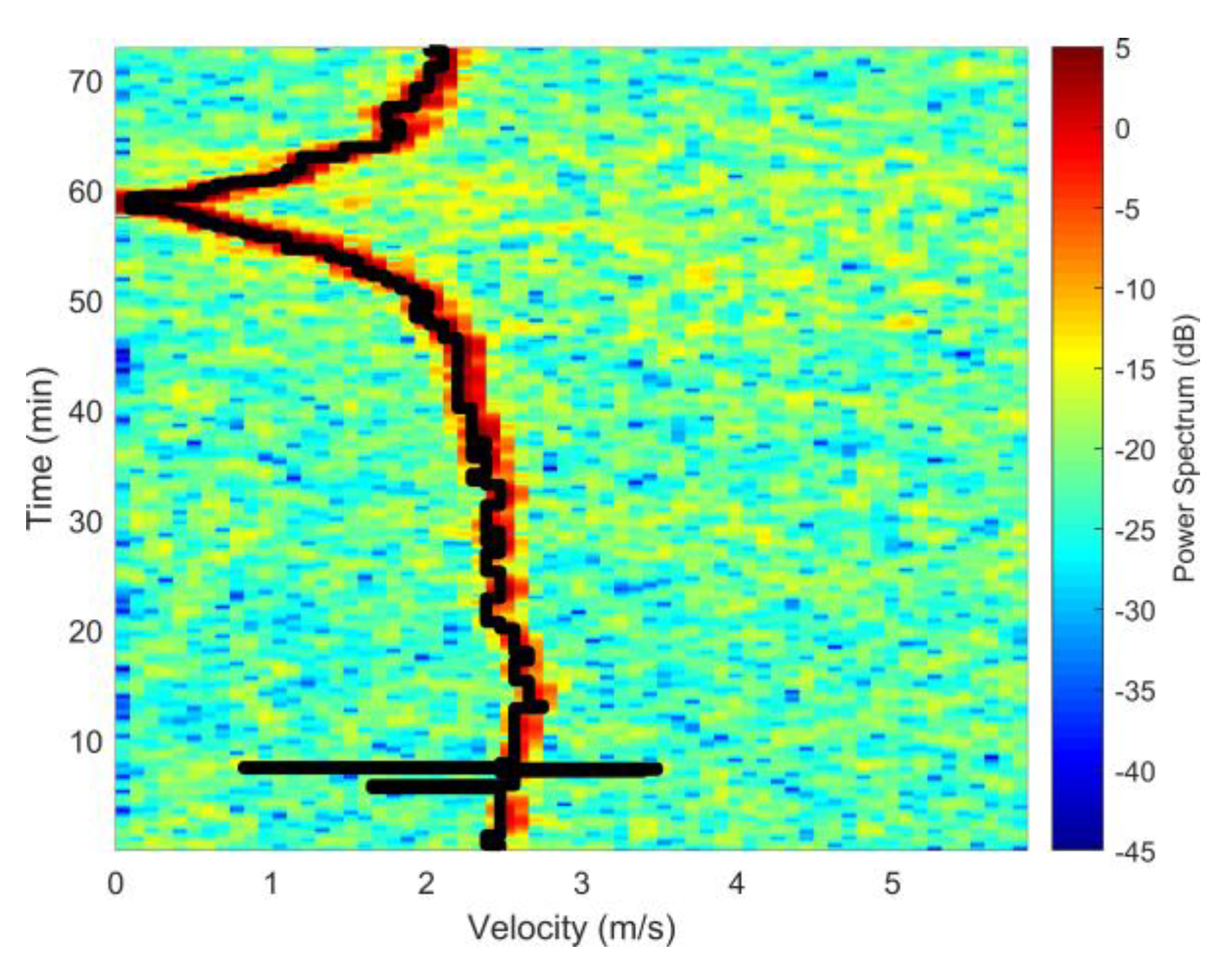
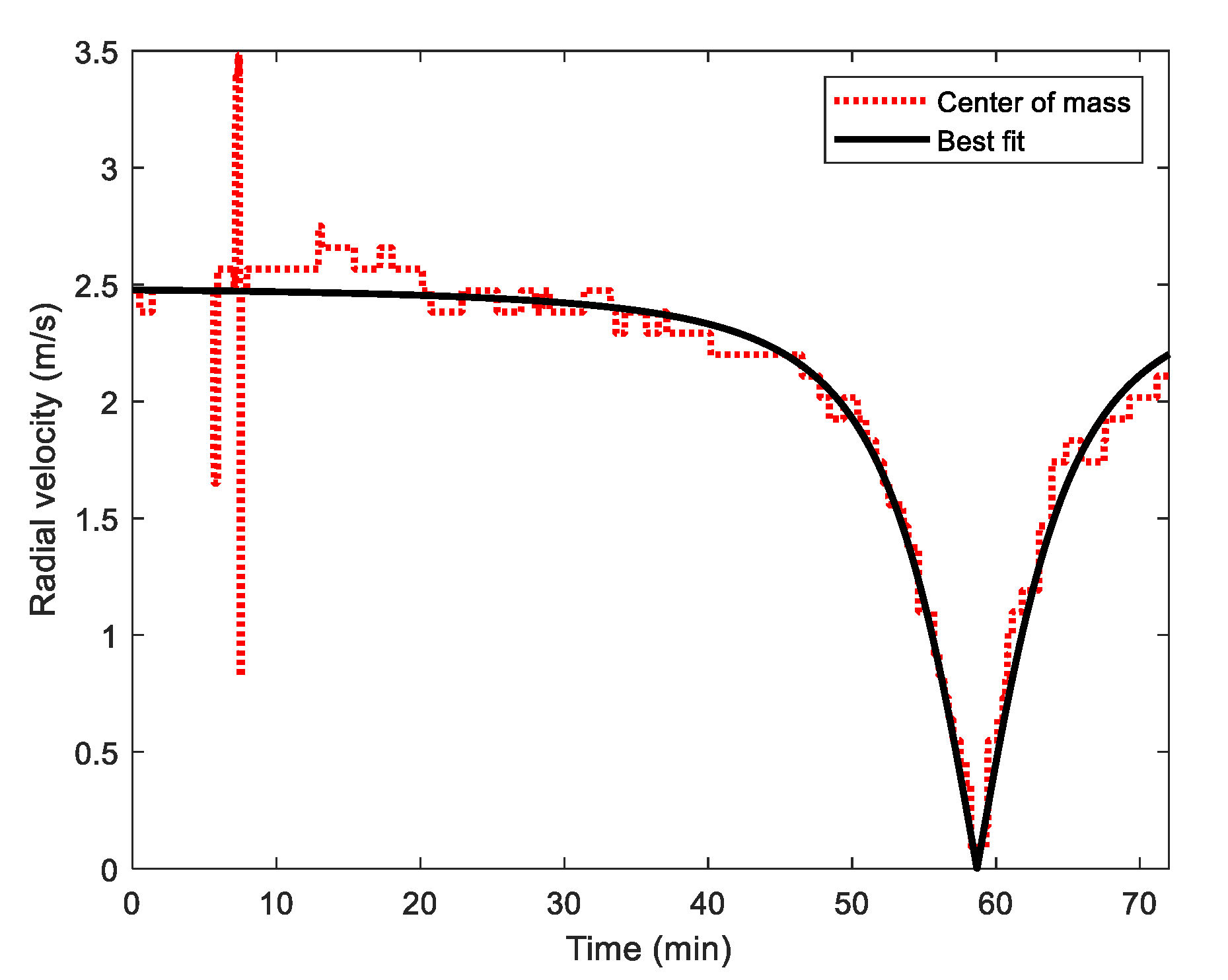
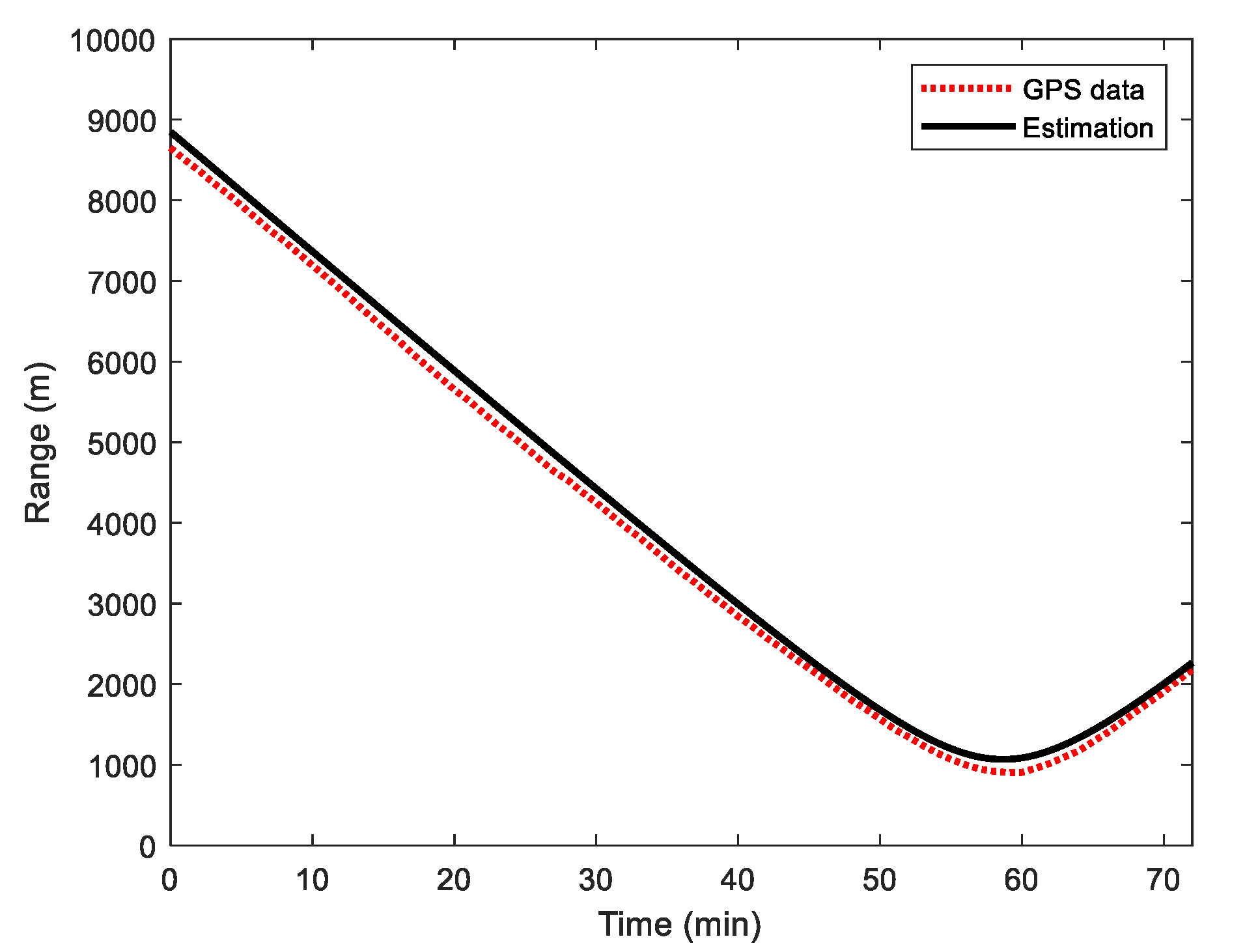
4.2. Data Processing Results and Analysis
4.2.1. Narrowband Source Range Localization
4.2.2. The Broadband Case
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bucker, H.P. Use of calculated sound fields and matched-field detection to locate sound sources in shallow water. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1976, 59, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggeroer, A.B.; Kuperman, W.A.; Mikhalevsky, P.N. An overview of matched field methods in ocean acoustics. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 1993, 18, 401–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, E.C.; Clay, C.S.; Wang, Y.Y. Passive harmonic source ranging in waveguides by using mode filter. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1985, 78, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.C. A method of range and depth estimation by modal decomposition. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1987, 82, 1736–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzo, D.R.D.; Feuillade, C.; Rowe, M.M. Effects of water-depth mismatch on matched-field localization in shallow water. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1988, 83, 2180–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolstoy, A. Sensitivity of matched field processing to sound-speed profile mismatch for vertical arrays in a deep water Pacific environment. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1989, 85, 2394–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zou, S. Robust adaptive matched field processing with environmental uncertainty. Acta Acust. 2006, 31, 255–262. [Google Scholar]
- Debever, C.; Kuperman, W.A. Robust matched-field processing using a coherent broadband white noise constraint processor. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2007, 122, 1979–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-W.; Sun, C.; Xiang, L.-F.; Yi, F. Robust source localization based on mode subspace reconstruction in uncertain shallow ocean environment. Acta Phys. Sin. 2014, 63, 034304. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.C. Data-based matched-mode source localization for a moving source. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2014, 135, 1218–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazer, L.N.; Pecholcs, P.I. Single-hydrophone localization. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1990, 88, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesus, S.M.; Porter, M.B.; Stephan, Y.; Demoulin, X.; Rodriguez, O.C.; Coelho, E.M.M.F. Single hydrophone source localization. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2000, 25, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cockrell, K.L.; Schmidt, H. Robust passive range estimation using the waveguide invariant. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2010, 127, 2780–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakotonarivo, S.T.; Kuperman, W.A. Model-independent range localization of a moving source in shallow water. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 132, 2218–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnel, J.; Thode, A.M.; Blackwell, S.B.; Kim, K.; Macrander, A.M. Range estimation of bowhead whale (Balaena mysticetus) calls in the Arctic using a single hydrophone. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2014, 136, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, G.; Kuz’kin, V.; Pereselkov, S. Spectrogram and localization of a sound source in shallow water. Acoust. Phys. 2017, 63, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.C. Source depth estimation based on synthetic aperture beamfoming for a moving source. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2015, 138, 1678–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisk, G.V.; Lynch, J.F.; Rajan, S.D. Determination of compressional wave speed profiles using modal inverse techniques in a range-dependent environment in Nantucket Sound. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1989, 86, 1928–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, A. Underwater Acoustic Propagation Modelling Software. Available online: https://cmst.curtin.edu.au/products/underwater/ (accessed on 17 December 2019).
- MPL. The SWellEx-96 Experiment. Available online: http://www.mpl.ucsd.edu/swellex96/index.htm (accessed on 10 October 2019).
- Sha, L.; Nolte, L.W. Bayesian sonar detection performance prediction with source position uncertainty using SWellEx-96 vertical array data. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2006, 31, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalopoulou, Z.-H. Matched-impulse-response processing for shallow-water localization and geoacoustic inversion. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2000, 108, 2082–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yardim, C.; Gerstoft, P.; Hodgkiss, W.S. Geoacoustic and source tracking using particle filtering: Experimental results. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2010, 128, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musil, M.; Chapman, N.R.; Wilmut, M.J. Range-dependent matched-field inversion of SWellEX-96 data using the downhill simplex algorithm. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1999, 106, 3270–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, J.-Y.; Liu, Z.-W.; Lü, L.-G. Range Localization of a Moving Source Based on Synthetic Aperture Beamforming Using a Single Hydrophone in Shallow Water. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10031005
Du J-Y, Liu Z-W, Lü L-G. Range Localization of a Moving Source Based on Synthetic Aperture Beamforming Using a Single Hydrophone in Shallow Water. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(3):1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10031005
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Jin-Yan, Zong-Wei Liu, and Lian-Gang Lü. 2020. "Range Localization of a Moving Source Based on Synthetic Aperture Beamforming Using a Single Hydrophone in Shallow Water" Applied Sciences 10, no. 3: 1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10031005
APA StyleDu, J.-Y., Liu, Z.-W., & Lü, L.-G. (2020). Range Localization of a Moving Source Based on Synthetic Aperture Beamforming Using a Single Hydrophone in Shallow Water. Applied Sciences, 10(3), 1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10031005




