Numerical Investigation of Erosion Wear in the Hydraulic Amplifier of the Deflector Jet Servo Valve
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
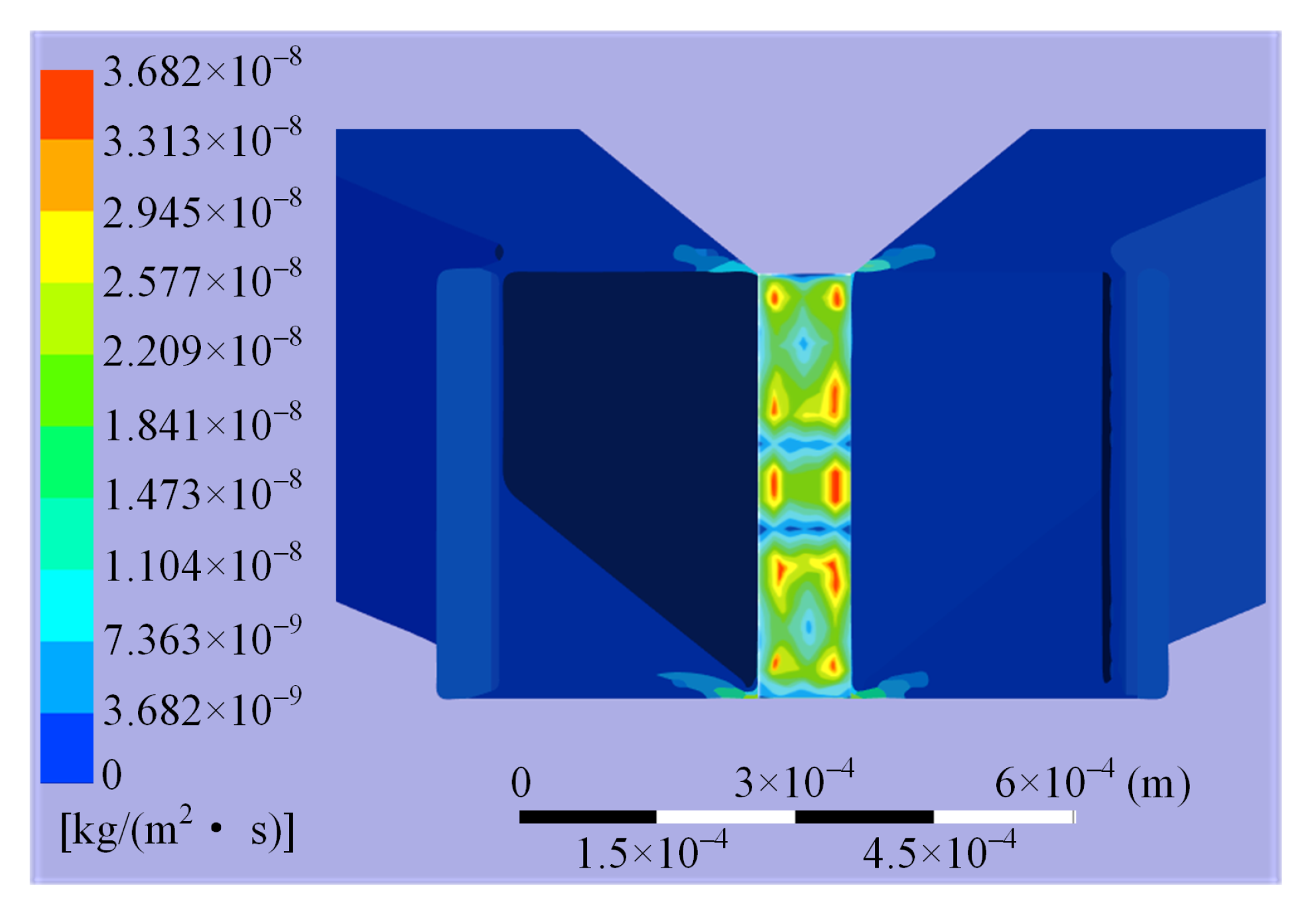
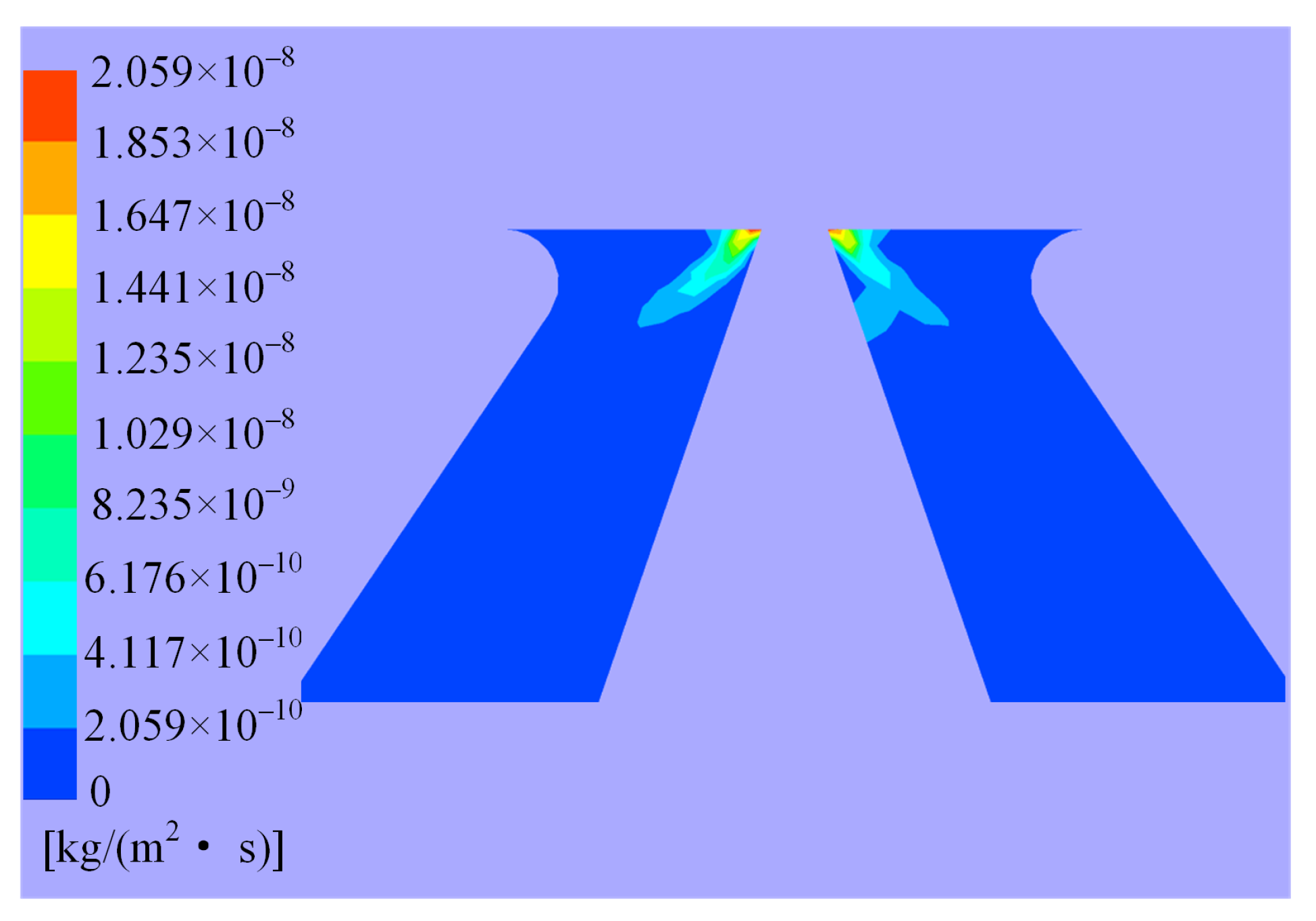
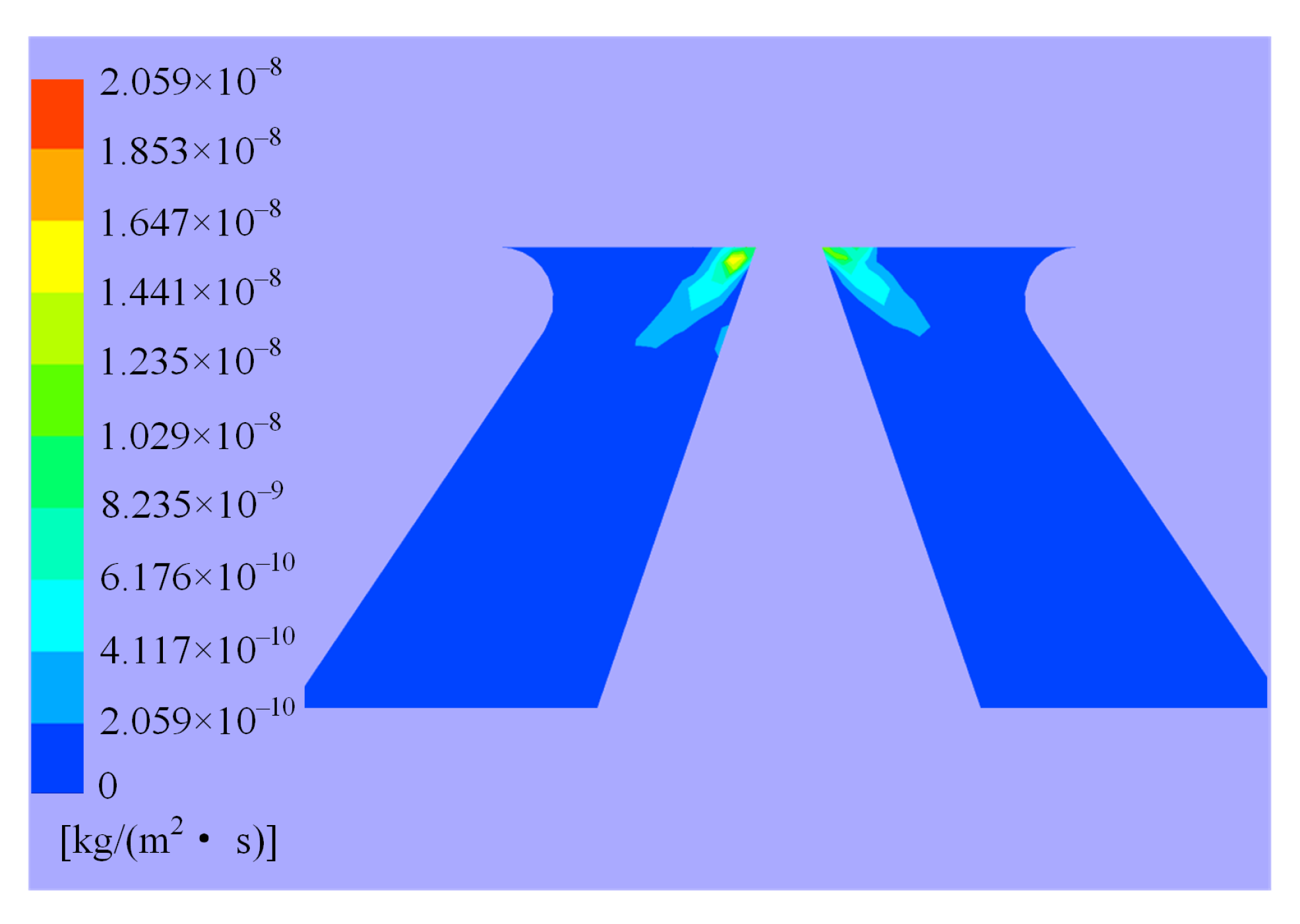
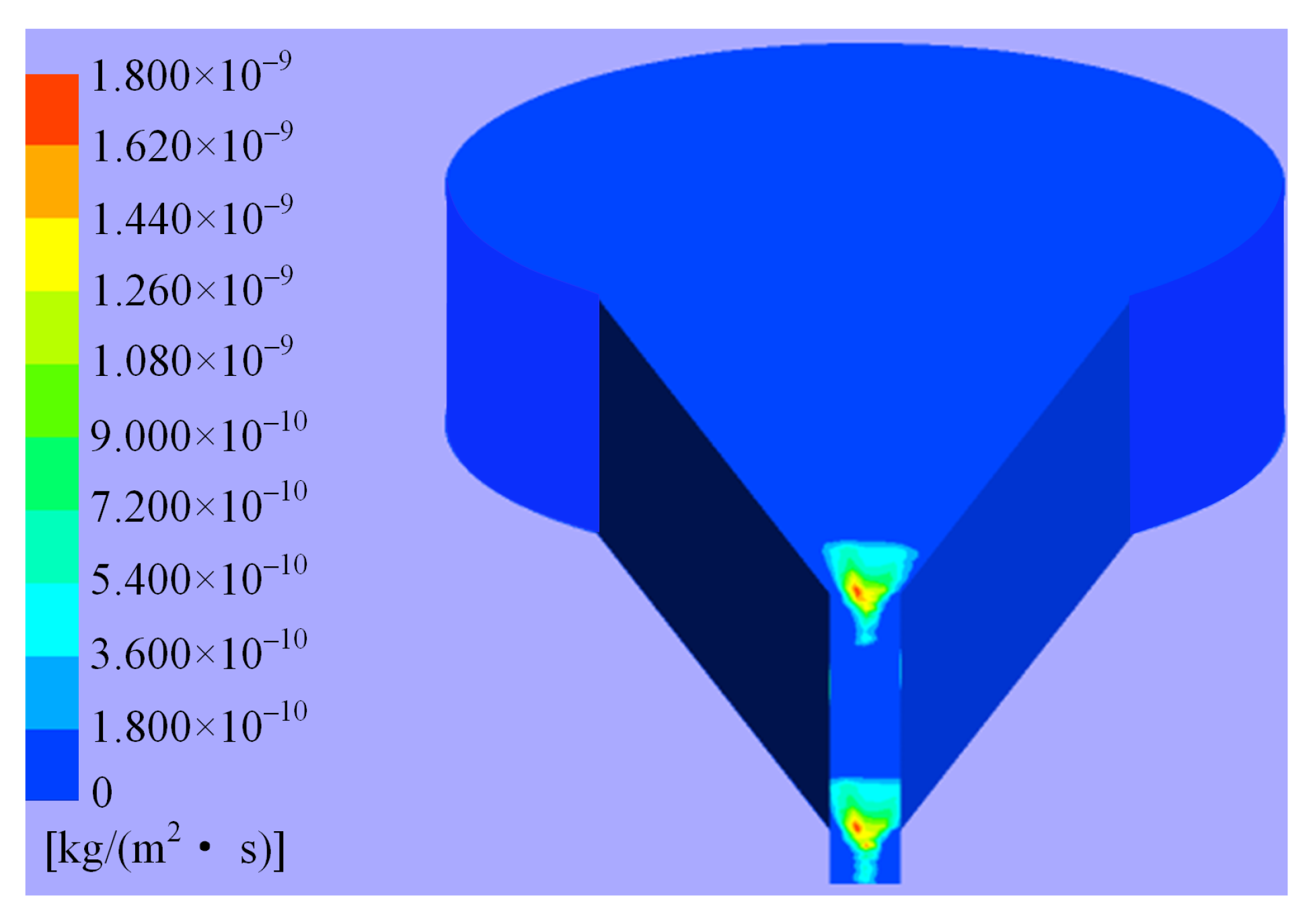
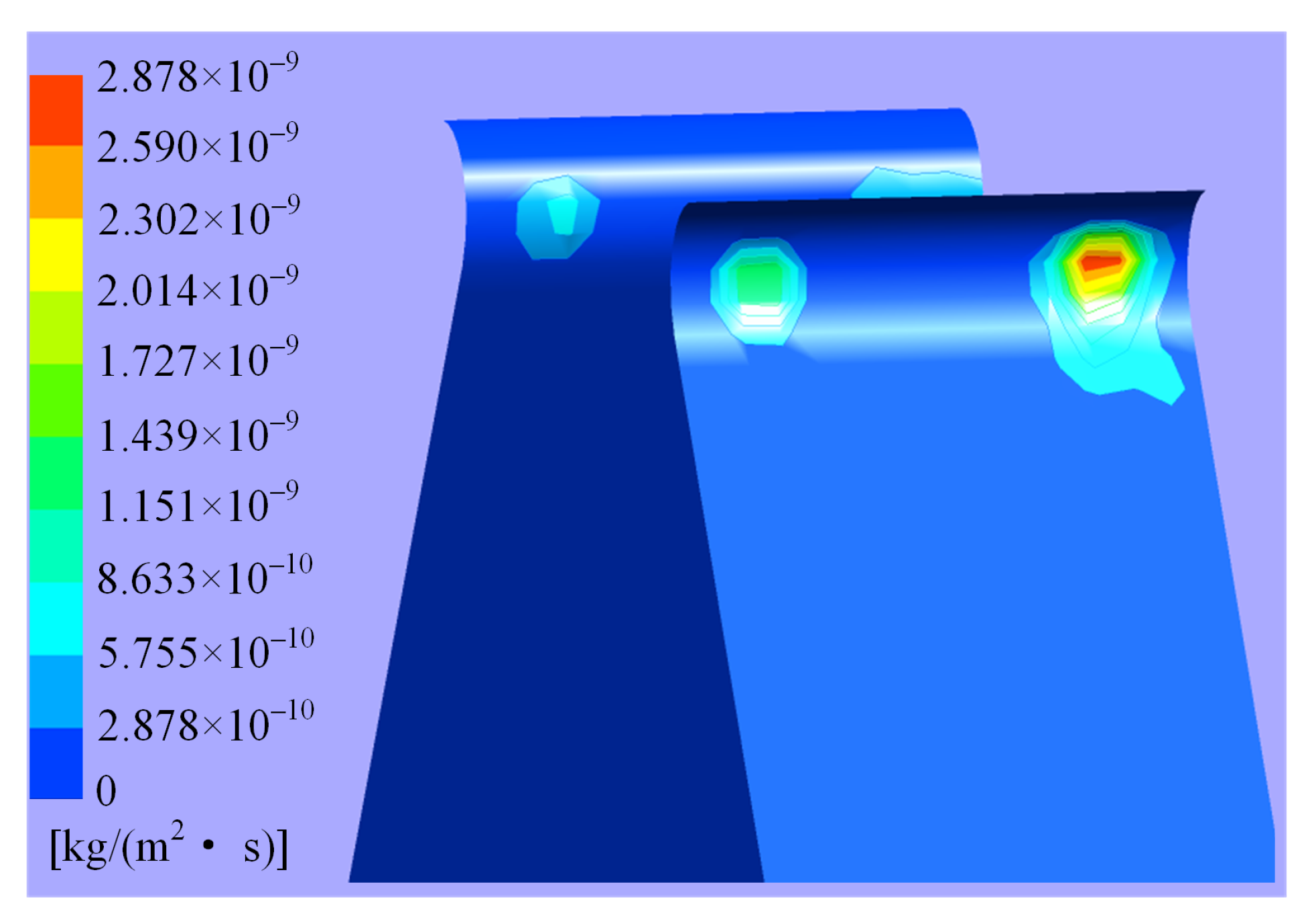
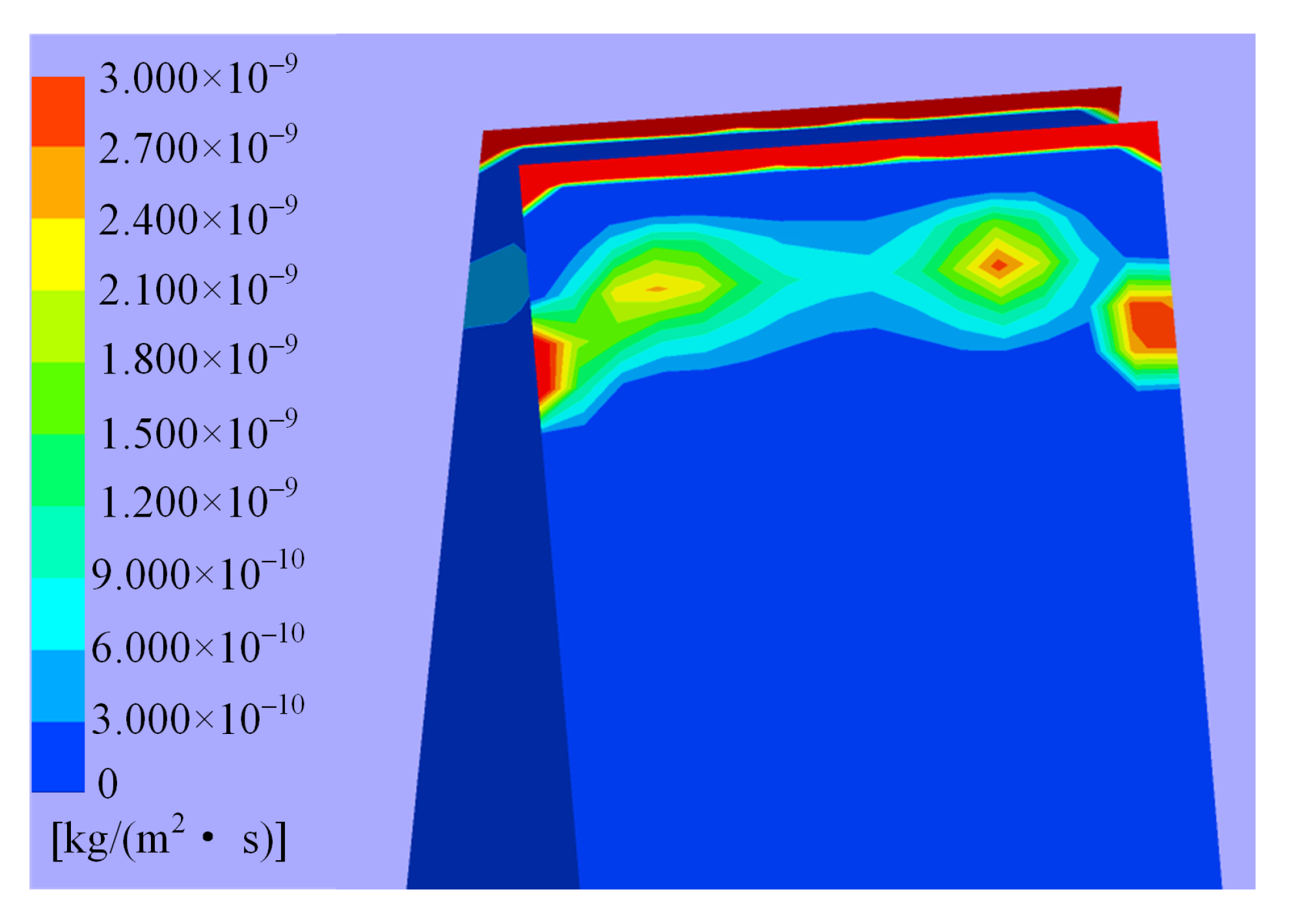
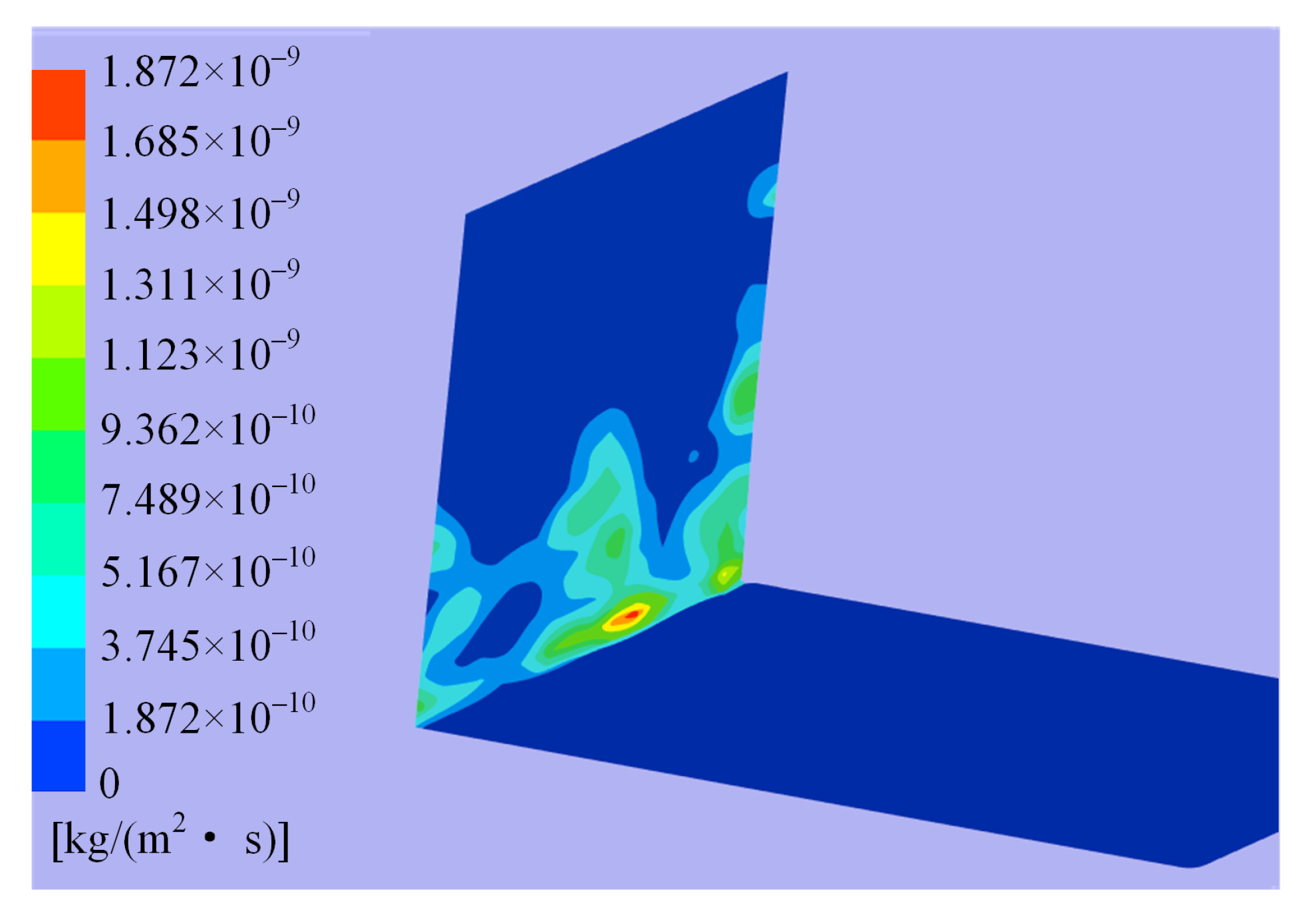
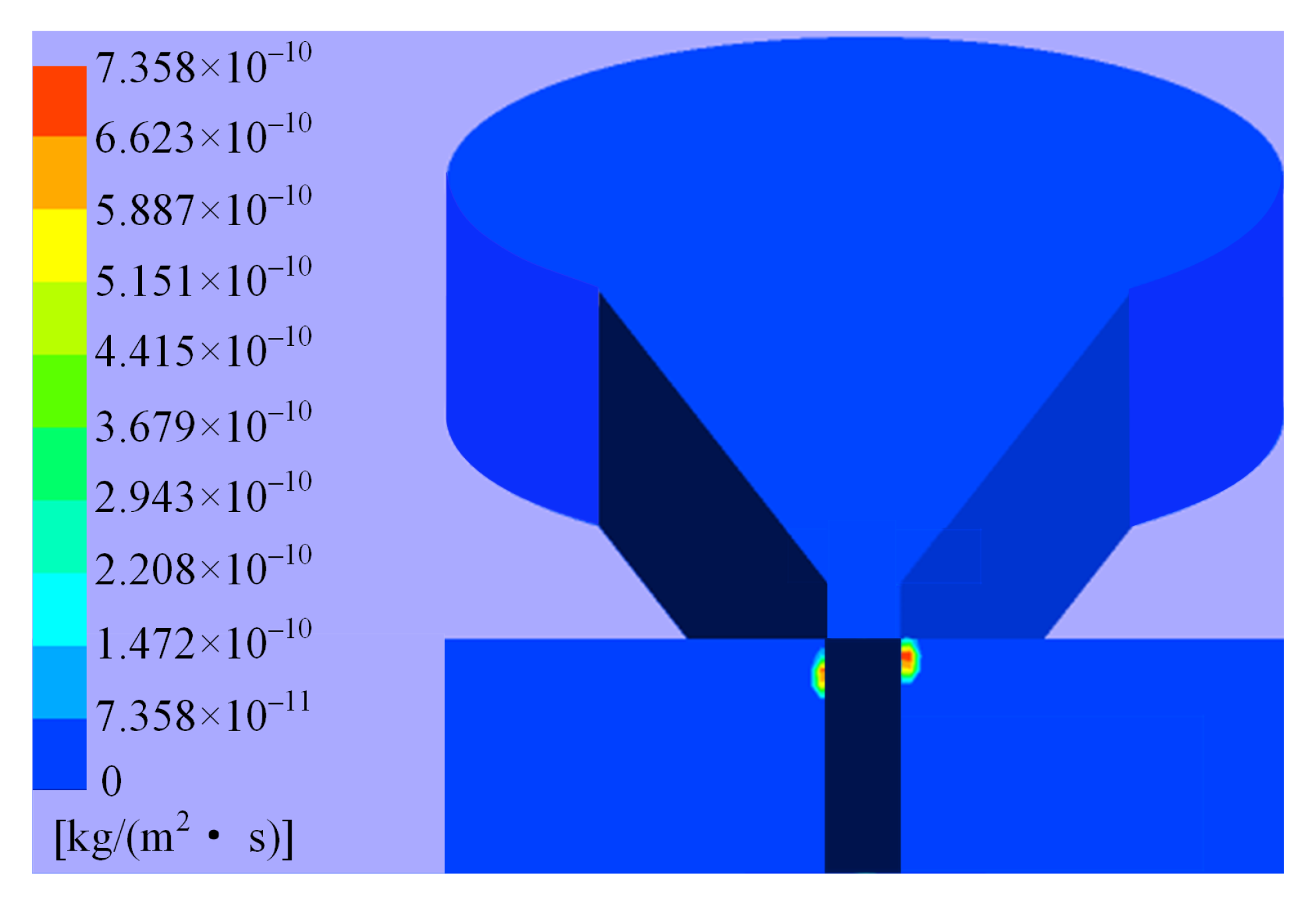
- It is found that the erosion wear in the hydraulic amplifier can be divided into four levels according to the order of magnitude of erosion rates, and the major erosion is determined to happen on the shunt wedge.
- (2)
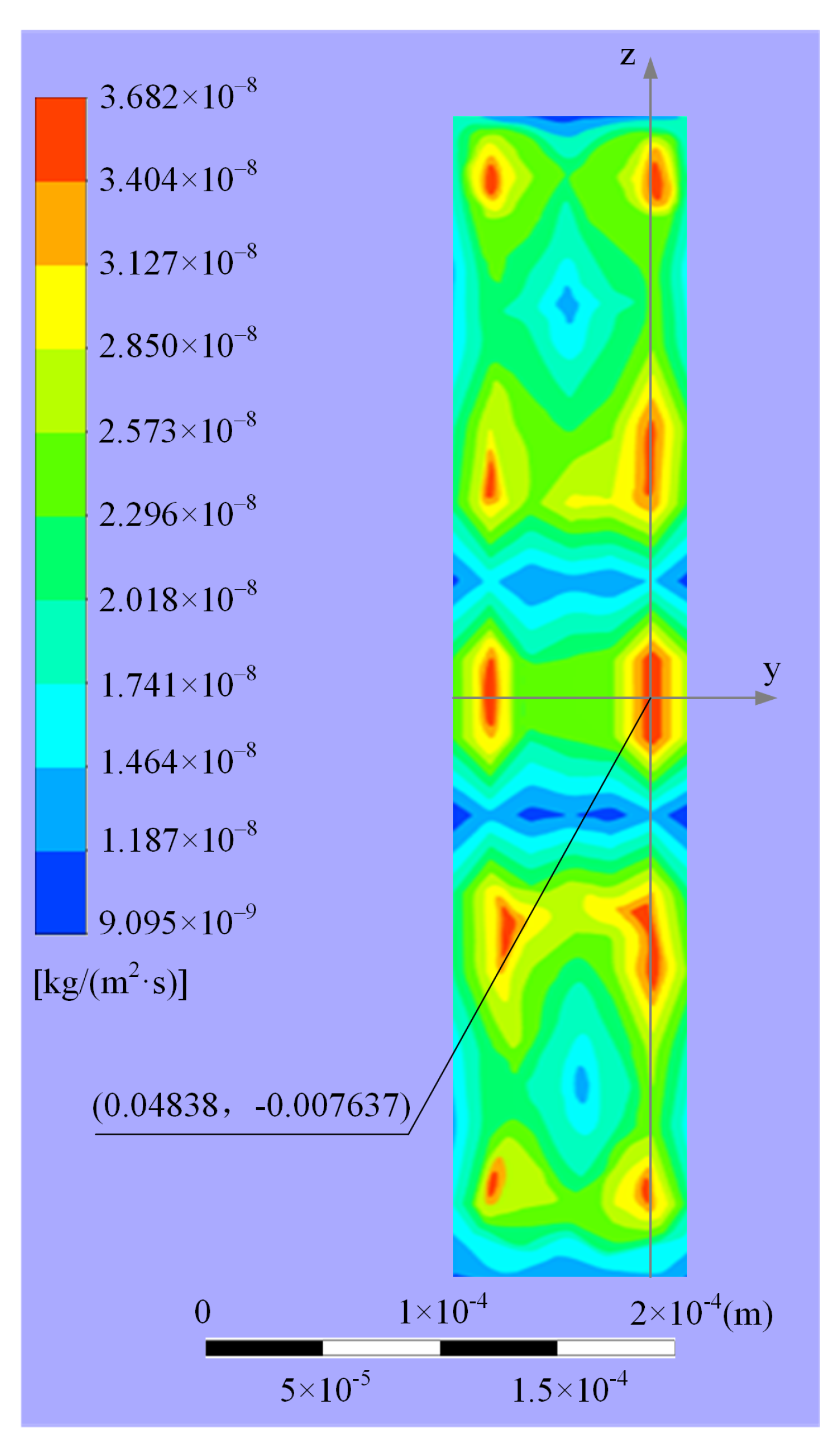
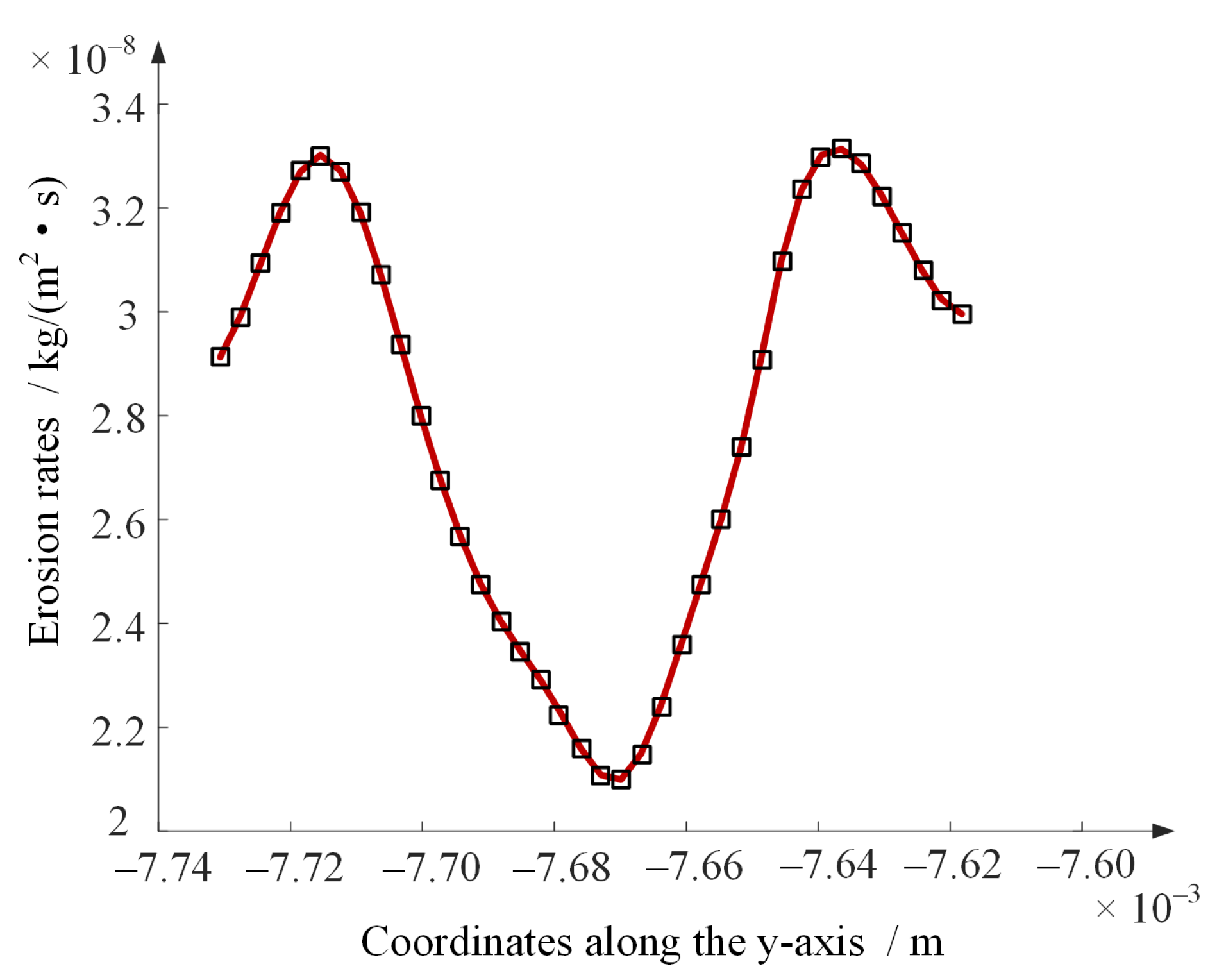
- It is observed that the erosion distribution on the shunt wedge caused by jet impact is characterized by regular fluctuations, and there exist multiple relative maximums of erosion rates occurring at places deviating from the jet center.
- (3)
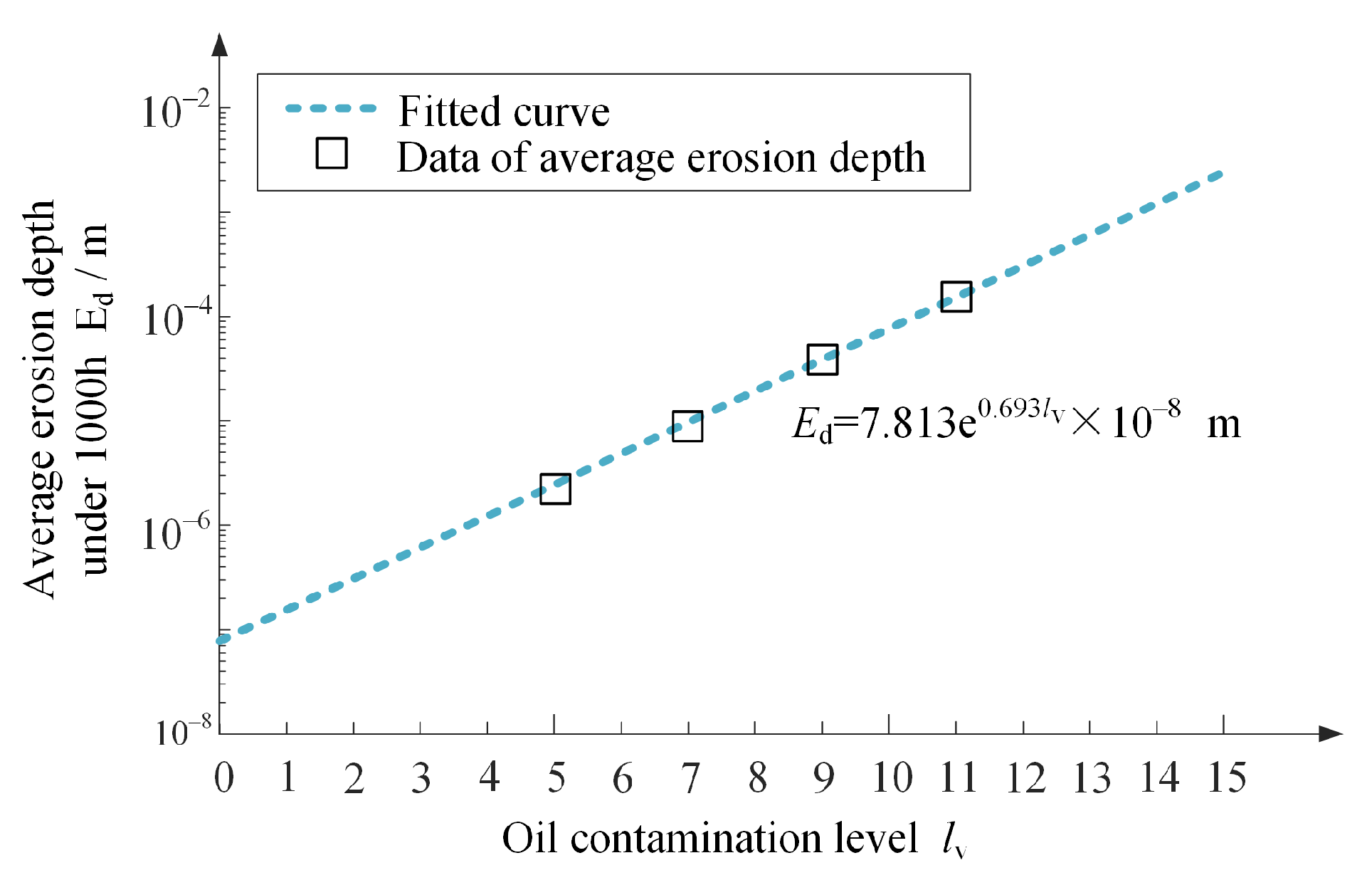
- The correlation between the contamination level of hydraulic oil and the extent of erosion wear is depicted and formulated mathematically, giving an intuitive means for understanding the erosion wear in DJVs.
- (4)
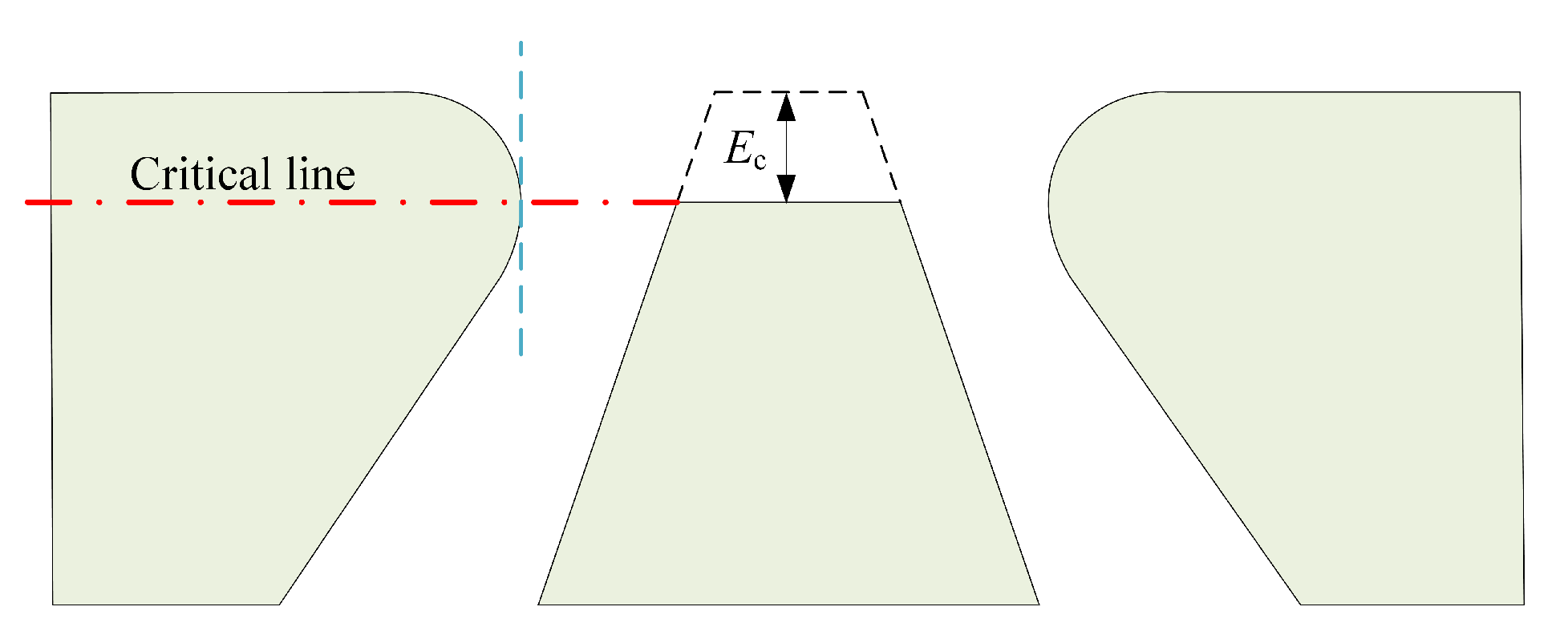
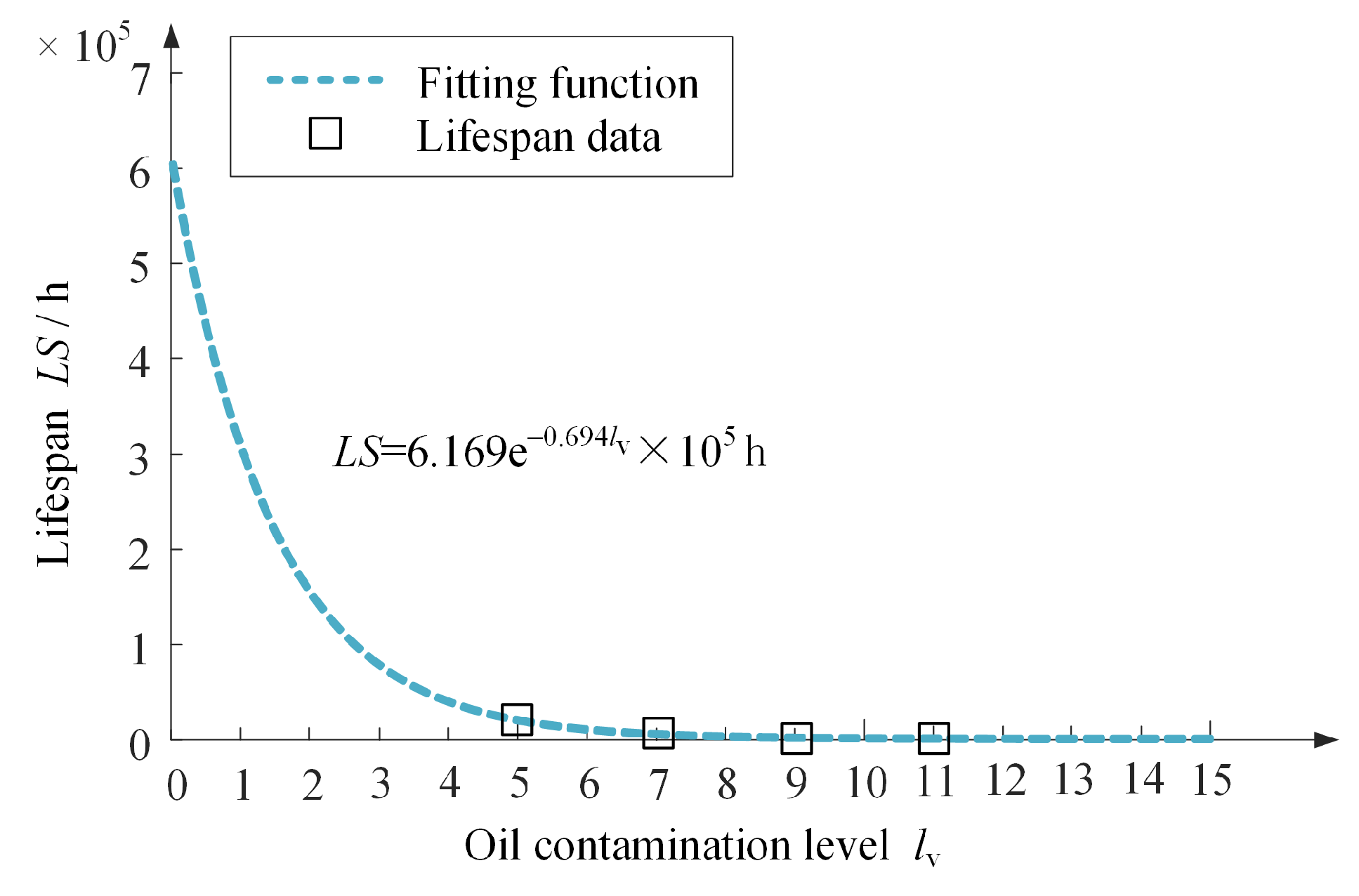
- A new failure criterion of DJVs is proposed and the lifespan prediction method is presented, which will aid in balancing the economy and the durability in DJV application.
2. Formulation of Erosion in Pilot Hydraulic Amplifier
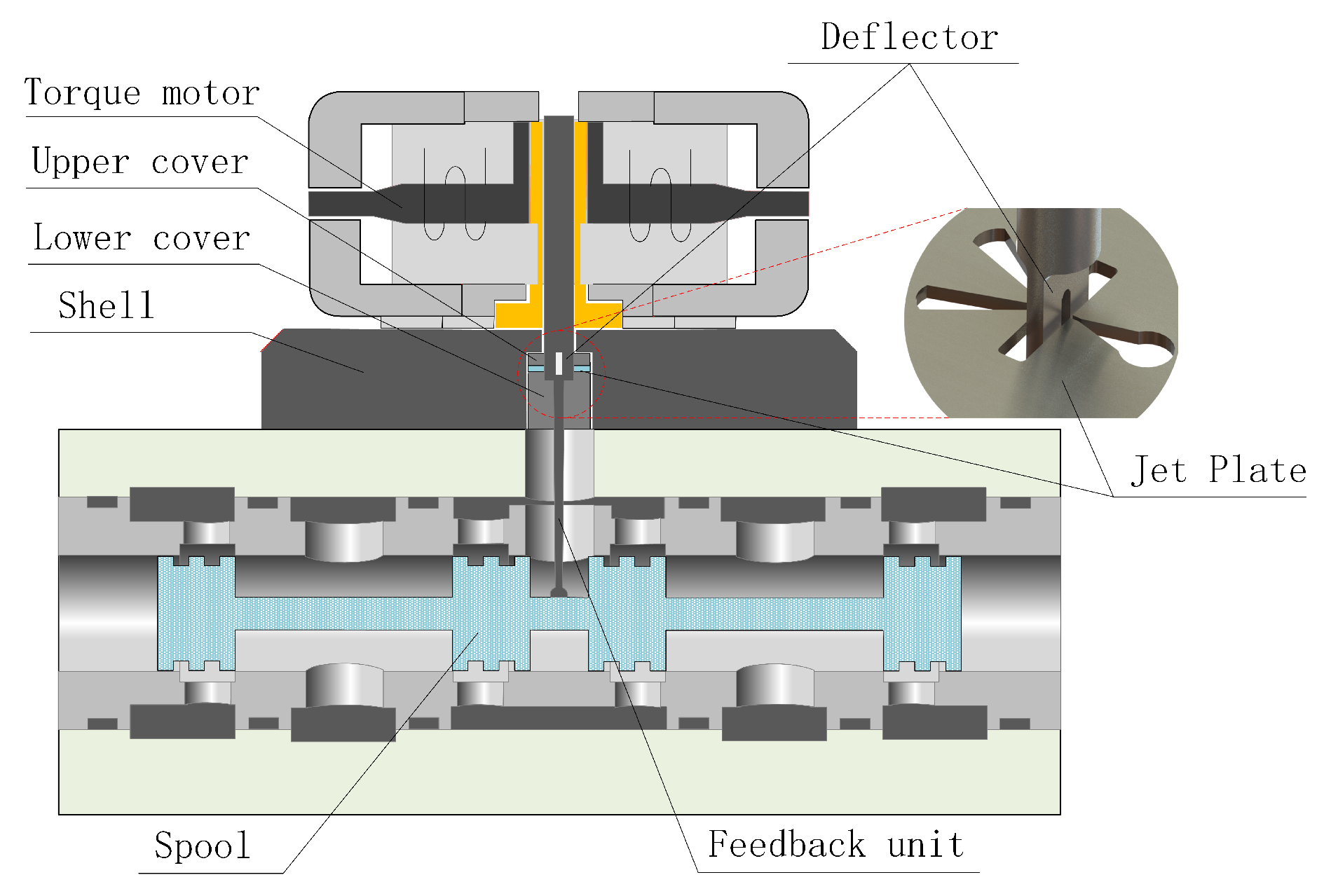
2.1. Mechanism of Hydraulic Amplifier Driving the Spool Valve
2.2. Erosion Wear in Hydraulic Amplifier
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Rans Simulation Method of Fluid
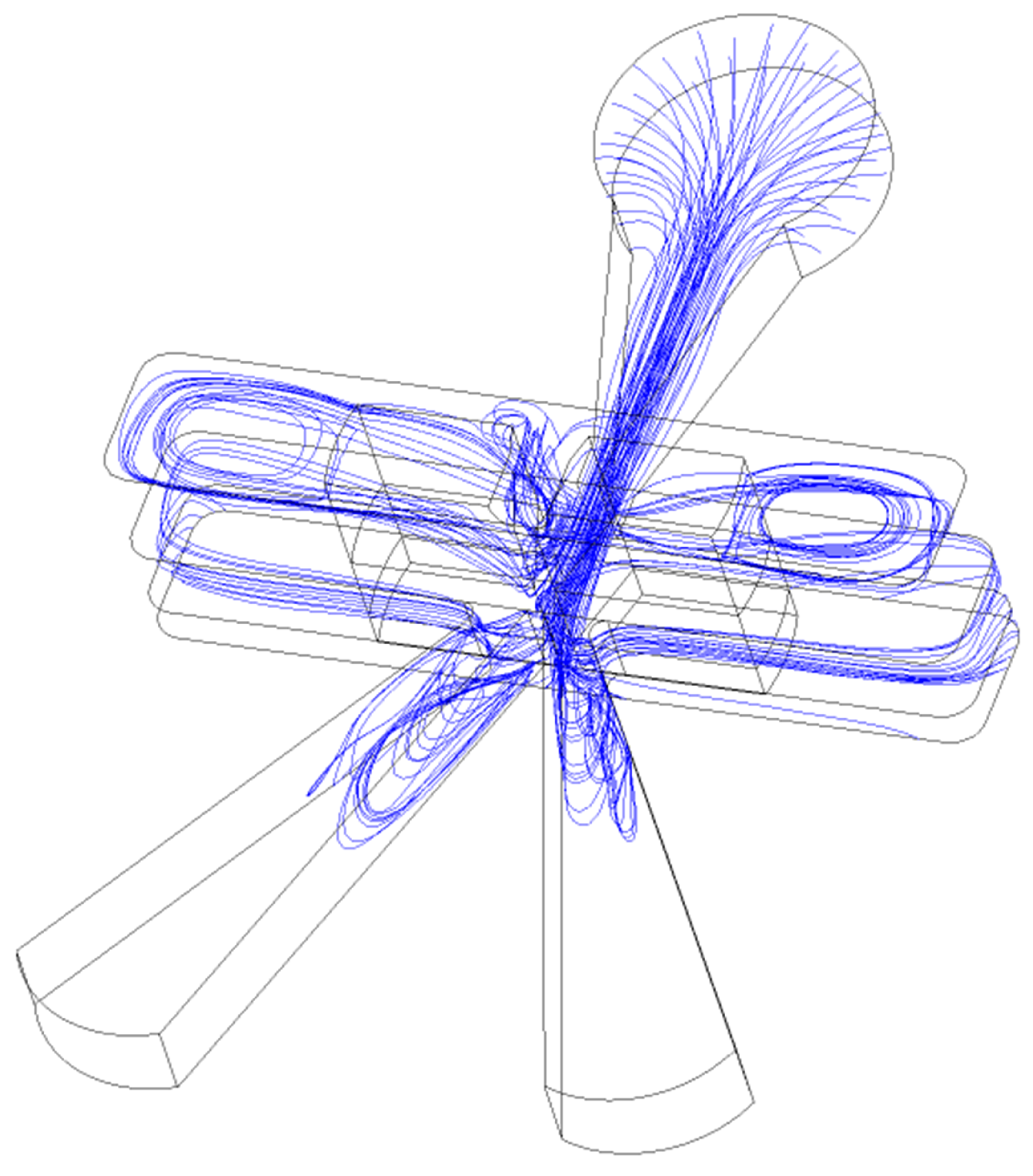
3.2. Particle Trajectory Generation
3.3. Erosion Rate Model
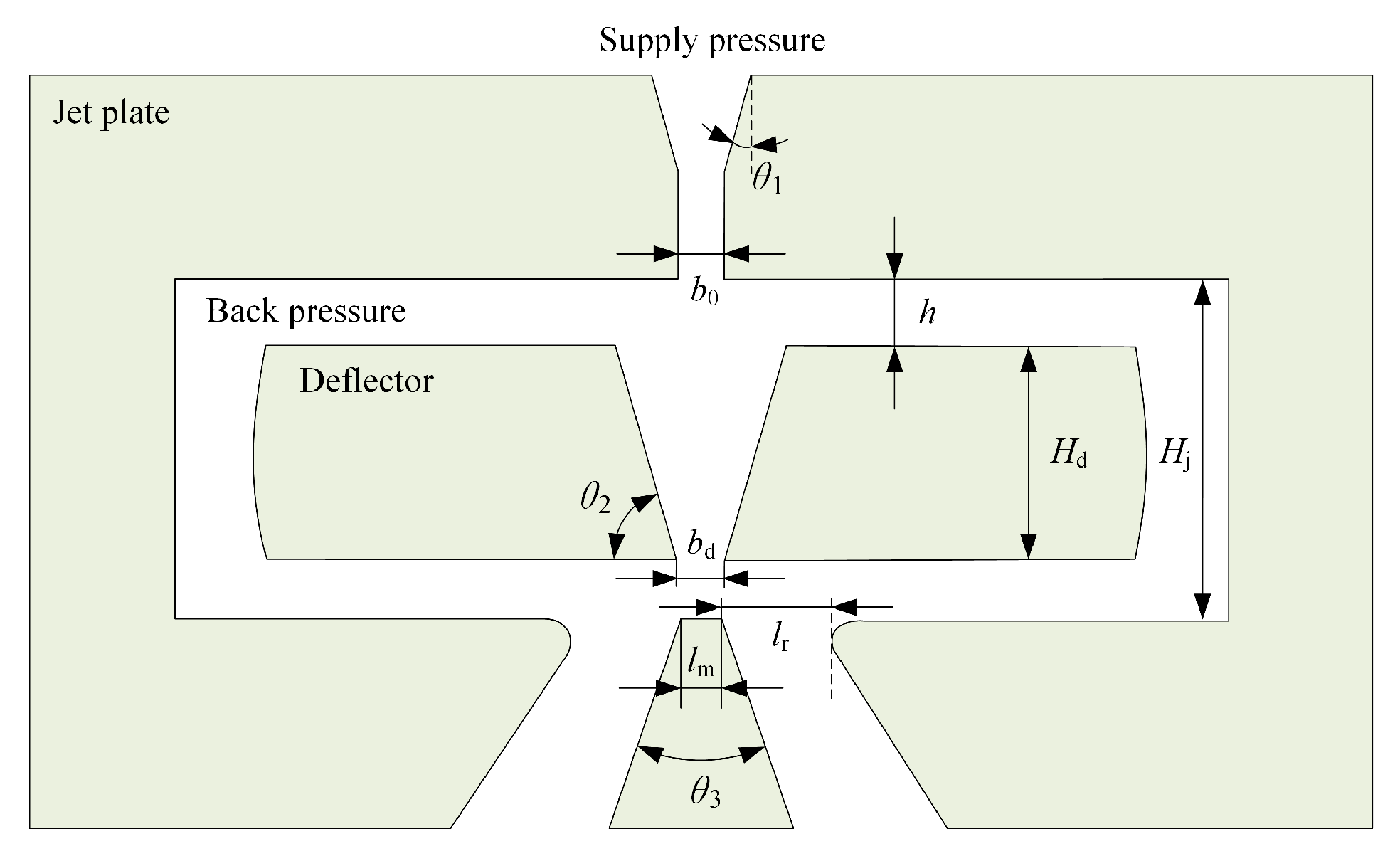
3.4. Numerical Modelling of Deflector Jet Mechanism
4. Results and Discussion
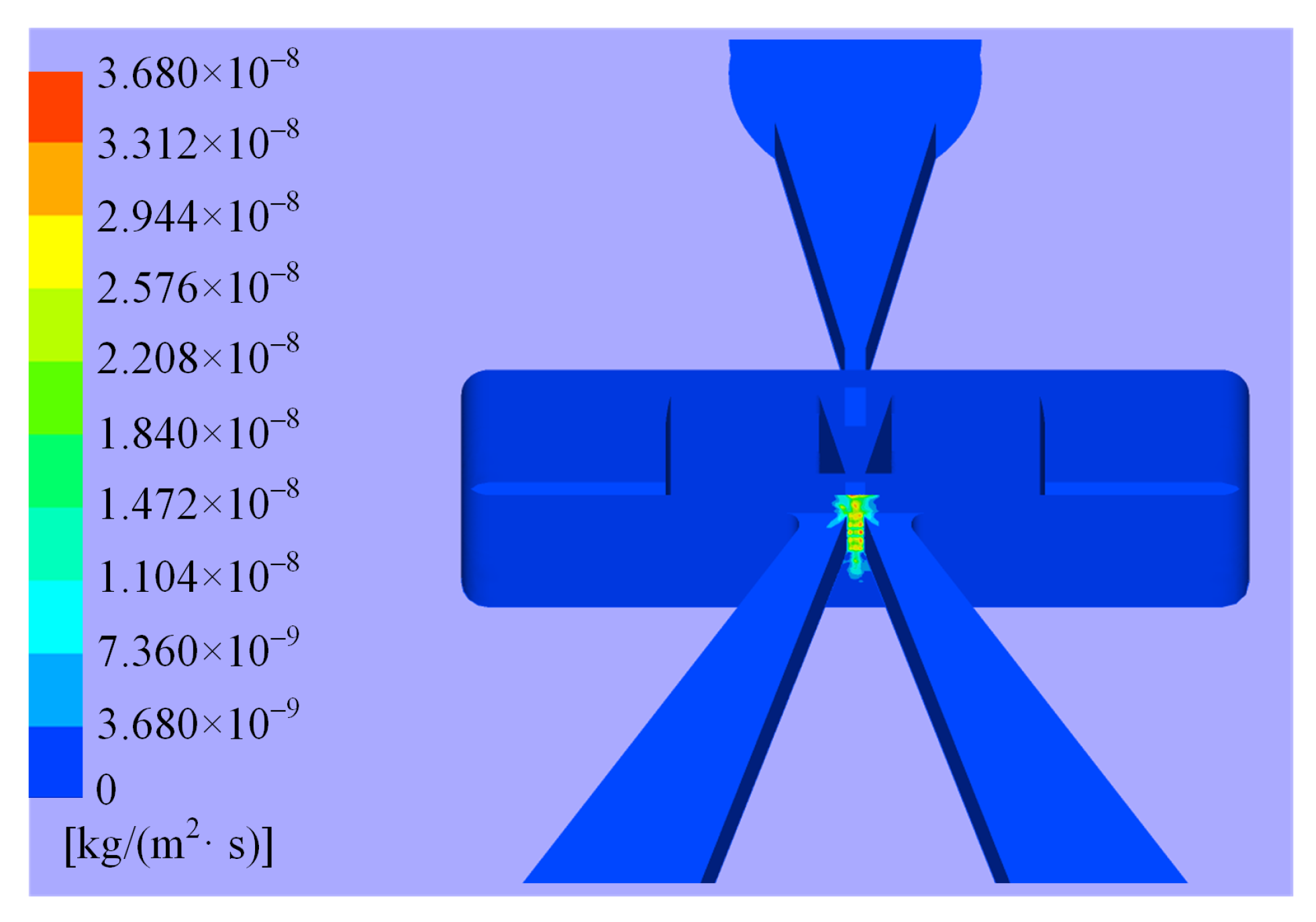
4.1. Distribution of Erosion in Valve
4.2. Characteristics of Major Erosion Wear
4.3. Correlation Between Oil Contamination Level and Erosion Wear
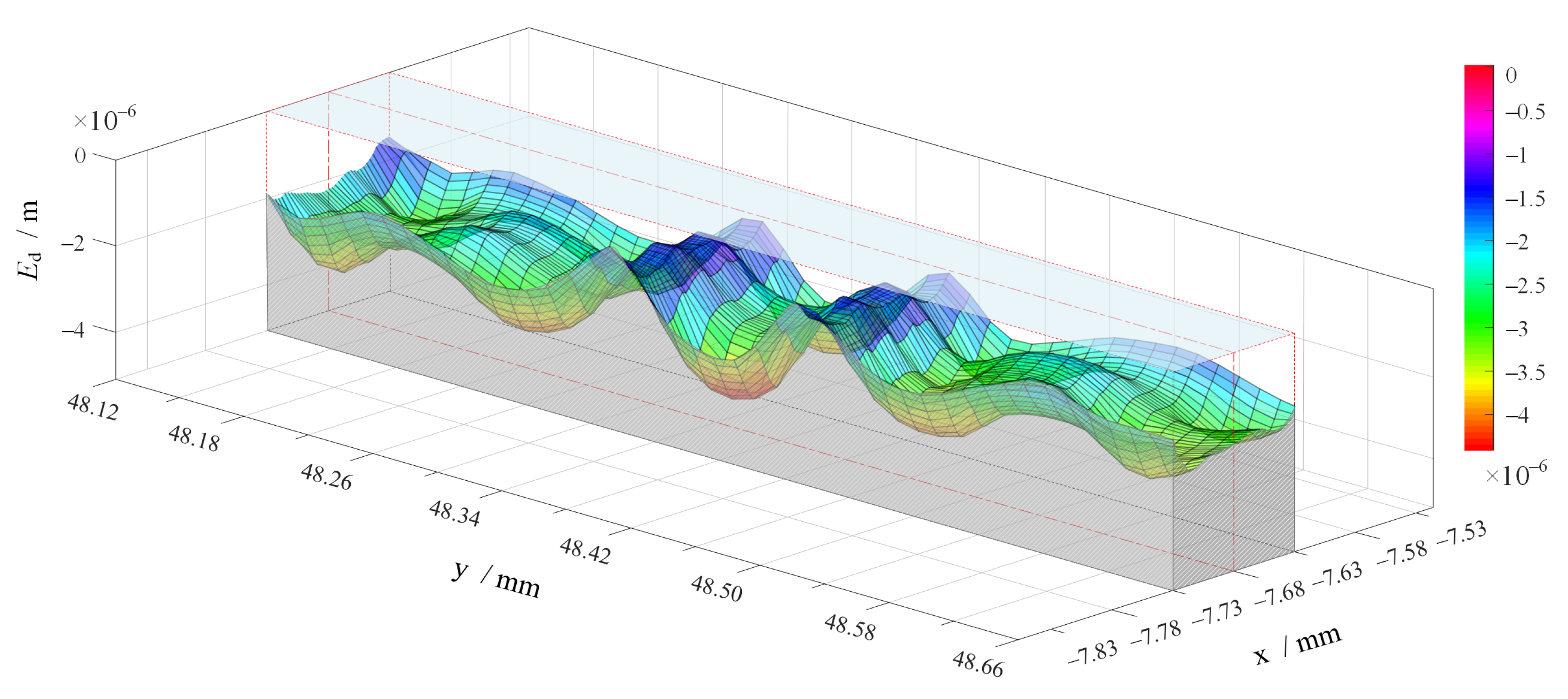
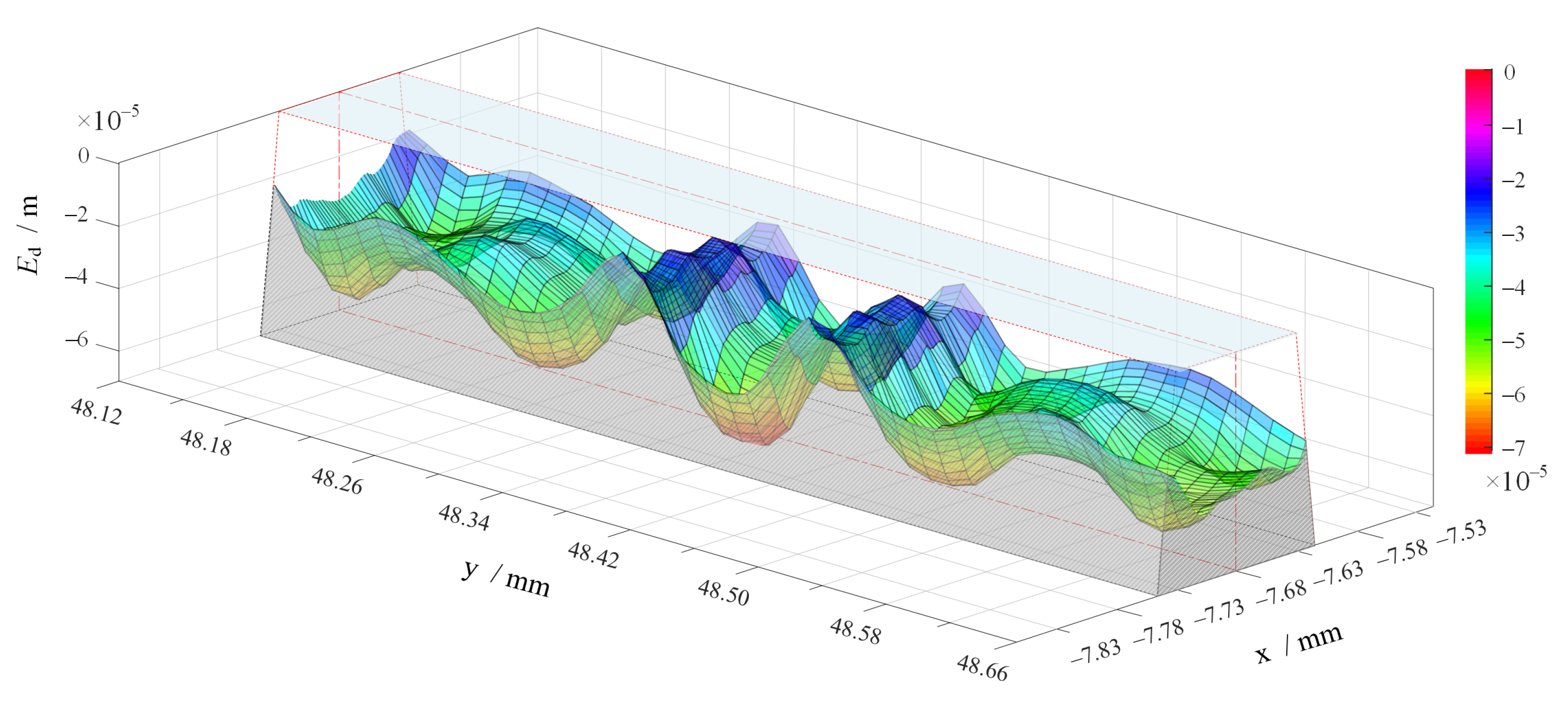
4.4. Lifespan Predication Based on Erosion Wear
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DJV | Deflector jet servo valve |
References
- Wellinger, K.; Brockstedt, H.C. Versuche zur Ermittlung des Verschleisswiderstandes von Werkstoffen für Blasversatzsohr sowie des Einflusses der Rohrverlegung bei Blasversatzanlagen. Glückauf 1942, 78, 130. [Google Scholar]
- Wellinger, K.; Brockstedt, H.C. Ermittlung des Verschleisswiderstandes von Werkstoffen für Blasversatzrohre. Stahl Eisen 1942, 62, 635. [Google Scholar]
- Wellinger, K.; Brockstedt, H.C. Sandstrahlverschleiss an Metallen. Z. Metallkunde 1949, 40, 361. [Google Scholar]
- Wellinger, K.; Uetz, H. Verschleissuntersuchungen an Gumi. Z. Ver. Deut. Ingr. 1954, 96, 43. [Google Scholar]
- Finnie, I. Erosion of surfaces by solid particles. Wear 1960, 43, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, A.A.; Tabakoff, W.; Rivir, R.B. Turbine Blade Surface Deterioration by Erosion. J. Turbomach 2005, 127, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlert, K.R. Effects of Particle Impingement Angle and Surface Wetting on Solid Particle Erosion of ANSI 1018 Steel. Master’s Thesis, University of Tulsa, Tulsa, OK, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Oka, Y.I.; Okamura, K.; Yoshida, T. Practical estimation of erosion damage caused by solid particle impact. Part 1: Effects of impact parameters on a predictive equation. Wear 2005, 259, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, Y.I.; Yoshida, T. Practical estimation of erosion damage caused by solid particle impact. Part 2: Mechanical properties of materials directly associated. Wear 2005, 259, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, M.S.; Dempster, W.M.; Scanlon, T.J.; Peters, J.; Mcculloch, S. Prediction of impact erosion in valve geometries. Wear 2004, 256, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Yang, W. Erosion of an Arrow-Type Check Valve Duo to Liquid–Solid Flow Based on Computational Fluid Dynamics. Fail. Anal. Preven. 2019, 19, 570–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulanger, A.J.; Wong, C.Y.; Zamberi, M.A.; Shaffee, S.A.; Johar, Z.; Jadid, M. Fines erosion: Turbophoresis can be harmful. J. Comput. Multiph. Flows 2017, 9, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Ge, S.; Yao, J. Numerical and experimental investigation of erosion by liquid-solid impinging jet. J. Cent. South Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2018, 49, 1289–1296. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.; Fu, J.; Jin, Y. Numerical simulation of erosion wear of pre-stage of jet pipe servo valve. J. Zhejiang Univ. Eng. Sci. 2015, 49, 2252–2260. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, Y.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, Y. The erosion wear characters of the jet pipe servo valve. Acta Aeronaut. Astron. Sin. 2015, 36, 1548–1555. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, Y.; Yuan, C.; Li, C. Durability simulation analysis of jet pipe servovalve. J. Northwest. Polytech. Univ. 2015, 33, 326–331. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S. The Simulation of Erosion on Servo Valve Orifice and Changes of Valve Characteristics on Jet Deflector Servo Valve. Master’s Thesis, Lanzhou Univ. Tech., Lanzhou, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, T. Contamination control. In Hydraulic Engineering Manual, 1st ed.; Mach. Ind. Press: Beijing, China, 1990; pp. 1736–1737. [Google Scholar]
- Contamination Control; QJ2724.1-2724.7-95; Aviation Industry Corporation of China: Beijing, China, 1995; pp. 1–5.
- Technical Specifications for Hydraulic Filters; GB/T20079-2006; General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016; pp. 1–2.
- 3J1 and 3J53 Alloy for Elastic Component; YB/T 5256-2011; Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2012; pp. 1–5.
- Njobuenwu, D.O.; Fairweather, M. Modelling of pipe bend erosion by dilute particle suspensions. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2012, 42, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dianat, M.; Jones, M.F.P. Reynolds stress closure applied to axisymmetric, impinging turbulent jets. Theor. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 1996, 43, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosman, A.; Ioannides, E. Aspects of computer simulation of liquid-fuelled combustors. In Proceedings of the 19th Aerospace Sci. Meeting(AIAA), St. Louis, MO, USA, 12–15 January 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Sommerfeld, M.; Huber, N. Experimental analysis and modelling of particle-wall collisions. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 1999, 5, 1457–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Number of Particles in 100 mL Oil | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contamination Level | Particle Size Range | ||||
| 100 | |||||
| 00 | 125 | 22 | 4 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 250 | 44 | 8 | 2 | 0 |
| 1 | 500 | 89 | 16 | 3 | 1 |
| 2 | 1000 | 178 | 32 | 6 | 1 |
| 3 | 2000 | 356 | 63 | 11 | 2 |
| 4 | 4000 | 712 | 126 | 22 | 4 |
| 5 | 8000 | 1425 | 253 | 45 | 8 |
| 6 | 16,000 | 2850 | 506 | 90 | 16 |
| 7 | 32,000 | 5700 | 1012 | 180 | 32 |
| 8 | 64,000 | 11,400 | 2025 | 360 | 64 |
| 9 | 128,000 | 22,800 | 4050 | 720 | 128 |
| 10 | 256,000 | 45,600 | 8100 | 1440 | 256 |
| 11 | 512,000 | 91,200 | 16,200 | 2880 | 512 |
| 12 | 102,400 | 182,400 | 32,400 | 5760 | 1024 |
| Parameter | Property and Value |
|---|---|
| Material | 3J1 |
| Main chemical constituents (mass fraction) | Ni: 34.5%–36.5% |
| Cr: 11.5%–13.0% | |
| Ti: 2.70%–3.20% | |
| Al: 1.00%–1.80% | |
| Fe: the Rest | |
| Tensile strength (N/mm) | 1372 |
| Density (g/cm) | 8.03 |
| Vicker hardness (kgf/mm) | 400–480 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Jet orifice width of jet plate (mm) | 0.15 |
| Outlet width of deflector (mm) | 0.14 |
| Distance between deflector and jet orifice h (mm) | 0.18 |
| Distance between jet orifice and receiver (mm) | 1 |
| Deflector thickness (mm) | 0.64 |
| Receiver width (mm) | 0.34 |
| Shunt wedge width (mm) | 0.1 |
| Inflow angle () | 13 |
| Sidewall inclination angle () | 16.5 |
| Shunt wedge angle () | 38 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Densities of oil (kg/m) | 850 |
| Oil viscosity (kg·s/m) | data |
| Densities of wall (kg/m) | 0.0085 |
| Densities of particles (kg/m) | 8030 |
| Average diameter of particles d (mm) | 1550 |
| Pressure of inlet (MPa) | 21 |
| Pressure of outlet (MPa) | 0 |
| Total flow rate (kg/s) | |
| Shape factor | 0.6 |
| Reference erosion rate (kg/kg) | |
| Wall material Vickers hardness (GPa) | 4.0 |
| Material hardness exponents | 0.8 |
| Particle properties exponents | 1.3 |
| Velocity exponent | 2.35 |
| Diameter exponent | 0.19 |
| Reference diameter (m) | 0.326 |
| Reference velocity (m/s) | 104 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, H.; Li, J.; Cai, C.; Ren, Y. Numerical Investigation of Erosion Wear in the Hydraulic Amplifier of the Deflector Jet Servo Valve. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10041299
Yan H, Li J, Cai C, Ren Y. Numerical Investigation of Erosion Wear in the Hydraulic Amplifier of the Deflector Jet Servo Valve. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(4):1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10041299
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Hao, Jing Li, Cunkun Cai, and Yukai Ren. 2020. "Numerical Investigation of Erosion Wear in the Hydraulic Amplifier of the Deflector Jet Servo Valve" Applied Sciences 10, no. 4: 1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10041299
APA StyleYan, H., Li, J., Cai, C., & Ren, Y. (2020). Numerical Investigation of Erosion Wear in the Hydraulic Amplifier of the Deflector Jet Servo Valve. Applied Sciences, 10(4), 1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10041299




