Year 2020: A Snapshot of the Last Progress in Flexible Printed Gas Sensors
Abstract
:1. Toward Flexible Gas Sensors Era
- -
- -
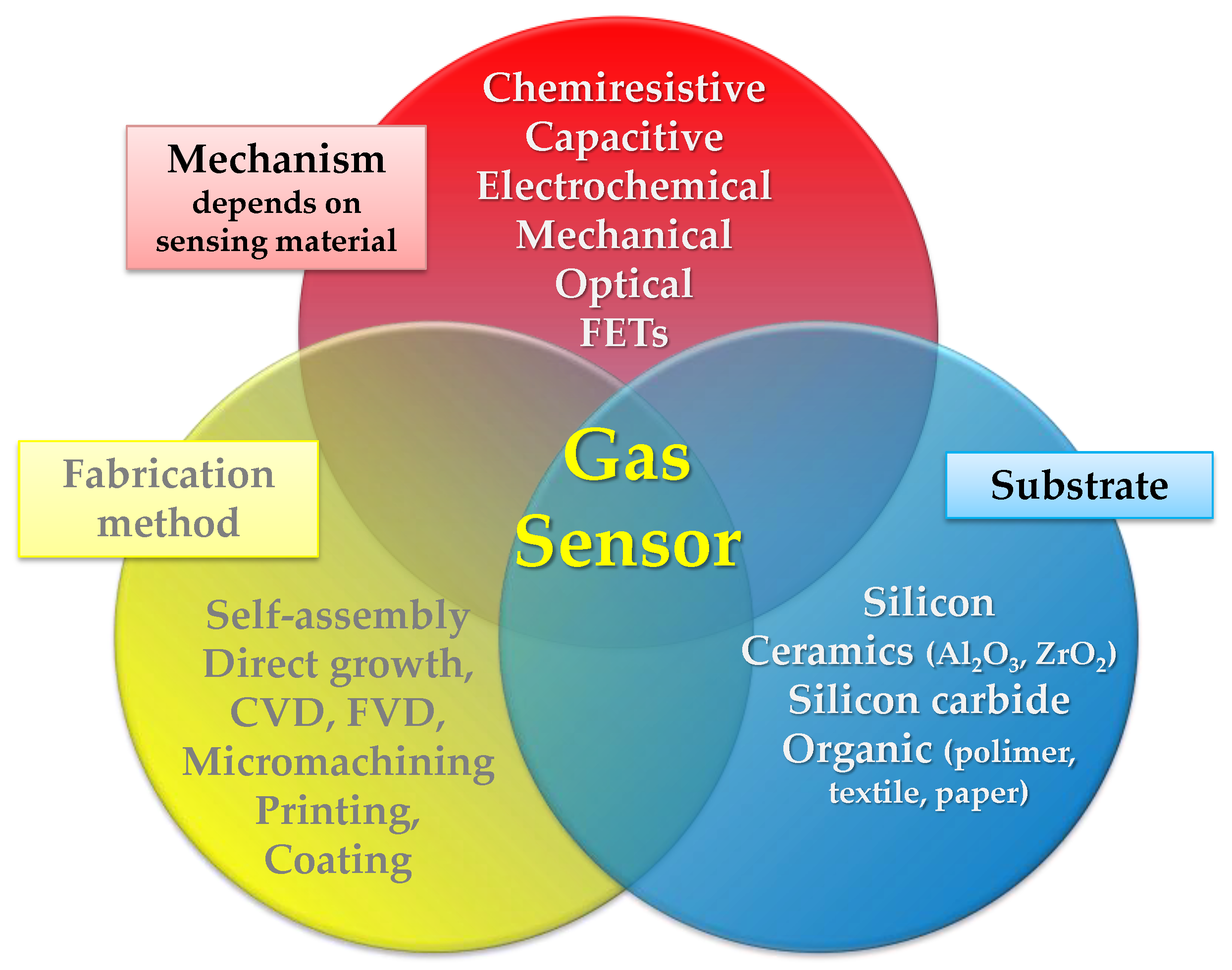
- A variation of sensing layer conductance proportional to the concentration of the target gas (chemiresistive gas sensors) [24];
- -
- A variation of the capacitance of the sensing element proportionally to the concentration of the target gas when an optimized signal frequency is applied (capacitive gas sensors) [25];
- -
- A variation of the source-drain current as a function of the concentration of the target gas (field-effect transistor-based gas sensors) [26];
- -
2. Printing Techniques
3. Flexible Substrates
4. Functional Materials
5. Target Gases
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilson, J.S. (Ed.) Sensor Technology Handbook; Elsevier Inc.: Burlington, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
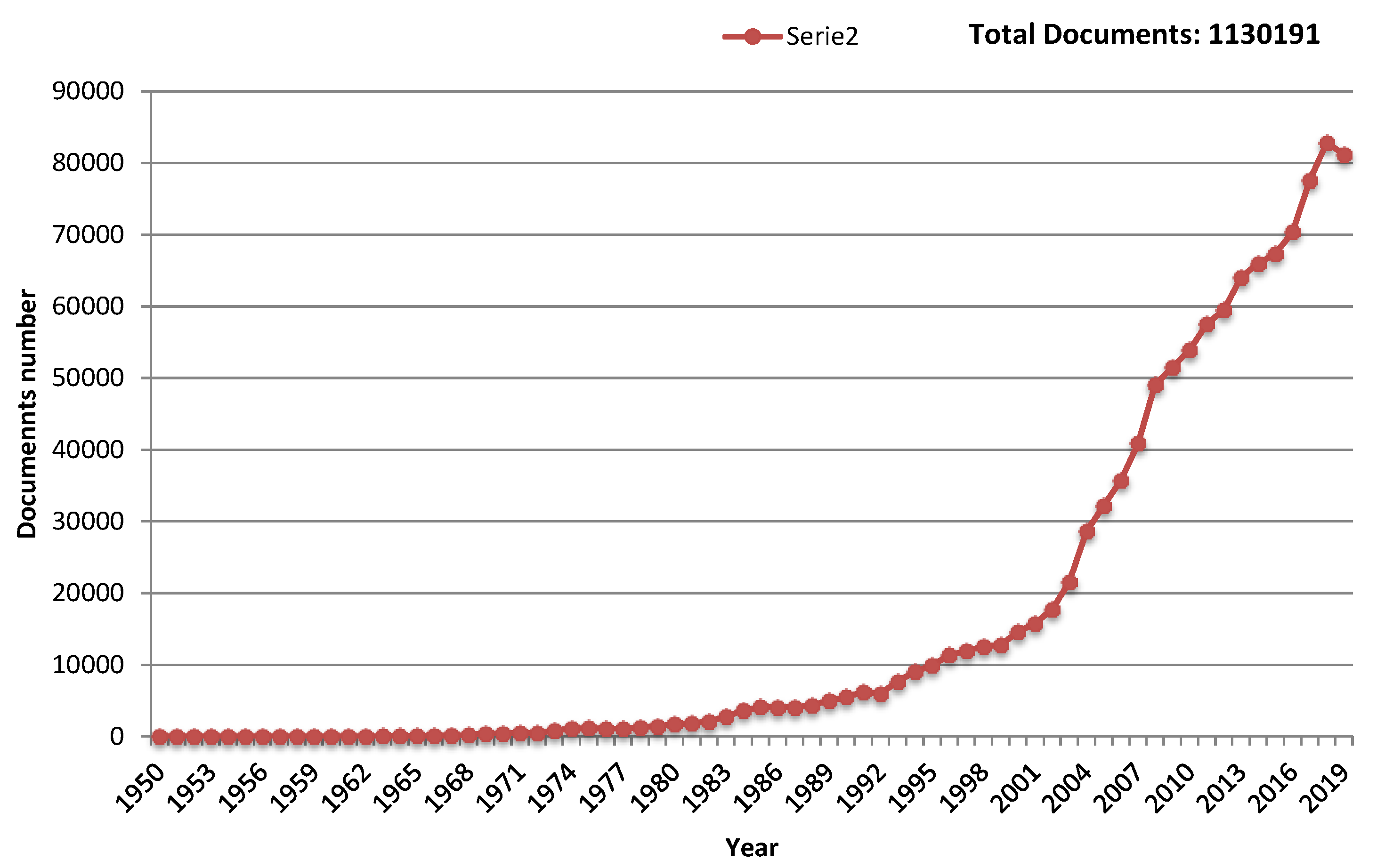
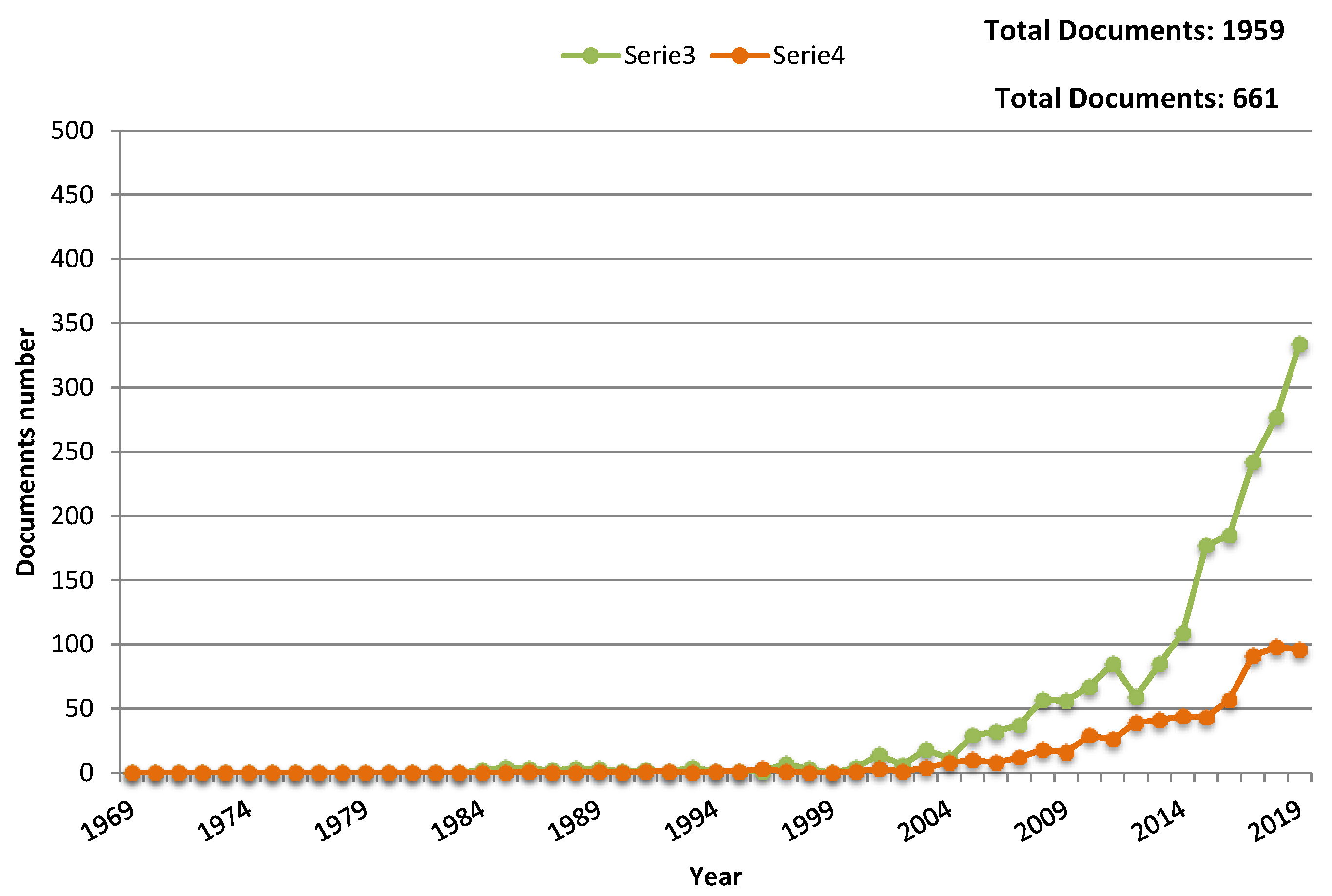
- Scopus. Available online: https://www.scopus.com/search/form.uri?display=basic (accessed on 9 January 2020).
- Atzori, L.; Iera, A.; Morabito, G. Understanding the Internet of Things: Definition, potentials, and societal role of a fast evolving paradigm. Ad Hoc Netw. 2017, 56, 122–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formisano, F.; Massera, E.; De Vito, S.; Buonanno, A.; Di Francia, G.; Delli Veneri, P. Tinynose, an auxiliary smart gas sensor for rfid tag in vegetables ripening monitoring during refrigerated cargo transport. In Sensors; Compagnone, D., Baldini, F., Di Natale, C., Betta, G., Siciliano, P., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 217–221. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, M.; Hisano, K.; Zhu, M.; Toyoshi, T.; Pan, M.; Okada, S.; Tsutsumi, O.; Kawamura, S.; Bowen, C. Flexible multifunctional sensors for wearable and robotic applications. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saddik, A.E. Digital twins: The convergence of multimedia technologies. IEEE MultiMed. 2018, 25, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, K.H.H.; Tan, O.K. Microhotplates for metal oxide semiconductor gas sensor applications—Towards the CMOS-MEMS monolithic approach. Micromachines 2018, 9, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ortiz Perez, A.; Bierer, B.; Scholz, L.; Wöllenstein, J.; Palzer, S. A Wireless Gas Sensor Network to Monitor Indoor Environmental Quality in Schools. Sensors 2018, 18, 4345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carotta, M.C.; Martinelli, G.; Crema, L.; Gallana, M.; Merli, M.; Ghiotti, G.; Traversa, E. Array of thick film sensors for atmospheric pollutant monitoring. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2000, 68, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riegel, J.; Neumann, H.; Wiedenmann, H.-M. Exhaust gas sensors for automotive emission control. Solid State Ion. 2002, 152–153, 783–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, B.; Xiao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Lu, G. Ultrasensitive and low detection limit of nitrogen dioxide gas sensor based on flower-like ZnO hierarchical nanostructure modified by reduced graphene oxide. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 249, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Choudhary, A.; Haranath, D.; Joshia, A.G.; Singh, N.; Singh, S.; Pasricha, R. ZnO decorated luminescent graphene as a potential gas sensor at room temperature. Carbon 2012, 50, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.Q.; Cheng, H.Y. Flexible and stretchable metal oxide gas sensors for healthcare. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2019, 62, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staerz, A.; Weimar, U.; Barsan, N. Understanding the potential of WO3 based sensors for breath analysis. Sensors 2016, 16, 1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peris, M.; Escuder-Gilabert, L. A 21st century technique for food control: Electronic noses. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 638, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Formisano, F.; Massera, E.; De Vito, S.; Buonanno, A.; Di Francia, G.; Delli Veneri, P. Auxiliary Smart Gas Sensor Prototype Plugged in a RFID Active Tag for Ripening Evaluation. In Proceedings of the 2015 XVIII AISEM Annual Conference, Trento, Italy, 3–5 February 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorji, U.; Pobkrut, T.; Kerdcharoen, T. Electronic Nose Based Wireless Sensor Network for Soil Monitoring in Precision Farming System. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Knowledge and Smart Technology (KST), Pattaya, Thailand, 1–4 February 2017; pp. 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.M. Sir Humphry Davy and the coal miners of the world: A commentary on Davy (1816) ‘An account of an invention for giving light in explosive mixtures of fire-damp in coal mines’. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2015, 373, 20140288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sarf, F. Metal Oxide Gas Sensors by Nanostructures; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gas Sensors Market Research Report-Forecast till 2023. Available online: https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/reports/gas-sensors-market-5459 (accessed on 12 January 2020).
- Chanson, G.; Pugh, D. Environmental Gas Sensors 2017–2027: Technologies, Manufacturers, Forecasts. 2017. Available online: https://www.idtechex.com/research/reports/environmental-gas-sensors-2017-2027-000500.asp (accessed on 12 January 2020).
- Miura, N.; Sato, T.; Anggraini, S.A.; Ikeda, H.; Zhuiykov, S. A review of mixed-potential type zirconia-based gas sensors. Ionics 2014, 20, 901–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shimizu, Y. Challenges for the Development of Toxic Gas Sensors by Employing Semiconductors and Solid Electrolytes. In Proceedings of the IMCS 2018 Conference, Vienna, Austria, 15–19 July 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratoddi, I.; Venditti, I.; Cametti, C.; Russo, M.V. Chemiresistive polyaniline-based gas sensors: A mini review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 220, 534–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.J.; Chen, S.J.; Feng, C.Y. Characterization of silicon nanoporous pillar array as room-temperature capacitive ethanol gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 123, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petz, A.L.; Skoglundh, M.; Ojamäe, L. FET Gas-Sensing Mechanism, Experimental and Theoretical Studies. In Solid State Gas Sensing; Comini, E., Faglia, G., Sberveglieri, G., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Devkota, J.; Ohodnicki, P.R.; Greve, D.W. SAW sensors for chemical vapors and gases. Sensors 2017, 17, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bueno, A.; Lahem, D.; Caucheteur, C.; Debliquy, M. Reversible NO2 optical fiber chemical sensor based on LuPc2 using simultaneous transmission of UV and visible light. Sensors 2015, 15, 9870–9881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hodgkinson, J.; Tatam, R.P. Optical gas sensing: A review. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2013, 24, 012004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cava, C.E.; Salvatierra, R.V.; Alves, D.C.B.; Ferlauto, A.S.; Zarbin, A.J.G.; Roman, L.S. Self-assembled films of multi-wall carbon nanotubes used in gas sensors to increase the sensitivity limit for oxygen detection. Carbon 2012, 50, 1953–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Sudarshan, T.S. Chemical Vapor Deposition. In Surface Engineering Series; The Materials Information Society: Russell, OH, USA, 2001; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Mattox, D.M. Handbook of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) Processing, 2nd ed.; William Andrew Publishing: Boston, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.Y.; Hung, W.N.P. Micromachining. In Comprehensive Materials Finishing; Elsevier: Kidlington, Oxford, UK, 2017; Volume 1, p. 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prudenziati, M.; Hornmadaly, J. (Eds.) Printed Films, Materials Science and Applications in Sensors, Electronics and Photonics; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Makhlouf, A.S.H. Current and Advanced Coating Technologies for Industrial Applications. In Nanocoatings and Ultra-Thin Films; Makhlouf, A.S.H., Tiginyanu, I., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Mishra, S.; Yeo, W.-H.; Hesketh, P.J.; Kumar, S. Carbon Nanotube Based Flexible Gas Sensors Using Printing Techniques. In Proceedings of the IMCS 2018 Conference, Vienna, Austria, 15–19 July 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Chachuli, S.A.; Hamidon, M.N.; Mamat, M.S.; Ertugrul, M.; Abdullah, N.H. A hydrogen gas sensor based on TiO2 nanoparticles on alumina substrate. Sensors 2018, 18, 2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mattana, G.; Briand, D. Recent advances in printed sensors on foil. Mater. Today 2016, 19, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.C.; Spina, F.; Lugoda, P.; Garcia-Garcia, L.; Roggen, D.; Münzenrieder, N. Flexible sensors—From materials to applications. Technologies 2019, 7, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crowley, K.; Morrin, A.; Hernandez, A.; O’Malley, E.; Whitten, P.G.; Wallace, G.G.; Smyth, M.R.; Killard, A.J. Fabrication of an ammonia gas sensor using inkjet-printed polyaniline nanoparticles. Talanta 2008, 2, 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dua, V.; Surwade, S.P.; Ammu, S.; Agnihotra, S.R.; Jain, S.; Roberts, K.E.; Park, S.; Ruoff, R.S.; Manohar, S.K. All-Organic vapor sensor using inkjet-printed reduced graphene oxide. Angew. Chem. Int. 2010, 49, 2154–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongchoosuk, C.; Jangtawee, P.; Lokavee, S.; Udomrat, S.; Sudkeaw, P.; Kerdcharoen, T. Novel flexible NH3 gas sensor prepared by ink-jet printing technique. Adv. Mat. Res. 2012, 506, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammu, S.; Dua, V.; Agnihotra, S.R.; Surwade, S.P.; Phulgirkar, A.; Patel, S.; Manohar, S.K. Flexible, all-organic chemiresistor for detecting chemically aggressive vapors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 4553–4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfraz, J.; Määttänen, A.; Ihalainen, P.; Keppeler, M.; Lindén, M.; Peltonen, J. Printed copper acetate based H2S sensor on paper substrate. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 173, 868–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfraz, J.; Ihalainen, P.; Määttänen, A.; Peltonen, J.; Lindén, M. Printed hydrogen sulfide gas sensor on paper substrate based on polyaniline composite. Thin Solid Films 2013, 534, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorwongtragool, P.; Sowade, E.; Watthanawisuth, N.; Baumann, R.R.; Kerdcharoen, T. A novel wearable electronic nose for healthcare based on flexible printed chemical sensor array. Sensors 2014, 10, 19700–19712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seekaew, Y.; Lokavee, S.; Phokharatkul, D.; Wisitsoraat, A.; Kerdcharoen, T.; Wongchoosuk, C. Low-cost and flexible printed grapheme—PEDOT: PSS gas sensor for ammonia detection. Org. Electron. 2014, 15, 2971–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieu, M.; Camara, M.; Tournier, G.; Viricelle, J.-P.; Pijolat, C.; de Rooij, N.F.; Briand, D. Fully inkjet printed SnO2 gas sensor on plastic substrate. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 236, 1091–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stempien, Z.; Kozicki, M.; Pawlak, R.; Korzeniewska, E.; Owczarek, G.; Poscik, A.; Sajna, D. Ammonia gas sensors ink-jet printed on textile substrates. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Sensors, Orlando, FL, USA, 30 October–3 November 2016; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Zhang, X.; Huang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, C.; Chen, H. High-Performance wireless ammonia gas sensors based on reduced graphene oxide and nano-silver ink hybrid material loaded on a patch antenna. Sensors 2017, 17, 2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Briand, D. All-printed low-power metal oxide gas sensors on polymeric substrates. Flex. Print. Electron. 2019, 4, 015002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.; Chen, W.; Shen, W.; Peng, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, R.; Xu, L.; Xu, W.; Song, W.; Tan, R. Enhanced flexible room temperature ammonia sensor based on PEDOT: PSS thin film with FeCl3 additives prepared by inkjet printing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 298, 126890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krcmar, P.; Kuritka, I.; Maslik, J.; Urbanek, P.; Bazant, P.; Machovsky, M.; Suly, P.; Merka, P. Fully inkjet-printed CuO sensor on flexible polymer substrate for alcohol vapours and humidity sensing at room temperature. Sensors 2019, 19, 3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Timsorn, K.; Wongchoosuk, C. Inkjet printing of room-temperature gas sensors for identification of formalin contamination in squids. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 4782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, O.; Saadaoui, M.; Rieu, M.; Viricelle, J.-P. A novel approach to a fully inkjet printed SnO2-based gas sensor on a flexible foil. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 12343–12353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhiraman, R.P.; Singh, E.; Diaz-Cartagena, D.C.; Nordlund, D.; Koehne, J.; Meyyappan, M. Plasma jet printing for flexible substrates. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 108, 123103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubourg, G.; Segkos, A.; Katona, J.; Radović, M.; Savić, S.; Niarchos, G.; Tsamis, C.; Crnojević-Bengin, V. Fabrication and characterization of flexible and miniaturized humidity sensors using screen-printed TiO2 nanoparticles as sensitive layer. Sensors 2017, 17, 1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radovic, M.; Dubourg, G.; Dohčević-Mitrović, Z.; Stojadinović, B.; Vukmirović, J.; Samardžić, N.; Bokorov, M. SnO2 nanosheets with multifunctional properties for flexible gas-sensors and UVA light detectors. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2019, 52, 385305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Pu, J.; Lin, S.X.Y.; Shen, L.; Chen, Q.; Shi, W. Fully printed, rapid-response sensors based on chemically modified graphene for detecting NO2 at room temperature. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 7426–7433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuberský, P.; Syrový, T.; Hamáček, A.; Nešpůrek, R.; Stejskal, J. Printed flexible gas sensors based on organic materials. Procedia Eng. 2015, 120, 614–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, L.H.Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, J.; Shen, L.; Chen, Q.; Shi, W. Fully gravure-printed NO2 gas sensor on a polyimide foil using WO3-PEDOT: PSS nanocomposites and Ag electrodes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 216, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calheiro, D.S.; Bianchi, R.F. Tuning the detection limit in hybrid organic-inorganic materials for improving electrical performance of sensing devices. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2019, 298, 111480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.H.; Radha, B.; Chan, J.Y.; Saifullah, M.S.M.; Kulkarni, G.U.; Ho, G.W. Flexible palladium-based H2 sensor with fast response and low leakage detection by nanoimprint lithography. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 7274–7281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrysiewicz, W.; Krzeminski, J.; Marszalek, K.; Sloma, M.; Rydosz, A. Flexible gas sensor printed on polymer substrate for acetone detection in portable exhaled breath analyzers. Multidiscip. Digit. Publ. Inst. Proc. 2019, 14, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, S.; Lorenzelli, L.; Dahiya, R.S. Technologies for printing sensors and electronics over large flexible substrates: A review. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 3164–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakafosis, V.; Rida, A.; Vyas, R.; Yang, L.; Nikolaou, S.; Tentzeris, M.M. Progress towards the first wireless sensor networks consisting of inkjet-printed, paper-based rfid-enabled sensor tags. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 1601–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Kumar, R.; Bandodkar, A.J.; Wang, J. Advanced materials for printed wearable electrochemical devices: A review. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2017, 3, 1600260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucat, C.; Menil, F.; Debeda, H. Printed Gas Sensors Based on Electrolytes; Woodhead Publishing: Cambrige, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, M.; La Flor, S.D.; Llobet, E.; Romero, A.; Ramírez, J.L. Performance of flexible chemoresistive gas sensors after having undergone automated bending tests. Sensors 2019, 19, 5190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koh, W.S.; Lee, K.M.; Toh, P.Y.; Yeap, S.P. Nano-graphene and its derivatives for fabrication of flexible electronic devices: A quick review. Adv. Mater. Lett. 2019, 10, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.-H.; Zheng, F. Chapter 5: Polyimides for Electronic Applications; Yang, S.Y., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 195–255. [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald, W.A.; Looney, M.K.; MacKerron, D.; Eveson, R.; Adam, R.; Hashimoto, K.; Rakos, K. Latest advances in substrates for flexible electronics. J. Soc. Inf. Disp. 2007, 15, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zardetto, V.; Brown, T.M.; Reale, A.; Carlo, A.D. Substrates for flexible electronics: A practical investigation on the electrical, film flexibility, optical, temperature, and solvent resistance properties. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2011, 49, 638–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinkeldei, T.; Zysset, C.; Münzenrieder, N.; Tröster, G. Influence of Flexible Substrate Materials on the Performance of Polymer Composite Gas Sensors. In Proceedings of the 14th International Meeting on Chemical Sensors (IMCS), Nuremberg, Germany, 20–23 May 2012; pp. 537–540. [Google Scholar]
- Briand, D.; Oprea, A.; Courbat, J.; Bârsan, N. Making environmental sensors on plastic foil. Mater. Today 2011, 14, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundy, W.M.; Ishley, J.N. Kaolin in paper filling and coating. Appl. Clay Sci. 1991, 5, 397–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattana, G.; Ataman, C.; Ruan, J.J.; Quintero, A.V.; Nisato, G.; Tröster, G.; Briand, D.; Rooij, N.F. Woven temperature and humidity sensors on flexible plastic substrates for E-Textile applications. IEEE Sens. J. 2010, 13, 3901–3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.H.; Oh, K.W.; Kang, T.J. Polyaniline—Nylon 6 composite fabric for ammonia gas sensor. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 92, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.-W.; Kim, B.; Li, J.; Meyyappan, M. A carbon nanotube based ammonia sensor on cotton textile. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 193104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Ali, S.; Bermak, A. Substrate dependent analysis of printed sensors for detection of volatile organic compounds. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 134047–134054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carotta, M.C.; Fioravanti, A.; Gherardi, S.; Ghiotti, G.; Malagù, C.; Morandi, S.; Sacerdoti, M. (Ti, Sn) binary oxides as functional materials for gas sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 194, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fioravanti, A.; Bonanno, A.; Gherardi, S.; Carotta, M.C.; Skouloudis, A.N. A portable air-quality station based on thick film gas sensors for real time detection of traces of atmospheric pollutants. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 108, 012005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morandi, S.; Fioravanti, A.; Cerrato, G.; Lettieri, S.; Sacerdoti, M.; Carotta, M.C. Facile synthesis of ZnO nano-structures: Morphology influence on electronic properties. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 249, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morandi, S.; Amodio, A.; Fioravanti, A.; Giacomino, A.; Mazzocchi, M.; Sacerdoti, M.; Carotta, M.C.; Skouloudis, A.N. Operational functionalities of air-quality W-Sn metal-oxide sensors correlating semiconductor defect levels and surface potential barriers. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 135731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galstyan, V. Porous TiO2-based gas sensors for cyber chemical systems to provide security and medical diagnosis. Sensors 2017, 17, 2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eatemadi, A.; Daraee, H.; Karimkhanloo, H.; Kouhi, M.; Zarghami, N.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Abasi, M.; Hanifehpour, Y.; Joo, S.W. Carbon nanotubes: Properties, synthesis, purification, and medical applications. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2014, 9, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Yeow, J.T. A review of carbon nanotubes-based gas sensors. J. Sens. 2009, 2009, 493904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hester, J.G.D.; Tentzeris, M.M.; Fang, Y. Inkjet-Printed, Flexible, High Performance, Carbon Nanomaterial Based Sensors for Ammonia and DMMP Gas Detection. In Proceedings of the 2015 European Microwave Conference (EuMC 2015), Paris, France, 7–10 September 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, P.B.; Alam, B.; Sharma, D.S.; Sharma, S.; Mandal, S.; Agarwal, A. Flexible NO2 gas sensor based on single-walled carbon nanotubes on polytetrafluoroethylene substrates. Flex. Print. Electron. 2018, 3, 035001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, E.; Meyyappan, M.; Singh Nalwa, H. Flexible graphene-based wearable gas and chemical sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 34544–34586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dideikin, A.T.; Vul’, A.Y. Graphene oxide and derivatives: The place in graphene family. Front. Phys. 2019, 6, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, B.; Shepherd, R.L.; Crowley, K.; Killard, A.J.; Wallace, G.G. Printing conducting polymers. Analyst 2010, 135, 2779–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, S.V.; Malik, A. Hydrogen breath tests in gastrointestinal diseases. Ind. J. Clin. Biochem. 2014, 29, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mridha, S.; Basak, D. Investigation of a p-CuO/n-ZnO thin film heterojunction for H2 gas-sensor applications. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2006, 21, 928–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanf, S.; Bögözi, T.; Keiner, R.; Frosch, T.; Popp, J. Fast and highly sensitive fiber enhanced Raman spectroscopic monitoring of molecular H2 and CH4 for point-of-care diagnosis of malabsorption disorders in exhaled human breath. Anal. Chem. 2014, 87, 982–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.; Wu, Y.; Lin, C. High Performance Oxygen Sensor Utilizing Ultraviolet Irradiation Assisted ZnO Nanorods under Low Operation Temperature. In Proceedings of the 8th Annual IEEE International Conference on Nano/Micro Engineered and Molecular Systems, Suzhou, China, 7–10 April 2013; pp. 72–75. [Google Scholar]
- Colindres, S.C.; Aguir, K.; Sodi, F.C.; Vargas, L.V.; Salazar, J.M.; Febles, V.G. Ozone sensing based on palladium decorated carbon nanotubes. Sensors 2014, 14, 6806–6818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duvall, R.M.; Long, R.W.; Beaver, M.R.; Kronmiller, K.G.; Wheeler, M.L.; Szykman, J.J. Performance evaluation and community application of low-cost sensors for ozone and nitrogen dioxide. Sensors 2016, 16, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessler, A.E.; Sherwood, S.C. Atmospheric science. A matter of humidity. Science 2009, 323, 1020–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oprea, A.; Barsan, N.; Weimar, U.; Courbat, J.; Briand, D.; de Rooij, N.F. Integrated temperature, humidity and gas sensors on flexible substrates for low-power applications. Sensors 2007, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, H.; Lan, C.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, P.; Wei, D.; Li, C. Transparent, flexible, and stretchable WS2 based humidity sensors for electronic skin. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 6246–6253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Tong, J.; Xia, B. Humidity-sensing properties of chemically reduced graphene oxide/polymer nanocomposite film sensor based on layer-by-layer nano self-assembly. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 197, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giberti, A.; Carotta, M.C.; Guidi, V.; Malagù, C.; Martinelli, G.; Piga, M.; Vendemiati, B. Monitoring of ethylene for agro-alimentary applications and compensation of humidity effects. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2004, 103, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Rasyid, M.U.H.; Nadhori, I.U.; Alnovinda, Y.T. CO and CO2 Pollution Monitoring Based on Wireless Sensor Network. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Aerospace Electronics and Remote Sensing (IEEE ICARES 2015), Bali, Indonesia, 3–5 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gatty, H.K.; Leijonmarck, S.; Antelius, M.; Stemme, G.; Roxhed, N. An amperometric nitric oxide sensor with fast response and ppb-level concentration detection relevant to asthma monitoring. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 209, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, J.H.; Wikle, H.C.; Chin, B.A. Passive chemiresistor sensor based on iron (II) phthalocyanine thin films for monitoring of nitrogen dioxide. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 148, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabassum, R.; Pavelyev, V.S.; Moskalenko, A.S.; Tukmakov, K.N.; Islam, S.S.; Mishra, P. A Highly sensitive nitrogen dioxide gas sensor using horizontally aligned SWCNTs employing MEMS and dielectrophoresis methods. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2017, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, M.; Jayatissa, A.H. Ammonia gas sensing behavior of graphene surface decorated with gold nanoparticles. Solid State Electron. 2012, 78, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakimi, M.; Salehi, A.; Boroumand, F.A.; Mosleh, N. Fabrication of a room temperature ammonia gas sensor based on polyaniline with n-doped graphene quantum dots. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 2245–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Dutta, P.K. Selective detection of part per billion concentrations of ammonia using a p–n semiconducting oxide heterostructure. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 226, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmer, B.; Olthuis, W.; van den Berg, A. Ammonia sensors and their applications—A review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 107, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Samanta, S.; Singh, A.; Roy, M.; Singh, S.; Basu, S.; Chehimi, M.M.; Roy, K.; Ramgir, N.; Navaneethan, M.; et al. Fast response and high sensitivity of ZnO nanowires—Cobalt phthalocyanine heterojunction based H2S sensor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 17713–17724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doujaiji, B.; Al-Tawfiq, J.A. Hydrogen sulfide exposure in an adult male. Ann. Saudi Med. 2010, 30, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.R.; Siddiqui, M.J.A. Review on effects of particulates; sulfur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide on human health. Int. Res. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 3, 70–73. [Google Scholar]
- Tyagia, P.; Sharma, A.; Tomar, M.; Gupta, V. Metal oxide catalyst assisted SnO2 thin film based SO2 gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 224, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, M.S.; Razzak, S.A.; Hossain, M.M. Catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs)—A review. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 140, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Pal, S.; Mitra, M. Significance of exhaled breath test in clinical diagnosis: A special focus on the detection of diabetes mellitus. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2016, 36, 605–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreira, R.G.; Moreira, L.H.; dos Santos Filho, S.G. Sensing Different Mixtures of H2, CH4 and CO Through an Array of Chemiresistors. In Proceedings of the 29th Symposium on Microelectronics Technology and Devices (SBMicro), Aracaju, Brazil, 1–5 September 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouma, P.I. Isoprene Sensor/Breathalyzer for Monitoring Sleep Disorders. In Proceedings of the 17th International Meeting on Chemical Sensors—IMCS, Vienna, Austria, 15–19 July 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, A.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, S.S. Resistive-based gas sensors for detection of benzene, toluene and xylene (BTX) gases: A review. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 4342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güntner, A.T.; Koren, V.; Chikkadi, K.; Righettoni, M.; Pratsinis, S.E. E-Nose sensing of low-ppb formaldehyde in gas mixtures at high relative humidity for breath screening of lung cancer? ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, A.; Donato, N.; Saitta, G.; Bonavita, A.; Rizzo, G.; Neri, G. Flexible ethanol sensors on glossy paper substrates operating at room temperature. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 145, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, S.; Li, D.; Liang, S.; Chen, X.; Xia, X. A novel flexible room temperature ethanol gas sensor based on SnO2 doped poly-diallyldimethyl ammonium chloride. Sensors 2013, 13, 4378–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgut, P.; Arif Gurel, M.; Kadir Pekgokgoz, R. LPG explosion damage of a reinforced concrete building: A case study in Sanliurfa, Turkey. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2013, 32, 220–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, S.; Deshpande, P.; Gole, P.; Bhosale, P. LPG gas detector and prevention. J. Curr. Res. 2017, 9, 60140–60142. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Wei, Z.; Xu, L.; Peng, S.; Zeng, W. Synthesis of hollow nanofibers and application on detecting SF6 decomposing products. Front. Mater. 2019, 6, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Dang, T.; Duc Hoa, N.; Van Duy, N.; Van Hieu, N. Chlorine gas sensing performance of on-chip grown ZnO, WO3, and SnO2 nanowire sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 4828–4837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massa, C.B.; Scott, P.; Abramova, E.; Gardner, C.; Laskin, D.L.; Gow, A.J. Acute chlorine gas exposure produces transient inflammation and a progressive alteration in surfactant composition with accompanying mechanical dysfunction. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2014, 278, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blanco-Rodríguez, P.; Fernández-Serantes, L.A.; Otero-Pazos, A.; Calvo-Rolle, J.L.; de Cos Juez, F.J. Radon mitigation approach in a laboratory measurement room. Sensors 2017, 17, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nikezic, D.; Yu, K.N. Are radon gas measurements adequate for epidemiological studies and case control studies of radon-induced lung cancer? Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2005, 113, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Novoa, O.; Fernández-Caramés, T.M.; Fraga-Lamas, P.; Castedo, L. A cost-effective IoT system for monitoring indoor radon gas concentration. Sensors 2018, 18, 2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Printing Technique | Substrate Material 1 | Functional Material 1 | Gas Detected 2 | Working Condition | Gas Concentration | Year, Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inkjet printing | PET | PANI | NH3 | RT | 100 ppm | 2008 [40] |
| Inkjet printing | PET | rGO | NH3 NO2 | RT | 100 ppm 10 ppm | 2010 [41] |
| Inkjet printing | Photo paper | PEDOT/PSS | NH3 | RT | 100 ppm | 2012 [42] |
| Inkjet printing | Cellulosic paper | CNT | NO2 Cl2 | RT | 100 ppm 20 ppm | 2012 [43] |
| Inkjet printing | Paper with barrier layes | CuAc | H2S | RT | 10 ppm | 2012 [44] |
| Inkjet printing | Kaolin-coated paper | PANI-CuCl2 | H2S | RT dry/wet | 15 ppm | 2013 [45] |
| Inkjet printing | PEN | (PVC/Cumene-PSMA/PSE/PVP)—CNTs | NH3 | RT | 100 ppm | 2014 [46] |
| Inkjet printing | Plastic substrate | Graphene, PEDOT/PSS, PEDOT/PSS- graphene | NH3 | RT | 500 ppm | 2014 [47] |
| Inkjet printing | PI | SnO2 | NO2 CO | 300 °C | 20 ppm 20 ppm | 2016 [48] |
| Inkjet printing | Textile | PANI | NH3 | RT | 15–100 ppm | 2016 [49] |
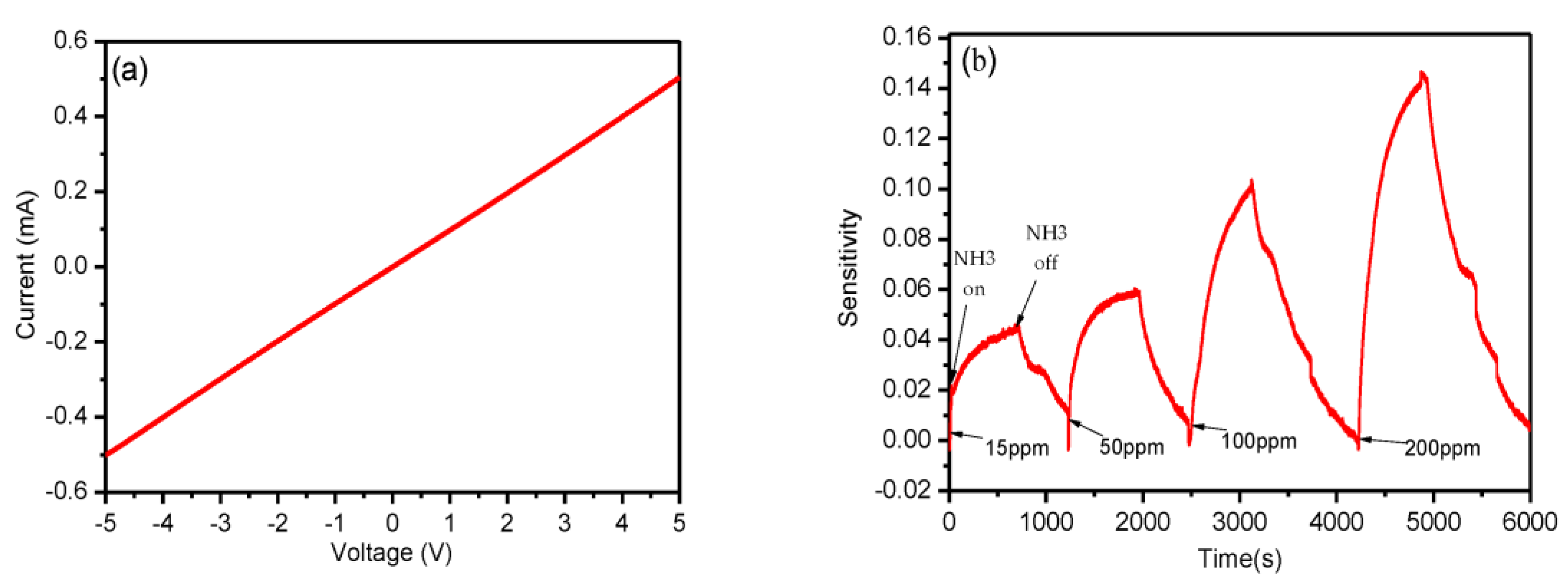
| Inkjet printing | PET | rGO-Ag | NH3 | RT | 15 ppm | 2017 [50] |
| Inkjet printing | PI | Pd-SnO2 | CO NO2 | 250 °C dry/25%RH | 20, 35, 50 ppm 1, 3, 5 ppm | 2019 [51] |
| Inkjet printing | PI | PEDOT:PSS with FeCl3 additives | NH3 | RT | 0.1–200 ppm | 2019 [52] |
| Inject printing | PET | CuO | H2O C2H5OH Methanol | RT | 45–100% RH | 2019 [53] |
| Inkjet printing | Flexible, transparent | PEDOT:PSS/MWCNTs-N2 | CH2O | RT | 10–200 ppm | 2019 [54] |
| Inkjet printing | PI | SnO2 | C2H5OH NH3 CO | 300 °C | dry and wet air | 2019 [55] |
| Plasma jet printing | Paper | MWCNTs | NH3 | RT | 60 ppm | 2016 [56] |
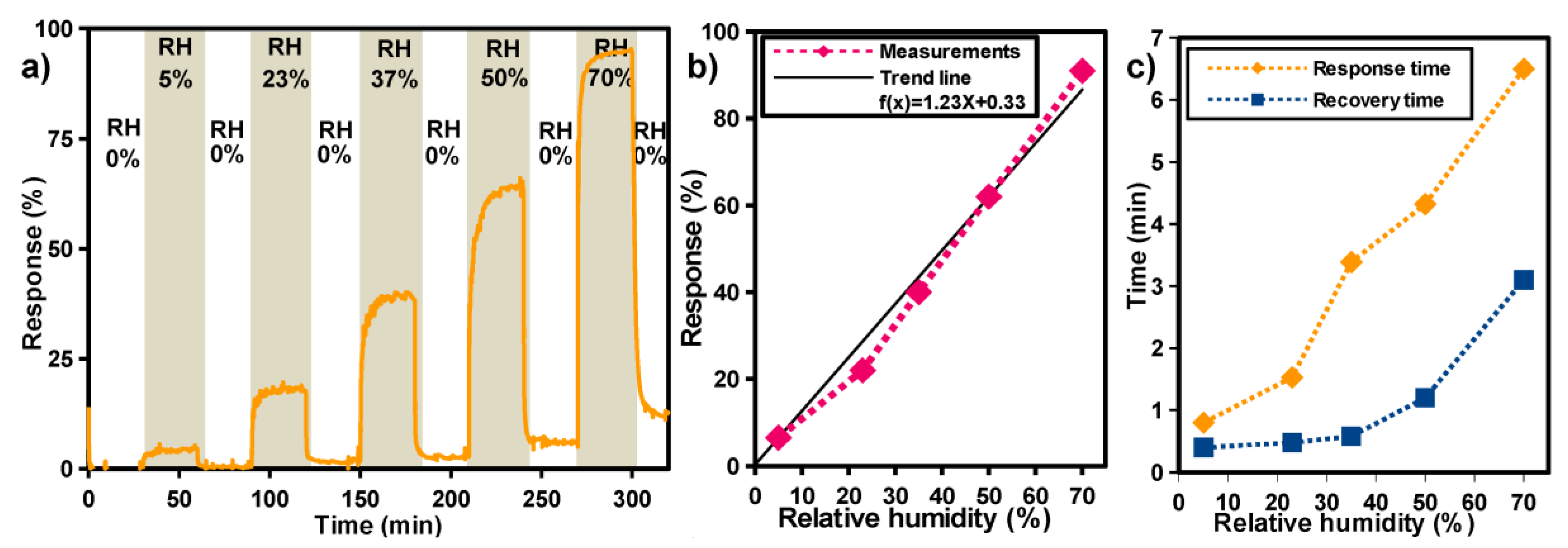
| Screen printing | PET | TiO2 | H2O | RT | 5–70% RH | 2017 [57] |
| Screen printing | Flexible substrate | SnO2 | C2H5OH 2propanol C6H3O | RT 30% RH | 1–500 ppm 1–500 ppm 1–500 ppm | 2019 [58] |
| Gravure printing | PI | Ag-S-rGO | NO2 | RT | 500 ppb | 2014 [59] |
| Gravure printing | PET | PEDOT/PSS PANI | H2O NH3 | RT | 40% RH 100 ppm | 2015 [60] |
| Gravure printing | PI | WO3-PEDOT/PSS | NO2 | RT | 5 ppb | 2015 [61] |
| Gravure printing | HDPE | PANI-ITO | NH3 | RT 50% RH | 1–100 ppm | 2019 [62] |
| Nanoimprint lithography | Polycarbonate | Pd | H2 | RT | 3500 ppm | 2013 [63] |
| Printing | Polymer | - | C6H3O | - | - | 2019 [64] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fioravanti, A.; Carotta, M.C. Year 2020: A Snapshot of the Last Progress in Flexible Printed Gas Sensors. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10051741
Fioravanti A, Carotta MC. Year 2020: A Snapshot of the Last Progress in Flexible Printed Gas Sensors. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(5):1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10051741
Chicago/Turabian StyleFioravanti, Ambra, and Maria Cristina Carotta. 2020. "Year 2020: A Snapshot of the Last Progress in Flexible Printed Gas Sensors" Applied Sciences 10, no. 5: 1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10051741
APA StyleFioravanti, A., & Carotta, M. C. (2020). Year 2020: A Snapshot of the Last Progress in Flexible Printed Gas Sensors. Applied Sciences, 10(5), 1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10051741






